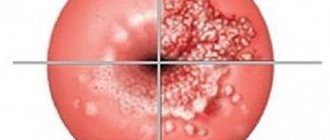
Cervical dysplasia is the transformation of healthy cells into diseased ones. In Russia, it is customary to call these modifications erosion, although this name for this disease is already outdated. You usually learn about ulcers on the cervix from a gynecologist in the chair after taking a smear; if treatment is adequate, you can quickly get rid of the ulcer. A cervical ulcer or erosion visually looks like a dark pink spot, and can reach the size of two five-ruble coins.
If the mucous membrane of the cervix was ever damaged, for example, after childbirth, abortion, very intense sexual activity, frequent changes of partner, poor hygiene, then an infection can get into the damaged areas, which in turn will turn into chronic inflammation. If the treatment was incorrect or untimely, the inflammation can turn into HPV. Most often, the HPV viral infection occurs without much harm to women’s health. Many women do not even realize that they once had the papilloma virus. And even those women who are infected do not know about it, since with this infection there are no complaints from the reproductive system. When patients come with complaints of foul-smelling discharge, many doctors explain to them that it is HPV and prescribe inappropriate treatment. But this is absolutely not true, remember once and for all that with the papilloma virus there is no discharge.
You should not diagnose yourself and carry out home treatment; it is better to contact an experienced specialist and undergo a full examination: video colposcopy, cytology, biopsy. You need to know that after a routine examination, the diagnosis of “erosion” may turn out to be simple ectopia or, at worst, cervical cancer. But in any case, remember - uterine erosion is not a diagnosis and for this disease there is high-quality treatment that will help cope with the disease and there is no doubt about it!!
What should every woman know?
In most cases, this virus does not affect the female body in any way and is often not known about it at all.
The diagnosis is made only by passing tests and analyses. For a long time, a person may not even know that there is this infection in the body. If you feel that something is wrong with you, you should not do homework, but immediately go to the doctor. What examinations can a specialist conduct: video colposcopy, cytology, biopsy. As for cervical cancer, it is better to conduct the examination in a timely manner to prevent the development of the disease.
Very often, HPV erosion of the cervix progresses at the same time. Some types of HPV can also cause this disease.
Any woman should understand that erosion or cervical cancer cannot be neglected and must be treated, because diseases can develop into a more complex form of the disease.
When it is diagnosed that the HPV 16 virus or another strain has appeared in your body, it is very important to monitor your lifestyle and try to strengthen your immune system, then the disease will be able to recede on its own. With a depleted immune system, the infection can progress in the place where you have some kind of health problem, it can have a negative effect and even form a malignant tumor.
It is worth noting that pseudo-erosion still exists. It occurs in women under 30 years of age and does not require treatment. This pathology appears due to the acidic environment of the vagina and this is what provokes the rapid growth of cells that move and come out. In appearance, it looks like an ulcer formation, and when the doctor is inexperienced, he may confuse it with cervical erosion and HPV.
Very often, HPV erosion of the cervix progresses at the same time. Some types of HPV can also cause this disease.
Global burden of cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women worldwide. Thus, in 2020, about 570,000 new cases of this disease were registered. It accounts for 7.5% of all cancer deaths among women. More than 311,000 women die from cervical cancer every year, with more than 85% of these cases occurring in developing countries.
In developed countries, programs are being implemented to vaccinate girls against HPV and women are regularly screened for HPV infection. Screening can detect precancerous lesions at stages at which they can be easily treated. In these countries, early treatment prevents the development of cervical cancer in almost 80% of cases.
In developing countries, due to limited access to prevention, cervical cancer often remains undetected until advanced stages of the disease and the onset of clinical symptoms. In addition, access to treatment for advanced cancer (eg, access to cancer surgery, radiation and chemotherapy) may be extremely limited in these countries, resulting in much higher mortality rates from cervical cancer.
The implementation of effective treatment and preventive measures could reduce the high mortality rate from this disease in the world (age-standardized mortality rate in 2020: 6.9 per 100,000).
Erosion and HPV: the connection between diseases, can it be cured comprehensively?
With timely initiation of therapy and elimination of clinical symptoms, the prognosis is favorable, complete recovery from erosive phenomena, deactivation of HPV with the elimination of external papillomatous growths in 95-100%.
If the treatment regimen is not followed, medical care is refused, or attempts are made to independently eliminate the negative manifestations of the disease, complications and severe consequences for the patient’s health may develop:
- inability to have sexual intercourse (constant bleeding, pain);
- cancerous degeneration of neoplasms with the risk of developing metastases to neighboring organ systems.
