Features of cysts in the groin
An inguinal cyst (atheroma) is a cavity formation that develops as a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands.
The tumor is benign and resembles an inflamed lymph node in appearance. Atheromas have a dense structure, which is explained by the presence of a dense capsule that hides the liquid contents.
The risk group for developing inguinal cysts includes men and women aged 20-40 years. This is due to the fact that neoplasms are formed due to blockage of the sebaceous glands.
The work of the latter is regulated by androgens and testosterone. And this group of people more often experiences fluctuations in hormonal balance.
https://youtu.be/oWG_FEv0qXI
Causes
The growth of atheroma begins with blockage of the sebaceous glands. Despite the obstacle, the latter continue to produce the secret. Over time, a tumor forms in the groin with a capsule that covers sebum and dead epithelial cells.
On this topic
Adenoma and carcinoma
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 9, 2020
A black dot remains in the central part of the tumor, representing the exit site of the duct. Therefore, atheroma is differentiated from other inguinal tumors.
The following factors can provoke the appearance of cysts in the perineum:
- hormonal imbalance;
- increased sweating;
- metabolic disease ;
- genetic predisposition;
- injuries and other tissue damage in the groin area;
- poor nutrition;
- toxic effects on the body;
- failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules.
The most likely causes of atheroma include mechanical damage to the skin or hair follicle. Wearing low-quality or uncomfortable clothing, shaving hair in the groin area - this contributes to infection and blockage of the sebaceous ducts.
The second probable reason lies in profuse sweating. This explains the high incidence of cysts in the groin area compared to other parts of the body.
The perineum contains many hair, sweat and sebaceous glands. This combination (especially in the warm season) creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
On this topic
How to improve urination with prostate adenoma
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- November 29, 2020
In women, cysts in the groin often occur during pregnancy. This period is characterized by changes in hormonal balance and an increase in body weight.
Both factors contribute to a decrease in immunity, as a result of which the body cannot resist the effects of pathogenic agents.
Causes of atheromas
A lump in the groin area is a dense, mobile neoplasm that protrudes above the surface of the skin. The appearance of a lump may be accompanied by pain, burning and itching, an increase in body temperature, or it may be asymptomatic, disturbing the woman as a cosmetic skin defect.
Only a doctor can correctly establish the cause that provoked the development of a neoplasm, determine the degree of danger to the body and select appropriate methods of therapy after an initial examination and palpation of the lesion, as well as studying the results of laboratory tests. Lumps in the groin area can be a symptom of the following pathological processes:
- Folliculitis. Caused by the penetration of a bacterial infection into the hair follicle, the development of the inflammatory process in the hair follicle is usually accompanied by the formation of a dense subcutaneous formation - a painful purulent compaction surrounding the hair shaft and the adjacent sebaceous gland. The appearance of a small (from 1 to 3 mm in diameter) lump on the pubis with pus can be caused by microtrauma of the skin received during depilation, increased sweat production, and irritation by synthetic fabrics of the underwear. Antibacterial drugs are used to treat the disease.
- Furunculosis. When folliculitis becomes complicated due to overactive sweat glands or irritation of the skin, foci of infection can rapidly spread to the surface of the skin. This process is accompanied by the formation of dense, painful neoplasms filled with purulent exudate, enlarged lymph nodes, and an increase in body temperature. In order to relieve inflammation and eliminate the pathogenic influence of infection, a course of antibiotics and local application of antibacterial ointments are prescribed.
- Inguinal lymphadenitis. Against the background of the development of a sexually transmitted disease, as well as during inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, concomitant inflammation of the lymph nodes is observed with an increase in their size, the appearance of noticeable pain and discomfort when performing movements. This process is also accompanied by an increase in body temperature and general weakness. At an early stage of pathogenesis, conservative drug therapy is prescribed. If a purulent process develops at the site of compaction, surgical intervention is recommended.
- Lipoma. If there are metabolic disorders, weakened immune defenses, or diabetes mellitus, a benign tumor formed by adipose tissue cells may appear in the groin area. Lipoma has the appearance of a limited, painless new growth of soft consistency, not fused with the surrounding tissues. The elasticity and color of the skin at the site of tumor development are preserved. A benign lump is removed surgically to prevent its degeneration into liposarcoma, a malignant tumor.
- Pseudofolliculitis. When the direction of hair growth is disrupted, when the hair shaft does not break through the skin and begins to grow deep into the epidermis, a red, painful and itchy lump is formed. Hyperkeratosis and shaving of unwanted hair in the intimate area can provoke pathology. The inflamed purulent abscess is opened by a doctor using a sterile instrument.
- Atheroma. Atheroma is often localized in the groin area - a benign cyst that occurs against the background of poor personal hygiene, hormonal imbalance, sexually transmitted infection or mechanical trauma to the skin. Such a seal is movable, elastic, outlined with a clear contour. When atheroma suppurates, swelling, pain and redness are observed. To prevent secondary infection and transformation of the tumor into a purulent abscess, the lump is surgically removed.
- Inguinal hernia. Women who have suffered damage to the ligamentous apparatus of internal organs or who are obese may develop an inguinal hernia. A movable seal appears on the pubis, which protrudes when exerting itself or coughing. The hernia must be removed through surgery.
A lump in the groin of women on the left is formed under the influence of the same reasons as on the right. The pathogenesis of the disease differs only in the opposite location of the tumor. Seals can also be formed on both sides simultaneously. Self-medication of pubic lumps in women on the right, on both sides or on the left is strictly not recommended.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with boil boil on the butt, causes of appearance and methods of treatment
The use of traditional and alternative medicine methods and self-removal of the seal is fraught not only with the development of sepsis and the rapid spread of infection on the surface of the skin, but also with the formation of malignant tumors. To protect your health and effectively get rid of an uncomfortable problem, you need to promptly seek medical help.
The causes of atheroma include:
- violation of personal hygiene;
- poor nutrition;
- metabolic disease;
- hormonal disorders;
- frequent temperature changes;
- increased sweating;
- inflammation of the hair follicle;
- anomaly in the structure of the sebaceous glands;
- skin tendency to form acne and blackheads;
- injury to the skin.
