Benign neoplasms of the mammary glands reduce a woman’s quality of life and can become the basis for dangerous complications. The nodular form of mastopathy is a breast disease, the symptoms of which indicate the risk of oncological pathology and require a comprehensive diagnosis. Therapeutic tactics depend on the diagnosis: against the background of some types of mastopathy with proliferation, surgery is necessary. If there is a proven absence of precancerous changes, medication and folk remedies can be used.
Causes of pathology
Tumor diseases of the mammary glands are usually genetically determined. Proliferating nodular mastopathy often becomes a family disease when close relatives develop the same type of pathology. Hereditary predisposition determines a high risk of the disease in women who have the following predisposing factors:
- age (women over 40 years old);
- general dishormonal disorders (metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, thyroid disease);
- menstrual dysfunction caused by hormonal problems;
- gynecological pathology (leiomyoma, endometriosis);
- characteristics of reproductive function (infertility, frequent abortions, first pregnancy after 35 years);
- unmotivated and complete refusal to breastfeed the baby;
- inadequate lactation (less than six months);
- long-term psycho-emotional stress.
Nodular mastopathy and breast cancer are successive links of one pathological chain in women with an unfavorable combination of several factors (genetic predisposition, infertility and lack of lactation, hormonal imbalance and chronic stress).
Types of disease
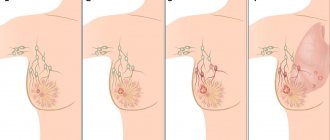
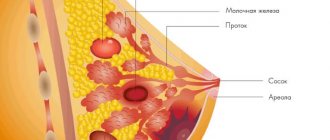
Nodular mastopathy in the mammary gland is much less common than the diffuse form of the disease. It is important to distinguish between disease and age-related changes in glandular tissue, which occur in every third woman during perimenopausal age. A mandatory criterion for the nodular form of fibrocystic mastopathy (FCM) is the presence of isolated and limited compactions in the breast tissue. The following types of pathology are distinguished:
- diffuse version of nodular mastopathy, when examination can detect several small nodules;
- cystic variant of the disease with the identification of large cystic cavities, which during the initial examination can be mistaken for a node;
- a single large node in one or both glands.
As doctors' reviews show, the latter option is the most dangerous for a woman: in this case, a tumor with a high risk of malignancy is most often detected.
Symptoms of breast pathology
Small nodules and asymptomatic disease lead to late detection of the disease during a preventive medical examination. Signs of nodular mastopathy occur when a proliferative mass forms in the breast more than 3 cm in size, when a woman independently detects a nodule. Typical symptoms of the pathology include:
- pain of varying duration, associated or not associated with the menstrual cycle;
- spontaneous discharge from the nipples;
- palpation detection of a limited and dense neoplasm in the chest.
Mastalgia or pain in the mammary gland occurs in all women. Usually this problem occurs 2-3 days before your period and does not cause any serious concern. You should worry if the pain syndrome appears long before the expected menstruation (more than 7 days) or if the discomfort in the chest is not at all related to the cycle.
All women who have given birth before their next menstruation have discharge from the nipples when pressed. You should be wary of spontaneous lactorrhea, especially if the appearance of the discharge is unlike colostrum (pus-like, bloody).
Monthly self-examination (palpation) of the mammary glands should be carried out regularly. The time for examination is the first week after the end of menstruation. The detection of any nodular formations is a reason for a full examination by a mammologist or gynecologist.
https://youtu.be/CaqeoYAR-HU
Thematic pages > Expert advice > Mastopathy and breast cancer: prevention, diagnosis and treatment
Mastopathy and breast cancer: prevention, diagnosis and treatment
Over the past 20 years, the incidence of breast cancer has doubled. Women die from this disease more often than from all other cancers. These are the annual statistics of deaths from breast cancer. In most of these patients, the disease was detected with a delay incompatible with life. Even with all the efforts of doctors. An increase in the incidence of breast cancer is observed throughout the world. Every year, about 1 million women fall ill around the world.
Causes of breast cancer Risk factors Research methods Stages of the disease Treatment Self-examination What changes should you report to your doctor?
Causes of breast cancer
Cancer tumor
develops inside our body, from our own cells, which for some reason have mutated. Scientists around the world have been struggling with the cause of cancer for decades and come to the conclusion that the destructive mechanism of the disease is triggered not by one, but by many factors.
Various factors play a role in the occurrence of breast cancer. An early start of menstruation - before 12 pets - is unfavorable, as is a late end - after 55 years. Fertility is of fundamental importance - if the first birth at 30 years of age is unfavorable, after 40 years of age this is already a risk group.
