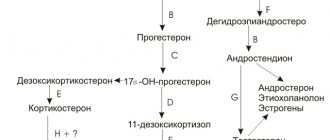
From the moment menstruation begins at 11–14 years of age until they completely stop during menopause, representatives of the fair sex monitor such indicators of women’s health as the duration and regularity of the menstrual cycle. Many girls and women experience irregular periods of menstruation, but not everyone knows why this happens and in what cases it is necessary to see a doctor and treatment.
What is a normal menstrual cycle?
A normal period lasts three to six days once a month. The enlarged but unclaimed endometrium comes out with the secretions. After the unnecessary tissue is rejected, the capillaries close, and the growth of new mucous membrane begins. Therefore, normally, blood loss during menstruation is small and does not cause anemia or asthenia. On average, up to 150 ml of blood comes out during menstruation, without clots.
The full menstrual cycle consists of the follicular phase, when the egg matures in the ovary, ovulation, the growth of the endometrium and its preparation for the possible attachment of the fertilized egg. Therefore, there may be anovulatory periods, and this does not apply to pathologies. They do not change the length of periods or the interval between them.
They begin during puberty and indicate the body’s readiness to conceive. With normal development, the first menstruation appears at 9-15 years of age (usually at 12-14). The range of possible onset of full maturation depends on heredity, nutrition, nationality, health status, etc. The end of the reproductive period is called menopause. It occurs at approximately 46-50 years of age.
Which doctors treat menstrual irregularities?
In order for menstruation to recover, you need to eliminate all pathological phenomena and exclude some undesirable factors from your life. And then you won’t have to anxiously wait for the next arrival of “red days” or lie in bed during your period. If they are severe, you shouldn’t just take painkillers. If you feel a lot of pain in the first days, there is nausea, chest pain, this means that something is wrong inside the body.
The first thing that is best to do in such a situation is to go to a gynecologist. He will oversee the entire process. Most likely, he will order hormone tests at the beginning of the menstrual cycle. Blood is taken from a vein, and it can be donated in any laboratory. If your hormones are out of balance, you will most likely be prescribed combined oral contraceptives for 6-12 months. Your periods will become regular and less heavy.
Don't forget to visit your doctor regularly after you stop having your period after menopause. If there were no menstruation for 1-1.5 years, and then they resumed, this cannot be considered the norm.
Types of violations
A menstrual cycle is considered a violation if its duration increases by more than 7 days or the interval between flows is reduced by a week. Moreover, they talk about diseases if such phenomena become systematic.
In this case, a full examination is necessary.
Deviations in the normal course of menstruation are divided into several categories:
- Amenorrhea. This is when menstruation is absent for several cycles. Amenorrhea can be primary, when there is no discharge until the age of 16, but the signs of puberty are obvious. It is called secondary when menstruation begins, but disappears for a long time.
- Dysmenorrhea. Deviations in menstruation can occur in any direction - reduction or increase. Dysmenorrhea can appear regardless of age. However, if the cyclicity is just beginning and is not fully regulated (adolescence, postpartum periods), then this does not apply to pathologies.
- Oligomenorrhea, when menstruation is very infrequent. Bleeding lasts no more than two days, there is little discharge. Primary oligomenorrhea occurs due to underdevelopment of the uterus, secondary - due to abnormalities in the hypothalamic-pituitary system, tumors, and after infectious diseases. Usually, menstrual irregularities are typical for overweight women. Problems with conception often occur.
- Hypomenorrhea. In this case, a scant amount of discharge is observed - blood loss is less than 50 ml. Menstruation is delayed and accompanied by negative symptoms - headache, nausea, lack of appetite, weakness in the legs, etc. The cause of hypomenorrhea can be dysfunction of the ovaries, pituitary gland, changes in the uterine mucosa.
- Proyomenorrhea. This is a reduction in the period to 21 days. Most often, periods are short - they last only a couple of days. Most often the discharge is small, but it can also be copious. Proyomenorrhea is often accompanied by ovulation, sometimes anovulatory periods.
- Opsomenorrhea is when the cycle increases to at least 35 days (but not more than 3 months). At the same time, the discharge is scanty and menstruation is short. This is often accompanied by infertility. Women with opsomenorrhea tend to be obese, may have some masculine features, and often suffer from acne.
- Polymenorrhea. Bleeding lasts for more than a week.
- Hypermenorrhea. In this case, the volume of discharge increases greatly, but the duration of menstruation remains normal. This can be caused by gynecological diseases, a decrease in platelets in the blood, polyps, and endocrine diseases.
- Menorrhagia. The duration of menstruation increases, there is a lot of discharge.
- Metrorrhagia. Characterized by severe uterine bleeding caused by tumors, diseases, and lack of ovulation.
Menstrual irregularities are divided into several categories depending on the causes:
- Hypothalomic abnormalities are caused by infectious-toxic injuries, injuries, and mental disorders. At the same time, the concentration of gonadotropic hormones remains normal, but luteinizing hormones become less. The reactivity of the uterus decreases, and secondary amenorrhea appears. Atrophic changes can be detected in the genitals.
- Pituitary diseases develop due to a deficiency of gonadotropic hormones. This happens during pregnancy and childbirth. Further, atrophy of the ovaries and external genitalia, and hair loss may occur. Menstrual irregularities first manifest themselves in the form of hypo- and oligomenorrhea, then amenorrhea. Deviations are provoked by a pituitary tumor, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, and hyperplasia.
- Ovarial. This menstrual cycle disorder can be hyper- and hypohormonal and is divided into hyper-estrogenic and progesterogenic. They appear as a result of a follicular cyst, purulent salpingo-oophoritis. Early atresia and scarring leads to hypo- and amenorrhea.
- A large amount of progesterone is released. The cause may be luteal cysts or persistent corpus luteum (but this is rare). The structure of the endometrium is disrupted and if not restored, this leads to menorrhagia.
- Another menstrual cycle disorder is ovarian failure. They can be primary or secondary, when there is a deficiency of gonadotropic hormones. The causes may be mental trauma or anatomical abnormalities.
Most often, disruptions in menstruation occur against the background of gynecological diseases - vaginal fistulas, tumors, salpingo-oophoritis, endometritis. The cycle gets disrupted due to anemia, vitamin deficiency, infectious diseases, when hard work is accompanied by poor nutrition. The classification of disorders includes damage to the central nervous system, endocrine and reproductive systems, malfunctions of internal organs caused by chromosomal and genetic abnormalities.
When is a cycle considered abnormal?
