- Main causes of botulism
- Incubation period of botulism
- Treatment at home
Botulism
Many infectious diseases claim lives every year due to dangerous complications. At the same time, they can be successfully treated if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, and can resolve without serious consequences for the body. Is botulism one of these diseases? What is botulism? In what forms does it occur in people? How is this serious disease treated?
Disease "botulism"
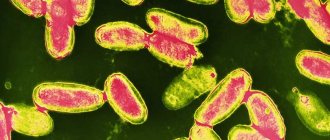
The disease “botulism” refers to acute infectious diseases of humans, the main symptoms of which relate to damage to the nervous system. The causative agent of this dangerous disease is called Clostridium botulinum.
There are several types of botulism disease:
- Foodborne (infection with botulism through food);
- Wound (the causative agent of botulism enters the wound from the soil);
- Botulism in infants (the bacteria that causes botulism enters the digestive tract).
Infection with botulism through food occurs in more than 99% of all cases of infection.
The causative agent of botulism
The causative agent of botulism is a bacteria. This is a gram-positive rod that is mobile. The bacteria that cause botulism are anaerobes, that is, they do not require oxygen to function. Several serological types of bacteria are recognized. In our country, the disease is caused by types A, B, E. The causative agent of botulism secretes an insidious toxin, which causes a certain clinical picture when it enters the human body.
Features of bacteria that cause botulism
In order for the botulism pathogen to release the toxin, it does not need oxygen. The optimal temperature for sufficient toxin formation is about 30-35 degrees. Some serotypes of bacteria do not require such strict conditions: they multiply well in a regular refrigerator and even in the presence of oxygen.
The bacteria (the culprit of botulism) is very easily produced in the laboratory. They are so toxic that they are even considered as candidates for biological weapons. Currently, the toxin of the causative agent of botulism is actively used in cosmetology (Botox).
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
The causative agent of the disease exists in the form of vegetative (active) forms and spores (“dormant” forms). If you heat the pathogen in its vegetative form for half an hour at a temperature of 80 degrees, it will die. But the spores are very resistant to such influences: they will not die even after five hours of boiling. Even high concentrations of disinfectants are not harmful to spores. They are not afraid of drying, ultraviolet irradiation, or freezing.
Properties of botulinum toxin
Botulinum toxin is one of the most powerful toxins that is pathogenic to humans. The toxin of the causative agent of botulism, released into the external environment, retains its pathogenic properties for about a year. But the poison of the causative agent of botulism, found in canned food, remains very dangerous for humans for several years.
How can you inactivate the pathogenicity of a dangerous toxin? Alkalies and ten-minute boiling have a detrimental effect on it. Enzymes of the human digestive tract reduce the activity of botulinum toxin, with the exception of toxin E, which, on the contrary, becomes even more active. Also, the toxin of the causative agent of botulism decreases activity under the influence of liquids containing ethanol.
Botulism in humans occurs with damage to the nervous system in the form of pseudoparalysis. Pseudoparalysis differs from true paralysis in that there is no anatomical damage to the nerve structures. That is, after adequate treatment of botulism, complete restoration of lost functions is possible.
The occurrence of pseudoparalysis is caused by the toxic effect of botulinum toxin on nerve synapses, which leads to disruption of the transmission of nerve impulses along the fibers. This causes the development of symptoms of botulism, which are associated with disruption of the activity of striated and smooth muscles.
Prevention of botulism
To prevent and timely identify sources of botulism, epidemiological surveillance is carried out over canned food sold in retail chains, their timing of sale and appearance. If bacteria are detected in any product, not only the entire batch is subject to inspection, but also the place of its production. Bacteriological control of food raw materials, which are used to create canned fish, meat and vegetables, is carried out with no less care.
Botulism got its name from the Latin word botulus - “sausage”: in the first officially registered case, infection with the toxin occurred after eating homemade sausage. And now the main risk factor is home-cooked products that have not undergone proper sanitary and hygienic processing. Smoking, ozonation, freezing, drying, drying, adding large amounts of salt and pepper to dishes do not affect the toxin in any way.
