Every expectant mother needs to know how to cleanse the intestines during pregnancy. During pregnancy, a woman is responsible not only for her own health, but also for the child; she needs to think about cleansing the body. Harmful substances usually come to us through food. This leads to problems such as constipation, gas, belching, heartburn and even abdominal pain. To protect themselves and their fetus, pregnant women need to know how their body works.
If there is a need to cleanse the intestines during pregnancy, then you should give preference to traditional methods in consultation with your doctor.
- 4.1 Contraindications
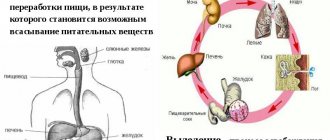
Intestines and its functions
The intestines perform several important functions in the body. It is located in the middle and lower abdomen, its structure is very complex. This part of the digestive system ensures the absorption of nutrients and the absorption of vitamins. Along the way, they produce the necessary digestive enzymes. The next important stage is the elimination of waste in the form of feces.
The intestines contain colonies of microorganisms that provide the appropriate stage of food digestion, including lactic acid bacteria. These bacteria supply the body with lactose, B vitamins, and also produce ethyl alcohol. With their help, fats, carbohydrates and proteins are broken down.
It is necessary to maintain a normal balance of intestinal microflora, since the baby in the womb does not have its own bacteria. He receives them from his mother during childbirth and breastfeeding. During pregnancy, many women suffer from dysbiosis, which also affects the health of the unborn baby.
Treatment
Treatment of pain in the intestines should be carried out under the supervision of a gastroenterologist, as well as in consultation with a gynecologist. Since many medications cannot be taken by pregnant women, you should not buy or drink them yourself.
The doctor may prescribe painkillers (No-shpu), drugs that will remove gases (Espumizan), antibiotics to influence pathogenic microorganisms, probiotics to restore intestinal microflora, mild laxatives to eliminate constipation (Duphalac), hormones to restore hormonal balance and other drugs.
Location of organs during pregnancy
Internal organs experience increased stress during pregnancy. Hormonal levels are actively changing, and this is reflected in the functioning of all body systems. The uterus enlarges: already in the 4th week it reaches the size of a chicken egg, and subsequently extends beyond the pelvic bones. The location of the organs shifts, which sometimes causes stomach pain.
As the fetus develops, a woman's anatomy changes more and more. The need for oxygen increases, the lungs process a larger volume of air. Breathing quickens, but the hormone progesterone regulates the functioning of the bronchi, and this allows you to avoid shortness of breath at least in the early stages. In the second and third trimesters, the diaphragm shifts, causing breathing to become more frequent and shallow.
The fetus takes up more and more space in the abdominal cavity, and the gallbladder, bladder, and kidneys experience increasing pressure. The liver moves to the side and higher, the normal flow of bile becomes difficult, this leads to the appearance of colic. In the tissues of the uterus, the number of vessels supplying the fetus with blood increases, the load on the heart muscle increases, and its volume increases.
The stomach and intestines also move from their usual places. In the first trimester, they begin to rise upward, a side effect of which is that gastric juice enters the esophagus. Before birth, the intestines move apart and the uterus descends. Gases accumulate in the intestines, a feeling of fullness, pain, and defecation may occur.
Liver, kidneys, bladder
All major organs rise upward during pregnancy, but the structure and location of the bladder does not allow it to rise above the fetus. Therefore, it is exposed to strong pressure from the uterus and the constantly moving fetus. Due to this, urination becomes more frequent. Over long periods of time, there are cases of involuntary urination, which is caused by the baby carelessly pressing on the bladder. During childbirth, the urinary tract is subjected to strong pressure; sometimes a special catheter must be inserted to restore the normal process of urination. Soon all processes are restored, and bladder problems disappear.
The kidneys also bear a double burden. They are busy filtering, purifying, and removing harmful substances from the body.
How does pregnancy affect the intestines?
During pregnancy, due to changes in hormonal levels and displacement of internal organs, intestinal function becomes more difficult. The amount of microflora decreases, women suffer from gas accumulations and spasmodic pain. Fermentation often occurs in the intestines, increasing unpleasant symptoms. Diet while expecting a baby does not mean reducing calories, but including in the menu foods that contain all the nutrients necessary for the mother and fetus. A balanced diet allows you to normalize the balance of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in the intestines and improve digestion.
