The rectus muscles are two vertically located muscle cords lying in the middle of the abdominal wall from its upper edge to the lower sections. Each of the two muscle formations is surrounded by a dense membrane - an aponeurosis. The fibers of neighboring aponeuroses intertwine with each other, forming a “white line” between the rectus muscles, located vertically in the middle of the abdomen. It contains the navel. Normally, the width of the white line is up to 2 cm.
What is diastasis recti?
Under the influence of certain factors, the fibers that form the white line are weakened and stretched, and the muscle strands move apart. This discrepancy is what the medical term “diastasis” means. About 1 in 100 people have it.
Hernia of the white line of the abdomen - definition
Hernia of the white line of the abdomen is a disease manifested by an abnormal protrusion in the midline. Pathology in the initial stages can only manifest itself as aesthetic defects. But, in the process of development of white line defects, expansion of the hernial orifice, pain of varying degrees and intestinal dysfunction (nausea, vomiting) are added to the symptoms. The most dangerous condition with a hernia is strangulation of its contents. This complication requires emergency surgical intervention to save the patient’s life. Only a qualified specialist, a surgeon, can correctly diagnose and predict the course of the disease. He will be able to determine whether a hernia of the linea alba can be treated without surgery, or whether there are direct indications for surgical treatment.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic method involves an initial examination of the patient by a surgeon. The doctor palpates the site of the protrusion and takes a medical history.
Some instrumental diagnostic methods can also be used. Many people wonder why such an accurate diagnosis is needed if the hernia is visible even with the naked eye and the diagnosis is clear?
The need for instrumental studies is explained by the fact that these methods make it possible to determine at what stage the disease is, what are its characteristic features and which organs are in the hernial sac.
In addition to the examination, they may prescribe:
- gastroscopy;
- X-ray of the duodenum and stomach;
- Ultrasound of hernia formation;
- CT scan of the abdominal cavity;
- herniography using contrast.
A very important role is given to a correct diagnosis. Diagnostics and its various approaches help the specialist with this.
The diagnosis of “hernia of the white line of the abdomen” is made after the surgeon examines and palpates the protruding neoplasm. In unclear cases, they practice listening to the hernia with a stethoscope, since a peculiar rumbling can be heard in its place.
Even if the presence of a hernia is obvious, other diagnostic methods are often required. This helps to clarify at what stage the disease is and which internal organs are affected.
Additional examinations:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity,
- gastroscopy,
- Ultrasound of the white line and the hernial sac itself,
- herniography using a contrast agent,
- multislice tomography.
An abdominal hernia, localized on the linea alba, can be located above, near or below the navel. The latter are quite rare. The doctor makes a diagnosis based on:
- Inspection data. When palpating the white line, a compaction is detected, and the patient may feel pain.
- X-ray examination of the contents of the hernial sac with preliminary administration of a contrast agent (barium).
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound).
- Computed tomography.
What is the linea alba?
Muscles in the human body are attached to the bones of the skeleton and connected to each other through tendons and aponeuroses (natural extensions of muscle fibers). In the middle of the anterior abdominal wall, a thin strip of fusion of tendon fibers is formed - the linea alba.
The linea alba is conventionally named so because of the color of the tissues that form it. On this midline, from the xiphoid process of the sternum to the symphysis pubis, the tendon (aponeurotic) fibers of the broad abdominal muscles come together. Typically, the width of the white line is no more than 3 cm; with muscle divergence (diastasis), it can increase to 12 cm. Normally, there are always several holes, but small ones. With certain anatomical features of the individual’s structure, the presence of predisposing factors:
- Decreased connective tissue strength, for example, with Marfan syndrome;
- Congenital weakness of intermuscular fusion;
- With frequent or constant increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity - with obesity, heavy lifting, pregnancy, prolonged, painful cough, chronic constipation;
- If there are postoperative scars in this area, either preperitoneal fat (this can be called a preperitoneal lipoma), or the omentum, or parts of the intestine begin to get into the gaps between the tendon fibers along the white line of the abdomen. The hernia can be single, when the protrusion appears only in one place along the white line, or multiple. The size of the hernial orifice (pathological openings) varies from 1 cm to 10-11 cm.
