March 13, 2020
Share: | | |
Meconium is the first stool of a newborn baby. It is formed in utero when amniotic fluid is swallowed and is released in the first hours of life. It is a viscous, thick, homogeneous mass of dark green color and odorless. Meconium contains mucus, desquamated intestinal cells, vellus hair, bilirubin, and drops of fat.
The weight of meconium in newborns ranges from sixty to one hundred grams, its acidity is 6 pH.
If stool gets into the amniotic fluid, do not be alarmed. Doctors will definitely do everything possible to eliminate this small problem. However, it is within your power to prevent the situation.
Meconium is a special original stool, the one that comes out of the intestines first in the form of feces. In terms of its characteristics, meconium differs significantly from the baby's future feces. It is very sticky, viscous, practically odorless, the color range is predominantly deep dark green, reaching almost black (it is worth mentioning that mekonion means “poppy seed” in Greek).
Norms of indicators of original feces
Meconium in newborns does not have any strong odor. The consistency of this mixture is viscous and sticky, resin-like. The color of the original feces in a newborn can be dark green or green-black, eggplant. The greenish or swampy tint of stool is due to the content of bilirubin, which is formed during the breakdown of red blood cells.
Newborn booties for boys and girls: diagrams and descriptions
The average amount of stool reaches 60-100 grams. A newborn's feces are usually sterile and do not contain any germs.
Important! If a baby's poop is green in color and has a distinct putrefactive aroma, this may be a sign of dysbiosis or lactase deficiency.
Diaper with feces
How long does it take?
Many young parents are interested in how many days a newborn has meconium. In healthy children, meconium is passed on the first day, from the third to the twentieth hour after birth.
On the second or third day, bowel movements are called transitional: they contain the remains of meconium and digested food. First, streaks and impurities are visible in the feces.
But gradually the feces become mushy and homogeneous. A baby's normal stool is yellow and runny.
When should meconium pass?
How long does it take for newborns to pass meconium? As a rule, four out of five babies pass their first stool 8-10 hours after birth or directly during the birth process. Within 2-3 days, the meconium completely leaves the baby’s intestines, and the baby begins to have transitional stool (it may contain particles of milk and meconium residues). At the age of one week, the baby's stool is completely normal.
Stool in newborns during breastfeeding
Since original feces have a very viscous consistency, it is quite difficult to remove from the newborn’s body. In those children whose mother began breastfeeding immediately after birth, meconium passes much faster. This is due to the fact that colostrum released from the breast contains a sufficient amount of nutrients and has a mild laxative effect on the baby’s body.
Note! While in the mother's womb, meconium is excreted by about 10% of babies, the remaining 90% get rid of the original feces during the birth process or within 2-3 days after birth. Komarovsky states that passing meconium after 24 hours is normal.
Since meconium has a sticky and viscous consistency, it is not easy to wipe it off the baby’s skin - it will not be washed off with ordinary running water and soap. In order to wash it without extra effort and not cause harm to the baby, it is better to use special baby oil, gel or diaper cream. By dropping a few drops of the product onto a cotton pad, you can easily wipe off stuck poop from the butt and wash your baby in the shower. To avoid injuring the baby, do not rub the delicate skin too much.
The process of changing a diaper for a newborn baby
Aspiration syndrome
Another problem is associated with a condition where meconium enters the baby's lungs. This can happen before and during childbirth. Thus, meconium is found in amniotic fluid in the case of pregnancy. If labor is prolonged, there is always a danger of developing asphyxia or hypoxia.
Such conditions are extremely scary, since the carbon dioxide accumulated in the circulatory system irritates the brain's respiratory centers; the child reflexively takes his first breath already in the womb, and therefore there is a danger of swallowing water. When they are contaminated with meconium, it penetrates the respiratory organs, and this can cause severe pneumonia.
If a newborn has swallowed clean or fecal-contaminated water, his airways are cleaned and then his condition is carefully monitored in order to exclude the development of pneumonia or begin to treat it in time.
Thus, the state of meconium is a very important sign of the baby’s health. Most often, no problems arise with it, only in rare cases resuscitation measures may be required to restore the respiratory or digestive functions of the baby.
Now we know how much meconium is passed in newborns.
Meconium aspiration is a dangerous condition. With this syndrome, the original feces enter the lungs of the newborn. This problem can arise not only after the birth of a child, but also in the last months of intrauterine development.
An alarming signal is the presence of meconium in the amniotic fluid. Original feces, if they enter the baby’s lungs, can cause a serious inflammatory process or pneumonia.
Causes
Post-term infants are at risk of developing meconium aspiration. In the later stages of intrauterine development of the fetus, natural processes begin to work in such babies, including bowel movements.
Early passage of meconium provokes its entry into the amniotic fluid. Under the influence of certain pathological conditions, the fetus takes a deep breath, as a result of which feces penetrate into its lungs.
