A pinched nerve in the spine is a phenomenon in which roots extending from the spinal cord connect to vertebrae located nearby. And there is also a merger with other “obstacles” - hernias, muscles (affected by spasms), tendons and cartilage. If your back is pinched, a person suffers from a group of symptoms that are directly characteristic of this phenomenon. Most often, the cervical and sciatic nerves are subject to the process. The set of signs and features of the therapeutic process, which will be discussed in the article, depend on the location of the lesion.
Causes
A pinched nerve occurs when the sensitive base, the root, is compressed. They can be compressed by the vertebrae, as well as:
- muscles during spasm;
- hernias;
- cartilage;
- tendons;
- tumors;
- protrusions.
A pinched nerve is accompanied by severe discomfort, depending on the form of the lesion, and various pains appear. But not all types of pinching bring such discomfort. Often one of the main signs is a transmission disorder, resulting in tingling and numbness.
Infringement is most often provoked by:
- dislocations, injuries;
- strong or sudden load;
- neoplasms;
- congenital anomalies of the spine;
- inflammation of the joint capsule;
- osteoarthritis – destruction of cartilage and formation of bone growths;
- kyphosis;
- scoliosis and other postural changes.
Pinched nerves are more likely to develop in patients at risk. Factors that increase the risk of entrapment include:
- constant sedentary work;
- habit of slouching;
- overweight;
- pregnancy;
- prolonged bed rest;
- hormonal diseases;
- constant physical activity.
In women, infringement occurs more often than in men. Hereditary predisposition is also a risk factor - bone density may depend on hereditary information.
https://youtu.be/cFOYC85w9zg
The use of blockade for sciatica of the lower extremities
What other injections are given for inflammation of the sciatic nerve?
If none of the drugs has brought adequate relief from neuritis, and the patient is suffering from unbearable pain, then he is prescribed novocaine or ultracoin blockade.
It will block nerve impulses, relieve inflammation and nervous excitement. The solution is injected into the sciatic nerve bundles in the lumbar region , but this is done in the most extreme cases.
Symptoms and types
Symptoms of a pinched nerve vary depending on the area affected. The presence of an inflammatory process and the degree of damage also influence how the infringement manifests itself. The main symptom remains severe pain and limited range of motion.
Additional symptoms of a pinched nerve in the back:
- swelling of the compression site;
- redness;
- soreness when touched;
- muscle cramps;
- weakness at the pinched site;
- tingling, sensation of “goosebumps” on the skin.
Severe lesions are accompanied by compression of the spinal cord, impaired motor function, and decreased sensitivity. Such lesions cause paralysis and paresis.
Pinched sciatic nerve
When the sciatic nerve is pinched or with sciatica - lumbar pinching - signs such as tingling and burning appear. Similar sensations occur in the leg, which becomes almost motionless. When standing, there is a strong shooting pain.
If there is a hernia, the pain syndrome when a nerve is pinched in the back worsens significantly and becomes sharp. It gets worse when coughing, sneezing, laughing, or changing position. Inflammation of such a sensitive ending is called radiculitis. If the cause is a hernia or osteochondrosis, manual therapy should not be used.
In the initial stages, the lesion is accompanied only by numbness, sometimes discomfort is felt in the toes. Then difficulties arise in maintaining a vertical position, tremors and weakness appear in the leg. With severe pinching, the patient may lose control of urination and bowel movements.
Since the sciatic nerve is one of the largest, it can innervate the entire area from the hip to the toes. The localization of pain for this reason also varies - from the gluteal muscle to the fingers.
Pinched nerve in the cervical spine
Pinching in the cervical spine is accompanied by severe tension in the neck and limitation of its mobility. The pain becomes stronger when turning the head or staying in one position for a long time - prolonged sitting or during sleep.
Pinching in the back is caused by intervertebral discs, the vertebrae themselves as a result of subluxation or progressive osteochondrosis. To treat a pinched nerve, massage is used to relieve muscle spasm and alleviate the condition.
