Causes of spotting outside of menstruation
Spotting is a scanty discharge from the vagina mixed with blood.
Normally, blood is released from the vagina only in non-pregnant women during menstruation. But with some gynecological diseases and various cycle disorders, spotting may appear in the middle of the cycle, before and after menstruation. Let's consider the possible reasons for such deviations. Nowadays, gynecological diseases such as endometriosis and endometritis are quite common among women of reproductive age. Endometritis is an inflammatory disease of the internal tissues of the uterus. The reason for this could be, for example, abortion. The onset of the disease is usually acute - pain, fever, etc. If a woman does not receive adequate treatment, then at best the disease becomes chronic. And in the chronic stage, spotting outside of menstruation is no longer uncommon. Endometriosis, which causes the same symptoms, is a disease that causes the endometrium to grow outside the uterus. It predominantly develops in women 35-50 years old. The reasons are hormonal, genetic, immune disorders, etc. If you notice spotting after your period and before it, we would advise you to go to the gynecologist, since it is quite possible that the cause of this is endometriosis. Diagnosis is carried out using several methods at once: ultrasound, hysterography, laparoscopy. Treatment is carried out using single-phase combined oral contraceptives or drugs containing only one hormone - levonorgestrel. In some cases, a woman is recommended to install the Mirena hormonal device. In advanced cases, surgical treatment may be necessary.
It is not uncommon for spotting brown discharge, and sometimes even bleeding, to occur when taking oral contraceptives - birth control pills. In the case of “daubs,” it is usually recommended to wait 2-3 months, since this may be an individual reaction of the body, and everything will recover on its own. In other cases, it is recommended to switch to another drug. For example, a nursing woman whose baby is already 6-7 months old can switch to combination pills (containing estrogen) instead of mini-pills, which often cause spotting before menstruation and in the middle of the cycle. If a woman is already taking combination pills, then she may need to switch to a drug containing a slightly larger amount of estrogen (for example, 30 mcg instead of 20 mcg). Both are considered last-generation contraceptives, low-dose and safe if taken as directed by women who have no contraindications to them. The same “daub” can occur when using another hormonal contraception, for example, the Nova-Ring vaginal ring or the Mirena coil.
Another possible reason for the appearance of “spotting” in the second half of the cycle is the implantation of a fertilized egg into the wall of the uterus. This is also called implantation bleeding. It is quite rare, but is considered a completely reliable sign of pregnancy.
Bleeding, strong and weak, often occurs outside of menstruation in women with uterine fibroids.
In addition, spotting often occurs in the early stages of pregnancy, especially during periods when, according to the calendar, there should have been regular periods if conception had not occurred. If the discharge is insignificant, and an ultrasound shows that the fetus is developing, the woman is advised to reduce sexual activity and reduce physical activity. If there is significant discharge, the woman is admitted to the hospital “for preservation.” Otherwise, if you refuse treatment, a miscarriage may occur.
As you can see, the reasons for the appearance of bloody vaginal discharge are very diverse. But only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
If brown discharge appears between periods, is this an alarming symptom or normal? 4
Ideally, women should not have any bloody or brown discharge from the genital tract outside of menstruation.
But often girls notice spotting before or after menstruation, as well as after sexual intercourse. It is necessary to pay attention to this; often such minor manifestations hide serious diseases.
When should you sound the alarm and run to the doctor? In what cases can brown discharge between periods be normal?
Discharge is normal
Discharge from a girl's genital tract can change throughout the menstrual cycle. It depends on age, hormonal levels, the presence of various diseases and some other reasons.
During puberty, when puberty just begins, the body, saturated with estrogen, begins to stimulate the formation of mucus in the vagina. It can be transparent and whitish in color.
Most often it has a viscous consistency, sometimes like “lumps”.
All this indicates a favorable development of puberty, the girl’s complete health and the fact that her menstrual function will soon improve.
During menopause, discharge from the genital tract becomes significantly less, often women do not notice it at all. The appearance of spotting brown or bright scarlet bloody discharge at this age indicates the progression of some disease.
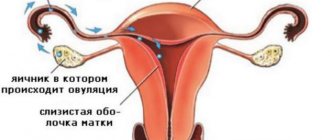
As you approach ovulation, the discharge becomes more and more mucous and viscous. Some girls figuratively compare them to the white of a chicken egg. As soon as ovulation occurs, they acquire a thicker consistency and a whitish tint. But such changes do not always occur, but only with an ideal hormonal background in a healthy girl.