Causes of meconium aspiration include the following:
- consequences of fetal asphyxia;
- Rh conflict during pregnancy;
- complications during labor stimulation;
- excessive presence of carbonic acid in the blood;
- the birth of a baby from the first birth in a woman over 35 years old;
- abuse of bad habits during pregnancy;
- consequences of oligohydramnios during pregnancy;
- consequences of diabetes in women;
- fetal presentation in late pregnancy;
- intrauterine developmental delay or fetal growth;
- regular toxicosis in women;
- fetal hypoxia.
Aspiration syndrome can be detected at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus. The amniotic fluid changes color and acquires a greenish tint.
We suggest you read: Ointments and creams for skin allergies for children
This pathology is clearly visible during a routine examination of a pregnant woman. If a newborn has aspiration syndrome, then this condition cannot be asymptomatic. It is determined by a number of characteristic features.
Signs of aspiration syndrome are the following factors:
- excessively enlarged chest;
- the presence of fecal particles on the skin of the newborn;
- the presence of meconium in the oral cavity of a newborn baby;
- blueness of the baby’s skin after birth;
- lack of breathing (such children cannot take their first breath on their own);
- breathing problems (rhythm may be intermittent or shallow).
Necessary measures
The method for eliminating meconium aspiration depends on the period of detection of this condition. Pathology can manifest itself at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus or after the birth of the baby.
Regardless of the time of the procedure for cleaning the child’s lungs, all methods differ in the complexity of implementation.
After them, the little patient cannot be fed for the first day. His body recovers completely in about two weeks.
Meconium aspiration can be treated in the following ways:
- Suction of amniotic fluid followed by tracheal intubation.
- Using antibiotics to prevent pneumonia.
- Performing artificial ventilation of a child.
- Thermal effects on a newborn (in a maternity hospital).
- Cleaning the respiratory system of a small patient with special solutions.
Another problem is a condition where meconium enters the baby's lungs. This can happen both before and during childbirth. For example, original feces are sometimes found in the amniotic fluid when the pregnancy is intermittent.
During prolonged labor there is always a risk of developing hypoxia or asphyxia. Such conditions in themselves are extremely dangerous: accumulated carbon dioxide in the circulatory system irritates the respiratory centers of the brain, and the child reflexively takes his first breath in the womb, which is why there is a risk of swallowing amniotic fluid. And if they are contaminated with meconium, the feces enter the respiratory organs, which can lead to the development of severe pneumonia.
Amniotic fluid protects the baby in the womb. But if fragments of meconium get into them, there is a serious threat of lung aspiration and, as a result, inflammation develops
That is why it is so important in the last stages of pregnancy not to miss visits to the doctor and to do all the necessary examinations, including ultrasound. Particular attention is paid to women who have oligohydramnios and have signs of discoloration of the amniotic fluid.
In the event that a newborn has swallowed water (it doesn’t matter whether the water is clean or contaminated with meconium), neonatologists clear the airways right in the delivery room, after which the child is monitored to make sure there is no pneumonia or to begin treatment on time if inflammation does begin. .
Summarize. Meconium on the first day of a baby’s life is an important indicator of the baby’s well-being and health. As a rule, there are no problems with its passage. And only in rare situations are resuscitation measures aimed at restoring the digestive or respiratory function of the newborn required.
Why doesn't meconium pass?
Microlax for newborns - how to use an enema for infants
If original feces (another name is meconium) do not leave the newborn’s intestines during the first day of life, this is considered delayed meconium passage. This situation can happen for some reasons.
Possible reasons
The most common reasons why meconium is delayed:
- Congenital pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, which leads to impaired patency;
- A disease called Hirschsprung syndrome. A congenital anomaly in which the intestinal nerve fibers responsible for regulating its motility are absent or underdeveloped. In this condition, obstruction of the affected area occurs. The intestinal sections become filled with foul-smelling feces and become greatly dilated;
- Underdevelopment of the function of the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, secretion and intestinal motility decrease, which causes blockage of the stool;
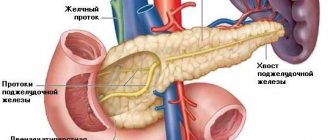
- Cystic fibrosis. This is a severe congenital disease that is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. With this deviation, the pancreatic secretion acquires a viscous consistency. The organ begins to produce insufficient amounts of the necessary enzymes. Liquid absorption from the intestinal lumen begins to increase. With such an anomaly, the consistency and process of passing meconium change;
- Meconium plug syndrome. Occurs when original feces accumulate in the large intestine. This may occur due to impaired motor skills of this organ. Meconium plug syndrome most often occurs in babies born to mothers with hypermagnesemia or diabetes mellitus.
