Chronic hemorrhoids of the 3rd degree are detected in people who refuse treatment at earlier stages. The disease occurs due to increased load on the cavernous venous formations of the rectum and stagnation of blood in the pelvis. Causes: circulatory disorders, dystrophic changes in the walls of blood vessels and supporting muscle formations.
The pathology is common among adult men and women of “sedentary” professions who spend most of their time on their feet lifting weights. Pregnancy and childbirth can provoke the formation of hemorrhoids. In the history of the disease, a tendency to constipation or frequent diarrhea, dietary habits (passion for heavy fried meat foods, alcohol, spicy seasonings), and heredity factor are important.
Existing classifications interpret grade III hemorrhoids as prolapse of nodes from the anus during defecation with the impossibility of returning to their place on their own and the need for manual reduction (according to Banov L.Jr.). Goligher adds a mandatory element - bleeding, and the Russian Institute of Coloproctology emphasizes the same possibility of bleeding or prolapse without it.
Symptoms of 3rd degree hemorrhoids
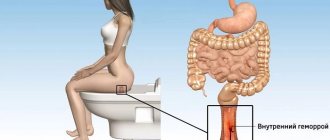
Hemorrhoids of the 3rd degree are said to be when the hemorrhoids no longer retract into the rectum on their own, fall out of the anus not only during bowel movements, but also with any strenuous efforts, but can still be set manually.
The third stage of hemorrhoids is characterized by the following symptoms:
- increased pain during bowel movements;
- constant itching and burning in the anal area;
- significant increase in hemorrhoids;
- prolapse of vascular formations with minimal physical activity: sudden movements, coughing or sneezing;
- swelling of the anus;
- frequent bleeding from the anus.
Anal fissures and rectal erosions often develop. In addition, there is a risk of pinching and ischemia of the nodes with subsequent necrosis of the affected tissues, thrombosis of hemorrhoids, paraproctitis with the formation of a fistula, and anemia due to constant blood loss.
What to do to prevent the disease from returning?
Correct nutrition will protect against the return of the disease
After successful surgery for grade 3 hemorrhoids has been performed, you need to pay special attention to your health. Taking care of your health will help you avoid a possible relapse, which is quite possible. The very first thing to start with is adjusting the nutrition system, and immediately after surgery it is especially important to follow a diet. Give preference to fruits and vegetables, consume low-fat dairy products, drink plenty of water, and do not overuse fried, smoked, salty and spicy foods.
Hemorrhoids are a disease that every person initially has. It sounds scary, but it’s true: cavernous tissues are formed in the prenatal period. The hemorrhoids themselves consist of these tissues. They are provided by wise nature for a reason; it is the nodes that perform the holding function - thanks to which feces are retained in the anus. But under the influence of certain factors, these nodes become inflamed, fill excessively with blood, and fall out. Is this normal? Of course not.
Loss of nodes is characteristic of the second stage of hemorrhoidal disease. But at the same time, the nodes both fall out and are inserted into place. During and after defecation, a person feels as if something foreign is falling out of the anus and sagging, and then it seems to be sucked inside. Stage 3 hemorrhoids do not require such reverse reduction: the nodes can be inserted into the passage, but only with your own hands.
Forms of hemorrhoids
Chronic hemorrhoids are characterized by mild symptoms, a long latent period, and a continuously progressive course with exacerbations. An exacerbation is manifested by a sharp, sudden pain, the external bumps become inflamed and swollen, burning, itching and bleeding appear in the area of the anal canal.
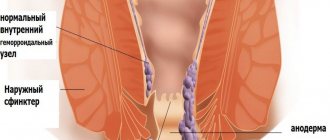
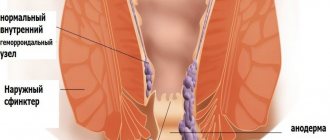
Hemorrhoids are divided into external, internal and combined depending on the location of the hemorrhoids. With external hemorrhoids, pathological changes in the cavernous vessels are localized in the outer region of the rectum, around the anus. Internal hemorrhoids are characterized by the location of hemorrhoidal formations under the intestinal mucosa, inside the anus. Combined (mixed) hemorrhoids are characterized by inflammation of both internal and external hemorrhoidal growths.
The development of pathological changes in cavernous tissue occurs gradually, the first manifestations of the disease are subtle, occur periodically and often go unnoticed.
Postoperative period
In the postoperative period, unpleasant symptoms often occur:
- pain;
- postoperative bleeding;
- urinary disorders.
Sometimes the postoperative period is complicated by wound inflammation. This occurs when the rules of asepsis and antisepsis, bed rest, and diet are not followed. When bacterial flora attaches, purulent inflammation occurs.
The duration of the rehabilitation period depends on the type of surgery. If the wounds were left open during surgery, the postoperative period will take longer. If the wounds are sutured, the duration of the rehabilitation period will be shorter. On average, the patient stays in the hospital for 3–7 days. All this time it is necessary to observe bed rest. Nutrition should be gentle, food should be liquid and warm.