Brown discharge is normal
If a woman once experiences bloody, very slight discharge from the genital tract outside of menstruation, then most likely it is associated with functional changes in her body.
If brown daub is a constant companion, then there is a high probability of a pathological process. In this case, it is better to immediately consult a doctor rather than wait for everything to correct itself.
In the middle of the cycle
Some women “feel” their ovulation. One of the signals may be spotting brown or even menstrual-like discharge in the middle of the cycle. Usually they last no more than 1 - 3 days.
This is due to sharp fluctuations in hormonal levels due to overwork, lack of sleep, positive emotions, etc. Often there are no obvious reasons for this. But you should be wary if such a daub appears monthly.
This is a signal for a more in-depth examination and identification of the true causes.
Days of ovulation in a woman
After sexual intercourse
Stormy intimate relationships, especially under the influence of alcohol or drugs, often lead to injuries to the genital organs. Moreover, their nature varies from small cracks to serious ruptures.
In the first case, you don’t have to worry too much; a slight smear will go away in a day or two. But with heavy discharge, surgical intervention is often indispensable; you should seek medical help.
While taking oral contraceptives
In the first month of taking hormonal drugs, including for the purpose of contraception, various types of bleeding from the genital tract are often observed. This can be a short-term daub, or sometimes more abundant and long-lasting regulation.
Similar disruptions to the menstrual cycle are allowed during the first month. If symptoms persist, you should consult a doctor for examination. This may indicate an inadequate dose of the hormone in the drug or that it is not suitable for this girl.
Minor cycle disturbances, more often in the middle, can occur even with long-term use of hormonal contraception.
If brown discharge appears once between periods, it does not pose a particular threat and only indicates the body’s adaptive reactions (subject to the pill taking schedule). But a repetition of this requires further examination by a specialist.
If the intake of oral contraceptives is disrupted, this entails, in most cases, brown spotting or even spotting.
Before and after menstruation
Spotting brown discharge can be a signal of the onset of menstruation. Also, after the end of critical days, similar ones can be observed. But it should be borne in mind that such discharge can normally last no more than 1 - 2 days. Longer ones indicate some kind of pathology and require examination.
Pathological discharge
And yet, bloody-brown discharge between periods is not normal in a large percentage of cases. Especially if they are combined with the following symptoms:
- pain not associated with menstruation, it often occurs during sexual intercourse;
- if such discharge is permanent and almost always occurs after sex;
- if the woman has been in menopause for a long time.
To clarify the cause in such situations, you should contact a gynecologist.
Watch the video about which discharges should alert you
Problems in the uterine cavity
Most often, irregular spotting results in various pathological processes in the uterine cavity. These could be polyps, endometrial hyperplasia, etc.
This pathology occurs more often in premenopausal women, after numerous abortions and other interventions in the uterine cavity. But there are also cases of the disease in young nulliparous girls.
Most often, brown discharge occurs between periods without pain. Sometimes they can be mistaken for ovulation, but their constant nature forces us to look for a more serious cause.
Endometrial hyperplasia and polyps, in addition to intermenstrual discharge, are the cause of heavy, clotted periods.
Malignant neoplasms
The oncological process also manifests itself with irregular bleeding. Their nature can be different - from smearing to abundant. Their appearance is often noted, including after sexual intercourse.
Bloody discharge during menopause in 30% of cases indicates endometrial cancer.
Pathology of the cervix
In the presence of cervical erosion or a polyp of the cervical canal, periodic brown bleeding may appear between menstruation. They are provoked by sexual intercourse, physical activity, etc.
Endometriosis
A characteristic feature of endometriosis is the appearance of spotting brown discharge on the eve of menstruation and after it. Usually their duration is more than 2 - 3 days. In this case, pain and discomfort may appear, including during sexual intercourse.
Pathology of the thyroid gland and other endocrine organs
The thyroid gland, to a greater extent than other internal secretion organs, affects the functioning of the genital organs and the regularity of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, with its pathology, disorders more often occur, including intermenstrual discharge.
Availability of an IUD
The intrauterine device can cause spotting on the eve of menstruation and after it. Moreover, sometimes they last up to 3 - 5 days, which brings considerable discomfort to the woman. All this may be accompanied by heavy periods. This is how the body reacts to such a foreign body. Only by removing the IUD will it be possible to get rid of the symptoms.
What does color tell you?
Bloody discharge may vary in color. But it is impossible to say based on this alone what the cause of the violations is.