The female breast must perform all the functions assigned to it by nature. Namely, to feed children. The longer the lactation period, the lower the risk of developing breast cancer.
Sexual function itself is of fundamental importance: lack of sexual activity, late onset after 25-30 years, and methods of contraception are also important. A woman should consult a gynecologist - mechanical methods are especially unacceptable for women prone to dyshormonal diseases that contribute to the development of tumors.
Cancer is associated with metabolic disorders in a woman’s body. Overweight, obesity, diabetes mellitus - the list of negative factors is also supplemented by arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis, severe liver and thyroid diseases.
Mastopathy
belongs to the category of benign dishormonal diseases. A large number of women suffer from them. It is believed that every second woman suffers from a dishormonal disease. In fact, this is not so, it’s just that sometimes they are mistaken for the usual swelling of the mammary glands as a physiological factor before menstruation. Dyshormonal diseases, as a rule, are associated with disturbances in the metabolism of hormones associated with ovarian function; the period of their occurrence is from 25 years.
A tumor does not appear out of the blue. Development is preceded by changes in the mammary gland. Diffuse mastopathy is a background condition that can develop into a focal one. Patients should be observed by gynecologists; if any changes occur, surgical treatment is necessary - the focus of mastopathy is excised. There is another disease - intraductal papilloma. The symptom is blood from the nipple, and surgery is also necessary here. This is cancer prevention - identifying precancerous diseases and their treatment.
Risk factors
Typically, breast cancer occurs in women over 50 years of age
. This is caused by a failure in hormonal metabolism due to the decline of ovarian function. However, in recent years, cancer has become significantly younger.
Trauma is also important
. Single - to a lesser extent, often repeated, chronic, leads to hemorrhage in the mammary gland, scars, against which breast cancer can occur.
In pursuit of fashion, women use all kinds of underwear with underwires.
, there are also metal parts that put quite a lot of pressure on the chest and, in particular, on the mammary gland during the day. Therefore, constant wearing of such bras is undesirable.
Cancer often has hereditary roots
. The presence of malignant tumors of the breast, ovaries, colon or rectum, or thyroid gland in close relatives can add a woman’s name to the list of patients with breast cancer.
And, of course, exogenous factors
. This is the direct impact of ionizing radiation on the mammary gland and smoking in women; chemical carcinogens and polyaromatic hydrocarbons also play a role. The development of cancer is caused by the simultaneous action of 5-7 negative factors over a long period of time.
The disease develops differently in 2 individuals. When doctors ask how the tumor developed, patients say “oh, nothing last week, but this week it’s already there” - this is unrealistic. The tumor develops over several years, and sometimes even ten years, but patients simply do not notice this growth.
Research methods
Instrumental research methods are used for both preventive and clarifying purposes. First of all, mammography. But it is shown only to women over 40 years old.
Until the age of 45, a woman should undergo an ultrasound every year, after which mammography is recommended. Glandular tissue is denser than adipose tissue, and after 45 years it turns into adipose tissue and radiation is retained in this tissue. As an early diagnosis after 45 years, mammography is recommended for all women once a year. Depending on the structure of the mammary gland, repeat examination after 1.5-2 years or after 6 months.
There are risk groups of women who need to have their mammary glands examined, primarily women with a hereditary predisposition, with precancerous conditions and benign tumors. Mammography
allows you to clearly determine the malignant potential of the tumor and identify its smallest foci.
Ultrasound
- a method that is more harmless and accessible than x-ray examination. It can be performed on a woman of any age, an unlimited number of times. Ultrasound can distinguish benign breast formations and identify a malignant tumor, but does not detect microcarcinoma. Ultrasound is recommended for women under 35 years of age - detection rate is 87%. The combination of mammography and ultrasound gives almost 100% detection. Ultrasound is also applicable when examining the axillary fossae to look for breast cancer metastases in the lymph nodes. This, in turn, distinguishes the method favorably from mammography.
The biopsy method helps to analyze the cellular composition and distinguish a benign tumor process from a malignant one.
. It is carried out both on its own and under the control of ultrasound or mammography. Thanks to the method of puncture biopsies, it is possible to detect early cancer, when there are no metastases or palpable formations yet - that is, when neither doctors, nor women, nor other methods can detect it.
Stages of the disease
First stage of the disease
is a single tumor up to 2 cm in size that does not have regional metastases. They are located in the lymph nodes, in close proximity to the affected organ - in the armpit.