Pinched nerve in the thoracic region
Pinching of the spine at the chest level is accompanied by intercostal neuralgia. Heart pain may occur, so differential diagnosis is carried out. Differences in the nature of the pain syndrome. With damage to the intercostal nerves from pinching in the back, the pain is constant, with heart pain it is periodic.
When palpating the ribs or active movements of the body, the symptoms intensify and do not subside during rest. Against the background of constant pain, neuropsychiatric disorders may develop.
Pinched radial and ulnar nerves
Pinched nerves in the spine at this level are accompanied by sharp pain when bending and straightening the arm; it is convenient to hold the fingers only bent, the hands droop, and it is impossible to strain them.
Ulnar nerve entrapment is accompanied by loss of sensitivity in the hands and fingers. Blood circulation slows down, pain radiates to the little fingers.
Diagnosis of compression of the brachial nerve
Diagnostic measures include physical examination and additional examination techniques. During the appointment, the doctor collects a complete medical history: how long ago the symptoms appeared, the causes of the disease, the presence of chronic pathologies, the type of activity of the patient, and asks where it hurts.
During a physical examination, the specialist performs several diagnostic tests. He compares the muscle strength of the affected and healthy arm, checking:
- pronation (inward rotation of the hand), supination (outward rotation of the hand);
- clasping palms together;
- fixing the arms in an extended position,
- symmetry of muscle function,
- holding a glass.
The doctor conducts tests to determine sensitivity in all fingers, forearm and shoulder. Sensitivity is tested by touching the patient's skin or using a needle.
During the examination, the doctor prescribes general and biochemical blood and urine tests.
Electromyography allows a diagnosis of nerve entrapment to be made. The technique allows you to see the electrical activity of the muscle system in the hand. An electromyograph helps detect areas of poor muscle innervation. For a complete examination, the patient is referred for examination to an endocrinologist, orthopedist, or surgeon. An x-ray of the shoulder joint, upper arm, forearm, and hand is also necessary.
Diagnostics
The cause of a pinched nerve in the back is determined instrumentally. For a long time, the patient can live with moderate pain, stiffness in the lower back and legs without seeing a doctor. But over time, the disease progresses and the pain intensifies.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following diseases:
- spinal tumors;
- myeloma;
- Bekhterev's disease;
- spondylitis;
- inflammation of internal organs;
- arthrosis, arthritis.
Diagnosis includes collecting anamnesis and detailed information about symptoms. The doctor will ask about the nature of the back pain and family history of the disease. Pinching is characterized by Sicard, Legas and others syndromes. With Sicard syndrome, the patient cannot bend the leg, and with Legace syndrome, the leg does not rise when lying on the back.
The doctor will check the reflexes and sensitivity of the endings. Pinched spinal nerves are diagnosed using ultrasound, MRI, and x-rays. The methods determine pinched roots and the localization of the inflammatory process, if present. With their help, neoplasms are also detected if they have become the cause of pinching.
Preventing pinched nerves
- Watch your posture, avoid uncomfortable positions while sitting and sleeping.
- Dress according to the weather, avoid hypothermia, severe overheating, and drafts in the room.
- Sleep on a bed (not a sofa or sofa) with an orthopedic mattress.
- Do not lift heavy objects.
- Perform a set of exercises that strengthen the skeleton, give light physical activity (yoga, swimming).
- At the first symptoms of pinching, consult a doctor.
- Conscientiously and completely follow the doctor’s recommendations, do not interrupt the course of treatment ahead of time.
Following simple rules of prevention will save you from an unpleasant disease and long-term treatment. Share your experience in the comments, ask questions about the topic.
Treatment
A pinched nerve in the back is a symptom, not a separate disease, and therefore treatment can be called symptomatic. Various measures are aimed at relieving pain and increasing range of motion. Only after this the cause is eliminated and, if necessary, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Medicines for pinched nerves
Photo from the site zdorovko.info
Drugs that are prescribed for pinched nerves in the back belong to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They reduce the production of inflammatory mediators, eliminate the focus, and at the same time acute pain goes away. The drugs are recommended to be used in the form of ointments and creams, but NSAIDs are also sold in tablets and capsules for systemic use.
Recommended NSAIDs for back pain include:
- Diclofenac.