The predisposition to the appearance of atheromas can be transmitted genetically. Hormonal imbalance plays a big role in the formation of atheromas on the skin.
If a lump or protrusion appears in the groin area, most men do not attach any importance to it. Some people are embarrassed to go to the doctor with such a delicate problem. Others feel sorry for wasting their time visiting a specialist.
An important role is played by the erroneous opinion that attention to minor health problems is a sign of weakness, unworthy of a real man.
For what reason can a lump occur in the groin area in men?
For correct diagnosis, you should first of all determine where exactly the lump appeared: in the middle between but or the seal is located to the right or to the left.
There are two main causes of a lump in the groin area.
WE ADVISE! Weak potency, a flaccid penis, the absence of a long-term erection are not a death sentence for a man’s sex life, but a signal that the body needs help and male strength is weakening.
There are a large number of drugs that help a man gain a stable erection for sex, but they all have their own disadvantages and contraindications, especially if the man is already 30-40 years old.
Pantosagan capsules for potency help not only to get an erection HERE AND NOW, but act as a preventive measure and accumulation of male power, allowing a man to remain sexually active for many years!
Symptoms
Atheromas are localized mainly in the pubic area. Less commonly, such neoplasms occur on the labia of women. The development of the cyst is asymptomatic, except in cases where the problem area becomes inflamed.
Atheromas protrude slightly above the surface of the skin. When pressed, the tumor moves slightly to the side, which is explained by the growth of the cyst in the fiber layer.
As the tumor grows, it causes discomfort. The nature of the symptoms is determined by the location of the tumor. In some cases, atheromas interfere with sexual intercourse or complicate the process of urination.
If the cyst is injured, the contents come out, which is accompanied by an unpleasant odor. Due to damage, pathogenic bacteria penetrate into the neoplasm.
The activity of pathogenic microorganisms causes an inflammatory process, in which painful sensations appear, the problem area turns red and swells. A short-term increase in body temperature is also possible.
In the case of the formation of a cystic cavity in women, the Bartholin gland becomes blocked in the vestibule of the vagina. The latter produces a secretion necessary to moisturize the mucous membrane of the vulva during arousal.
Bartholin gland cysts also develop predominantly asymptomatically. If the tumor grows, movement causes discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse.
On this topic
What do calcifications in the testicles mean?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- November 29, 2020
Infection of this tumor leads to a sharp increase in body temperature (up to 39 degrees) and intoxication of the body. The neoplasm increases to 12 cm in diameter, which provokes intense pain of a pulsating nature.
Due to the fact that a tumor of the Bartholin gland occurs against the background of infection with sexually transmitted infections, signs of colpitis or urethritis may be added to these symptoms.
Another unpleasant neoplasm that occurs in the perineal area is a paraurethral cyst. This tumor forms near the urethra.
The cyst occurs due to blockage of the Skene gland, which is responsible for moisturizing the urethra. In addition to the symptoms characteristic of other similar neoplasms, this type of tumor provokes frequent urination and involuntary release of urine.
Possible complications
Inflammation of atheromas is the most common complication caused by constant friction of the tumor with items of clothing. Cysts on the labia become infected due to unprotected sexual intercourse. In both cases, due to the proximity of the location, the inflammatory process can transfer to the organs of the reproductive system.
When a cyst ruptures, pus and other contents leak out. Over time, the problem area is restored. However, the cystic membrane remains inside, as a result of which atheroma relapses in the future.
Complications develop when the tumor breaks through. In this case, the contents penetrate into the bloodstream and neighboring tissues.
On this topic
Prostate adenoma and potency
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- November 29, 2020
As a result, the inflammatory process spreads downwards. Also, when atheroma breaks through, sepsis develops, which requires immediate medical intervention.
Paraurethral cysts without treatment contribute to the appearance of fistulas and hematomas. The prolonged course of the inflammatory process causes a narrowing of the urethra.
Unlike other tumors that arise in the groin area, cysts do not degenerate into malignant neoplasms.
Treatment
Conservative treatment of inguinal cysts is ineffective. Medications are used to suppress bacterial microflora, as well as accelerate the release of pus from the problem area.
Cyst removal is carried out using open surgery, laser excision, electrocoagulation or radio wave exposure. The choice of method depends on the characteristics of the atheroma.
Uncomplicated small cysts are removed using laser treatment. This method is one of the least traumatic. Complications and relapses rarely develop after laser removal.
On this topic
What are the symptoms of prostate adenoma?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- May 27, 2020
Radio wave exposure is considered a more effective treatment method. The latter is used in cases where the size of the cyst does not exceed 5 cm in diameter.
During this procedure, radio waves are applied to the problem tissue, which leads to the death of local cells. After the procedure, a crust remains on the treated area, which disappears within a week.
Electrocoagulation helps achieve similar results. In this procedure, alternating current is applied to the cyst, which causes cell necrosis.
Minimally invasive treatment methods are not used during pregnancy, oncological pathologies, inflammatory processes, or disorders of the hematopoietic system.
In case of suppuration of the cyst, open surgery is used. This procedure is carried out in several stages.
First, the surgeon excises the problematic tissue and drains the cavity, treating the latter with antiseptic and antibacterial drugs: Vishnevsky ointment or propolis, Solcoseryl. Later, when the medications eliminate the inflammatory process, the doctor removes the cyst capsule and sutures the wound.
To speed up tissue recovery after surgery, Troxevasin, Heparin, and Mederma are used. If necessary, during the rehabilitation period, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed: UHF, magnetic therapy and others.
Treatment options
There are only three ways to get rid of atheroma in the groin once and for all - using a scalpel, laser or radio wave. All other options, such as synthetic drugs or grandma's recipes, will bring nothing but disappointment from wasting time. Such drugs are effective only for treating a postoperative suture or accelerating the spontaneous opening of a festering cyst for its further removal.
Pharmacy and folk medicines for topical use
Ointments and gels for atheroma in the groin are used in cases where it is necessary to provoke a rapid outflow of pus. After the contents come out, an operation is performed to remove the atheroma. There is no point in using ointments in the hope that the lump in the groin will resolve on its own.
