Using a general blood test, you can identify numerous diseases that are not accompanied by obvious symptoms. The diagnostic results always include several main components of the biomaterial, each of which indicates a specific list of ailments.
One of the most representative groups are eosinophils - important representatives of the immune system. Their quantitative ratio is a kind of litmus test for the state of human health. If serious deviations from the norm are detected, specialists prescribe a series of more accurate studies to make a reliable diagnosis. Medical intervention is especially important when eosinophils in the blood are elevated.
Etiology
An increased content of eosinophils can be caused by both physiological and pathological factors.
The pathological reasons that eosinophils are higher than normal are the following:
- parasitic diseases – helminthic infestations, giardiasis, ascariasis;
- malignant tumors;
- allergic reactions;
- asthma;
- tuberculosis;
- acute leukemia;
- rheumatic reaction;
- vagotonia;
- hypothyroidism and other diseases of the endocrine system;
- blood diseases;
- gastroenterological disorders.
A hereditary form of eosinophilia cannot be ruled out either.
Eosinophils in the blood may be physiologically elevated in the following cases:
- the beginning of the menstrual cycle;
- during sleep;
- use of drugs - hormonal drugs, beta blockers, antibiotics, sulfonamide drugs;
- unhealthy diet – excessive amounts of sweets and alcohol.
Separately, we should highlight the reasons why eosinophils in the blood will be elevated in a child:
- in newborns - Rh conflict, allergic reaction, hemolytic disease, staphylococcal infection;
- from 1.5 to 2 years - Quincke's edema, atopic dermatitis, allergic reaction to food or medications;
- in children over three years old - helminthiasis, viral or infectious diseases, allergic reactions.
Only a doctor can determine exactly why a person has high eosinophils by carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures. Therefore, if any symptoms are present, it is necessary to seek medical help rather than carry out symptomatic treatment at your own discretion.
Causes of increased eosinophils
Increased normal eosinophil levels
In hematology, a condition in which eosinophils are elevated in an adult or a child is referred to as eosinophilia. This condition in itself is not a disease, but acts as a kind of marker of pathological changes in the body. There are three forms of eosinophilia:
- mild – the eosinophil count does not exceed 10 percent;
- moderate – up to 15 percent;
- pronounced - more than 15 percent.
At the same time, a number of hematologists expand the border of moderate eosinophilia to 20 percent, and expressed, accordingly, according to this gradation, starts from 21 percent. There is also a confirmed correlation between the form of eosinophilia and the complexity of the pathological process, which led to the growth of eosinophils in the blood: a higher degree of eosinophilia in most cases characterizes the complex course of the pathological process.
The reasons for the increased level of this type of leukocytes can be a number of reasons:
- atopic diseases (bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, hay fever);
- parasitic diseases (malaria, ascariasis, giardiasis);
- non-atopic skin diseases (pemphigus, dermatitis, epidermolysis);
- gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, ulcers, cirrhosis of the liver);
- rheumatic diseases;
- hematological diseases (leukemia, anemia, polycythemia, lymphogranulomatosis, eosinophilic leukemia);
- lung diseases (pneumonia);
- weakened immune system;
- allergic reactions of all kinds. They are considered the most common cause of increased eosinophils in the blood;
- side effects from taking medications (most often eosinophilia is provoked by banal aspirin and a number of antibiotics in the form of injections).
Following the detection of a high level of eosinophils in the blood, the doctor prescribes additional diagnostics, which includes a biochemical blood test, ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs and stool sampling to determine the presence of worm eggs. In addition, if eosinophils exceed normal limits, it entails an immediate consultation with an allergist, who must confirm or rule out the presence of allergies - a prerequisite for the development of eosinophilia.
Classification
The following degrees of severity of eosinophilia are distinguished:
- light – up to 10%;
- average – 10-15%;
- severe - more than 15% (this form of the pathological process can be accompanied by oxygen starvation of tissues, which is extremely life-threatening).
To determine the severity of the pathology, a general blood test is performed with the calculation of abs eosinophils, that is, the absolute number.
