The appearance of blood from the anus can be both a symptom of diseases that do not threaten human life, and a sign of very serious diseases in which you should not hesitate to consult a doctor, as this can be vital. Bleeding from the anus during or independent of bowel movements is a symptom of a pathological process, most often occurring in the colon or near the anus.
Blood in the stool (blood from the anus, bloody stools, anal bleeding, intestinal bleeding) is a sign of damage to the intestinal mucosa and/or blood vessels. In most cases, when scarlet blood appears from the anus, you need to react more like a car horn that irritates your ears than an air raid siren. While bleeding from the anus is certainly worth seeing a doctor about, it usually presents a colorful and dramatic message from your body. One way or another, bleeding from the anus belongs to the group of symptoms of internal bleeding and requires urgent help.
When to call an ambulance?
There are several factors when you need to immediately call an ambulance if you are bleeding from the anus:
- When the bleeding is intense and does not stop for a long time;
- If the bleeding is accompanied by vomiting mixed with blood;
- During bleeding there is discharge from the nose, with the formation of bruises and hematomas;
- When, during bleeding, the patient experiences severe weakness and deterioration in general condition;
- Along with bleeding, the patient's temperature rises and severe abdominal pain appears.
Treatment
Treatment of chronic bleeding from the anus consists of eliminating the causes of the underlying disease. In some cases, emergency treatment for bleeding will be needed.
In case of bleeding hemorrhoids, treatment is as follows:
- Conservative therapy. Tamponade of the anus with gauze turundas soaked in hemostatic agents - hydrogen peroxide or aminocaproic acid. At the same time, high doses of venotonics and angioprotectors are used to normalize blood circulation. The drugs are used in the form of tablets, ointments, and suppositories.
- Surgical treatment. If conservative measures do not provide hemostasis, the bleeding plexuses are sutured or removed.
Vikasol injections and tablets
Bleeding caused by polyps or decaying tumors is stopped with the help of coagulants - vikasol, etamsylate, aminocaproic acid. In the absence of hemostasis, the bleeding focus is detected by endoscopic methods and cauterized. In emergency cases, abdominal surgery is performed.
Causes of bleeding
Causes of bleeding from the anus:
- Erosive gastritis and duodenal ulcer;
- For cirrhosis of the liver and thrombophlebitis of the veins of the spleen and esophagus; Signs of liver cirrhosis in men can be found here.
- Various oncological formations;
- Intestinal tuberculosis;
- Intestinal polyps;
- Ulcerative colitis of a nonspecific nature;
- Crohn's disease;
- Anal fissures;
- Varying degrees of hemorrhoids;
- Dysentery;
- Typhoid fever;
- Hemorrhagic fever;
- Helminthic infestations that can affect and injure the intestines;
- Venereal diseases of the genital organs;
- Salmonellosis;
- Enteroviruses.
Blood diseases:
- Leukemia;
- Mesenteric thrombosis.
Blood diseases
In diseases of the bone marrow and peripheral blood, clinical analysis shows intense anemia, a decrease in nominal cells and platelets. There are tumor cells in the bone marrow fluid.
For blood diseases, all symptoms are divided into several categories:
- All symptoms characteristic of anemia;
- Frequent fungal, colds and bacterial diseases, which also indicate a decrease in immunity;
- Acute platelet shortage. This indicates frequent nosebleeds, bruises and hematomas for no reason.
The cause of blood disease is the replacement of healthy blood cells with blast cells. These parasitic cells do not perform the necessary functions for the blood. To stop the process of replacing healthy cells with diseased ones, it is necessary to take cytostatics. If heavy bleeding is observed, the patient is transfused with red blood cells or other blood substitutes.
Why does bleeding occur?
There are many reasons why bleeding from the anus is possible. Among them the following main groups can be distinguished:
- acute proctological diseases (acute anal fissure, thrombosis of hemorrhoidal vessels);
- chronic proctological diseases (chronic hemorrhoids, chronic anal fissure, rectal prolapse);
- chronic diseases of the small and large intestine (UC or ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease);
- chronic diseases of the stomach and duodenum (chronic peptic ulcer, hemorrhagic gastritis);
- cancer of any part of the gastrointestinal tract.
It should be noted that bleeding from the anus may vary in color and consistency . If the blood comes from the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract, the stool will be black (due to the interaction of blood hemoglobin with hydrochloric acid), from the upper parts of the intestine it will be dark, possibly with clots, and from the lower parts it will be bright scarlet. Each of the diseases has its own specific symptoms and manifestations, which need to be considered in more detail.
What to do if there is bleeding from the anus during bowel movements?
When you notice a slight admixture of blood in the stool, you need to contact a proctologist, who will prescribe you to undergo an examination and determine the cause of the bleeding. If the bleeding is intense and accompanied by poor health, then you need to call an ambulance.
There are several types of examinations that will help determine the nature of bleeding:
- The patient is prescribed to undergo sigmoidoscopy. This will help examine the lower intestines. As a result, hemorrhoids, anal fissure and neoplasms in the rectum and sigmoid colon can be identified;
- Colonoscopy . Deeper examination of the large intestine;
- Irrigoscopy. It is carried out by introducing a contrast agent and x-ray into the intestines;
- Fibrogastroduadenoscopy. An endoscope is used to examine the stomach and duodenum. During the study, a piece of tissue may be taken from the patient for a biopsy;
- Laparoscopy. This is a joint diagnostic and therapeutic procedure. This will allow you to completely examine the abdominal cavity and take fluid for a biopsy;
- Fecal occult blood test. It is very common that there is no bleeding, but there is an admixture of blood in the stool. If blood is detected in the analysis, then it is necessary to undergo the above examination. Treatment for bleeding from the anus depends only on the identified cause. And these may not always be serious pathologies, but it is simply necessary to see a doctor and get diagnosed.
What is blood from the anus
This is not an independent disease, but an unpleasant symptom that indicates the course of a pathological process. This often happens with anal fissures, inflammation and rupture of hemorrhoids. Heavy bleeding requires immediate hospitalization; moderate blood loss can be effectively managed at home. If blood stains appear on the surface of the underwear in the anal area, you should not ignore this symptom; it’s time to make an appointment with a doctor to identify the cause of the pathological process through clinical examinations.
Haemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are accompanied by bleeding as a result of the expansion of hemorrhoids and their prolapse from the intestine. Bleeding usually occurs after bowel movements. When the blood does not completely leave the passage, it later appears in the stool in the form of clots. Also, mucous discharge from hemorrhoid cones leads to itching.
Manifestations
Hemorrhoids and bleeding occur in various pathologies:
- With constipation, childbirth and heavy lifting, pressure in the abdominal cavity is observed;
- Sedentary lifestyle and little movement;
- With stagnation of blood in the pelvis;
- Alcoholic drinks and spicy foods.
Treatment
Treatment for hemorrhoids can be conservative or surgical. Nowadays, there are many effective and modern methods of treating this disease.
Conservative treatment is as follows:
To begin with, the patient is prescribed the use of rectal suppositories. The drug contains hemostatic components to quickly stop bleeding, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- It is also necessary to take a special diet during treatment. The food should contain fiber; it is this that relieves the patient from constipation, which leads to the development of hemorrhoids. It is not recommended to consume spicy food and alcoholic drinks.
- You can use Zdorov cream wax. Price and instructions are described here.
The surgical treatment method is based on:
- The patient undergoes electrocoagulation of the hemorrhagic node , after which the tissue on it dies and falls off;
- Sclerotherapy is based on the introduction of a special agent into the node, which leads to the collapse of its walls. This technique can eliminate hemorrhoids of the first and third degree;
- Latex ligation. A ring is put on the base of the hemorrhagic node, as a result of which the node does not receive nutrition, and the blood supply to it is disrupted, and the tissue in it dies; During the surgical procedure, the surgeon excises nodes and lumps, and the wound is stitched.
How to stop bleeding from hemorrhoids
As a rule, it stops on its own after bowel movement. If the bleeding continues, but there is no way to go to the hospital, you should try to stop it on your own.
- Exposure to cold. You can wash yourself with cold water, make a compress, lotions, or apply a compress to the anus. After this, the blood vessels will narrow and the blood will stop.
- Use hemostatic drugs (vicasol, etamzilate). These tablets are contraindicated during pregnancy and if the person has drunk alcohol.
- Use local hemostatic agents – collagen sponges. After insertion into the anus, they swell and press on the vessels. The sponges dissolve on their own, so they do not need to be removed.
Using suppositories for hemorrhoids
Suppositories are very popular for treating illness. They eliminate the main symptom, help heal tissue, microcracks, reduce itching and pain, and stop the growth of hemorrhoids. They need to be inserted into the anus while lying down and remain in a horizontal position (on the stomach) for 30 minutes. The following suppositories are effective: Anuzol, Relief, Aurobin, Anestezol and others. Pregnant women are prescribed suppositories with ichthyol, glycerin, and papaverine.
Folk remedies
To eliminate bleeding, people actively use ice suppositories. They are prepared as follows: the paper is rolled into a cone, ice water or a decoction of herbs is poured into it. A homemade candle is placed in the refrigerator to freeze and then carefully inserted into the anus. Important: if there is inflammation in the bladder or kidneys, such treatment is prohibited.
If the blood does not stop on its own during bowel movements, you can use herbal decoctions, administering them through enemas. Chamomile helps well: 20 g. The flowers need to be brewed in a glass of boiling water, left to stand for 5 hours, filtered and used. An enema with a decoction of yarrow is effective (the plant has astringent and antibacterial properties).
Intestinal polyps
Polyps are considered benign intestinal growths. They are mushroom-like formations on a stalk. Sometimes the patient does not even realize that he has a polyp.
In exceptional cases, polyps can develop into tumors. The surface of the polyp itself may begin to bleed. When the polyp reaches a large size, in most cases it begins to bleed, which leads to bleeding from the anus.
We present to your attention an additional article about the causes of pain in the anus in men.
Additional Research
If you discover symptoms similar to any of the above diseases, you should not make a diagnosis, much less self-medicate! A mandatory consultation with a proctologist is required. A thorough examination is required - this is an examination by a doctor, palpation examination, general blood test, coagulogram, biochemical blood test, urine test, stool test, as well as instrumental methods such as fibrogastroduodenoscopy, colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, ultrasound, X-ray, MRI, CT.
Blood from the anus indicates the presence of pathology of the gastrointestinal tract; the main task is to correctly diagnose the disease and cure it.
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter
Intestinal diverticulosis
With this pathology, pouches and protrusions form on the intestinal walls. This could cause weakness in the intestinal wall. Diverticulosis can also develop when pressure in the abdominal cavity increases. Basically, these sacs - diverticula - do not cause discomfort.
But when the sac ruptures and the inflammatory process begins, it is characterized by the following condition:
- The patient's temperature rises;
- The muscles in the lower abdomen tense;
- Bleeding appears;
- Sometimes, depending on the part, the blood may be scarlet or dark red;
- This condition is quite serious and requires immediate surgical intervention.
Crohn's disease
This is a chronic pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. It affects any part of the digestive system. The mucous membranes and submucous membranes of the intestines and, rarely, the stomach and other parts of the gastrointestinal tract are affected. The disease can progress with exacerbations and remissions.
Doctors have not yet established the exact reasons for the appearance of this pathology. But doctors identify the main factors that contribute to the appearance of pathology:
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are dangerous diseases that affect the intestines and are accompanied by a pronounced inflammatory process
- Heredity.
- The formation of antigens that provoke inflammation of the intestinal walls.
- Infectious diseases in the body.
The disease occurs in the following forms:
- Spicy.
- Chronic.
- Subacute.
Symptoms:
- Prolonged diarrhea.
- Loss of appetite.
- Temperature.
- Blood in stool.
- Bloating.
- General malaise.
The disease is usually diagnosed using laboratory methods after examining the patient by a doctor. Based on blood tests, inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract can be detected.
Treatment of nonspecific ulcerative colitis is a complex task that usually faces a gastroenterologist
The following diagnostic methods are also used:
- X-ray with contrast.