Too heavy menstruation
When a woman uses more than 10 sanitary pads a day or bleeds for a week, we talk about heavy menstrual periods (hypermenorrhea). What could be the reasons? In the first years of menstruation, the cause is usually immaturity of the genital organs. In this case, you need to go to the doctor and ask for a referral for examination, because excessive bleeding can lead to anemia. Heavy bleeding can also be caused by hormonal imbalances. The thyroid gland and its improper functioning can cause irregular menstruation. Endometriosis, polyps, fibroids, a contraceptive intrauterine device (called the IUD), or a developing infection can also affect the frequency of menstrual bleeding. Very rarely, heavy bleeding is associated with ovarian cancer.
Too scanty menstruation
Too scanty menstruation (hypomenorrhea) lasts no more than 48 hours. A woman does not need more than two sanitary pads during the day. Rarely such light bleeding is a feature of the physiology of a particular woman. Most often they indicate more serious hormonal imbalances. For example, the cause may be polycystic ovary syndrome, low estrogen levels caused by anorexia. However, this is not the end of the list of possible problems. Damage to the endometrium produces the same symptoms.
The cause of scanty menstruation can also be mechanical damage (for example, after curettage) or acute inflammation of the reproductive organ. This occurs when scars or adhesions form on the mucosa, limiting the surface from which the mucosa must be peeled off. Unfortunately, such adhesions cannot be completely removed from the endometrium even surgically, so in such cases it is impossible to restore the normal course of menstruation. To determine the true cause of very scanty menstruation, it is necessary to determine the level of hormones, perform an ultrasound and hysteroscopy. Only after an accurate diagnosis of the disease can the doctor prescribe targeted treatment, that is, treatment chosen for a particular patient. If it turns out that menstrual irregularities are the result of a significant hormonal imbalance, it is enough to start taking appropriate medications to improve the woman’s health.
Rare menstruation
When menstruation occurs less frequently than every 31 days (oligomenorrhea), it can be assumed that the woman is not ovulating, which is usually due to a pituitary gland disorder. Such situations often arise as a result of very high stress or the presence of some traumatic events, for example, a car accident, the death of a loved one. When the stress passes, everything usually returns to normal. Treatment is carried out only when a woman wants to get pregnant very quickly. Psychotherapy brings very good therapeutic results, especially individual therapy, which allows you to calm down and forget about unpleasant experiences. The reason for a woman’s lack of ovulation may also be the presence of polycystic ovary syndrome, which you can read more about here.
Frequent menstruation
Frequent menstruation (polymenorrhea) occurs when bleeding occurs more often than every twenty-four days. With such disorders, numerous abnormalities appear, for example, ovulation can occur on the eighth day of the cycle, because the maturation phase of the ovarian follicle is significantly reduced. Ovulation may also occur at a normal time, but bleeding occurs too early because the uterine lining is not mature enough. Treatment is prescribed only after hormonal tests. Once they are done, the doctor decides which treatment to use and what dosage of medications to prescribe.
Menstrual irregularities - causes
Most often, the main cause is a hormonal imbalance. This occurs against the background of various diseases and pathologies, negative external factors, and stress. The main causes of menstrual irregularities:
- Pituitary adenomas (chromophobic, baso- and acidophilic). They compress the pituitary gland and lead to its atrophy.
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome and disease.
- Adrenal adenomas. And also due to congenital hyperplasia of their tissues - adrenogenital syndrome.
- Taking medications that affect the production of norepinephrine and dopamine in the brain, which causes a malfunction of the pituitary system. For example, MAO inhibitors, Reserpine, phenothiazine derivatives, antipsychotics, metoclopramide, antidepressants.
- Some types of mental disorders are depressive states, acute endogenous pathologies, reactive disorders, chronic stress, anorexia nervosa.
- Stein-Leventhal syndrome (sclerocystic ovaries).
- Hyper- and hypothyroidism.
- Syndromes of resistant ovaries and premature withering of the gonads.
- Sudden changes in hormonal balance. The cause may be abortion. Taking medications, etc.
- Failure of the normal functioning of the ovaries and their connection with the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
- Abnormal development of the uterus, organ defects, chromosomal pathologies.
- Tumors affecting the reproductive system.
- Menstrual irregularities can be a consequence of surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation treatment.
- Inflammatory processes in the genital organs.
- Infectious lesions of organs located in the pelvic area.
- Obesity.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Diabetes mellitus (see).
- Unbalanced diet, long-term diets, deficiency of essential microelements.
- Anorexia (more details – https://www.diet-menyu.ru/diety/pitanie-pri-anoreksii.html).
- Intoxication.
In teenage girls, cycle failure is often associated with uneven maturation of the reproductive system. During this period, congenital and chromosomal pathologies may appear, and abnormal development of the organs of the reproductive system may be detected. Also the cause is malnutrition, which manifests itself in the form of secondary amenorrhea.
After 40 years, menstrual irregularities are provoked by age-related changes in the reproductive system. Natural depletion occurs in the follicular reserve of the ovaries, the number of anovulatory periods increases, reproductive function fades, and hypoestrogenism progresses. The changes are especially pronounced before the onset of menopause. The cycle loses regularity, and uterine bleeding appears.
The hereditary factor is also important. If the mother or grandmothers had period disorders, then there is a possibility of this being transmitted at the genetic level to subsequent generations. Also, menstrual irregularities often occur in those who are awake at night.
Irregular menstruation - causes
Irregular menstruation is common in girls who have just started menstruating. The hormonal system of a young woman can take up to 17 years to develop. In the first two years from the start of the first menstrual cycle, bleeding may be irregular and this is not associated with any disease.
Hormonal fluctuations, and therefore irregular cycles, also apply to mature women who are approaching menopause, the last period of their lives. During menopause or perimenopause, the ovaries begin to reduce estrogen production. Their “extinction” can take up to several years.
Important The most common cause of irregular cycles can be hormonal disorders. Often this is also the first sign of serious discomfort, for example, adnexitis, endometriosis and even genital cancer. It is difficult to determine the cause of irregular, excessive or infrequent bleeding without special tests.
Other causes of random bleeding in women may include:
- chronic stress;
- depression;
- too strict diet;
- frequent climate change;
- ovarian cancer;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- damage to the ovaries during surgery;
- thyroid disease;
- pancreatic diseases;
- disruption of the immune system.
Unfortunately, many women downplay the symptoms or simply do not want to pay attention to their irregular cycles, attributing the problem to the fast pace of life and the associated stress and poor nutrition. Although the most common cause is hormonal changes, it is important to check for more serious conditions. If left untreated, it can lead to serious health consequences.
