What is gas formation
The human body, and in particular the digestive organs, contains gas, which includes:
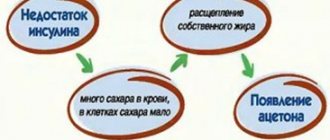
Acidophilus bacteria absorb oxygen, the lungs absorb hydrogen gas and methane. As a result of the functioning of the intestines, nitrogen is released, as well as hydrogen sulfide.
Excessive gas formation provokes digestive disorders. The accumulation of gases is called flatulence. This condition causes pathologies in the digestive process, sleep disturbances, heartburn, unpleasant belching, and colic.
Flatulence is classified depending on the causes of gas removal disorders:
- Alimentary species. It develops as a result of swallowing a very large amount of air when chewing food, while smoking or talking while eating. In addition, it is found among lovers of soda and chewing gum. Also, alimentary flatulence can form after consuming foods that cause increased gas formation.
- Digestive type. Formed as a result of various pathologies of the digestive organs, in which food in the stomach is not completely broken down.
- Dysbiotic flatulence. Occurs as a result of changes in intestinal microflora caused by pathogenic bacteria.
- Mechanical type. There is an impaired removal of gases due to interrupted intestinal function caused by parasites, neoplasms, and excessively dense feces. It also occurs in pregnant women.
- Dynamic flatulence. Appears as a result of failures of intestinal motility. In this case, the intestinal walls do not push food through well, causing stagnation and fermentation.
- Circulatory view. Caused by liver pathologies.
- High-rise type. The cause of the disease is low atmospheric pressure.
- Dysphagic flatulence. Occurs when swallowing is impaired due to diseases of the nervous system. Strokes are often a complication of this condition.
Flatulence is a manifestation of intestinal dyspepsia. Excessive accumulation of gases causes an unpleasant odor.
In an adult, the foul odor of gases occurs as a result of the presence of hydrogen sulfide gas, indole, and skatole, formed during the work of the large intestine. When gas formation is impaired, foam appears on the intestinal mucosa, which disrupts the production of enzymes and the digestion process and complicates the absorption of nutrients.
Causes of smelly gas
To eliminate the smell of hydrogen sulfide released from the intestines, you should find the root cause of its appearance. This condition can be caused by poor egg intolerance, overeating and poor nutrition.
Gas may smell like rotten eggs when the following foods are consumed in large quantities:
- raisins;
- legumes;
- cabbage;
- prunes;
- any varieties of onions;
- boiled sausage;
- chicken eggs;
- beer and seafood.
In addition, foul-smelling gas may occur when eating expired or stale food. Usually the problem disappears after the power supply is normalized.
However, gases that smell like rotten eggs are not always caused by food. Very often this condition occurs as a result of the development of diseases of the digestive organs:
- with gastritis;
- stomach ulcer;
- for liver pathologies;
- in case of gallbladder diseases.
All these diseases require immediate treatment, since if left untreated, other dangerous symptoms and attacks that threaten the patient’s life will occur.
What makes your breath smell like rotten eggs?
There are cases when the breath smells unpleasant due to certain foods that a person has recently eaten (onions, garlic, smoked fish) or due to non-compliance with hygiene measures - then the bad breath can be easily eliminated, and the fetid amber will no longer bother the person. However, this category does not include the regularly occurring smell of rotten eggs from the mouth - a very serious symptom that indicates abnormalities in the functioning of the body.
The reasons for the appearance of this symptom may lie in the improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and gallbladder . Less common causes include advanced dental problems or chronic diseases of the tonsils. Stomach problems are often accompanied by rotten breath, be it the taste of rotten eggs or meat.
Manifestations of flatulence
The gas coming out of the stomach is considered a waste product of bacteria. As a result of the active production of enzymes, food that enters the intestines decomposes. This process provokes the formation of various gases.
Pathologies of the digestive organs usually occur with the following symptoms:
- bloating of the intestines, a hard abdomen is noticeably enlarged in size;
- smelly farts;
- regular belching of air;
- painful sensations and discomfort in the abdomen;
- nausea and rumbling;
- disruption of the process of excretion of feces (diarrhea or constipation).
In addition, flatulence may be accompanied by heart rhythm disturbances, sleep disorders, weakness and mood swings.
Flatulence in infants
According to statistics, flatulence occurs in most children in the first months of life. Very often, a child farts with the smell of rotten eggs as a result of a violation of the diet by the nursing mother, an incorrectly selected formula, constipation or dysbacteriosis. Most often, flatulence in infants is not treated with medications. If the disease is not caused by pathologies of the digestive organs, then the problem can be solved by changing the mother’s diet and replacing the formula.
Why does your breath smell like rotten eggs?
