Reasons for lack of menstruation (amenorrhea)
The reasons for the absence of menstruation can be divided into three groups.
- woman's physiology;
- anovulation (or ovarian failure);
- pathologies in the structure or function of the uterus.
Amenorrhea, which occurs depending on the woman’s physiology, includes such periods of life as:
- from birth to the onset of puberty;
- period of bearing a child;
- breastfeeding period;
- late menopause.
Anovulation is the inability of the ovaries to produce eggs; this can be caused by various diseases and certain factors in the patient’s life.
- Lack of gonadotropin hormone in the body, which can be caused by severe stress, depression, anorexia, sports or heavy physical labor, or a sharp jump in body weight.
- Insufficient production of the hormone progesterone. This may occur due to the presence of serious diseases such as tumors of various types or tuberculosis.
- Impaired functioning of the pituitary gland due to the formation of a benign or malignant tumor on it.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome. Multiple formations (cysts) on the ovaries prevent the egg from being released.
- Genetic disorders. They are expressed in the early onset of menopause (up to 35 years).
The two main diseases that affect the functioning of the uterus are trophoblastic disease (tumor of the placenta) and Asherman's syndrome (adhesions in the uterus).
Amenorrhea can be accompanied by a number of alarming symptoms.
- Excessive sweating, deepening of the voice, male-pattern hair growth, sudden weight changes. These signs indicate serious changes in hormonal levels.
- Nagging pain in the lower abdomen in the area of the appendages and problems with urination indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the pelvic organs.
- Mental problems are expressed in mood swings, stress, excessive excitability, attacks of aggression or laughter.
- Tachycardia, rapid pulse, and surges in blood pressure may be signs of hormonal imbalance.
https://youtu.be/AjzaSiDbsu0
Treatment of amenorrhea
Since amenorrhea is not an independent disease, but only a symptom of disorders in the body, the main cause of the absence of menstruation is treated.
The basis of treatment is hormonal drugs. With the permission of the doctor, herbal treatment can be used. If a woman has psychological disorders, then it is necessary to undergo a course of psychotherapy.
For some pathologies in the structure of the female genital organs, surgical intervention is prescribed.
At the first delay of menstruation, a woman needs to consult a gynecologist to find out the reason for the absence of menstruation, since amenorrhea can be the cause of various dangerous diseases.
Every woman has to face the menopause, as it is a natural process in the female body. Therefore, it is important to know how to behave if pathological symptoms occur.
One of the manifestations that signal an unhealthy reproductive system is long and heavy periods during menopause. There are a number of reasons that provoke this condition.
Every woman is advised to know when to see a doctor and how treatment is carried out.
When it's ok
In most cases there is no need to worry. Below I will list the most common ones.
Sudden weight change
The menstrual cycle can be disrupted by a sudden change in weight. With obesity or weight loss, the amount of the hormone estrogen produced by adipose tissue changes, the body does not have enough substances to ripen the egg and restore the endodermis.
My friend Sveta got a similar problem with her diet and complained that her periods had been lasting for a very long time. I advised her to go to the doctor. He said that the problem was a sudden change in weight that affected hormonal levels and advised me to return to the way I was eating before the problem appeared.
Menopause
An unstable cycle caused by the gradual decline of ovarian function - menopause (menopause). The period is typical:
- Inconstancy of hormones
- Their spasmodic behavior in the blood
- Unpredictability of ovulations
Long periods during menopause are a natural phenomenon. The cycle is already irregular and may be absent for several months, then resume, lasting a long time. But go to the hospital - sometimes it’s not prolonged menstruation during menopause, but bleeding.
After childbirth
Depending on the individuality of the woman, a different amount of discharge is observed. To ensure that the amount of discharge is normal or not, compare them before pregnancy.
Monitor the color of the bleeding; if it is red for more than 10 days, you should consult a doctor. The volume of blood lost during normal postpartum menstruation does not exceed 150 milliliters.