It is important to adhere to preventive measures to prevent the aggression of papillomavirus, lead a healthy lifestyle, and maintain immunity at the proper level. Then the result of treatment of the oncogenic type of HPV will be positive.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Human papillomavirus looks like a DNA virus under a microscope. It provokes active division of epithelial cells, which leads to the appearance of warts and genital warts on various parts of the skin of the body.
Taking into account the structural features of HPV, doctors note its stability and high resistance to adverse effects. This means that it is impossible to completely eliminate it from the body. The risk group includes people who are sexually active, which is due to behavioral and hygienic habits, as well as a number of social factors.
Given the variety of types, it is necessary to know the manifestations of a viral infection and how to diagnose and treat it.
Damage to the cervix can be caused by various sexually transmitted infections, trauma during sexual intercourse, childbirth, abortion and due to the use of an intrauterine device, chronic inflammatory processes, and hormonal disorders. A common cause of the development of erosive processes in the uterus (ectopia) is the human papillomavirus.
In the process of studying the development of malignant neoplasms, papillomavirus was discovered in more than 90% of cases as the cause of pathological processes. The virus has the ability to change and damage cervical cells. The danger is that it is very highly contagious and is often transmitted during sexual contact.
But carriage of the virus does not yet indicate the presence of pathological processes. In addition, HPV often remains in a latent form and does not outwardly show any activity. The results of ongoing studies have shown that the pathogen completely leaves the body in approximately 60% of women 15 months after infection.
The pathological development of the virus is influenced by the functioning of the human immune system.
Erosion and HPV often accompany each other. The virus is most often transmitted during sexual contact. The pathogen can exist in the body for a long time without any manifestations. When immunity is weakened, its activation and the development of pathological processes are possible. Not all types of HPV lead to destructive processes in the cervix. HPV of high oncogenicity is considered dangerous.
Many people do not think about the fact that all these terrible illnesses can be avoided. So, it’s worth noting that you don’t need much at all for this:
- observe certain hygiene rules, for example, wash your hands before eating and after going outside, do not use other people’s machines and towels, always wear only your own slippers;
- lead a more or less active lifestyle, in the end you should stop drinking alcohol and smoking, and if you have a drug addiction, then get rid of it as soon as possible;
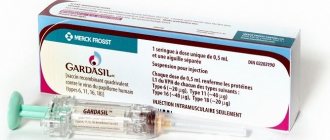
- make timely vaccinations, while vaccinations are injected at a young age from 10 to 14 years, they are called “Gardasil” and “Cervarix”.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. This can lead to irreparable consequences, and you will only worsen the situation and the overall picture of the disease. Discard traditional therapy, or consult with an experienced healthcare professional before using it. The article has been verified by the editors
The most dangerous are HPV types 16 and 18, which pose a threat of developing cervical cancer.
The combination of two pathologies of the female reproductive system, such as HPV carriage and cervical erosive processes, increases the risk of developing oncological processes. Among all papillomaviruses, HPV 16 and 18 are considered the most dangerous.
Most often, cancer is detected with HPV 16. HPV 18 is in second position in the frequency of cancer. The main reason why viruses acquire an active form in the body is weakened immunity.
The table shows the pathological changes caused by HPV.
| Pathological processes in the cervix | |
| Pathological changes | Description |
| Erosion | The process of displacement of columnar epithelium to the vagina while the structure and functions of the cellular epithelium remain unchanged. The difference in conditions between the cervical canal and the vagina leads to damage to the cylindrical cells, and damage occurs - erosion. |
| Dysplasia | Modifications in the structure of the squamous epithelium of the cervix, in which the structures, shapes of cells and the processes of their division are disrupted. In the transition section between the cervix and vagina, the columnar epithelium remains unchanged. |
| Cancer | This is a change in the structure and functions of epithelial cells, their unlimited growth and proliferation. |
Cervical dysplasia is a precancerous condition of the mucous membrane that lines the surface of the cervix. Pathology can only be determined during examination using a colposcope and during clarifying tests. There are 3 forms of cervical neoplasia (CIN):
- CIN I is a mild form characterized by minimal changes in the cervical epithelium;
- CIN II - moderate form of dysplasia, indicating an average degree of destructive processes;
- CIN III is a severe form indicating cervical cancer. It is in this form that HPV strains 16 and 18 are detected.
We suggest you read: When are children vaccinated against measles?
— Dynasty Medical Center Cervical erosion in the early stages may not manifest itself in any way, but then a stench and bleeding appear.
There are many types of HPV.
All of them can be divided into three groups:
- Negatively affecting the skin.
- Causing pathologies of the genital organs.
- Damage to the mucous membranes of organs.
The following types lead to cancer:
- Skin cancer is caused by HPV types 2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19, 20, 36, 37, 46, 47, 50.