Aerobic bacteria live in the mouth and use oxygen for metabolism. They break down organic matter into carbon dioxide and water. Their antipodes are anaerobic bacteria that use other substances, including non-organic ones. As a result of their vital activity, hydrogen sulfide is released with the smell of rotten eggs.
A clean oral mucosa, pink gums, and tongue are indicators of normal aerobic microflora of the oral cavity. Plaque on the tongue, teeth, and cheeks is a medium for the development of anaerobic bacteria. The reasons for the formation of plaque are various. If you remove its source, the odor problem will be solved.
Causes of gestosis
The problem may be local or occur as a symptom of a disease. Unpleasant odor is caused by:
- caries;
- diseases of the oral mucosa - glossitis, stomatitis, candidiasis;
- respiratory tract diseases – runny nose, polyps;
- diseases of the pharynx – pharyngitis, tonsillitis;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- diabetes;
- kidney diseases;
- oncology;
- emotional overload;
- eating disorders, fasting;
- medications that cause dry mouth.
Treatment
Usually, foul-smelling gases can be gotten rid of with the help of drug therapy and traditional methods, as well as by regulating diet.
Drug therapy
For the complex treatment of flatulence, the following are usually prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- carminatives;
- painkillers.
In some situations, medications are prescribed to restore damaged intestinal microflora.
Drug treatment includes taking the following medications:
- Motilium. Available in the form of a suspension for the treatment of children and in tablet form for resorption. The dosage is calculated taking into account the patient's age. Contraindicated in case of liver pathologies and bleeding.
- Mezim forte. Available in tablets. Contraindications: childhood, acute or chronic form of pancreatitis. The dosage is calculated taking into account the severity of the disease.
- Motilak. Available in tablet form for resorption. Used to treat children over 5 years of age. Contraindicated in case of intestinal obstruction or bleeding.
- Metospasmil. Available in capsule form. Not prescribed for children under 14 years of age.
Since medications have a number of contraindications, traditional recipes are often chosen for treatment.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional medicine methods effectively normalize the natural output of gases and improve digestion. In addition, such methods have almost no contraindications and are characterized by a calming and anti-inflammatory effect.
Dill water is considered one of the most effective recipes.
To prepare it, leave 2 teaspoons of dill seeds in 400 ml of boiling water for half an hour. Afterwards, strain the product and drink 100 ml before meals.
Oral care
The rules of oral hygiene are simple, do not require any effort, are easy to remember, and easy to follow regularly. It is imperative that you pay proper attention to your health.
Some useful hygiene tips:
- Brush your teeth 2 times a day, morning and evening. During the day, a lot of bacteria accumulate in the mouth; it is advisable to get rid of them before going to bed.
- Brushing your teeth should take at least 3 minutes.
- The brush needs to be changed at least once every 3 months.
- Toothpaste is selected individually, taking into account the condition of the gums and teeth, starting with oral diseases. There is no need to skimp on this.
- Your tongue, gums and cheeks require proper care, and it's best to go beyond just brushing your teeth.
- You need to use modern care products after every meal. These include all kinds of mouthwashes and dental floss.
- A visit to the dentist should be made once every six months.
Gas formation in the intestines
Each person's gastrointestinal tract contains about 200 ml of gases. They gradually accumulate, and during the day they come out in the form of farts (flatulence) through the intestine. Gases are formed mainly due to the ingestion of air. This happens during a meal or conversation.
Also, certain foods can cause excessive gas formation. That part of it that remains undigested first decomposes and then rots. A certain proportion of complex carbohydrates is not digested and with an abundance of pectin, plant fibers, and cellulose in the intestines, the microflora is disrupted.
As a result, flatulence occurs. The passage of gases with a foul-smelling “aroma” is often accompanied by pain. Other symptoms that cause discomfort may also appear.
Why do gases have a foul "aroma"?
Hydrogen sulfide gas, ammonia and aromatic carbohydrates (skatole, indole, mercaptan) give them an unpleasant stinking odor. Foul gases are formed due to excessive consumption of foods rich in proteins and sulfur.
Mercaptan is produced after the breakdown of methionine. Constant gases in the intestines with a foul odor also appear as a result of a number of diseases, mainly due to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
The intensity of the “aroma” depends on the percentage of certain substances in the bubbles. They are produced by a number of bacteria. Therefore, a number of foods are excluded from the diet:
- cabbage;
- meat;
- eggs;
- milk;
- soy;
- fish;
- cereals;
- any carbonated drinks.
The stench is mainly due to hydrogen sulfide, which has the smell of rotten eggs, methanethiol - rotten cabbage. A person’s nose can smell how hydrogen sulfide stinks even in small concentrations, so the sense of smell detects even a small or silent release of gases.
