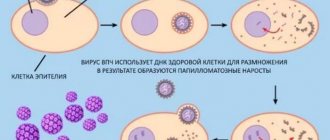
What is a polyp?
An endometrial polyp in women is a benign neoplasm that arises from the cells lining the uterus. Most often, this disease can be found in patients aged 35 years and above.
The cause of the appearance of polyps can be an imbalance of hormones in a woman’s body, damage to the uterus during abortion and other gynecological manipulations, the development of inflammatory processes and infectious pathologies in the reproductive organ.
In medical practice, there are several types of such polyps: fibrous, glandular, adenomatous, glandular-fibrous. As a rule, glandular neoplasms are detected.
Subject of research
The subject for research is material from fabrics of different origins. It is examined under a microscope after pre-staining the preparation.
Microscopic examination allows us to detect the following processes occurring in tissues:
- inflammation
- blood flow disturbance,
- internal hemorrhages,
- vascular thrombosis,
- detection of cancer cells,
- presence of malignant tissue.
Important! Histology studies the microscopic structure of organs and textures. Using the method, it is possible to establish the presence of an inflammatory process and detect cancer cells before the appearance of clinical symptoms.
Time favorable for diagnostic curettage
Without histology of the polyp, it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis of the patient and prescribe effective treatment. This method of research helps the attending physician solve the following problems:
- Confirm the diagnosis made to the woman earlier, or refute it.
- Determine the exact diagnosis if there were several assumptions.
- Detect neoplasms in the organ.
- Assess how quickly the tumor is growing.
- Identify the malignancy of any neoplasm.
For anovulatory bleeding, a scraping is taken several days before menstruation.
https://youtu.be/mEsCduyzzdc
For menorrhagia, curettage is performed on days 5-7 of the cycle.
In case of infertility, scraping is taken before menstruation, but not in the very last days.
Acyclic dysfunctional bleeding requires curettage in the first days of bleeding.
Amenorrhea is a reason for repeated 4 line scrapings at weekly intervals.
A scraping for hormones is taken between the 17th and 24th day of the menstrual cycle, and to identify tumors, scraping can be done at any time.
Curettage should be carried out carefully, without making hasty movements, so that the result is large fragments of tissue. For this purpose, the doctor removes the curette from the cervix after each passage along the uterine wall.
The most informative method of taking tissue for histology is curettage. It allows you to obtain high-quality, large enough material for research.
The professional training of a laboratory assistant is of priority importance, since the pathologist is required to know the characteristics of tissues depending on the phase of the cycle.
Uterus
Uterus ( uterus
) is a muscular organ designed to carry out the intrauterine development of the fetus.
Development.
The uterus and vagina develop in the embryo from the distal portion of the left and right paramesonephric ducts at their confluence. In this regard, at first the body of the uterus is characterized by some bicornuity, but by the 4th month of intrauterine development the fusion ends and the uterus acquires a pear-shaped shape.
Structure.
The wall of the uterus consists of three membranes:
- mucous membrane - endometrium;
- muscle membrane - myometrium;
- serous membrane - perimetry.
In the endometrium
There are two layers -
basal
and
functional
. The structure of the functional (superficial) layer depends on ovarian hormones and undergoes deep restructuring throughout the menstrual cycle. The mucous membrane of the uterus is lined with single-layer prismatic epithelium. As in the fallopian tubes, ciliated and glandular epithelial cells are secreted here. Ciliated cells are located mainly around the mouths of the uterine glands. The lamina propria of the uterine mucosa is formed by loose fibrous connective tissue.
Some connective tissue cells develop into special decidual cells
large size and round shape. Decidual cells contain lumps of glycogen and lipoprotein inclusions in their cytoplasm. The number of decidual cells increases during the formation of the placenta during pregnancy.
The mucous membrane contains numerous uterine glands
, extending through the entire thickness of the endometrium and even penetrating into the superficial layers of the myometrium. The shape of the uterine glands is simple tubular.
The second lining of the uterus is the myometrium.