There are also relative and absolute forms of the disease. The relative stage is rarely a manifestation of a serious disease, since in this case they speak of an increase in the number of eosinophils, and their percentage remains within acceptable limits. The absolute form is of concern: in this case, it is the percentage of increased cells that is diagnosed, which indicates the development of the disease.
Causes of low levels of eosinophils in the blood
A decrease in the level of eosinophils in the blood below the standard value is designated by the term eosinopenia. At the same time, there is a decrease in this indicator down to zero, which is a very dangerous condition. If eosinophils are practically absent in the blood, this may indicate the development of acute appendicitis, typhoid fever or diphtheria, as well as an advanced form of leukemia.
In the case of a non-critical drop in this indicator, eosinopenia may be a consequence of a person’s post-operative condition, a consequence of injuries and burns, sepsis, or evidence of the onset of the development of any infectious disease.
Clinical studies also show that persistently low levels of eosinophils are characteristic of people with Down syndrome and people with chronic fatigue syndrome.
Symptoms
Elevated eosinophils in the blood of an adult do not have a specific clinical picture, since this is not a separate disease. Symptoms will depend on the underlying cause.
The following symptoms may occur:
- disruption of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- relapses of chronic diseases, if any;
- skin rashes, which may be accompanied by itching, peeling, formations of various nature;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- increased or high temperature;
- symptoms of ARVI, influenza;
- disorders of the genitourinary system - frequent urination, itching and burning in the genital area, pain in the lower abdomen and groin area, foreign discharge;
- in women - menstrual irregularities;
- headaches, dizziness for no apparent reason;
- frequent cases of ARVI, protracted recovery process.
It is impossible to determine from the current clinical picture alone whether eosinophils are increased or decreased in an adult, so it is advisable to seek medical help rather than carry out symptomatic treatment.
General information
What are eosinophils in a blood test? These are white blood cells, a type of leukocytes responsible for the body’s fight against foreign proteins and microorganisms. This type of cell has many functions, including:
- formation of a persistent immune response;
- fight against bacteria;
- relief of foci of inflammation;
- neutralization of allergens and parasites.
The formation time of eosinophils is 72-96 hours. It is this period of time that is required for the CCA to reflect the occurrence of the body’s response to the stimulus. Next, eosinophils penetrate the mucous membranes and continue to exist on them for another 2 weeks. A large number of eosinophils or conditions where eosinophils are below normal require special attention.
It should be noted that slightly high eosinophils are a normal manifestation in preschool children. Their immune system is not yet sufficiently developed, so it can react violently to some microorganisms. In addition, children actively explore the world around them, which makes it inevitable that parasites and protozoa will enter the body.
What blood tests are there?10807
It must be remembered that an increased number of eosinophils does not indicate the presence of pathology. It is much more dangerous if children have low eosinophils. This may indicate a serious decrease in immunity and the development of pathologies. If the body has managed to eliminate the danger, the number of cells quickly returns to normal. A condition where eosinophils are elevated in an adult necessarily requires consultation with a specialist, as it may indicate a dangerous disease.
The norm of eosinophils in the blood is:
- up to 1 year – 1-6%;
- 1-2 years – 1-7%;
- 2-5 years – 1-6%;
- from 5 years - 1-5%.
The norm is the same for women and men. Indicators may increase slightly. This usually causes concern among doctors and requires additional examinations. However, it must be remembered that one-time changes in the analysis do not play a significant role in diagnosis and require additional and repeated studies.
Diagnostics
Determination of the level of eosinophils in the blood is carried out using a general blood test from a finger prick.
In order for the result to be correct, you must adhere to the following rules for the procedure:
- donate blood only in a calm, emotional state;
- one day before the procedure, you need to stop using medications (if possible), alcoholic beverages, and also avoid excessive physical and emotional stress;
- If the patient is taking medications, then it is mandatory to notify the doctor about this before the test.
Not only the number of eosinophils is taken into account, but also other blood components.
The most commonly used combinations are:
- increased monocytes and eosinophils - an infectious or parasitic disease is probably developing in the body;
- eosinophils are increased and neutrophils are decreased - a consequence of taking medications, cancer, inflammatory process;
- eosinophils and basophils are increased - an allergic reaction, an infectious disease at the peak of development.