External remedies for atheroma in the groin can be used in the following situations:
- After opening and draining the cyst, anti-inflammatory ointments are prescribed - Solcoseryl, Vishnevsky ointment, propolis ointment.
- For resorption of postoperative sutures, Troxevasin, Heparin, Mederma are prescribed.
At home, you can try to open the inguinal atheroma using traditional medicine methods:
- Compress from coltsfoot leaves: clean fresh leaves of the plant are applied to the cyst, fixed with a bandage, changed 2 times a day. Therapy is carried out for 3-5 days. After the atheroma breaks through, the wound still needs to be shown to a doctor.
- A compress of plantain leaves: fresh, cleanly washed and slightly mashed leaves should be applied to the sore groin area and changed every 12 hours. If the cyst does not come out within 10 days, be sure to consult a doctor.
- Compress from cabbage leaves: take a fresh leaf, mash it slightly so that it releases the juice, and fix it on the wound. Change the compress as the sheet dries.
The main rule when treating with traditional medicine is: you must be confident in your diagnosis. Therefore, before starting therapy, be sure to consult with your doctor.
Radical cyst removal
Many patients mistakenly believe that only large atheromas in the groin need to be removed. In fact, the smaller the tumor, the smaller the postoperative mark and the better the cosmetic effect of treatment.
Large and purulent atheromas are surgically removed. As a rule, surgery to remove a cyst is urgent when it becomes inflamed, ruptures and provokes an abscess or sepsis. During the procedure, the pus is squeezed out and a drain is placed for several days. After the inflammation subsides, the capsule is removed from the duct and sutures are applied. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia. After the procedures, a visible scar remains on the skin of the groin, but the risk of relapse is completely excluded.
Laser surgery can be performed as planned - it is less traumatic, and the risk of wound infection and large blood loss is minimized. The essence of the method is to evaporate the inguinal atheroma along with its membrane. This excludes her subsequent relapse. After the operation, the wound is also sutured, but after the sutures are removed, a barely noticeable mark remains in its place.
The most progressive way to get rid of atheroma in the groin area is the targeted destruction of cells in the cyst itself using radio waves. It is used only on small cysts - up to 5 mm. After the procedure, a crust remains, which dries and disappears after 5-7 days.
Prevention
Atheromas develop in men and women of any age. To reduce the risk of such neoplasms, it is recommended to regularly follow the rules of intimate hygiene. When removing hair in the groin area, you must contact a specialist in the field of hair removal. You should also avoid unprotected sex.
In the warm season, women and men should wear comfortable underwear made from natural materials.
If clothes rub the groin area, you should change your wardrobe. With increased sweating, you need to perform hygiene procedures more often and treat the perineum with drying substances (talcum powder, baby powder).
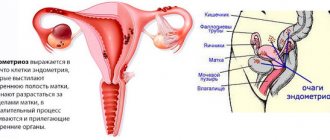
Benign neoplasms appear in different parts of the body when the excretory ducts are blocked. In the presence of risk factors, atheroma may form on the pubis in women. Since it can reach large sizes, its removal is indicated. Large lumps cause discomfort, and an inflammatory process can develop inside them.
Atheroma on the pubis
The favorite location for atheroma is any part of the body that has sebaceous glands and hair. Cysts of the sebaceous glands are most often detected on the head, the armpits, groin, and pubis follow each other, not too inferior in the frequency of development of subcutaneous neoplasms.
Glandulae sebaseae - sebaceous glands, located throughout the body, excluding the area of the palms and soles of the feet, these alveolar structures regularly produce lipid secretion, which is needed to protect the skin and lubricate the hair, thus, for the most part, the glands are closely related to the folliculus pili - the hair follicle. In the pubic area, glandulae sebaseae are localized, having a multilobed structure; in addition, the number of glands in this area, as well as in the area of the labia and women, is very large.
Atheroma on the pubis is caused by various factors, among which may be the following:
- Dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
- Dysfunction of the hormonal system, failure of regulation.
- Dysfunction of the peripheral nervous system.
- Metabolic disorder.
- Pregnancy in women.
- Menopause in women and men.
- Viral diseases.
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease.
- Decreased function of the adrenal cortex.
- Diseases of the anterior pituitary gland.
All of the listed pathologies are accompanied by a violation of secretory production from the sebaceous glands, seborrhea, this is especially evident in the genital area, including the pubic area. Such disorders lead to the formation of lipid plugs located in the excretory ducts of the glands; they often take the form of comedones, as well as atheromas and steatomas. Also, factors provoking atheroma on the pubis may be the following situations:
- Failure to comply with the rules of personal intimate hygiene
- Consequences of unsuccessful depilation
- Mechanical irritation of the skin due to tight underwear.
- Allergic reaction, including drug allergy.
Atheroma in the pubic area looks like a small compaction with clear contours; the cyst does not hurt until an inflammatory process develops in it, which happens quite often. A simple retention cyst, which forms as a result of an accumulation of cystic dentritis, is removed surgically without serious complications. Purulent atheroma on the pubis is operated on only after opening the abscess, draining it, and treating inflammation. Such atheromas are subject to enucleation only if the purulent exudate is completely removed from the cyst cavity and the symptoms of the inflammatory process subside. Removing a sebaceous gland cyst in intimate areas is not difficult; such procedures are often performed on an outpatient basis; the main thing is to consult a doctor in time and prevent the atheroma from festering.
What is atheroma?
Atheroma in the groin is a rounded compaction that occurs due to blockage of the excretory duct in women. Since the secretion is not removed, it forms a cyst or atheroma. It consists of a capsule filled with liquid contents. There may be pus or blood clots inside (if the vascular walls are damaged).
Unlike lipoma, this neoplasm is more mobile. In women, it rolls under the skin if you touch it with your finger. The lipoma remains in place, while the atheroma on the labia moves in different directions. The lump often contains a black dot. It is a blockage of the duct, which is located in the center.
Benign tumors are often localized where the sebaceous glands pass. In the groin of women, the contents sometimes leak out of them and settle on the skin. They smell bad.