Symptoms of the disorder
Symptoms of cycle failure may vary or not appear at all. Main features:
- algomenorrhea (pain during menstruation);
- change in the duration of the period (too short or long period of blood release);
- delays or absence of menstruation for six months or more;
- change in the amount of discharge (large or scanty blood loss);
- severe uterine bleeding;
- the appearance of several common symptoms at once - headaches, surges in blood pressure, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, general weakness and other negative symptoms.
Failures in menstruation can provoke the development of iron deficiency anemia. A woman experiences a strong heartbeat, increased fatigue, fainting, and decreased blood pressure. The condition of nails, hair and skin worsens. Cognitive impairment may develop. Failures in menstruation can cause infertility.
How to restore the cycle?
Since cycle irregularity is not a disease, but only a single symptom, treatment for the process may vary depending on the cause of the failure. We are talking about the following treatment approaches:
- Identification and treatment of the underlying disease.
- Prescription of contraceptives.
- Changing the method of contraception.
- Lifestyle changes.
- Symptomatic treatment.
Drug therapy for the underlying disease
The most common causes of irregular periods are thyroid disease and polycystic ovary syndrome. In the first case, medications are prescribed to normalize its functioning (Iodomarin, Eutirox). When hormone concentrations are reduced, hormone replacement therapy is prescribed. With active hormone production, treatment is carried out by suppressing the activity of the gland. In some cases, surgery is recommended.
When it comes to polycystic ovary syndrome, hormonal contraceptives (Jess, Midiana, Yarina) come to the patient’s aid. If there is a prolonged delay due to the development of pathology, Duphaston may be prescribed.
Contraceptive therapy
Combined oral contraceptives or COCs can be used to treat irregular menstruation even in the absence of sexual activity. Among the most common representatives: Marvelon, Silest, Ovidon, Rigevidon, Non-Ovlon.
Sometimes COCs are prescribed to women planning pregnancy in the absence of regular periods. Taking these medications for six months or more leads to normalization of the cycle.
Changing your contraceptive method
If irregular uterine bleeding is caused by taking birth control pills, specialists will prescribe the woman a suitable alternative: a drug with a different hormonal composition or a higher concentration.
When the problem is caused by an intrauterine device, the only way out of this situation is to prescribe a different type of contraception.
Lifestyle change
If a malfunction in the body is caused by excessive physical exertion, stress, or malnutrition, it is worth taking a break and observing how the situation changes as conditions change.
Symptomatic therapy
To “extinguish” the following types of drugs that appear against the background of irregular menstrual symptoms:
- analgesics (to relieve pain);
- hemostatic agents (Ditsinon, Vikasol);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antibacterial drugs (for inflammation);
- vitamin complexes (if the body is weakened).
In case of severe uterine bleeding that does not subside with conservative treatment, curettage of the uterine cavity is performed.
Folk remedies
To restore regular periods, traditional medicine methods are used as maintenance therapy. Among the most proven means are:
- ginger. Relieves pain, restores the cycle. Ginger tea is used for medicinal purposes: ½ tsp. Pour the ground root into a glass of water and boil. Strain, add a little sugar and drink three times a day;
- sesame seeds. We are talking about the plant equivalent of the female sex hormone. 2 tbsp. l. Grind the raw materials in a coffee grinder, pour in 1 tsp. palm oil, mix the ingredients and eat 1 tsp. once a day;
- cinnamon. Relieves spasmodic pain in the uterus during menstruation. You need to add 1 tsp. ground seasonings in 200 ml of milk or kefir. Drink the drink for 14 days;
- aloe and honey. Mix 1 tsp. honey and the same amount of aloe juice and eat ½ tsp. remedies on an empty stomach for 30 days.
For medicinal purposes, you can also use turmeric, coriander, fennel, mint, mixing the components with honey.
Features of disorders depending on age
In the juvenile period, hypomenstrual syndrome is often observed, in which pubertal bleeding appears. Primary amenorrhea may occur. This diagnosis is made if menstruation has never occurred before the age of 15.
Juvenile bleeding is a consequence of hormonal imbalances, alternating with delayed menstruation, changes in hair growth, and a sharp gain (or loss) of body weight. Changes can be triggered by stress, nervous tension, sleep disturbances, and sudden climate change.
Reproductive period
During the reproductive period, cycle disruptions often manifest themselves in the form of delayed menstruation or repeated bleeding after a short period of time. At the same time, physiological and pathological changes differ.
Normally, menstruation stops during pregnancy, after childbirth, and during lactation. The reason for the failure of the period may be the installation of spirals or contraceptives.
The lengthening of the period is caused by the persistence of the follicle. Without ovulation of a mature egg. It dies, and a cyst forms instead of a follicle. This leads to the growth of the endometrium and is accompanied by a delay of menstruation by up to 5-8 weeks.
Then metrorrhagia appears. Such bleeding is called dysfunctional. They can also be provoked by insufficiency of the luteal period.
If bleeding appears during the ovulatory period, it is prolonged, but not heavy. Menstrual irregularities can also be caused by an abortion. Then the next menstruation begins later, and is restored to normal within three months.
If the abortion had complications, then the body may require a long rehabilitation. At this time, there will be bloody discharge, and there is a possibility of algodismenorrhea.
Pre- and menopause
Most often, menstrual irregularities occur before menopause and immediately during menopause. During these periods, anovulatory intervals, frequent delays, and bleeding caused by follicular atresia become more frequent. If menstruation resumes during menopause, this is an alarming symptom indicating the development of a cancerous tumor.
What to do if your menstrual cycle is disrupted?
Random failures, which can occur due to a severe stressful situation, sudden change in situation or climate, are considered normal and do not require special examinations. The main signal that everything is in order will be the rapid restoration of the cycle and the absence of similar disruptions in subsequent hormonal cycles. Similar disorders can result from bad habits, poor environmental conditions or exposure to radiation. Such conditions can be corrected by going on vacation, quitting smoking and alcohol, and changing the rhythm of life. It is important to devote enough time to sleep and rest, play sports, and take vitamin supplements in courses recommended by nutritionists.
A more serious question of what to do if the menstrual cycle fails arises in the following situations:
- if menstruation is delayed by more than 2 weeks;
- with a sharp change in cycle length;
- when the duration of menstruation is less than 3 days and more than 7 days.
All of the above failures of regular discharge should not only alert you, but serve as a reason for a visit to the doctor. In order to assess the possible risks and understand the seriousness of the situation, let's try to understand the possible causes of menstrual irregularities.
Expert opinion
In addition to a change in the frequency of monthly discharge, a disruption of the menstrual cycle can be characterized by a change in its volume. Thus, hyper- and hypomenorrhea (heavy and scanty menstruation, respectively) are also a reason for gynecological screening.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
Is pregnancy possible with an irregular menstrual cycle?
