27.11.2019
Dental periodontal disease is a serious disease in which the last stage of gum inflammation occurs. This is often the cause of the development of infectious diseases, gastritis, stomach ulcers or cirrhosis of the liver. Even more often, the patient’s teeth simply fall out, and he cannot lead his usual lifestyle or eat his favorite food.
Gum periodontal disease: what is it?
Dental periodontal disease is a pathological process that causes disturbances in the blood circulation in the oral cavity. Due to disruptions in blood circulation, a gradual thinning of the mucous membrane occurs, which in turn leads to exposure of the roots of the teeth and bone tissue atrophy. But this is not all the consequences that periodontal disease can lead to: in the advanced stages of the development of this disease, teeth begin to become loose and may begin to fall out.
In this case, malocclusion and the appearance of an unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth are also noted. In order to prevent such unpleasant phenomena, treatment of periodontal disease should be started immediately, at the first manifestations of the disease. It is also worth knowing that periodontal disease has its own classification - according to distribution, form and stage of development. The choice of method and means for treating periodontal disease will depend on the type, form, and stage of the disease. According to the degree of distribution, the following types of periodontal disease are distinguished:
Traditional recipes for periodontal disease
Funds from the people will not be able to cure periodontal disease, but will significantly affect the positive dynamics in treatment.
Rinses
- Using garlic infusion. It is necessary to peel, crush the garlic and pour boiling water over it. Give the product time to brew. Afterwards rinse your mouth 2 times a day. The effect of the treatment will become more noticeable if you keep the solution in your mouth for 5 minutes while rinsing. You can simply rub your gums with a clove of garlic.
- Rinse with sea salt solution. Dosage: teaspoon per glass of warm water. Rinse in several steps for 30 seconds.
- Using calendula infusion. You need to rinse your mouth with the product 7 times a day. To prepare it you need to take 2 tablespoons of the herb, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes.
- Rinse with kombucha infusion. The product is very rich in vitamin C, which in turn restores blood circulation in soft tissues.
- Rinsing with a decoction of lingonberry leaves. Pour a glass of boiling water over the leaves (a teaspoon), boil, cool and strain. Rinse at least 5 times a day.
- Rinse with water and Kalanchoe juice. Squeeze the juice from the leaves of the plant, dilute it with water and carry out the procedure.
- Using hydrogen peroxide. The drug is drunk, rubbed on the gums and rinsed in the mouth. For internal use: add three drops of the product to 50 ml of water. Drink three times a day. Course: 10 days. Then the treatment can be repeated. The main note: you need to consume peroxide on an empty stomach. For rubbing: moisten a tampon in the product and begin to rub the medicine well into the gums. For rinsing: dissolve two tablets of hydroperite in 100 ml of clean water.
Recipes from nature
- Application of bee products. Propolis and honey help restore blood circulation and relieve irritation. The products have a bactericidal and wound-healing effect. Propolis tincture is used in treatment. Pharmaceutical preparation (10%) in the amount of 25 drops is diluted in a glass of water. Rinse your mouth with this solution after each meal. The tincture in its pure form can be used internally, but only after consultation with a periodontist. From propolis tincture (only 4%) you can make compresses on the sore spot. In addition to propolis, you can rub honey into your gums. Treatment continues until recovery.
- Application of calamus. To do this, calamus is grated, mixed with toothpaste and brushed. The treatment method helps strengthen the gums.
- Application of alum. Mix one teaspoon of alum with ¼ spoon of salt, add a few drops of mustard oil. Directions for use: massage the mixture onto the gums for several minutes.
- Drink cranberry and lemon juice. The products stimulate the immune system, fight bacteria, and have an anti-inflammatory effect. You need to drink 100 ml of any juice every day. If you mix lemon juice with extra salt, you get a medicinal paste that you use to brush your teeth.
- Drink only green tea (avoid black tea). Green leaves heal the entire body, thereby helping it cope with periodontal disease faster.
Free consultation on the cost of treatment in our dentistry
Leave a request and the clinic administrator will contact you within 15 minutes!
- Local, affecting a certain area of the dentition and not spreading to other areas of the oral cavity;
- Generalized, affecting the dentition in the upper and lower jaw.
According to the nature of the course, acute and chronic forms of periodontal disease are distinguished, and five phases of the development of the disease are distinguished, each of which has its own specific symptoms. We will examine in detail the phases of development of periodontal disease, symptoms and treatment of different stages of the disease in the following sections of the article.
Symptoms
For a long time, the disease passes without clear signs, but the process is already developing inside the gums. A person may notice minor discomfort and increased sensitivity of the gums.
The main symptoms of periodontal disease are:
- bleeding gums on exertion;
- the appearance of gaps between teeth;
- pale gums;
- increased sensitivity;
- burning sensation on the oral mucosa;
- mobility and pain of the crowns;
- exposure of the neck and root of damaged teeth.
If several symptoms appear, you need to go to the doctor. He will make a diagnosis, assess the severity of the condition, and prescribe treatment.
Symptoms of dental periodontal disease
How to treat periodontal disease? The answer to this question will largely depend on the stage to which the development of the disease has reached. There are five phases of the development of periodontal disease and each stage has its own symptoms:
- The initial phase of periodontal disease. At this stage, the inflammatory process is just beginning and therefore the disease has no symptoms. Periodontal disease can be detected at this stage of development only during an examination in the dentist’s office.
