The presence of any disease in the body is a cause for concern. Pancreatitis is no exception. What you need to know about it is that the acute form of the disease that occurs for the first time is susceptible to healing.
It is the first acute pancreatitis that can be cured completely, but it can be fatal in this phase. In any case, the only answer to the question of how to live with pancreatitis is that it must be treated. To live with pancreatitis, you need to know well the differences between acute, exacerbation, and chronic. You can live long and happily, despite the disease.
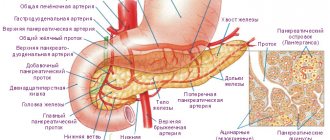
Functions of the gland and types of pathology
In the human body it performs the following functions:
- digestive – synthesizes enzymes for breaking down food;
- hormonal - produces substances that affect all organs and systems of the body.
The main hormone synthesized by the pancreas is insulin. This substance regulates glucose levels in the body. In chronic inflammatory pathologies of the pancreas, insufficient insulin is produced, which leads to the formation of diabetes mellitus.
https://youtu.be/6vGZS0O9ZAg
Features of diagnosing pancreatitis in older people
Pancreatitis in older people can only be detected by a gastroenterologist. However, it is almost impossible to give an accurate forecast of what kind of disease it is based on external signs. The examination begins with general and biochemical blood tests, as well as urine and stool tests.
Pancreatitis is characterized by a lack of protein, which can be determined by the results of a biochemical blood test, and an increased level of fat found in the stool. Ultrasound plays an important role in the diagnosis of pancreatitis. Using it, you can determine how uneven the organ’s shares are, detect the presence of stones, cysts, seals, as well as dilation of the duct. When pancreatitis is detected and a diagnosis is made, it is necessary to treat the disease.
Read material on the topic: Folk remedies for the elderly: healthy recipes
Signs of inflammation
The most common clinical picture of pancreatitis is represented by the following symptoms:
- intense pain in the abdomen of a girdle nature;
- fever (not always);
- pale skin or jaundice;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dry mouth and unpleasant taste;
- drop in blood pressure;
- belching or hiccups.
How does pancreatitis manifest in older people?
Elderly people experience acute pancreatitis if, first of all, they feel pain, which varies in intensity and can occur in any part of the abdominal cavity.
Sometimes it can be so strong that it even causes painful shock. The pain is of a girdling or constricting nature; tingling may occur in the kidneys or liver, and this occurs either in periodic attacks or constantly over a period of time. The following symptoms may indicate pancreatitis in older people:
- Periodic vomiting in small quantities, which may be accompanied by the release of bile or blood.
- Intestinal paresis, which is characterized by severe pain, softness of the abdomen and lack of tension in the muscles. With such indicators it is quite difficult to make a diagnosis.
- Coated tongue.
- Human skin is pale and bluish in color.
- The whites of the eyes become yellow.
- Rapid pulse, low blood pressure.
- Poisoning with toxic substances.
- Body temperature rises, but in the case of a weakened body it can remain within normal limits.
- Increased body temperature, but in weakened patients it may remain normal.
- Voskresensky syndrome is the absence of a pulse in the abdominal aorta.
Not all people experience these symptoms.
Even if pain is felt in the back or lower back, it is not very pronounced, and the person does not feel sick or vomit. Chronic pancreatitis also begins with pain. If the symptoms of pancreatitis are similar to an acute disease, there is a high probability that the diet was disrupted or the body was given excessive physical activity. In the absence of attacks, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- Weight loss. The patient begins to lose weight due to the fact that he does not produce enzymes responsible for digestion and, as a result, for the supply of nutrients to the body.
- Attacks of nausea and heartburn.
- Decreased appetite.
- Bloated belly.
- Loose stools followed by constipation.
Pancreatitis in older people can occur in a latent form, thus, due to mild symptoms, patients do not undergo treatment.
However, do not forget that if the disease progresses, this can lead to the fact that the pancreas ceases to contribute to the production of necessary enzymes and hormones. Read material on the topic: Health of older people
Forms of the disease
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is characterized by the rapid development of the inflammatory process and pronounced clinical signs. The pathology is rare, but death in this case is quite common. Men aged 40-50 years are most susceptible. The cause of the development of this form of pancreatitis in the vast majority of cases is chronic alcoholism.
Death from acute pancreatitis during the first few days occurs in 50% of cases. The likelihood of such an outcome increases significantly when seeking medical help late.
As a result of the rapid development of the inflammatory process, a large number of toxic substances are released, which the body cannot cope with on its own.
The cause of death from pancreatitis can be complications:
- bleeding;
- renal failure;
- respiratory failure;
- pseudocyst rupture;
- infection;
- obstruction of the intestines or bile ducts;
- cardiovascular failure.
Chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis develops against the background of acute inflammation of the pancreas or independently under the influence of external factors. Over the course of many years after the initial damage to an organ, cells undergo increasingly greater deformation. The prognosis for chronic pancreatitis is more favorable. They live with chronic pancreatitis almost as long as healthy people, provided they follow the diet and doctor’s recommendations. If the diet is violated and there is no treatment, life expectancy decreases significantly: about 30% of patients die within 10 years, about 55% die within 20 years.
