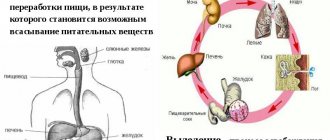
Causes
Abdominal cramps can occur under various pathological conditions. The most common are:
- Increased gas formation. Typically, the deviation develops when the diet is violated (consuming large amounts of legumes, cabbage, juices and carbonated drinks). The increasing volume of air in the intestines causes overstrain and stretching of the smooth muscles, which, trying to return to their original position, contract.
- Impaired movement of feces. With constipation, food particles accumulate in separate parts of the large and small intestines and put significant pressure on its walls. Increased afferent impulses cause muscle contraction. With diarrhea, the mechanism is reversed - significant secretion of fluid into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract promotes hypermotility, which manifests itself externally as spastic pain.
- Stress and neuropsychic disorders. Against the background of these conditions, discoordination of the activity of the central nervous system develops. As a result, inadequate efferent impulses to various parts of the gastrointestinal tract occur.
- Acute inflammatory processes. The affected intestinal wall reacts reactively to the movement of feces and the muscles contract.
- Renal colic. Any disorders of the kidneys can excite local pain receptors (in the ureters, bladder, pyelocaliceal system). Due to the irradiation of excitation, muscle cells contract.
- Uterine disorder. The reproductive organ is a large muscle in our body. With various pathologies (from neoplasms to menstrual irregularities and infections), spasms of the intestines and abdomen may occur.
- Spasms of the sphincters (esophageal, Oddi) and cystic ducts. In pathologies, usually caused by dysregulation and the appearance of hyperplastic processes, “muscle valves” begin to work inadequately, which is expressed by pain.
- Gastric colic. The presence of open lesions of the organ leads to the fact that gastric juice irritates the stomach wall and causes sharp pain, in response to which the stomach wall contracts.
- Changes in normal intestinal microflora. The growth of opportunistic and pathogenic microflora contributes to the development of inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane, and their toxins cause spasms and contractions of the smooth muscles of the abdomen.
When is this considered normal?
The main cause of pain is the increased release of oxytocin into the blood, which is responsible for uterine contractions and breast milk production. The opening of the cervix is necessary to expel the fetus, and after the placenta is separated, the vessels of the uterine walls bleed heavily. Activation of platelets is not enough for hemostasis, so the body provides increased production of the hormone. This helps stop the bleeding, but causes a feeling of cramping pain in the abdomen. Its intensity weakens towards the end of the first week after birth. In multiparous women, the period lasts longer, since the tone of the uterus is weaker.
There are a number of physiological reasons when the lower abdomen hurts a week after childbirth:
- Lactation. When the baby sucks, stimulation of the nipples occurs, which is accompanied by the production of oxytocin. With each feeding, the uterus contracts, which causes increased pain.
- Divergence of the pelvic bones caused by the passage of a large child through the birth canal. The woman does not immediately experience discomfort due to the production of relaxin, but after a while pain occurs in the lower abdomen and pubic area.
- A full bladder that puts pressure on the uterus. The presence of cracks and other damage to the birth canal additionally provokes a burning sensation when urinating.
- Tissue and muscle ruptures. After stitches are placed, the stomach hurts until they heal, about 10–14 days.
If the birth took place by cesarean section, then the discomfort is due to the presence of a scar on the uterus. The stomach will hurt for 2-3 months until complete healing. It is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations - do not lift heavy objects, treat the suture area in a timely manner. To relieve severe pain, analgesics are used, which in small doses do not pose a threat to the child.
Types of spasms
Depending on the number of areas involved, pain can be:
- limited (no more than 1 square abdomen);
- widespread (2 or more quadrants).
Depending on the duration:
- periodic (quickly arise and stop);
- constant (pursues all the time).
According to the severity of pain there are:
- low intensity;
- medium intensity;
- expressed.
Painful sensations, in some cases, can disrupt a person’s normal functioning (inability to change body position, move, etc.) Accordingly, spasms can be:
- with impaired functioning;
- without disruption of life.
There are also:
- with irradiation;
- without irradiation.
Irradiation is the spread of pain beyond the affected segment due to the close proximity of nerve fibers innervating different parts of the body.
How does a woman feel before giving birth?