Epigastric (supra-umbilical) hernias appear most often. Supra-umbilical hernia of the white line of the abdomen occurs in more than 80% of cases. Less commonly detected are paraumbilical (umbilical) hernias that appear in the area of the umbilical ring. Even less common are infraumbilical hernias of the white line of the abdomen (here the density of the muscle connection is high, so protrusions appear infrequently).
Causes
The disease is more common in women. The predominant form is diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles after childbirth. The most dangerous time for this is the first months. The likelihood of developing pathology increases after a cesarean section, since this disrupts the integrity of the muscle aponeurosis and its ability to contract decreases.
The connective tissue, which, in particular, makes up the aponeurosis of the abdominal muscles, becomes looser under the influence of hormones during pregnancy. This allows the pelvic ligaments to prepare for the passage of the baby through the birth canal. In addition, muscle stretching is necessary for the normal growth of the baby in the uterus. After the birth of a baby, the connective tissue spontaneously strengthens, and the shape of the abdomen is restored within a year. If you do not give the body time to rehabilitate and begin intense training or heavy physical work, the connective tissue will not contract and will become fixed in a stretched position. There will be a divergence of the rectus abdominis muscles.
The appearance of this disease is facilitated by obesity, as well as a rapid decrease in body weight, when the aponeurosis does not have time to contract behind the muscles that have lost volume, as a result of which a “surplus” is formed.
Any factor that increases pressure in the abdominal cavity can contribute to muscle separation: constant hacking cough, hard work, sports involving heavy lifting, chronic constipation.
Finally, in medicine there is such a thing as connective tissue dysplasia. This is a congenital condition characterized by an altered structure of ligaments, tendons and other elements that form the basis of the body. Dysplasia is manifested, in particular, by increased extensibility of connective tissue. Therefore, hernias of different localization and muscle diastasis may occur.
The causes of abdominal muscle diastasis in men are all of the above factors, of course, except pregnancy.
photo of diastasis rectus abdominis muscles
Hernia of the white line of the abdomen in children
A hernia of the linea alba in a child under 5 years of age is rare. At older ages, the risk of being diagnosed with the disease increases, especially among boys. A hernia of the linea alba appears in children more often with congenital defects; surgery for a hernia of the linea alba helps prevent the most dangerous complication - strangulation. But doctors may postpone surgical treatment, it all depends on the size and contents of the hernia. Concomitant infectious diseases and severe chronic pathologies are reasons for postponing surgical treatment. In this case, to prevent further increase in the defect, wearing a special bandage, massage and therapeutic exercises are indicated. But such conservative methods are not able to eliminate a hernia of the white line of the abdomen.
A long-term respiratory disease accompanied by a cough (especially whooping cough, bronchial asthma) can provoke the appearance of a preperitoneal lipoma. Constipation is also one of the important predisposing factors.
Prevention of hernia and complications
In preventive measures, the emphasis is on strengthening general tone, a healthy lifestyle and preventing stretching of the white line of the abdomen. You should avoid situations where abdominal injuries are likely, carefully normalize the load and carefully follow the doctor’s recommendations:
- Follow a diet and eat well.
- Watch your weight.
- Avoid alcohol and nicotine.
- Regularly strengthen the anterior abdominal wall, observing moderation in exercise and following the doctor’s recommendations.
- Treat diseases in a timely manner, the symptom of which is cough.
- Use caution when lifting heavy objects.
- Wear a special bandage if recommended by your doctor.
- Monitor timely bowel movements.
- Adjust your lifestyle, alternate sedentary activities with activity.