Diagnostics and differential analysis
The formation of a growth on the labia can be caused by damage to the hair follicle during shaving, poor hygiene, constant contact with tight underwear, problems with glandular function and other reasons. Perineal atheroma can be single or multiple. More often, the neoplasms resemble whitish or yellowish tubercles. In most cases, the inflamed lump causes pain and discomfort to the patient.
A feature of the epidermal cyst in the perineum is frequent inflammation and suppuration due to inevitable contact with clothing. This causes mechanical injury to the tumor body, which is accompanied by irritation of the atheroma. In medical practice, there were many cases of spontaneous breakthrough of a cystic formation, which significantly alleviated the patient’s condition, but after a while the disease recurred.
If you find a lump in the groin, you should not delay visiting a doctor. A gynecologist or surgeon works with such problems. It will not be difficult for an experienced doctor to visually determine the type of tumor. Examination of the neoplasm, adjacent skin and palpation of the pathological site is all that is necessary to make a diagnosis.
| Analysis | Description |
| Visual inspection and palpation | The appearance of atheroma in the groin, its location, symptoms and the patient’s sensations when pressed are determined |
| Ultrasound | Determines the pathology of neoplasm development, the effect on surrounding tissues and organs, and the structure of the compaction |
| Biopsy | Carried out in extreme cases to determine the presence of cancer cells |
| Histological analysis | Carried out after removal from the cut material to establish good quality |
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Vilprafen for Gardnerella. Gardnerella in women - symptoms and treatment. Photo gallery: physiotherapy in gynecology
The greatest danger from atheroma in the groin is the development of extensive suppuration.
Causes
Atheroma occurs on the labia, pubic area, vulva and other groin areas. The exact reasons for its formation are unknown. Experts name the main risk factors due to which women may encounter a neoplasm:
- hormonal disorders, endocrine disruption;
- mechanical damage to the skin, increased trauma to the skin and hair follicles;
- hereditary factor;
- frequent use of underwear made of synthetic materials that restrict movement;
- excessive use of low-quality cosmetics intended for intimate care for women;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- eating large amounts of fatty, spicy foods, as well as confectionery;
- diseases associated with excess sebum production.
Perineal atheroma
Atheroma most often forms in the sebaceous glands associated with the hair follicle. Therefore, any hairy part of the body is a potentially dangerous area for the development of benign retention cysts.
Perineal atheroma is due to the fact that the skin in this area is very vulnerable and is often involved in the process of hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands. The perineum requires careful care in a hygienic sense, since any contamination, irritation, rash, or damage to the skin is fraught with secondary infection and the development of inflamed purulent cysts of the sebaceous glands.
Subcutaneous neoplasms of the perineum are characterized by small sizes, most often they are multiple, located throughout the vulva area. The clinical manifestations of atheroma are nonspecific; they may look like small pimples or whiteheads. More severe symptoms are typical for inflamed cysts, which quickly increase in size, fester and cause pain. Such atheromas are prone to spontaneous opening and ulceration. Delayed diagnosis and lack of adequate therapy leads to recurrence of the process and the formation of extensive abscesses.
Diagnosis of perineal atheroma is carried out using an examination on a gynecological chair, taking a smear, and less often a biopsy is required. Removal of multiple atheromas of the vulva is possible using non-surgical laser and radio wave methods; single cysts larger than 1 centimeter are removed surgically using total excision within healthy, intact tissue.
Vulvar atheroma can be operated on at any stage of development; removal of the cyst is considered the only reliable and effective way to get rid of this tumor today.
[29], [30], [31], [32], [33], [34]
A formation that occurs in the thickness of the epidermis at the site of blockage of the sebaceous ducts is called atheroma. This is a dense and elastic round benign cyst. It can occur on any part of the body where there are hair follicles. But patients experience particular anxiety when atheroma appears in the groin.
Symptoms of atheroma
When atheroma appears in the groin in women, signs may not appear for a long time. In most cases, this tumor slowly increases in size, so it does not bother the woman. It is often not noticed until a mechanical injury occurs that damages the capsule.
In this case, an inflammatory process develops. The body temperature rises, the thickening hurts even when it is not touched. The affected area swells.
In women, the appearance of atheroma on the labia is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the tumor is mobile, moves under the fingers and is not tied to a specific place in the groin;
- Abscessation of the labia majora contains a dark dot in the center - a blocked duct;
- When inflamed, the skin in the localized area in women turns red and becomes hot to the touch.
Since perineal atheroma is located in a sensitive area, underwear or clothing often puts pressure on the capsule, causing constant friction. Because of this, a tumor in women can spontaneously open. In this case, the unpleasantly smelling light-colored contents will end up on the skin and underwear. After this, the capsule will begin to fill again and the thickening will form again.
Symptoms and types of formations in the groin
Lipomas in the groin area can be the following types of subcutaneous neoplasms:
- Xanthoma - formed from adipose tissue, not limited by the membrane or it is insignificant, so it looks flat. The skin over it is white or yellow.
- Diffuse lipoma - formed from fat cells, has a lobulated or grape-shaped structure (palpable), which is provided by connective tissue. The skin over it is flesh-colored.
- Fibrolipoma - consists of fibrous and adipose tissue, therefore it is dense to the touch. The color of the skin above it does not differ from natural.
- Myolipoma - includes muscle, fibrous and fatty tissue. Outwardly, it is a dense, mobile unit with a normal skin tone.
- Angiolipoma - such a wen in the groin is a myolipoma, but permeated with blood vessels, which is why the skin over it has a red-blue tint.
The fat between the legs can increase with varying intensity. When the tumor grows to a certain size, it begins to sag under the influence of its own gravity. As a result, a hanging lipoma on the leg is formed.
In order to determine the method of treatment for the formation, it is necessary to diagnose the type of tumor in the groin and make sure that the tumor is not malignant. A lump in the groin area may have the following characteristics:
- the appearance of a growth can provoke an inflammation process in the lymph nodes that are localized nearby;
- An inguinal hernia may look similar to a lipoma in appearance, but its symptoms are distinguished by pain and a feeling of heaviness at the site of the pathology. You can accurately determine the bulge in the groin using an ultrasound examination;
- the lipoma body, exposed to constant contact with linen and other clothing, is prone to activation of the development of pathological cells and degeneration into liposarcoma. This malignant tumor is more common in male patients. The survival rate of patients with this disease is about 50%.