Each expectant mother feels the approach of the birth process in her own way, but there are also typical signs, for example, nagging pain in the lower abdomen. This is how false contractions manifest themselves, which are provided by nature in order to prepare the body for delivery. During training contractions, the stomach may become hard, which worries the woman, but if there is no discharge, the expectant mother can be sure that everything is in order. Secondary women may not have false contractions.
The most powerful and unusual sensations, especially during the first birth, may be the day before the long-awaited moment:
- loss of appetite;
- anxiety appears;
- suffers from insomnia;
- repetition of false contractions becomes more frequent;
- Sometimes diarrhea begins and nausea appears.
If the frequency of repetitions of pain attacks has decreased to 10 - 20 minutes, in the intervals between contractions the uterus instantly relaxes, and the pain has become pressing - this is the beginning of labor. The water may break before or after the above symptoms appear.
Possible diseases and symptoms
The reasons leading to abdominal cramps are many, the most common ones are presented in the table.
| Name of pathology | Clinical picture |
| Acute intestinal infection, toxic infections | Spastic pain - in the initial stages. Then nausea and vomiting follow. The pain becomes constant and becomes acute. Possible fever and dehydration |
| Acute appendicitis | In the initial stages, spasms are observed in the epigastric region. Then they gradually descend into the iliac region of the abdomen on the right and are replaced by aching, dull or sharp. Body temperature rises. |
| Malignant and benign neoplasms | In the initial stages, rare spasms occur in one part of the intestine. As the tumor grows, its frequency, strength and duration increases. In the later stages, the pain is dull and aching. There may be intestinal bleeding (stool turns black), fever (up to 37-37.5 degrees), cachexia (weight loss). |
| Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum | Pain may occur in the stomach area 30-90 minutes after eating food. If absorption processes are disrupted, intestinal motility changes - pain in any part of the abdomen. |
| Nephroptosis, urolithiasis, pyelonephritis | Spasms can be in the right and left parts of the abdomen, as well as in the lumbar region. Less often - all over the abdomen or encircling. If infected, there is a rise in body temperature, symptoms of intoxication (weakness, headache). After the attack, the spasms stop |
| Miscarriage, uterine bleeding, heavy menstruation | Against the background of incoordination of contractions of different parts of the uterus, painful sensations arise that can spread to the entire abdomen. |
| Dysbacteriosis | Against the background of constant diffuse dull pain of low intensity, sharp and strong spasms occur in the lower abdomen, which stop after a few minutes. May experience: diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, heartburn. |
| Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction | Abdominal pain in the right hypochondrium occurs periodically. Accompanied by bitterness in the mouth, nausea and vomiting. |
| Gastroesophageal reflux | After eating, gastric contents are thrown into the esophagus. Against the background of irritation, its walls contract. Spasms are localized behind the sternum, in the epigastrium and in the navel area. |
| Psychogenic disorders (stress, depression, psychasthenia) | In addition to mental disorders, there may be short-term spasms and pain in any part of the abdomen, followed by constipation or diarrhea. |
Severe colic in the lower abdomen in women - causes
Colic in the lower abdomen is always a rather frightening sign, although the problem in some cases may spontaneously resolve on its own, for example, pain from bloating due to the accumulation of gases in it (although there can be many reasons for a bloated abdomen in women).
However, it also happens that spasms and pain are a symptom of a more serious illness that requires seeing a doctor. The main causes of severe colic in women are often the following:
Spikes
Adhesions are bands of scar tissue that form between internal tissues and organs in women, often as a result of surgery or infections such as pelvic inflammatory disease. There is disagreement as to whether adhesions can cause pain or colic. It has been suggested that when adhesions interfere with the normal movement of internal organs such as the intestines, severe colic in the lower abdomen occurs from time to time.
Endometriosis
This condition occurs when tissue that normally grows inside the uterus grows somewhere else in the body, usually in other parts of the pelvis, such as the outside of the uterus, ovaries, or fallopian tubes. The two most common symptoms of endometriosis are pain and infertility. It occurs mainly in women of childbearing age, but there are also many cases of endometriosis in women over 40 years of age.
Interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome
This syndrome is associated with pain in the bladder area and the need to urinate frequently and urgently. The pain may appear as colic in the bladder or in the opening where urine comes out (the urethra), and there is often relief after emptying the bladder. Often found in women with endometriosis.