Menstruation after childbirth can be confused with spotting as a result of childbirth (lochia). Their duration is no more than 6-8 weeks after childbirth, and they are not associated with PMS, but due to labor, where the endometrium of the uterus is damaged.
The uterus gradually normalizes:
- During the first 10 days it drops, its size decreases, and its weight drops to 50 grams in the first week.
- The internal os is formed in 10 days
- After three weeks, the external pharynx becomes slit-shaped and until the endometrium is restored
- After 2-3 menstruation – the cycle should be completely restored
Therefore, heavy and prolonged periods after childbirth are not some kind of complication, but a visit to the doctor is recommended.
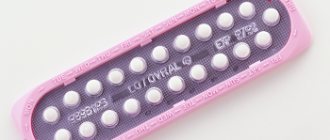
Birth control pills
Birth control pills are one of the main types of modern synthetic hormonal contraception. But there is a side effect in the form of menstruation, the duration of which differs from the normal cycle before taking it.
There are a couple of types of hormonal drugs: COCs (combined oral contraceptives), consisting of progesterone and estrogen.
The second type - progestogen contraceptive pills, based on progestogen, are indicated for breastfeeding girls and those for whom estrogen is contraindicated. According to the degree of the amount of hormones in the composition, combined ones are divided into: microdosed, low-dose and high-dose.
- The first group is intended for young women with an active sex life, and women from 35 years of age and before the onset of menopause (“Mersilon”, “Jess”, “Logest” and others)
- The second group is intended for young girls who have not yet given birth, who have not taken the previous dosage of the contraceptive and cause bleeding as a reaction after 3 months of adaptation of the drug, who have given birth and women of declining reproductive age (“Fimoden”, “Silest”, “Midiana”, “ Demoulin" and others)
- The third group is therapeutic for diseases of the hormonal type and a contraceptive during disorders of the hormonal system, this type is accepted when prescribed by a hospital (Ovidon and Non-Ovlon and others)
- Progestogens are prescribed to breastfeeding women and those who cannot be given estrogen; these include the drugs Microlut, Laktinet, and Exluton.
I personally used Postinor tablets - they prevent fertilization by suppressing ovulation and changing the endometrium of the uterus. The action turned out to be effective, but a hormonal imbalance occurred and menstruation came two days later, plus it also dragged on for up to 10 days.
I went to the doctor and received a recommendation from him for the drug “Yarina”, which suits me, so it is advisable to choose the right type of drug in advance to avoid long periods as a side effect.
Surgical intervention
Long periods as a result of surgical interventions are common and not life-threatening, except in cases where a doctor is needed. I describe the operations that are most often encountered:
- The IUD (intrauterine device) is a contraceptive that affects the duration of menstruation, but saves from conception. The installation of the spiral is done in the last days of PMS for precise installation without pain in the slightly open uterus. Menstruation becomes less intense and does not occur according to schedule. There is a spiral in the uterus, and the body gets used to it. We will soon have to return to normalcy and cyclicality
- One of the surgical causes of heavy and prolonged periods is medical abortion. Proper operation does not guarantee normal periods. The first menstruation differs from previous menstruation in the duration and intensity of bleeding. When menstruation increases to 7 days, this is a normal reaction of the body to a medical abortion. You should consult a doctor if the period increases beyond a week.
- The curettage procedure (hysteroscopic examination) affects the endometrial layer and subsequent menstrual cycles. An increase in the duration of menstruation after cleansing is a woman’s individual reaction to the procedure, which does not indicate severe complications. If your periods are too heavy, when the pad is changed every 3 hours, you need to be examined by a doctor; if there is no such problem, then an increased cycle duration is normal
Menopause and its phases
The onset of menopause is usually observed when a woman reaches the age of 40-45 years, however, menstruation still continues for some time.
