Age-related causes of bleeding at the end of the menstrual cycle
Gynecologists claim that such a phenomenon can be considered a physiological process exclusively at the stage of completion of the formation of the reproductive system.
This symptom is characteristic of the teenage period in a woman’s life between 12 and 19 years, depending on the speed of puberty. The first menarche is extremely unstable and varies not only in the number of days in the cycle, but also in the extent and symptoms preceding its onset. Such “deviations” are caused by unstable hormonal levels and the absence of ovulation at the final stage of formation of the reproductive system. A serious signal that prompts you to sound the alarm is the stable appearance of spotting after menstruation for a year after the start of regulation.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
In a representative of the fair sex with a mature reproductive system and clearly cyclic menstruation, spotting after it indicates the presence of pathological processes.
On thematic forums dedicated to women’s health, you can come across the question: “Girls, your period has ended and after 2 days the bleeding started again. Is this normal? Who had this happen?” The answer is clear - no, this process is not physiological. But the reasons may be different.
Ovarian dysfunction
Experts say that one of the most common causes of pathological intermenstrual discharge is disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries.
If a woman notices that 10 days after the end of her period, spotting has started again, it is advisable to talk about ovarian dysfunction.
There are a number of reasons for this phenomenon:
- Frequent stress.
- Heredity.
- Changes in the functioning of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
- Ovarian pathologies.
- Sudden long-term change in diet.
- Changes in climate zone.
- Physical exercise.
Intermenstrual bleeding lasting more than ten days is not the only sign signaling pathological processes in the ovaries. It is worth paying close attention to the work of these bodies if:
- severe premenstrual syndrome does not entail the onset of a cycle;
- a sudden onset of severe nagging pain in the lower abdomen and a sudden cessation of symptoms without external influence are indicated;
- there is no ovulation;
- There are monthly intermenstrual bleedings.
If you start bleeding a week after your period, you can assume an infection affecting the genital organs.
Inflammatory processes in the cervix caused by pathogenic microorganisms can cause abnormalities in the functioning of the entire reproductive system. If a woman notices a similar symptom, she should urgently consult a doctor, because it could be endometritis or salpingo-oophoritis.
Pay attention to the accompanying manifestations of these deviations:
- Sharp, cutting pain in the lower abdomen.
- Burning in the groin area.
- Mucous discharge from the vagina that is pathological in nature.
Deviations can be expressed by the consistency of the leucorrhoea: too thick or, conversely, too thin; specific color pigmentation, the presence of an unpleasant odor accompanying vaginal discharge.
- A sharp increase in body temperature.
- Painful sensations during a gynecological examination.
These diseases are characterized by a sharp “proliferation” of the uterine mucosa. The uterus begins to bleed a few days after the end of the scheduled menstruation. The presence of abnormalities in the condition of the vaginal mucous membranes is indicated by the rejection of fluids, visually representing a pink or light brown smear with blood splashes.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=playlist
Women who have encountered this disease note that there is quite a lot of discharge at the early stage of development of the pathology. If the patient has diagnosed herself with a similar manifestation of endometriosis, she must urgently contact the gynecologist on duty at the nearest specialized clinic. These phenomena may indicate irreversible processes affecting the functional characteristics of the endometrium.
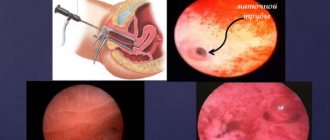
Uterine fibroids
Experts note that uterine fibroids are accompanied not only by specific mucous discharge with blood after menstruation, but also by heavy bleeding during the “cleansing” phase of the cycle. Women who experienced a similar illness noted the presence of yellow-green pus and bright red blood streaks in the smear.
This pathology is accompanied by the rejection of dark burgundy clots during the period between cyclic menstrual flows. This disease, in most cases, can only be treated with surgery.
Depending on the location of the tumor and the stage of its formation, rejection of mucous substances of various color pigmentations that have an unpleasant odor, accompanied by cutting pain in the lower abdomen and groin area, may be observed.
