An imbalance of hormones in the female body can lead to various consequences: cycle disorders, problems with conception, etc. Often, as a result of such processes, as well as under the influence of other factors, follicular and corpus luteum cysts can form. Sometimes only a few weeks are enough for the development of a pathological condition; signs may be asymptomatic or even absent. What is a hormonal ovarian cyst, does it need to be treated and how to do it correctly? Does it affect the possibility of conception?
Development of pathological formation
Almost every cycle, the growth of a dominant follicle begins on one of the ovaries. Follicle-stimulating hormone - FSH, which is produced in the pituitary gland of the brain, is responsible for its maturation. This is also affected by estrogens and some other biologically active substances. Usually the follicle with the egg reaches a size of 14 - 18 mm, after which the ovarian capsule ruptures in this place - ovulation. The process is normally not accompanied by pain or any other sensations. For a combination of reasons, in some cases the rupture and release of the egg may not occur; this is called persistence of the follicle. Such violations lead to disruption of the menstrual cycle. Typically this is a delay. Conception cannot occur this month.
The persistent follicle can then take two paths. In the first case, there is a significant decrease in size to several millimeters. If such violations are repeated, polycystic ovaries are formed. In another case, the follicle begins to grow due to the fluid formed inside it - it is soaked from the blood vessels located in its walls. A cyst is formed, which can sometimes reach 10–15 centimeters or more in size.
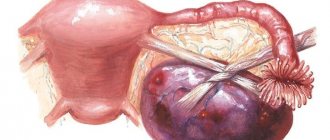
If ovulation occurs, a corpus luteum forms at the site of the rupture. It is called that because of its color. The corpus luteum is formed under the influence of luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary gland. It itself secretes progesterone, a pregnancy hormone, the lack of production of which can lead to miscarriage. Under the influence of many factors, lymph and other liquid components begin to accumulate in the tissues of the corpus luteum. This leads to the formation of a luteal cyst. It can appear both outside of pregnancy at the site of a ruptured follicle, and after conception.
Reasons for appearance
Hormonal formations include two types: a follicular cyst and one that appears in place of the corpus luteum. The latter often occurs during pregnancy. The symptoms and treatment tactics are the same; it is not always possible to determine which one is exactly formed - follicular or corpus luteum.
The exception is the detection of such tumors in the early stages of pregnancy. In 90% of cases, in these situations we are talking specifically about corpus luteum cysts; they can be detected as early as 4–5 weeks, and regress on their own by 16–18.
Such formations can occur at absolutely any age, but more often they appear in women of the reproductive period. Many factors influence this process.
Age variations
The formation of hormonal cysts is typical during the period of formation of menstrual function in teenage girls and for women on the eve of menopause. Almost everyone, 5 to 7 years before menopause, notices disruptions in the cycle, an increase in the volume of menstrual blood - in most cases this is associated with dysfunction of the ovaries and the formation of similar formations in them.
Hormonal imbalance
Of course, sex hormones play a role in the formation of ovarian cysts. Especially in cases of artificial stimulation of the body, for example, during preparation for IVF. All the methods used put very hard pressure on a woman’s reproductive system. Using artificial methods on the ovaries, the growth of several dominant follicles is stimulated simultaneously. After 2–3 IVF attempts, not only the risk of cysts on the ovaries, but also malignant tumors in the organ increases.
All drugs used to increase the likelihood of pregnancy, for example, with polycystic disease, act in a similar way. Of course, their impact is milder, but can still lead to further functional failures.
Uncontrolled use of drugs for emergency contraception, more often than 2-3 times a year, can also ultimately lead to the formation of follicular and corpus luteum cysts.
A woman’s hormonal background changes dramatically even after abortions or miscarriages. Not only the mammary glands respond to these processes (mastopathy occurs), but also the ovaries (the formation of functional cysts).
Inflammatory processes
Any infectious processes in the pelvic cavity, uterus or ovaries lead to hormonal imbalance, which ultimately transforms into luteal and follicular cysts.
Their formation occurs in most cases at the end of the acute period, a month or two after treatment. If the infection is subclinical (with a minimum number of symptoms), the woman may not be aware of the changes occurring in her body.