- Primary phase of periodontal disease. It is characterized by insignificant receding of the gums, but the dental units in the sockets are held quite firmly, and it is possible to detect the beginning of bone tissue atrophy only through radiography.
- Secondary periodontal disease reveals itself by the obvious exposure of the cervical part of the teeth and the appearance of interdental spaces; radiography clearly shows pathological changes in the alveolar process. The patient may begin to experience severe tooth sensitivity.
- At the third stage of development of periodontal disease, the roots of the teeth are exposed by more than half, the spaces between the teeth grow in width, and the teeth begin to loosen in the sockets. Teeth sensitivity to sour, sweet, cold and hot foods increases.
- In the fourth phase of the development of periodontal disease, the teeth become so mobile that the patient cannot speak or eat normally.
In order to correctly select remedies for periodontal disease and methods of its treatment, it is important to promptly diagnose the disease and determine its phase of development. This can be done by visiting Vanstom dentistry in Moscow. Our clinic uses the most effective treatments for periodontal disease and innovative techniques that can help avoid the disease becoming chronic and all the associated negative consequences.
Stages of disease development
There are 3 stages of periodontal disease:
- Easy. The patient has no complaints; very rarely there is a reaction to cold or hot food. The presence of periodontal disease can be determined during a dental examination. The mild stage of the disease is best treated.
- Average. The roots of the teeth are exposed by an average of 4-6 mm. The patient begins to experience a burning sensation in the mouth, and there is an acute reaction to eating hot, cold or sour foods.
- Heavy. The roots of the teeth are exposed by 8-10 mm. Chewing food causes severe pain.
Causes of periodontal disease
It is impossible to name a specific reason why periodontal disease occurs, but dental experts have found that this disease always occurs against the background of metabolic disorders in the body, which can arise due to a number of pathologies. Most often, dental periodontal disease is accompanied by the following diseases:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, severe hormonal imbalance;
- Gastrointestinal pathologies;
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- The patient’s bad habits – in particular, tobacco and alcohol addiction;
- Neurological diseases;
- Bite abnormalities.
Also, periodontal disease is often observed with weakened immunity, against the background of injuries to the jaws and oral cavity. To choose the most effective treatment for periodontal disease in a specific clinical case, you need to identify the cause that triggered the onset of the disease, and this can only be done by conducting a series of tests prescribed by a periodontist.
Periodontal disease: causes of the disease
The causes of periodontal disease in adults can be caused by a number of circumstances. The most significant of them is a violation of the blood supply to the jaw bones, which always leads to the development of periodontal disease.
Due to this failure, the nutrition of this bone area is stopped, which negatively affects the mineral metabolism occurring here.
In addition, periodontal disease can develop as a result of the following reasons:
- Manifestation of hypovitaminosis associated with impaired reactivity of the body.
- Hereditary predisposition, which consists in aggravating the situation by bad habits and the development of certain diseases.
- Frequent smoking. Daily numerous “puffs” negatively affect not only the teeth, but also the gums, leading to the development of periodontal disease.
- Taking a separate category of medications that help reduce habitual salivation. A lack of saliva negatively affects the condition of the entire dental system, as this causes the teeth and gums to lose protection from pathogenic microorganisms. An insufficient amount of saliva cannot fully protect the gums and teeth, so the development of the inflammatory process begins. This effect can be expected from regular use of anticonvulsants.
- Diseases that weaken the immune system: HIV infection.
Somatic pathologies: gastrointestinal diseases, heart pain, manifestations of atherosclerosis. With atherosclerosis, there is a blockage of the blood vessels that are responsible for supplying the dental tissues. All this leads to the development of atrophy and hypoxia.
- Hormonal changes that occur in connection with puberty, menopause, and pregnancy. Hormonal imbalances can also be caused by diseases of the endocrine glands.
In addition to general factors, the development of periodontal disease is preceded by local ones, namely:
- The labial frenulum is small in size;
- Underdeveloped oral vestibule;
- Anomalies in the formation of periodontal structures.
The development of periodontal disease is also preceded by a banal failure to comply with hygienic rules for caring for the oral cavity.
The appearance of tartar and yellow plaque stimulates the proliferation of microbes, which causes the development of inflammatory processes and a decrease in immune properties.
If signs of periodontal disease are detected in the body, it is recommended to contact the dental office for an unscheduled check of the condition of the teeth.
Professional methods of treating periodontal disease
Practice shows that it is most effective to treat periodontal disease in the clinic, rather than at home, since professional dentistry has in its arsenal powerful and targeted drugs and technologies that can prevent the development of periodontal disease until the critical phase. The course of treatment for periodontal disease in dentistry will consist of many stages, each of which we will consider in detail below:
Professional Inspection
Before beginning the process of treating periodontal disease, the patient undergoes a professional examination by several specialists: a dentist, a hygienist, an orthodontist and a periodontist. Each specialist prescribes a different series of tests for the patient and carries out a set of specific procedures for the effective treatment of periodontal disease. An obligatory step in the treatment of dental periodontal disease will be an X-ray examination, which will help to accurately determine the degree of destruction of dental units.
Based on the tests and x-rays performed, the treating specialist will draw up a detailed treatment plan for periodontal disease in a specific clinical case.
Sanitation of the oral cavity for periodontal disease
Dental deposits and bacterial plaque are not the causes of periodontal disease, but it has been proven that they accelerate the rate of its development and therefore treatment of periodontal disease will be effective only if high-quality sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out before it. The procedure is carried out in the periodontist’s office and uses ultrasound, which ideally cleans the dental surfaces of all types of deposits.