Irritable bowel syndrome
The exact cause is not known today, but it is believed that the muscle wall of the intestines becomes sensitive and contracts unevenly, leading to pain and bloating. This type of colic improves after passing gas or stool and is often resolved by avoiding possible triggers—certain foods—and reducing stress.
Pelvic floor disorders
Occurs when the muscles and connective tissues that hold the pelvic organs in place become weak or injured (for example, during childbirth).
These organs include the uterus, bladder, and rectum. Pelvic floor disorders can cause both discomfort and functional problems, such as uncontrollable loss of urine (urinary incontinence) or bowel movements (fecal incontinence). In pelvic floor disorders, pain can also be caused by colic or increased muscle tone. The pain can be sharp, stabbing pain in the vagina or rectum, occurs during sex or when using tampons, and is often worsened by exercise, especially Pilates and squats.
Uterine fibroids
Fibroids are growths of muscle cells in the wall of the uterus. These non-cancerous tumors can cause heavy, irregular or painful periods and local pressure symptoms, including cramps and frequent urination, problems with bowel movements and lower back pain.
Vulvodynia
This condition involves pain or discomfort of the vulva (external female genitalia), especially during sexual intercourse. The pain can range from acute colic to burning and itching. Despite the fact that this type of pain is located outside the abdomen, it can also radiate to its area.
Diagnostics
The first auxiliary sign indicating the affected organ is the localization of pain. Then the doctor begins palpation (the affected organs are painful) and auscultation (listening to the sounds of mass movement through the intestines). To accurately determine the causes of pain, additional research methods are prescribed:
- General blood analysis. With inflammation, ESR and leukocyte levels increase. An increase in the number of neutrophils will indicate a bacterial etiology, and an increase in the number of lymphocytes will indicate a viral etiology. In the presence of bleeding, the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin decreases.
- General urine analysis. An increase in leukocytes, red blood cells, and casts in the urine is a sign of an inflammatory process in the urinary system.
- Fecal occult blood test. The test is aimed at detecting minor bleeding.
- Blood chemistry. The contents of amylase and lipase (increase with damage to the pancreas), AST and ALT (indicators of liver destruction), bilirubin (concentration changes with pathology of the gallbladder and biliary tract) are assessed.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Using ultrasound, the condition of parenchymal organs (kidneys, liver, spleen, pancreas) is assessed.
- Survey radiography of the abdominal organs. The method detects gas accumulation (in case of perforation of an ulcer), intestinal obstruction (for example, in case of tumors), and the presence of fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity (in case of bleeding or heart failure).
- FGDS. A flexible endoscope with a camera inserted into the stomach allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
- Colonoscopy. The procedure is similar to FGD, but the probe is inserted through the anus and the rectum and colon are visualized.
- CT and MRI are the most informative methods. Allows you to assess the nature of the lesion with millimeter accuracy.
Colorectal cancer detected by colonoscopy
How to get rid of pain
To relieve mild menstrual pain and “contractions” of moderate intensity, the advice of our grandmothers is quite suitable:
- a warm heating pad placed on the lower abdomen;
- warming shower;
- circular massaging movements in the navel area.
See also: Right or left side hurts before menstruation
Drugs prescribed as an antispasmodic or analgesic also help (popular ones include No-Shpa, Ketanov, Baralgin). Hormonal agents regulate the cycle, stabilize the balance of hormones, minimize the risk of pathologies, and reduce the incidence of painful menstruation.
It is imperative to return critical days to normal, but this should be done after a preliminary medical diagnosis. When the presence of pathologies is excluded, but menstruation still deprives you of a full life, it is recommended to reconsider your lifestyle:
- Quit smoking and alcohol.
- 3-4 days before the start of your period, exclude coffee, fatty, spicy foods, pastries and sweets from your diet.
- Regularly perform exercises to strengthen the abdominal and pelvic muscles.
- Move actively, regardless of your menstrual period, take long walks in the fresh air every day.
- Give priority in nutrition to protein and plant foods.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Minimize excessive physical activity.
- Protect yourself from stress and shock.
Many women also note that yoga asanas, which allow maximum relaxation, are very effective remedies for menstrual pain.