If a lump is detected in the groin area, it is necessary to seek medical help to determine the nature of the tumor and begin timely treatment.
If nerve trunks are located near the neoplasm, then their compression by the body of the wen may be accompanied by pain. But often the compaction does not manifest itself with any symptoms. The subcutaneous neoplasm does not hurt, does not itch, and does not change the color of the skin. On palpation, the inguinal lipoma has a soft consistency, spherical shape with clear boundaries.
- diffuse - formations of adipose tissue that do not have a shell and precise boundaries;
- xanthomas are flat-shaped neoplasms whose capsule is very thin or completely absent;
- pedunculated lipomas are characterized by sagging subcutaneous wen;
- fibrolipomas - neoplasms from connective fibrous tissue and fat cells;
- angiolipomas - tumors with interlacing blood vessels;
- myolipomas are formations consisting of smooth muscle tissue.
Some of the changes in the area of the external female organs, especially if there is a compaction in the form of a ball, acquire threatening features due to the degeneration of connective tissue. The appearance of nodules is often combined with the development of cervical cancer if there is high oncogenic HPV in the body. With sarcoma of the vagina, there is always a large amount of secreted pus, blood, mucus, which has a pungent odor.
Hidradenoma is also dangerous - a fast-growing formation that reaches a compaction diameter of up to 1 centimeter. The dermis adjacent to the compaction dies off, eventually exposing muscle tissue.
Skin lesions increase the risk of secondary infection. Usually the changed tissue does not hurt or bleed. When diagnosing hidradenoma, there remains an increased likelihood of the spot becoming malignant.
A malignant formation between the labia refers to cancer of the vulva, which most often develops in patients with diabetes mellitus, infected with HPV or HIV. The first symptoms are the appearance of nodules, which then ulcerate, itch and grow. The deterioration of the condition is accompanied by a painful syndrome and serous-purulent exudate. Treatment is excision and radiation therapy.
To date, experts have not come to a consensus on the causes of wen. However, several risk groups have been identified, which, if placed, increases the likelihood that a girl may develop a benign neoplasm on her body, in particular, a wen on the labia.
1. Skin type prone to oiliness. It has been established that wen in the groin in women whose skin suffers from increased greasiness, acne and clogged pores occurs more often than in women with normal and dry skin;
2. Increased sweating;
3. Hormonal disorders or metabolic disorders leading to malfunction of the sebaceous glands;
4. Mechanical damage to the skin of the labia, microtrauma caused, for example, by friction against underwear that restricts movement, occurring during sexual intercourse or depilation;
5.Genetic predisposition. It has been revealed that the tendency to develop wen can be inherited.
6. Contamination of the skin in the groin area, caused, in particular, by failure to comply with the rules of intimate hygiene.
Danger of complications
In most cases, in women, atheroma in the groin does not pose a threat to life or health. However, this statement is valid only until the neoplasm reaches a large size and there is a risk of its suppuration. The contents can penetrate the internal tissues, and sepsis will develop.
If the thickening is not removed in time, the woman risks encountering the following complications:
- an infection will penetrate into the wound, which will provoke increased growth of a benign tumor;
- the process of suppuration leads to spontaneous rupture of the capsule and the entry of purulent contents into the body;
- benign atheroma in some cases can transform into cancer;
- if the membrane opens spontaneously, long-term non-healing wounds often form in its place.
Therefore, if a suspicious lump appears in the groin area, a woman should definitely visit her doctor.
Prevention and treatment
Treatment at home is allowed only if you are sure that the cause lies in folliculitis or a regular purulent pimple. And even here there is a risk of infection, which can lead to an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system. As for seals in the groin, which can be lipomas or atheromas, the need for their removal is determined by the doctor. Inflammatory processes are treated with medication.
As a preventive measure, it is recommended to avoid casual sexual contact, hypothermia and injury to the groin area. If you find hard or soft lumps, it is better to consult a doctor immediately. Timely treatment can help avoid surgery.
Preventing atheroma in the groin means saving yourself from unaesthetic formations, discomfort and possible surgical intervention. Prevention of sebaceous cysts includes:
- regular showering and personal hygiene (especially in hot weather);
- maintaining a healthy diet;
- minimizing constrictive underwear (especially if it is made of artificial fabric);
- avoiding promiscuity and using contraceptives.
And, of course, the most reliable guarantee against atheroma is regular visits to a doctor, who will always notice the slightest signs of deviation from the norm and take measures to prevent the pathology from reaching a critical stage.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the causes of the disease
Treatment for this disease depends on its true causes. Only proper qualified treatment will bring relief.
For inflammatory processes, special antibiotic drugs are prescribed. Physiotherapy may be used. Local treatment rarely produces results, bringing only temporary relief.
Sometimes surgical intervention is productive. This applies not only to straightening a hernia or tightening blood vessels for varicose veins. If the size of the tumor increases rapidly, surgical methods are used. It is possible to remove lymph nodes.
Preventive measures in the fight against diseases that may cause a tumor in the groin in women are a healthy lifestyle. proper nutrition. hardening of the body. It is worth protecting yourself from lifting weights, hypothermia, overfatigue and overheating of the entire body.
Read: Can pregnant women and breastfeeding eat bananas?
Casual relationships and unprotected sex should be avoided so as not to be at risk of contracting serious diseases that can cause serious complications. for example, a tumor in the groin.
Any deviation from the norm, be it the appearance of a tumor or pain in the groin, requires medical intervention and professional treatment. You need to be attentive to your health, and if you feel unwell, do not self-medicate.
There are a number of preventive measures, the implementation of which will prevent the appearance of a wen in the groin area. First of all, prevention involves maintaining intimate hygiene (especially for people with oily skin).
There are other rules to prevent the appearance of lipoma. These include:
- maintaining a healthy and balanced diet;
- giving up bad habits such as smoking and alcohol abuse;
- maintaining an active lifestyle, especially with sedentary work;
- exclusion from the diet of foods containing GMOs;
- control your own weight.