Drug therapy for periodontal disease
The most effective treatment for periodontal disease is complex therapy, in which a separate place is occupied by a course of medications selected by your attending physician. Usually these are vitamins, hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs that strengthen the immune system. Often, when treating periodontal disease, the patient is prescribed a course of injections with drugs that will saturate the tissues affected by the disease with oxygen and slow down the rate of development of the inflammatory process. If a patient's periodontal disease is diagnosed in an acute form, antibiotics and rinses with antibacterial solutions may be prescribed.
Physiotherapy for periodontal disease
The purpose of using physiotherapeutic procedures in the treatment of periodontal disease is to normalize blood circulation in the soft tissues of the oral cavity. Physiotherapy also helps eliminate swelling of the gums and saturate the tissues with oxygen. The range of physiotherapeutic measures is determined by the doctor when drawing up a treatment plan for periodontal disease.
Periodontitis and periodontal disease: what is the difference
Many patients do not see the difference between periodontitis and periodontal disease and therefore often confuse these two diseases. But there are big differences between them, both in the etiology of origin and in the general symptoms of manifestations.
For example, the main cause of periodontitis is considered to be a lack of oral hygiene and, as a consequence, the formation of bacterial plaque on the teeth and gums. As well as long-term ignorance of such diseases as gingivitis. Elementary gum bleeding during eating and hygiene procedures is considered by people as the most standard, unforeseen phenomenon. Therefore, they are in no hurry to see a doctor and are faced with a worsening situation.
As for the symptoms of periodontitis, a person who has developed such a disease observes the following picture: the gums bleed, gum pockets appear (when the gums tightly gripping the tooth begin to peel off from it), pus may appear from the gum pockets, the mucous membrane looks bright red or even cyanotic. All this is accompanied by an increased pain reaction, but only with pressure and touching the mucous membrane, and not the teeth, as with periodontal disease.
With periodontal disease, there are no such symptoms - the gums are whitish and fit tightly to the surface of the teeth. But they are simply reduced in size. There is no inflammatory process. Periodontal disease in its “pure” form is rare; much more often it is a consequence of long-term treatment of periodontitis, when the inflammation has been removed, but atrophy of periodontal tissue remains.
Important! These two dangerous dental diseases have one thing in common: if left untreated for a long time, they will gradually become a threat to the normal functioning of all teeth. In the most advanced cases, the issue generally has to be resolved radically, i.e. remove all diseased teeth and replace them with dentures or implants.
Elimination of caries, diseased teeth and splinting for periodontal disease
In order for the treatment of periodontal disease to be effective, caries must be treated. A huge number of pathogenic microorganisms accumulate in carious cavities, which provoke gum inflammation. If the destruction of a dental unit has reached a significant stage, it is removed.
If periodontal disease has developed to the stage at which tooth mobility appears, a splinting procedure is performed. It is necessary because the instability of the teeth provokes active atrophy of bone tissue, and this is fraught with the loss of teeth from the sockets and their divergence in different directions. Splinting reduces the degree of tooth mobility and stops the process of bone tissue destruction.
An important nuance: if a decision is made about the need for surgical intervention in the treatment of periodontal disease, splinting is mandatory.
How to save teeth?
Once periodontal disease is diagnosed, the main goal is to save teeth. To do this, it is necessary to stop tissue degeneration, improve blood circulation in them and start periodontal regeneration. In this regard, physiotherapeutic procedures have a good effect:
- gum massage;
- shower for gums (gingival);
- darsonvalization;
- acupuncture;
- electrophoresis (calcium gluconate is used).
As a medical treatment for periodontal disease, the following may be prescribed:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (antibiotics, biogenic stimulants, antitoxic serums).
- Injections (aloe extract is often used).
- Oxygen enrichment (delivered to the base of the gums).
Surgery
Surgical techniques are actively used in the treatment of periodontal disease. They can be reconstructive and radical.
Photos before and after treatment
Curettage is a reconstructive technique . This procedure involves cleaning the sockets of the teeth.
- If there is no tooth mobility, then closed curettage is performed. In this case, infiltration anesthesia is performed and unnecessary deposits, epithelium and granulations are removed.
- If teeth are mobile, open curettage is performed, which is a flap operation. It is performed under local anesthesia. The operation involves making an incision in the gums, cleaning the roots of the teeth from tartar and other deposits. If the bone tissue is damaged, it is replaced with grafts (artificial or bone).
Radical surgery includes tooth extraction and gingivectomy . Teeth have to be removed when periodontal disease becomes severe, when they are very mobile and the gums bleed. After removal, you can resort to prosthetics or implantation.
Gingivectomy involves removing the affected part of the gum to save the canals and roots of the teeth.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies help enhance the effect of traditional medicine.
- Mouth rinses help a lot. Tinctures of elderberry, kombucha, calendula, oak bark, blackberry leaves, and strongly brewed green tea are suitable for this.
- Sea buckthorn oil has a healing effect. For periodontal disease, you can make applications with it.
- To strengthen gums and reduce bleeding, you can add calamus root (crushed into powder) to regular toothpaste.
Remember that treatment should only be prescribed by a specialist. Self-diagnosis and self-medication can only do harm!
