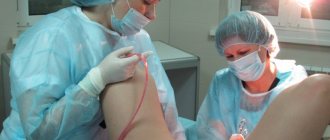
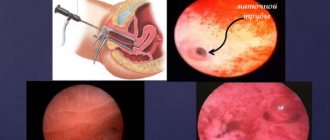
Hysteroscopy is a low-traumatic method for diagnosing and treating gynecological diseases. Even a visual intervention, not to mention therapeutic manipulations, provokes the release of mucus and a small amount of bloody streaks from the genital tract.
Few women know what discharge should be like normally after hysteroscopy. Information about the duration of smearing and its nature, how much blood should come out after the procedure, will help patients monitor their condition and consult a doctor in time if there are complications.
What discharge should be there after hysteroscopy and is considered normal?
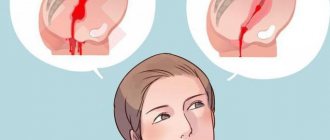
In most women, after hysteroscopy, the discharge looks like a scanty daub consisting of particles of mucus and ichor. However, the appearance and characteristics of this phenomenon vary depending on what type of procedure was used. The characteristics of the female body can also play a role: the appearance and nature of the smear after hysteroscopy may differ depending on the degree of blood clotting, the ability to regenerate and existing diseases.
Experts say that after diagnostic hysteroscopy, during which only an examination of the uterine cavity is carried out, the volume of ichor is small. Most often it is a pinkish, slightly watery discharge streaked with blood. Similar smearing fractions are also released during a diagnostic procedure involving taking a smear or scraping from the surface of the endometrium.
More abundant and brightly blood-stained lochia are associated with hysteroresectoscopy, after which a wound remains on the endometrium after removal of fibroids, polyps or other neoplasms. The appearance of discharge of this nature is considered normal consequences resulting from surgical hysteroscopy. During a therapeutic procedure, such as resectoscopy or diagnostic RDV of the uterine cavity, many small vessels of the endometrium may bleed. At the same time, there is a discharge very similar to normal menstruation. After a few days they turn brown, indicating normal healing.
Important! A slight spasm and nagging pain that accompany bleeding are considered normal if they occur in the first 1-3 days after hysteroscopy.
After endometrial polyp removal
Discharge during hysteroscopy of an endometrial polyp can be either watery with an admixture of ichor or bloody. Their characteristics will depend on which polyp was removed:
- removal of small tumors on a thin stalk causes the release of clear or slightly colored mucus within 1-3 days:
- excision of large pedunculated polyps provokes short-term, scanty bleeding, followed by the transformation of the daub into watery mucus;
- after hysteroresectoscopy of a wide-based polyp, regardless of its size, in the first 1-3 days the patient releases about 50 ml of blood.
Gynecologists pay attention: if on the first day a clot comes out of the genital tract along with the mucous lochia, there is no reason for alarm. Removal of a polyp is almost always accompanied by the release of blood, which can clot in the cavity of the organ and then come out naturally.
After scraping
As a rule, discharge after hysteroscopy with curettage resembles normal menstruation. In the first days, patients may experience pain in the abdomen and lower back. In general, this is normal, because as a result of curettage, almost the entire inner surface of the uterus is an open wound that can hurt.
Normally, the release of blood and mucus continues until secretion is restored after curettage. It usually takes about 3-5 days. In rare cases, endometrial bleeding continues for up to 10 days. The intensity of bleeding decreases over time, turning into a brown spot.
If there is no or very little discharge
A small amount of discharge is considered normal during the review procedure. If there is no discharge at all, especially after removal of tumors, this may indicate a hematometer. This gynecological problem occurs due to spasm of the cervix, as a result of which the contents of the organ cannot be released and accumulate in its cavity. Similar symptoms are caused by uterine atony, in which blood is not pushed out and forms clots that block the cervical canal. Repeated cleaning will help solve the problem.
https://youtu.be/iic6weFsXzs
Types of hysteroscopy
There are two types of this medical procedure. Their differences are due to the purposes for which it is carried out.
- Diagnostic testing is used directly to identify pathological changes in the reproductive system, and also sometimes for the purpose of monitoring previously carried out treatment. At its core, this is simply a targeted examination that does not entail damage to the mucous layer lining the internal reproductive organs.
- Therapeutic pursues more comprehensive goals. In such a case, not only optics, but microsurgical equipment are used. Hysteroscopy is an excellent option, for example, for performing curettage, removing polyps in the uterus, determining the patency of the fallopian tubes, resection of myomatous nodes, and taking material for a biopsy.
Hysteroscopy serves as both an examination method and a treatment method. In practical gynecology, three main options for hysteroscopy are used - diagnostic (or emergency), therapeutic and planned. Each type of hysteroscopy has its own characteristics in indications and conditions.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is a method for identifying intrauterine pathology, performed on an emergency basis. As a rule, the indications for this type of manipulation are massive uterine bleeding. It is advisable to try to pass at least some of the necessary tests before this.