For prevention purposes, doctors also recommend limiting sexual intercourse. Compliance with all these recommendations will significantly reduce the likelihood of wen formation.
Atheroma in the groin in women is not absolutely safe. Relative harmlessness does not guarantee that the cyst will not fester and spill onto nearby tissues. Inflammation can lead to many other consequences.
Ignoring the problem and untimely treatment can lead to the following complications:
- an infection gets into the capsule, which provokes intensive growth of atheroma;
- with severe inflammation, the capsule can rupture outward and inward, infecting other tissues;
- cyst suppuration;
- transformation of a benign formation into a malignant tumor;
- the cyst may turn out to be cancer (for example, liposarcoma);
- after spontaneous opening of the cyst, painful wounds and ulcers remain.
Diagnosis of pathology
To accurately determine atheroma on the labia, a woman will need to make an appointment with a gynecologist. The doctor may prescribe an additional consultation with a surgeon. The diagnosis is made based on examination of the groin area, as well as by palpating the lump. Usually this is enough to diagnose the pathology.
Additionally, the doctor takes a smear, prescribes an ultrasound, as well as a biopsy. Using a puncture, the contents of the capsule are pumped out and then sent for histological examination. This will exclude the malignant nature of the tumor.
Treatment of sebaceous cysts in the groin
For atheroma, the same treatment methods are used as for other cystic formations. Since they are not amenable to drug therapy, the woman is recommended to have the capsule removed surgically.
However, if there is suppuration, the procedure is not carried out. In this situation, drugs are first used to eliminate the inflammatory process, and then surgery is prescribed.
Removal methods
To eliminate atheroma, doctors use one of the following intervention methods:
- classic surgical operation. This is the most common way to remove benign tumors in women. With this type of intervention, the skin is excised, as well as the capsule is opened. It is removed along with the contents, then stitches are applied. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and is most often prescribed if the lump has reached a large size. In this case, traces of the stitches remain, and they are removed after a couple of weeks, after the excised tissue has healed. The possibility of re-development of atheroma with the classical procedure is minimized;
If a woman has inflammation of the atheroma or its spontaneous opening, treatment with antibiotics and treatment with antiseptic drugs is prescribed. After removal of the purulent contents, 2 to 3 months must pass before the surgical procedure can be performed.
Diagnostics
If the tumor has already reached a large size, the doctor can detect it when examining the patient, but the doctor is unlikely to detect the formation of a small cyst in this way. Moreover, neoplasms can be located throughout the cervical canal.
In order to clarify the diagnosis, the following studies are performed:
- Ultrasound of the diseased area.
- Colposcopy, which helps to see changes in the structure of the cervix, characterize the changes, and make an accurate diagnosis.
- Biopsy. Can be used to screen a patient for cancer.
- Immunoenzyme test, through which female hormonal levels are studied.
- Taking a smear that can determine the presence of oncocytology or infections.
- In addition, your doctor may order blood and urine tests.
So much research is needed in order to identify the cause of the formation of a cyst, since it is often a complication of other gynecological diseases or accompanied by some diseases.
Rehabilitation after surgery
The intervention itself takes little time, but after it the woman requires care and medical supervision for several months. In most cases, sutures are used that dissolve on their own 1 to 2 weeks after the operation.
During the recovery period, you will need to take medications prescribed by the doctor, as well as daily treat the area where the atheroma was excised with antiseptic solutions. This procedure must be performed several times a day to prevent the wound from becoming infected.
For 2–3 days after surgery, water should not come into contact with the seam. You can swim only after this. On average, healing takes about 2 weeks. If classic atheroma removal was used, a small scar will remain on the skin. However, after a few months it will be practically invisible.
If there is a benign tumor in the groin area, mandatory monitoring by the attending physician is required. Atheroma does not heal on its own, so it must be removed. The operation is performed using the classical surgical method or using a laser or radio waves. The recovery period lasts on average 2 weeks.
Related publications
Intraligamentary ectopic pregnancy (clinical case)
Bartholin gland cyst (clinical case)
Clinical cases were provided by the surgeon of the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution of the Children's City Hospital K.N. Timokhina.
Bibliography
Nuck A. Adenographia curiosa et uteri foeminei anatome nova. — Leyden, 1691.
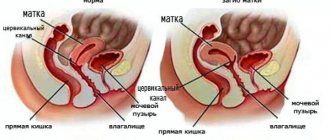
The cause of the Nucca canal cyst is incomplete obliteration of the vaginal process ( Processus vaginalis ). When the proximal part of the Processus vaginalis is partially obliterated, the distal part remains open and causes the formation of a Nucca canal cyst, which is equivalent to the occurrence of a hydrocele in men.
Pathogenesis
Rice. 1 - Embryogenesis
During intrauterine development, the so-called conductor (hibernaculum) clears the way for the ovaries from the upper abdominal cavity towards the inguinal canal (Fig. 1). The guide completes its path in the labia majora, passing through the inguinal canal. The upper part of it later turns into the ovarian ligament, the lower part into the round ligament of the uterus. The round ligament inside the inguinal canal is covered by the processus vaginalis of the peritoneum. The space between the layers of the peritoneum and the round ligament (processus vaginalis of the peritoneum) is normally obliterated at the time of birth. In the complete absence of obliteration, the Nucca canal is formed, communicating in the abdominal cavity; in the case of partial obliteration, a Nucca canal cyst is formed.
Development of a child with ID (finished).
Discussion
8 cm is a very large fibroid, but you can take medications aimed at this (Lukrin, Buserelin, Esmiya) before surgery; They will shrink the fibroids and maybe then lapara is still possible? Ask your doctor, he should know. I haven’t heard about the vaginal method, by the way, I know laparotomy, abdominal, UAE... I also looked through a lot of information when my myoma was found. But fortunately, I didn’t need surgery after the course of Esmya, but the size was of course significantly smaller. Did your fibroid manifest itself in any way? I just had heavy periods, but I thought it was just like that with age. It’s good that I got a job and started undergoing medical examinations, otherwise maybe I would have grown to 8 cm....(
Structure and functions of the ovaries. Than an ovarian cyst. Diagnosis of ovarian cysts.