Surgery for the treatment of periodontal disease
Surgical intervention is used at critical stages of the development of periodontal disease, in which the depth of the periodontal pocket reaches ten millimeters or more. A periodontal canal is a depression formed when the natural attachment of the soft gum tissue to the tooth is disrupted. If such a pocket is shallow, then in the process of treating periodontal disease you can do without using the surgical method. However, in the third and fourth phases of development, the pocket depth can reach 7-11 millimeters and the use of medications in such circumstances will not give any positive changes in the treatment of periodontal disease, and only surgical intervention can help correct the situation.
During the operation, the dental surgeon restores bone tissue, using for this purpose special materials that catalyze the growth of natural bone material. This manipulation allows you to strengthen loose teeth and prevent further development of the disease.
Also, in the treatment of periodontal disease, prosthetics may be prescribed. It is mandatory even if only one tooth is missing in the dentition. If all the patient’s teeth are intact, but periodontal disease has caused the formation of significant gaps between them, the defect is eliminated by installing metal-ceramic bridges.
Another technique that can be used for periodontal disease is laser treatment. This technology should be considered exclusively as an auxiliary means of therapy that can help remove the unpleasant symptoms of the disease as quickly as possible - swelling of the gums, bleeding.
Let us write once again that complete treatment of periodontal disease is always a whole complex of the most diverse measures, and only such therapy can save you from this unpleasant disease.
conclusions
- Periodontal disease is a rare disease in dentistry that causes thinning of the orthodontist. In the early stages, the disease is asymptomatic, which complicates early diagnosis.
- Pathology develops, as a rule, against the background of non-compliance with personal hygiene. Provoking factors are identified - smoking, poor diet, systemic diseases and metabolic disorders.
- Despite the nature of its origin, the disease is not contagious. Read more about how periodontal disease is transmitted in this material.
- There are a large number of diagnostic methods aimed at assessing the condition of the gums, bone tissue and dentition.
- Treatment options include medications and surgery. In advanced cases, surgery cannot be avoided.
Is it possible to treat periodontal disease at home?
It is impossible to cure periodontal disease at home - it is a serious disease, the successful treatment of which requires a professional and comprehensive approach. However, a number of procedures can and should be carried out at home; they will help speed up the process of treating periodontal disease. Home remedies for periodontal disease are prescribed by your doctor.
Experts usually prescribe patients to use various ointments and gels with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects at home. In the early stages of the disease, a special paste for periodontal disease may be an effective treatment. You cannot cure yourself with such a paste, but it will help remove swelling and bleeding gums and bad breath. Patients who have been treated for periodontal disease write in reviews of pastes that the best results in eliminating the unpleasant symptoms of the disease are provided by formulations with natural ingredients - herbs and vitamin complexes.
Medicines for treatment
To get rid of periodontal disease, complex therapy is required. If you have a chronic disease, you need to take measures to treat it in order to reduce the impact on gum pathology. Antibiotics will be the mainstay of treatment. They will destroy a significant part of the bacteria.
Pills
Lincomycin is often prescribed for periodontal disease. This is an effective antimicrobial drug that can cure the disease even in severe form. Trichopolum helps get rid of most bacteria that cause diseases of the soft tissues of the oral cavity. Metronidazole, Doxycycline, Rondomycin are also recommended. These are antibiotics that cause dysbiosis, malfunction of the excretory system and liver. To mitigate these side effects, probiotics are prescribed.
To strengthen the bone structure, biosphosphonates are prescribed. After surgery, they are not used as they slow down the healing process. The drugs Zolerix, Aclasta, Rezorba show good results. Biogenic stimulants, for example, Apilak, liquid aloe extract, Befugin, can stop degeneration of soft gum tissue.
The general well-being of the patient is supported by immunomodulatory compounds: Imudon, Prodigozan, Timalin. They stimulate metabolic processes, prevent the spread of inflammation, and provide protection against diseases.
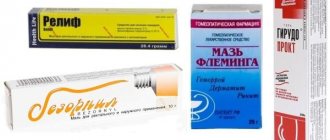
Ointments and gels
Medicines for periodontal disease are used externally for application under the gums and for rubbing in. The main gels and ointments are presented in the table.
| Name | Effect of action |
| Troxevasin | Increases the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels, increases their tone, thereby reducing gum bleeding. Reduces swelling of soft tissues, has anti-inflammatory properties. |
| Heparin ointment | Strengthens microcirculation in the gums, stops degenerative changes in bone tissue. |
| Metrogil Denta | Prescribed when gingivitis occurs. Has a strong antimicrobial effect. |
| Solcoseryl | Helps in tissue restoration, stimulates wound healing, and quickly soothes pain. When applied topically to wounds, it forms a protective film. |
| Holisal | It has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effects, and is effective against pain. It is quickly absorbed into the surface of the gums and has a long-lasting therapeutic effect. |
| Asepta | Relieves itching and irritation. Helps strengthen gums and stimulate healing. Destroys pathogenic microflora. The active substance is propolis. |
Due to good penetration into tissues and the formation of a protective film, the use of gels and ointments has a great therapeutic effect in the treatment of periodontal disease.
Sprays
In addition to ointments and tablets, there are medicinal sprays. They have a noticeable antiseptic effect, successfully fight the proliferation of bacteria, and improve tissue restoration. Popular sprays are Miramistin and Parodontocide.
Before using sprays, you need to rinse your mouth, hold the bottle with the product vertically, and point the sprayer into the oral cavity. Press the dispenser three times. Next, you should close your mouth and not talk, drink or eat for 30 minutes. The treatment must be repeated three times a day.