Symptoms of strangulation
Patients with hernias of the white line must know the symptoms of strangulation so that, if they appear, they can immediately seek emergency medical help.
- Increasing pain in the protrusion area;
- Absence of defecation (stool) - not always;
- Lack of intestinal gas release;
- Blood in vomit and feces;
- Increasing nausea;
- A sharp deterioration in health – in combination with the above symptoms;
- The hernia stops being reduced when lying down.
Symptoms
In the first stages of the development of the disease, there may be no obvious signs, there is no deterioration in health or visual manifestations, the quality of life remains at the same level. In the following stages, minor pain appears, which is localized in the upper abdomen and occurs, as a rule, with strong bending and muscle tension. Periodic pain occurs due to several factors:
- When muscle tension occurs, compression of the nerves of the parietal peritoneum occurs.
- The digestive organs get into the gap that has formed and they are pinched. This factor poses a threat to human life and requires immediate medical attention. There is a disruption in the blood supply to the prolapsed organs, peritonitis develops, and necrosis may begin.
- The stomach is tightened with an omentum, which can move it out of place. Because of this, strange sensations form in the abdomen, and minor signs of pain are noted after eating.
A hernia is often accompanied by vomiting, nausea, lack of appetite, and constipation. When making a diagnosis, the doctor must exclude diseases of the digestive tract and confirm the hernia. Epigastric forms of the disease are pinched even if they are small in size; due to their symptoms, they are often mistaken for intestinal diseases. It is important to begin treating bulges in the initial stages to minimize possible complications.
Among women
There are no clear sex differences between symptoms in men and girls. In some cases, the disease manifests itself only in the form of protrusion, which is typical for the first stages of development of the pathology. Then painful sensations appear, they intensify with load, pressure during active movements. The nature of the pain may vary: sharp, pulling, dull, prolonged or paroxysmal. In women and men, the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- stretching of the midline abdominal muscles;
- pain of a different nature;
- nausea and vomiting;
- hiccups, heartburn, belching;
- pain after eating.
When the hernia progresses, the following symptoms are noted:
- the pain becomes stronger, unbearable for the patient;
- constant vomiting;
- blood appears in the stool;
- it becomes impossible to straighten the protrusion.
Surgery and other treatments
Removal of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen is possible only by surgical methods - hernioplasty. Patients with a hernia of the linea alba in the medical history may have a long period of use of folk remedies for a hernia of the linea alba. Such treatment methods, at best, bring zero results; most often, ignoring the methods of official medicine for treating the disease leads to an increase in the size of the hernial protrusion, the development of adhesions and inflammatory changes in the area of the hernial sac.
The most effective way to get rid of the disease is surgery to remove a hernia of the white line of the abdomen (hernioplasty). During the operation, under anesthesia, surgeons remove adhesions, obstacles to the reduction of the hernia into the abdominal cavity, and reduce the contents of the hernial sac. And then the defect (hole) in the leaves of the aponeurosis is sutured. Depending on the stage of the disease, the size of the hernial orifice, the condition of nearby tissues and the characteristics of the patient, the following may be used:
- Tension hernioplasty. The patient's own tissue is used. Simply put, the layers of the aponeurosis are duplicated (layered) on top of each other at the site of protrusion. In this way, the tissue connection at the site of the former hernial protrusion is strengthened, and diastasis (divergence) of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall is reduced. In each case, individually, the surgeon can choose this tactic as the best. The method is applicable for small uncomplicated hernias. Its significant disadvantage is the possibility of relapses (repetitions of the hernia), due to tension in the area of the postoperative scar and weakness of the surrounding tissues.
- Tension-free hernioplasty. During this operation, special biologically inert (safe for the body) synthetic endoprostheses - meshes - are used to strengthen the abdominal wall. The mesh is secured with sutures around the hernial orifice and in areas of “potential risk”, weakened aponeurotic connections. In this way, a reinforced frame of their synthetic and the patient’s own tissues is formed, preventing hernial protrusion. The method is very reliable and gives a low relapse rate.