Discussion
My mother was diagnosed with an ovarian cyst of 8 cm throughout the entire ovarian cavity. And cancer cells in the blood are 2 times higher than normal. Now they want to puncture the cyst. Will the cancer process be accelerated due to the puncture? And does she have a chance of treatment? Thank you in advance for the answer!
07/07/2008 15:03:53, Aleksa
Good afternoon. My name is Sabrina, I’m 26 years old, I’m not married, (according to our customs, we can’t start having sex before marriage, that is, I didn’t have sexual intercourse) 2 years ago I had bleeding and they discovered a cyst on my right ovary, I was prescribed hormonal The treatment improved, but after only 2 years, now I have started bleeding again. Is it possible to cure this disease with surgery?
06/28/2008 09:50:08, Sabrina
Quite often, many women are diagnosed with a formation such as a cyst of the round ligament of the uterus. This is why many ladies are interested in all the features of its appearance, development and, of course, treatment.
Clinical picture
In most cases (87%), the Nucca canal cyst is located on the right labia majora.
Diagnostics
Complaints
Patients mainly complain of swelling in the labia majora and pain on palpation.
Inspection and palpation
In girls, the groin area is palpated, especially the inguinal area. It is difficult to recognize a hernia of the uterine appendages when the latter descend into the area of the labia majora. A rectal examination with simultaneous palpation of the hernial protrusion area with the other hand helps clarify the diagnosis. A hernia is characterized by a cord going into the canal. Always examine the contralateral groin area. Positive results of the study, along with updated medical history, make the diagnosis of an inguinal hernia undoubted.
Rice. 3 - Photograph of a Nucca cyst during examination
Differential diagnosis
Basically, Nucca canal cysts are differentiated from:
Rice. 4 — Differential diagnosis of Nucca cyst
The contents of the hernial sac in girls in the Nukka canal, as a rule, are the uterine appendages, which descend into the area of the labia majora and are prone to rotation and rapid necrosis. Differential diagnosis is carried out mainly with Nucca canal cysts, femoral hernias and inguinal lymphadenitis.
Ultrasonography
- Nucca canal cyst is a subcutaneous hypoechoic retention formation with fluid contents located along the length of the round ligament (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5 - Sonographic picture of a Nucca cyst
- Malignant lymphoma - similar to a cyst, but with pronounced vascularization.
- Hernias contain fluid, there is a hyperechoic component protruding from the hernial opening into the sac, which is the omentum or intestine. When straining, signs of hernia excursion are noted. Sliding inguinal hernias of the female genital organs can be either congenital or acquired. The congenital nature of hernias is evidenced by the fact that they are often observed in childhood, combined with such developmental defects as: non-closure of the Nucca canal, shortening of the round ligament of the uterus, elongation of the ovarian ligament, high position of the genital organs (ovaries, tubes, uterus), long vagina, vaginal atresia, underdevelopment or bicornuity of the uterus. The most common site in inguinal hernias is the ovary, less commonly the fallopian tubes, and even more rarely the uterus. Combinations of these organs can also be observed, for example: slippage of the ovaries and tubes or the uterus and appendages.
Rice. 6 - Hernia of the ovary and fallopian tube Fig. 7 - Sonographic picture of an ovarian hernia
- Abscesses - there is a capsule with hypoechoic walls and a liquid component containing gas.
Endometroid cysts of the Nucca canal - a multi-chamber formation with homogeneous hypoechoic content and diffuse internal echo structures is detected in the inguinal canal and in the labia area.
CT, MRI
Laparoscopy
Nucca canal cyst on the left, extending through the internal opening of the inguinal canal retroperitoneally.
Int Surg Case Rep 2014;5(11):861-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2014.08.016. Epub 2014 Oct 8.
Laparoscopic diagnosis and treatment of a hydrocele of the canal of Nuck extending in the retroperitoneal space: A case report.
Matsumoto T, Hara T, Hirashita T, Kubo N, Hiroshiqe S, Orita H.
A similar patient in the Children's City Hospital at the age of 37 years with a Nucca canal cyst on the right and an unreducible inguinal hernia. The cyst went deep into the inguinal canal and further retroperitoneal.
Rice. 9 — Surgical removal of a Nucca cyst with capsule
Treatment of Nucca canal cyst is surgical.
The purpose of the operation is to remove the cyst and its capsule.
Stages of surgical intervention for Nucca canal cyst:
Rice. 10 — Surgical removal of a Nucca cyst with capsule
- A skin incision above the Pupart ligament is of sufficient length with a transition to the anterior surface of the labia to completely expose the cyst wall.
- Opening the inguinal canal with subsequent isolation of the round ligament connected to the wall of the cyst.
- Complete enucleation of the cyst with a capsule from the surrounding tissues with partial resection of the round ligament.
- Restoring the continuity of the round ligament followed by plastic surgery of the inguinal canal
Possible consequences and complications
A round ligament cyst of the uterus can lead to various complications if left untreated. The consequences that a cyst without treatment can lead to are different.
- Cyst rupture. It can occur when performing heavy physical activity or a sudden change in body position. Accompanied by acute pain in the lower abdomen and deterioration of the woman’s condition. To eliminate the complication, urgent surgery to remove the cyst is necessary.
- Torsion of the cyst stalk. Triggered by physical activity. Accompanied by sharp pain and rapid deterioration in general condition. Nausea, vomiting, and increased body temperature may occur. Hospitalization and surgery are required.
- Infertility. Caused by hormonal imbalance and menstrual irregularities.
- Malignization. The complication is very rare. A cyst of the round ligament of the uterus is a benign formation, however, a long course without treatment can lead to the appearance of atypical cells.
Any complication can lead to death if the woman does not receive medical care.
