The main function of the esophagus is to move masses of food from the mouth into the abdominal cavity, which is achieved by contracting the fibers located on the wall of the organ. Insufficiency of the cardia rosette leads to improper functioning of the esophagus, which is fraught with various pathologies, since the pressure in the abdominal cavity is higher than in the esophagus.
A malfunction of the esophagus can provoke severe pathologies.
Structural features
Role
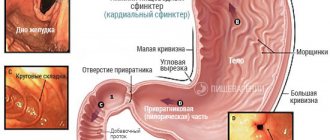
The fibers form the sphincter. When the muscles contract, the opening in the sphincter area closes (reduces in diameter). The organ has two sphincters:
- Cardiac or lower esophageal sphincter. This sphincter is located at the border of the esophagus and the stomach. As food moves into the stomach, the cardiac sphincter opens slightly. Before this, it is closed due to muscle tone. This prevents stomach contents from entering the esophagus.
- Pyloric sphincter or pylorus (superior). Separates the pyloric region of the stomach from the duodenum. Its functions include regulating the flow of stomach contents into the duodenum.
Job
The cardia of the stomach is a valve that separates the abdominal cavity from the tissues of the esophagus (it is located between them). In other words, this is the vestibule of the stomach. The cardia has the main function of blocking the reflux of food. The contents of the organ include acid, and in the esophagus the reaction can be neutral or alkaline. The pressure in the stomach is higher than inside the esophagus, so it is important that when the lower sphincter opens, the contents do not end up on the esophageal mucosa.
What is cardia?
The human body contains a large number of sphincters - these are devices similar to a valve, in this capacity the circular muscle acts, which, when contracted, narrows and closes. The combination of folds of mucous tissue and the vascular system forms the sphincter apparatus.
Gastric cardia or lower esophageal sphincter (LES) - acts as an inlet valve into the stomach from the esophagus. Normally, it maintains a closed position, preventing acidic contents from refluxing into the esophagus. During eating, the cardia opens, allowing the food bolus to pass further.
It is important to note that the pressure in the stomach is higher than in the esophagus. Therefore, the anti-reflux barrier must exert force to resist the natural movement of stomach contents up the digestive tract.
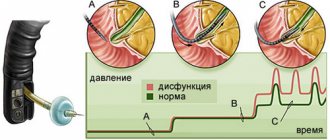
When pathology appears, the cardiac sphincter stops closing, resulting in the backflow of gastric contents into the esophagus, and its walls are not adapted to the acidic environment. Failure to close the valve is insufficiency of the gastric cardia - a functional disease of the digestive tract in which reflux is observed.
Types of disorders and diseases
If the functioning of the cardia rosette is disrupted (insufficient), the esophageal sphincter does not completely close (does not close). During non-closure, gastric secretions, gastric enzymes, and food particles penetrate the esophagus, causing irritation, erosions, and ulcers. In medicine, the following main types of sphincter disorders are distinguished:
- Increased tone. With this disorder, it does not open completely when food particles pass through. The patient has impaired swallowing function. This pathology develops when exposed to ANS impulses. It is customary to distinguish between two types of this condition (the classification depends on where the pathology is located). Thus, improper functioning of the pharyngeal esophageal sphincter provokes disturbances during swallowing food. In this case, painful sensations arise, the patient may choke, and sometimes a cough appears when food enters the larynx area. If the esophageal sphincter, located between the abdominal cavity and the esophagus, begins to function incorrectly, then food can accumulate in the esophageal sections, which leads to expansion of the organ.
- Decreased tone. This pathology is characterized by the reflux of food particles or stomach contents into the upper esophageal region, sometimes into the pharynx. The socket begins to close insufficiently. Such disturbances in the functioning of the cardia can affect the lower esophageal sphincter or both sphincters simultaneously. Sometimes non-closure (when the sphincter does not close completely) and pressure provoke vomiting and nausea.
- With the 3rd degree of insufficiency, a gaping sphincter is formed.
Stages
Today, there are several stages of pathology development:
- Stage 1. Temporary decrease in sphincter tone, no expansion of the lumen yet.
- Stage 2. The condition is almost the same as at stage 1, but a mild degree of dilatation is gradually developing.
- Stage 3. At this stage of the disease, a stable expansion of the esophagus is already observed with simultaneous suprawall narrowing of the lower part of the esophagus. Scar changes form.