Patients must clearly understand that each exacerbation injures the organ. As a result of another acute inflammation, a scar forms at the site of damaged tissue. The more exacerbations, the less functionality of the gland.
Pancreatitis is dangerous due to the formation of cysts, stones, and neoplasms in the tissues of the gland. These changes can significantly worsen the situation. Treatment in such cases is surgical.
How to extend lifespan
In addition to drug therapy and proper nutrition, it is important to remember your overall health. Moreover, both physical condition and psychological health matter. Doctors advise patients to avoid stressful situations and undergo medical examinations in a timely manner.
Even if the pathology appeared in childhood, following certain rules will help you live a full life. To improve the prognosis of the disease, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- completely eliminate alcohol, cigarettes and drugs;
- exercise moderately;
- develop a positive attitude and resistance to stressful situations.
Constant nervous tension negatively affects the state of the digestive system, so it is important to avoid stress
The diet of people with this diagnosis should be selected by a doctor. However, there are certain recommendations that can be given to all patients. The main goal of nutritional correction is to reduce the load on the digestive organs. Thanks to this, you will be able to cope with pain and nausea.
General dietary recommendations
All recommendations are primarily aimed at changing your diet. It is important to eat food quite often, but portions should be small - no more than 250 grams. People with this diagnosis should eat up to 6 times. The intervals between meals are at least 2.5 hours, but no more than 3 hours.
Product processing plays an important role. To reduce the severity of inflammation, you should eat pureed food. It is also perfectly acceptable to eat foods that have been cut into pieces. However, in this case they must be chewed very carefully. You need to choose dishes that are boiled, stewed or baked.
Even for dessert, you should prefer fresh fruit baked in the oven.
For pancreatitis, it is best to stick to a protein diet. The amount of these substances in the diet should be up to 150 grams per day.
It is worth paying attention to the drinking regime. People with this disease need to consume 2 liters of water. In this case, it is best to take a few sips every half hour.
However, some products are prohibited. So, doctors advise avoiding fatty foods and foods with high levels of carbohydrates. Such dishes put a lot of stress on the pancreas. The daily amount of fat should be no more than 70 grams, and carbohydrates - a maximum of 300 grams.
Factors influencing the patient's life expectancy
- The severity of the inflammatory process in the pancreas. In the case of severe disease, mortality reaches 30%, if organ necrosis occurs - 50%. A severe inflammatory process leads to disruption of the functionality of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, and liver.
- Complications of the disease. Additional disturbances in the body become apparent in the second week of the disease. Often complications of pancreatitis are represented by intestinal obstruction, bleeding, rupture of a pseudocyst, and the spread of infection. In such cases, the chances of dying from pancreatitis increase sharply. A mild form of inflammation of the pancreas ends in death in no more than 2% of cases.
- Age. Among elderly people, the mortality rate as a result of the disease reaches 20%, even with a moderate course of the disease.
- Elimination of bad habits.
- Adequate treatment.
- Compliance with the dietary regime.
Cause of mortality in pancreatitis
The disease is characterized by severity and a high risk of death. Why this condition is dangerous and why the patient dies, we will consider further.
Pancreatic necrosis
Pancreatic necrosis is a complication in which the death of parts or the entire pancreas occurs. The main reason for this condition is damage to the organ by its own enzymes and the occurrence of inflammatory processes. Provoking factors are considered to be alcohol abuse, calculous cholecystitis, abdominal trauma and previous surgical interventions.
Pancreatic necrosis has a far from high survival rate: in 40–70% of cases death occurs. If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, the indicator increases significantly.
Pancreas cancer
It is characterized by an aggressive course and rapid spread throughout the body. In most cases it leads to death. If cancer is detected at an operable stage, surgery is performed to completely remove the organ or its diseased part. The most common causes of cancer are: smoking, poor diet, excessive alcohol intake, impaired digestive function, and genetic factors.
Mortality after surgery
Pancreatic surgery is difficult and has high mortality rates. Removing an organ is associated with difficulties, since it is located in proximity to large vessels, kidneys, and shares blood flow with the duodenum. Highly active enzymes often digest parenchymal tissue, and it is quite difficult to suture it.
The patient has to remain in bed, spending a lot of time lying down. All this threatens the development of complications in the postoperative period, which increases the risk of death. If the operation is successful, the patient faces a long road to recovery.
Bad habits
Alcohol abuse is often the main cause of the disease. Alcohol provokes spasm of the ducts, as a result of which the outflow of pancreatic juice and bile becomes difficult. As a consequence of this, an inflammatory process develops. Alcoholic drinks cause destruction of gland cells, tissue scarring, and disruption of the blood supply to the organ. This occurs due to the impact of the breakdown products of ethyl alcohol or surrogates on the gland tissue. The type of alcohol is not important in this case. You can die from pancreatitis within 5-10 years if the patient continues to abuse alcohol. The survival rate for chronic pancreatitis is no more than 50% over the next 20 years.
Smoking has an equally harmful effect. Inhalation of cigarette smoke increases the synthesis of pancreatic enzymes, which digest organ tissue in the absence of food in the stomach.