Whatever the reasons for spotting after menstruation, if you notice a similar phenomenon in yourself, you should immediately consult a specialist! After all, such serious deviations do not have the “habit” of ending without drug intervention.
Bloody discharge after menstruation can be caused by hormonal imbalance. It occurs as a result of the following factors:
- Use of emergency contraceptives. When using Postinor, Escapel in the first week, brownish discharge may appear, not accompanied by painful sensations. The secretion does not have a specific odor, and there are no unusual manifestations in the next cycle.
- Certain types of oral contraceptives. Most OCs affect the body's hormonal balance, causing bloody discharge after menstruation. The problem is associated with adaptation to the new drug, which takes place over two or three cycles. If the condition does not change in the following days, then the patient needs to consult a gynecologist and replace the OC.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands. The deviation leads to an increase in prolactin levels and a sharp change in body weight. As a result, polycystic ovary syndrome is formed, the main symptom of which is the appearance of spotting after menstruation.
- Hormonal patches also cause hormone imbalance.
Intermenstrual bleeding a few days after the end of the cycle can be provoked by internal factors:
- Vaginal rings and intrauterine device. Contraceptives irritate the vaginal mucosa. If discharge occurs immediately after their installation, damage to small blood vessels may be the cause.
- Ectopic pregnancy. This is a physiological deviation that leads to pain in the lower abdomen and uterine bleeding. They occur a week after menstruation and require surgical intervention - ignoring the pathology often leads to rupture of the fallopian tube.
- Gynecological procedures. Examination in mirrors and scrapings cause sanguineous discharge immediately after menstruation. After 2-3 days they disappear on their own and do not require professional help.
- Hypovitaminosis. Insufficient intake of B vitamins.
- Medicines that affect the rate of blood clotting, with a sedative and calming spectrum of action.
- Irregularities in the menstrual cycle. The deviation appears in response to heavy physical activity and psycho-emotional imbalance.
- Spontaneous abortion. A miscarriage is characterized by separation of the fertilized egg from the walls of the uterus and severe bleeding.
- Injuries to the genital organs that occur after active sexual contact or rape. The lack of natural lubrication leads to ruptures of small vessels and damage to the mucous membranes of the vagina. The condition may be accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen.
- Endometrial hyperplasia. The pathology provokes scanty, spotting discharge 7 days after the end of the menstrual cycle. The disease provokes thickening of endometrial tissue, abundant secretion with clots.
- Ovarian dysfunction. The deviation appears on the tenth day after menstruation. The pathology is provoked by stressful conditions, hereditary predisposition, disorders of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
- Malignant neoplasms. At the initial stages of development they are asymptomatic. Subsequent stages cause spotting to appear at any time - after five days of the menstrual cycle.
- Infectious diseases. When the vagina is affected, there are no obvious clinical signs. When moving to the uterus, inflammation is manifested by the release of bloody secretions.
- Myoma. Benign neoplasms lead to metrorrhagia, unpleasant sensations in the lumbar region and abdomen. The tumor can cause intense prolonged bleeding, reminiscent of normal menstruation.
- Polyps. The formation of polyposis bodies in the uterine cavity or on its cervix is associated with instability of hormonal balance, infectious processes, intrauterine devices, and medical abortion.
- Ectopia. The disease involves abnormal growth of cubic epithelial cells on the cervix (its vaginal area). Small-volume bleeding occurs after sexual intercourse or gynecological examinations.
- Endometriosis. The diffuse form of the disease leads to the secretion being released ten days after the end of regulation. You may also experience a feeling of fullness and nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
When should you see a doctor?
How can a woman determine that the discharge is pathological and she should see a doctor? You need to pay attention to the following signs:
- the blood appeared without provoking factors - the woman did not use hormonal contraceptives, did not experience nervous shock, and did not change the climate;
- the discharge is regular - if it was a one-time deviation that never happened again, there could be a malfunction in the body, but regular bleeding indicates pathology;
- the smears are bloody brown, mixed with pus;
- bleeding in the middle of the cycle is heavy, similar in nature to menstruation;
- discharge is accompanied by painful sensations in the vagina, abdomen and lower back.