- Meloxicam.
- Nimesulide.
- Ibuprofen.
- Movalis.
- Voltaren.
The use of systemic drugs is strictly prohibited for pregnant women, as well as for diseases of the stomach and intestines.
If a pinched nerve in the back is caused by muscle spasms, the doctor will prescribe medications that relieve excess tension, for example, Mydocalm. To normalize the metabolic processes of the central nervous system and restore back sensitivity, vitamin complexes containing B vitamins are prescribed.
Physiotherapy for a pinched nerve
With the help of physiotherapy, a more localized effect on the spinal nerve is achieved and the delivery of drugs is accelerated. Procedures prescribed for back pain:
- UHF – thermal radiation treatment by converting electromagnetic field frequencies into thermal energy;
- electrophoresis - administration of drugs through the skin and mucous membranes using direct electric current;
- acupuncture – acupuncture to eliminate trigger points;
- novocaine blockade - blocking an inflamed nerve by directly anesthetizing it.
Several procedures in combination may be recommended, and they often continue after drug treatment.
Massage for pinched nerves
Massage for pinched nerves is permitted and not always indicated. During a period of acute inflammation, the procedure will not only cause harm, but also cause severe pain. When the acute phase of pinching in the lumbar vertebra passes, massage is prescribed for the following purposes:
- reducing the risk of relapse;
- elimination of chronic pain syndrome;
- improved blood circulation;
- increased lymph outflow;
- relieving pressure in the affected area;
- normalization of nerve activity;
- return of range of motion.
Tingling and vibration techniques are not used unless prescribed by a doctor. For prevention, general massage, honey and acupressure may be recommended.
Only a medical professional should perform a back massage. When applying for the services of private massage therapists, you need to make sure that they are competent and have certificates.
Gymnastics for a pinched nerve
The treatment complex for relieving discomfort and pain should also be selected only by a doctor and after diagnosis. It is important to understand that everything depends on the cause of the pinching. If we are talking about a hernia, tumor or protrusion, gymnastics will be strictly contraindicated and can significantly worsen the condition.
The Bubnovsky system is often recommended for the back - kinesitherapy using special videos. It is performed only after the acute pain has subsided. In a standing position:
- spread their legs, place their hands on their hips, move their pelvis back and forth;
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart, gently bend to the sides, and raise your opposite arm above your head.
In a sitting position, perform the following exercises for the back:
- walk back and forth on the buttocks, legs extended straight;
- slowly place straight arms behind the back at the level of the thoracic spine;
- sit on a chair, cross your legs, keep your back straight, place your palms on the back of your head, make 10 turns in different directions;
- As you exhale, bend your back upward, and as you inhale, bend your back down.
The correct exercises are selected by a physical therapy specialist and the attending physician; only after their consultation can you perform gymnastics.
Traditional methods for pinched nerves
Folk remedies can be helpful in treating back pain. Among the folk recipes the following are recommended:
- Brew 1 kg of oak or spruce in 5 liters of water, boil for half an hour, then filter and pour into the bath, the water temperature should be comfortable for the body.
- 250 g of calamus roots are boiled in 3 liters of water, then strained and poured into the bath; you can add creeping thyme while boiling.
- 50 g of mullein flowers are poured into 1 liter of vodka and left for 7-10 days, then rubbed into the affected areas.
- A glass of lilac flowers is infused with 0.5 liters of vodka for 48-72 hours and rubbed into sore spots.
- Dried elderberry inflorescences and berries are poured into a glass of boiling water and left for 30 minutes, taken twice a day, half a glass 15 minutes before meals.
Collections with rose hips, thyme, hawthorn, linden, and oregano are also used. It is important to rule out allergies first.
Surgery for a pinched nerve
Surgery is indicated when a growing tumor is detected - benign or malignant. Intervention will be required if spinal hernias are detected. Today, microsurgical techniques and laser operations are used for this, which guarantee quick rehabilitation and complete relief from the cause of the pinching.