How to identify a disease with a symptom of rotten egg odor from the mouth?
When the smell of ammonia or hydrogen sulfide appears from the mouth of an adult, the reasons are also very different, so identifying them can be very difficult. The main thing to do if the symptom recurs is to immediately consult a doctor as soon as the breath from your mouth resembles the unpleasant smell of rotten eggs or meat .
Before visiting a doctor, you should pay attention to other signs of abnormalities in the body. Perhaps these symptoms will tell the doctor exactly where to look for the problem, and then treatment will help get rid of the unpleasant smell of rotten eggs from your mouth as quickly as possible.
Diseases that cause odor
Foul flatulence, or why gas smells so bad, occurs for a variety of reasons. Including due to a number of diseases, which include intolerance to dairy products. Other pathologies that cause foul-smelling gases:
- paresis;
- dysbacteriosis;
- proctitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- worms (helminthiasis);
- intestinal obstruction;
- peptic ulcer;
- intestinal infections;
- constant stress;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- gastritis;
- pancreatitis;
- peritonitis;
- colitis;
- gastric atony;
- neuroses;
- duodenitis;
- gastroptosis.
You might be interested in watching a video on this topic:
According to statistics, in adults, foul-smelling flatulence due to illness appears in 40 percent of cases with pathologies of the digestive tract. Moreover, an excess of gases does not depend on age. For example, in infants, flatulence appears due to an immature digestive system. In older people, the cause of gas formation is an elongated intestine (age-related change).
Attention! If the processes of formation and removal of excess gases fail, they can accumulate in the gastrointestinal tract in the form of foam. This reduces the activity of some important digestive enzymes.
Another pathology is malabsorption in an adult, when the processes of natural absorption of various substances from foods are disrupted.
What to do if foul gas forms
When gas with an odor appears, you need to immediately reconsider your diet. Diet is always the basis for the treatment of flatulence and any gastrointestinal diseases. A properly designed menu helps improve digestion and reduce the release of smelly gases. It is also a good idea to seek advice from a gastroenterologist. If frequent gases with an unpleasant odor appear, an examination is prescribed. Can be assigned:
- colonoscopy;
- blood biochemistry;
- Ultrasound of the peritoneum;
- general blood, urine and stool tests;
- coprogram;
- fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy.
If the examination reveals pathologies, then treatment will initially be aimed at eliminating the disease. In other cases, it is enough to simply reconsider your diet.
Drug therapy
In some cases, when there is strong gas production with an unpleasant odor, drug therapy is necessary. It includes carminatives, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. Agents that restore microflora are also prescribed. If following a diet does not help, medications that reduce flatulence are indicated:
| Types of medications | Titles | Action |
| Antispasmodics | "Spazmol", "No-Shpa" | Eliminate pain, discomfort, relieve spasms. |
| Defoamers | "Infacol", "Espumizan", "Bobotik", "Sab Simplex" | They provoke the rupture of bubbles and the release of gases. |
| Probiotics | "Enterol", "Acipol", "Linex", "Bifikol". | Restores the intestinal microflora, filling it with beneficial microorganisms. |
| Sorbents | “Enterosgel”, “Smecta”, “Polyphepan”, activated carbon. | Absorb toxins and harmful substances and remove them naturally. |
Some medications (more often used for children) are available in the form of suspensions or absorbable tablets. For example, "Motilium", "Motilak".
Traditional methods of therapy
Drug therapy is not always used. Sometimes folk remedies are enough to eliminate the strong smell of gas from the intestines. There are many recipes from medicinal plants and herbs. The most effective infusion is made from dill seeds. Take 2 tsp of them. They are filled with 400 ml of boiling water. The product should be infused for half an hour, and then it should be drunk before each meal, 100 ml.
How can homeopathy help?
Today there are a huge number of effective drugs, so let’s take a closer look at them:
- “Phosphalugel” contains aluminum phosphate, which neutralizes hydrochloric acid. Prescribed for gastritis. It is not recommended to use it for liver diseases.
- “Mezim Forte” includes pancreatin, which promotes food digestion.
- “Parodontocide” helps eliminate pain and relieve inflammation. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with this product.
- “Asepta” has a beneficial effect on the gums and relieves inflammation.
What to do if there is bad breath? The causes and treatment of this disease can be individual for each person. Only a qualified doctor can help you cope with this disease.
A method such as homeopathy has now become known throughout the world. Homeopathic remedies are very popular. Many say that these are very effective drugs. If the main cause of the smell is hidden in a disease of the pharynx, it is quite possible to use “Aconite”, “Belladonna” or even “Capsicum”. If bad breath is a consequence of tonsillitis, then you can use Fitolakk.