- consists of three layers of smooth muscle cells - the internal submucosal (
stratum submucosum
), the middle vascular with an oblique longitudinal arrangement of myocytes (
stratum vasculosum
), rich in vessels, and the external supravascular (
stratum supravasculosum
) also with an oblique longitudinal arrangement of muscle cells, but cross in relation to the vascular layer. This arrangement of muscle bundles has a certain significance in regulating the intensity of blood circulation during the menstrual cycle.
Between the bundles of muscle cells there are layers of connective tissue replete with elastic fibers. Smooth muscle cells of the myometrium, about 50 microns in length, greatly hypertrophy during pregnancy, sometimes reaching a length of 500 microns. They branch slightly and are connected by processes into a network.
Perimetry
covers most of the surface of the uterus. Only the anterior and lateral surfaces of the supravaginal part of the cervix are not covered by peritoneum. The mesothelium lying on the surface of the organ and loose fibrous connective tissue, which make up the layer adjacent to the muscular lining of the uterus, take part in the formation of perimetry. However, this layer is not the same in all places. Around the cervix, especially on the sides and front, there is a large accumulation of adipose tissue, which is called pyrometry. In other parts of the uterus, this part of the perimeter is formed by a relatively thin layer of loose fibrous connective tissue.
Cervix uteri
The mucous membrane of the cervix is covered, like the vagina, with stratified squamous epithelium. The cervical canal is lined with prismatic epithelium, which secretes mucus. However, the largest amount of secretion is produced by numerous relatively large branched glands located in the stroma of the folds of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. The muscular layer of the cervix is represented by a thick circular layer of smooth muscle cells, which makes up the so-called uterine sphincter, during the contraction of which the mucus is squeezed out of the cervical glands. When this muscle ring relaxes, only a kind of aspiration (suction) occurs, facilitating the retraction of sperm that has entered the vagina into the uterus.
Preparation of material for analysis
The manipulation is carried out in stationary conditions. Material for research is selected by biopsy - taking prints, smears, films or tissue sections.
For each method, instructions have been developed, the exact execution of all points of which is mandatory. A tissue sample is fixed with ethanol or formaldehyde, sectioned, stained, and examined using an electron microscope.
To conduct studies under light, fluorescent, phase-contrast or scanning magnifiers, complex preliminary preparation is required.
Tissue sections are placed in a specialized balm or filled with paraffin. Material is collected from various organs or textures using a punctate needle, trepanation, or aspiration method.
MORE DETAILS: Histology analysis and cytology smear interpretation normal || Cytology is there a possibility of error?
The selected material goes through the following processing steps:
- Fixation with formaldehyde or alcohol. Proteins coagulate, enzymes are inactivated, the cell dies, but does not disintegrate.
- Wiring. The sample is dehydrated and impregnated with paraffin.
- Filling. The container with the prepared material is filled with a hot liquid that hardens at room temperature. A solid formation is created, which can be conveniently divided into thin layers using a microtome.
- Cutting. Different thicknesses are recommended for different microscopes.
- Mounting. The slice is placed on the surface of warm water, and from there onto a glass slide to avoid wrinkles.
- Coloring.
- The final stage. The prepared section is covered (enclosed) with a protective film of Canada balsam or its equivalent. The drug can be stored for a long time.
How many days is the analysis done? This is a labor-intensive process that, together with decryption, takes from 7 to 10 days.
2 days before the histological examination, you should refrain from sexual intercourse. Toilet the genital organs without using cosmetics, and also avoid douching and baths.
The use of any medications is possible only with the permission of the attending physician, since this may affect blood clotting and also conflict with some medications used during manipulation.
Before histology, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive examination:
- vaginal smear for flora;
- coagulogram and general blood test;
- examination for infections (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis);
- cytology;
- tests for hepatitis, syphilis, HIV;
- colposcopy.
If inflammation or infection of the genital organs is detected, curettage is postponed until cure.
Method of carrying out after organ excision
Histology is one of the most effective diagnostic techniques.