Despite the irregular menstrual period, a woman can become pregnant. However, the likelihood of conception decreases. How much depends on hormonal imbalance, full development of the uterus, diseases and other factors.
But most often the disorder is accompanied by infertility. However, it is not always possible to get rid of it using conservative methods; modern reproductive technologies may be required. Some women can conceive a child but are unable to carry it to term.
Any endocrine abnormalities lead to inferiority of the endometrium, which makes it difficult for the fertilized egg to implant. This increases the risk of miscarriage. In this case, the woman may not even suspect that conception has occurred, but there will be a slight delay.
The possibility of getting pregnant is reduced if, up to this point, disruptions in the menstrual cycle have become chronic. Then hormonal treatment is required before conception. After childbirth, menstruation usually returns on its own.
Preventing irregular periods
Irregular periods are not a disease, but a symptom, so there are no specific preventive measures. However, a woman can prevent the occurrence of provoking factors by strengthening the body’s natural defenses:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- minimize stress;
- eat well;
- take multivitamin complexes twice a year;
- exercise moderately;
- protect yourself from sexually transmitted diseases.
Loading...
Share with friends!
Diagnosis of causes
To determine the cause of menstrual irregularities, the gynecologist performs a general examination of the vagina and palpation in the pelvic area. Finds out how severe the blood loss was, how often the discharge occurred.
Attention is paid to concomitant diseases, age, nutrition, weight and other factors. Finds out whether the IUD is in place and whether the woman is taking contraceptives.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include a smear from the vagina and from the uterine cervix to check for the presence of oncology. The cleanliness of the urethra, cervical canal, size and location of the ovaries, and fallopian tubes are checked.
Blood is submitted to the laboratory for hormones, sugar levels, and general standard parameters are checked. Additionally, a pelvic ultrasound is prescribed. If necessary, to obtain a clearer picture, the rectal method is used. Diagnostics can also be supplemented by histological examination, PET, CT, MRI.
Long menstrual cycle - probable causes
- The long gap between cycles sometimes reaches several months; the ovaries cannot produce predictable levels of estrogen and progesterone. This imbalance can lead to the uterine lining becoming too thick, and then leaving the body completely after the first pause.
- Prolonged bleeding may indicate the presence of polyps in the uterus, due to which bleeding lasts longer than usual.
- Prolonged bleeding may also indicate a high probability of fibrosis - a non-tumor tumor that grows in the muscular wall of the uterus (or it could be multiple fibroids).
- If unnatural fatigue occurs as a result of such bleeding, there is a possibility of anemia as a result of excess blood loss. But simply taking iron in this case cannot eliminate the problem. It is important to find out the cause because other, more serious conditions - precancerous and cancerous growths of the uterus - can also cause difficult periods.
Why does the cycle go wrong after a summer holiday?
The menstrual cycle consists of several phases and ends with menstruation or otherwise menstrual bleeding.
Physiologically, a woman’s reproductive system goes through 3 stages of the cycle during the month:
- During the first follicular stage, the body produces the hormone “estrogen,” which helps the follicles mature. And later, inside the largest follicle, which is called dominant, the egg matures.
- During the ovulatory stage, an egg is released from the dominant follicle over several days. She is already fully matured and ready to meet sperm and fertilization.
- During the third luteal stage in the female body, the corpus luteum synthesizes the hormone progesterone, which prepares the endometrium for the “implantation” of a fertilized egg into it. If fertilization has occurred and the egg has successfully attached to the walls of the endometrium, then the woman can observe a few drops of blood. This process is called "implantation bleeding." And if conception and implantation do not take place, the corpus luteum is gradually destroyed, the level of progesterone decreases sharply and the process of cleansing the endometrium begins. This is menstrual bleeding.
Bleeding comes from a wound that forms at the site where endometrial tissue is torn from the wall of the uterus. During menstruation, endometrial particles come out with blood. Blood and mucous clots may also come out, causing the woman to feel tolerable pain. This is fine. Menstrual bleeding includes not only the layers of the endometrium, but also particles of an unfertilized egg, blood from damaged vessels and the mucous membranes of the endometrial walls.
The regularity of the cycle indicates the good condition of the reproductive system and the general well-being of the woman. However, for a number of reasons, deviations can occur that lead to pathology. Physiological, emotional state, difficult situations - all this affects the appearance of irregular periods. The calendar system also leads to a failure in calculations, when one month of the year is shorter than another, therefore, with an average cycle length, the start dates of menstruation in the calendar will be different.
A normal menstrual cycle is more common among women who have given birth. Irregular menstrual periods are common in girls because it takes one to two years for the normal physiological process to develop. Before the onset of menopause or when there is a hormonal imbalance, the menstrual schedule also changes. The first menstruation is characterized by a short cycle, with hormonal imbalance or menopause - a maximum or long break.
In the summer it’s so nice to visit unfamiliar places and change your lifestyle to a more active one. But flights, unfamiliar food, and heavy physical activity can cause disruption of the menstrual cycle. As a rule, this phenomenon is temporary, and menstruation occurs regularly after some time (several months). No action needs to be taken. If the ovulatory-menstrual cycle has not recovered within 2 months, you will have to remember the phone number of your gynecologist.
Recommendations for holidays are very simple:
- Eat your usual food.
- Increase the loads only gradually.
- Do not overheat in the sun, especially if you have benign tumors such as cysts or endometriosis.
Attention! Delays in menstruation after a vacation are normal only if there is no minor bleeding between cycles. Be sure to pay attention to this. Spotting in the middle of your cycle can be signs of endometrial hyperplasia, endometriosis, fibroids, and even the threat of miscarriage, which you may not even be aware of.
Cutting pain in the lower abdomen, periods are painful
If you regularly experience severe stabbing pain in your lower abdomen (called dysmenorrhea), your doctor may recommend trying prescription and over-the-counter medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as Ibuprofen and Naproxen, can be purchased without a prescription. Treatment works best if started several hours before pain begins. If the pain begins, the likelihood of it decreasing after taking medication is low, so you should start taking pills before it starts - according to the instructions. This will also help reduce heavy bleeding.
- Oral contraceptive pills are also effective for menstrual cramps. If the active tablets are taken continuously for 90 to 120 days in a row, periods will only occur three to four times a year.
- Other ways to relieve symptoms include warm compresses to the abdominal area and mild exercise.
- Hysterectomy is the only treatment that completely guarantees that heavy menstrual bleeding will end forever. However, this is a radical operation in which the uterus is removed and you will no longer be able to have children.