- Colonoscopy.
- Gastroduodenoscopy.
- Ultrasound.
- CT.
- MRI.
During therapy, the doctor prescribes medications, diet, and preventive measures to prevent complications from occurring.
Infection
An intestinal infection develops when various pathogens enter it.
There are the following types of infection, which are divided according to the location of the process:
- Colitis;
- Pancreatitis;
- Duodenitis;
- Gastritis.
Causes:
- Water containing microbes;
- Poor quality products;
- Poor personal hygiene;
- Communication with an infected person;
- Expired food products;
- Working on the ground.
Almost all intestinal infections are accompanied by the development of the following symptoms:
- Abdominal pain;
- Increased gas formation;
- The temperature rises;
- Nausea and vomiting appear;
- Diarrhea.
You cannot treat the infection on your own . Disordered stools, especially those mixed with blood, lead to dehydration.
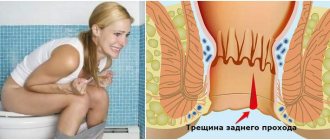
Anal fissures
When stool is dense, it can expand the intestinal walls. In this case, blood will be noticeable in the stool when visiting the toilet or on the underwear. A person will experience pain at such moments. Often blood may appear in the anus due to heavy load on the body or constipation. This type of pathology is diagnosed when there are no hemorrhoidal cones, but blood is visible in the stool and there is pain when visiting the toilet.
Read also
Types of hemorrhoids
Rectal fissure is also a common cause of blood in the stool.
With these two ailments, there is usually not a lot of blood in the stool itself. It may be there along with mucus in small quantities. When blood and mucus are in the stool itself, this already indicates damage to the intestines and the appearance of tumors there. They can be either malignant or benign.
Digestive diseases
When the digestive system malfunctions, diseases begin to appear.
There are several most common diseases of the digestive tract:
- Gastritis;
- Dysbacteriosis;
- Stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- Colitis;
- Gastroduodenitis;
- Reflux – esophagitis;
- Cholecystitis;
- Pancreatitis;
- Constipation;
- Diarrhea.
Causes:
Poor quality food;
- alcohol abuse;
- stress and depression;
- smoking;
- taking medications for a long period;
- heredity;
- Decreased immunity;
Symptoms:
- Pain of varying localization and intensity;
- Soreness can radiate to various organs and systems;
- The patient's appetite decreases;
- Heartburn and belching appear;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Increased flatulence;
- Constipation or diarrhea.
Treatment of diseases of the digestive tract is based on taking medications to reduce inflammation and pain. Also, together with the medicine, the patient is prescribed a special diet.
Causes of blood in stool after constipation
Delayed bowel movement occurs due to an unbalanced diet, dieting, a sedentary lifestyle, and insufficient fluid intake. Constipation develops in women during pregnancy and menopause due to hormonal changes in the body. The cause of the pathology can be chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system, taking medications, abuse of laxatives, and frequent stress.
The appearance of blood in the stool during delayed bowel movement may indicate the following pathologies:
- haemorrhoids;
- anal fissures;
- proctitis, paraproctitis;
- polyposis, intestinal diverticulosis;
- malignant tumors;
- ulcerative colitis;
- helminthic infestation;
- Crohn's disease;
- systemic scleroderma;
- rectocele;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- viral, bacterial infections of the gastrointestinal tract.
Bloody feces are observed in persistent, chronic constipation. Hard stool damages the intestinal wall, causing hemorrhage. In inflammatory diseases, swelling of the mucous membranes develops, erosions, ulcers, scars, and adhesions form. Pathological processes lead to deformation, narrowing of the lumen and obstruction of the intestine, which complicates the movement of feces and causes delayed fecal ejection.
Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Constipation with blood in adults can be observed with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. These are inflammatory pathologies that develop when the immune system is disrupted. Nonspecific ulcerative colitis affects people who have a genetic predisposition, lead an unhealthy lifestyle, or have had intestinal infections.
In the acute stage of UC, the mucous membranes of the intestinal walls become inflamed and swollen, and areas of ulceration form. Any segment of the colon can be affected, including the rectum. The disease is accompanied by diarrhea, which is followed by delayed fecal ejection. When passing solid feces, inflamed mucous membranes are easily damaged and bleed, which is why patients find blood on toilet paper after constipation.
The stool may also contain mucus and pus. Associated symptoms of ulcerative colitis include: increased body temperature up to 39˚, decreased appetite, flatulence, joint pain. After defecation, there remains a feeling of incomplete bowel movement, and a false urge to go to the toilet is disturbing.
In Crohn's disease, the inflammatory process can affect the entire digestive tract from the mouth to the rectum. The pathology is of an autoimmune nature, can develop in both an adult and a child, and affects all layers of the intestinal wall with the formation of deep ulcers, pseudopolyps and scars.
Constipation and blood from the anus can appear during the chronic course of the disease and the formation of strictures. Due to the narrowing of the lumen of the colon, partial or complete obstruction develops, bowel cleansing is delayed, and liquid is absorbed from the stool. Feces harden and injure inflamed tissues, causing drops of blood to appear on the paper after defecation.
In the recurrent form of the disease, the person loses a lot of weight, to the point of anorexia, and suffers from abdominal pain that gets worse after eating. There is an increase in body temperature, nausea, and vomiting. Some patients develop fistulas and anal fissures, which can also cause hemorrhage, the appearance of mucus and purulent masses in the stool.
Haemorrhoids
This disease develops with pathological expansion and thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins that form nodes around the rectum. During the act of defecation, the inflamed areas are injured and blood appears in the stool. Patients suffer from severe pain in the rectal area and often restrain the urge to defecate in order to avoid discomfort.
Irregular bowel movements lead to dehydration and hardening of stool, and the development of chronic constipation. If the nodes fall out or are pinched, bleeding may occur; this occurs during or immediately after a bowel movement. Blood in the stool during constipation is bright scarlet in color, may look like clots or dark streaks, and flows out in a trickle when bleeding. The disease is complicated by anemia, strangulation, necrosis of hemorrhoids, and the development of purulent paraproctitis.
