Normal menstrual cycle
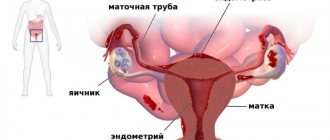
To understand the reasons for the violation of cyclicity, you must first become familiar with its characteristic features and physiological basis. A significant place in the proper functioning of the body is given to hormonal balance, which is maintained in a normal state by a regulatory system consisting of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and ovaries.
The resulting regulators coordinate the activity of the female genital organs in order to create favorable conditions for conceiving a child. The female cycle is usually divided into two stages:
- Follicular.
- Luteal.
The cycle begins with the separation of the functional layer in the uterine cavity. This happens over 5–7 days. Subsequently, thanks to the pituitary gland, which enhances the synthesis of follitropin, the follicle grows and the hormone estrogen is produced. At this point, the endometrium begins to form.
The final stage of the first phase ends with ovulation, the release of the egg from the follicle. Next, luteinizing hormone is transformed into the corpus luteum, which is capable of synthesizing progesterone. At this time, the mucous glands also grow. Thus, the second phase ends either with the beginning of the next menstruation or with the conception of a child.
Ensuring regular menstruation is the main task of women's doctors and the fair sex themselves. Cycle regulation is especially important for women preparing for pregnancy.
Physiological processes
The short cycle in teenage girls is physiological in nature. The menstrual cycle consists of 3 phases:
- menstruation;
- 1 phase;
- Phase 2.
Menstruation lasts on average 4 days. During this period, the endometrium is rejected, as there is no pregnancy. The duration of the first phase is 14 days. During this period, follicles with eggs grow. Estrogens enter the blood. Under their influence, the endometrium grows in the uterus.
Before the end of the first phase, the follicles regress. Only 1 follicle grows. Ovulation occurs. The egg then unites with the sperm. A “corpus luteum” is formed from the edges of the ruptured follicle. Then phase 2 of the cycle begins. It lasts 12-14 days. During this period, the female body awaits a possible pregnancy. The “corpus luteum” is growing. In the absence of pregnancy, the uterus rejects the endometrium. My period is coming.
The duration of each phase depends on the duration of the cycle. If a full-fledged follicle has not grown in phase 1, then another phase will not begin (long cycle). The first phase lasts until spontaneous rejection of the endometrium. This period can last several months. If ovulation occurs in the next cycle, then irregular periods are observed. Due to the prolonged work of the “yellow body,” the cycle lengthens. Otherwise, early periods are observed.
idVDzDnpsy8
The functioning of the reproductive system is directly affected by the following factors:
- stress;
- active sports;
- extreme weight loss;
- frequent pathologies;
- bad habits.
Violation of the menstrual cycle
A short menstrual cycle occurs due to a number of external and internal factors, and represents a disruption in the hormonal profile, leading to loss of periodicity and a change in the duration of phases, a decrease in the volume of discharge, etc.
In modern medical practice, there are several types of menstrual irregularities:
- proyomenorrhea - a failure in menstruation, in which its duration decreases, that is, the intervals between menstruation vary up to 20 days, with the norm being 21-35;
- amenorrhea is a pathological case in which menstruation is absent for 3 months or more;
- polymenorrhea - characterized by an increase in the period of menstruation from 7 days or more, without exceeding the normal volume of blood discharge;
- Oligomenorrhea is a disorder manifested by a reduction in menstruation to 1-2 days. The volume of discharge can be either regular or irregular;
- hypomenorrhea - regular periodicity of the cycle is observed, but the discharge is scanty in volume;
- hypermenorrhea is the opposite of hypomenorrhea, a situation when the regularity of menstruation is maintained, and the volume of discharge increases significantly compared to the norm and amounts to more than 100 milliliters;
- Dysmenorrhea is a disorder associated with the physical condition of a woman and manifests itself in severe pain before and during menstruation.
According to statistics, about 30% of women are susceptible to this type of menstrual cycle disorder called hypermenorrhea. Hypomenorrhea is often observed in girls with late puberty aged 14-16 years, as well as in women over 46 years of age, when the functioning of the reproductive system deteriorates. But polymenorrhea usually worries women after 35-40 years of age, who are hyper-emotional.