The menopausal period is divided into three stages:
- premenopause _ The duration of this period varies from 2 to 5 years. During premenopause, menstruation continues, but a stable cycle is no longer observed. The discharge also does not have a clear and characteristic manifestation. They can be both scarce and abundant. The cause of this condition is hormonal imbalance;
- menopause _ This is the period when menstruation stops. You can understand that the body is in a state of menopause by the absence of discharge, which has not appeared for more than a year. If you start taking medications that contain hormones, there is a possibility of menstruation, however, they are often very scanty;
- postmenopause . During this period, the appearance of bleeding or any discharge is a deviation . If discharge appears during this period, especially if it is clots, then urgent help from a specialist is needed.
Why is it dangerous?
Excessive blood loss, whatever its causes, threatens not only human health, but also human life. But if incessant menstruation is only a symptom, then an untimely identified cause can be fraught with the following dangers:
- great blood loss. If the critical days are not only long, but also abundant with the presence of large clots, iron deficiency anemia can quickly develop with all the ensuing consequences;
- spontaneous abortion. If your period does not end for a long time, perhaps the woman is pregnant and for some reason had a miscarriage;
- during prolonged critical days, there is a danger that they are caused by malignant neoplasms or fibroids.
In order not to worry in vain and to find out exactly the cause of protracted periods, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible if you notice this symptom.
Why and how menstruation ends during menopause
Primordial follicles, or rather their number, are formed during the development of the fetus in the womb. A decrease in their number is observed over time and depends on the age of the woman. Follicles disappear completely at the moment when the ovaries lose the ability to produce mature follicles and maintain menstruation.
If we consider this process at the biochemical level, we can say that after a reduction in the number of mature follicles, there is a significant decrease in the concentration and decrease in the amount of estrogen produced , therefore, the level of progesterone also decreases. Over time, the process exhausts itself and menstruation may suddenly stop.
The average age for menopause is 50-52 years. Data were identified through surveys. The average age at which menstruation stops completely was found to be 51.3 years. This period can vary up to 1.8 years.
What determines the duration of this period?
How long the menopause will be, namely its stages, as well as the moment of its onset, primarily depends on the hereditary factor .
In some cases, a woman involuntarily postpones the onset of this period due to poor nutrition, bad habits and an unstable, unhealthy lifestyle. The duration of menopause, like menstruation, is directly influenced by the state of the body in which biological aging began.
The instability of menstrual cycles, as well as how many days menstruation will last, and increased symptoms of menopause can be provoked by the following factors:
- the presence of gynecological diseases that appeared during reproductive age;
- the appearance of hormone-dependent formations in the mammary glands;
- failure of the endocrine system;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- hypertension.
Prevention of bleeding
Prevention of bleeding during postmenopause includes the following actions:
- Regularly visit a gynecologist every six months. Medical examinations make it possible to detect hormonal imbalances in the body, as well as the development of a pathological process in the organs of the reproductive system at the initial stage and immediately prescribe treatment.
- Correct hormonal levels with herbal preparations and homeopathic remedies, which are prescribed exclusively by a doctor, based on the results of a blood test for hormones.
- Contact a gynecologist immediately after the onset of symptoms of the disease and cure it completely.
- Visit an endocrinologist annually and monitor the state of the endocrine system.
It is important to avoid stress, as well as strong emotional and physical stress, which provokes hormonal imbalance.
https://youtu.be/4epLEzVtL68
Can menstruation continue?
The reasons why menstruation does not stop during menopause are similar to those that provoke heavy bleeding during the same period.
There are several reasons for this phenomenon:
- malfunction of the genital organs;
- dysfunction of the uterus, fallopian tubes or ovaries;
- prolonged periods provoke a significant disruption of the hormonal system;
- prolonged menstruation, as well as heavy bleeding, are often provoked due to uterine atrophy;
- incessant menstruation indicates that there is a lack of any female sex hormone in the body;
- provoked by taking certain medications, especially those used for contraception or containing hormonal substances;
- various diseases associated with a woman’s reproductive system are often the root cause of not only prolonged periods during menopause, but also heavy bleeding.