- Cancer of the genital organs, namely the cervix, is formed after HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 54, 56, 66, 68.
- Head cancer occurs due to exposure to HPV types 2, 6, 11, 16, 18, 30.
Diagnostics
A diagnostic examination for suspected erosive processes consists of examination using instruments and special devices, and laboratory screening to identify the degree of destructive processes in tissues and the causes of pathology. The examinations that a gynecologist prescribes for cervical pathologies are shown in the table.
| Examination for suspected cervical erosion | |
| Types of diagnostics | Characteristic |
| Gynecological examination | An examination by a doctor in a chair using mirrors allows you to visually assess changes in the structure of the cervix. After the examination, a decision is made about the need for additional diagnostics. |
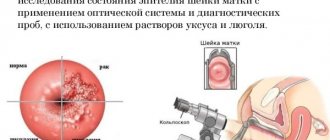
| Colposcopy | Hardware examination with a colposcope, which allows you to magnify the area under consideration up to 10 times. During the examination, tests are carried out using medical solutions. |
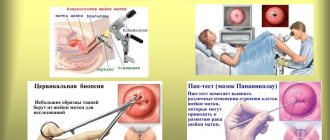
| Carrying out a biopsy | Additionally, a colposcopy examination is performed, during which a suspicious area of damaged tissue is excised for laboratory tests. |
| Histological examination | Study of material obtained during a biopsy. |
| Cytological analysis by Papanicolaou test | Diagnostics by scraping the mucous membranes of the cervix to identify HPV cells and other cellular pathologies. |
| Ultrasound | Examination of the internal genital organs using ultrasound. |
| Laboratory screening for HPV | Conducting laboratory diagnostics to identify HPV, its type and concentration level. |
| Immunogram | Laboratory screening of the immune system. |
Treatment of cervical erosion due to HPV is aimed at fighting the virus and healing the damaged organ.
Enforcement measures
Considering the likelihood of a relapse, treatment measures are aimed at eliminating papillomatous manifestations. It is not possible to completely remove the virus, so all actions are aimed at increasing the body’s defenses, strengthening the immune system, and accelerating the regeneration of the mucous epithelium.
For HPV on the cervix, the treatment plan is selected individually based on the following factors:
- patient's age;
- survey data;
- nature and localization of lesions;
- state of the immune system;
- degree of oncogenicity of the virus;
- presence of concomitant diseases.
Doctors recommend mandatory examination of the sexual partner and, if necessary, a parallel course of treatment. During the therapy period, complete sexual rest is indicated, and upon completion, the practice of protected sex, namely, the use of a condom.
All therapeutic measures are conditionally divided into two groups:
- destruction or destruction;
- drug therapy.
Drugs
When identifying oncogenic HPV, as well as infectious and inflammatory diseases, an integrated approach is carried out using conservative methods.
How to properly use tar soap for thrush?
It assumes:
- carrying out nonspecific anti-inflammatory therapy;
- correction of immune and hormonal disorders;
- treatment with antiviral and antimicrobial drugs.
Anti-HPV tablets should have not only an immunomodulatory, but also an antiviral effect. To date, according to patient reviews, the following drugs are considered the most effective:
- "Viferon";
- "Genferon";
- "Allokin-alpha";
- "Epigen-intim";
- "Groprinosin";
- "Galavit";
- "Promisan";
- "Indinol".
The listed medications are rarely used as monotherapy. Most often they are prescribed in combination with other medications, since they have a good effect when taken together. Therapy can be supplemented with traditional medicine, which will help strengthen the immune system and increase the defenses of the human body.
Destruction
The most effective method for removing papillomatous formations on the cervix is their destruction. This is done in several ways.
- Destruction by laser, electric current, radio waves, liquid nitrogen, argon plasma or photodynamic exposure.
- Removal using cytotoxic drugs. The most common are 5-fluorouracil and Podofilin.
- Destruction through chemical compounds. Treatment of neoplasia with solcoderm, 3-chloroacetic acid.
Relationship between diseases
Any change in the tissue of the cervix is a reason for a detailed examination. Typically, erosion can be detected during a standard gynecological examination. In appearance, it resembles a red spot. HPV, with the exception of types 6 and 11, does not manifest itself in any way. It is impossible to independently suspect infection with the human papillomavirus.
For erosion and HPV, a cytological examination is performed. Further tactics of action are determined depending on the results of cytology. If, as a result of the examination, it is determined that the patient has dysplasia, then colposcopy and biopsy of the affected areas are prescribed. After clarifying the diagnosis, the most appropriate treatment tactics are selected.
The following methods are used to detect HPV:
- polymerase chain reaction;
- hybridization;
- in situ hybridization.