The cost of surgery can vary significantly depending on the size of the hernia, the presence of complications and the surgical correction methods used.
Location and boundaries
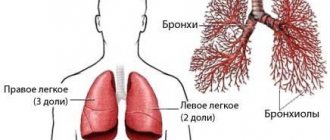
The abdominal cavity is closed in front and behind by walls, and on top by the diaphragm. The lower border is located at the entrance to the pelvis. Posteriorly – retroperitoneal space. The organs of the abdominal area are located as follows.
| Location in relation to the peritoneum | Organs | Coating |
| Intraperitoneal | Stomach, spleen. The initial part of the duodenum, almost the entire intestine. | Covered with visceral peritoneum on all sides, except for the attachment points of the mesenteries. |
| Mesoperitoneal | Liver. The ascending and descending colon and the upper part of the rectum. | Closed on three sides. |
| Extraperitoneal | Pancreas. The rest of the duodenum, the lower part of the rectum. Kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, bladder. | The organs are closed on one side or are located outside the peritoneum. Separated by fascia or loose tissue. |
Organs are constantly moving. Passive mobility is caused by the act of breathing and the work of the diaphragm, and changes in body position. Active depends on physiological functions - intestinal motility, the state of the muscle corset.
The mobility of organs is directly dependent on the fixation apparatus. Some have fascial sheaths, neurovascular pedicles, and peritoneal ligaments. For example, the spleen and kidneys are equipped with an anatomical bed.
Fixation in the correct position depends on abdominal pressure, which in turn is related to the condition of the muscles. Decreased tone leads to prolapse of organs - splanchnoptosis.
Recovery after surgery
In the very early period, while in hospital, the load on the muscles in the suture area should be sharply limited. So as not to cause any discrepancies. As healing progresses, the stitching site will become scarred, and at the same time the strength of the tissue in the scar area will increase, and then it will be possible to significantly expand the range of movements. After the sutures are removed (usually on days 8-12), the patient has the opportunity to fully take a shower. In older people and people with concomitant diseases, the healing period may increase to 2 weeks or more.
Depending on the condition of the body, the stage of the disease, and the extent of surgical procedures performed, the recovery period can range from 1 to 6 weeks. The time for starting work after surgery for a hernia of the linea alba depends on the type of work performed (for example, with significant physical exertion, it will be possible to start work no earlier than after 1.5 months).
Hernia of the white line of the abdomen, the diet after surgery should prevent excessive formation of intestinal gases and constipation (legumes, cabbage, carbonated drinks, fatty, spicy or smoked foods, high-carbohydrate foods, baked goods made from premium flour, rich bakery products, beer, etc. are excluded from the diet. alcoholic drinks). To restore microflora and improve peristalsis during the use of antibiotics, it is useful to eat fermented milk products, foods rich in coarse fibers and fiber.
Stages of disease development
There are 3 main stages of protrusion growth: preperitoneal lipoma, initial stage, final formation. Almost always the pathology is large and especially large in size. Sometimes the process can stop at the formed lipoma without further progression. In medicine, the following stages of pathology growth are distinguished:
- At the first stage, preperitoneal tissue exits through a slit-like defect in the tendon fibers. A hernial sac begins to form, into which part of the small intestine or omentum penetrates.
- When a hernia has already formed at the second stage, all the classic manifestations of pathology are noted: vomiting, a sac with hernial contents.
- At the final stage, pathology is determined visually and by palpation. Reduction can no longer be performed because it is dangerous.
White hernia
A white abdominal hernia occurs in the center of the part that joins the tendons on either side of the oblique muscle, located from the pubis to the chest.
At the very beginning, the malaise does not manifest itself in any way and does not bother the client, but a little later it develops and, expanding, can compress the digestive system. If this happens, it will pose a serious threat to human life.