An infant with gastrointestinal pathology
MYSELF
In simple words, this pathology can be explained as follows: the child, while still in the mother’s womb, swallowed amniotic fluid, which contains meconium. Why this happens and what to do in this situation - we will consider further.
Causes
The main reason for feces getting into the amniotic fluid is hypoxia of the newborn of any etiology, while blood circulation shifts towards the main organs. As a result, the intestines lose their tone (including the sphincter) and premature bowel movements occur.
Simultaneously with hypoxia, the respiratory center is irritated, which stimulates the child to take a reflex breath. This is how the amniotic fluid, which contains meconium, is aspirated.
Risk factors include the following:
- post-term pregnancy;
- intrauterine hypoxia;
- wrapping the umbilical cord around the baby's sternum;
- asphyxia.
Signs
The main symptom of meconium aspiration is respiratory distress syndrome in newborns, which determines the form of MAS: moderate or severe.
With moderate severity, the following symptoms appear:
- tachypnea (shallow breathing of the newborn);
- moderate bluishness of the skin;
- Moist rales are heard.
With moderate severity of SAM, the antenatal and intrapartum periods of fetal development are not complicated by hypoxia, which is typical for a severe form of SAM.
Did you know? A newborn's eyes are equal to the size of an adult's eyes, which is why they appear so large to us.
During life, the eyes do not change in size. A severe form of pathology also has other signs:
- the presence of copious amounts of meconium in the trachea at birth;
- pale bluish skin;
- bloating of the chest;
- participation in the act of breathing of auxiliary muscles;
- heart rate is 80 beats per minute.
Necessary measures
For diagnostic purposes, a chest X-ray, blood gas analysis, and hemoglobin level are performed. The most effective way to alleviate a child’s condition and save a life is to timely suction and wash out meconium from the lungs and stomach.
Oxygenation is also carried out. If ingestion of feces causes an infectious infection, it is necessary to use antibiotic drugs - cephalosporins of the 1st and 3rd generations in combination with aminoglycosides.
Possible consequences
This pathology can lead to dangerous consequences:
- chemical burn of the respiratory tract with bile and meconium;
- atelectasis (collapsed lung);
- inflammation and scarring of the alveoli;
- necrosis of the bronchial and alveolar epithelium;
- edema;
- air leak syndrome;
- pneumonia as a result of the addition of a bacterial infection.
Important! The mortality rate for SAM is 10%, so it is necessary to undergo a timely ultrasound scan from a gynecologist to prevent possible fetal hypoxia - the main cause of the pathology.
Meconium ileus
Meconium ileus is a congenital pathology in which obstruction and blockage of the large intestine occurs with original feces. In 15 out of 100 premature babies, such an anomaly occurs together with cystic fibrosis, a systemic disease that disrupts the proper functioning of the respiratory, reproductive, and digestive organs.
Additional Information. Meconium ileus begins to develop due to the lack of a pancreatic enzyme (trypsin). The lack of this hydrolase in the body provokes an increase in the viscosity of gastrointestinal secretions. Because of this, the stool becomes like caviar, sticks to the intestinal mucosa and cannot leave the rectum.
Symptoms
The main symptom of meconium ileus appears during the first two days of a newborn's life. You can suspect that something is wrong with the baby by the absence of stool within 1-2 days after birth. On the second or third day, the baby’s condition begins to deteriorate significantly. The child behaves very restlessly and constantly cries. He stops eating and cannot sleep properly. The baby begins to spit up frequently. In the vomit you can notice an admixture of feces and bile.
As the disease begins to progress, additional symptoms are added:
- The stomach becomes swollen and begins to hurt sharply;
- Skin turgor decreases;
- The skin turns pale;
- The child develops pronounced apathy;
- The baby becomes very inactive.
Then obvious signs of dehydration and intoxication begin to appear:
- Heartbeat accelerates;
- Blood pressure increases;
- The baby feels very thirsty;
- The dryness of the skin increases.
Intestinal obstruction is easy to identify by palpating the anterior wall of the abdomen - through the baby’s soft tummy you can clearly feel the blockage of feces. In this case, the child needs help as quickly as possible.
baby crying
Diagnostic methods
To confirm the diagnosis and identify the cause of the pathology, the doctor usually prescribes the following diagnostic methods:
- Plain radiograph of the abdomen. In the picture you can see distended intestinal loops. The presence of gases and solid meconium will appear as ground glass and soap bubbles.
- Irrigography. Gastrografin is injected into the rectum through an enema and an x-ray is taken. With meconium ileus, the large intestine will be empty, it will be very narrow, and filling abnormalities will be visible in the distal ileum - hard lumps of original feces. Using this study, you can easily determine the location of intestinal blockage.
- Computed tomography. With the help of such diagnostics, you can detect the causes of intestinal obstruction, conduct an X-ray examination from different angles, and then obtain a three-dimensional picture on a computer monitor.