In early pregnancy, as the fertilized egg moves to the site where it attaches to the wall of the uterus, women experience abdominal pain. In the future, unpleasant sensations are caused by the growth of the fetus, due to which the uterus puts pressure on the intestines. In this case, there is a stabbing sensation in the lower abdomen, and sometimes even slight bleeding appears. If the bleeding does not stop, seek medical help. Deterioration of the condition is indicated by spasms, a feeling of pressure, and prolonged constipation.
READ ALSO: abdominal distension during pregnancy: causes of bloating and pain in the intestines
Lungs
The task of the lungs is to saturate the body with oxygen. To cope with this task, the lungs increase their volume, the bronchi become greatly enlarged, and breathing becomes deep. Due to compression by the diaphragm, the load on the lungs increases.
At the end of pregnancy, all organs in the body return to their places and fully restore their functions.
Changes in female organs are temporary. After childbirth, 90% of them restore their previous condition.
Pain of a paroxysmal nature in the lower abdomen or in the iliac region may indicate problems with the intestines. In pregnant women, such problems occur in all trimesters for various reasons. You should not let the process take its course - a consultation with a doctor will help restore good health, and proper therapy will be the key to the full development and health of the unborn baby.
Pain in the intestines: what is the cause?
To successfully deal with intestinal pain, it is necessary to determine its cause. In addition to natural compression due to a developing pregnancy, a woman may suffer from a number of diseases, both existing before conception and those that developed after it. Peristalsis disturbances can be associated with both physiological causes and infection. For example, the hormone progesterone, the amount of which is significantly increased at this time, reduces the level of peristalsis.
Physiological changes in the body of a pregnant woman
In order for the uterus to grow and provide space for the development of the fetus, muscle tone in the body is reduced. This is necessary for the child, but bad for the intestines, which become “lazy”. Digestion worsens, constipation occurs more often, gas is tormented, and intestines hurt.
Towards the end of pregnancy, the uterus is already quite large, it puts pressure on the organs that are located nearby. Their blood supply is disrupted and their functioning is complicated. Women suffer from stomach rumbling, colic and bloating. Expectant mothers are forced to change their diet and eat unusual foods, which also causes digestive problems. At the same time, the functioning of all digestive organs, in particular the pancreas, liver, and spleen, deteriorates.
Infectious lesions
In cases where pain in the intestines is accompanied by diarrhea, fever, nausea or vomiting, infection is likely. The disease can be caused by viruses or bacteria and is in no way related to pregnancy. This may look like:
- dysentery;
- salmonellosis;
- rotavirus infection;
- enterovirus infection;
- “conquered diseases” - cholera, typhoid fever - brought from foreign trips.
Infectious diseases during pregnancy are very dangerous and threaten to terminate the pregnancy. In this case, it is necessary to urgently call a doctor and take auxiliary measures - often drink water in small portions, take rehydration medications, and cleanse the digestive system using sorbents or activated carbon. The doctor will prescribe antimicrobial drugs and recommend restorative therapy and diet.
Neoplasms of various etiologies
Pregnancy forces all the body’s hidden reserves to come into play, but at the same time latent diseases are also activated. Due to a decrease in immunity and hormonal changes, pathologies may appear that the woman did not know about before. One of the most dangerous is the appearance and activation of neoplasms. Polyps may appear in the intestines, which, as they increase in size, cause regular pain.
Unfortunately, surgical treatment of such diseases during pregnancy is undesirable. Surgical intervention in the pelvic organs increases the tone of the uterus and can provoke a miscarriage. Treatment is carried out immediately in cases where the threat to a woman’s life outweighs the possible risks. In the presence of tumors, only maintenance therapy is indicated.
Colitis or enterocolitis
Pain in the abdominal area can be caused directly by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (see also: can the stomach hurt during pregnancy?). With the increased load placed on the intestines during pregnancy, the manifestations of colitis, enterocolitis or Crohn's disease intensify. These conditions are distinguished by:
- severe pain in the iliac region;
- aching or stabbing pain near the navel;
- increased gas formation, flatulence;
- the appearance of blood, mucus or even pus in the stool;
- frequent constipation or diarrhea.