Diagnostics
Primary diagnosis is carried out by collecting anamnesis, visual examination and digital rectal examination. During an external examination, the proctologist may ask the patient to strain hard or cough in order to assess the condition of the internal nodes, their bleeding, and the possibility of repositioning prolapsed hemorrhoids.
If it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, they resort to instrumental research - sigmoidoscopy
The doctor will also prescribe a general blood and stool test, laboratory and clinical tests of stool for the presence of hidden blood and mucus.
For clarifying diagnostics, instrumental methods are used:
- Anoscopy – assessment of the condition of the rectal mucosa, determination of changes and violations of its integrity, the presence of inflammation, cracks, erosions. The study is carried out using a special instrument - an anoscope (proctoscope);
- sigmoidoscopy – examination of the rectum using a sigmoidoscope. The method allows you to see the presence of internal hemorrhoids and assess the condition of the rectum, even when the hemorrhoids are located high in the anal canal.
If necessary, additional types of studies are prescribed: irrigoscopy, colonoscopy, biopsy of a section of the rectal mucosa.
Why refusing medical help is very dangerous
Do not ask friends and traditional healers how to cure stage 3 hemorrhoids. The only correct answer and real help will be offered to you by a proctologist. It is worth noting that rare patients ignore a disease that has already developed to the third stage. Usually its symptoms are simply no longer tolerable. Especially if you have a strangulated hemorrhoid, which equals severe pain.
In addition, the lack of treatment for stage 3 hemorrhoids is dangerous:
- Thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins is an indication for inpatient therapy;
- Paroproctitis is the so-called inflammation of the perirectal tissue, this is a disease that easily becomes chronic and can only be treated surgically;
- Bleeding is a threat to the patient's life.
Conservative medicine alone will not help; surgical methods must be used. Medicinal methods will only relieve the painful symptoms, but the nodes will not stop falling out, and all the risks of complications remain.
Treatment of hemorrhoids stage 3
How to treat grade 3 hemorrhoids? Depending on the clinical picture, the condition of the hemorrhoids, concomitant inflammation and complications, treatment can be conservative or surgical.
Starting from this stage, i.e., when hemorrhoids no longer move back into the rectum on their own after prolapse, curing hemorrhoids at home becomes problematic.
With external hemorrhoids, pathological changes in the cavernous vessels are localized in the outer region of the rectum, around the anus.
Depending on the diagnosis and condition of the patient, the proctologist prescribes complex therapy, the purpose of which is to relieve pain, normalize venous outflow and increase vascular tone, relieve itching and swelling, eliminate focal inflammation and bleeding. Medicines for internal and external use are prescribed - rectal suppositories, ointments, creams. Treatment of grade 3 hemorrhoids necessarily includes following a diet and performing therapeutic exercises aimed at eliminating blood stagnation in the pelvis.
If conservative treatment is not sufficiently effective, the issue of surgical removal of hemorrhoids is considered. In most cases, this can be done at stage 3 using one of the minimally invasive methods.
Description of the disease
The main symptom of the third stage of the disease is spontaneous prolapse of hemorrhoidal cones. They don't just fall out, they don't retract themselves. The patient understands: in order for the bumps to return to their place, they need to be set by hand. This means that your illness has already started, and you can’t just delay contacting a doctor, you need to go to him as quickly as possible.
The muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the anal canal cannot hold the venous plexuses, and degenerative processes occur. In this case, signs of previous stages may also be observed - bleeding, irritation in the anus, burning and itching, painful bowel movements, etc. But at stage 3 of hemorrhoids, it is simply impossible to calmly live with these symptoms: the disease forces you to give up your usual things, makes physical activity difficult, and puts your sexual life into question.
And if previously pain was felt during bowel movements, then at the third stage it is also present in the period between visits to the toilet. The pain will be especially severe if the hemorrhoidal lump is pinched. Bleeding may also become more intense as the rectal lining thins and even the slightest impact causes bleeding.
The hemorrhoidal node grows, and therefore it is much more often damaged by feces.
This is a dangerous time and a serious threat: just imagine, the bleeding becomes so severe that the patient has to be hospitalized. Finally, there is the risk of the nodes falling out - you will not always have the opportunity to set them back, but outside the rectum the nodes are not protected from adverse factors. What to do? Go to the proctologist faster!
Treatment methods for hemorrhoids at stage 3
Is it possible to treat stage 3 hemorrhoids without surgery? This is determined by the doctor on an individual basis. In general, minimally invasive methods for removing hemorrhoids are preferable, as they are associated with significantly lower risks and do not require a long recovery period after the intervention.