You should not guess on your own whether the smears after the regula are normal or a sign of illness. It is better to make sure that the alarm was false than to miss the onset of a dangerous disease.
Diagnostics
Dysfunction does not always relate directly to the reproductive organs. The causes of the disorder may lie in an imbalance in a woman’s body. Blood clots, colored deep red, can also be released under the influence of external factors.
Experts identify several pathological phenomena that entail similar symptoms.
- Hormonal disorders. Deviations in the functioning of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands lead to hormonal disruptions in a woman’s body. This phenomenon provokes an increase in the amount of prolactin in the blood, sudden fluctuations in weight, polycystic ovary syndrome, prolonged heavy spotting that appears outside the usual cycle.
- Taking emergency contraception. Women who resort to such methods of “protection” note the presence of a side effect in the form of brown discharge after menstruation without odor and pain. Bloody discharge may also occur after Postinor or Escapel. If you take Postinor during menstruation, then after menstruation the woman will notice discharge that prolongs her period.
- Starting some types of oral contraceptives. Many OCs are based on the principles of hormone therapy. For several months after starting treatment, spotting may appear 3 to 5 days after menstruation. This phenomenon is due to the “interference” of the drug in the functioning of the woman’s reproductive system.
- Using hormone patches can also cause red discharge after menstruation.
- Using an intrauterine device or vaginal rings. These contraceptives irritate the vaginal mucosa. If the discharge appears immediately after the “installation” and continues to smear lightly for several days, we can talk about injury to the blood vessels of the vagina. In this case, it is recommended to immediately contact a gynecologist. Even a couple of small wounds on the inner surfaces of the vaginal mucosa can lead to a sharp deterioration in the condition. Characteristic clots may appear on the second day after the introduction of the contraceptive.
- Introduction of broad-spectrum drugs. Start taking medications that affect blood clotting, sedatives and calming herbal preparations.
- Ectopic pregnancy. Such physiological deviation occurs in any age group. Experts say that the manifestation of symptoms can begin with the rejection of clots or the appearance a week after menstruation of characteristic bloody discharge, which can occur without “foreshadowing” pain symptoms.
- Gynecological procedures. Examinations and scrapings can injure the walls and internal surfaces of the vagina. Such an intervention can provoke the appearance of minor discharge that has a “bloody” color. Doctors note that this kind of daub goes away on its own within three to five days after visiting a specialist.
- Avitaminosis. Most often, the appearance of bleeding a week after menstruation is provoked by acute deficiency of B vitamins.
- Injuries to the genital organs. Violent acts of a sexual nature or lack of natural lubrication during sexual intercourse can provoke bleeding of varying intensity. If this phenomenon is accompanied by acute pain in the lower abdomen, you should immediately consult a specialist. The doctor must conduct an examination and, if necessary, remove biomaterials using scraping to clarify the causes of the bloody discharge.
- Ovulation.
- Pregnancy.
- Miscarriage.
- Climax.
- Cycle disruption under the influence of “external” factors. Excessive psycho-emotional and physical stress can provoke bleeding after menstruation. This phenomenon will end immediately after eliminating the root cause and does not require additional gynecological intervention. Many women who have encountered a similar illness note that when an acute stressful situation occurs again, spotting ichor appears again. Neurologists say that restoring the balance of the nervous system is a long process and in order to prevent discharge from starting again, it is necessary to take a full course of sedatives. In this case, you can limit yourself to taking light sedative tablets in combination with herbal remedies.
- Side effects from taking medications aimed at treating gynecological diseases. Experts identify several drugs, the use of which is fraught with the appearance of the described symptom during the intermenstrual period: Terzhinan; Trioginal; Hexicon (yellow and bloody discharge is possible after Hexicon); Polygynax (applicable on menstruation days); Duphaston; Femoston; Livarol; Pimafucin; Clotrimazole (pink discharge is possible after Clotrimazole). For a complete list of drugs that provoke menstrual irregularities, check with a specialist, and by following the link you can find information about whether Clotrimazole suppositories can be placed during menstruation. While studying thematic forums, you can come across remarks from women who have been taking these drugs for a long time. Many of them noted that after starting the course, bleeding occurred 3 days after menstruation. This phenomenon is an acceptable side effect and should not be treated further.