Other means
Homeopathy is used as an auxiliary method. It is used as an additional treatment. Acidum nitricum 6 is often prescribed for sore soft tissues and unstable teeth. Phosphorus 6 helps well with gum damage. Natrium carbonicum 6 + silicea 6 is used for periodontal disease, which arose as a complication of diabetes mellitus.
Treating periodontal disease with medications in the form of injections has a good effect. They are placed in the gums, which allows the active substances to act directly in the affected area. Injections help to contain the development of the disease in a minimum period of time and begin the restoration of gum tissue.
Will traditional medicine help?
On the Internet, on many sites, you can find recipes for the treatment of periodontal disease with folk remedies. However, let’s say right away that traditional treatment of periodontal disease may turn out to be completely useless, since it is only possible to stop the development of the disease by using professional techniques. Moreover, the use of some recipes can be harmful, provoking the active development of inflammatory processes.
If you still want to try folk remedies or homeopathy to speed up the pace of periodontal disease treatment, be sure to coordinate all your actions with your doctor.
What does the disease look like on an x-ray?
The first diagnostic method for suspected periodontal disease is radiographic examination. The image will show progressive loss of bone tissue and depletion of tissue around the tooth.
At the initial stage of the disease, x-rays will show a uniform decrease in the height of the wall between the alveoli without signs of osteoporosis and widening of the periodontal gap.
At the moderate and severe stages, the height of the interdental septa is reduced by more than 1/3.
Prices for periodontal disease treatment in Moscow
Without an examination and a series of tests, it is impossible to say exactly how much periodontal disease treatment will cost. The price of the service will take into account those measures that will be included in the treatment plan drawn up for you at the dental clinic, and will also depend on the stage of development and form of periodontal disease. To find out the exact amount of treatment, visit our dentistry in Moscow “Vanstom” and get detailed advice from our specialists.
It is important to know that the sooner measures are taken to treat periodontal disease, the higher the chances of its final cure. If the disease reaches critical phases of development, medicine will be powerless, since chronic periodontal disease is incurable. Therefore, if, based on a number of symptoms, you suspect that you have periodontal disease, do not delay a visit to the dentist. In our Vanstom clinic you will find the highest level of quality services, innovative techniques for the treatment of periodontal disease, modern equipment and materials, and an individual approach to each patient.
ICD-10
According to the generally accepted international classification of diseases ICD-10, periodontal disease belongs to class XI (diseases of the digestive organs) and is designated K05.4 (K05 - gingivitis and periodontal diseases). As an explanation for this disease, the ICD-10 reference book indicates “juvenile periodontal disease.” This phenomenon is also called juvenile periodontal disease, as it occurs in children under 5-6 years of age and young people aged 12-18 years. More often, people in adulthood are exposed to this disease.
A neighbor of periodontal disease according to the ICD-10 classification is periodontitis (chronic - K05.3 and acute - K05.2). Although many people confuse periodontitis and periodontal disease , the differences between these diseases are quite significant.
Complications of periodontal disease
Lack of treatment leads to serious consequences, one of which is tooth loss. The periodontal tissues gradually atrophy, the teeth become mobile and some will have to be removed. Advanced periodontal disease can develop into more dangerous diseases - periodontitis, gingivitis, leading to pulpitis, periodontal abscesses and even osteomyelitis of the jaw. Untreated periodontitis can cause diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, heart and respiratory system. Therefore, treating periodontal disease carelessly is not just frivolous, but also fraught with serious health consequences.
List of sources
- Nikolaev A.I. Practical therapeutic dentistry / A.I. Nikolaev, L.M. Tsepov. — 2nd ed., revised. and additional - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2003.
- Muravyannikova Zh. G. Fundamentals of dental physiotherapy / Zh. G. Muravyannikova. - Rostov n/a: “Phoenix”, 2002.
- Aggressive forms of periodontitis. Guide for doctors / Bezrukova I.V., Grudyanov A.I. - M.: Medical Information Agency LLC, 2002.
- Periodontal diseases. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment / [A.S. Grigoryan, A.I. Gudyanov, I.A. Rabukhina, O.A. Frolova]. - M.: Med.inform. agency, 2004.
Consumer Reviews
Bubble_gum (irecommend.ru)
“Hello to everyone who stopped by! As you already understand, today I will share my experience of using Asepta Active mouth rinse.
Problems with my gums have been tormenting me for a long time - they constantly bleed and become inflamed. One of the reasons is tartar, which I recently went to remove. You can read about how it was and whether you need it here.
After treatment, the doctor prescribed this mouthwash to me. They didn’t tell me how long I needed to use it, but I already understood that it was a week and then a break. Otherwise, as the dentist said, the microflora of the oral cavity can be disrupted.
Indications for use:
- acute and chronic gingivitis;
- acute and chronic periodontitis;
- stomatitis;
- post-extraction alveolitis;
- toothache of infectious origin.
I purchased Asepta Active because it is aimed at treating gums. Simply "Asepta" is intended for freshness of the oral cavity.
When using it, it stings and burns a little. The tongue becomes numb if the mouthwash is not diluted with water.
Asepta mouth rinse is ready for use. Pour 10 ml of mouthwash into a measuring cup and rinse your mouth for 20 seconds. It is not recommended to drink or eat within 30 minutes after using the mouthwash. Use 2-3 times a day for 5-7 days.