If you have a serious illness, the pain does not stop at night. Crohn's disease is accompanied by high fever. With constant constipation, anal cracks may appear, which will definitely worsen during childbirth. Hemorrhoids are likely to appear in the event of a difficult or prolonged labor. With diarrhea, a woman suffers from dehydration, which threatens the health of the fetus.
The cardiovascular system
During pregnancy, another, third circulatory system appears in a woman’s body – the placental. Now the mother’s heart supplies blood and necessary substances not only to her body, but also to the baby’s body. Thanks to all this, the amount of blood in the woman’s body increases, the heart muscles also increase - they need to pump blood with double force, the load increases, the mother’s heart performs up to 90 beats per minute!
In the first trimester of pregnancy, for this reason, loss of strength, decreased blood pressure, dizziness, etc. may be observed. From the second trimester until childbirth, another reaction appears - blood pressure increases. The attending physician should monitor the slightest changes in the condition of a pregnant woman, because his task is to save the fetus and the expectant mother.
Lungs
The task of the lungs is to saturate the body with oxygen. To cope with this task, the lungs increase their volume, the bronchi become greatly enlarged, and breathing becomes deep. Due to compression by the diaphragm, the load on the lungs increases.
At the end of pregnancy, all organs in the body return to their places and fully restore their functions.
Changes in female organs are temporary. After childbirth, 90% of them restore their previous condition.
Improving digestion, methods
First of all, in order to get rid of digestive problems, you need to reconsider your diet. In this case, you should pay attention not only to the quality of food, but also to the quantity, as well as the frequency of meals per day.
What foods should you avoid?
For example, to get rid of heartburn and heaviness in the stomach, you need to exclude some foods and limit others. A pregnant woman should avoid spicy, overly spicy, fatty and fried foods. Limit the consumption of pickles and canned food, and it is better to refuse them. Even these simple actions will have a positive effect on the function of the digestive tract.
Also, a pregnant woman can pay attention to those foods, after consuming which, dyspeptic symptoms appear. So, these products also need to be excluded from the diet, and if they have a high energy value, replace them with similar ones.
It is worth noting the need to prevent conditions such as bloating as a result of increased gas formation. To do this, you just need to stop eating foods that contribute to this process (legumes, grapes, milk, white cabbage).
Improved digestion
Experts recommend not only avoiding a certain type of food, but also introducing smaller meals. That is, a woman eats food almost every three hours in small portions (about three hundred milliliters). This mode activates rapid metabolism and does not overload the stomach with large volumes of food, resulting in a reduced risk of reflux of its contents into the esophagus. But it is worth remembering that a pregnant woman’s last meal should not be later than three hours before bedtime.
Experts do not recommend taking a horizontal position of the body after eating, much less starting physical activity, since even the most “proper” nutrition may not help, and the symptoms will resume, and digestion will not improve.
In order to help normalize stool, intestinal motility should be strengthened by eating fiber. Fresh vegetables are prominent representatives of fiber. They must be eaten together with meat products.
The cardiovascular system
During pregnancy, another, third circulatory system appears in a woman’s body – the placental. Now the mother’s heart supplies blood and necessary substances not only to her body, but also to the baby’s body. Thanks to all this, the amount of blood in the woman’s body increases, the heart muscles also increase - they need to pump blood with double force, the load increases, the mother’s heart performs up to 90 beats per minute!
In the first trimester of pregnancy, for this reason, loss of strength, decreased blood pressure, dizziness, etc. may be observed. From the second trimester until childbirth, another reaction appears - blood pressure increases. The attending physician should monitor the slightest changes in the condition of a pregnant woman, because his task is to save the fetus and the expectant mother.
Liver, kidneys, bladder
All major organs rise upward during pregnancy, but the structure and location of the bladder does not allow it to rise above the fetus. Therefore, it is exposed to strong pressure from the uterus and the constantly moving fetus. Due to this, urination becomes more frequent. Over long periods of time, there are cases of involuntary urination, which is caused by the baby carelessly pressing on the bladder. During childbirth, the urinary tract is subjected to strong pressure; sometimes a special catheter must be inserted to restore the normal process of urination. Soon all processes are restored, and bladder problems disappear.
The kidneys also bear a double burden. They are busy filtering, purifying, and removing harmful substances from the body.