The principle of infection of spores by honey, which can pose a danger to infants, has not yet been studied. It is believed that the spores of the bacterial bacillus fall first into the nectar of plants, and then, thanks to the bees, into honey. An adult can tolerate the use of such an ingredient painlessly, but honey is often added to dry infant formula, which causes illness.
Therefore, to prevent botulism, you should adhere to the following measures:
- control the expiration dates of consumed products;
- be attentive to the appearance, smell and other methods of organoleptic evaluation of food;
- avoid eating foods whose quality you are unsure of;
- do not buy in spontaneous markets;
- do not give honey to children under six months;
- check the composition of formulas for artificial feeding of infants;
- When preparing home preserves, heat the jars at a temperature of 100 degrees for at least half an hour, as well as tin lids;
- Before canning, all berries, fruits and vegetables must be cleaned of dirt with a stiff brush;
- fish and meat cannot be prepared for future use at home.
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to determine the presence of botulism infection by the appearance of products. Knowing what botulism is and how dangerous it is, you need to limit your consumption of foods or completely eliminate them from your diet:
- wild mushrooms in any form (raw, fried, boiled, canned);
- fish, pickled, salted or dried along with intestines (the pathogen is more common in freshwater than in seawater);
- homemade sausage and any meat products, if you are unsure of compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards when preparing them;
- home canning, especially after “bloating”;
- overripe and stale vegetables, berries, fruits.
When opened, such products must be subjected to heat treatment - boil for half an hour. This will help destroy toxins formed during storage. Particular attention should be paid to the quality of nutrition of young children, as they suffer from severe disease.
A vaccine against botulism has now been developed. It is not included in the mandatory vaccination program approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation due to the low effectiveness of the drug. However, if desired, vaccination can be done at your own expense.
Botulism infection
The disease “botulism” occurs in a person if the toxin of the pathogen enters his body with food. Disease due to infection with bacterial spores can also occur, but much less frequently. Such infections cause wound botulism or botulism in infants.
Where do the spore forms of the pathogen come from? They surround us: they are found in water, in dust and even in the silt of water bodies, in the soil, in food products contaminated with soil. They easily penetrate the intestines of animals, fish and birds. After the death of animals, the spores turn into vegetative forms, which begin to actively release toxin.
There is oxygen in reservoirs. But, if most of it is absorbed by algae or other bacteria, then conditions will be created for the active proliferation of bacteria that cause the disease “botulism”.
Main causes of botulism
For the botulism infection, the reasons for its development lie mainly in improper preparation, storage and consumption of food (mainly home canning). This is confirmed by the fact that the pathogen that causes botulism and its toxin are found in home-prepared canned food.
In addition to detecting the bacteria that causes botulism in canned food (especially in mushrooms), it can be detected in house dust, in soil, and in other food products that were improperly stored and poorly thermally processed.
The causative agent of botulism in home canning jars
Most cases of human botulism occur from the consumption of low-quality home-canned products. The bacteria that cause botulism multiply in cans of canned food (vegetables, legumes, home-canned meat and fish).
The causative agent of botulism in home canning jars can exist for several years. It is resistant to salt and spices and does not deteriorate in an acidic environment. In those countries where the population is widely involved in canning vegetables, meat or fish, botulism is most common.
If the causative agent of botulism is present in canned food, then their color, smell and taste do not change, that is, a person may well mistake these products for benign.
Sometimes “bombing” happens to cans: the lids are torn off. In addition to this, there is a taste of rancid oil and an unpleasant odor. But these changes are usually associated with the presence of accompanying flora in the jars, also anaerobic.
The causative agent of botulism in mushrooms (homemade preparations)
Very often, the pathogen that causes botulism is found in home-canned mushrooms. This is because mushrooms are often not properly processed before canning, leaving them with spores of the bacteria that cause botulism.