Prevention
In order for your period to arrive on schedule, you need to follow simple recommendations:
- avoid overwork, stress and increased loads;
- when the climate changes, take vitamins;
- avoid hypothermia;
- give up casual relationships - they often lead to infections that change the cycle;
- go to the gynecologist twice a year and monitor your health;
- take contraceptives only as prescribed by a doctor;
- wear cotton underwear;
- maintain hygiene.
The menstrual cycle never shortens without a reason. It is important to identify and eliminate it in a timely manner.
A short menstrual cycle not only brings a number of inconveniences and discomfort to a woman, but can also indicate serious problems in the functioning of the body. More often, delays in menstruation cause concern, and early menstruation only makes a woman happy. To understand whether you should worry, it is important to know when early menstruation is pathological and when it is normal. Only a specialist can tell why menstruation begins earlier than expected.
A woman’s menstrual cycle is a natural physiological process that indicates her health and readiness to conceive and bear a child. It consists of two phases, follicular and luteal, which are separated by ovulation. The first phase of the menstrual cycle is characterized by the maturation of the follicle and ends with the rupture of this membrane and the release of the egg.
Afterwards it begins, which lasts until the start of menstruation. Under the influence of the hormone progesterone, which is produced by the corpus luteum, the endometrial layer grows. If conception does not occur, the uterus rejects the unnecessary lining. All these natural processes take time, the first phase of the cycle normally lasts 13-15 days, the second takes the same amount, and ovulation occurs within 1-2 days. Shortening any of the phases causes the entire cycle to shorten. This phenomenon is called proyomenorrhea, when menstruation comes earlier than expected.
A pathologically short cycle is its duration of less than 21 days. This happens mainly due to hormonal imbalance, the causes of which may be hidden in diseases of internal organs or exposure to external factors. Dysfunctional disorders of the ovaries provoke, which are mistaken for natural menstruation; they can shorten the normal process.
Normally, such disorders can occur in women during the formation of the menstrual cycle, as well as at the onset of menopause. During childbearing age, such changes lead to serious disorders and consequences. For a woman of childbearing age, a shortening of the menstrual cycle may be the first signal of the development of infertility.
Menstruation that comes every two weeks and lasts less than 3 days should be the reason to consult a doctor to undergo a full examination and identify the causes of this type of pathology.
Reasons for shortening the menstrual cycle
There are many factors that cause a short menstrual cycle. Among them there are those that are associated with diseases of the reproductive system itself; it is quite difficult to identify them on your own. Among the reasons influencing the decrease in cycle frequency are the following:
- Sudden weight loss, rapid weight loss - the cycle depends on the woman’s nutrition and body weight. If the body is insufficiently supplied with nutrients (for example, vitamins K and C), the regular periodicity of menstruation is disrupted. Following an overly strict diet can lead to loss of periods.
- Use of birth control pills. Violation of the menstrual cycle and its short duration indicate a malfunction in the body. As a rule, such consequences can occur after three months of using contraceptives. In such a situation, it is important to consult a gynecologist and stop taking the drug.
- Early pregnancy is an absolutely normal reason for missing periods.
- Menopause - with age, the functioning of the reproductive organs deteriorates, this first leads to a shortening of the menstrual cycle, delays or light discharge, and then to menopause - the final stage of menstruation in a woman. Reproductive functions are gradually blocked by the hormone progesterone, produced in the ovaries.
- Disruption of the functioning of the endocrine system. The potency of the reproductive system is also determined by the functioning of the thyroid and adrenal glands. Hormonal imbalance in the body can lead to endocrine infertility.
- Gynecological diseases are another reason that affects the shortening of the cycle. One of the indicative problems is endometriosis, which manifests itself in the growth of tissue resembling the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity onto neighboring organs. Treatment of endometriosis is carried out depending on the degree of organ damage: hormonal therapy at an early stage and surgery at a later stage.
- Unfavorable external factors: overwork, stress, depression, change in climatic conditions, consequences of an interrupted pregnancy and a number of others.
Intermenstrual discharge
It also happens that during menstruation a woman perceives bloody spotting that appears in the middle of a normal cycle. This situation is normal only if you have started taking hormonal medications within the previous three months. If the three-month period has passed or the woman does not take hormones at all, if spotting appears after menstruation, an urgent appointment with a gynecologist is necessary. When using hormonal contraception, the doctor replaces such a product with another containing a larger or smaller dose of the active substance.