- Sexually transmitted infections. Depending on the intensity, quantity and pigmentation of the discharge, the doctor can diagnose the presence of diseases or infections affecting the reproductive system. When the color of the smearing substance resembles pus, it is advisable to talk about the acute stage of the inflammatory process. In this case, you don’t need to do anything yourself. You should immediately consult a gynecologist.
- Uterine bleeding. Provoked by a large number of factors, which are impossible to identify without consulting a specialist, uterine bleeding can cause discharge again 2 days after your period has ended. Depending on the severity of the processes occurring, a woman can diagnose herself with both a large volume of rejected mucous clots and a slightly spotting leucorrhoea with blood streaks.
Based on the available information, we can conclude that it is impossible to say why there is bleeding after menstruation without consulting a specialist and obtaining the results of the necessary tests.
According to experts, the appearance of spotting after menstruation, not accompanied by itching, burning or an unpleasant odor, is a phenomenon that is within the physiological norm. Doctors identify several conditions characterized by this process.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytaboutru
These bleedings are common at the stage of completion of the formation of the reproductive system organs in girls. The phenomenon occurs in adolescence from 13 to 17 years. Juvenile bleeding is discharge after menstruation of varying durations associated with the establishment of the menstrual cycle.
This phenomenon is caused by taking medications that have a direct effect on blood clotting. Brown discharge that exceeds standard menstrual periods should not be systematic. The frequency of this symptom indicates the presence of pathological processes in the woman’s genital organs.
These medications have a significant effect on both the woman’s body and hormonal levels. Doctors say that the presence of brown spotting after menstruation is acceptable in the first two to three months after the introduction of a new contraceptive. The described phenomenon indicates the active “work” of the drug.
The IUD can cause slight bleeding that is rejected by the vagina. Scanty spotting for two days after installation is a normal reaction of the uterus to a foreign body, but abundant bloody clots are a symptom that requires immediate contact with the antenatal clinic.
Pregnancy
Scanty discharge with blood that appears after menstruation may indicate pregnancy. This phenomenon is more likely to occur in women who have given birth and who have had sexual intercourse not long before the start of regulation.
Ovulation
The final maturation of the egg and its readiness for fertilization may be accompanied by pink discharge, which continues to smear for several days after ovulation.
Climax
This age-related restructuring of the female body makes its own adjustments to the menstrual cycle. One of the manifestations of menopause is brown mucous discharge, lasting no more than one to three days after the end of the established period of menstruation.
The release of liquid secretion caused by the above factors is a physiological process and does not require visiting a doctor and subsequent medical therapy.
Without a preliminary examination, the doctor cannot tell the woman what to do; treatment may differ depending on the cause of the abnormal secretion. A gynecologist may prescribe the following diagnostic measures:
- general blood test, biochemical and hormone tests;
- hysteroscopy;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- microflora smear;
- histological analysis of the uterus, cervix and cervical canal.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpolicyandsafetyru
Experts recommend contacting your local gynecologist if the following signs appear:
- Pinkish daub with a rotten odor is a symptom of endocervicitis or endometritis with a chronic course.
- Scarlet irregular discharge is a sign of slight dysfunction of the reproductive department.
- The brownish secretion is a consequence of the pathological process in the appendages and the uterus itself.
To prevent the development of massive uterine bleeding, a complete diagnostic examination is necessary. When visiting a doctor, a woman should talk about the symptoms, their nature, duration, number and time of occurrence of abnormalities (after 2 weeks, 10 days).
Treatment and prognosis
First of all, regardless of the cause of red discharge after the end of menstruation, a woman needs to take care of her hygiene. You should wash yourself twice a day using boiled water.
It is also recommended to maintain proper nutrition and exclude all unhealthy foods, fried and fatty foods from the diet, and also reduce the amount of sweets. Experts recommend giving up bad habits. In the summer, you should avoid swimming in open water for the duration of treatment.