Latex ligation is a minimally invasive method of treating hemorrhoids, used at stage 3
The most popular minimally invasive methods for removing hemorrhoids:
- latex ligation . During the procedure, a special elastic ring is applied to the base of the hemorrhoid using a ligator. As a result, the blood flow to the external node stops, it dies and is rejected by the body along with the latex ligature;
- sclerotherapy is the introduction of a sclerosant into the cavity of the internal hemorrhoidal formation, after which gluing (sclerosis) of the vessel occurs. Blood circulation in it stops, the node dies;
- disarterization - cessation of blood supply to hemorrhoids by ligation of the arteries. Simultaneously with stopping the flow of arterial blood, the internal nodes are fixed in the rectum;
- radio wave hemorrhodectomy – destruction of node tissue by high-frequency radio waves. The dissecting effect is achieved by heating tissues with waves of a certain frequency. Radio wave ablation is carried out with a radio knife using a non-contact incision technique in which there is no contact of the electrode with the tissue;
- infrared (photo, laser) coagulation - exposure of hemorrhoids to a light flux, a focused infrared beam. Under the influence of light energy, proteins are denatured and blood vessels are sclerosed.
There is a risk of pinching and ischemia of the nodes with subsequent necrosis of the affected tissues, thrombosis of hemorrhoids, paraproctitis with the formation of a fistula, anemia due to constant blood loss.
If treatment with a minimally invasive method is contraindicated, they resort to radical hemorrhoidectomy - surgical excision of hemorrhoids is performed using the Longo or Milligan-Morgan method.
What methods exist?
Stage 3 hemorrhoids cannot be treated without surgery
How to cure stage 3 hemorrhoids without surgery? The first question that any sane person will ask after learning about an unpleasant diagnosis. After all, no one wants to fall under the surgeon’s knife. And the doctors themselves believe that the most successful operation is the one that was not needed. After reading a lot of information and consulting with specialists, you will quickly understand that the slogans read: hemorrhoids of the 3rd degree, treatment without surgery! – nothing more than a myth and a publicity stunt. Unfortunately, in this case it is impossible to do without the intervention of a surgeon. Treatment of stage 3 hemorrhoids without surgery is simply not possible. Drug therapy will no longer have the desired effect, and it is used as an auxiliary method, and not the main one.
Don't be scared or panic about this. Modern methods of treating stage 3 hemorrhoids offer different ways to remove hemorrhoids. So the intervention can be minimal. Minimally invasive methods include:
- Infrared photocoagulation. When treated with this method, the nodes are influenced by high temperatures using a special apparatus. This procedure blocks the blood supply to the nodes, which causes them to dry out. Using photocoagulation, you can remove up to 4 bumps at a time, then you should take a two-week break and, if necessary, repeat the procedure;
- Chronic grade 3 hemorrhoids can be cured by resorting to sclerotherapy. The procedure involves the introduction of a specially developed drug into the lumen of the vessel, which will glue its walls, and later the node will resolve.
- Ligation. Treatment of chronic hemorrhoids of the 3rd degree using the ligation method consists of tightening the vessels that supply the hemorrhoid with blood using special latex rings;
- Cryodestruction. Destruction of hemorrhoids by exposing them to low temperatures, which can reach -1960˚C.
- Laser treatment of stage 3 hemorrhoids without surgery. As the name implies, in order to relieve the patient of the disease. The Doctor uses laser beams, just like in a science fiction movie. The laser can be used to cut off the external nodes and cauterize the internal ones. No blood loss is observed.
If none of the listed minimally invasive methods is suitable for some reason or it does not give the expected results, then there is only one option left - surgery for grade 3 hemorrhoids.
Possible complications
If surgery was performed, there is a possibility of certain complications. Minimally invasive therapy techniques do not provide a 100% guarantee against certain secondary body phenomena for the procedure performed. Doctors talk about bleeding after any technique. To minimize the danger, it is necessary to prepare well before the operation.
If complications occur, then depending on the level of manifestation of symptoms, a specific therapy method is used. In addition, after the surgical process there is a possibility of wound infection. It is possible that such a phenomenon may occur after the use of minimally invasive techniques. For this purpose, after the operation, the doctor may prescribe an antibiotic. And for patients after “gentle” methods, there is certain advice: “If you have an elevated temperature after the procedure for more than 1.5 days, you need to consult a doctor.
Do not forget: with longer tolerance of pain, the disease progresses more. For this reason, it is important to eliminate fear and seek help from a specialist.
Diet after surgery
She will be one of
important postoperative appointments. The convalescent menu should include foods that soften stool. This will help normalize digestion processes and, accordingly, bowel movements.
Among these products:
- Dried plum;
- Fermented milk products (except cottage cheese);
- Oatmeal;
- Broccoli;
- Bananas;
- Dried apricots;
- Zucchini;
- Pearl barley and buckwheat porridge;
- Beet;
- Vegetable oil.
On the first day of rehabilitation, doctors prescribe laxatives to patients to prevent difficulty in defecation.
Restorative therapy involves normalizing the diet, maintaining a truly active lifestyle, controlling physical activity, and giving up tobacco and alcohol. The doctor will tell you in more detail, because each patient has his own picture of the disease and features of the postoperative period.