Anal fissures
An anal fissure is a defect in the mucous membrane of the anus. Damage occurs with prolonged diarrhea, anal sex, injury to the anus by hard feces, foreign objects, and in women during childbirth. Rupture of the soft tissues of the anus is often diagnosed in persons suffering from vascular atherosclerosis, chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, thrombophlebitis, and vasculitis.
Symptoms of anal fissure:
- cutting pain during or after bowel movements;
- feces with blood;
- discomfort when sitting on a chair;
- irritability;
- inhibiting the urge to defecate, constipation.
The bleeding is minor, the patient notices brown drops on paper, the surface of stool or underwear. But with a deep fissure, hemorrhage can be quite profuse; emergency medical care is required to stop blood loss.
Oncological diseases
Blood in the stool after constipation may appear in patients with benign or malignant tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. When a cancerous tumor forms, the frequency of stool changes, flatulence and diarrhea occur, followed by delayed bowel movements. At a later stage, during the process of breakdown of atypical tissues, streaks of blood, pus, and mucus appear in the stool. Feces acquire a sharp, fetid smell of rotting.
Oncological diseases of the digestive tract, in which bleeding comes from the anus and chronic constipation develops:
- colorectal cancer;
- neoplasms in the anorectal canal;
- cancer of the rectum, colon;
- gastrointestinal stromal tumors;
- cancer of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas;
- perianal skin tumors;
- stomach cancer.
All types of oncology, except for anorectal cancer, are almost asymptomatic in the early stages; clinical manifestations are noted when the tumor reaches a large size and metastases form in other organs. When the anus is affected, symptoms are diagnosed quickly.
In patients, blood is released from the anus upon palpation, after constipation or normal bowel movements. The surrounding skin is hyperemic, swelling and ulceration of soft tissues occur. The act of defecation is accompanied by painful sensations, since a large number of nerve endings are located in the anorectal area.
Intestinal polyps
Intestinal polyposis refers to precancerous conditions in which single or multiple pathological growths form in the mucous membranes. When small in size, polyps do not cause discomfort or disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, but when they reach a large diameter, the neoplasms can ulcerate, provoke bleeding, partial obstruction of feces, and a general deterioration in well-being.
Patients experience persistent constipation or diarrhea lasting 7 days or more. The stool takes on a dark brown or black hue due to the blood content; scarlet streaks may be visualized in its composition. In severe cases, intestinal bleeding occurs, which is life-threatening for the patient.
Blood from the anus in men
Causes of bleeding from the anus in men:
- Haemorrhoids;
- Anal fissure;
- Intestinal polyp;
- Intestinal diverticulosis;
- Rectal cancer;
- Crohn's disease;
- Intestinal infection.
It is quite difficult to independently determine the cause of blood from the anus. To establish an accurate diagnosis and cause of the pathology, it is necessary to undergo an examination. Many men believe that blood is just the cause of hemorrhoids and put off visiting a proctologist. But this is a serious symptom that can eventually develop into cancer.
Gastric and duodenal ulcers and erosive gastritis
Causes peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, as well as erosive gastritis for the following reasons:
- Helicobacter pilari bacillus;
- increased acidity;
- long-term use of non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drugs;
- unbalanced diet;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse.
An accurate diagnosis is established after fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Symptoms:
- Pain in the epigastric region;
- Typically, pain is characterized immediately after eating or on an empty stomach;
- Flatulence;
- Bloating;
- Belching and heartburn.
Intestinal and other infections
An intestinal infection is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Loose stools mixed with mucus and blood;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Temperature increase.
The cause of such symptoms may be salmonellosis, dysentery, or infestations.
Tumors of the digestive organs
The most common tumors of the digestive organs are:
- Stomach cancer;
- Bowel cancer.
Risk factors:
- Heredity;
- Smoking;
- Helicobacter pilari bacillus;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Consuming a small amount of plant fiber;
- Intake of refined foods;
- Polyps.
Varicose veins of the esophagus
Varicose veins of the esophagus are characterized by a violation of the outflow of blood from the veins of the esophagus. According to statistics, the age of this pathology occurs at 50 years. This occurs more often in men than in women.
Causes:
- Hypertension in the portal vein basin;
- Cirrhosis of the liver. Its symptoms in men are highlighted here.
- Hepatitis; We present to your attention an article about the first symptoms of hepatitis C here.
- Disease of the heart and blood vessels;
- Tuberculosis.
Symptoms:
- Belching;
- Heaviness in the chest;
- Heartburn;
- Nausea and vomiting.
Inflammatory bowel diseases
Nowadays, pathologies such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease are quite common.
These are different diseases, but they have the same symptoms:
Pain and colic on the right and left sides of the abdomen;
- Presence of feces in the blood;
- Bleeding from the anus;
- Dehydration;
- Loss of body weight;
- Damage to the eyes, liver, heart, blood vessels;
- Skin rashes;
- Thromboembolic complications.
Diagnostics
Since the list of causes, along with sometimes similar symptoms of the appearance of blood from a man’s rectum, is extensive, only a complete examination of the patient will help determine the diagnosis.
You should seek help from a proctologist; if your local clinic does not have one, you should consult a therapist. After the examination and collected tests, he will refer you to the regional center to a specialist (gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, oncologist).
The examination begins with a general examination, direct palpation of the rectum and questioning of the patient; it is necessary to find out the duration of bleeding, associated symptoms and the presence of chronic pathologies.
Next, a general blood test is necessary, since the hemoglobin level is extremely important, as a clear sign of beginning and developing anemia.
Fecal analysis (coprogram) will help identify the presence of even a small amount of blood, as well as mucous secretions, bacteria, and parasites.
Next, you will need irrigoscopy - an X-ray examination of the intestines and other organs. A special substance is injected into the rectum, which, when photographed, highlights the desired areas. In this way, the relief and integrity of the intestines are checked.
Gastroduodenoscopy will help identify pathologies of the gastric mucosa and duodenum. It is carried out using a special device, a gastroscope. The procedure is also therapeutic in nature, since during the examination the doctor is able to immediately eliminate bleeding and remove tumors.