The most common pathologies that provoke long periods include:
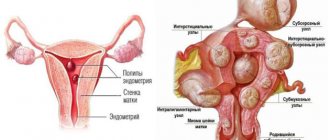
- uterine fibroids;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- the appearance of polyps;
- various diseases that affect the circulatory system, for example, it may be a lack of platelets or poor blood clotting;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland.
When to go to the hospital
Long periods may indicate health problems that require a doctor's examination and subsequent treatment.
- “Chaos” of hormones from childbirth, menopause and other reasons not related to surgical or therapeutic interventions. Occasional periods are standard stages in a woman's development, but periods can be long and heavy. Provided that these periods did not occur, but there is bleeding, a doctor’s examination is needed to examine the cause of the bleeding.
- Hormonal diseases are caused by the thyroid gland; when the organ malfunctions and the production of hormones fails, it leads to serious consequences for the body: prematurity or difficulty conceiving a child. Heavy menstruation that lasts a long time is one of the signs of thyroid failure, and an examination by an endocrinologist is one of the solutions to develop the necessary treatment.
- Without hysteroscopy operations during hormonal imbalance, polyps form on the endometrium, accompanied by prolonged menstruation. When the endometrium grows in the muscles of the uterus and nearby tissues, the disease Adenomyosis occurs. Prolonged PMS with pronounced pain is the main companion and indicator of the disease.
- Uterine fibroids (a benign formation on the walls of the uterus) are characterized by symptoms associated with heavy bleeding during PMS, cycle disruption, shift towards duration or contraction, constant pain in the abdomen and lower back. Myoma is provoked by stress, abortion, infertility, heredity, improper metabolism and menstrual problems. Myoma leads to anemia, because of the tumor, organs are compressed - there is a problem with urination, constipation, the tumor can die and threatens to rupture inside the uterus, constant bleeding, abdominal pain and high temperature, as well as problems with conception, poor delivery.
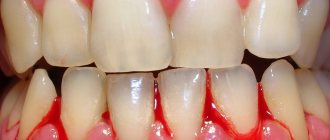
- When platelet clotting in the blood is impaired, a copious amount of discharge during menstruation and its long-lasting nature is characteristic. This leads to severe anemia (anemia). Other symptoms help distinguish platelet blood disease: the gums bleed.
- Contraception with an intrauterine device causes an increase in the cycle and profuse bleeding. The spiral needs to be removed - the individuality of the body does not allow it to be worn.
- Menstrual imbalance is caused by taking birth control pills due to their hormones. Change of cycle, passage of two menstruation in one cycle, heavy bleeding. Without the selection of hormonal contraceptives by a doctor: problems arise during pregnancy, pathologies of the endocrine system, problems with conception, impaired fetal development and deterioration in well-being, weight gain, and changes in features to male ones.
- Hysteroscopy causes pathology due to an incorrectly performed operation: long and heavy periods, anemia, decreased hemoglobin in the blood, a drop in pressure and general weakness of the body.
The most terrible complication revealed by acyclic long and heavy menstruation is uterine cancer. One of the most common cancer diseases.
At work, a friend had a problem with cycles and heavy bleeding during menstruation; she was afraid to go to the doctor for a long time, hoping that it would go away, but when they persuaded her to have her examined, they managed to detect the first stage of the tumor and cure it with therapy without surgery.
What to do if your cycle is disrupted
If there is any concern about the state of the body during menopause, then the first thing to do is to analyze what was typical for this period for the mother and grandmother. Most often, the manifestations during menopause in the female line are identical.
Manifestations that are alarm signals and require immediate treatment include:
- the appearance of bleeding after intimacy;
- the menstrual period is protracted, lasting more than a week ;
- In addition to the fact that the duration of menstruation exceeds the norm, there is blood loss (80 ml or more) ;
- of blood clots is observed in the discharge ;
- if during menopause menstruation appears for less than 2 days ;
- there is the appearance of discharge between cycles ;
- there is a pronounced pain syndrome in the lower abdomen, the duration of which is 7 or more days.