Drugs: method of use and mechanism of action
The main drugs used for spastic pain are:
| Name of the medicine | Indications | Mechanism of action | Mode of application |
| Atropine, Platifilin | Acute inflammatory diseases of the upper intestines, pancreas and biliary tract, renal colic. | They block M-cholinergic receptors, preventing the conduction of impulses. | To eliminate an attack - 1 ml intramuscularly. |
| Mebeverine | Inflammatory bowel disease, functional dyspepsia. | Blocks smooth muscle sodium channels, causing membrane depolarization and impaired contraction | Take 1 tablet orally in the morning and evening. |
| Otilonium bromide | Motor disorders of the gastrointestinal tract due to peptic ulcer disease, tumors. | Disturbs the passage of calcium ions from the intercellular space into myocytes, as a result the cells do not contract | Orally 1 tablet 1 time per day |
| Drotaverine, Papaverine, No-Shpa. | Urolithiasis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, dyskinesia of the gallbladder. | Suppresses the activity of the enzyme - phosphidediesterase, which is involved in the contraction of smooth muscle cells | 1 tablet 3 times a day |
| Phenobarbital | Severe spastic pain of any location and etiology. | Affects the autonomic centers of the brain, causing a general anticonvulsant effect (relaxation of all muscles). | 1 tablet (100 mg) up to 3 times a day |
How many days before giving birth can your stomach feel tight?
A pulling sensation in the lower abdomen may begin to bother you from the 20th week after conception. The pain is mild, but gets worse every day.
At 32–33 weeks, the ligaments begin to stretch, which also causes a pulling, unpleasant sensation. Frequent and pronounced false contractions, provoking pain, form 2 to 3 weeks before delivery. The stomach begins to ache, the uterus is tense, contractions last up to a minute. For women who are about to give birth for the first time, discomfort may occur just 2 days before the baby is born.
Ways to improve the condition
If there is a pain syndrome reminiscent of abdominal pain, as during menstruation, it is necessary to establish the cause of this condition. Obligatory steps are an examination by a doctor. It allows you to assess the size of the uterus, how well they correspond to the term, consistency, mobility of the organ, and the prevalence of pain.
An ultrasound is also required. With its help, you can notice the enlarged uterine cavity, the presence of clots, and remnants of the placenta. If the cause is a placental polyp, a mass formation will be noticeable. An inflammatory infiltrate around the uterus speaks in favor of the development of an inflammatory process.
Additional diagnostics depend on the information obtained in the first two stages. Hysteroscopy, laparotomy, and x-ray diagnostics may be required.
It is possible to improve a woman’s condition and reduce pain depending on the causes of pain.
In the postpartum period, medications should be used with caution; most of them pass into breast milk. Those minimum concentrations for a small fetal weight may be enough to cause adverse reactions.
Pain associated with the natural process of uterine involution is not relieved with antispasmodics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Labor-like contractions are a natural process and only appear when the baby is breastfeeding. They are short-term and do not interfere with general well-being. When they appear, you need to make several calm breathing movements. Gradually these symptoms will disappear on their own.
Subinvolution of the uterus, which has not yet led to the appearance of endometritis, is treated by removing the remnants of the fetal place from the uterine cavity. Further tactics are to prescribe reducing agents and antibiotics to prevent infection.
If pain is associated with inflammation, it is necessary to assess the severity and prescribe appropriate treatment. For endometritis, antibiotic therapy is carried out, which prevents the infectious process from spreading further, and detoxification using intravenous infusion solutions.
After relief of acute inflammation, to prevent adhesions, which leads to chronic pelvic pain, it is necessary to prescribe physiotherapy:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- diadynamic currents;
- medicinal electrophoresis.
Constipation after childbirth must be treated with diet and laxatives. We recommend products that act gently in the intestinal lumen. Sometimes a spoon of castor oil is enough to start the intestines. Lactulose is also used, which is sweet to taste and without an unpleasant odor. It is safe for newborns.
A diet for constipation includes foods that are rich in fiber and have a laxative effect. You need to eat several dried apricots or prunes a day, a boiled beet salad or beetroot soup. But you should not overdo it, abuse of a laxative diet will lead to a pronounced acceleration of peristalsis and cramping pain in the abdomen.
The divergence of the symphysis pubis takes a long time to treat; bed rest is necessary. If possible, the woman is not in a traditional bed, but in a special hammock that helps bring the pelvic bones together. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used for pain relief.