If tests confirm that the number of such cells in the blood is significantly higher than it should be based on age, then a repeat blood test and the following diagnostic measures are performed:
- general urine analysis;
- general stool analysis and parasite analysis;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- allergy tests.
The exact list of diagnostic measures will be determined on an individual basis.
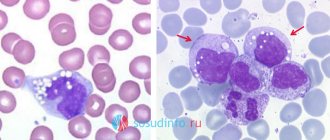
What are eosinophils
Leukocytes, which ensure the internal safety of the body, are divided into several main categories: lymphocytes, basophils, neutrophils, monocytes and those same eosinophils. The last formed elements of blood, after rapid maturation in the bone marrow, are transported by the blood flow to the sites of inflammation. Thanks to their amoeba-like movement, they easily overcome natural barriers on their way to the affected tissues.
Large protective bodies envelop harmful bacteria or viral particles and then absorb them. If pathogens turn out to be too persistent in the process of confrontation, eosinophils undergo active self-destruction: the ongoing process, like an alarm beacon, attracts the attention of other leukocytes, which are sent to the place of death of their “brothers” and destroy dangerous antigens.
The granulocytes in question are a natural marker of latent diseases. The number of granular cells changes at the slightest violation of the integrity of the body, which is due to their increased sensitivity to regressive changes.
Analysis transcript
When taking an analysis to detect the level of eosinophils, you should be aware of the influence of certain factors on the result.
Such factors may include:
- recent surgery,
- recent birth,
- taking certain medications.
If these events occurred less than 2 weeks ago, the test result may be distorted and the eosinophil level will be lower than normal.
When testing blood, it is necessary to look at the level of leukocytes, including eosinophils, since they are the ones that perform the protective functions of the body.
The normal level of eosinophils in a healthy person is 0.5-5% of the total number of leukocytes. Their increase may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process, allergies or the presence of parasites in the body.
Prevention measures
To prevent the occurrence of reactive eosinophilia it is necessary:
- avoid contact with allergens;
- do not take medications without a doctor’s prescription or without following the dosage;
- promptly sanitize foci of chronic infection;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene when in contact with dogs and cats;
- do not eat raw fish or meat;
- wash your hands before eating, as well as vegetables and fruits;
- avoid traveling to countries with endemic areas;
- Conduct tuberculin diagnostics for children under 15 years of age (Mantoux test), and lung fluorography for adults annually.
At any age, eosinophilia requires a careful approach to diagnosis and treatment. The causes of the syndrome can be both age-related characteristics of premature newborns and many other diseases, including cancer. Early detection of elevated levels of these blood cells helps prevent death.
- Author: Olga Dolyuk
Hello! I am a doctor who knows how and loves to write medical articles. I became interested in copyright 2 years ago. Creating interesting and informative texts helps not only to earn money, but also to constantly improve oneself in the field of medicine. Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(1 vote, average: 5 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
Increased levels of eosinophils
If eosinophils are elevated in a general blood test, then this condition is called eosinophilia. It is divided into several degrees:
- Mild eosinophilia. It is characterized by a cell number of up to 10%.
- Moderate eosinophilia. Eosinophils are contained in an amount of 10–15%.
- Severe eosinophilia. Cells more than 15%.
But these are far from definitive values, since many hematologists still argue and argue that moderate eosinophilia in children and adults has a range of 10–20%.
The severity of the pathological process will depend on the degree of eosinophilia, because the higher it is, the more severe the pathology.
conclusions
Eosinophils are protective blood cells from the group of leukocytes that resist allergens, parasites, and atypical cells. The proportion among all leukocytes is considered to be up to 5% and the absolute value is up to 0.3*10⁹/l. An increase may indicate:
- allergies;
- autopathology;
- malignant diseases;
- infection with worms or other parasites.
A decrease in the level of eosinophils is detected much less frequently, but may be associated with the development of oncology, chronic infectious diseases, and occurs while taking certain medications. Some conditions can threaten human life and therefore require timely diagnosis and treatment. Read more about this in the article: “Eosinophils are low - what do these blood counts indicate and what to do.”