Anoscopy is informative for hemorrhoids. This method comes down to inserting a small funnel (anoscope) through the rectal opening to a depth of 15 cm.
Rectoscopy is a method that helps identify problems in the mucosa of a larger area of the colon and a small area of the sigmoid colon. Additionally, during gastroduodenoscopy and rectoscopy, it is possible to take material from the affected areas for biopsy.
Colonoscopy is another method of examining the rectum, performed using an endoscope. Unlike rectoscopy, this diagnostic method allows you to identify problems in the entire colon.
Ultrasound is performed to identify structural changes in organs.
Bottom line
If there is minor bleeding from the anus, you must contact your local physician or proctologist and undergo an examination. Frequent bleeding can lead to anemia and the formation of a malignant tumor.
Mostly in men, bleeding is associated with hemorrhoids and anal fissure . If treatment is not started in time, the disease will become chronic and difficult to respond to treatment. When the bleeding is profuse and does not stop within 15 minutes, you need to call an ambulance and take the patient to the hospital.
Rectal bleeding in women during menstruation and during pregnancy
If a pregnant woman finds blood stains on her underwear, she should immediately consult a doctor. The most common causes of this phenomenon are hemorrhoids and anal fissures, the provoking factors of which are:
- frequent constipation;
- decreased motor activity;
- insufficient fluid intake;
- relaxing effect of progesterone on the smooth muscles of the rectum;
- fetal pressure on the intestinal wall.
If blood from the rectum appears in a woman during her period, this may be a sign of endometriosis.
Why do women often pass blood in their stool?
Signs and symptoms of diseases
Staining of stool with blood is always a sign of some disease, and the color of the blood indirectly indicates the location of the pathological process.
In this case, the reasons for the appearance of blood from the anus in women are exactly the same as in men, with the exception of the period of pregnancy. The basic rule for self-diagnosis is that the brighter the color of the blood in the stool, the closer to the anus the source of the disease.
Scarlet blood from the anus is most often caused by an anal fissure or inflammation and trauma to the hemorrhoids, while dark brown or black blood indicates bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
More: fecal occult blood test
Blood from the anus without pain is most often observed with erosive damage to the large intestine or a bleeding duodenal ulcer. Painless bleeding from the anus may be a sign of polyposis in the large intestine.
Blood in the stool, depending on the cause of its appearance, is accompanied by the following clinical symptoms:
- Sharp sharp pain in the anus during straining and defecation - this symptom is most characteristic of an anal fissure. After defecation, bright scarlet blood remains on the paper, and the patient may suffer from chronic constipation due to fear of recurrence of pain;
- Sensation of a foreign object in the anus, feeling of heaviness, pressure, pain during bowel movements, protrusion of hemorrhoids outward when straining. The stool contains an admixture of bright blood in the form of veins;
- Diarrhea, vomiting, elevated body temperature, frequent urge to defecate (false in most cases), bowel movements in the form of rectal “spit”, blood and mucus in the stool - these clinical symptoms are characteristic of dysentery;
- Spasmodic abdominal pain, high fever, vomiting, diarrhea, increasing weakness, blood in the stool and large amounts of mucus - similar symptoms are observed with salmonellosis and various enteroviral infections.
In almost all cases of anal bleeding, the patient has a reduced hemoglobin level in blood tests and clinical symptoms of iron deficiency anemia are observed:
- Weakness;
- Lethargy;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Increased heart rate;
- Paleness of the skin;
- Dyspnea;
- Loss of consciousness or fainting;
- Brittle hair and nails;
- The appearance of bizarre taste preferences, for example, eating chalk or clay.
Rectal bleeding: a reason to panic?
Despite the fact that there are no minor reasons that could provoke such a phenomenon, situations can still be different.
Sometimes you can wait a few hours before the start of a new working day and go to see a doctor as usual, but sometimes the situation is urgent: you should call a doctor and often agree to hospitalization. Such situations are the following:
- Copious bleeding that cannot be stopped;
- Vomiting, with contents in which traces of blood are visible;
- Bloody discharge from the nasal passages;
- Detection of hematomas, bruises, the nature of which is not mechanical (bruise, blow, etc.);
- General deterioration in health: increased body temperature, abdominal pain.
If, after visiting the toilet, you find traces of blood on the paper, and one of the listed conditions is present, call an ambulance immediately.
Causes of symptoms and diseases associated with them
Anal bleeding is a sign of dangerous gastrointestinal diseases that can cause serious damage not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient.
With various diseases, the color of the blood released also changes. Some diseases can be judged by its color.
It is also important not only what color it is, but also the nature of the bowel movements, quantity and other factors. If fermented foods are present in the food, the shade of such secretions will also be distorted.
In men and women, the reasons for bleeding from the anus are the same. The following diseases may cause this symptom.
Haemorrhoids
It ranks first among the most common causes of bleeding from the anus. Blood usually appears after defecation; it is not mixed with feces; the color is usually light scarlet.
Colitis
Inflammation and ulceration occurs in any part of the gastrointestinal tract, usually in the large intestine. Patients with this disease, in addition to bleeding, are bothered by intense pain in the lower abdomen, lack of appetite, and high fever. The stool may be almost black in color.
Manifestations of hemorrhoids
The disease in most cases occurs in adults, with an increase in frequency in older age groups (from 45-50 years old) and during pregnancy and after childbirth. The process of pregnancy is accompanied by changes in the hormonal background of the body, leading to changes in the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels, which, in combination with increased pressure of the growing uterus on the intestinal veins, disorders of digestion and bowel movement, leads to varicose veins of the anus, in the walls of the rectum.
The onset of the disease is most often noted in the postpartum period, when excessive pressure on the veins during the pushing period leads to inflammation of hemorrhoids and fissures, and the absence of bowel movements in the first days aggravates the problem with subsequent constipation.
The disease is expressed in varicose veins of the lower intestine, which may be accompanied by bleeding during defecation, pain, anal itching, a feeling of heaviness, discomfort, etc. The first stage of the disease may be asymptomatic and accompanied by minor discomfort during defecation. At the most severe stage, hemorrhoids may be accompanied by constant bleeding, pain, chronic anemia and require surgical treatment.