Hyperestrogenism of any origin
An increase in the amount of estrogen in the blood also contributes to the formation of cysts and all the ensuing consequences. It is also necessary to take into account that adipose tissue is the source of these hormones. Accordingly, all women with excess body weight have risk factors for the development of such a pathology.
Stress
Psycho-emotional experiences always entail a disruption of the relationship between all structures and organs. The genital organs receive “commands” from the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, which are located in the brain. It is here that LH and FSH, as well as other important biologically active substances, are formed.
Endocrine diseases
The reproductive system is in close relationship with other organs. Especially those that perform an endocrine function. First of all, these are the thyroid gland and adrenal glands. Chronic thyroiditis, hypothyroidism and other diseases can lead to the formation of functional cysts on the ovaries.
Symptoms of a cyst
In some cases, both luteal and follicular cysts are asymptomatic and are an incidental finding during surgery or on pelvic ultrasound. Various symptoms associated with the development of this condition may also occur.
Treatment of ovarian cysts with hormonal drugs in most cases helps to cope with all the signs of the disease. And this:
- Periodic or constant nagging pain in the lower abdomen, right or left. They can radiate to the lower back, perineum and rectum. In most cases, pain intensifies after physical activity, sexual intercourse, or during sudden turns or bends.
- The nature of menstruation changes: regularity is disrupted, more often there are delays of 14 or more days (even up to several months). Your periods become heavier, often with clots (some compare them to pieces of liver). Critical days are more painful than usual.
- Sexual desire decreases. Cysts often cause the inability to get pregnant for some time.
- When charting basal temperature or performing ovulation tests, it is impossible to accurately determine the time of egg release—this process does not occur when cysts form. The temperature measured in the rectum, as a rule, does not rise above 36.9 degrees throughout the entire cycle.
Painkillers for cysts in the appendages
For the most part, the presence of a cyst in the ovary does not reveal itself in any way, that is, signs of this pathology may not be noted. But it is quite possible that pain may occasionally occur. In such a situation, the gynecologist usually advises the use of painkillers, for example, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen. Antispasmodic drugs help dull the pain: Spazmalgon or No-Shpa. But you shouldn’t abuse them either. Severe and sharp pain may indicate a complication of the cyst. Here you need to react quickly and not delay your visit to the doctor.
Signs of ovarian rupture
Follicular and luteal cysts do not become malignant. The most dangerous complication of such formations is their rupture. In this case, intra-abdominal bleeding develops; without urgent surgical intervention, the woman may die.
Rupture of an ovarian cyst can occur either without obvious reasons or during physical activity, including sexual intercourse. The clinical picture develops gradually, it all depends on the rate and volume of blood loss.
Often, when a breakup occurs, girls report an acute pain in the abdomen, which soon goes away. It can be localized on the right, left or in the very lower abdomen in the center. Then minor nagging pain appears in the same place, the intensity of which increases, and taking analgesics does not stop the attacks. Over time, a feeling of pressure on the rectum and bloating occurs. At this time, the pain no longer has a clear localization; it is scattered throughout the abdomen.
As blood loss increases, blood pressure drops and the pulse quickens, the skin turns pale, the eyes become dark, dizziness, drowsiness and weakness, even fainting, may occur. If these symptoms occur, emergency surgery is indicated, otherwise the consequences can be dire.
Treatment
The choice of method for carrying out therapeutic measures is based on the results of the patient’s study. In this case, it is necessary to take into account some indicators:
- type of neoplasm;
- what age category the patient belongs to;
- the likelihood of malignancy of the pathological process;
- the importance of maintaining reproductive function;
- risk of complications.
Treatment of hormonal cysts can be carried out in several ways.
Medication
For the treatment of cystic neoplasms, hormonal drugs are prescribed. In most cases, the specialist recommends taking oral contraceptives, the action of which is aimed at stopping the growth of the cyst, reducing its size, and also to prevent the formation of new growths.
Duphaston is the most popular. It is prescribed to normalize the concentration of the hormone progesterone, since the drug is its synthetic analogue.