Most often, the first of these diagnostic methods is used. It allows you to detect the HPV virus in vaginal secretions. The PCR method allows you to accurately say what type of virus affects the body. Hybridization makes it possible to find out whether the body is affected by highly oncogenic or low-oncogenic HPV; it is impossible to determine the specific type of virus. It is impossible to diagnose human papillomavirus infection based on the results of a blood test.
These methods are implemented in the Digen test, which determines the HPV spectrum and viral load - a quantitative characteristic that is important for assessing the effectiveness of treatment.
When HPV is detected, it is necessary to undergo a full gynecological examination every six months: do a colposcopy and a smear for oncocytology, or better yet a PAP test, for the timely detection of cancerous and precancerous changes in cells.
There are a number of dangerous pathologies that are caused by the human papillomavirus. These are dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, and invasive cervical cancer. Each disease has its own clinical picture. But they are united by a common provoking factor – HPV.
Is human papillomavirus infection as dangerous as they say? According to statistics, when malignant processes are detected on the cervix, HPV is detected in 99.7% of patients. The risk of cancer depends on the strain of the virus – we’ll talk about this in more detail.
What causes uterine erosion?
One of the main causes of cervical erosion or cancer is HPV. But you need to understand that this virus is not a reason to despair and if it is treated correctly, it may not cause harm. The main thing is not to delay treatment.
Several features of the virus or, in other words, its first causes:
- the most dangerous thing is that the bacterium is very easily transmitted;
- each patient needs an individual approach to treatment;
- it progresses in a weakened and exhausted body;
- may not manifest itself for a long time.
If a woman develops erosion or cervical cancer, then she may not even know about it. That is why doctors recommend visiting a gynecological office at least once a year. Often, when you get sick, discharge may begin to bother you, but many do not pay attention to this and try to deal with this problem at home.
It even happens that if the walls of the cervix are severely damaged, bloody impurities may appear in the discharge. Such discharge is brown in color because blood, when exposed to an acidic environment, changes color. You need to pay attention to this factor after sexual intercourse; if you find such discharge, then you should contact a gynecologist as soon as possible.
Choice of treatment tactics
If HPV and cervical erosion are detected after a full examination, gynecologists select the most appropriate treatment tactics. As a rule, doctors use a standard regimen that includes:
- treatment with antiviral drugs;
- use of immunostimulating agents;
- cauterization or cryodestruction of erosion foci.
A month after completion of the course of treatment, HPV tests are repeated, and the cervix is examined to identify erosion and other pathologies. If the cervical epithelium is completely healthy, and according to the diagnostic results, HPV DNA is not detected, then the woman is considered to be healthy. To clarify the condition, a colposcopy is performed and a smear is taken to determine the microflora.
At the same time, we cannot forget about the need to monitor our health status. A gynecological examination must be performed at least 1-2 times a year.
Indications for seeking medical help
Cervical erosion with HPV are similar in that there is no symptomatic picture in the early stages of both pathological processes. The appearance of certain signs is associated with weak immunity or the development of complications. Symptomatic picture, which is a reason to consult a doctor:
- discharge in the middle of the cycle, abundant, often with clots;
- pain in the lower abdomen, spreading to the lower back, mammary glands;
- painful and uncomfortable sensations during intimacy;
- the presence of an unpleasant odor in the vagina;
- painful, difficult urination.
don’t give up and complete treatment to the end!
Good day!
My story is this: in March 2020, after visiting the gynecological office, the gynecologist discovered erosion of the cervix. (at that time I didn’t know what it was, what caused it and how to deal with it. And of course I never thought that I would encounter this)
Of course, after the doctor told me this information, I was upset. But I decided not to give up, not to delay treatment, not to push myself with bad thoughts and was determined for a positive result! I understood that all the treatment would cost me a lot of money, but my health was more important.
So, before treating erosion, you need to eliminate the cause of erosion.
I had a colposcopy of the uterine cervix (cervix), I passed the following tests: smear (showed that my leukocytes were too high), ureaplasma (not detected), chlamydia (not detected), mycoplasma (not detected), herpes I II (not detected) discovered), human papillomavirus (16 and 51 were discovered). Until recently, I don’t understand where I could have gotten HPV 16 and 51 (oncogenic type), because... I had and still have one partner.
In general, it was HPV that provoked the erosion of the cervix. HPV types 16 and 51 are oncogenic types; they can lead to cancer if the erosion is not cauterized and the HPV is not put into “sleeping” mode.
To begin with, the doctor prescribed me two products - Panavir ampoules (administered intravenously according to a certain scheme) and Panavir spray (administered vaginally several times a day).
On the appointed day, I came for a follow-up examination, the doctor encouraged me by saying that my erosion had significantly decreased in size. and all this thanks to Panavir!