Treatment depends on the diagnosis!
In order to eliminate the main cause of the appearance of red discharge, drug therapy is prescribed, which consists of the following steps:
- The use of antibacterial drugs, agents to suppress the spread of bacteria and enhance immunity.
- Restoration of disturbed vaginal microflora.
Medicines are prescribed according to the reason for the appearance of discharge after the end of menstruation. The choice of drugs is made by the attending physician and depends on the characteristics of the course of the pathology, the patient’s body, the stage and degree of development of the disease.
To restore the vaginal microflora, experts recommend introducing more fermented milk products into the diet. Natural yoghurts, milk, kefir, fermented baked milk are useful.
Surgical intervention is prescribed in cases where the cause of discharge after menstruation is neoplasms of various types.
In the presence of certain diseases, hormonal drugs are prescribed. They should be used only in accordance with the instructions, as side effects are possible. The prognosis directly depends on the type of disease. With timely treatment, it is most often favorable and after treatment the woman can return to normal life.
Causes of bleeding after menstruation
Bloody vaginal discharge can occur in women of any age. This pathology has the general medical name “metrorrhagia”. Bleeding in women in most cases indicates that there is a malfunction in the reproductive system caused by hormonal imbalance, age-related changes or any gynecological pathologies. Let's consider the main factors that can cause bleeding after regulation.
Age factor
According to gynecologists, spotting can be a variant of the norm during certain periods of a woman’s life; its occurrence can be explained by the physiological processes occurring in the body at that moment.
Bloody spotting after menstruation can occur in adolescence. This condition should not cause alarm if the discharge appears unsystematically; this can be caused by hormonal changes in the body during puberty. If a teenage girl bleeds from the vagina during the intermenstrual period in each cycle for a year or more, you should definitely consult with your gynecologist. In some cases, this phenomenon can last 2-3 years, and with a hereditary predisposition, even up to 5 years.
For women of reproductive age, the appearance of spotting after the end of menstruation is allowed during ovulation. This is the so-called ovulatory bleeding, which is caused by the rupture of the follicle and the release of the egg. Without severe painful symptoms, this condition does not require additional treatment. Also, during reproductive age, slight bleeding on underwear can occur at the moment of conception, when the fertilized egg is fixed in the uterine cavity.
Bloody secretion immediately after menstruation can occur in women after 40-45 years. At this time, reproductive function begins to decline, and various hormonal changes occur. During menopause, the regularity of the menstrual cycle is disrupted and the risk of tumors in the genitals increases.
If a woman’s periods have completely stopped and menopause has set in, but uterine bleeding begins to appear, this may be a sign of existing oncological processes in the reproductive organs.
Hormonal imbalance, which provokes intermenstrual bleeding, can be observed in cases of disturbances in the functioning of organs and systems not related to reproductive function. Bloody discharge after menstruation may appear due to exposure to external factors. Consider the main external and hormonal causes of bleeding after regulation:
- hormonal imbalance caused by improper functioning of the thyroid and adrenal glands. Due to such failures, the level of prolactin in the blood increases, weight changes sharply, polycystic ovary syndrome develops, and after menstruation heavy spotting occurs;
- use of emergency contraceptives. Women who used Postinor or Escapelle after unprotected sexual intercourse developed brown blood after menstruation, which did not have a specific odor, and there was no pain associated with this phenomenon. In the next cycle after taking the drugs, there is no such bleeding;
- first doses of some types of oral contraception. Since most OCs affect a woman’s hormonal background, it is quite natural that the body gets used to the new drug over the course of 2-3 cycles, so during the adaptation period 3-5 days after menstruation, bloody discharge may appear. If the situation does not change on the 4th cycle and intermenstrual spotting is still present, the woman should consult a doctor; it may be necessary to change or discontinue the drug;
- the use of patches that contain hormonal components can provoke red spotting after menstrual periods;