I use it according to the instructions - I dilute half a measuring cup with water, otherwise it makes my mouth ache, but not too much and not scary, in principle. I use this rinse 1-2 times a day, but not daily. One such bottle lasted me a little more than 1 month. Very economical. But let me emphasize once again: the consumption depends on your personal volume of use of the product.
What effect are we promised from using this mouthwash?
Mouthwash "Asepta®":
- has a pronounced antibacterial effect;
- relieves inflammation and bleeding of gums;
- prevents the formation of dental plaque;
- freshens breath...
...I have been using this rinse for more than 4 months, intermittently, and I can say that there is a result. Of course, not only does it solve my problems, I also use Asept toothpaste, and, of course, the correct movements with the toothbrush. And in case of severe inflammation, I save myself with dental gel (this and this)
Action.
The gums have become less bleeding, although this is the merit not only of this rinse, but of other products as well.
After use, you feel fresh for a long time.
Dental plaque began to form less.
….I didn’t look into the ingredients here, the main thing is that the rinse aid helps, and that’s good. I don’t take it internally...
...I recommend purchasing Asepta Active mouth rinse if you have found your corresponding symptoms in the Indications for Use.”
Minuto4ka (otzovik.com)
“Mint is an acquired taste, in everything. For example, I can completely tolerate it and love it. But I know a lot of people who can’t stand tongue-biting additives.
These are the first associations that arose for me when I first used this mouthwash.
It is sweet and has a lime flavor. And absolutely non-biting.
They prescribed it to me for absolutely no reason, of course.
My dentist prescribed it for me. For gums, which really bother me due to the periodic eruption of wisdom teeth. Which I'm terrified of deleting.
The rinse aid is sold in pharmacies, I haven’t seen it in supermarkets, which captivates me. I would like to believe that it is truly therapeutic in nature. They prescribed me this mouthwash along with Asepta dental gel. I don’t know which of them helped in the end. Maybe all together.
I think the advantage of the bottle is the presence of a measuring cup. It is very comfortable. Not all mouthwashes have it. I once suffered with Splat mouthwash
The price of the rinse aid, however, is higher than its analogues. Other brands can be purchased at a more modest price. Overall I recommend it. At least it will win over its audience with its taste.”
Prevention of periodontal disease and periodontitis
Prevention of gum disease is very important - it is better to prevent the development of pathology than to then undergo a long and difficult recovery. If you notice the first signs of a problem, you should immediately consult a doctor. The specialist will tell you in detail how to strengthen your gums, what paste and brush to use in your particular case. General principles for the prevention of periodontal disease include the following:
- monitor your health, promptly treat not only dental diseases, but also problems in the body as a whole,
- do not avoid moderate physical activity, eat right, increase immunity,
- maintain oral hygiene, brush your teeth twice a day, with an individually selected brush and paste, rinse your mouth after each meal with plain water or an antiseptic, use floss and an irrigator,
- treat carious processes in a timely manner, do not ignore bite defects,
- limit alcohol consumption and smoking as much as possible,
- undergo preventive examinations at the dentist at least 2 times a year, and also undergo professional cleaning every six months.
Proper dental hygiene is important to maintain your smile.
There is no need to try to solve the problem yourself. While it is still in its infancy, qualified help will stop the process and prevent irreversible consequences. Modern medicine has effective advanced methods, technologies and medications that, together, will help stop the pathological process and restore a healthy and beautiful smile.
- According to WHO.
How periodontal disease and periodontitis manifest themselves - signs of pathologies
Periodontal disease as such does not lead to redness and bleeding of soft tissues - the mucous membrane turns pale, weakens and loses vitality. But with inflammation, periodontal pockets are formed, in which plaque and hard deposits begin to actively accumulate. The gums swell, turn red, and move away from the crowns. Gradually, the deposits begin to rot, which causes an unpleasant odor and other related problems. These are already symptoms of periodontitis.
Important! Many people are interested in the question of whether the disease can be cured forever. Unfortunately, both periodontitis and periodontal disease are irreversible phenomena. They can only be stopped, further spread stopped and the condition stabilized, but only an integrated approach to the problem will help here.
The more advanced the stage of the disease, the more pronounced its symptoms (we are talking specifically about periodontitis as the most common and most dangerous gum disease):
- discomfort and pain while chewing,
- bleeding - may be a constant concern or occur during mechanical stress, for example, when brushing or biting on hard foods,
- redness of the mucous membrane - the gums acquire a bright red tint and may become bluish in the area of the gingival papillae,
- the formation of voluminous gum pockets - the mucous membrane moves away slightly from the crown, resulting in the formation of a pocket in which a large amount of plaque and deposits accumulates,
- bad breath as a consequence of the onset of purulent processes in the contents of the pockets,
- gum recession and gradual atrophy of bone tissue - the crowns seem to stretch out in length, but this is only a consequence of subsidence of the mucous membrane along with the bone tissue,
- mobility due to a violation of the ligamentous apparatus - from subtle in the first stage to serious in the second, when the tooth literally rotates in the hole and is already on the verge of falling out.
The mucous membrane becomes looser, the tissues turn red and swell.
Over time, the general condition of the patient's body worsens. There may be an increase in body temperature in the acute phase of the disease, general weakness and malaise.