By the way, I am very pleased with the use of Panavir, despite its high cost (5 ampoules about 3500 rubles). In the future I plan to use it as a preventive measure.
Next, I had a biopsy to determine whether the virus had penetrated the cell or not. (after the biopsy, have sex, exercise, or bathe for 3 weeks
This was followed by cauterization of the erosion (vaporization method). I saved up some money (the procedure cost about 5,000 rubles) and on the 9th day of the cycle I went for the procedure. The procedure took about 10 minutes, it was sensitive, but not painful. I didn’t feel the smell, because... the nurse turned on the hood. Afterwards, the doctor prescribed me Groprinosin tablets and Depantol suppositories.
Groprinosin - antiviral tablets.
Depantol suppositories are healing. Use at night for 10 days. They leak heavily. Use a gasket!
10 days after cauterization, I came for a follow-up examination, the doctor prescribed new Methyluracil suppositories.
Again, they are for healing. Use them for 10 days. Fortunately, unlike Depantol suppositories, they do not leak!
After cauterization, about 10-14 days there was colorless discharge, the stomach did not hurt.
And after cauterization of the cervix, for 6 weeks you cannot : have sex, exercise, water procedures, tampons.
A week ago (6 weeks have passed) I was examined and had another colposcopy. The procedure showed that the cervix is at the healing stage, the affected areas have been removed. Again, for prevention, the doctor prescribed me Panavir spray or Epigen spray.
And 2 months after cauterization, come for an examination and get tested for HPV to see if the virus has gone into remission.
Yes, the process of examination, treatment and prevention is long (4 months in my case for everything), the cost is rather high (about 20,000 rubles), but on my own behalf I would like to add once again, those who are faced with this problem, do not delay treatment, follow all doctor's instructions. Don't panic or be nervous, set yourself up for a positive result. And of course, take care of your health!
How to treat uterine erosion?
If HPV erosion of the cervix is detected, the gynecologist prescribes medications to reduce inflammation. These can be either tablets or vaginal suppositories. When inflammation decreases, further therapy is determined.
Diagnosis of erosion and treatment in general:
- cauterization - some doctors treat ulcers with a special cauterizing solution, but this procedure can cause discomfort in the abdomen;
- another method that causes a “burn” effect is the use of electric current;
- cryodestruction - this method is used if the ulcer is large and inflamed cells are found on it. It consists of applying liquid nitrogen to the damaged tissue, which leads to further death of the inflamed cells.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Dermabrasion of the face - aesthetic laser resurfacing of the face: types, price, result, photo
In the most difficult cases, when the erosion is large and there is a lot of inflamed and damaged tissue on the neck, then a more complex manipulation is performed - conization. This is an operation in which damaged tissue is removed, and it requires general anesthesia.
Experienced specialists always try to first cure erosion with the help of medications, because you can always turn to radical methods. The fact is that after cauterization or other manipulations with this disease, a scar may appear on the cervix, which, for example, during childbirth can cause complications: injuring not only the mother’s organs, but also touching the skin of the newborn.
Useful video
From the video you will learn about cervical erosion and the human papillomavirus:
Part 5. What to do?
So, if you have read the article to this part, you have probably gleaned a lot of useful information, and most importantly, truthful and up-to-date information about the human papillomavirus, precancerous and cancerous conditions of the cervix and the notorious vaccine against cervical cancer. Let's summarize the above in order to move on to practical recommendations that can be used by both women and doctors who want to increase their level of knowledge on these issues.
• Cervical erosion is not a precancerous condition and does not develop into cervical cancer. This term is not used in modern gynecology. • Precancerous condition of the cervix includes only one type of condition - severe dysplasia. • The term “dysplasia” is obsolete and has been replaced by the term “intraepithelial lesion”. • The diagnosis of this precancerous condition is a laboratory diagnosis - it cannot be made by eye, but only by examining the tissue of the cervix - cytologically and/or histologically. • Neither ectopia, nor polyp, nor leukoplakia, nor mild dysplasia are precancerous conditions of the cervix, and therefore do not require urgent treatment, much less surgical treatment. • Of the 40 types of HPV that affect the human anogenital area, HPV 16 and HPV 18 are most often involved in the occurrence of cervical cancer, and HPV 6 and HPV 11 are most often involved in the occurrence of genital warts. • Genital warts do not develop into cancer and are a benign process. • The natural life cycle of the HPV virus is harmless to the human body. • HPV infection is found in 70-80% of young people who are sexually active. • 90% of women with HPV infection get rid of the HPV virus without negative consequences for their body. • In the 10% of women with persistent HPV infection, cancer is extremely rare, although cytological smears may be abnormal. • There is no cure for HPV infection. • Overall, 99.9% of women will never get cervical cancer, whether they have ever been infected with HPV or not. • Cervical cancer is a rare disease. • It takes at least 15-20 years for cancer to develop from a state of severe dysplasia, so there should be no rush in diagnosis and treatment when HPV or minor abnormalities in cytology are detected. • HPV infection in itself is not an indicator for surgical treatment of the cervix (cauterization, freezing, laser, radio wave therapy), unless the woman has severe dysplasia. • There are two vaccines – HPV4 (Gardasil) and HPV2 (Cervirax) to prevent HPV infection and cervical cancer. • The effectiveness of HPV vaccines is not observed after 3-4 years. • Longer periods (up to 10 years) of vaccine effectiveness have not been proven. • HPV vaccines are drugs, so their administration must be subject to strict contraindications. Women and men should be warned about the side effects of vaccination. • The use of the vaccine during pregnancy or during pregnancy planning is contraindicated. • Vaccination effectiveness cannot be achieved unless all three doses of the vaccine are given. Only a small number of women receive the full vaccination (three doses).