This type of research helps to study the structure and condition of healthy tissues and tissues with pathologies. Its main goal is to detect pathological processes and recognize the disease. The science of g is a branch of anatomy. He studies in detail the structure of human and animal tissues. Modern diagnostics in medicine performs several important tasks:
- studying the reasons for the transformation of healthy cells into atypical ones;
- study of the occurrence and development of benign formations
- and malignant in nature;
- establishing methods for combating neoplasms.
What does cervical histology show? This science is closely related to medicine. It is thanks to such diagnostics that it is possible to identify the development of the disease in the early stages and determine the method of treatment. The event is most widespread in surgery, gynecology, and therapy.
Important! Doctors often refer to histology as microscopic anatomy. This is due to the fact that the study of tissues is carried out using a microscope. By studying thin environments, a specialist can monitor even the most minor changes in tissues.
Unfortunately, oncology is one of the most common pathological conditions. The disease is not always fatal, but most people are afraid to hear a frightening diagnosis.
Oncological disease is a pathological process that is accompanied by the appearance of a tumor of a benign or malignant nature.
The tumor does not appear in any specific organ; it can occur anywhere. When determining a diagnosis, doctors specify the location of the tumor, for example, cancer of the liver, stomach, or kidneys.
The disease must be treated as early as possible, and the sooner it is diagnosed, the better. If no measures are taken, the tumor will begin to metastasize, and it will quickly spread to neighboring healthy tissues and organs.
If a woman was unable to give birth and a spontaneous abortion occurred, it is imperative to conduct a thorough diagnosis. Often, after a miscarriage, doctors give the woman a special cleaning.
Attention! The consequences of such renunciation can be very dangerous. A woman can become infected, up to the spread of the infectious process throughout the body.
During diagnosis, the specialist carefully examines the woman’s genitals, uterus and fallopian tubes. If the doctor finds remains of the fertilized egg, it is necessary to carry out cleaning.
After curettage, the woman is under the supervision of doctors for some time, after which she can go home.
Before carrying out the procedure, it is necessary to carefully listen to the patient's complaints. The results directly depend on what type of tissue was sent for research.
The decoding is quite complex, and only a specialist can understand it. Typically, the results are given to the patient immediately after completion of the study. Decoding for cervical histology consists of the following points:
- Patient’s personal data (first and last name, address, contacts).
- Method of research.
- Doctor's report.
The leaflet usually does not indicate specific recommendations. The attending physician studies the results and determines the methods and duration of treatment, prescribes medications, and sends for procedures.
The study helps to refute or confirm the presence of benign and malignant formations, pathologies, and infections. As a result, you can get the following results from cervical histology:
- tissues are completely healthy;
- there is an inflammatory process associated with hormonal changes or the presence of a pathogen;
- low degree of malignancy;
- high degree of development of malignant tumors;
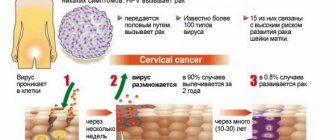
- cervical cancer.
Thanks to the analysis, it is possible to accurately determine the degree of cell atypia, the nature of cell changes: the lesion is partially present or occupies most of the cells.
The procedure helps to accurately study the structure of any tissue and detect deviations.
On average, the study lasts from 5 to 10 days. Histology of the cervix is performed according to the following instructions:
- The material is treated with a special liquid to prevent the natural process of decay.
- The tissue becomes dehydrated.
- The fabric is impregnated with paraffin to prepare a hard and dense protein. This way you can get a high-quality cut.
- The resulting material is cut into the thinnest plates using special equipment.
- The section is stained with special substances to determine its structure.
- The material is covered with protective glass, thereby preserving it for a long period of time.
- The resulting section is examined under a microscope.
This procedure is often performed in gynecology; it is used to study the condition of the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, and fetal tissues. Diagnosis can be made at the slightest discomfort, unpleasant sensations, bleeding, or after a miscarriage.
The reason for prescribing an analysis may be pain in the lower abdomen, abnormal menstrual cycle, or discomfort during sex. This research method is used for pathologies of the cervix, the main reproductive organ. A timely examination will give a chance to begin therapy in the early stages of the disease.