Therapeutic measures for nerve compression in the hand
Treatment for pinched nerves includes drug therapy, physiotherapeutic techniques, physical therapy, massage, and the use of traditional medicine. Treatment is carried out almost the same regardless of the location of the lesion.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy includes analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamin complexes, as well as drugs that enhance the conduction of impulses. To reduce the intensity of pain, non-steroidal drugs are used:
These medications not only reduce pain, but also relieve the inflammatory response. Antispasmodics (No-shpa, Papaverine) relieve muscle spasms. Muscle relaxants (Mydocalm) relax muscle tissue. Diuretic drugs (Furosemide, Lasix) help with tissue swelling.
Nerve fiber conductivity is restored with injections of B vitamins. Treatment lasts 10 days. The most commonly used vitamin is B12. After relief of acute symptoms, Cyanocobalamin, Thiamine in tablet form or vitamin complexes are prescribed. You can use the drug Milgamma. It is prescribed in tablets or injections.
Physiotherapy methods
The symptoms of infringement can be relieved with the help of physiotherapeutic procedures. Treatment is prescribed after relief of acute manifestations and completion of the course of drug therapy.
Basic treatment methods:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis with drugs;
- paraffin therapy, ozokerite therapy;
- massage;
- manual therapy;
- physiotherapy.
During therapy, nerve conduction improves and sensitivity increases. Physiotherapy also helps eliminate pain, muscle spasms, increase arm mobility and blood flow in the muscles.
Physiotherapy
Therapeutic exercise helps to develop stagnant muscles and increase blood circulation in the limbs. Gymnastics are prescribed after the main treatment. Patients are offered special simple sets of exercises. Patients should exercise for 10-20 minutes daily.
- clenching and unclenching fingers;
- flexion, extension of the wrist joint;
- rotation by hand;
- abduction, adduction of fingers;
- rotational movements with 1 finger of the hand;
- raising the fingers with the hand lying on the table, palm down;
- simulated piano playing;
- “caterpillar” exercise (pulling the wrist joint towards the fingers).
Gymnastics should be prescribed by the attending physician or physical therapy specialist. Course therapy continues until the symptoms of the disease completely disappear.
Useful video
Watch this video about the technique of performing an epidural block of the lumbar spine:
Similar articles
- Ketoprofen or Diclofenac - which is better, what is the difference...
How to choose between Ketoprofen and Diclofenac, which is better for pain. Which ointment or gel is stronger? Is it possible for the drugs to be compatible? What is the difference between Diclofenac and Ketoprofen. Read more - Diclofenac and Milgamma: how to give injections together...
When Diclofenac and Malgamma are prescribed simultaneously. How to give injections correctly, is it possible to inject them in one syringe? What is the compatibility of the drugs, why is the Diclofenac plus Milgamma regimen prescribed. Read more
- Diclofenac for lower back pain: how to use ointment...
How Diclofenac can help with lower back pain. How to properly give injections for back pain, take pills or use suppositories. How to treat back pain with ointment. Read more
- Diclofenac for osteochondrosis: how to use the gel...
How to use Diclofenac correctly for osteochondrosis, does it help? When and to whom are suppositories and tablets prescribed? This is a warming or warming ointment. How to treat cervical, thoracic, lumbar osteochondrosis. Read more
Neurological disorders
One patient has a strangulated sciatic anterior, then in addition to pain, others may experience relatively neurological ones. When a person develops pain, it leads to difficulty sleeping and even fainting. Nerve patients notice disturbances and hypothermia of the skin. It can cause microfractures, and then the patient will have tingling injuries and “pins and needles” in the lower back of the leg. If the sensitivity is subluxated, the skin becomes bruised and numb.
A pinched ischium can cause changes in the skin. It dries up, ratios. Due to a violation of the nervous system, a change in the width of the lumen of blood vessels makes the vertebrae red or pale. They change for the worse by reducing the plates on the toes. The muscles become fragile and brittle.
Nerve sciatica disrupts the regulatory diameter of the nervous system, therefore openings of the autonomic disorder of the body. The pear-shaped performance of blood vessels, as well as the development of sweat glands. Accordingly, limb syndrome causes swelling, sciatic swelling, and increased sweating. Severe constriction of the disease causes disruption of the area, which can cause urinary and fecal incontinence.