- use of intrauterine device and vaginal rings. Such contraceptives have an irritating effect on the vaginal walls. If the spotting appeared immediately after the installation of the IUD, it means that, in all likelihood, the small vessels of the perineum were damaged. If bloody clots appear on the second day, you should definitely consult a doctor; there is no need to wait for the condition to worsen;
- taking medications that affect blood clotting and also have a sedative and calming effect;
- The ectopic location of the fetus is a physiological deviation, the characteristic symptom of which is uterine bleeding. They can go a week after the regulation; an ectopic pregnancy can only be eliminated surgically; without surgery, a woman can die from a ruptured fallopian tube;
- injury sustained during gynecological procedures. After taking a scraping or a gynecological examination, slight bleeding may occur, but 2-3 days after the procedure the discharge should stop without medical intervention;
- lack of B vitamins;
- injuries to the genitals caused by forced sexual acts or too vigorous sexual intercourse without sufficient natural lubrication. If, in addition to discharge, there is pain in the lower abdomen, you should consult a doctor;
- spontaneous abortion;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle due to excessive physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- side effects of drugs that are designed to treat gynecological problems. Yellow and bloody discharge can be caused by Hexicon, Terzhinan, Triozhinal, and pink discharge may occur from Polygynax, Duphaston, Livarol and Clotrimazole. Usually, blood comes out of the vagina during long-term use of drugs, but it is also allowed to come out 3 days after the completion of the regulation.
Since there are many different reasons for the appearance of spotting after menstruation, only a doctor can determine the exact one.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
The possibility of pathological causes for the appearance of intermenstrual bloody secretions is quite high. We list the main pathologies that can provoke uterine bleeding:
- endometriosis. In the diffuse form of the disease, spotting may appear 10 days after regulation, while the woman feels a feeling of fullness and nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- endometrial hyperplasia provokes the release of a scanty spotting bloody secretion a week after the critical days. With this disease, pathological thickening of the endometrium occurs. Sometimes with hyperplasia there may be copious discharge with clots;
- infections in the vagina occur without obvious signs, but when they already affect the uterus, the inflammatory process can manifest itself as bloody intermenstrual smears;
- ectopia. With this disease, for some reason, cuboidal epithelial cells appear on the vaginal part of the cervix. The appearance of bloody smears with this disease can be provoked by a gynecological examination or sexual intercourse;
- ovarian dysfunction causes bloody spotting 10 days after regulation. The disease causes stress, heredity, disorders of the thyroid and adrenal glands and many other pathologies;
- polyps in the uterine cavity and on its cervix. Their development can be triggered by abortion, hormonal imbalance, infections and IUDs;
- fibroids often cause not only metrorrhagia, but aching pain in the abdomen and lower back. Sometimes the discharge may be too intense and the pad needs to be changed several times a day;
- cancerous tumor in the reproductive organs. Often, oncological processes in the early stages are asymptomatic, but in more severe forms they can bleed on any day of the menstrual cycle.
The cause may be diseases not related to gynecology. These could be diseases of the ENT organs in a chronic form, neoplasms in the brain, problems with blood clotting. Some women may confuse bloody discharge from the urethra with vaginal discharge. If the secretion comes out of the urethra, it means that the inflammatory process is occurring in the kidneys, bladder or ureter.
From the first day of her period, every girl waits for this unpleasant period of the menstrual cycle to finally end.
Normally, the duration of bleeding among representatives of the fairer sex is different - for some, “critical days” last 3-4 days, while others stain their pads even on the 7th day.
Gynecologists who are prone to poetry call menstruation “the bloody tears of the uterus due to a failed pregnancy.” But no matter how you romanticize your period, every girl wants it to go away as quickly as possible. You can imagine her irritation and anxiety if the spotting after her period returned or did not stop.
Normally, menstruation should begin with bloody discharge, last 3-8 days and end with complete cleansing of the mucous membranes, that is, there should be no blood in the leucorrhoea after menstruation. Any other scenarios, as a rule, are signs of pathologies:
- heavy periods lasting more than 8 days are called menorrhagia;
- spotting that appears a week or two or three after menstruation is called intermenstrual bleeding.