Periodontal disease and periodontitis: features and stages of pathology, the importance of complex treatment
Periodontal disease is a disease of the periodontal tissues, which over time leads to their weakening and tooth loss. The development of pathology is accompanied by impaired blood circulation in the mucosa, its thinning and atrophy, and exposure of the roots. In its true meaning, periodontal disease is not an inflammatory disease, but such a pathological phenomenon occurs extremely rarely - in 3-5% of cases. Today, periodontal disease is quite often considered as a consequence of the aggressive course of periodontitis - a common inflammatory gum disease. Further in this article we will understand how periodontal disease differs from periodontitis, what are the causes and symptoms of such phenomena, and how they are treated in dentistry today.
Symptoms of the disease and degree of development
Due to the absence of a noticeable inflammatory process, signs of periodontal disease appear already with the active destruction of the dentofacial apparatus. The initial stage of periodontal disease is almost asymptomatic ; the patient may experience mild discomfort, accompanied by itching of the gums and bleeding.
The subsequent stages of progression of the disease are accompanied by the following main symptoms:
- At the first stage, which corresponds to a mild degree, the gums become red and slightly swollen, and tooth instability appears. X-ray images already show the first degenerative signs.
- At the second stage, corresponding to the average degree, the signs of periodontal disease intensify. The gums take on a bluish tint, bleed more often, noticeable gaps appear between the teeth and a periodontal groove up to 6 mm deep. Tooth mobility increases, purulent-serous discharge appears.
- At the third stage, corresponding to a severe degree of pathology, the tooth becomes loose in all directions and can even be displaced by the tongue. The gums are sensitive to hot, cold, sour foods and recede. The recess in which the tooth root is visible is enlarged by more than half a centimeter. Pus continues to be released, and difficulty speaking and chewing food appears.
- At the fourth stage, the cervix is exposed by more than 2/3 of the radix and is covered with dental plaque. Due to pathological changes, the color of the mucous membrane becomes pasty and pus is released. The tooth is extremely mobile; on an x-ray, it communicates with the bone at its apex.
What complications can gum disease cause?
When answering the question about how dangerous the disease is, we cannot limit ourselves to problems in the oral cavity. Along with the fact that these pathologies lead to gum recession and tooth loss, they negatively affect the functioning of other internal organs and systems. Pathogenic bacteria inevitably enter the stomach and cause disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract.
In addition, scientists have proven that periodontitis increases the risk of developing pyelonephritis, that is, inflammation of the kidneys, as well as various pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the blood and secrete a special protein there, similar to the cellular structure of kidney tissue. The body’s defense system is activated, but in attempts to destroy harmful substances, it also destroys its own cells.
The photo shows advanced periodontitis
In addition, when toxins enter the bloodstream, they provoke the formation of blood clots. This significantly increases the risk of heart attack and other heart pathologies. The likelihood of atherosclerosis, diabetes, and breast cancer also increases.
Surgery
Surgical treatment methods are the only effective options for getting rid of periodontal disease in the later stages. They consist of removing subgingival deposits, restoring bone and soft tissues, and stabilizing mobile teeth.
Surgical treatment is prescribed for:
- pocket depth from 5 mm;
- looseness and displacement of units;
- intense inflammatory processes;
- severe bleeding.
There are 4 types of surgery for periodontal disease:
- Curettage. This is a mechanical cleaning of gum pockets. It is carried out using closed and open techniques. The second involves removing stone with a preliminary incision and exfoliation of the gingival margin. The deposits are removed using hook-shaped instruments (curettes), laser or ultrasound, after which the surfaces of the roots are polished, and the pockets are washed with antiseptics, and reparative and anti-inflammatory drugs are placed in them.
- Osteoplasty. The operation consists of implanting osteoreplacement materials that restore atrophied areas of bone tissue. After a couple of months, they begin to synthesize new bone cells and, thus. participate in the formation of the alveolar process and strengthen loose units.
- Gum regeneration. Implemented along with osteoplasty. The periodontium is revived by integrating stem cells, fibroblasts or protein structures.
- Autotransplantation of the gingival margin. Used for gum recession. The intervention consists of replacing the degenerated mucosa with patch graft material from another part of the oral cavity, usually from the palate.
In case of periodontal disease, curettage of periodontal pockets is often performed.
Gels and ointments
These products are intended for topical use. Thanks to their structure, they adhere well to the gums until completely absorbed. Indicated for home treatment:
- "Cholisal" (gel) - has pronounced antimicrobial and analgesic effects. Main component: choline salicylate, additional component – cetalkonium chloride. The gel is rubbed into the gums or placed in the gum pockets 2 times a day. The duration of the course is determined by the doctor. Cost about 340 rubles. for 10 gr.
- "Metrogil Denta" (gel) - has an anti-inflammatory, anesthetic effect. Active ingredients: metronidazole benzoate, chlorhexidine digluconate, auxiliary ingredients: propylene glycol, disodium edetate. Apply twice a day for up to 10 days. Cost 20 gr. from 190 rub.
- "Kamistad" (gel) - designed to reduce pain and reduce inflammation. Main components: chamomile infusion, lidocaine 2%, auxiliary components: carbomer, benzalkonium chloride. Apply 2 times/day for 10-14 days. The cost starts from 220 rubles. per tube 10 g.
- "Asepta" (gel) - is used to treat inflammation of the mucous membrane, as it has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. The active substance is propolis extract, the auxiliary substance is carbomer, propylene glycol. Apply after brushing your teeth three times a day for 10-14 days. Price for 10 g. about 170 rub.
The use of these products has a good result in the treatment of periodontal disease. But you can’t use them without a doctor’s prescription!