This pathology will not go away completely with the use of drug therapy alone; it requires urgent medical intervention to carry out further surgery. You should not be afraid to go under the knife of a qualified doctor, because this type of surgery is very simple and always takes place without unnecessary complications.
Contraindications
Giant ventral hernias in patients over 70 years of age with cardiac disease or pathology of the bronchopulmonary system are considered contraindications to elective surgical intervention.
It is necessary to postpone the operation during pregnancy.
It is necessary to postpone the operation during pregnancy, and it is better to refrain from it in patients with cirrhosis of the liver, accompanied by ascites, varicose veins of the esophagus and rectum; diabetics in the absence of effect from insulin administration; patients with severe chronic renal failure.
Rehabilitation
The postoperative period depends on the general condition of the human body and the chosen method of surgical intervention. The fastest restoration of your own tissue occurs after laparoscopy. With other methods, rehabilitation takes longer.
The patient must wear an abdominal bandage, the duration of wearing is determined by the attending physician.
The operated patient should not lie down for a long time; he needs to start moving literally the next day, as walking speeds up the healing process. The patient must wear an abdominal bandage, the duration of wearing is determined by the attending physician.
In the first 2-3 months, physical activity is strictly prohibited, then you need to start doing exercises that strengthen the abdominal muscles, recommended by a physical therapy doctor.
If there are problems with excess weight, then they need to be addressed urgently. The bandages are changed 2 times a week, and after 10-12 days the stitches are removed.
Nutrition in the postoperative period
It is necessary to adhere to the prescribed diet and rules of eating behavior. Initially, the patient can drink water and liquid broths. A daily drinking regime is established (at least 1.5 liters of water), as this helps restore fluid after surgery and prevents constipation.
[morkovin_vg video=”HIPZ5oLLzPM;jhiefT0LO0I”]
Meals should be fractional and divided into 4-6 meals. Products that cause constipation and excessive gas formation are prohibited. In the first months, liquid porridges, soups, and purees are recommended. Products should be easily digestible. If you follow all the doctor's recommendations, the risk of relapse is minimal.
How is surgery to remove an abdominal hernia performed?
Surgical treatment of the disease can be planned or emergency. The planned procedure is prescribed to patients who experience unpleasant (sometimes painful) sensations in the area of protrusion, but do not suffer from pinching. In case of strangulation, the patient needs emergency surgery to remove an abdominal hernia, since any delay leads to the death of internal organs (due to impaired blood flow) and the subsequent development of an inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity (peritonitis).
Conclusions about pinching can be drawn based on:
- Acute abdominal pain;
- Inability to reduce the protrusion even while lying on your back;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- No bowel movements or blood in the stool.
A symptom of a strangulated abdominal hernia can also be excessive discharge of gas.
Preparing for surgery
Before surgery, the patient is recommended to undergo special training, namely:
- Do not drink alcohol 3 days before surgery.
- Do not take medications containing acetylsalicylic acid 2 weeks before the procedure (it reduces blood clotting).
- Provide yourself with adequate nutrition and vitamins 2 weeks before treatment.
- Do not eat since 20.00 the previous day.
In addition, the procedure is contraindicated for people who have recently suffered from colds and inflammatory diseases. After recovery, 2 weeks should pass (with the exception of emergency indications for surgical treatment).
In addition to self-preparation, the patient requires a medical examination, which is prescribed by the doctor. In private clinics, the cost of treatment may include a full course of examination. Otherwise, it will be charged separately. On average, the price of surgical treatment of an abdominal hernia ranges from 30 to 50 thousand rubles. This indicator depends on the level of the clinic, the number of procedures performed, the cost of the surgical equipment used and the quality of the implants. However, hernia treatment is available in the Russian Federation and is free within public hospitals. In order to get an operation, you need to have a health insurance policy and a referral from a local physician from the clinic.