Treatment of menstrual disorders
Depending on the results of the diagnostic procedures performed, the patient’s age, duration and type of disease, the doctor prescribes complex therapy, which usually includes the following courses of drugs:
- Hormonal agents that are used as primary ones. Progestogen-estrogen drugs are prescribed by a doctor depending on the data of a blood test, which indicates the patient’s hormone level. As a rule, the duration of hormonal therapy is 3 months. After the first course of therapy, the patient is re-examined, which reveals the need for re-treatment. If necessary, the next course of hormone therapy is prescribed after six months.
- Hemostatic drugs.
- Uterotonics, which are prescribed to contract the uterus and stop blood flow.
- Vitamins.
- Drugs for the correction of iron deficiency anemia.
- Treatment using herbal infusions.
- Surgery. Operations are used quite rarely, but if necessary, the uterus and appendages are removed. Such unpopular and drastic methods of treatment are carried out in rare cases in the absence of effect from curettage and in case of heavy blood loss.
To preserve menstrual-like function in patients of reproductive age, part of the endometrium is preserved during surgery. Thanks to this, cyclical changes and processes accompanying menstruation continue to occur in the female body. As a result, the patient recovers faster and adapts to postoperative changes.
Menstruation disorders, which must be treated promptly and professionally, can lead to irreversible consequences. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Advantages of the Gynecology Medical Department
Make an appointment by calling +7 or filling out the online form
The administrator will contact you to confirm your appointment. The confidentiality of your application is guaranteed.
Today, menstrual irregularities are one of the most common gynecological abnormalities. Almost all women experience this at least once in their lives. But a “random” failure caused by stress is one thing, constant delays are another. Passion.ru - about how to return the body to its usual biological rhythm.
For women born and raised in our latitudes, the first menstruation occurs, as a rule, from 12 to 13.5 years. During the first year the cycle is established. And yet, during this first year (as, in fact, the subsequent ones) at least 8 cycles must pass. If after 14 years of age the period still has not started, the girl needs an examination .
The duration of the cycle is counted from the beginning of one menstruation to the beginning of the next: a minimum of 21 days, a maximum of 33. A delay of 14 days or more (sometimes up to 6 months) is considered a serious problem - the so-called state of oligoovulation. There are also opposite situations when menstruation, on the contrary, comes too often.
On the other hand, if for many years your cycle lasted 21-22 days, and then suddenly became longer, this may also be a red flag. It is worth paying attention to the duration of the discharge itself: for example, if from 5-7 days this process has been reduced to 1-3.
Search for the “culprits”
5 reasons for menstrual irregularities
1. The most common (and most commonplace) cause of failures is pelvic organ infections. Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to be examined for the pathogen (this could be, for example, chlamydia, uroplasma, mycoplasma) and carry out anti-inflammatory treatment. If the problem was an infection, as a rule, cycle disturbances do not recur.
2 . The situation is much more complicated when hormonal disorders . They can occur at different stages of hormone formation, so there is a specific list of them that must be checked.
The general examination plan includes a study of the functioning of the thyroid gland , and disturbances here can be associated both with its hyperfunction and, conversely, with a decrease in activity. Sometimes the problem is related to changes in adrenal function.
3. Hormonal disruptions can also occur in the ovaries themselves. However, it is not necessarily due to inflammation at the moment. Alas, the cause may be, for example, a high infectious index in childhood: that is, frequent colds in a girl under 12 years of age.
4. Previous rubella and chicken pox can also affect the formation of follicles in the ovary and sometimes disturbances occur literally from the very first cycle. The difficulty here is that teenagers themselves rarely pay attention to this, which is why the problem is diagnosed much later.
It happens that cycle disorders reflect a whole range of reasons, including hormonal ones.
Is hormonal correction necessary?
5 reasons for menstrual irregularities
This issue is resolved individually. If the patient has minor changes in hormonal levels in the form of small delays of 5-10 days and already has some kind of structural pathology in the ovaries, it is often possible to regulate the cycle with homeopathic medications in combination with cyclic vitamin therapy .
Other non-drug treatments (eg, physical therapy) are also widely used. To achieve success, an integrated approach is extremely important here.
A consultation with a medical psychologist can also be very helpful, because hormonal changes manifest themselves not only in cycle disorders: acne on the skin, male-pattern hair growth easily become reasons for complexes.
At the same time, one cannot expect an immediate effect from the treatment, since it is carried out over a period of 9-10 months.
Diagnostics
Therapy for NMC begins with determining the root cause, which is possible after an accurate diagnosis. The first doctor a woman should contact if she has symptoms of a cycle disorder is a gynecologist.
Diagnostics is a set of measures that includes:
- Questioning and inspection. The doctor records complaints, performs an examination, and takes swabs for analysis. If any deviations from the norm are detected, the patient is sent for an ultrasound of the reproductive system.
- Ultrasound. It is considered the safest method of examining the pelvic organs. Ultrasound examination makes it possible to determine the presence of malignant or benign tumors, erosion or dysplasia, deviations from the norm in the size, position and shape of the uterus and ovaries.
- Analyzes. NMC can be caused by a disorder in the functioning of the internal secretion organs. To confirm the diagnosis, tests are needed:
- hormone levels;
- ESR concentration;
- blood chemistry;
- blood clotting test.
- Consultation with a neurologist. Necessary in case of suspected pathology of the pituitary gland, as well as in case of cycle disorders associated with the onset of menopause.
- Hysteroscopy. The study is carried out using an endoscope, which allows you to examine the uterine cavity from all sides. It helps to identify pathologies such as mucosal atrophy, polyps and other neoplasms.
- Histology. The examination is carried out if NMC is associated with inflammatory processes or the presence of malignant tumors in the body.
After a thorough analysis of the data obtained, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Treatment methods
There is no specific method for restoring the menstrual cycle, since its course is influenced by many factors. The main point of therapy is to detect and eliminate the root causes of irregular menstruation.
In most cases, along with drug treatment, it is necessary to adjust the diet, optimize the “wake-sleep” mode and reduce the level of stress.
Treatment of menstrual disorders in adolescents and women of reproductive age is approximately the same and includes the following measures:
- Hormone therapy: carried out to correct menstrual dysfunction and stabilize the reproductive system. For teenagers, gentle drugs with low dosages are selected.
- Intravenous infusion of special solutions and taking medications containing iron: to replenish blood loss during anemia. If severe bleeding is observed, accompanied by a decrease in hemoglobin, dizziness and general weakness, curettage may be prescribed.
- Adjustment of nutrition and physical activity: for extragenital pathology.
In uncomplicated cases, cyclic vitamin therapy is prescribed, which is sometimes supplemented with sedatives.