So, we can highlight the following:
- brown,
- very dark, almost black,
- bright scarlet, bloody.
Spotting after intercourse
“Contact” spotting that appears in a woman immediately or several hours after sex always alarms doctors. This is one of the most common and first signs of cervical cancer. That is why, in the event of such complaints, it is necessary to undergo a full examination in order to identify the pathology in an unadvanced form.
But not only with cancer of the cervix and vagina, brown discharge appears between menstruation; the causes may be hidden in a polyp of the cervical canal or uterine cavity, erosion, an inflammatory process and some others. Only a doctor can finally figure it out after an examination.
Cervical erosion as a cause of brown discharge
Diagnosis of the presence of pathology
Dark and light brown discharge between menstruation may indicate both a pathological process and some functional malfunctions in a woman’s body. What needs to be done to detect or exclude a pathological process? Basic diagnostic procedures:
- examination of the cervix and vagina in the speculum;
- smears for oncocytology, colposcopy and biopsy are additionally possible if a suspicious lesion is detected;
- study of the flora of the vagina and cervix;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- if necessary, diagnostic curettage or hysteroscopy;
- blood test for sex hormones, thyroid gland.
We recommend reading the article about ultrasound during menstruation. From it you will learn about ultrasound examinations of the pelvis, chest and abdominal cavity, and whether diagnostics can be carried out during menstruation.
A woman's intermenstrual discharge should not be ignored. Especially if they tend to recur or are supplemented by other symptoms.
Particular caution should be paid to contact bleeding, since this most often hides a malignant pathology.
In any case, only a specialist can understand the problem and identify the cause after a comprehensive examination.
Source: https://ProMesyachnye.ru/korichnevye-vydeleniya-mezhdu-mesyachnymi/
Causes
Various menstrual cycle disorders can lead to the appearance of bloody clots in the mucus. If bleeding is accompanied by pain, you should immediately consult a doctor. They may be one of the signs of endometriosis. Estrogen supplements often cause the endometrium to shed prematurely, leading to blood clots. Problems in the functioning of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands can affect the ovulation process and cause premature monthly bleeding. The following are the main causes of blood clots:
- Taking hormonal drugs. After taking the pills there is no pain, the discharge is scanty.
- Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system. Depending on the type of illness, nagging or sharp pain, fever, nausea, and weakness may appear.
- Sexual infections. The discharge has a characteristic unpleasant odor. Accompanied by minor pain, itching, burning.
- Uterine fibroids, polyps. In the initial stages of the disease, bleeding appears in the middle of the cycle. Towards the end of menstruation they temporarily stop. If the disease is not treated, it becomes permanent.
- Ectopic pregnancy. The condition is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen of varying intensity. The woman experiences severe weakness. Pre-fainting condition.
- Endometritis. Aching pain in the lower abdomen. In the chronic form of the disease, the temperature rises.
- Cervical erosion. More often it occurs secretly without any pronounced symptoms. Blood appears during sex.
Treatment and prevention of bleeding in the middle of the cycle
Treatment methods for bleeding in the middle of the cycle depend on the causes of this deviation, as well as on the woman’s age.
Treatment can be conservative or surgical. In case of ovulatory bleeding, conservative treatment is carried out. For anovulatory bleeding (not associated with ovulation), both surgical and conservative treatment may be necessary. The exception is anovulatory bleeding in adolescents, when surgical treatment is used only as a last resort. Conservative treatment is based on the use of hormonal drugs to normalize the irregular menstrual cycle and stop bleeding. Your doctor may also prescribe sedative medications to treat untimely periods caused by stress.
For severe bleeding, women are prescribed iron supplements. It should be remembered that a balanced diet (including foods such as beef, legumes, liver, vegetables and fruits), proper rest and sleep will help restore health faster.
To prevent bleeding in the middle of the cycle, you need to: regularly see a gynecologist, refuse abortions, have a regular sex life, control your weight, play sports, give up bad habits.
If you notice that your period starts earlier or later each time, please consult a qualified healthcare professional. Untimely treatment of pathologies that cause disruption of the monthly cycle and bleeding can lead to anemia, infertility, and cervical cancer.
Spotting in the second half of the cycle causes
Published by admin on 07/20/2019
Perimenopause is a natural transitional stage in a woman's life that precedes menopause. Perimenopause is a stage in a woman's reproductive life that begins several years before menopause, when the ovaries gradually reduce estrogen production. This condition usually develops by age 40, but for some women, changes in the reproductive system can begin as early as age 30. Brown spotting may occur in some women during premenopause.