The causative agent of botulism in industrial products
Can the causative agent of the disease “botulism” penetrate industrial products? Very rarely, meat and fish products and canned goods from the store turn out to be dangerous due to the presence of botulinum toxin. But the pathogen can get there after purchase and begin its active reproduction in them (for example, in sausage, smoked fish).
This occurs due to improper storage and heat treatment of products. Moreover, in a solid product, the toxin can form locally. In this case, when eating a low-quality product, signs of botulism may not appear in everyone who ate it.
The causative agent of botulism in other products
The disease “botulism” can occur when consuming homemade meat and fish products. This usually occurs in case of poor handling of initially contaminated products or improper storage.
Causes of botulism
To find out how to avoid getting this disease, you need to understand what causes it. As a rule, the main reason for the development of the disease is the use of low-quality preserved food. Also, when purchasing questionable food products that are sealed, there is a possible risk of clostridium botulinum entering the body. But it is also worth noting that you can become infected with botulism not only through food, this disease has the same transmission as tetanus, that is, the microbe that causes it can enter a person through open wounds, for example, through the soil.
Signs of botulism
The most important signs of botulism are associated with damage to the nervous system and the development of myasthenia gravis and pseudoparalysis. The oculomotor and respiratory muscles, the muscles of the pharynx and larynx suffer. In addition, intestinal paresis occurs, the amount of saliva and gastric juice produced decreases. Under the influence of a number of factors, the pathogenic effect of the toxin can increase. These include: a layer of secondary infection, ionizing radiation, some medications, etc.
Incubation period of botulism
When botulism infection develops, the incubation period usually lasts about one day, sometimes two or three days. Very rarely, the incubation period of botulism extends for more than a week.
It has been noted that botulism is more severe in humans if the incubation period of the disease was very short. But this doesn't always happen. The disease itself can occur with varying degrees of severity.
Main symptoms of botulism
With botulism infection, symptoms can occur in the following order (two scenarios):
- First, gastroenteritis develops, and then signs of damage to the nervous system appear.
- There are no signs of damage to the digestive tract, but neurological symptoms immediately appear.
Gastroenteritis due to botulism is characterized by vomiting, diarrhea, high fever, and abdominal pain. After a few hours or a day, the patient develops neurological symptoms.
Neurological symptoms of botulism include muscle weakness, headache, and a feeling of dizziness. This is often accompanied by high fever (short-lived, less than a day). Following these symptoms, visual impairment occurs: the patient sees blurredly, everything “blurs” before his eyes, he cannot read, although he sees well in the distance. Such disorders with botulism occur due to paresis of the ciliary muscle.
Other signs of botulism related to the organ of vision are the following: a feeling of double vision, strabismus, drooping of the upper eyelid, dilation of the pupil, different sizes of pupils, immobility of the eyeballs, lack of reaction of the pupils to light (in severe cases), pathological farsightedness and others. Pathological signs of botulism from the eyes persist the longest. The development of these symptoms is limited to a mild form of the disease.
In more severe cases of botulism, the muscles of the tongue, pharynx and larynx suffer due to damage to the fibers innervating them. The patient's speech becomes silent (aphonia) or slurred, problems with swallowing appear, and choking on food is often noted. When examining the pharynx and laryngoscopy, the doctor notes paresis of the tongue, palate and glottis. Sometimes there is paresis of the facial nerve on both sides. These symptoms fit into the moderate course of the disease.
If botulism in humans is severe, respiratory problems occur. These disorders in botulism occur due to paresis of the respiratory muscles, including the diaphragm. The lungs become less mobile. Symptoms of respiratory failure gradually increase. A person may experience a feeling of lack of air. A symptom such as speech interruption appears. The lips become cyanotic (blue), and breathing is shallow and rapid.
Sometimes, with botulism, symptoms of respiratory failure develop gradually, over several days. But in some especially severe cases, there is a rapid deterioration in the condition up to respiratory arrest (“death in mid-sentence”).
Separately, it is worth noting the symptoms of damage to the parasympathetic nervous system. This is manifested by dry skin and mucous membranes, salivation below normal. Intestinal paresis develops, which can be complicated by intestinal obstruction. The innervation of the urinary tract also suffers. Patients may be bothered by both impaired urinary excretion and constant involuntary urination.