What to do
Normally, menstruation should reduce its intensity closer to 3-4 days, but if they not only drag on for more than 7 days, but also become even more abundant, you must definitely seek medical help. If you have a long period, what is not recommended to do is self-medicate and use folk remedies without a doctor’s prescription.
If heavy blood loss is accompanied by severe pain, loss of strength and pale skin, you should immediately call an ambulance. Before the ambulance arrives, a cold compress to the lower abdomen will help alleviate the condition, while you need to lie horizontally, put your legs above body level, you can put a bolster or pillows under them.
How to stop prolonged discharge
Only a doctor can state the fact that menstruation during menopause has acquired signs of deviation and is prolonged. It is not recommended to stop the process of menstruation on your own; there is a risk of causing irreparable damage to your health.
However, if you are confident in the correctness of your decision to self-medicate, then you can use the following list of drugs:
- contraceptives or oral contraceptives are used to stop long periods for an extended period. If the patient is already using such medications, it is not recommended to stop taking them;
- Vikasol . Used to almost instantly stop bleeding by enhancing the blood clotting process. This remedy can stop prolonged menstruation during a specific period, however, this will not completely solve the problem;
- Tranexam . The drug is available in the form of tablets or injections and is aimed at stopping bleeding. As in the case of the previous remedy, it cannot be used as a therapeutic measure to eliminate the root cause of the pathology;
- Duphaston . The drug contains hormonal substances that help stop bleeding. Its advantage lies in the fact that its action is in no way connected with enhancing the process of blood clotting.
Treatment of bleeding during menopause
If bleeding occurs after menopause, the following medications are prescribed:
- Oral contraceptives - help stop prolonged bleeding.
- Hormonal drugs including progesterone. Duphaston is often prescribed.
- Artificial vitamin K, which affects blood clotting. The drug Vikasol is popular.
- Medicines whose active ingredient is tranexamic acid, which treats bleeding. An effective drug Tranexam.
You cannot self-medicate so as not to harm your health. You should definitely contact a gynecologist who will conduct a diagnosis and prescribe medications based on its results.
Menses
Menstruation is the final stage of the monthly cycle. They begin if fertilization does not occur and the body’s preparation for pregnancy is in vain. In order to begin preparing for conception again, the uterus rejects the inner layer of its lining. Particles of mucous membrane along with bloody discharge are menstruation. That is why the first thought when your period disappears will be about a possible pregnancy. Since the endometrium has not been rejected, it is likely that an embryo has attached to it, and the woman’s pregnancy is progressing.
Features of menstruation before menopause
At the stage of premenopause, complex processes occur in the female body associated with the decline of reproductive function. One of the first symptoms of this stage is a change in the menstrual cycle and the nature of menstruation.
How do your periods go before menopause?
Before the onset of menopause, the following changes in menstrual flow and monthly cycle may be observed:
- The cycle ceases to be regular.
- The period between critical days increases.
- The volume of menstrual flow is reduced.
- Mucus may appear in the discharge. It is considered normal if the color of the blood is not scarlet or brown.
During critical days, a woman may feel pain in the lower abdomen, general malaise, and mood swings, even if there were no such manifestations before.
Long periods in premenopause
Hormonal imbalance leads to changes in the length of menstruation. In women, the number of critical days is often reduced to 2-3. Some ladies, on the contrary, begin to have long periods, which last up to 7 days, and sometimes up to 10 days.
Heavy periods before menopause
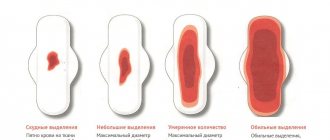
During the premenopausal stage, heavy periods are possible, but there should be a tendency for blood loss to decrease with each new cycle. If, after the first symptoms of menopause appear, there is heavy discharge during each cycle for six months, then you should see a doctor. Heavy periods are considered to be:
- duration of critical days up to 7 days;
- daily blood loss up to 80 ml.
At this stage of the menopause, alternating scanty and heavy menstruation is considered normal.