The volume of blood released depends on the degree of the disease and the characteristics of its manifestation: most often, the quantitative indicators of bleeding are insignificant, but in the later stages the bleeding can be severe, leading to anemia and deterioration of the general condition. Treatment is carried out by a proctologist; in most cases, conservative methods are sufficient.
Hemorrhoids or cancer
The cause of blood discharge from the anus can be a disease such as hemorrhoids or colon cancer. How to recognize these diseases at the initial stage? Hemorrhoids are inflammation and prolapse of varicose veins of the rectal plexus. Bloody discharge occurs after bowel movements. They are insignificant. They can only be seen on toilet paper or in feces. When the venous plexus ruptures, the hemorrhage is profuse.
The cause of blood during defecation is severe straining or injury to the rectal mucosa with hard feces. Blood does not mix with excrement and is on the surface. No pain is felt. Regular rectal hemorrhages can cause anemia.
If treatment is not started in time, hemorrhoids become more complicated. The patient may develop paraproctitis. The nodes are easily injured and become inflamed when infected. Symptoms include itching and burning in the anus, pain during bowel movements and the sensation of a foreign object in the anus.
Stages of development of hemorrhoids (Click on the picture)
Treatment of hemorrhoids at stages 1-2 is carried out with medication. Suppositories, ointments and gels are considered effective. They quickly relieve pain, stop bleeding, restore damaged tissue, relieve swelling and improve blood circulation. In advanced stages, medications are not effective. Doctors resort to more radical methods of treatment: infrared coagulation, ligation with latex rings, hemorrhoidectomy. The treatment method is chosen by the attending physician.
If blood clots in excrement are mixed with mucus, then this is a symptom of oncology. Blood in the stool is dark brown or black. Colon cancer can be recognized by frequent urges, poor appetite, bloating and rumbling in the abdomen, weight loss, weakness, high fever, and pale skin. Many of the symptoms are characteristic of other diseases, so if discomfort occurs or changes in the nature and shape of excrement, you should consult a specialist.
Important! Diagnostics will allow you to identify the tumor at an early stage. People over 45 years of age are recommended to undergo preventive examinations and donate blood for hidden diseases every year.
Without treatment, the tumor grows rapidly and affects neighboring organs. Colon cancer requires complex treatment. The treatment plan is drawn up individually. The type of surgery depends on the size of the tumor and its location. If the tumor has metastasized, then the tumor is completely removed along with the surrounding tissues and affected lymph nodes. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are performed in combination with surgical treatment. The prognosis for the patient depends on a timely diagnosis and surgery performed.
Worm infestations
When parasites multiply excessively in the intestines, they disrupt the integrity of the mucous membrane, which leads to bleeding of the injured surface, which can result in chronic anemia and general depression of health indicators. Parasitosis is accompanied by decreased immunity, allergic reactions, an abundance of respiratory viral and bacterial diseases, and dysfunction of internal organs. At the stage of detection of bloody discharge due to helminthic infestations, the patient needs urgent specific therapy, often in a hospital setting.
Other reasons
Other factors traditionally include mechanical damage to the rectum or gastrointestinal tract. For example, this could be an injury sustained during sports, a street fight, even in crowded public transport. The presence of a foreign body in the intestine can also provoke blood loss through the anus.
Women need to pay attention to activities such as anal sex. It must be prepared, which includes thoroughly lubricating the entrance to the rectum. If the partner does not bother to monitor his movements, or his penis is too large, it is strongly recommended to refuse anal sex, since sooner or later the rectum and sphincter will still be injured, and this is almost guaranteed bleeding.
If a woman detects bleeding from the anorectal area, she should seek help from specialized specialists as soon as possible. It is possible that this phenomenon is a symptom of a more serious disease. And most importantly, in no case should you self-medicate or ignore the fact of bleeding - this can only further harm your own body and, accordingly, your health.
Possible diseases
Bleeding from the anus during stool may be a symptom of a minor malfunction or evidence of a dangerous disease.
There are cases when it is necessary to take urgent measures and call an ambulance, these include situations when:
- Bleeding does not stop for a long time;
- Bleeding is accompanied by vomiting blood;
- Bleeding is accompanied by the appearance of blood from the nose and the appearance of bruises on the body;
- Bleeding causes general malaise in the patient;
- Bleeding is accompanied by significant abdominal pain and increased body temperature.
Haemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can be internal or external. The disease is the formation of hemorrhoids. With internal hemorrhoids, the nodes are practically invisible and do not cause discomfort. Externally, there is obvious prolapse of the nodes, accompanied by acute pain.
The description of the problem of blood discharge during defecation fits the case of internal hemorrhoids, when the hemorrhoids are located under the intestinal mucosa and do not hurt. A feature of this type of hemorrhoids is the absence of mixing of blood with feces.
Cracks in the intestines
The crack is characterized by the presence of a defect in the mucous membrane of the canal. The cause may be excessive stretching of the canal walls with feces, which is caused by constipation and the subsequent release of a large amount of compressed feces.
A crack can remind you of itself while doing hard work. A feature of the disease is the absence of mixing of brightly colored blood with feces, so blood can be found on toilet paper or underwear.
Colitis
Colitis is inflammation of the colon. It is characterized by stool failure, flatulence, pain in different locations of the abdomen, and an unpleasant odor of stool.
There are acute and chronic colitis. Acute colitis occurs violently and quickly, while chronic colitis occurs over a long period of time. There are several types of colitis based on the method of exposure, the most common are:
- Ulcerative;
- Ischemic;
- Infectious;
- Drug.
Proctitis
A disease that is an inflammation of the rectal mucosa. Symptoms vary from person to person; common ghosts include:
- Pain in the intestines;
- Discomfortable sensations;
- Pain in the perineum: in women it can radiate to the labia and vagina, in men – to the scrotum and genital organ;
- Lumbar pain;
- Slight increase in body temperature;
- General malaise;
- Abnormal stool;
- Excessively frequent urge to defecate;
- Pain during bowel movements;
- The appearance of bloody discharge from the anus.