Medications
In traditional therapy for menstrual disorders, the following drugs can be prescribed:
| A drug | Purpose | Dosage | Minimum price, rub. |
| Cyclodinone |
| 1 tablet per day (in the morning). Drink plenty of water. Course 3 months without interruption during menstruation | 530 |
| Dysmenorm |
Homeopathic remedy used in combination with other medicines | 1-2 tab. 3 times a day 30 minutes before or after meals. The drug must be absorbed slowly. The course is at least 3 months. | 540 |
| Cyclovita |
Vitamin complex is not a medicine | Dosage - 2 tablets. per day (morning and evening) during meals. Drink plenty of water. | 391 |
| Duphaston |
| The dose and duration of administration are individual for each case. They are determined by the attending physician | 550 |
| Utrozhestan | Menstrual disorders caused by progesterone deficiency. Hormonal drug | The daily dose is 200-300 mg of the active substance. Application can be carried out in 2 doses: 200 mg in the evening and 100 in the morning (if necessary). The dosage and duration of use may vary depending on the disease. | 420 |
Drug treatment is prescribed by a doctor after diagnosing the disease. Independent selection of drugs based on consultation with a pharmacist in a pharmacy is unacceptable.
Traditional methods
Herbal remedies can successfully help with the painful sensations that often accompany menstruation in teenagers.
There are several simple but effective decoctions recommended for dysmenorrhea:
- Sweet clover infusion. Effectively eliminates spasms that cause pain. To prepare, you need to pour 15 grams. Collect with 2 cups of boiling water. Leave in a thermos for 2 hours, then strain. Take half a glass 2-3 times a day.
- Melissa infusion. This herb has not only an analgesic, but also a sedative effect. 15 gr. The collection is poured with 200 ml of hot water and left for 30 minutes. After straining, the infusion is ready for use. Take 1-2 tbsp. Spoons every 2 hours.
In case of prolonged delay of menstruation, the following remedies are recommended:
- Parsley infusion. A bunch of fresh herbs should be thoroughly chopped and poured with a glass of boiling water. Keep in a thermos for 2-3 hours. Take 0.5 cups during breakfast and with your last meal.
- Decoction of onion peels. Pour 1.5 liters of boiling water over the peels of 1 kg of onion and cook over low heat until the liquid darkens. Strain the broth. Take 100 ml 30 minutes before meals 2 times a day.
In case of delays associated with nervous overstrain, infusions of soothing herbs are helpful: mint, hawthorn, valerian.
Other methods
If during the examination a tumor was discovered that became the cause of NMC, the issue is resolved surgically.
How serious intervention is required depends on the size and location of the tumor:
- resection and enucleation – when removing small submucosal polyps and fibroids;
- removal of the uterus - if a tumor of impressive size is detected;
- removal of the uterus with appendages and nearby lymph nodes - for oncology.
In case of complications after severe bleeding, curettage is used with further sending of the material for histological examination.
Diagnosis and treatment
Before prescribing treatment, an examination is carried out to determine the reasons why menstruation has become irregular.
When diagnosing, methods such as blood tests for hemoglobin, the content of individual microelements, sugar, as well as hormones and the presence of infectious agents are used. The presence of diseases can be determined using ultrasound and MRI.
If it is determined that there are no serious pathologies, then to restore the cycle, vitamins A, E, C and group B, sedative drugs are prescribed, and general strengthening procedures are recommended. If diseases caused by hormonal imbalance are detected, hormone replacement therapy is carried out. For women of reproductive age, taking oral contraceptives according to a specific regimen helps restore their cycle. If there is an excess of estrogen in the body, drugs based on progesterone (Utrozhestan, Duphaston) are prescribed, and if there is a deficiency, testosterone (Norkolut) or estradiol (Levonorgestrel).
Treatment of concomitant diseases of the liver, thyroid gland and other organs involved in the formation of hormones and hematopoiesis is carried out. Iron supplements are also prescribed to eliminate anemia, and antiviral and antibacterial treatment is carried out.
In the presence of uterine bleeding, the uterus is curetted and the endometrium, which has various defects, is removed. Subsequent hormonal treatment helps prevent the recurrence of disorders and the development of pathologies such as irregular periods.
To improve the functioning of the ovaries, medications are prescribed that stimulate the maturation of follicles and increase the production of estrogen and progesterone. Such drugs (“Choriogin”, “Pergonal”) are used in the treatment of infertility.
Video: Treatment of menstrual irregularities
Admit it, have you ever had to deal with the problem of menstrual irregularities? Please note that irregular periods can be a sign of hormonal imbalance and other serious health problems. In this article, we have collected the 6 most common causes of irregular menstruation.
Menstrual irregularities and delayed periods can be caused by various factors. That is why, if you have such a problem, we advise you to immediately consult a gynecologist to establish the correct diagnosis.
The menstrual cycle is a biological and hormonal process that women of a certain age regularly go through. The course of menstruation directly depends on the psychological and physiological health of a woman.
The average duration of the menstrual cycle is 28 days. Menstruation itself lasts from 3 to 6 days, but everything depends on the hormonal state of each woman.
During each subsequent menstruation, a number of changes occur in a woman’s body that affect her sexual and reproductive functions. However, unfortunately, some women ignore the first alarm bells, which may be indicated by irregular menstruation and a change in the nature of discharge.
The length and pattern of periods can change throughout life, and this is due to different hormone levels between puberty and menopause.
Every woman needs to be able to distinguish the signs of menstrual irregularities, because they may indicate hormonal changes in the body and serious disorders in the functioning of internal organs.
If your periods are often delayed or, on the contrary, begin earlier than the usual schedule, we advise you to consult a gynecologist to identify the cause of irregular menstruation.
Deviation syndromes
In general, cycle disorder deviations are divided into three syndromes, each of which has characteristic features.
Hypomenstrual syndrome.
In this case, the duration and intensity of menstruation is reduced. This syndrome is caused by decreased ovarian function. Each time it occurs differently and includes the following manifestations:
- oligomenorrhea – the duration of discharge is from 1 to 2 days;
- hypomenorrhea – characterized by rather scanty discharge;
- opsomenorea – exceeding the duration of the menstrual period by significantly more than a month to 50-60 days;
- amenorrhea is the most serious condition, which is characterized by a long delay of menstruation for six months or more.
Amenorrhea is considered the most complex and difficult to treat manifestation of this syndrome. Depending on its origin, it can be physiological or pathological. Physiological amenorrhea occurs during puberty of the female body, during pregnancy or during menopause. Pathological amenorrhea begins as a result of gynecological ailments (erosion, polyps, tumors). It is divided into two types: primary, which occurs due to genetic diseases, and secondary, which manifests itself as a consequence of previous diseases.
Hypermenstrual syndrome.