Standard preoperative examination includes:
- General blood analysis;
- Tests for sugar, group and rhesus, prothrombin index, APTT, biochemistry;
- Tests for infectious diseases (syphilis, hepatitis, HIV);
- ECG.
Based on this examination and study of the medical history, the doctor draws conclusions about possible complications and subsequent treatment.
Methods of hernia surgery
If there is no pinching, the procedure is carried out quickly and does not cause complications. To eliminate small defects, modern equipment is often used - a laparoscope. This is a special probe that can be used to carry out diagnostic and therapeutic procedures without extensive damage to the abdominal wall. It minimizes damage to soft tissues and the risk of bleeding, allows you to monitor what is happening on the monitor, ensures precise manipulation and speeds up the healing process. However, this method is contraindicated in patients with other abdominal diseases, so it is prescribed with extreme caution, based on a medical opinion.
Traditional treatment of abdominal hernia is carried out by stretching the weakened layers and fixing them with a synthetic thread. This method is effective only in 60-80% of cases. In 20-40% of cases, reviews of operated patients indicate temporary improvement and subsequent relapse. This picture occurs due to the heavy load on the seams. As a result of their strong tension, the weakened connective tissue is cut through by the thread, and a new defect appears.
The most optimal method of treating a hernia is considered to be prosthetics using synthetic mesh material. It is installed on the defect area and compensates for the weakness of the connective tissue, taking on the entire load. Its advantage is complete compatibility with the body and the absence of a rejection reaction. Over time, the area with the mesh grows with connective tissue and acquires a uniform, strong structure that is resistant to stretching and tearing.
The operation to remove an abdominal hernia is performed under local or general anesthesia. In adults, a nonstrangulated hernia is preferably operated on under local anesthesia, since this method of pain relief does not affect the heart, does not require long-term postoperative observation, does not cause nausea, and allows you to eat immediately after the procedure. In special cases, the patient may be prescribed spinal anesthesia.
Treatment
The most effective treatment method is surgery. Only this method gives a 100% result with the lowest chance of relapse. If you identify pathologies at an earlier stage, you can use some methods that will slow down the development of pathology and help avoid serious complications. These include:
- prevention of physical activity;
- diet;
- use of a bandage.
Treatment without surgery
This direction of therapy is allowed only if the aponeurosis gaps are very small and the lipoma is of insignificant size and there is no infringement. Medications do not provide the required effect for multiple hernias and severe divergence of the fibers of the white line. There is a possibility that the doctor will be able to simply straighten it at the initial stage of the lipoma. After this, you need to wear a bandage for some time, special underwear, you will need a therapeutic massage, which should be carried out by a specialist to eliminate diastasis.
Bandage
It is recommended to use this remedy after lipoma reduction, surgery to reduce pressure on the peritoneal wall, and prevent relapses. Without surgery, wall plastic surgery, or elimination of hernial openings, wearing a bandage will not provide any therapeutic effect. It is necessary to wear the device for at least 3-6 months after surgery, but to prevent divergence of tendon fibers, it is recommended to use the bandage for life.
Why is a hernia dangerous?
In addition to the pathology itself, its complications pose a real threat to humans. This leads to the appearance of a large number of unpleasant symptoms. In some cases, the pain is so severe that the patient receives a painful shock. The most dangerous consequences of a hernia include:
- peritonitis;
- intestinal obstruction;
- necrosis;
- infringement.
The latter consequence develops in the last stages of development of fiber divergence and protrusion formation. A strangulated hernia occurs when pathological changes are visible to ordinary eyes. According to medical statistics, 1 out of 10 cases of development of the disease is accompanied by this complication. Even in the absence of negative symptoms of protrusion, one should remember the possibility of strangulation, which will provoke a stop in the blood supply to the organ compressed in the hernial orifice and the development of peritonitis.