Eosinophilia is a laboratory term, a symptom of disorders in the body. To eliminate deviations, it is necessary to determine the nature of the pathology and begin pathogenetic treatment.
Source: cc-t1.ru
Preparing for a blood test
To obtain the most reliable test result, you should adhere to some rules for donating blood:
- Blood should be donated in the morning on an empty stomach.
- A few days before the test, you should stop eating sweets and alcoholic beverages.
- Women should not take tests during their menstrual cycle, as ovulation can affect or distort the test result. For this purpose, a special test has been developed that will help identify the peak of egg maturation. The level of eosinophils is inversely proportional to the level of progesterone in a woman's blood. And with an increase in estrogen, the level of eosinophils in the blood increases.
It should also be noted that the highest level of eosinophils is observed at night, when the indicator can exceed the norm by 30%, and the lowest level is observed in the morning and evening, when the indicator drops by almost 20% of the norm.
How to stop eosinopenia?
What does eosinopenia mean? This is a condition of the human body in which the concentration of eosinophils is below 200 in 1 ml of blood.
Low levels of white blood cells are observed in the following cases:
- Severe purulent infections, which include sepsis and other diseases. During these diseases, the body is unable to produce the required number of eosinophils.
- The first day after myocardial infarction.
- At the initial stages of inflammatory processes.
- For diseases requiring surgical intervention (appendicitis, pancreatitis).
- A state of shock, namely severe pain and infectious shocks. In such situations, the formed elements of blood stick together and settle on the walls of blood vessels.
- Leukemia of the developed form.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
- Poisoning by various metals such as lead, mercury, and arsenic. .
- Severe emotional stress.
A decrease in the level of eosinophils in the blood means the presence of a disease. There are many reasons for their occurrence, but the mechanism of development is still not clear.
There is no specific treatment for low levels of eosinophils; the fight is aimed at treating the disease that provoked this deviation.
Correct diagnosis and treatment of the disease that caused the decrease in eosinophils will lead to the elimination of eosinopenia and the patient’s recovery.
Also, do not forget that a decrease in eosinophils can occur during pregnancy, so before starting treatment you should conduct a test or undergo an examination by a gynecologist.
Reasons for the increase
There are three reasons that lead to an increase in the number of eosinophils in the human body:
- The presence of infectious parasites in the human body. When a protein from an infectious pathogen enters a cell, the secretion contained inside the cell nucleus begins to destroy it. The main task of eosinophils in this case is to complete the process of destroying the foreign element.
- The manifestation of an allergic reaction to the interaction of an antibody and an antigen. Eosinophils stop the activity of biological substances that provoke a negative reaction in the body.
- Prevention of blood clots in blood vessels. The task and function of eosinophils is to prevent the processes of gluing of colorless blood cells - platelets.
Reasons for deviations in eosinophil concentration from normal
Causes of eosinophilia at different ages:
If an increased cell content is detected, a blood test for biochemistry, a stool test for worm eggs, and an ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract are additionally prescribed. The woman is additionally examined by a gynecologist and endocrinologist. Without fail, regardless of age and gender, a nasal swab is taken to check for the presence of eosinophils, spirometry and an allergy test are performed.
A decrease in eosinophils is associated with severe purulent infections and recovery in the postoperative period. The number of cells decreases in the first day after myocardial infarction, with severe metal poisoning and with chronic stress.
Among women
Reasons for abnormal eosinophils in women:
What are the symptoms in women with eosinophilia:
- when the lymph nodes enlarge, general intoxication of the body occurs, and headache is present;
- with allergies, a rash appears, the face and eyelids swell, less often itching and spots appear;
- with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, a rash appears on the skin, pain in the liver area, diarrhea and nausea are disturbing.
Treatment will depend on the cause.
A regular increase in eosinophils at certain times of the year does not pose a health hazard, but is a sign of seasonal allergies or poisoning of the body.
In pregnant women
A normal eosinophil count during pregnancy will be between 0 and 5%. When this indicator increases, we are talking about an allergic reaction or helminthic infestation. Cell levels also increase after eating certain foods, including citrus fruits. Before donating blood for testing, a pregnant woman must undergo standard preparation.