Along with hormonal therapy, a course of vitamins is used. In particular, these are folic acid, vitamin A and E and others. Sedatives normalize the psycho-emotional state. Antibiotics help eliminate inflammatory processes.
The duration of therapy can be up to 12 months under the strict supervision of a specialist.
Operational
If there is no positive result from drug treatment, surgical intervention is performed.
The operation is also indicated in the following situations:
- the neoplasm is large ;
- there is severe pain ;
- the development of polycystic disease is observed ;
- the cyst compresses nearby organs;
- rupture occurred .
Tumor removal can be done using several methods.
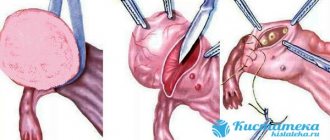
Laparoscopy
The essence of the procedure is to make three punctures in the peritoneal cavity. Through them, the entire process of excision of the cyst and surrounding pathological tissue occurs.
Laser
To remove the tumor, a laser beam is used instead of a scalpel. This technique is characterized by minimal trauma. Rehabilitation takes little time.
Laparotomy
If the cyst is large, or if it has ruptured and the process of suppuration has begun, this method is considered one of the most effective. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
In case of severe pathology, especially when the tumor becomes malignant, the uterus along with its appendages is completely removed.
Do I need treatment?
When detected, follicular and luteal cysts must be treated, starting with vitamin and hormonal medications; sometimes, if they are small in size and there are no complaints, the formation can be observed for 2 to 3 months. If there is no dynamics during this period of time, treatment is prescribed. If after this the cysts persist, surgical removal of the tumors is indicated, followed by their histological analysis. The method and method of treatment can only be determined by a doctor individually in each situation.
If cysts are discovered during pregnancy, they are observed without any treatment until 16 - 18 weeks. In most cases, they regress on their own. If they persist, surgical removal is indicated before week 20, as the risk of rupture and torsion increases, and a malignant process cannot be ruled out.
It is also important in the presence of any cysts on the ovaries to determine tumor markers, in particular, CA-125, HE-4 and the ROMA index. An increase in any of the indicators increases the risk of developing an oncological process in education. Such cysts require immediate surgical removal, even if they were initially thought to be functional.
Treatment of ovarian cysts with hormonal drugs is the most commonly used and effective method. In most cases, this therapy is combined with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and various types of absorbable drugs. Hormonal pills for ovarian cysts are ordinary oral contraceptives, which are selected individually taking into account the constitution and health status of the woman.
Surgical treatment involves removal of the cyst; it is safer and less traumatic to do this using laparoscopic techniques. After such treatment, oral contraceptives are also prescribed for a period of three to six months or more. This is a kind of relapse prevention.
We recommend reading the article about paraovarian ovarian cyst. From it you will learn about the pathology and the reasons for its development, symptoms of the neoplasm, types of paraovarian cysts, diagnosis and treatment.
Advantages of conservative treatment of ovarian cysts
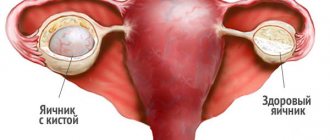
An ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm that appears inside the body of the ovary or on its surface. It looks like a hollow tissue bag filled with liquid or various semi-liquid contents. Capsules come in different sizes, sometimes significantly increasing the parameters of the ovary. They are divided into functional, capable of self-resolving in three monthly cycles, and pathological, requiring treatment or removal. The appearance is associated with:
- hormonal disorders
- overweight
- endometriosis
- inflammatory gynecological diseases
- menstrual irregularities
A functional cyst can resolve on its own within 3 months.
Diagnosed by other tests. The formation does not bother the patient and does not cause pain. The age of a woman with the disease varies from childhood to adulthood. A cyst discovered during examination does not always require surgical removal; sometimes conservative therapy, observation, and taking pills are sufficient. Acute symptoms occur when the leg is torsed, the capsule ruptures and cystic fluid leaks into the peritoneum. In this situation, urgent removal of the formation is required.
Types of ovarian cysts
They are divided into types:
- follicular;
- corpus luteum;
- parovarial;
- dermoid;
- endometrioid;
- polycystic ovary syndrome.