Premenopause, being a transitional period, can last from 2 to 11 years, until the complete cessation of menstruation. Perimenopause begins when a woman's reproductive system slows down, resulting in decreased production of hormones (mainly estrogen and progesterone).
Perimenopause is the interval in which the female body makes a natural transition from regular menstrual cycles and monthly ovulation to irregular menstrual cycles, anovulation and permanent natural infertility.
The first signal of premenopause is irregular menstruation - delays, absence of menstruation for several cycles, short and scanty menstrual bleeding, sometimes in the form of a brown spot.
Brown spotting during premenopause may appear during expected menstruation (instead of normal menstrual bleeding) or in the intermenstrual period in the form of irregular spotting. During perimenopause, women may also experience symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, sleep disturbances, vaginal dryness, etc. The replacement of menstrual bleeding with brown muck occurs due to a decrease in the level of female sex hormones and insufficient transformation of the endometrium. Typically, over time, the premenopausal brown spot gradually disappears and the woman enters menopause.
Brown spot during premenopause
Brown spotting during premenopause can be short (1-2 days) or long (up to a week) - it depends on hormonal status, lifestyle, physical activity, etc. So, some women observe brown spotting every month, others every few months. The duration of the period of irregular menstruation is individual for each woman. For some, this stage is short and ends with sudden menopause, for others it can last several years. However, as a rule, the duration of perimenopause and the period of irregular menstruation, including the appearance of brown discharge, lasts about a year.
Brown smear during premenopause appears from the moment of a physiological decrease in the level of female sex hormones and the onset of endometrial atrophy, against the background of which the vessels of the inner mucous membrane of the uterus become fragile and can bleed easily. Typically, an increase in follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels indicates the onset of menopause. A woman can check her FSH level on her own using special test systems.
Despite the fact that irregular brown spotting during premenopause can be observed frequently, in some cases of menstrual irregularities, consultation with a gynecologist is necessary:
- For vaginal bleeding that occurs after periods of brown spotting;
- For unexpected vaginal bleeding after 6 months of brown discharge in the form of a spot;
- For any vaginal bleeding that lasts longer than two weeks (with or without brown spotting).
Premenopausal women who experience such menstrual irregularities and suffer from arterial hypertension, obesity, and diabetes mellitus have an increased risk of developing endometrial cancer.
What causes discharge
Most often, scanty discharge in the middle of the cycle has completely natural causes.
Ovulation
The most common of these is ovulation. The maturation of the egg entails changes in hormonal balance, which can cause minor bleeding. Discharge in this case is a signal that the time has come favorable for conception, that is, the ovulation phase has begun.
Pregnancy
A spotting brown secretion can also appear in the early stages of pregnancy, when the egg is just beginning to attach to the wall of the uterus. At this stage, the structure of the endometrium changes greatly, it becomes more receptive, which causes minor bleeding.
After a month, everything should be settled and the discharge will stop. If the pregnancy is proceeding normally, then there cannot be any bleeding, even scant bleeding. Otherwise, you must immediately contact a specialist for qualified help.
Neoplasms
If we consider pathological causes, the most likely is the development of formations in the uterine cavity. With this disease, it may smear in the middle of the cycle. To confirm the fibroid, its size, and determine the degree of likelihood of a threat, the doctor will prescribe an ultrasound diagnosis. Based on the results of this test, a decision will be made about the need for treatment.
Endometriosis
Brownish discharge may be one of the signs of the growth of the endometrial layer outside the uterus. Scanty bleeding in this case is complemented by pain in the lower abdomen and nagging pain in the lower back. In addition, pain will be felt during sexual intercourse and during menstruation. The diagnosis can only be confirmed or refuted by a doctor after an examination.
Erosion
The systematic occurrence of minor discharge throughout the entire cycle can cause a disease such as cervical erosion. By the middle of the cycle, bleeding may intensify, the reasons for this are due to changes occurring in the hormonal balance during this period.
Spotting before menstruation as a sign of pregnancy
Every girl and woman knows for sure that the main sign of pregnancy is a delay in menstruation. What if there is strange discharge on the eve of menstruation?
Pregnancy is supported by progesterone. Before menstruation, its level should decrease. With a hormonal imbalance, there is not enough hormone for the pregnancy to develop fully, and too much for the onset of menstruation. Then brownish discharge appears. In some cases, doctors call the situation normal. The discharge continues for 3 months. But everything should be under the supervision of a doctor. In general, such discharge threatens miscarriage. If the pregnancy needs to be maintained, additional artificial progesterone in the form of tablets is prescribed. If you have an unwanted conception, you can do nothing, especially if the discharge turns from brown to reddish. This is followed by bleeding and rejection of the endometrium along with the embryo.