Pregnancy
How can you tell if the disappearance of your period is related to pregnancy? If a woman has had at least one sexual intercourse this cycle, first of all you need to think about possible conception. Preventive measures do not provide a 100% guarantee, regardless of their type.
Oral contraceptives, hormonal rings, local suppositories and ointments, and condoms do not exclude possible pregnancy. If the calendar method or interrupted sexual intercourse was used for the purpose of protection, then it becomes very likely.
In rare cases, pregnancy occurs even if sex occurred on the eve of the previous menstruation due to a shift in ovulation. And, although this phenomenon is not very common, conception cannot be ruled out. What to do if your periods have stopped and you suspect you are pregnant?
Even more interesting:
I infected my boyfriend with HPV
The ovary is enlarged and painful
Pregnancy confirmation
If, by all estimates, menstruation should occur, but it does not, it is better to buy a test to determine pregnancy. They are sold at any pharmacy and come in different prices and sensitivity.
Why do I have heavy periods with clots after 50 years?
With changes in the frequency and nature of menstruation, the entire reproductive system may change. Libido may decrease, dryness in the intimate areas, and pain during intercourse may occur. This is also a variant of the norm, so the main task of a woman is to experience hormonal changes in the body painlessly, to make sure that the body experiences as little discomfort as possible due to a decrease in the amount of hormones.
Usually, hormone replacement therapy, or phytoestrogens, that is, herbal preparations, is used for these purposes. Their structure is slightly reminiscent of natural estrogens, but they cause a minimum of adverse reactions. More information about phytoestrogens can be found here.
Climax
Heavy periods with clots after 50, reasons
- Please note that blood with clots can be a symptom of endometriosis, which is the growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus. This is a dangerous disease that causes a lot of trouble, so you need to see a doctor.
- Frequent, heavy periods with clots become a sign of uterine fibroids, as well as endometrial hyperplasia.
- All this is most often provoked by an increased content of estrogen and a lack of progesterone. Therefore, in such conditions, it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo all the necessary tests.
Menstruation
Reasons for delay
If there was no sexual intercourse the day before or pregnancy is excluded, you should think about other reasons for the disappearance of menstruation. There are quite a lot of them. Menstrual irregularities can be associated with both pathological and physiological processes.
Delay does not always mean illness. This may be temporary, a passing phenomenon, or even a variant of the norm. But in some cases, the disappearance of menstruation indicates serious hormonal imbalances in the body. There are three main groups of causes of an irregular menstrual cycle or complete absence of periods:
- physiological.
- pathological.
- external influence (reversible disappearance of menstruation).
Physiological reasons
Physiological reasons for the absence of menstruation include natural processes occurring in the female body. This is first of all:
- Growing up, transition from childhood to adolescence, puberty.
- Aging – menopause and menopause.
- The work of the reproductive system – pregnancy and lactation.
With a confirmed pregnancy, the disappearance of menstruation does not surprise anyone, just like their absence during breastfeeding. But in adolescence or after 45 years, the disappearance of regular bleeding can cause a woman or girl to seriously worry. In fact, there is usually no cause for alarm in these situations.
Teenage years
During adolescence, a girl gets her first period, which is called menarche. This happens between the ages of 10 and 16, most often between 12 and 14 years. Once the first bleeding appears, a teenager can expect it to happen again within a month. But menstruation disappears for a long time. Why does this happen, and is the absence of menstruation a pathology?
No, this is absolutely normal for the formation of the menstrual cycle. But not all girls and their mothers know about this. During the first year after menarche, the cycle may be very irregular. Menstruation may disappear for two to three weeks and then appear again, varying in volume and duration. The alarm should be sounded in two cases:
So that the disappearance of habitual bleeding does not come as a surprise to a teenager after the onset of menarche, it is worth recommending that she consult a pediatric gynecologist. The doctor will be able to clearly explain all the features of the female cycle during this period and the symptoms that should alert the girl.