After the analysis, an ectopic or frozen pregnancy, malignant or benign neoplasms can be detected. Diagnosis is made in case of chronic inflammatory process in the endometrial area, acyclic uterine bleeding, hyperplasia, suspected cancer of the uterine mucosa. The study is prescribed when a polyp or fibroid is detected.
The technique is used to identify various abnormalities and pathologies. Histological analysis is a study of the endometrium, a study of the structure of the fetus. The study allows you to study the exact structure of any tissue. Diagnostics are prescribed after curettage for various indications, for any abnormalities identified through a routine gynecological examination of the woman’s reproductive system in a chair.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OQAOsqVprcU
Conization of the cervix involves excision of tissue. The analysis allows us to identify the presence of pathology at an early stage and begin timely treatment. The obtained materials must be sent for histological examination. Tissue collection occurs using several methods:
- knife;
- laser;
- loopback.
The first method of collecting material is practically not used, since it can lead to serious consequences. Loop conization is often used. If during a previous examination the doctor diagnosed cancer, this research method is prohibited. The examination shows the presence of a malignant formation, polyp, cyst, cervical hypertrophy, dysplasia. After conization, some complications may occur, such as endometriosis on the cervix.
If the patient complains of pain in the lower abdomen and during sexual intercourse, as well as menstrual irregularities, then this is a clear reason to undergo a histological examination of the cervix.
In addition, diagnostic examinations are carried out:
- If it has been previously revealed that a woman is suspected of having cervical cancer. Symptoms: purulent vaginal discharge, unpleasant odor, intestinal problems, heavy bleeding after intercourse.
- If, when examining a woman in the mirrors, an uneven surface of the tissue is discovered. Normally, the cervix is pink, the outside surface is smooth, the inside is velvety and slightly loose.
- If at the time of screening a cell abnormality is detected.
Histological examination is also carried out in case of uneven reaction of interaction of cervical cells directly with a solution of acetic acid.
Important! Using a histological examination, you can not only detect cervical cancer, but also find out the degree of its development.
Contraindications include:
- Diseases accompanied by hypoagulation. This means that a woman has increased blood clotting, and hypoagulation can be physiological or pathological.
- Severe inflammatory process in the vaginal area.
- Period of the menstrual cycle.
Histological analysis of the cervix is also not performed at any stage of pregnancy.
Both before and after the examination, a woman must follow certain rules.
- You should not have sexual intercourse for 2 weeks.
- Do not engage in strenuous exercise as this may cause heavy bleeding.
- Do not take a hot bath, do not go to baths and saunas.
- Don't overheat.
In addition, a woman should not take any medications, especially without first consulting a doctor.
Cytological analysis in gynecology refers to microscopic examination of samples taken from the vagina and cervical canal to determine the typical cellular composition.
This diagnosis allows doctors to draw conclusions about the presence of inflammatory processes, precancerous diseases or cancer in the patient’s reproductive organs. Unlike histological examination, the cytological method is non-invasive.
That is, when taking biological material there is no need to perform a biopsy or puncture, and the integrity of the tissue is not compromised at all. Samples taken using a fingerprint or swab are analyzed. To obtain accurate results, you must carefully follow the rules for preparing for the examination.
It is also very important that the analysis is deciphered by the woman’s attending physician, who will take into account her complaints and data from other diagnostic methods. Cytological analysis usually takes no more than a day to complete.
If a precancerous condition or an oncological process is discovered, invasive diagnostic techniques are used to clarify the diagnosis - biopsy. Cytology is especially important when biopsy is contraindicated and when examining a large number of patients (when it is necessary to identify women at risk for developing malignant pathology).
A smear cytology (Pap test, Papanicolaou test) is a microscopic examination of a smear from the cervix for the purpose of early detection of cancer. This analysis is also called a hytological smear or oncocytology smear. This examination is easily tolerated by patients because it is completely painless and does not take much time.
Do I need to prepare for the study?