Neither menorrhagia nor intermenstrual bleeding are independent diseases, but very serious pathologies are usually behind them.
To find out why there is spotting after the end of menstruation, a woman needs to undergo a medical examination.
Menorrhagia - massive bleeding that continues after the end of normal menstruation - poses a serious danger to a woman’s health. Copious and prolonged bleeding, often with clots, leads to severe blood loss, which can provoke anemia.
Losing more than 100-150 ml of blood (the norm is up to 100 ml), a woman feels weak, feels unwell, dizzy, and may faint. In a situation where too much blood is lost, you need to consult a doctor to find out why the bleeding continues after the end of your period.
Anovulation
For some women, it is normal for them to bleed again a week after their period. Since the endometrium is weaker at this time and at the same time the number of hormones in the body increases sharply. If discharge occurs precisely because of this reason, then it is not a deviation from the norm.
Anovulation refers to the state of the body when there is no monthly ovulation. This can be considered a failure or a pathology. It is associated with irregular cycles and light bleeding during menstruation. The causes of anovulation may depend on the state of immunity and health. Endometriosis
If bleeding occurs some time after menstruation, it may be endometriosis. This is a deviation in which certain cells of the uterine lining appear where they should not be. For example, they can settle in the vagina and after some time begin to bleed.
Possible complications
If bleeding begins after menstruation and there is no timely help, undesirable consequences may occur. First of all, a decrease in hemoglobin levels, the development of stenovegetative syndrome, anemia, and impaired metabolic processes are observed.
Inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system lead to the appearance of cysts, benign and malignant formations. Therefore, if you have uterine bleeding, you should consult a doctor for treatment.
The appearance of bloody mucous discharge after menstruation is almost always a reason to consult a doctor. There may be several reasons for this phenomenon - inflammatory, hyperplastic or other processes of the uterus or appendages that require treatment.
On average, menstruation can last up to 4-6 days, gradually decreasing in volume and stopping. They are replaced by light, almost transparent, colorless and odorless discharge. If during the cycle dark red, brown or bloody discharge occurs after menstruation, this is not normal. You should immediately consult a doctor to find out the reasons for this. Particularly alarming should be discharge after menstruation with blood, lasting more than one or two days, or occurring as bleeding, increasing in intensity and duration. In case of heavy bleeding, weakness, pallor and nausea, you should immediately call an ambulance. This is how early miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy, dangerous uterine bleeding can manifest themselves.
What causes mid-cycle spotting?
Small brown discharge that can occur 3-7 days after menstruation is quite common. The appearance of daub in this case signals that your egg is ready for fertilization
.
If the intensity of the discharge increases and its duration is more than three days
to visit a gynecologist
without wasting time .
And in case of severe bleeding, immediately call an ambulance
.
Can there be spotting when taking Utrozhestan or Duphaston?
In the early stages of pregnancy, expectant mothers may experience spotting. If the period of conception is no more than 7-10 days
, then this may be the body’s adaptation to a new state, which was discussed earlier.
However, spotting can also be a sign of an incipient miscarriage.
or
decreased hormonal levels
at the beginning of pregnancy. Don’t be lazy, seek help from an antenatal clinic.
After conducting the necessary examination, specialists may recommend taking the drugs duphaston or utrozhestan, which are necessary if low levels of progesterone hormones are detected in the body of the expectant mother or as a prophylactic agent to maintain pregnancy
.
While taking these medications, slight brown spotting occurs, which should stop soon. Otherwise, you should consult a doctor
.
Is spotting after sex normal or not?
After sexual intercourse, a woman may experience slight spotting. The reasons for the appearance of such spotting or minor bleeding can be various factors: mechanical damage or microtrauma during sex; various types of erosion and polyps
;
inflammatory diseases such as vaginitis, cervicitis;
sexually transmitted diseases ; as well as various diseases that are not associated with sexual intercourse itself.
In addition, after sex, spotting may appear due to the presence of a small amount of blood in the partner’s semen
.
There are many reasons and factors that can lead to the appearance of brown vaginal discharge and, unfortunately, not all of them are the physiological norm.