In order to avoid complications, it is necessary to undergo an annual preventive gynecological examination and ultrasound of the pelvic organs. It is worth seeking medical help if any complaints from the reproductive organs occur and timely treatment of gynecological diseases.
anonymously
Hello, dear doctors! A month ago, in the left upper part of my pubis (f., 28 years old, due in July 2013, breastfeeding), a nagging pain appeared, radiating to the left leg and intensifying when walking. This was after I carried the baby in a carrier for quite a long time (6 months, approx. 8 kg). That same day, on the left side of my pubic area, I felt a sort of “ball” under the skin, which disappeared when I lay down and appeared when I got up (I don’t know if it was there before, I didn’t feel it...). The next day the pain was almost not felt, over the course of a week or two the “ball” was sometimes palpable, sometimes not, and about a week ago it began to be felt every day (when I stand and sometimes when I sit). The pain is not severe, but a nagging pain appears and intensifies when walking for more than an hour, usually in the afternoon. In the morning and when I lie down, nothing bothers me. Other symptoms included frequent urination (but I've always had that quite often). During pregnancy, at 5-6 months, the pubic bones hurt, then it went away on its own, symphysitis was questioned, but ultrasound did not confirm it. The birth was natural, without complications; epidural anesthesia was used during labor. I take eutirox (hypothyroidism). I visited the following specialists: therapist, urologist, surgeon, ultrasound diagnostics. The therapist said that I should go to the urologist, that perhaps the lymph node was enlarged due to some kind of inflammation, and prescribed cefradime for 2 days. The urologist treated cystitis (one-time amikocin injection, cefuroxime tablets for 3 days) until the urine test was normal. However, I learned that this “bump” is a separate problem, not a lymph node, but an inguinal hernia. Upon examination, the surgeon confirmed an inguinal hernia, but the ultrasound results did not confirm either an inguinal hernia or a lymph node. In the ultrasound diagnosis they wrote “an anechoic formation measuring 57*12 mm in the left groin area”, in the surgeon’s report it was written “subcutaneous cystic formation, the probable cause is childbirth.” Please tell me what this could be and how to proceed next, and how urgently? I would like to lead a healthy, active life, the “cyst” itself does not interfere, but the nagging pain does… Can this formation disappear on its own or is surgery necessary? Should physical activity be avoided - lifting the child less, housework, sex, etc., is it possible/needed to do gymnastics, yoga? with sincere gratitude, Ekaterina
Photo attached to the question
Hello. If the surgeon and another doctor find it in you, it means that you most likely have a hernia and it is advisable to have an operation. After the operation, you will be able to lead an active lifestyle with all physical activities. Walking with a hernia without surgery is not entirely correct, since theoretically the hernia could be strangulated, and this is already dangerous. But with a hernia, you do not have strict restrictions on a complete ban on any physical activity. The fact that a hernia was not found on you does not mean that you do not have one, since ultrasound is not the most informative method in diagnosing hernias, compared to simple examination and palpation. What is seen on the ultrasound is possibly a round ligament cyst, which is often the case with hernias in women, although not necessarily unique to hernias. During surgery for a hernia, it can also be removed.
anonymously
Hello, Sergey Valerievich! Thank you for your quick and informative response, which helped me make the right decision. I went to another surgeon, he confirmed the diagnosis of a reducible left inguinal hernia and on April 18 I was operated on. However, it turned out that my hernia was very small, but there was a large “protrusion” and what the ultrasound showed was a female hydrocele, a Nuka canal cyst. The operation went well, no mesh was installed, I was sent home the same day, painkillers were only needed on the day of the operation. From what I understand, this is a rare condition and I have found very little information about it. I would like to ask: 1) How much weight can I lift after the operation - can I lift an 8 kg child and hold it in my arms and carry it? 2) What needs to be done to prevent a relapse of this disease, what could lead to this? thank you very much, best regards, Ekaterina
They are of Müllerian mesonephric or mesothelial origin. The epithelium lining cysts may be nonspecific. The diameters of the cysts vary from microscopic to 20 cm. Complications of cysts of the broad ligament of the uterus can be distortion of the cyst, heart attack or infection.
The pedunculated bones (hydatid Morgagni) are of Müllerian origin. These are the most common paramesonephric cysts. They are located near the end of the fallopian tube. These cysts are usually lined by tubal epithelium, which may have tubal-like folds (possibly originating from an accessory fallopian tube). Broadly based cysts, but similar to hydatid Morgagni, may be located between the laminae of the broad ligament. Hydatid, unlike cystadenomas, does not have a stromal component. Some cysts are lined by cuboidal or flattened mesothelial cells and may appear as multilocular peritoneal inclusion cysts. Mesonephric cysts are lined by cuboidal epithelium and may have prominent basement membrane and vestigial remnants from which they are derived.
- Bartholinitis is an inflammation of the Bartholin gland in the vestibule of the vagina. Personal hygiene and visiting a gynecologist serve to prevent this disease[...]
- An endometrial polyp is a formation somewhere inside the uterus. But such formation is not cancerous. Treatment consists of surgical removal of the polyp. When endometrial polyps re-form in women [...]
- Verrucous carcinoma is a rare type of squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva. Occurs in women in late reproductive and postmenopausal age groups[...]
- Cytolytic vaginosis (Doderlein cytolysis). The existence of this disease continues to be debated. Physiological vaginal discharge consists of cervical mucus mixed with intact […]
- Atrophic vaginitis is caused by nonspecific flora. The marriage of estrogen leads to the thinning of the vaginal mucosa, which becomes more sensitive to irritation[...]
- Genital condylomas of the vagina are similar to those that develop on the vulva and cervix, although flat condylomas are more typical of the vagina. Exophytic condylomas usually [...]
- Characterized by a change or loss of polarity of different layers of the epithelium, cellular anaplasia (impaired cell maturation, keratinization of cells in the deep layers of the epithelium, the appearance of parabasal cells in the upper layers) […]
- Dotted, red, pink, yellow, blue, brown or white spots, pieces or nodules with a slightly raised or wrinkled surface may appear […]
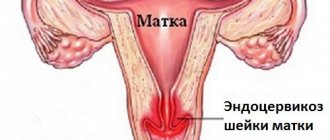
A uterine cyst is a benign tumor that is located on the cervix and is formed due to stagnation of mucus in the uterine glands. Sometimes it reaches up to 2 cm in diameter, which is a considerable size for the cervix.
In our article we will look at the types of cysts, the causes of their occurrence, symptoms, and we will talk about how diagnosis and treatment is carried out not only with medications, surgical methods, but also with folk remedies.