Crohn's disease
The disease is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by the formation of ulcers and scars. Crohn's disease can be a genetic or infectious disease, or a disease of a person's autoimmune system.
Accompanied by pain in the intestines and anus, as well as diarrhea mixed with bloody discharge.
Polyps
A polyp is a benign tumor that can increase significantly in size over time. Blood during defecation can form due to damage to the polyp during the movement of feces through the intestines.
Dysbacteriosis
A disease in which the composition of intestinal bacteria involved in the digestive process is impaired. The intestines contain an environment inhabited by different bacteria: good, bad and neutral. When the balance is disturbed and the advantage goes to the side of harmful bacteria, dysbiosis occurs.
Symptoms include flatulence, bowel movements, bad breath, and nausea.
Colon cancer
The disease is characterized by early symptoms in the form of mucus and blood discharge from the anus. The discharge can be of different colors, from bright red to black, and mixed with feces. There may be clots.
Patients with colon cancer complain of inconsistent bowel movements, including constipation and diarrhea, and abdominal pain. With the disease, profuse bleeding may occur.
Even young people whose relatives have not had cancer are at risk. Signs indicating the possible presence of colon cancer:
- Changes in stool, including changes in the shape, consistency, thickness of stool. Also include stool breakdowns in the form of constipation and diarrhea.
- Feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
- Nausea and bloating.
- Bleeding of any shade during bowel movements.
- Constant fatigue.
- Significant weight loss.
- Anemia and iron deficiency.
Diverticulosis
The disease is characterized by the formation of pouch-like protrusions on the intestinal walls. Doctors believe that the disease is associated with weakness of the intestinal wall. The diverticulum (sac) may grow and not cause discomfort to the patient until it ruptures.
Violation of the sac is accompanied by pain and bleeding from the anus. The patient may also be concerned about inflammation of the diverticulum when moving stool.
If the formation ruptures, scarlet blood flows out; if the diverticulum is in the colon, the blood will be dark in color. A broken diverticulum is extremely dangerous and requires urgent surgical intervention.
Angiodysplasia
The disease represents changes in the intestinal mucosa due to the patient's old age. The surface of the intestine is characterized by the presence of destroyed vessels, their increased fragility and expansion.
Bleeding from the anus without pain can continue for a long time.
Infection
The presence of an intestinal infection in the body can be determined by the following symptoms:
Carrying out diagnostics
Bloody discharge from the rectum is a dangerous symptom. It is prohibited to make any decisions on your own without finding out what was the source of the bleeding. The patient needs to seek qualified help from a therapist, proctologist, surgeon, and for women, in addition to a gynecologist. After diagnosing and establishing the cause and provoking factors, the doctor can prescribe treatment.
In case of rectal bleeding, a digital examination of the rectum is mandatory. This method helps to detect fissures, internal or external hemorrhoids and other oncological pathologies. If examination is not enough, then colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy is performed. These hardware diagnostic methods make it possible to detect even the most minor damage to the mucous membrane, and, if necessary, take a biopsy for further research.
Diagnosis is not complete without a blood test. Based on the data obtained, the doctor determines the hemoglobin level and the presence or absence of iron deficiency anemia.
Conditions when blood appears from the anus
The reasons for the manifestations may be different. To accurately determine them, you need to see a doctor. The most common reasons are:
- Anal fissures. Blood can be detected in stool during bowel movements. Pain in the anus may occur. A crack can occur due to constant constipation due to an unbalanced diet. For prevention, the child should be given vitamin D.
Blood from the anus is one of the most common symptoms of intestinal pathology, which occurs in people of all ages.
- Hemorrhoids. The discharge is noticeable in small quantities. They can be on linen or in stool.
- Lactase deficiency. The most common reason why a child will see blood in their stool. The baby will gain weight. The stool will be foamy and liquid. The stool may have a greenish tint.
- Allergy. Both adults and children suffer from it. In children, such pathologies often occur due to the intake of citrus fruits or milk in large quantities, as well as when consuming products with chemical dyes. The baby will suffer from diarrhea. Blood can sometimes be seen in the stool.
What to do if there is bleeding from the anus?
In such a situation, it is important to immediately contact a doctor and not self-medicate. Only a specialist can accurately diagnose the cause of the pathology and prescribe the correct therapy.
Sometimes the bleeding is profuse. This causes a person to feel worse. In this case, you should call an ambulance immediately. Before her arrival, the patient must be in a supine position.
The patient is hospitalized and diagnosed, during which the causes of the appearance of blood are identified. If necessary, he will have to undergo treatment. In case of such a disease, you should most often consult a proctologist.
Blood from the anus: therapy and prognosis
Treatment should be carried out when pathological discharge appears. Initially, the doctor must collect the patient’s medical history and prescribe the following studies:
- Ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Blood analysis.
- Consultation with a proctologist.
- Endoscopic examination.
- X-ray of the intestine with a contrast agent.
The majority of diseases that are accompanied by bleeding from the anus are not dangerous to humans. But there is no need to ignore them, since the pathology can develop into a chronic one, which will complicate its therapy.
A person must constantly ensure that he has a complete bowel movement when using the toilet. This will not allow feces to stagnate in the intestines and will not aggravate the course of the pathology.
Inflammatory bowel diseases
The course of nonspecific ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease have similar symptoms: pain in the abdomen, stool disorders, blood in the stool (from minor to extensive bleeding), additional systemic diseases (arthritis, dermatitis, liver dysfunction).
Without systematic therapy, these diseases lead to the formation of intestinal tumors, ulceration of the mucous surface, and rupture of intestinal sections. Therapy is predominantly conservative, using hormonal agents that suppress the autoaggression of immune cells, analgesics, and agents for normalizing stool and digestion.
Bleeding in intestinal and systemic infectious diseases
Diseases of infectious etiology can also manifest as bleeding from the anus. Common causes include the severe course of enterovirus and rotavirus infections, which occur with intestinal irritation, erosive damage to its internal surface, which is accompanied by the release of blood in feces in men. Also, blood flows without connection with the moment of bowel movement.