Planned hysteroscopy is a prepared manipulation. It is prescribed for frequent spontaneous abortions, abnormalities of the uterus, and infertility. In addition, it is used as a monitoring study after diagnostic and surgical curettage of the endometrium.
Therapeutic hysteroscopy is prescribed for radical measures - removal of tumors or areas of endometriosis.
Surgical hysteroscopy is used in case of complicated removal of intrauterine devices - IUDs or their parts.
Carrying out hysteroscopy
To carry out diagnosis, it is necessary to expand the uterine cavity. Depending on the medium in which it is performed, hysteroscopy can be liquid or gas. Sometimes so-called contact hysteroscopy is used when dilation of the uterine cavity is not required.
For liquid hysteroscopy, saline solution, Ringer's solution or distilled water are used. Gas hysteroscopy is carried out only as a diagnostic option for manipulation. In this case, the uterine cavity is expanded using carbon dioxide. Gas hysteroscopy is easy to use and provides a wide view.
What can be considered a deviation from the norm
After hysteroscopy, an infectious or non-infectious complication may occur, which may affect the nature of the discharge and its duration. However, any deviation from the previously described phenomena is considered normal if the color of the discharge turns brown over time, and the total volume of blood during the recovery period does not exceed 50 ml.
If the patient experiences heavy discharge with a high content of red blood and clots that saturate the sanitary pad in less than 2 hours, this is a cause for alarm. You should also consult a doctor if the period of bleeding increases beyond 10 days.
Important! At your appointment, you must tell the gynecologist how long the symptoms last, and what warning signs are present in addition to bleeding.
Bloody issues
If blood after hysteroscopy is observed for longer than 10 days, this may indicate problems with endometrial regeneration. There may be several reasons why bleeding takes so long:
- problems with clotting - lochia does not contain clots at all, scarlet blood comes from the genital tract;
- deep wounds on the endometrium or perforation of the uterus - in this case, after hysteroscopy bleeding for a long time, sometimes profusely and with clots, clear liquid comes out along with the blood, constant pain is felt in the abdomen;
- infection - yellow or greenish inclusions are observed in the bloody discharge, and an unpleasant odor is felt.
Each of the listed complications requires complex therapy, so you should not delay your visit to the gynecologist.
Purulent discharge
The presence of pus is indicated by abundant mucous discharge with an unpleasant odor. Their color can be whitish, greenish or yellow. The structure is varied, but they are united by a lack of transparency - pus, regardless of origin, is always cloudy. As a rule, purulent discharge is a sign of infection, which, if left untreated, can be complicated by sepsis, peritonitis and infertility. Therefore, its appearance in spotting is a direct indication for hospitalization in a gynecological hospital.
Brown or black
Brown discharge is not a sign of pathology. On the contrary, this phenomenon indicates the healing of the endometrium. However, if it smears brown, but black inclusions are also visible on the sanitary pad, there is cause for alarm.
Gynecologists say that black or brown masses may indicate excessive blood thickness. This phenomenon in itself is not dangerous, but in certain situations it can lead to blockage of the cervical canal and incomplete release of blood from the uterine cavity. In order to recognize the pathology in time, it is worth paying attention to how long the dark smudges last.
Yellow color
The appearance of yellow discharge after hysteroscopy can be interpreted as normal or pathological. If small yellowish veins are observed in the ichor on the first day after the procedure, and there are no other alarming symptoms, this is the norm. If the yellow discharge has an unpleasant odor, is abundant, and includes streaks of a darker color (even green), this indicates suppuration. The latter may be indicated by an increase in body temperature and increasing abdominal pain.
Main types of discharge
There are 4 main types of discharge in the postoperative period:
- Normal physiological. As the wound heals, their number decreases. Normally, with a low-traumatic operation, the discharge lasts 1-2 days. After complete curettage of the uterine cavity, they can last up to 2 weeks. In general, there can be 50 ml of them per day, they are transparent, sticky or pink (sacral). After complete healing, they stop.
- Uterine bleeding. If large vessels of the uterine wall were damaged during the operation, then the discharge appears in the form of blood. Most often, the blood is fresh and scarlet, but is released in small quantities. It is also possible to separate dark clots from the vagina, this is the blood remaining after the operation. If bleeding continues for more than 3-4 days, be sure to contact your doctor.
- Discharge in the form of pus. In the postoperative period, the discharge acquires a yellowish or greenish tint and does not become lighter, but, on the contrary, becomes more and more cloudy. An unpleasant odor appears. The cause of such a bacterial infection can be staphylococci, streptococci and various sexually transmitted diseases. If this moment is missed and you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, complications in the form of sepsis, peritonitis or infertility are possible.
- Putrid discharge. When clostridia enter the uterine cavity, a putrefactive infection occurs. Such microorganisms living in an airless environment multiply very quickly. The patient experiences sharp, severe pain in the lower abdomen. The discharge becomes foamy and has an unpleasant, putrid odor. If you have any of the signs, you should contact your doctor.
After such an operation, the menstrual cycle may not be restored immediately. Women should also not have sex for a month after surgery, take a hot bath, shower, go to the sauna, play sports, or take drugs that increase bleeding (aspirin). Be healthy and take care of yourself.