There are no external manifestations of minor deviations from the norm. In rare cases, a pregnant woman may experience peeling, redness of the skin and mild itching.
In men
The normal concentration of eosinophils at different ages does not depend on gender. For men, the norm is the same, ranging from 0.5 to 5%. In old age (after 70 years), the normal indicators change upward to 1-5.5%. The reason for the increase in cells are similar factors. The decrease may be associated with severe injuries, exhaustion of the body due to grueling physical activity. The indicator decreases with regular lack of sleep and stress.
Note! In severe diseases of infectious origin, eosinophils can completely disappear from the blood.
The blood contains a large number of different formed elements, among which are eosinophils. They are a marker of many diseases. Therefore, they are determined during the study of biological material (clinical blood test).
If their level changes up or down, it is necessary to identify the cause and carry out appropriate treatment. Doctors recommend donating blood for analysis at least once a year.
How to treat the syndrome
Therapeutic tactics for reactive eosinophilia do not make sense without eliminating the main cause. Therefore, all drugs are selected taking into account the underlying disease. But with pronounced symptoms of eosinophilia without specifying the root cause, to improve the quality of life they use in adults and children:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Paracetamol, Ibuprofen to reduce pain;
- antihistamines to eliminate itching and rashes: Fenistil (for children from 1 month);
- L-Cet (allowed from 6 months);
- Tsetrin (from 6 years old).
- Prednisolone;
- Montelukast, which can be used in children from 6 years of age;
The use of other medications until the underlying disease is clarified is not advisable.
If eosnophilia is caused by a food allergy, then the patient must adhere to dietary principles excluding foods to which his body reacts in this way. For other types of eosinophilic syndrome, the diet is not effective.
If, after diagnostic procedures, the primary origin of the syndrome is established, i.e., idiopathic eosinophilia, then in addition to symptomatic therapy, the treatment regimen includes Imatinib (approved from 18 years of age, but also used in children if necessary), which affects the degree of eosinophil formation in the red bone brain.
The use of traditional medicine methods is irrational, since they are not able to influence the cause of the disease.
Drugs for the treatment of eosinophilic syndrome - photo gallery
Paracetamol - an anesthetic drug for children and adults Fenistil eliminates itching and rashes L-Cet - an antiallergic drug from 6 months Prednisolone helps with severe symptoms of eosinophilia Montelukast is used for pulmonary forms of eosinophilia Imatinib is used for idiopathic eosinophilia
Treatment.
The treatment is carried out by a hematologist. There is no independent disease of eosinophilia, as such. Treatment as an independent pathology is not carried out.
The original causes of increased cell levels are eliminated.
Eosinophilia of allergic origin does not require special therapy. Treatment focuses on eliminating the allergic pathogen. In special cases, when the allergen cannot be identified, therapy is carried out using the drug Cetrin. 1 capsule 1 time per day. Oral administration is recommended until indicators improve after repeated tests.
Eosinophilia caused by pulmonary diseases does not require drug treatment in most cases. In severe cases and complications, the attending physician prescribes a course of corticosteroid hormones. The course of application is no more than 6 days. Prednisolone 15 mg is used every other day, orally. The course of treatment is short. Can be used for no more than 6 days.
In the presence of bronchial asthma and similar manifestations, an inhalation method of treatment is recommended. A drug such as Theophylline is used. Such patients usually require hospitalization and are required to be registered at a dispensary.
For the parasitic form, a course of anti-parasitic therapy is prescribed. The attending physician specialist prescribes a single dose of Mebendazole.
Myositis, fascistitis - glucocorticoids in a fairly high dosage - Prednisone. In the absence of long-term effect or obvious improvements, a cytostatic drug, Azathioprine, is prescribed.
If there are skin rashes or inflammation of the lymph nodes , the patient is sent for physical therapy - phonophoresis. In severe cases of the disease, hemosorption will give an excellent result, but this method is used only if the disease is stable after treatment.
When treating children, a “standby mode” is used. In case of rapidly progressing indicators, hormonal therapy is prescribed.
Source: analizkrovi.net