Second stage of the disease
- the tumor is small, up to 2 cm or a little more, but often has a single metastasis in the axillary fossa. The longer the cancer is in the body, the more actively its harmful cells travel throughout our body. And they can be fixed in any of its organs. This is how cancer metastasizes.
The third stage
of the disease
is more varied. This may be a small tumor, not reaching 3-4 cm, but with multiple metastases in the axillary fossa. In some forms, the entire mammary gland is affected, and the cancer is not palpable. Or a nodular tumor, 5-10 cm in size - this is also the third stage of the disease.
The fourth
stage of the disease
is the most dangerous stage - a tumor of any size that has metastases to other organs and tissues: bones, liver, lungs, brain. This stage of cancer most often renders doctors powerless.
The spread of the tumor process in the body depends on the histological form of the tumor. All tumors that we call cancer are malignant, but the forms of cancer are different and differ in the duration of the disease. If a patient whose cancer is diagnosed in the 1st stage of the disease does not seek help, in most cases, after a year it is already the 3rd stage, sometimes the 2nd, and sometimes the 4th.
Treatment
Some patients are held back from seeing a doctor in a timely manner by self-confidence and vain hopes for self-healing, others by distrust of doctors and, on the contrary, blind faith in other, alternative medicine. No spells or miraculous methods can cure a malignant tumor. This delays the pre-hospital stage and does not have a positive effect.
Late treatment also means a mortal fear of the disease and of treatment. Fear of losing breasts may deter women from seeking early treatment. Women should understand that such thoughts do not prevent the removal of the mammary gland, but only bring it closer. By delaying, you are depriving yourself and the doctors of the chance to save your breasts.
The lower the stage of the disease, the shorter the treatment in duration and intensity. At the first stage, organ-preserving operations
, tissue is transplanted - then it is possible to save the breast and cure it of malignancy.
In some cases, breast removal can be avoided. This is a trauma for a young woman, so the sooner she gets to the doctor, the less aggressive the treatment methods will be. If the tumor is small and there are no metastases, the focus is removed, radiation therapy, chemotherapy
. But the breast remains.
A later stage of the disease requires more serious interventions. Radiation therapy, which acts locally on tumor sites, remains an element of the complex effect on the tumor. In terms of surgery, complete removal of the mammary gland and regional lymph nodes is carried out.
Surgical stage
- one of the main ones. But thinking of breast cancer as an isolated tumor is a mistake. The development of distant metastases is the cause of death without treatment. Therefore, the use of chemotherapy is extremely important. Cancer is a systemic disease; surgery alone does not affect metastases.
Of course, chemotherapy is not harmless not only for cancer cells, but also for the human body as a whole. But this is an inevitable sacrifice in the name of life. Side effects of chemotherapy - nausea after administration of the drug, hair loss - are what women are afraid of. But the hair will return later, and there are special medications for nausea. Sometimes chemotherapy remains the only way to treat cancer if for some reason surgery is not possible.
hormone therapy helps influence the development of tumors in the body.
. It is carried out taking into account the hormonal sensitivity of the patient’s tumor. If it is sensitive, oncologists prescribe therapy - treatment is aimed at blocking the action of sex hormones so that the tumor grows less.
And only multicomponent complex treatment makes it possible to achieve results and cure the patient. This is difficult for both the doctor and the patient who is forced to undergo treatment. Oncologists gave this period their own medically “rigid” definition: “5-year survival rate.” The earlier breast cancer is detected and treated, the better a woman's chances of recovery. If the disease is detected in the first stages, in 95% of cases patients overcome the 5-year survival threshold. Stage 3 cancer reduces this percentage by half. In the 4th stage, we can only talk about prolonging life.
Patients should come for check-ups regularly. Malignant tumors can recur in other organs and tissues. It is necessary to undergo regular monitoring, during the first year of treatment - examination every 3 months. After 2 pets - under the supervision of local doctors.
Recurrence of the disease is an undesirable but possible development of the situation after the completed course of treatment for breast cancer. And a woman must be ready for this. There is an arsenal of drugs for the treatment of relapse and metastases. This gives its results. If left untreated, the result and prognosis are much worse.
Women treated for breast cancer are at risk of recurrence. But this does not mean that they should spend the rest of their lives waiting for him.
The patient’s mood plays a huge role in the outcome of the disease; the support of loved ones is also important, so that the spouse and friend understand and support at a difficult stage of life.
A diagnosis of cancer inevitably divides a woman’s life into “before” and “after”. No, after treatment it does not get worse, it just changes, sometimes radically.