Recovery period
As long as a woman experiences discharge after hysteroscopy, the rehabilitation period continues. During this time, it is highly advisable to maintain good hygiene, maintain sexual rest, if necessary, take medications prescribed by the doctor, and refrain from lifting heavy objects and playing sports. It is especially important to follow these rules after surgery on the endometrium of the uterus: removal of a polyp, fibroids or excision of synechiae.
How long does discharge last after hysteroscopy?
The normal duration of bleeding is several days. The healing time of the endometrium depends on the method used to perform hysteroscopy of the uterus:
- during the review procedure, the release of mucus and ichor lasts no longer than 3 days;
- when a small polyp is removed, bleeding stops on the third day, maximum on the fifth;
- When curettage or removal of fibroids, it bleeds for 10 days, but no longer.
In order not to miss alarming symptoms, a woman should carefully monitor and count how many days the blood flows and whether there is a trend towards a decrease in the volume of discharge.
When to see a doctor
There are not many symptoms in which bleeding after hysteroscopy is a sign of pathology. First of all, these are cases when there is abundant discharge of a bright scarlet color with clots. The result of severe bleeding can be a sharp decrease in blood volume, and, as a result, a critical decrease in blood pressure, followed by the patient falling into a coma.
In some cases, the pathology does not manifest itself so clearly. The following may indicate that complications are developing:
- prolonged persistence of abdominal pain;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness;
- dry mouth, increased sweating.
Such symptoms appear during the inflammatory process, internal bleeding, and infection of the uterus. All possible complications require urgent treatment, so if they appear, do not postpone a visit to the gynecologist or call an ambulance.
What is the operation
There are two main ways to get rid of benign growths:
- Polypectomy - removal of a polyp by curettage or unscrewing. This operation should only be performed by an experienced specialist.
- Hysteroscopy of endometrial polyp is the most popular method. The procedure goes like this: an endoscope equipped with a microcamera, as well as a set of microsurgical instruments, are inserted into the cervix. Internal tissues and genital organs are not injured. Microsurgery allows you to eliminate the polyp and perform curettage of the uterus correctly, without complications.
It is not enough to carry out one procedure to eliminate the formation. After this, diagnostic curettage is required.
Surgery is followed by restorative treatment. Here it is necessary to take into account the patient’s age and the cause of the polyps. The examination is carried out only by the attending physician. He also prescribes antibiotics.
After surgery, many women are bothered by spotting. If they are accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, you should urgently consult a doctor. It is necessary to exclude possible complications due to severe cervical spasm.
Recommendations from gynecologists
To reduce the risk of negative consequences after the hysteroscopy procedure, gynecology has a number of recommendations for patients:
- While there is bleeding, you should not use tampons. They can become a source of infection.
- Do not take a bath for two weeks after the procedure. Water can get into the genital tract and lead to inflammation.
- Hot showers, too warm baths, baths and saunas are prohibited for 2-3 weeks. Heating the body can cause bleeding.
- You should not drink alcohol even in small quantities. It thins the blood and dilates blood vessels, which can result in heavy bleeding.
- Do not lift objects heavier than 3 kg for two weeks. Physical stress can cause bleeding.
- Do not take aspirin or other blood thinners until the bleeding has completely stopped.
- Tell your specialist about any symptoms that do not seem normal to you. It's better to be safe than sorry.
If these recommendations are followed, bleeding after diagnostic or therapeutic hysteroscopy will stop on time. To make sure everything went well, you should visit a doctor after two weeks.
Possible complications and consequences
In rare cases, complications of the postoperative period occur during planned rehabilitation.
Most often, they appear due to insufficient preparation for surgery: if preventive measures were not taken before removing the polyp - treatment of acute diseases not only in the pelvis, but throughout the body. With the blood flow, the pathogenic factor under certain conditions can be transferred to the healing site. This causes a sharp deterioration in the rehabilitation process and creates a focus of inflammation in the operated area. Therefore, surgery to remove a cervical polyp is recommended not as an emergency procedure, but as a planned procedure, after serious preparation. This is only possible if the patient takes a responsible attitude towards her health: regular examinations by a gynecologist maintain women’s health at the proper level.
The following phenomena should cause caution:
- increased amount of mucous and/or bloody discharge;
- unpleasant odor of discharge;
- the appearance or intensification of pain in the lower abdomen, most often pulling;
- temperature rise to subfebrile level;
- abrupt cessation of all discharge;
- general deterioration of health.
Normally, none of this should happen. If at least one of these signs appears, you should immediately seek medical help. In the initial stage of inflammation it is much easier to cope with the situation than in an advanced case.
Important! If for some reason the operation was performed under general anesthesia using curettage, i.e. in a large volume, it may bleed a little more intensely and a little longer.
In the long term after surgery to remove a polyp, the cervical canal may bleed for many reasons, including those not related to the surgical intervention. In any case, unexpected bleeding of any intensity, with or without pain, should be a reason for a visit to the antenatal clinic.