In order for the histological examination to be successful and show the correct results, you should prepare for the collection of uterine tissue. Two days before this, you cannot be sexually active.
In addition, you must refrain from using any medications unless indicated by your doctor. This is necessary because some medications can negatively affect blood clotting and also react poorly with other drugs used by doctors during the cell collection process.
Before histology, you will also need to undergo an examination. It includes the following diagnostic measures:
- A gynecological examination, during which a smear is necessarily taken to check for infections.
- Laboratory tests of blood and urine.
- Ultrasound examination of the uterus.
- Colposcopy.
Cytology
What is the difference between histology and cytology? The latter studies the vital activity of living cells.
Cytological analysis makes it possible to diagnose oncological pathologies, precancerous conditions, inflammatory processes and benign tumors.
In gynecology, mucus is collected for a smear from the urethra, vagina or cervix. The method is simple and safe.
The analysis is done quickly, the result becomes known within a day. Cytology smears are recommended to be performed annually from the time a woman becomes sexually active.
In modern medicine, histological examination is often used, which allows us to determine the presence of dangerous processes in the human body with almost 100% accuracy.
Histology, by its definition, is the science of studying the development and structure of tissues of various organs and systems of the human body.
Embryology is a science that studies the appearance of an embryo and its subsequent development and tissue formation.
Cytology is the science that studies living cells. With the help of this science, the development and structure of cells, their functions and reproduction processes are studied.
READ MORE: Poor uterine cytology analysis
Cytological studies also help in making accurate diagnoses and determining treatment options. If everything is clear about embryology, then how histology differs from cytology is not entirely clear.
What is histology?
Histology is a branch of biology that microscopically studies the structure of tissues and cellular structures. Histology helps to identify any pathological changes in the endometrium, even at the stage of early cell degeneration. Material for histology is taken by hysteroscopy (hysteroscopy - gynecological examination of the cervix).
This test is called an endometrial polyp biopsy. Biological samples can be taken not only from the uterus and cervical canal, but also from the ovaries. Additionally, cervical mucus and vaginal fluid are analyzed.
Indications for the procedure are:
- the need to clarify the diagnosis;
- identification of the stage of oncology;
- control over tumor dynamics;
- the volume of the upcoming operation;
- monitoring the condition of the endometrium after radiation or chemotherapy.
Histological analysis is indicated when atypical symptoms appear in women:
- pain,
- hurts,
- pulling sensations
- abnormal discharge.
All this may indicate leukoplakia, signs of uterine fibroids, cysts and other neoplasms.
What does histology show?
Histological analysis of endometrial polyps allows us to identify any structural changes in tissues and mucosal cells. Each tissue has its own structure and order of cell arrangement. With any changes, you can suspect oncology or an inflammatory process.
In addition to histology, cytological analysis is performed. Cytology helps determine the structure of the cell (nucleus, membrane) and its functionality.
Both biopsy indicators are important in determining the final diagnosis.
Histological analysis indicates:
- atypicality of cells and tissues;
- structure of neoplasms;
- morphology of the base of the polyp.
Note! If there are no signs of atypia, then the analysis is negative. If positive results are obtained, further treatment tactics are determined. However, positive results indicate not only cancer, but also inflammation, chronic disease, and dysplasia.
How is the material collected?
The collection of affected polyp cells is carried out during the operation to remove this uterine tumor. In some cases, diagnostic curettage is prescribed to take the necessary material.
After this, it is placed in a special tube and sent directly for histology of the endometrial polyp. After such an intervention, a woman will need to avoid sexual intercourse for about a month, so as not to damage the already injured uterus. Otherwise, heavy bleeding may begin.
What is the difference between histology and biopsy?
Histology and biopsy are not different manipulations. To conduct a microscopic examination, it is necessary to select a piece of tissue from the location of the probable lesion.
A biopsy is the process of removing material for histological analysis. To undergo the procedure, a woman must fulfill the following preconditions:
- exclude dietary supplements from the diet for 14 days;
- abstain from intimate relations for 3-5 days;
- donate blood and do a vaginal smear for genital infections;
- carry out all tests before the planned menstruation;
- if the patient is taking medications, you should consult a doctor to avoid bleeding when collecting material;
- two days before the procedure, you must stop douching, as well as the use of cosmetics for the care of the genitals.