- Stage 4. Achalasia of the cardia at this stage progresses, complicated by fibrous mediastinitis, esophagitis or periesophagitis.
Causes
Insufficiency of the cardia rosette can be caused by changes in the structure or structure of various esophageal sections. Scar formation can lead to a narrowing of the sphincter, which persists if the muscles are relaxed. The diameter of the sphincters may increase with diverticulum. In addition, expansion sometimes provokes stretching of the tissues of the lower region of the organ due to disruption of the functioning of one of the sphincters (cardiac). In such cases, it is weakened and cannot work properly.
Valve operation
Before entering the stomach, food passes through several stages:
- oral cavity;
- larynx;
- esophagus.
Each of them has its own environment. The lower esophageal sphincter, otherwise called the gastric valve or gastric cardia, works as a barrier to the exit of food. This valve prevents acid from escaping into the esophagus. Normally, until a person consumes food, the sphincter closes, opening only when food passes into the stomach. Thus, neither the resulting nutrient mass nor the acid reaches the higher level. Due to some factors of poor nutrition, this process is disrupted, resulting in the development of chalazia, a condition of insufficiency of the gastric cardia.
Symptoms
Changes in the functioning of the sphincters affect the functioning of the organ, which causes the appearance of various symptoms - odor from the mouth, pain in the esophagus, dysphagia.
- Odor from the mouth. Changes in the diameter of the esophageal sphincters provoke the appearance of such a symptom. This is due to a number of pathogenetic reasons, including the accumulation of food particles and gastric contents in the esophagus. If the upper and lower esophageal sphincter do not function correctly, the ingress of gastric contents can cause inflammation of the membranes, the formation of erosions, and various infections.
- Painful sensations. Pain can appear due to various disorders of the sphincters. Sometimes pain develops when swallowing; at rest, such sensations may be absent. The development of the symptom is triggered by irritation and damage to the membrane due to the regular ingestion of gastric contents.
- Swallowing dysfunction. Dysphagia is considered the most common symptom of cardia failure. In most cases, it occurs when swallowing solid food particles. Drinks and dishes that have a liquid consistency do not cause discomfort when swallowed.
Symptoms
Heartburn is one of the first clearly manifested symptoms of the disease.
The most striking symptom of cardiac failure is heartburn, which makes itself felt regardless of food intake. In addition to this, the violation is accompanied by the following problems:
- belching of air with a bitter or sour taste;
- aching or burning pain in the sternum;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- rumbling sounds in the intestines;
- obsessive nausea, sudden vomiting;
- increased fatigue, dizziness, weakness.
These conditions may be accompanied by dizziness, rumbling in the stomach and the appearance of a white coating on the tongue, which indicates inflammation of the walls of the esophagus.
Return to contents
Diagnostics
If suspicious signs appear, the patient should consult a doctor as soon as possible. If necessary, the specialist will refer the patient for further examination. To examine patients suffering from this pathology, it is customary to use the following diagnostic methods:
- X-rays help detect reflux esophagitis;
- gastrofibroscopy is considered the most informative type of research, as it allows for visualization of pathologies;
- study of the work of the cardia, esophagotonokymography, determination of the pH level in the esophagus, etc.
Alkaline reflux esophagitis
In the presence of duodenogastric reflux, bile, pancreatic juice and bicarbonates enter the stomach. If such gastric contents are thrown into the esophagus during gastroesophageal reflux and come into contact with its mucous membrane, patients develop so-called alkaline reflux esophagitis. You can think about it if there is inflammation of the mucous membrane, and with daily monitoring the intraesophageal pH level does not decrease less than 4. For the treatment of these patients, it is necessary to give preference to sucralfate and prokinetics.
Treatment and strengthening
Cardia insufficiency can be cured using several methods:
- Diet. Proper nutrition will strengthen your immune system. In addition to strengthening the immune system, you should eat 4-5 times a day, and the portions should be small and equal. Patients should not overeat. You should have dinner two hours before bedtime. It is important to eat dietary boiled and lightly salted foods. It is beneficial to eat steamed food. Products that reduce acidity and relieve irritation caused by it will help improve the patient’s health. Kissels and porridges, which envelop the mucous membrane, are added to the diet. Citrus fruits, pickles, pickled vegetables, canned food, alcohol, and chocolate are excluded from the list. Doctors recommend giving up smoking. This bad habit stimulates the production of enzymes, which negatively affects the functioning of the digestive system.