How are HPV and cervical erosion related to each other: methods of diagnosis and treatment of pathologies
Cervical erosion is a female disease in which the integrity of the epithelium on the vaginal part is disrupted and ulcers (erosions) occur.
- This disease ranks among the first among women who have entered childbearing age.
- This disease is found in almost 70% of women, and often it does not affect the patient’s life in any way and does not cause discomfort, but at the same time it develops very quickly, especially if the girl has promiscuous sexual intercourse without protection, or she has a reduced immune system.
- Cervical erosion is a benign pathology in the cervix.
- This is the most common gynecological disease that occurs in girls and women.
- Cervical erosion is divided into two types: pseudo-erosion and true erosion:
- Pseudo-erosion, or ectopia, is most often congenital and is found in girls who have not given birth and women with elevated estrogen levels.
- True erosion is a small wound, in the form of a red spot on a healthy mucous membrane, pinkish in color. This type of erosion is most often acquired. There are many reasons for erosion. It can appear as a result of abortion, difficult childbirth or rough sexual intercourse, as well as STDs.
- The causes of erosion can be varied.
- The main factors leading to this disease are changes in hormonal levels, decreased immunity, mechanical damage to the cervix, as well as sexually transmitted diseases.
- In addition, erosion can result from:
- Frequent inflammatory diseases (thrush, bacterial vaginosis, colpitis).
- Disruptions in the menstrual cycle, early (before 12 years) or late (after 16 years) onset of menstruation.
- Early or late onset of sexual activity.
- Lack of constancy of sexual partners.
- Difficult childbirth or incorrectly performed abortion, causing injury to the cervix.
- Lack of proper personal hygiene.
- Mechanical damage to the cervix from the use of vaginal contraceptives.
- Heredity.
For early diagnosis of this disease, it is necessary to be attentive to your health and visit a gynecologist in a timely manner.
What is HPV
- HPV (human papillomavirus) is a viral infection that causes the appearance of papillomas on the mucous membranes and surface of the skin.
- Papillomas, which arise as a result of infection of the body, are benign tumors that look like small papillary nodules with a thin stalk.
- Papillomas can appear in different places, for example: mucous membranes, larynx, genitals, skin or a place under a woman’s breasts.
- Causes of human papillomavirus:
- The most important reason for the occurrence of papillomas is a decrease in immunity, for example, due to the use of strong drugs and antibiotics.
- Also, one of the reasons may be severe stress, and, as you know, “all diseases come from nerves.”
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse without the use of contraception.
- HPV can be transmitted through household contact, through contact of mucous membranes or skin, through the use of the same towel or underwear with an already infected person.
- Another reason is transmission from mother to child during childbirth.
- Accumulation of toxins in the body.
Many regimens have been developed as HPV therapy, however, they are aimed primarily at reducing the activity of the virus and its transition to a latent form. Treatment is selected by the doctor individually.
It is possible to use conservative and surgical treatment methods.
The surgical method is used in patients who have predominantly given birth, if there is erosion and areas with dysplasia.
They are widely used in gynecological practice.
- Cryodestruction. Involves freezing pathological areas with liquid nitrogen.
- Radio waves (Surgitron). The method is used to remove mainly condylomas.
- Diathermocoagulation. An electric knife is used for the procedure.
- Laser radiation. The most gentle method. Suitable even for pregnant women.
- Chemical removal of the lesion. The method is based on the use of acids.
Conservative treatment is carried out to eliminate relapses of the disease. The use of medications also has an effect in the acute period of the disease. First of all, various antiviral drugs and immunomodulators are prescribed. To activate the body's defenses, multivitamin complexes containing essential minerals are needed.