Toxic substances from cigarette smoke provoke the development of diabetes mellitus, malignant degeneration of glandular tissue, and malfunction of the cardiovascular system. These disorders in the human body remain for life.
How dangerous is chronic pancreatitis and does it affect life expectancy?
Each exacerbation affects the condition of the gland with a scar. It turns out that the tissues of the organ are increasingly unsuitable for their intended function due to the replacement of healthy tissue with fibrous growths.
The process goes slowly, but over a long period. During this time, cysts, tumors, and stones may appear in the organ. For such diseases, medication methods are ineffective. But while they are not there, we will continue treatment activities. They are aimed at avoiding exacerbations. Then the gland is less injured.
In the treatment of pancreatitis, diet dominates. Food culture should be familiar to every person. A diet is a special balanced diet that relieves stress on the pancreas. How long does it last?
Since in the chronic phase exacerbations are replaced by remissions, the diet for pancreatitis must be followed throughout life. But it can be stricter during periods of exacerbation and expanded during periods of remission. At the same time, you need to help the organ by taking enzyme preparations throughout your life.
The culture of dietary nutrition in case of illness assumes the following:
- Cooking methods require abandoning frying, boiling, baking, and chopping. Fortunately, there are no problems with household appliances now. Multicookers and blenders are at your service;
- fatty, salty, smoked and spicy foods;
- eat often and in small portions, i.e. avoid overeating;
- the menu is made up of permitted or loyal products;
- food temperature - neither cold nor hot, warm;
- You need to expand the menu with new dishes or products one at a time, observing the body’s reaction. This is especially true for fruits, berries, and vegetables in the summer season.
Dietary table No. 5P will tell you what dishes to prepare. There you can see an approximate menu. Based on its positions, you can come up with your own dishes. Poor nutrition or poor diet can provoke an exacerbation by overloading the pancreas. And exacerbation is just dangerous. By maintaining a diet, the longer the better, the process of tissue death can be greatly reduced or avoided altogether.
Treatment tactics
Treatment of any form of pancreatic disease requires an integrated approach. The patient may need consultations with a gastroenterologist, surgeon, endocrinologist, psychotherapist, or radiologist. The basis of treatment for pathology is abstinence from drinking any alcoholic beverages, as well as following a diet.
The set of measures for the treatment of pancreatitis includes the following points:
- Drug therapy.
- Diet.
- Maintaining immunity.
- Regular moderate physical activity.
- Adequate daily routine (healthy sleep, rest).
- Developing stress resistance and a positive attitude.
Quality of life of patients with pancreatitis
Having contacted the doctor who recognized the attack of pancreatitis, its treatment begins. We will not take acute pancreatitis into consideration. We will assume that he was completely cured. There are many similarities in the treatment of any pancreatitis. When healing a disease, there is always a set of measures that effectively influence its eradication:
- medications;
- diet;
- maintaining and stimulating the immune system.
Medications act by reducing pancreatic secretion. Conservative therapy includes:
- antispasmodics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- analgesics;
- H2 blockers;
- pancreatic enzymes.
Rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation after acute pancreatitis is a rather long and painstaking process, during which unquestioning adherence to all instructions of the treating specialist is necessary. Moreover, regular examination procedures and treatment in a sanatorium-resort are prescribed every six months. It is recommended to visit balneological resorts, where the main attraction is hydrocarbonate waters with medium and low levels of mineralization. Among the most popular resorts of this type are:
- Borjomi;
- Essentuki;
- Morshyn;
- Truskavets.
Carrying out physiotherapeutic procedures is possible only during a period of stable remission, when for a long period of time there are simply no symptomatic manifestations of pancreatic pathology.
The entire rehabilitation period is divided into three main stages, which we will consider below.
Among other things, the patient, together with his attending physician, draws up an individual diet menu with all his (the patient’s) culinary preferences.
Elimination of pancreatic pathology at the first stage of rehabilitation is based on abstaining from eating fried and fatty foods, as well as sweet and salty foods to ensure maximum rest of the parenchymal organ.
During the rehabilitation period, medications can be administered either intramuscularly or intravenously.
After 2-3 months of following a strict dietary diet, the patient, depending on the condition of his pancreas, may be allowed to eat lean varieties of meat and fish, fresh fruit crops, etc.
The next stage of the rehabilitation period after acute pancreatic disease is adherence to a simplified dietary diet, which may already include an impressive amount of protein foods and fats.
Drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking tobacco, even in small doses, is strictly prohibited during the rehabilitation period.
The last stage of rehabilitation is a complete transition to proper nutrition, eating only healthy foods in combination with an annual visit to the gastroenterologist’s office and undergoing a detailed examination.
Remember that acute pancreatitis can cause a prolonged period of disability. And after the patient’s general condition has normalized, employment should be carried out in conditions where the following will be excluded:
- physical stress;
- trauma to the abdominal area;
- various body concussions;
- contact with toxic substances.
A protracted type of acute form of pancreatic disease without prompt and timely treatment can lead to long-term disability and disability of groups II and III.