Can cramps be associated with menstruation and the cycle?
Most often, the cramping sensation is associated with cyclical changes associated with different periods of the menstrual cycle. For most girls, the symptom appears during menstruation.
The following provoking factors can lead to the appearance of spasms:
- inflammatory processes;
- infections;
- cystic formations;
- polyps.
All of the listed pathologies of the reproductive system are necessarily accompanied by menstrual irregularities. During menstruation, pain and cramps are often present.
Inflammation in the uterine cavity can cause pain
Nature and sources of pain
Uterine pain has various causes:
- Often occur during the monthly menstrual period and are called “algodysmenorrhea”. Painful menstruation occurs due to an increase in the production of prostaglandins, which are responsible for pain, and the presence of inflammatory (infectious) diseases.
- Uterine spasms also appear due to stressful situations. If the pain in the uterus does not subside, increases after physical activity, the stomach becomes hard and tense, you should rest a little. Fever, vomiting or nausea may occur at the same time. Often there is blood in the stool or urine, low blood pressure. If you experience such symptoms, you should consult a doctor immediately. Spasms in the uterus will not lead to anything good, especially if they appear frequently.
- The next cause of this symptom is pregnancy. Almost every woman feels nagging pain while carrying a baby. This is a normal phenomenon that occurs because the child grows and takes up more space. The reproductive organ stretches, significantly exceeding its original size. The hollow organ is subject to heavy stress, so pregnant women often complain that the uterus is being pulled. If the woman lies down to rest, the pain will go away within a short time.
The nature of the pain may be as follows:
Acute stomach
Intense cramping pain in the lower abdomen signals that smooth muscle contraction is occurring. This may indicate damage to organs located in the lower abdominal cavity, as well as in the pelvis. We are talking about the following organs: bladder, intestines, ureters, uterus, fallopian tubes.
Smooth muscle contraction occurs constantly, thus ensuring complete passage of the contents. If there are no pathologies, then the process is painless, so you cannot feel contractions of the bladder or intestinal peristalsis. Women do not feel the contractions of the fallopian tubes, which promote the egg, as well as the uterine tone, which ensures the elimination of menstrual blood.
Cramping pain in the abdomen is a dangerous signal indicating a failure in the movement of contents through the hollow organ. Delayed medical care can lead to dangerous complications. Spasms may occur due to functional disorders. For example, in women, such pain may indicate uterine fibroids, miscarriage, or painful periods.
Acute mechanical intestinal obstruction
One of the pathologies accompanied by such sensations is considered to be intestinal obstruction. This pathology is extremely dangerous; death is recorded in 10–26% of cases. According to statistics, most often, symptoms appear at night, which is caused by the daily rhythm of the gastrointestinal tract.
Clinical picture of intestinal obstruction at an early stage:
- colic;
- constipation;
- increased gas formation;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- pale skin;
- dizziness and loss of consciousness;
- the belly is “oblique” asymmetrical;
- abdominal movements are wavy;
- strong thirst.
Symptoms depend on the form of the pathology. There are strangulation and obstructive forms of obstruction. The obstructive form develops as a result of blockage of the intestinal lumen - a tumor, a ball of roundworms and other parasites, a foreign body, fecal or gallstone. The strangulation form manifests itself due to pinching of the intestinal mesentery with blood vessels. A similar pathology is possible against the background of intestinal volvulus, adhesions and intussusception. This disease is characterized by an early stage of necrosis of the entire intestine, peritonitis. Any form of intestinal obstruction requires emergency hospitalization in intensive care. Basically, surgical intervention is indicated.
Spontaneous termination of pregnancy
The presence of cramping pain during pregnancy may indicate a miscarriage. There are nagging painful sensations in the lower abdomen, which radiate to the sacrum, and bloody discharge from the vagina. These symptoms require urgent hospitalization. If you get help in time, there is a chance to save the pregnancy. As a result of self-abortion, part of the fertilized egg remains in the uterus, which must be eliminated. Otherwise, there is a risk of septic complications: peritonitis, sepsis, purulent salpingoopharitis, acute endometritis.
Cramping pain can be a signal from the body about the presence of a dangerous disease. If the pain lasts more than thirty minutes, it is recommended to call an ambulance.