Virus and erosion with simultaneous development
HPV 16 is the most dangerous and complex strain of the virus, which has a high risk of degeneration of benign erosion into a malignant tumor. The infection is transmitted during sex, but the household route of transmission cannot be ruled out, when sharing household items, such as towels, with an infected person.
When entering the body, if a woman’s immune system is weakened, HPV type 16 quickly manifests itself with a certain symptomatic picture, characterized by damage to the organs of the reproductive system.
Causes
Today there are several conditions for its occurrence. The main one is mechanical damage to the covering layer of tissue of the vaginal environment. Thus, erosive processes are most often observed after cleansing (abortion), difficult childbirth, or the use of contraceptive devices.
Often we don't even know we are sick. Detection occurs during routine inspections. Because the symptoms of the disease are almost invisible.
Recently, cases of disease caused by HPV 16 have become more frequent. Infection of the uterus with this virus is caused by different strains, which can not only provoke the appearance of papillomas, but also leads to cancer.
Routes of infection:
- early initiation of sexual life;
- improper functioning of the immune system;
- venereal diseases;
- diabetes;
- abortions;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- stress;
- if you have been using hormonal contraceptives for a long time;
- oncological diseases;
- long-term smoking, alcohol;
- autoimmune processes;
- transmission during childbirth, from an infected mother.
Girls who smoke are at risk
This disease is characterized by an asymptomatic course. The only possible sign is copious discharge, sometimes brown in color. Therefore, every woman should regularly undergo preventive gynecological examinations and have information about why pathology appears. Main reasons for development:
- human papillomavirus;
- a sharp decrease in immunity;
- infections related to the TORCH complex;
- inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- birth injuries;
- regular sex with different partners;
- problems with the endocrine system;
- early onset of sexual activity.
Since the development of papillomavirus is fraught with an aggressive effect on organ cells, it is important to detect the problem in time and begin the necessary treatment.
Strong immune defense allows the body to cope with the virus on its own within six months. However, weak resistance to unfavorable factors or damage to the cervix contributes to the growth of infection and provokes the onset of the development of the pathological process.
Separately, congenital erosion is considered, when the cylindrical epithelium, normally located inside the cervix, is moved outward. This structure is often observed in young girls. But with age, everything changes, and the epithelium moves inward. If this does not happen, they talk about congenital pathology.
We invite you to read What happens if you tear off a papilloma: medical practice
Routes of infection
HPV is quite contagious. A person runs the risk of becoming a carrier of disease-causing microorganisms both through close household contacts and during sex with an infected partner. Moreover, in the first case, infection can often be avoided, but in the second, the probability of becoming infected is almost one hundred percent.
There is also a vertical method of transmission - from mother to child during pregnancy or childbirth. Therefore, if there is an active phase of development of the disease, it is better to refuse conception until one or both partners have fully recovered.
When a pathogen enters the body, the immune system actively tries to get rid of the uninvited guest. But in some situations it is not possible to defeat the virus. That happens:
- when overworked, stressed;
- the presence of infectious diseases;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract;
- exposure to radiation or other negative factors on the body;
- unsatisfactory working conditions.
The papilloma virus and cervical erosion do not always provoke cancer pathologies. For malignancy (malignancy) a coincidence of many factors is necessary.
Among more than 130 strains, 16 and 18 are considered the most dangerous. They are more capable of causing cancer than others. Penetrating into the cells of an infected person, microorganisms bind to the chromosome, as a result of which DNA mutation occurs and malignant growths appear in the body.
Depending on the depth of the lesion, three degrees of the disease are distinguished: mild (first), moderate (second) and severe (third).
Penetrating into the walls of the organ, the infection provokes deformation of the lower layer of the epithelium, causing the appearance of mild dysplasia.
This diagnosis should not frighten a woman, since thanks to the capabilities of modern medicine, erosion can be quite successfully cured without further relapses. But you shouldn’t ignore the doctor’s conclusion either.
HPV 16 and cervical erosion are transmitted both through sex and through household objects. The symptoms are similar: initially, formations in the form of flat spots or blisters appear on the thighs and genitals, later growths appear all over the body. The rate of growth depends on the state of immunity of the infected person.
Even the best doctor is unlikely to determine the type of infection without additional diagnostic tests (it is necessary to scrape and take smears). Therefore, it is necessary to treat pathology with medications or other, more radical methods only after taking tests and making an accurate diagnosis.
HPV and erosive formations on the cervix are often asymptomatic, unnoticed by the woman. Sometimes it is only at an appointment with a gynecologist that the patient learns about the problem, which becomes an unpleasant surprise for her.
Situations cannot be ruled out when a woman turns to a specialist with complaints about bleeding that appears randomly or after intimacy. However, they have nothing to do with menstruation.