The following types of biopsy are available:
- Strokes are imprints.
- Punctures. The puncture is made with a thin needle.
- Trephine biopsy. The material is extracted using a thick needle.
- Stereobiopsy. For monitoring, ultrasound or another device is used, with the help of which the operator sees the tip of the sampling instrument.
- Brush biopsy. A sampling wire with small brushes is inserted through the catheter.
- Excision. Selection occurs from the affected organ during surgery.
- Transurethral. This is done using a cystoscope.
- Aspiration. It is performed through a needle with a syringe or using special devices.
Important! A biopsy is a method of collecting material intended for histological studies.
Many people confuse the concepts of “biopsy” and “histology”, but there are significant differences. The difference between biopsy and histology is that they are completely different definitions.
A biopsy is a procedure to take the required tissue sample. And histology deals with further study and research of the sample taken. In other words, for histology, tissue samples are taken by biopsy.
Moreover, a biopsy can be performed in different ways: under local or general anesthesia during surgery or using a puncture needle without additional anesthesia.
How is tissue studied?
Histological examination can be carried out in two types:
- Traditional. With this method, the cells obtained during the operation are filled with molten paraffin. After this, the specialist cuts the fabric into small plates and dyes it.
- Accelerated. It lasts no more than an hour. The specialist freezes the tissue, makes cuts on it and examines it using a microscope. This technique is very important if the doctor urgently needs to make a decision whether to remove the polyp along with the uterus or separately.
If histology needs to be carried out after some time, then the material is filled with a solution of formalin, osmic acid, and alcohol. This is necessary so that the cell structure is completely preserved.
The results of a histological examination of the endometrial polyp are deciphered by the attending physician. Their accuracy directly depends on the experience of the doctor who performed the diagnostic procedure and the laboratory itself where the material is studied.
MORE: Section of biology about cell cytology
An error is also possible if the laboratory does not fully comply with the conditions for preparing the storage of the material. It is also important for the correctness of the endometrial examination results to have as many tissue sections as possible.
This will ensure that the affected area is not missed. An error in the histology results after polyp removal may lead to an incorrect diagnosis and ineffective treatment.
Histology of the uterus
Uterine histology is an analysis involving the study of cells. This analysis allows you to study the structure of any tissue based on a thin section of tissue from the organ being examined or based on a smear. The main task pursued if uterine cavity histology is prescribed is the early detection of malignant neoplasms for timely treatment.
Histology of the endometrium of the uterus is prescribed in conjunction with other types of studies (blood tests, ultrasound) in the presence of serious symptoms, namely:
How is uterine histology performed?
To conduct uterine histology, the doctor, under local anesthesia and under sterile conditions, directly takes a small piece of the tumor from the uterus, which is later sent to the laboratory for examination. If material is taken from the uterine cavity for analysis, dilation of the cervix is required. However, such dilation is not required for cervical histology.
If histology of a cervical polyp or histology after removal of the uterus is performed, then all removed material (polyp, uterus) is sent for analysis. This is done in order to exclude cancer.
After taking the material for analysis, a histological examination is carried out directly. It is done under a microscope by a morphologist with preliminary preparation of the material (hardening, staining, etc.). One of the negative aspects of histology is the human factor, since when carrying out this analysis everything depends on the experience and skill of the doctor.
Histology of the uterus - results
Deciphering the histology of the uterus is the prerogative of the doctor. Based on the results of histology, analysis of the uterus can show the presence of atypical (cancerous) cells, as well as the presence of erosion and dysplasia. condylomas, other diseases of the uterus and cervix. As a rule, a person without a medical education cannot understand the results of a study. Usually what the patient should not know is written in Latin. You should not try to decipher the results yourself, as this can lead to unnecessary stress. Let the doctor do it.