Man is designed in such a way that he reacts difficultly to complex turns. Those who do not need to change anything feel best. But psychologically a woman must change, and she changes. In trying to answer the difficult question for herself - why did this happen to me - every woman invariably plunges into the abyss of her past mistakes. Their awareness gives her a unique chance to rewrite the story of her life. Life without cancer.
Self-examination
Coming to the clinic for the first time within a calendar year, a woman undergoes a full oncological examination, which includes an examination of the mammary glands. And it gives its results. In half of the cases, breast cancer is detected during such preventive examinations. But women themselves, without medical education, can identify signs of illness in themselves - by self-examination.
What changes should you report to your doctor?
You should inform your doctor about any newly detected changes if they do not disappear during the next menstrual cycle. About 80% of such changes are benign, but only a gynecologist can determine this for sure. Therefore, you should not risk your health and peace of mind, hoping to skip past the remaining 20%.
Unfortunately, self-examination of the mammary glands allows one to detect rather large formations of the mammary glands, and they may be already advanced forms of cancer.
Once every six months, examination and palpation of the mammary glands should be carried out by a mammologist-oncologist or gynecologist. You should also not forget about additional examination methods, such as ultrasound (for women under 40 years old) and mammography (for women over 40 years old).
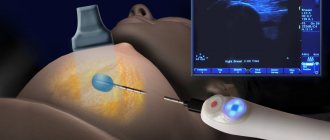
Diagnostics when identifying nodes
After examination by a doctor with mandatory palpation examination of the breast, the following examinations must be performed:
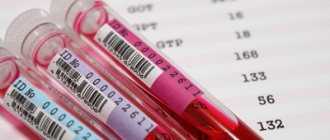
- take a blood test for a tumor marker (CA-15–3);
- X-ray examination of the mammary glands (mammography);
- ultrasound scanning (women under 35 years old);
- puncture and taking biopsy material from the node.
The possible risk and danger of malignant degeneration when nodular proliferations are detected in the mammary gland are the highest, therefore, in each specific case, the specialist will select the examination and treatment regimen individually.
Principles of therapy
A prolonged absence of symptoms is the reason for a woman’s delay in seeing a doctor. Independent and uncontrolled treatment of nodular mastopathy with folk remedies leads to the progression of the disease with the formation of a cancerous tumor, therefore it is strictly unacceptable to self-medicate. After a comprehensive examination with a mandatory puncture biopsy, the doctor will offer the following types of therapy:
- observation with drug therapy;
- surgical removal of the node (sectoral resection);
- hormone therapy.
Surgery for nodular mastopathy is performed for the following indications:
- lack of positive changes during drug treatment;
- high level of proliferation of cells obtained from biopsy;
- detection of any variants of precancerous changes.
After the operation, it is necessary to be constantly monitored by a mammologist with mandatory follow-up examinations and drug therapy.
Treatment of nodular forms of mastopathy without surgery is possible only with full confidence in the favorable course of the disease and the absence of the risk of malignant degeneration. For conservative therapy, herbal preparations, hormonal agents, antitumor drugs and vitamins are used. It is necessary to strictly and consistently follow the instructions of the mammologist in order to get rid of the disease and prevent surgical removal of the breast.
Fibrous nodular mastopathy
This form of breast disease leads to the development of a cancerous tumor. If this disease is suspected, an examination should be carried out by a mammologist, and this should be done in the early stages. After palpation, a complete diagnosis is carried out. This will help to accurately identify the form in which the disease occurs and develop the most appropriate treatment.
Preventive actions
The main goal of preventive measures is to prevent the formation of nodules in the mammary glands. It is optimal to prevent nodular mastopathy than to treat it. This is especially important for women at high risk of cancer. Important preventive measures are:
- refusal of artificial termination of pregnancy;
- use of oral contraceptives;
- timely treatment of hormonal disorders and gynecological diseases;
- performance of childbearing function;
- longest possible lactation.
Nodular mastopathy, the treatment of which is most often surgical, is a disease that requires timely diagnosis and comprehensive therapy under long-term supervision of a mammologist. It is undesirable to treat FCM with nodulation with folk remedies: traditional methods of therapy are the basis for a successful fight against a dangerous pathology.
Treatment methods
The main method of treating mastopathy is conservative therapy: this is a comprehensive method that allows you to correct hormonal imbalances.
The first step is to eliminate symptoms and normalize the functioning of the reproductive and endocrine systems using medications.
Of course, such treatment is unable to completely restore the condition of the mammary glands. And its main disadvantage is that it is effective only in the initial stages. If the disease has developed sufficiently, then only radical measures will help - surgery.