This syndrome is the most common and develops as a result of hormonal disorders. It includes the following states:
- polymenorrhea is a strong and long menstruation (much longer than usual), turning into uterine bleeding;
- hypermenorrhea, which is characterized by heavy menstrual flow;
- proyomenorrhea is a condition in which the discharge can be copious, regular and prolonged with short intervals.
Non-menstrual uterine bleeding.
Such bleeding can occur as a result of the development of various diseases and neoplasms on the genital organs. As a result of hypermenstrual syndrome, women may experience interruptions in the functioning of the ovaries, which cause dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
DMC develops due to diseases of the endocrine system, lack of sleep and rest, chronic fatigue, poisoning with toxic and chemical substances, infections of the genitourinary system, nervous overload, stressful situations, psychosis and depression. Depending on the factors that contributed to the occurrence of DMC in women, the following types are distinguished:
Ovulatory.
A rare type of DUB, which is caused by inflammation in the pelvic organs. Characteristic features of this type of abnormality include mild bleeding, which can occur at any time, regardless of the cycle. Sometimes ovulatory bleeding can contribute to the development of secondary infertility or premature termination of pregnancy.
Anovulatory.
This type of DMC occurs quite often during puberty and menopause. They are characterized by the absence of ovulation or failures in the formation of the future egg. During this period, the female body secretes only estrogen, which can provoke endometrial hyperplasia, that is, increased development of the uterine layer, which ultimately leads to heavy bleeding. With improper and untimely treatment, the patient develops a cancerous tumor - adenocarcinoma. Anovulatory DMB are divided into juvenile and reproductive.
Juvenile.
Such bleeding is common in girls during adolescence during the first two years after the appearance of their first menstruation. They are distinguished by copious and painless discharge, which contributes to the rapid development of anemia and secondary blood incoagulability. Factors that provoke juvenile DUB can be diseases of the genital organs, disorders in the endometrium, an underdeveloped state of the uterus, which still functions poorly and does not contract sufficiently. Therefore, hormonal therapy is not used to treat this disorder.
Reproductive.
This type of disease is also accompanied by excessive production of estrogen, which leads to the formation of glandular cysts in the uterus. The nature of the discharge depends on the degree of development of the process. Abundant uterine blood flow in this case is accompanied by the following symptoms: weak pulse, nausea, rapid heartbeat, etc. In the absence of therapy and frequent relapses, the patient may develop adenocarcinoma.
Menopausal.
This type of discharge is associated with age-related changes in the part of the brain that is responsible for the functioning of the ovaries.
Prolonged menstruation for more than a month in premenopause is associated with hormonal imbalance and menstrual dysfunction. The period of follicle maturation increases, the level of estrogen in the body increases. Such changes cause transformation of the uterine mucosa. Bleeding in postmenopause is considered a symptom of malignant neoplasms in the genital organs.
Diagnosis of a disrupted menstrual cycle
Many women who have problems with menstruation put off visiting the doctor because they are afraid of prescribing hormone therapy. In fact, hormones are indicated only in some cases, and careful diagnosis is necessary to select an adequate treatment regimen.
In addition to a gynecological examination, smear and general blood and urine tests, the following may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and thyroid gland;
- hormone analysis;
- hysteroscopy;
- studies to identify chromosomal pathologies;
- PCR, etc.
The doctor decides exactly what tests are needed after a detailed questioning, in which he can find out the presence of a genetic predisposition, features of the patient’s lifestyle and other nuances that affect the frequency and intensity of menstruation. You may also need to consult doctors of other specialties (endocrinologist, therapist) and additional studies (computed tomography, skull radiography, etc.).
How to treat a broken cycle?
Usually, after consulting a gynecologist, examination in a chair, ultrasound of the pelvic organs and hormone tests, treatment with the following drugs is prescribed:
- Analgesics (for severe pain).
- Antibiotics (for infections).
- Hormones (for endocrinological problems).
- Sedatives, adaptogens.
- Immunostimulants.
- Vitamins, especially vitamin E (there is a lot of it in various oils and sprouted grains).
In addition, traditional medicine and herbal remedies may be prescribed. Please note that you should not take them without consulting a doctor! Phytoestrogens are good at normalizing the cycle, but it is important that they do not conflict with the estrogens that are produced by your body. Otherwise there will be too much estrogen.
The effect of herbal drugs is milder; they need to be taken in long courses for the effect to be really noticeable. As for homeopathic remedies, today the attitude of medicine towards them is cool. They can be prescribed with other drugs, and such therapy only works if you believe in it.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Causes of brown discharge during pregnancy in the early and late stages, abundant and scanty
An infusion of water pepper and raspberry leaves helps well. You need to take the infusion 3 times a day, a dessert spoon. It relieves pain during menstruation well.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Jnw-6s1-LI8
If you have chronic fatigue, you should consider taking medications that increase your vitality. But only a doctor should prescribe them. Also pay attention to your lifestyle: before the onset of menstruation, walk more, do not overload yourself with work. This period is intended by nature for restoration.
The inability to relax is a primary problem for modern women. You can’t expect your cycle to be like clockwork if you’re constantly nervous, go to bed late and eat randomly. It is imperative to focus on a plant-based diet rather than an animal diet. Maybe strict vegetarianism is unnecessary, but vegetable salad, stewed, baked vegetables, fresh juices and smoothies should always be on the table of a woman who takes care of herself. Be sure to eat fruits in winter, freeze berries in the summer. You should absolutely not deprive your body of fat.
Causes of irregular cycles and methods of treatment
Irregular menstrual cycle, what does it mean and what does it threaten a woman with? Women often talk about delayed menstruation among themselves. They frighten with their uncertainty. What's happened? Why didn't my monthly bleeding start on time? Maybe there was a pregnancy? Modern doctors reassure that treatment of menstrual irregularities is not always necessary, and small errors of 5-7 days can not be taken into account at all. After all, the cycle is influenced by many factors, the external environment, psychological state, some bacterial and viral diseases, diets and much, much more. Women are not robots, so that they start bleeding every hour every hour.
About ovulation and the likelihood of pregnancy
And yet, let's return to the issue of possible pregnancy. How to get pregnant if your cycle is irregular, how to calculate ovulation? Doctors do not recommend that couples under the age of 35 and who do not have reproductive problems calculate ovulation at all. Regular sexual activity is enough, sex 2-3 times a week. Pregnancy should occur within a maximum of 2 years. For those who really want to speed up the process, there is a folliculometry procedure - this is the same ultrasound, but in which attention is paid to finding the dominant follicle in the ovaries and predicting the timing of its rupture, that is, ovulation. Well, timely sexual intercourse is a large percentage of the chance of getting pregnant.
You can also try to determine ovulation using tests similar to those for pregnancy, only they contain reagents for a different hormone. But there is a lot of evidence that these tests are often deceiving and do not give a clear picture.