Source: https://womanadvice.ru/gistologiya-matki
Significance in gynecology
Histology analysis is necessary when the following situations occur:
- frozen pregnancy;
- birth of a deceased child;
- permanent endometritis;
- questionable symptoms during colposcopy;
- tumors on the uterus;
- bleeding during menopause;
- infertility;
- histology in gynecology after curettage.
If the fetus died in the early stages, the gynecologist performs curettage to determine the cause of the miscarriage or fading. After eliminating the pathology, the patient has a chance for a successful course of subsequent pregnancies.
These include:
- diabetes,
- hormonal disorders,
- genital infections,
- endometrial abnormalities.
The operation is performed before the onset of the planned menstruation to identify altered cells. If during the manipulation there is a suspicion of oncological pathology, an express study is carried out, the results of histology will allow the operation to be adjusted.
Important! Histological diagnostic methods in gynecology make it possible to identify the causes of infertility, miscarriage and detect tumor cells before the onset of clinical signs of the disease.
Analysis transcript
If the analysis was carried out in a state institution on the direction of a gynecologist, then the woman will learn the results of the histological examination at a doctor’s appointment.
In a private clinic, the histology transcript is given to the patient on three forms. A woman who does not have a medical education should not try to understand the records.
Many histology results are written in Latin. It is reported what research methods were used - composition of solutions, brand of dyes. A long list of items in the conclusion does not mean that it is bad.
The doctor who deciphered the analysis describes everything he saw: pathological changes and tissues that correspond to the norm. What is histology in the diagnosis of gynecological diseases? It is an informative method that helps the doctor draw a conclusion about the state of health, prescribe treatment and preventive measures. The report does not contain recommendations for the treatment of the detected disease.
https://youtu.be/HGASoqTQuuM
Examination of scrapings
To make a scraping for histology, several types of manipulations are performed.
RDV – separate diagnostic curettage. First, the epithelium of the cervix is scraped out, and then its cavity.
There are 2 types of epithelial cells on the neck. On the side of the cervical canal, the epithelium is cylindrical single-layer, and flat multilayer on the side of the vagina. These cells are constantly exfoliated and enter the lumen of the cervix and vagina.
- During a cytological examination of a scraping of the cervix, the presence of infection is determined, tissue studies are carried out, during which it is possible to distinguish healthy cells from altered - atypical - but this diagnostic procedure does not provide a complete picture of the change, and is not therapeutic.
A cytological examination is carried out during a routine gynecological examination, the epithelium is exfoliated with a special brush, the manipulation is painless. There is no need to prepare for it. During scraping of the cervix, polyps or cervical hyperplasia - overgrown endometrium - are simultaneously removed.
RDV can be performed under hysteroscopy control. In this case, a tube connected to an optical device, a hysteroscope, is inserted into the uterine cavity. This procedure allows you to conduct a preliminary examination, identify existing pathology, and check the quality of the manipulations performed.
- For uterine fibroids, large tissue samples are submitted for examination during the diagnostic procedure. Hysteroscopy allows you to identify - and, what is very important, immediately remove - submucous fibroids, pedunculated tumors that are very difficult to identify. Uterine scrapings for fibroids also make it possible to determine how pathologically the structure of the organ tissue has changed, if the neoplasm is intramural - located in the inner muscle layer.
Curettage is performed very carefully if an oncological process is suspected, so as not to cause perforation of the wall damaged by the tumor. An experienced gynecologist can draw a conclusion even before receiving a scraping.
He analyzes the sample taken - if it does not crumble, in most cases it turns out that the neoplasm was benign in nature and in order to eliminate the symptoms that made one suspect a terrible disease, one will have to look for a different treatment regimen.
In benign formations, the mucous membrane of the uterus is separated in stripes; in malignant formations, it crumbles into small pieces.
- In case of a frozen pregnancy, a scraping from the cervix and uterine cavity must be sent for histological examination to determine the cause of the pathology. In this case, the mucous layer is removed in full so that no tissue of the embryo or its membrane remains in the cavity. Curettage is carried out in the same way as for curettage for diagnostic purposes.