Typhoid fever, dysentery, hemorrhagic fevers of various origins, accompanied by abnormalities in the blood count and massive internal bleeding, also lead to the appearance of blood from the anus and require urgent treatment in a hospital setting. The high mortality rate of these diseases obliges one to go to the clinic at the first suspicion of the possibility of infection or the presence of corresponding symptoms.
Gastric and duodenal ulcers and erosive gastritis
Peptic ulcer disease, caused by bacteria, occurs in waves. Periods of relative well-being are followed by exacerbations. If the ulcerative defect or erosion due to gastritis is small, then it can only manifest itself as “hunger” pain or pain immediately after eating. Over time, the ulcer grows wider and deeper, eventually perforating the wall of the stomach or intestines. If a blood vessel is damaged, severe and life-threatening bleeding can occur.
Diagnosis and at the same time treatment are carried out using gastroscopy: the ulcerative defect is found and cauterized. After normalization of the condition, inflammation in the stomach is treated and harmful bacteria are removed.
Nutrition
Organizing proper nutrition plays an important role in anal bleeding. They prefer foods that stimulate intestinal motility, facilitate bowel movements and eliminate pain.
Indicated are lactic acid products that normalize the activity of intestinal microflora and vegetable oils that facilitate the passage of food. daily intake. Avoid fried, smoked, salted, fatty foods, spices, alcohol, and foods that increase gas formation.
You will have to forget about confectionery, chocolate, scrambled eggs and barbecue. But you will have to get used to kefir and stale bread with bran. The daily meal is divided into six parts.
Anal hemorrhage is a manifestation of a hidden disease. You should not limit yourself to hemostatic measures. Identifying the cause of the pathology and eliminating it is the only path to healing.
Features of anal bleeding
This term traditionally refers to any mechanisms that cause the appearance of blood masses from a specific location. Blood can flow independently, and in very significant volumes, or be present as an impurity in the stool. The nature of the pathology, as well as its complexity, as well as the physical parameters of the released blood (color, smell, etc.) can answer a specific question that interests not only the doctor, but also the patient - what led to the bleeding.
The color of blood provides very valuable information. If it is scarlet, it means that it is of local origin. A cherry tint indicates problems with the colon. Red is an alarming signal, as it may indicate the presence of cancerous changes in the body. Dark or even black clot-like discharge is the result of serious pathologies present in the gastrointestinal tract.
In the case of women, there is a risk that vaginal bleeding may be confused with anal bleeding. It is difficult to determine exactly where the leak is coming from underwear or bedding, so you should pay special attention to this. For example, after defecation, inspect the toilet paper or the contents of the toilet. To eliminate the possibility of vaginal bleeding, it is recommended to put on a regular panty liner for a while - if there are no marks on it, then it is not the genitals.
Any, even the slightest, leakage of blood from the anal must necessarily be the reason for an immediate visit to the doctor. In some cases, emergency assistance is required - then you need to call an ambulance. For example, this will be relevant for the following pathological processes:
- profuse bleeding, which, moreover, cannot be stopped by any of the methods available at home;
- the problem is aggravated by constant nausea and vomiting. At the same time, vomit can also contain both small and significant amounts of blood impurities;
- anal bleeding is accompanied by the spontaneous formation of bruises and hematomas throughout the body, although there was no physical impact in these places. Blood may also flow from the nose;
- rectal blood loss led to a significant deterioration in the woman’s condition;
- there is a significant increase in temperature, there is a pronounced pain syndrome in the lower abdomen or along its entire perimeter.
Symptoms
When determining the causes of anal bleeding, pay attention to the appearance of blood in the stool.
There are the following types of hemorrhages:
- Fresh blood.
- Blood mixed with feces.
- Diarrhea accompanied by the release of blood and mucus.
Fresh blood
Bleeding hemorrhoids
- Haemorrhoids. Bleeding most often occurs with hemorrhoids. Hemorrhages are detected with any bowel movement. They are addictive and the patient does not respond to the pathology. The discharge is not abundant and short-lived, stopping spontaneously after the pressure of feces on the inflamed nodes decreases.
- External hemorrhoids. Blood oozes from the inflamed venous plexuses, which the diagnostician detects by palpation.
- Internal hemorrhoids. Palpation does not reveal inflamed hemorrhoids. Scarlet drops or weak streams appear at the end of bowel movement.
- Anal fissure. Defecation causes pain and slight bleeding.
- Polyps of the anus and rectum. Pathogenic growths of small size do not cause bleeding. They are discovered during a preventive inspection. Large growths cause the appearance of discharge of pure blood or blood mixed with fecal matter. Damage to minor vessels is accompanied by mild anal bleeding. Defects of large vessels cause severe hemorrhage.
- Benign and non-benign neoplasms of the rectum and S-shaped intestine. Symptoms of the disease resemble signs of bleeding from polyps. Occur spontaneously or after defecation. There are weak, short-lived and profuse hemorrhages.
- Traumatic injuries to the mucous membrane of the anus and rectum. The symptoms resemble those of hemorrhages due to polyps. They arise as a result of an accident, careless performance of diagnostic procedures, enema placement, or anal intercourse.
- Rectal prolapse. A protrusion of the mucous membrane appears, accompanied by bleeding. Small children suffer.
The reasons for the discharge of bloody fecal matter from the anus are:
- Tumor growths in the colon and S-shaped intestines.
- Polyps in the large intestine.
- Sac-like protrusions of the walls of the colon.
If measures are not taken promptly, severe bleeding may occur.
Discharge of bloody mucus from the anus is regarded as anal hemorrhage of inflammatory etiology.
The following diseases cause diarrhea with blood:
- Inflammation of the rectum.
- Inflammation of the S-shaped intestine.
- Crohn's disease.
- Colitis.
- Ulcerative colitis.
Such pathologies cause oncological degeneration of the digestive organs or are a consequence of cancer. The defect occurs as a result of the breakdown of tumor tissue. If the symptom appears after excision of the tumor, a relapse of the disease is diagnosed.