What is considered normal
There is no reason to worry if minor discharge appears one day before the expected date of your period. The death of one egg and the birth of another may be marked by scanty brown discharge - this condition is not considered a deviation from the norm.
There is no reason to worry if discharge occurs at the end of the cycle. This is a natural process of cleansing the uterine cavity, which entails the elimination of residual menstrual blood. However, if the discharge lasts longer than two to three days and is accompanied by other symptoms (pain, cramps, burning, etc.), then this is no longer considered the norm and a consultation with a gynecologist is required.
Diagnostics
Successful treatment largely depends on a correct diagnosis. The specialist must find the original source of the problem that caused the disruption of the natural course of physiological processes. Timely intervention will allow you to quickly determine the cause and take measures to eliminate the problem.
The following are carried out as diagnostic measures.
- The history of hereditary diseases suffered earlier, the regularity of sexual contacts and their nature, as well as the individual characteristics of the monthly cycle are taken into account.
- External examination of the genital organs using special instruments.
- A smear is taken and analyzed.
- If necessary, an ultrasound examination of the genital organs is performed.
- General tests are performed.
- A blood test is taken to check hormone concentrations.
When there is cause for concern
If your period starts at the wrong time, this may be a cause for concern. This occurs in cases where they last a long time and occur on a regular basis. If the discharge passes quickly, the situation does not need comment and is normal. Because there are stress hormones in the female body, they can suppress the amount of estrogen produced. In this regard, it is recommended to avoid stressful situations and rest as often as possible. But when visiting a gynecologist, you should tell him about the problem.
In the case when such discharge becomes stronger and is accompanied by unpleasant sensations of a painful nature, and does not stop after 2-3 days, you should urgently contact a gynecologist. Only an experienced doctor will be able to delicately and fully determine why menstruation came out of time, and how to deal with this phenomenon. If the bleeding has noticeably increased, and this is accompanied by a deterioration in general health, this is a serious reason to call an ambulance, because such signs are clear evidence of health problems that require prompt and urgent treatment.
There are conditions when false menstruation lasts more than 3 days and is accompanied by discomfort. Feelings of this kind may indicate a serious illness and require a more thorough check of the body. There is a possibility that the bleeding went away on its own, but returned prematurely and is not normal in quantity. If this happens, there is a reason to contact a specialist for an examination. The most effective way of research in this situation will be ultrasound, which will help identify diseases, even if they are of a hidden nature.
If the sensations are so unpleasant that they interfere with normal life activities, the woman feels extremely unwell, and the situation is accompanied by a clear deterioration in well-being, and the bleeding intensifies, it is necessary to call an ambulance. The danger is posed by a situation where a strong flow of blood discharge begins abruptly and spontaneously. You will likely need immediate professional intervention. If you delay the provision of this assistance, you may later face serious health problems, since such signs signal dangerous diseases.
Treatment
If a discharge occurs in the middle of the cycle, which is not accompanied by negative signs, such as pain, for example, then therapeutic therapy is not required. In this case, it is enough to take time to rest, try to avoid tension, stress and relax the muscles of the body.
If disruptions in the cycle are caused by diseases of the pelvic organs, then the doctor, after the examination, should prescribe treatment with drugs suitable for this case and conduct a course to prevent complications. If scanty brownish discharge is due to ovulation, then specialist intervention is also not required. After a few days, the problem will resolve on its own.
If polyps are found in the genitals, then such formations require treatment, which is selected taking into account the size of the polyp. Small ones are removed using current, medium and large ones are removed with forceps.
For diseases that are sexually transmitted, it is necessary to undergo a detailed examination to identify the causative agent of the disease. After the tests, therapeutic therapy is determined, which is mainly aimed at combating the factor that provoked the pathology.
Hormone therapy is most often used to treat endometriosis. As a rule, this is sufficient in the early stages of the disease. In complex or advanced cases, surgical intervention is performed to separate the overgrown endometrium.
If a brownish secretion appears due to the development of fibroids in the uterine cavity, then the operation is performed in some cases: in case of exacerbation (severe bleeding, etc.), rapid growth of the formation. If the condition is stable and urgent measures are not required, then the fibroid may completely stop growing or even decrease in size over time.