Pregnancy
A sudden decrease in the menstrual cycle can also alert a woman to the early stages of pregnancy, both normal and ectopic. For women who have regular sexual intercourse, it is advisable to use a pregnancy test. If the test result is positive, the next step is to visit a gynecologist to rule out disorders and pathologies. An ectopic pregnancy must be stopped immediately, since it is clearly harmful to health and can lead to the death of the woman.
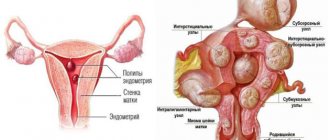
Endometriosis disease
Endometriosis is a disease in which the lining of the uterus thickens. Its most serious consequence is infertility. Modern medicine is able to cure endometriosis through hormonal regulation and, if necessary, surgery. The presence of endometriosis is indicated by a reduction in the cycle and duration of menstruation, and the blood becoming darker in color.
Signs indicating a problem
Disease of the internal genital organs may be accompanied by changes in the menstrual cycle. A shortened cycle may be due to the presence of a follicular or luteal ovarian cyst. The danger of this problem lies in the fact that similar manifestations usually do not recur by subsequent menstruation. A reduction in the interval between periods and an increase in their duration are hallmarks of diseases such as fibroids or polyps in the uterus. In this case, bloody discharge is observed in different phases. A visible sign indicating problems with the reproductive system is an increase in the size of the uterus.
Disruption of the coordinated activity of the ovaries or pituitary gland, which regulate the functioning of the productive system, often causes changes in the menstrual cycle.
Among the factors leading to a short cycle are:
- endometrium;
- inflammatory diseases, such as tuberculosis.
Insufficient secretion of hormones leads to deterioration of blood circulation inside the uterus, and this directly affects the volume of discharge.
Surgical intervention in the genital system can also lead to negative consequences - hypomenorrhea. A shortening of the menstrual cycle is also due to severe exposure to external chemical irritants.
Women experiencing short menstrual cycles report the following symptoms:
- nausea;
- headache and slight dizziness;
- pain in the lumbar region and back;
- disruption of digestive processes.
Treatment options
Therapy depends on the reasons why your menstrual cycle has shortened, so you need to see a doctor and get examined. If a short cycle is caused by endocrine disorders, first of all, it is necessary to correct the hormonal levels. There are two treatment methods:
- Hormonal contraceptives are prescribed to women who do not want to have children. Birth control pills allow the ovaries to rest and work properly. After their cancellation, hormonal levels are restored, and the menstrual cycle returns to normal.
- When planning pregnancy, the main goal of therapy is to normalize both phases of the cycle, increase the cycle and correct it. It is also important to ensure the onset of ovulation.
For infections and other diseases that lead to a menstrual cycle of 21 days, specialized treatment will be required. After recovery, the situation does not return to normal immediately. In some cases, additional hormonal treatment is necessary to enhance reproductive functions.
Nutrition and lifestyle are of no small importance - they are very important for restoring the menstrual cycle. It is also recommended to limit exercise and give up bad habits that can cause serious disruptions in the functioning of the body.
When is it necessary to contact a gynecologist?
How to identify a failure that requires immediate treatment? As a rule, in the case of inflammatory processes in the reproductive system, a short cycle is accompanied by a number of symptoms that are difficult to miss:
- various pain sensations in the lower abdomen;
- copious vaginal discharge;
- reproductive dysfunction;
- decreased sexual desire.
Polymenorrhea is a sign of pathology of the reproductive organs and can be a harbinger of serious diseases: cervical cancer, ovarian tumors and others. Transformations in the ovaries or malfunction of the genital organs can also cause polymenorrhea. In this case, treatment is prescribed only by a gynecologist. If you identify signs that are uncharacteristic of the normal physiological state of the female body, you should consult a specialist.
Symptoms
In itself, the condition of a shortened menstrual cycle is not a disease. Violation of the cycle twice a year can occur without pathology. This condition should be analyzed in conjunction with other manifestations. Proyomenorrhea has three types.
- The cycle is correct - two-phase. At the same time, the follicular phase is shortened. Ovulation occurs earlier. Basal temperature is recorded within normal limits. The corpus luteum performs its work normally.