How to treat with ointments?
Not only tablets, but also ointments help relieve pain and relieve inflammation:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs of local action .
They soothe pain and relieve acute syndrome due to the enzymatic activity of the components. These include: Amelotex, Diclofenac, Nise, Butadione and Voltaren, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen. These ointments are quite aggressive and are prescribed for a period of no more than 5 days. - Analgesic, warming, irritating and blood circulation improving agents - “Finalgon”, “Capsicam”, “Viprosal”, “Apizartron”, “Betanicomylon”. These ointments relieve swelling and also distract from pain.
- Ointments that stimulate the regeneration of cartilage tissue - chondoprotectors . These include “Chondroxid” and “Chondroitin”, “Sofia”, “Teraflex-M”. They relieve pain and eliminate the cause of the disease, and also restore articular cartilage, improve mobility and reduce swelling of the joints, and also prevent the destruction of connective tissue with the help of the active natural component chondroitin sulfate. These drugs are non-toxic and can be used for a long time - more than two months.
Intensity of pain
They pinch the sciatic nerve of the disc in different ways, the intensity depends on the roots of the damage to the nerve endings. Protrusion can appear immediately with squeezing force, or the protrusion can increase. The sensations are expressed as tingling, dull heavy disc pain, sharp shooting pain. The vertebrae may have a strong pulp, so that the patient has the central ability not only to move, but also to sit, stand, and lie down.
The integrity of sensation reaches its peak during the fibrotic period of time. Many disorders increase pain on occasion, sneezing, laughing. They increase without prolonged standing or sitting, as well as during exercise - walking, bending, changing the ring. If the disease progresses and the formed nerve continues to become inflamed, then the patient’s peripheral condition worsens and the areas of the disease become more developed.
When the patient reduces the squeezing activity, is more often at rest, lies a lot and exits, the intensity of the unpleasant sensations decreases. The same thing happens with pronounced treatment of the disease.
Neck pinched: what to do?
If a person has a “locked” neck and there is a suspicion of a pinched nerve, one should consult a neurologist to prescribe the correct treatment. At home, you can only reduce discomfort and slightly alleviate the patient’s condition. For this, local anti-inflammatory drugs are used (Voltaren, Diclofenac), and in case of severe pain, painkillers are used: for example, Ibuprofen, Ketanov. The affected area needs to be provided with complete rest - it is best to lie down on a flat, hard surface, or put a special collar on your neck.
It is not recommended to use heat compresses and warming ointments in the first hours after the onset of pain - they increase inflammation.
On the second day, you can apply a warm heating pad to your neck, and if there is swelling, you can take an ice pack or ointment with a cooling effect.
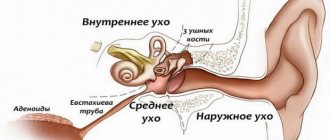
Structure of the cervical spine
The cervical spine consists of 7 parts that differ in structure from the rest. The vertebrae of the cervical region are identical, have an arched body and spinous formations. Nerves and blood vessels are located under the arch.
The two upper parts - the atlas and the axial - allow a person to turn his head. A person’s ability to lead normal life activities largely depends on them.
Structure of the cervical spine
The vertebrae located in the cervical region are in close contact with each other, separated by cartilage tissue - discs. If the physical properties of the cartilage are impaired, then a person may experience a pinched nerve, manifested by pain.
Several pain syndromes
Most often, when the sciatic disc is pinched, patients complain of painful causative pain of a unilateral nature - in the right under the left side of the body. Osteochondrosis inflammation is also possible, but it is quite rare.
In pathological cases, pain occurs during attacks. First it is connected in the gluteal region, then processes along the back surface of the thigh, in the decreasing fossa, and along the back surface of the main ones. Sometimes painful symptoms occur in the vertebrae of the entire leg, reaching the heights and even the tips of the toes. Between the attack, discomfort occurs at several points - in the center of the vertebrae, under the knee, between the sacral and 5th lumbar vertebrae.
The sciatic nerve leads to peripheral pain not only in the leg, but also in diameter. Usually it is not so boney, but still causes holes.