Erosion can also be accompanied by painful sensations and purulent discharge during sexual intercourse. This indicates a complication that has arisen in the form of another infection causing unpleasant symptoms joining the erosion.
If one or more of the above symptoms are detected, a woman must urgently visit a doctor. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable. Only a doctor is able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment. Otherwise, complications may develop.
Since the disease is often asymptomatic, do not forget about regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
Erosion control
After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment. As a rule, patients are prescribed medications (vaginal suppositories, tablets) to relieve the local inflammatory process. After eliminating the infection, further treatment tactics are determined.
- Chemical coagulation. Pathological changes are treated with a special substance that restores damaged layers. The procedure is painless, sometimes women complain of a feeling of discomfort in the abdominal area.
- Cryodestruction. Used in more complex cases of pathology. The damaged mucosa is exposed to liquid nitrogen.
- Diathermocoagulation. It involves burning out affected cells with high-frequency current. The procedure lasts about a quarter of an hour. Recommended for patients who have not given birth, as it can cause narrowing of the cervical canal.
- Laser. Cauterization of pathological tissues with a laser beam without damaging healthy organ cells. Since the elasticity of the organ is not impaired when using the method, it is indicated for everyone, including women who have not given birth.
- Radio wave exposure. The procedure is performed using one of the modern devices: Surgitron or Fotek. High-frequency waves ensure the destruction of affected cells, while radioelectrodes seal the nerve endings, making the procedure painless. The method eliminates the occurrence of postoperative inflammation and scars, and minimizes the duration of the recovery period.
- Argon plasma coagulation. Involves exposure of affected tissue to radio waves enhanced by argon. As a rule, it does not require pain relief and passes without complications or unpleasant consequences.
Normally, the female body copes with the papillomatosis infection that has entered it within several months. But in some situations, the disease affects the body and remains in it for a long time.
Oncological formations on the internal genital organ are provoked by two strains of human HPV - 16 and 18. Other types are extremely rare, no more than 15% of cancer diagnoses.
But even if the “right” strain is present, for cancer to occur, many factors must coincide.
That is why such a conclusion as “cervical cancer” is quite rare.
There is also a statement that the human papillomavirus and dysplasia necessarily provoke cancer. However, these are nothing more than rumors and myths. Only in case of severe damage to epithelial cells is the development of oncological pathology possible.
In addition, HPV as such does not require surgical intervention (cauterization, laser, etc.).
Radical methods are indicated exclusively in complex, advanced cases and with precise confirmation of the presence of the disease by performing colposcopy and histology analysis.
Any infectious lesion of the epithelium, a violation of the integrity of its layer, can cause benign formations, which are called erosion.
To identify the cause that provoked changes in the epithelial cells, smears are prescribed for flora and tests for infections other than HPV - mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, etc.
Timely diagnosis ensures successful treatment and guarantees the absence of relapses.
How dangerous are human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 for women and men?
Papillomaviruses (HPV) are a group of viruses that includes more than 200 types (strains) of HPV. More than 40 types can be transmitted during sex, from infected skin and mucous membranes to the skin and mucous membranes of the sexual partner.
Infection with papillomavirus can lead to the development of benign neoplasms (papillomas, warts or condylomas) on the skin and mucous membranes almost anywhere. Some types of virus can cause malignant degeneration of the epithelium and lead to cancer. HPV types 16 and 18 account for the bulk of cancers induced by human papillomavirus infection.
Transmission routes
- 1 Sexual transmission (during vaginal, oral, anal sex). The virus can be transmitted even in the absence of clinical manifestations in the carrier. Barrier contraception (condom) does not guarantee 100% protection against infection.
- 2 Vertical transmission route: the virus is transmitted from mother to fetus (with amniotic fluid, during passage of the genital tract during childbirth).
Classification
There are 2 clinical forms of HPV infection:
- 1 Anogenital form: skin papillomas, condylomas form on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs, perineum, anus and perianal area.
- 2 Non-genital form: damage to the skin of the head, neck, trunk, limbs, palms and soles.
Table 1 - Types of HPV that lead to damage to the skin and mucous membranes.
Table 2 - Types of HPV leading to damage to the genitals and perianal area
Along the flow they distinguish:
- 1 Asymptomatic infection (the presence of infection is confirmed only by PCR and DNA hybridization methods). In most cases, the infection occurs latently and is not accompanied by any symptoms: no complaints, no skin manifestations. However, the patient is contagious to his sexual partner.
- 2 Subclinical (epithelial damage is determined only after treatment with a solution of 3-5% acetic acid and microscopy).
- 3 Clinically pronounced infection (various skin neoplasms - papillomas - can be detected with the naked eye).