- Ultrasound. After conducting such a study, you can see structural disorders in the abdominal organs, pseudocysts, and calcifications in the intestines.
- Sweat test. Using this test, you can determine the presence of chlorides in the secretion of the sweat glands. This is the most important laboratory test that helps diagnose cystic fibrosis. The test is performed on all newborns with meconium ileus.
Why is it dangerous for a child's life?
The most dangerous consequences of this condition are necrosis of all parts of the intestinal tract and inflammation of the abdominal cavity (peritonitis). Other extremely undesirable consequences include perforation of the colon, neoplasms in the form of pseudocysts, and very severe intoxication of the body with feces.
Oligohydramnios and its causes
Oligohydramnios (oligohydramnios) is less common than polyhydramnios. A decrease in the amount of water is associated with insufficient development of the endometrium, which lines the aqueous membrane, or with a decrease in its secretory ability.
Currently, the causes of oligohydramnios are not well understood, although some patterns have been identified:
- developmental abnormalities of the fetal urinary system;
- maternal hypertension;
- inflammatory diseases of women (both extragenital and genital diseases);
- metabolic disorders (obesity);
- oligohydramnios in one of the identical twins (due to uneven redistribution of blood circulating in the common placenta between the twins);
- post-maturity;
- fetoplacental insufficiency.
When to call a doctor
Problems with the passage of primary stool can occur during the first 1-2 days of a newborn’s life; they can be diagnosed in the maternity hospital during an examination of the baby by a pediatric neonatologist.
While in the maternity hospital, all mothers need to know in what cases they should urgently seek help from a doctor:
- The child started vomiting;
- The baby's body temperature increased;
- The baby does not have a bowel movement for more than 24 hours after birth;
- The baby cries for a long time and behaves restlessly;
- The newborn refuses to eat.
Crying baby
Long-term treatment
Most children with aqueous aspiration syndrome make a full recovery and do not require much long-term care. Some children may be at increased risk of infection during the first few years of life.
In very severe cases, aspiration syndrome can cause permanent damage to a baby's lungs. Additionally, the side effects of radical procedures such as mechanical ventilation and ECMO can cause permanent damage requiring long-term care. Finally, remember that aspiration syndrome deprives the baby of oxygen. Lack of oxygen can cause permanent brain damage.
Alena Paretskaya, pediatrician, medical columnist
1, total, today
( 49 votes, average: 4.82 out of 5)
Hyperthyroidism during pregnancy: consequences, effects on the fetus, treatment
Depression during pregnancy: causes, symptoms, treatment
Related Posts
Normal stool transformation in children
It is worth considering the normal and abnormal stool of a newborn baby. 5-7 days after birth, when the original feces are completely expelled, the newborn’s stool becomes baby-like, acquires a yellowish color, a mushy consistency, and the baby’s feces may also have a sour smell.
Important! A sour smell of stool in a breastfeeding baby is normal if nothing bothers him and the stool has a normal consistency.
Normally, a newborn's stool can be all shades of yellow and brown. Even a slightly greenish tint will be normal due to the fact that the baby has elevated bilirubin levels. As soon as the correct functioning of the enzymes responsible for digestion is adjusted, everything will return to normal. Sometimes the stool may contain mixed lumps and streaks of undigested food.
A one-month-old baby's stool may be too watery, similar to diarrhea, or thick, like sour cream. You should only worry if black stool appears too liquid or too hard, contains streaks of blood and may smell bad.
A breastfed baby of 3 months may have very frequent stools, almost after every meal. Having bowel movements up to ten times a day - this may be called a variant of the norm.
As the baby grows, the frequency of bowel movements also changes, for example, if a two-month-old and a three-month-old baby pooped up to 10 times a day, then a 6-month-old baby’s bowel movements will decrease to 5-6 times a day, and by one year it will be 1-2 times a day. day.
Often mothers worry about why their newborn’s stool has an odor? Babies who eat formula are more likely to suffer from constipation or an upset stomach, and the smell of feces can be putrid and smelly.
Note! Deviations may appear due to diseases of the digestive organs or changes in the diet of a nursing mother. It is important for mom to know what she can eat.
If, some time after birth, meconium is detected in the newborn, this is a clear reason to rejoice, since the baby’s intestines are working correctly. If the original feces are not in a hurry to pass, you should consult a doctor. Timely recognized pathology will increase the chances of recovery.
https://youtu.be/_EaUw6tn4ww
Polyhydramnios and its causes
Polyhydramnios develops due to the increased secretory function of the aqueous membrane and its causes are quite diverse:
- infectious and viral diseases of women during pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- kidney and cardiovascular diseases;
- incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus according to the Rh factor;
- multiple pregnancy (one embryo has oligohydramnios, and the other has polyhydramnios);
- diseases of the placenta (chorioamnionitis, placentitis).