- The cycle is two-phase. The luteal phase is shortened. Ovulation occurs on time. Basal temperature rises briefly. The dominant follicle matures. The corpus luteum stops functioning earlier than expected.
- The cycle is single-phase. Ovulation does not occur. The follicle lasts longer. This condition is called persistence; it is short-term in nature. The corpus luteum is absent. Basal temperature is variable. Changes in the endometrium are observed, including glandular hyperplasia.
The luteal phase is often shortened. Despite the short cycle, a woman can experience both heavy and long periods. The second and third subtypes of cycle disorders lead to infertility. A decrease in cycle duration is one of the symptoms of dysfunction of the female reproductive system as a whole.
General symptoms with a short cycle:
- Pain in the lumbar region;
- Headache;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Constipation;
- Increased gas formation;
- Emotional discomfort;
- Fatigue;
- Decreased performance;
- Decreased libido;
- Nosebleeds.
Gynecological symptoms:
- The duration of menstruation does not exceed 3 days;
- The cycle is less than 21 days;
- Menstruation once every 14 days or more often;
- Spotting, scanty discharge.
Doctors' opinion
A shortened menstrual cycle does not always indicate problems in the body. So, every gynecologist will assure you that this is the norm in the following situations:
- Primary menstruation in teenage girls. Menstruation, lasting 1-2 days with a frequency of up to 21 days, occurs in girls during the first time after menarche. The cycle usually levels out over two years, after which it becomes regular.
- Decreased functioning of the reproductive system during menopause.
- Pregnancy and postpartum period. The absence of menstruation or its irregular occurrence occurs during breastfeeding and is not a serious problem. Stabilization of the cycle usually occurs after the baby stops breastfeeding.
Reasons for changing duration
A normal menstrual cycle should last from 21 to 34 days. It is divided into 2 phases: follicular and luteal, during which egg maturation, ovulation and menstruation occur under the influence of sex hormones.
Shortening of the menstrual cycle or proyomenorrhea can occur due to various reasons. Before you begin to correct this condition, you need to understand why this happened.
A short menstrual cycle can manifest itself in different ways. Most often, this looks either like the arrival of menstruation every 15–17 days, or as a strong reduction in the amount of discharge, both in volume and in time.
Physiological reasons
The most common physiological reasons that cause the period between menstruation to become shorter are overwork and stress. Severe emotional shocks can change hormonal levels, causing an increase in the concentration of the hormone prolactin. In this case, dealing with a short menstrual cycle is quite simple. The body needs proper rest, minimizing any stressful situations and increasing resistance.
If the menstrual cycle has become short, then vitamin deficiency may be another reason. A lack of vitamins A, E, B and K can cause metabolic disorders and affect blood characteristics. This also includes a condition of the body that appears with excessively rapid weight loss. Usually, when going on any diet, a woman sharply reduces the amount of nutrients consumed, which can lead to the period between menstruation becoming shorter. Also, excessive thinness often leads to hormonal imbalances.
Physiological causes of cycle changes that are very easy to detect include recent surgery on the reproductive system, childbirth, abortion, and menopause. In these cases, practically no adjustment is required and you just need to wait out this period.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
A menstrual cycle of 14 days can also be established for this reason. With this syndrome, a woman’s body produces a large amount of male hormones. They are the ones who suppress ovulation.
As a result, women with polycystic ovary syndrome experience irregular, unstable menstrual cycles. It may be too short, too long. Also, sometimes menstruation is completely absent for several months.
Premature ovarian failure (another name is primary ovarian failure) is diagnosed when, due to a hormonal imbalance, the ovaries of a girl or woman of fertile age cease to function normally.
The short cycle here is explained simply: if the ovaries do not function correctly, it means that the body does not receive the required amount of the hormone estrogen. And this is fraught with both irregular and shortened menstrual cycles.
In the case of this disease, a woman’s body produces a large amount of male hormones, which will suppress ovulation. “Women with PCOS will constantly suffer from irregular menstrual cycles. And in some months, they will not have “critical days” at all, notes obstetrician-gynecologist Leisisha Richardson.
Premature ovarian failure or primary ovarian failure occurs when, due to hormonal imbalance, the ovaries of a woman of fertile age cease to function normally. “If your ovaries are not working correctly, then the body does not produce the right amount of estrogen. This can lead to short and irregular menstrual cycles,” explains Lacisha Richardson.