Methods for restoring teeth against the background of periodontitis or periodontal disease
The presence of periodontal diseases, even in the compensated stage, creates certain difficulties with the choice of methods for restoring lost teeth. Let's consider which options in such a situation will be effective and safe.
Is it possible to install bridges and removable dentures?
Bridges fixed to their teeth are the most unsuitable prosthetic option even at the initial stage of periodontitis. The gradual loosening of the teeth does not allow them to become a reliable support for the orthopedic structure, which will eventually also become mobile. It is better to choose removable prosthetics, but only as a temporary solution - while the course of therapy lasts.
For a temporary solution, you can choose a removable denture
Thus, it is strictly forbidden to carry out implantation while the disease is in the active phase - this can lead to rejection of the structures. Until the pathological process is completely stopped, a removable denture can be used. But this is not a solution for the future, since such orthopedic solutions have too many disadvantages - further bone atrophy, difficult adjustment, pain and rubbing, weak fixation, etc.
Why is implantation the best solution?
Implantation is the best solution, but only after undergoing complex treatment, stopping the pathological process and normalizing the patient’s condition. In this case, special implants with a smooth neck surface should be used, which prevents the accumulation of bacteria. In addition, the structures must have high levels of primary stability and have a special coating for better osseointegration in conditions of bone of varying degrees of softness. Similar models are in the assortment of Nobel Biocare, an undisputed leader in the production of dental implants with half a century of experience and a huge clinical base.
Implants cannot be implanted next to affected teeth, even if they are on the opposite jaw and the disease is in the active phase. And this is another good reason to start undergoing a full course of treatment, and only then proceed with prosthetics.
“I thank the doctors of the clinic for such high-quality, fast and well-coordinated work! A month ago I had a full basal implantation. My case turned out to be difficult - due to periodontitis, my teeth literally fell off, but the problem also turned out to be loss of bone tissue, which made it impossible to install simple implants. Here I was offered to undergo complex gum treatment, which took a little over a year, and then they carried out full implantation. Yes, it was scary, even despite the course I completed, but everything ended more than well, for which I thank you immensely! Rehabilitation went quickly, and now I’m smiling and enjoying life again! I don’t yet risk chewing solid food, but I’ll gradually come to this! Thank you so much again! I recommend to everyone!"
Natalya V.P., review on the website of the Moscow dental clinic
The optimal solution in such a situation would be to use comprehensive solutions for the complete restoration of the jaw. First of all, this is basal implantation, in which implants from the Swiss company Oneway Biomed are usually used - the manufacturer has been on the market for more than 40 years, has proven clinical studies on the safety and successful engraftment of its structures. For cases of the initial and medium compensated stages, the all-on-6 complex on Nobel implants can also be used, including using zygomatic models, which involve not only the jawbone, but also the zygomatic bone of the skull, which ensures their reliable fixation.
Photos “before” and “after” basal implantation
All these methods refer to immediate loading complexes, which means that the prosthesis is installed in the shortest possible time, without the need for a long wait until the implants are completely accustomed. Firstly, it allows patients to quickly return to their normal lives, restore the aesthetics and functionality of the jaw apparatus. Secondly, the implants are literally splinted due to the strong base of the prosthesis, which does not allow them to move. Through artificial roots, the bone tissue begins to again receive chewing load, and this stimulates its restoration and improves the engraftment of titanium rods.
Answers to frequently asked questions:
Is it possible to cure periodontal disease forever?
Periodontal disease is not completely curable. Dystrophic processes in the gums and bone structures are irreversible: you can only slow them down. Therefore, patients with this diagnosis have to visit the dentist several times a year for life and receive appropriate treatment.
The best results are obtained from therapy in the initial stages, when deep periodontal pockets have not formed, there is no mobility of teeth and there are no significant changes in the periodontium and periodontium.
But due to blurred and mild symptoms at the beginning of the development of the disease, patients rarely apply in the early stages. Most patients come to the clinic when their teeth are already very loose; they have to be splinted or completely removed and replaced with dentures or implants. The chances of tissue restoration and preservation of units in such cases are minimal.
Which doctor treats periodontal disease, who should I contact?
Any problems with the gums are dealt with by a periodontist. However, in practice, in public hospitals and private offices, gum treatment is carried out by a general dentist. Keep in mind that such a doctor, no matter how good he is, cannot fully master one area: his specialization implies knowing a little of everything.
Gum diseases are treated by a periodontist
Therefore, it is advisable to take the course in a large dental center, where there is a periodontology department, as well as physiotherapy rooms.
Is it possible to place implants with periodontal disease?
Yes, definitely. And even necessary. In fact, this is the only reliable method to restore lost teeth due to gum disease. But there are nuances.
Because periodontal disease is accompanied by atrophy of not only soft but also bone tissue; there is nowhere to attach a conventional dental implant - the cortical layer of the bone is resorbed. Therefore, special artificial roots are installed - basal ones.
Such implants are implanted into the deep, basal layers of the jaw. Hence their name. Titanium basal posts are the only option for people with sore gums. In addition, they are suitable for patients with diabetes, which often accompanies periodontal disease.
Periodontal diseases. What gum diseases are there?
Rate this article:
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
gum disease
1 Beloklitskaya G.F. Clinical forms of generalized periodontitis and their significance for its differentiated therapy.
Consulting specialist
Geraskina Inna Igorevna
Doctor rating: 9 out of 10 (2) Specialization: Dentist-therapist, orthodontist Experience: 9 years