Restoring the esophageal sphincter is impossible without following a diet.
- Drug therapy. There are a number of areas of such treatment. Strengthening the body is achieved with the help of antacid medications (for example, Almagel) - they help relieve heartburn and eliminate pain. Treatment with such means helps protect the mucous membranes of organs from the harmful effects of acid. The therapy includes medications that are intended to restore the mucous membrane (for example, Omeprazole). Medications that improve motility overcome poor closure and prevent food retention. A doctor should prescribe antiemetic medications, since vomiting in such cases can be stopped at a reflex level. Painkillers can only be taken after the recommendation of a specialist, since pain can be specific and cause damage to the membranes and tissues. In such cases, analgesics may be ineffective. Sometimes treatment is supplemented with antibiotics and antiprotozoal drugs, which is sometimes associated with infection of erosions and other complications.
- Good results can be achieved by treating pathology with natural remedies. For example, inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes are relieved using a decoction of fennel and anise. Pain and heartburn can be eliminated by drinking potato juice, chewing dried raspberry leaves, teas made from peppermint, chamomile, raspberries, cabbage juice, and a solution of crushed activated carbon. In addition, infusions and infusions made from plantain, flaxseed, motherwort, oregano, licorice roots, shepherd's purse, and calamus root are effective. It is important to remember that the preparations and dosage of herbs and other folk therapeutic remedies should be prescribed by a specialist. The doctor will take into account all the characteristics of the patient’s body and select an individual therapy method. When choosing remedies, it is necessary to take into account how damaged the mucous membranes of the organs are.
- If the therapy does not produce a positive effect, the gastroenterologist refers the patient to a surgeon, since severe cases of the disease require surgery. The patient may be prescribed pyloroplasty or other types of surgery.
About heartburn
09.23.2018 admin Comments No comments
The main function of the esophagus is to move masses of food from the mouth into the abdominal cavity, which is achieved by contracting the fibers located on the wall of the organ. Insufficiency of the cardia rosette leads to improper functioning of the esophagus, which is fraught with various pathologies, since the pressure in the abdominal cavity is higher than in the esophagus.
A malfunction of the esophagus can provoke severe pathologies.
Prevention of the esophageal sphincter
To prevent illness, you should eat food often, but in small portions, and do not overeat. It is important to reduce the amount of coffee, garlic, and onions in the diet, not to eat fatty, overcooked foods, and to keep alcohol and carbonated drinks to a minimum. In addition, you need to limit the consumption of citrus fruits, mint tea, and chocolate. The patient should perform abdominal exercises and at the same time avoid exertion after meals and do not eat before bed. Smoking cessation is necessary. Avoid wearing tight clothing (belts, tight pants, etc.). In addition, it is important to undergo a timely examination and contact a specialist if any suspicious symptoms appear.
Diet food
Proper and healthy nutrition for gastric sphincter insufficiency is the basis of the entire therapeutic approach. In order to quickly recover and prevent exacerbations of the disease, you should:
Feel free to understand the problem that interests you together. >>>
- Avoid consuming foods that can cause a decrease in tone. These include: chocolate products, carbonated drinks, pepper, tea, coffee, seasoned foods.
- Avoid spicy and fatty foods.
- Completely eliminate the consumption of alcohol and tobacco products.
Meat protein, on the contrary, helps to increase the tone of the LES and reduce symptoms.
The main condition for the complete absorption of food is its frequent consumption in small portions. A minimum 4-hour interval should be observed between main meals. At the end of the meal, refuse to take a lying position, and preferably sleep with the head end raised.
Infections
Reflux esophagitis can be caused by bacteria (Helicobacter), viruses (herpes, cytomegalovirus) and fungi (Candida). In this case, only tests can make an accurate diagnosis and determine the type of causative agent of inflammation in the esophageal tube.
There are universal remedies for eliminating infectious reflux esophagitis, which can reduce the symptoms of the disease, reduce the number of pathogenic microorganisms, and strengthen the immune system:
- Chamomile, yarrow, calendula flowers, taken in equal proportions, are poured with boiling water in a ratio of 1:4. Take the drink 4 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
- Tea made from the fruits of viburnum and rose hips.
- A course of vitamins and immunomodulators.