You can measure your basal temperature and keep a chart. For so many years, Soviet doctors not only predicted the days of ovulation, but even determined hormonal disorders in patients. But you need to take into account that not every woman’s basal temperature will be an informative indicator. Its information content will depend on the presence of progesterone receptors in the rectum, as well as compliance with all measurement rules.
Bleeding during menopause
If bleeding appears during menopause, the woman must undergo curettage of the uterine cavity, since such bleeding may be signs of endometrial adenocarcinoma or atypical hyperplasia. In this case, the issue of hysterectomy is resolved (see indications for hysterectomy). After the results of histological examination:
Progestins are prescribed: 17-OPK, Duphaston, Depo-Provera. It is also possible to prescribe antiestrogenic drugs, such as danazol, 17a-ethynyl testosterone, gestrinone in a continuous mode.
It doesn’t matter at what age the menstrual cycle disorder occurred, this pathology is only a consequence of some underlying disease, so it is necessary to identify and treat the underlying pathology, because only after eliminating the cause is it possible to restore the normal cycle. And, of course, it is necessary to remember about normalizing the daily routine and rest, nutritious nutrition and minimizing stress. In case of obesity, it is often enough just to normalize the weight to restore the menstrual cycle. The same applies to emaciated women (in this case, a high-calorie diet is indicated).
Prices for treatment of menstrual disorders
| Description | price, rub. |
| Appointment with a gynecologist with extended consultation | 1800 rubles |
Factors caused by pathological conditions:
- Caused by ovarian pathology
These include a disrupted connection between the ovaries and the pituitary gland, stimulation of ovulation with medications, ovarian cancer, insufficiency of the second phase of the cycle, occupational hazards (vibration, radiation, chemical exposure), ovarian surgery (removal of most of the ovarian tissue), trauma to the genitourinary organs and the formation of fistulas and so on.
- Disruption of interaction between the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary gland
Insufficient or excessive release of releasing factors and gonadotropic hormones, pituitary tumors, hemorrhage into the pituitary gland or necrosis, brain tumors compressing the pituitary gland/hypothalamus.
It doesn’t matter whether it’s genital or extragenital endometriosis; in any case, the disease is hormonal in nature and leads to hormone imbalance.
- Impaired blood clotting (hemophilia, genetic pathologies).
- Liver diseases and gallbladder diseases.
- Curettage of the uterine cavity - artificial termination of pregnancy or therapeutic and diagnostic curettage contribute to damage to the endometrium, which disrupts its growth or may be complicated by inflammation of the uterus and appendages.
- Hormone-dependent tumors - cancer of the breast, uterus, adrenal glands, thyroid gland.
- Diseases of the adrenal glands (tumors, injuries, etc.).
- Polyps of the uterine mucosa.
- Chronic endometritis - a full-fledged endometrium is not formed.
- Rapid weight change - losing weight or obesity leads to disruption of the menstrual cycle, because adipose tissue produces estrogens.
- Anomalies of the uterus - sexual infantilism, septum in the uterus, double uterus and others.
- Infections - both infections suffered in childhood (rubella, chickenpox) and sexually transmitted infections can negatively affect the ovaries.
- Pathology of the uterus - this item includes tumors of the uterus and pathology of the endometrium (hyperplasia).
- Mental illnesses (schizophrenia, epilepsy, alcoholic psychosis).
- Endocrine pathology.
- Chromosomal abnormalities (for example, karyotype 46XY with a female phenotype).
- Arterial hypertension (see medications for high blood pressure).
- Bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse).
- Hypovitaminosis and avitaminosis.
Treatment
It is necessary to treat an irregular menstrual cycle differentially, depending on the identified pathology. If the changes are functional and mediated by the influence of external factors on the woman’s body, then you can not take radical measures, but limit yourself to general recommendations for improving your lifestyle. These include:
In certain cases, this is enough, especially for girls of asthenic physique who are prone to neuroses. However, when organic diseases are detected, it is necessary to carry out therapy aimed at restoring a regular cycle. And it is not always possible to correct the situation using conservative methods alone, but you have to resort to surgery.
Conservative treatment
The basis of conservative therapy is taking medications. Any medications are used in strict accordance with approved clinical recommendations and standards for the treatment of menstrual cycle pathologies. You need to take medications only as prescribed by a doctor, otherwise you can increase the imbalance of physiological processes and provoke a worsening of the condition. Typically, the following medications are used:
Causes
The menstrual cycle is highly sensitive to the influence of various factors and is very sensitive to changes in a woman’s body. The causes of irregular periods can be very different, but largely depend on age. For young girls who have just begun menstruating, some deviations from the generally accepted norm are not critical, and, moreover, are considered quite physiological. The same can be said about women after 40 years of age, who begin to show age-related changes in the functions of the reproductive system.
However, irregular periods can be the result not only of physiological changes, but also of various pathological conditions. And if in young girls such disorders are mainly of a functional nature, then for women after 40 years of age, organic causes of instability of menstruation are more typical. Thus, we can identify the most common factors influencing the regularity of the cycle:
- Stress, neurotic reactions.
- Physical and mental fatigue.
- Fasting, unhealthy diet.
- Obesity.
- Endometriosis.
- Tumors, uterine polyps.
- Ovarian diseases.
- Endocrine pathology.
- Infections of the reproductive system.
- Taking certain medications (contraceptives, antihypertensives).
- Bad habits (smoking, alcoholism).
This is not a complete list of conditions that can cause changes in the nature of menstruation. The cause can be almost any disease that is characterized by a pronounced effect on the body's metabolic processes.
It is possible to determine why a woman has an irregular cycle through a medical examination and additional diagnostics.
Menstrual cycle calendar. Why is it needed, how and when to conduct it?
When using any of the above methods, the data is transferred to a special diary called the menstrual cycle calendar. It can be performed in various forms: in the form of a regular circling of numbers on a calendar, in the form of a graph or chart, or in the form of a printout - in computer calculations. There is only one goal - to find out your menstrual cycle and monitor its fluctuations.
The menstrual cycle calendar performs the following functions:
- Determines the duration, nature and duration of menstruation;
- Helps to avoid unwanted pregnancy (detects the period of ovulation - dangerous days);
- Helps in creating a nutrition schedule (for losing weight or maintaining an ideal weight);
- Detects a delay in menstruation;
- Makes the gynecologist's work easier.
In what cases is it necessary to maintain such a calendar:
- For girls - at the onset of the first menstruation;
- Women over 40 years of age (premenopausal period);
- When planning a pregnancy (determines favorable days for conception);
- In case of menstrual irregularities at any age.