A follicular cyst appears if there is inflammation of the appendages or hormonal imbalance, with an imbalance of estrogen and progesterone in the body of a woman or girl. A capsule is formed if ovulation has not occurred.
This is a functional neoplasm, if it does not disappear on its own within three monthly cycles, it is good to treat it with medications.
A corpus luteum cyst is formed when the functioning of the corpus luteum is disrupted, when the outflow of fluid from the follicle is difficult, exudate accumulates and a cyst is formed. It is observed against the background of inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs, hormonal disorders. Happens during pregnancy.
Follicular cyst can occur during pregnancy
Endometrioid cysts occur in women with endometriosis. Areas of endometriosis germination in the ovary are subject to cyclicity, as in the body of the uterus. Endometriosis lesions grow, are rejected, and are excreted in the blood. Since removal from the ovary is not possible, cysts with brown contents form. Removal is carried out surgically. A dermoid cyst or teratoma is a benign, tumor-like formation containing in its cavity various tissues, cartilage, sebaceous glands, and hair.
Education is associated with disorders in embryonic development. These cysts are large in size and have a long stalk that is prone to twisting. Treatment is surgical removal.
Polycystic ovaries are many cystic formations on the surface of the ovary. An endocrine disease that leads to infertility. It can be treated with medications; if treatment is ineffective, surgery is performed. A parovorial cyst does not form on the body of the ovary, but is localized on the mesentery near it and the fallopian tube. Referred to as an ovarian cyst due to its proximity. It is motionless, torsion is rare, but it grows to large sizes and puts pressure on neighboring organs. She is not hormonally active. Treatment is surgical removal.
Diagram of polycystic ovary syndrome
Symptoms and diagnosis
Ovarian cysts capable of self-resorption are detected occasionally during other studies of the body. They are clearly visible on ultrasound and computed tomography. With large sizes, inflammation and suppuration, they show the following manifestations:
- pain, distension in the lower abdomen;
- irregular, painful periods;
- frequent urination;
- pain during examination;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
Signs of an “acute abdomen” with torsion, necrotization of the cyst stalk, violation of the integrity of the capsule and the threat of peritonitis are emergency indications; removal and surgery are required.
Diagnosis, in addition to random detection, during an examination, a gynecologist can detect enlargement and tenderness of the ovary. Prescribe an ultrasound examination, which is very indicative of this disease. Modern transvaginal ultrasound can easily recognize a cyst. Hormone tests are prescribed. Gynecological smears are taken to detect inflammation.
In complicated cases, laparoscopic diagnosis is used. General blood and urine tests are prescribed to rule out inflammation of the appendages.
To exclude inflammation of the appendages, you need to take a blood test
Treatment of ovarian cyst
Ovarian cysts can be cured conservatively with medication. Not everyone requires surgery. Uncomplicated diseases are treated with oral contraceptives. Contraceptives suppress the growth of new formations and promote their resorption. Vitamin therapy is used (vitamins A, E, groups B, C). Diet correction for overweight. In the drug treatment of follicular and corpus luteum cysts, observation tactics are used. If it does not go away within three monthly cycles, conservative hormone therapy (progesterone preparations, birth control pills) is started.
If there is no effect after three months of treatment with tablets, as a result it has not disappeared, and the size of the formation at the initial examination is more than 8 cm, this is an indication for surgery.
In addition to treatment with gestagens and oral contraceptives, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial treatment is prescribed. Hormonal drugs even out the disturbed background of a woman’s body. Prescribing contraceptives has a therapeutic and preventive effect. They reduce the likelihood of the formation of new cysts and prevent cancer.
Hormonal contraceptives are prescribed for the treatment of ovarian cysts
Reproductive function does not suffer with conservative treatment, hormonal levels are normalized, and the woman can conceive and bear a child. Mothers of girls should not worry that their children are prescribed such “adult” hormonal pills. Conservative treatment of ovarian cysts will help cure the child without surgery and harm to health. But if surgery is necessary, drug therapy and rehabilitation will be required in the postoperative period.
vrachlady.ru