Menopause and menopause
As reproductive function declines, menstruation becomes irregular and one day disappears completely. Most women are aware of these features of their body and perceive them calmly. Menopause usually occurs after 50–55 years. However, in some situations, the disappearance of menstruation can alert a woman. When does this happen?
Sometimes menopause starts early. It can occur at 36 years of age. Typically, such pathologies are observed in women over several generations. There are also artificial menopause caused by surgical removal of the ovaries, uterus or drug suppression of their function. If a woman has received appropriate treatment, the doctor must warn her about the subsequent disappearance of monthly bleeding.
There is another situation. Gradually disappearing periods during menopause do not exclude the possibility of becoming pregnant. And their sudden disappearance after a few months can turn into a surprise for a woman. Moreover, some people retain the ability to conceive even one or two years after menopause, so it is better not to tempt fate and not forget about contraceptives even during menopause.
Pathological causes
The pathological absence of menstruation (amenorrhea) is caused by many diseases. Since the female cycle is regulated by many hormones, the cause of amenorrhea in the vast majority of cases is dishormonal diseases. They can be gynecological or endocrinological and manifest with different symptoms.
If your period disappears after a regular cycle has been established, this phenomenon is called secondary amenorrhea. What symptoms will help to suspect a pathological disappearance of menstruation? Most often these will be the following unusual manifestations:
What should you do if a woman suddenly stops menstruating and has these symptoms? First of all, you should contact a gynecologist to establish a preliminary diagnosis. He will refer you for the necessary examination and, if necessary, for an examination by an endocrinologist.
Of the diseases accompanied by disruption of the female cycle, endocrinological pathologies are quite common. These include:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Galactorrhea-amenorrhea syndrome.
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
As the name implies, with this pathology the structure of the ovaries changes. Many cysts form in them, which leads to dysfunction. The ovaries are responsible for the exchange of female sex hormones and the release of eggs capable of fertilization. With this syndrome, their work can be significantly impaired.
In mild cases, polycystic ovary syndrome manifests itself only in periodic anovulatory cycles. This means that in the middle of the month the mature egg does not exit into the fallopian tube, and fertilization is impossible. However, bleeding at the beginning of the cycle persists.
Severe forms of the disease are characterized by a complete cessation of menstruation. In addition, hormonal metabolism is significantly disrupted. Women with polycystic ovaries are characterized by obesity, acne, and excess hair growth. If these symptoms have appeared recently and your periods have disappeared, you should contact a gynecologist-endocrinologist as soon as possible to clarify the diagnosis.
Polycystic ovary syndrome can be cured with adequate therapy. Sometimes surgery has to be performed. Why is polycystic ovary syndrome so dangerous? Lack of treatment for this disease leads to persistent infertility.
Galactorrhea-amenorrhea syndrome
There is another endocrinological pathology in which menstruation suddenly disappears. It is also characterized by a second specific symptom - white discharge from the breast, which looks like milk or colostrum. Actually, that's what they are. Galactorrhea-amenorrhea syndrome is caused by excess prolactin production. Its second name is hyperprolactinemia syndrome. Why is such amenorrhea dangerous for a woman?
What diseases cause long periods?
Among the many reasons that form long, protracted periods (hypermenorrhea or mennorrhagia), several groups of painful factors can be distinguished:
- poor blood clotting;
- weak inelastic vessel walls;
- hormonal disbalance;
- the need to clean the internal cavity of the uterus.
Let us consider the diseases in which the listed factors are formed. Menstruation does not stop with the following diseases of the female body:
- stress;
- chronic anemia (anemia);
- malignant and benign formations;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- gynecological diseases (for example, endometriosis or gynecological inflammation).
Endometriosis is expressed in excessive growth of the mucous layer of the uterus. The mucous membrane (endometrium) grows with the formation of additional cavities. During menstruation, the mucous membrane is rejected and comes out in the form of bleeding. The endometrium, enlarged several times, forms abundant and longer periods. When menstruation lasts a long time with endometriosis, what to do - there is only one answer: treat the disease.