Articles on the topic
- Speech impairment during stroke - treatment
- Vertebro-basilar arterial system syndrome: causes and diagnosis
- Precursors of stroke - provoking factors, methods of treatment and prevention, nutritional rules
Umbilical hernia
An umbilical hernia of the abdomen appears as a result of low muscle tone. It is observed at birth, when the navel ring is slightly expanded, and the scar has a hole and does not reach the end. Doctors may not notice this feature. But the hernia will make itself felt after some time.
It also occurs in girls who have given birth multiple times, due to an increase in the abdomen during pregnancy. At the same time, the navel stretches, and eternal constipation increases the pressure inside the stomach.
Causes
Hernias occur when the fibers of the aponeurosis of the rectus muscles diverge; this occurs in the following conditions:
- Congenital weakness of connective tissue.
- Anatomical defects in the area of the aponeurosis.
- Abdominal injuries.
- Obesity.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- A sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure (severe physical strain, frequent coughing, pregnancy, excessive screaming and crying in young children).
The fibers that form the white line, under the influence of certain reasons, become thinner, expand, and diverge. In some areas, cracks and aponeurotic defects form, through which first the adipose tissue passes, and then parts of the internal organs - intestinal loops, the lesser omentum.
Prevention
To prevent the development of pathology, it is necessary to perform actions that will be aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles, and to avoid factors that can provoke protrusion. You can reduce the likelihood of developing the disease by following these recommendations:
- in case of obesity, it is necessary to normalize body weight;
- strengthen abdominal muscles with exercises;
- during pregnancy, wear a bandage that will prevent injury to the tendons and abdominal muscles;
- maintaining proper nutrition;
- When working with heavy weights in the gym, you need to use special belts.
Diet
Full recovery and long-term maintenance of results requires constant adherence to a diet. Nutrition is aimed at solving basic problems:
- weight loss and subsequently maintaining it;
- normalization of the gastrointestinal tract (elimination of constipation, excessive gas formation).
The basis of the diet is lean meats and fish, fermented milk products, fresh vegetables, fruits, cereals (do not overuse rice), and whole grain bread. Food can be boiled, stewed, baked or steamed. The daily diet should be divided into 5 meals - 3 full meals and 2 snacks. Portions should be small! You can eat your last meal 2-3 hours before bedtime. It is also necessary to maintain fluid balance and drink enough clean drinking water without additives.
Fatty, fried foods, fast food, processed foods, alcohol, sweet carbonated drinks, store-bought sweets, and baked goods should be excluded. Such food not only increases weight, but also provokes fermentation in the body and impairs digestion.
Rehabilitation period
After a planned operation, that is, when the hernia was not strangulated, recovery occurs quite quickly. The patient is kept in the hospital for no more than three days. During this period, the nurse regularly makes dressings, and the doctor monitors the condition of the stitches and the patient’s well-being to exclude the possibility of infection. For the same purpose, a prophylactic course of antibiotics is prescribed.
On the first day after surgery, the patient is prescribed a liquid diet, which consists of broths and purees. This helps restore bowel function and does not overload the digestive system. It is necessary to exclude foods that take a long time to digest and cause increased gas formation.
During the healing period, the patient takes painkillers. After discharge, until the stitches are removed, regular dressings can be done at home or come to the hospital.
Long bed rest is not required, it can only harm and slow down the healing process. A few days after the operation, you are allowed to go outside for short walks. Moderate physical activity promotes rapid rehabilitation.
Note!
You can start walking or any other physical activity after your doctor’s permission. Each body is individual, that is, it requires different amounts of time to recuperate.
The rehabilitation period requires compliance with certain rules:
- It is forbidden to lift weights over 5 kg (the restriction is valid for at least 3 months from the date of surgery);
- Leaning forward, sudden movements and too intense training are prohibited;
- moderate physical activity is indicated, especially walking;
- it is necessary to take laxatives prescribed by the doctor (constipation can cause sutures to come apart);
- It’s worth reviewing your diet and switching to a balanced diet.
People whose profession involves heavy physical labor are transferred to light work for a period of up to 6 months.