Moderate and severe forms of botulism are characterized by disorders of the cardiovascular system: tachy- or bradycardia, high blood pressure, various arrhythmias and blockades, pathological changes in the electrocardiogram (ECG), increased levels of certain specific enzymes in the blood. Severe cardiac arrhythmias can cause death in patients if botulism is not treated in a timely manner and emergency care is delayed for life-threatening conditions.
The full clinical picture of botulism is not characterized by intoxication and high temperature. The consciousness of the patients remains clear, there are no meningeal symptoms.
In the second week of the disease, a complication such as myositis (inflammation of the muscle) often occurs. The muscles of the legs or neck muscles are usually affected. This complication is very unpleasant for the patient, as he cannot walk normally and experiences severe pain in the affected muscles.
Often with botulism secondary bacterial infections occur. Most often they occur in the form of tracheitis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis and even sepsis. Oddly enough, complications of the disease may occur due to its treatment. This occurs during invasive intervention in the body (catheterization of the bladder, artificial ventilation, etc.) and when prescribing certain medications.
Patients recover very slowly. An early sign that the patient is recovering is the restoration of normal salivation. Neurological symptoms then begin to subside. Lastly, muscle strength and visual acuity are restored.
Food poisoning and botulism - what's the difference?
A person may experience a combination of common food poisoning and botulism. This is due to the fact that products may simultaneously contain botulinum toxin and accompanying flora, which are also pathogenic for humans. This is the flora that also reproduces in the absence of oxygen, like clostridia botulism. As the usual symptoms of poisoning fade, the patient's condition does not improve, as neurological symptoms of botulism appear.
How to distinguish banal food poisoning from botulism when the latter is isolated? Food poisoning is similar to botulism only on the first day of illness, and sometimes only in the first few hours. Repeated vomiting, severe intoxication, frequent loose stools, abdominal pain for several days are characteristic of poisoning, and with botulism these symptoms are short-lived and are quickly replaced by neurological symptoms.
In addition to poisoning, botulism has similar symptoms to diphtheria polyneuritis, various meningitis and encephalitis, acute cerebrovascular accident and other diseases. Each disease has its own characteristic features. When making a choice in favor of botulism, the doctor pays attention to the absence of intoxication, symmetry of damage to the nervous system, preserved sensitivity, clear consciousness, absence of focal symptoms, involvement of the respiratory muscles in the pathological process and other nuances.
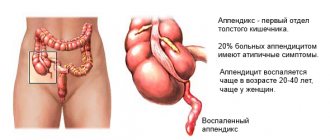
Wound botulism in humans
Wound botulism can occur when spores of the bacteria that cause this infection enter a person’s wound. They can get into the wound when it is contaminated with soil. If favorable conditions are created, the spores will turn into active vegetative forms, which will lead to the production of botulinum toxin.
The disease occurs with intoxication. The incubation period of wound botulism lasts from several days to two weeks. Neurological symptoms are the same as with foodborne botulism.
Botulism in infants
Botulism in infants is a disease that mainly occurs in babies in the first six months of life. Mostly children who are fed artificial formula (at least partially) suffer. In addition to Clostridium botulinum, other clostridia can cause pathological processes.
Previously, honey was used to prepare mixtures, which could contain pathogen spores. Spores can also enter the child’s body from the environment (dust, soil, mother’s hands, etc.).
The first symptoms of this form of botulism are refusal to eat, poor and ineffective sucking, and problems with stool. Then the typical symptoms of botulism appear, as with food contamination.
Infants can die from severe forms of botulism. Often the disease is complicated by pneumonia.
The first signs that make you think
The very first symptoms of botulism can be confused with ordinary poisoning or intestinal disorder. If you see at least one sign of intoxication, you should visit a doctor and make sure.
The patient complains of:
- very severe pain and cramping in the center of the abdomen;
- headache (dizziness);
- attack of diarrhea;
- general weakness, impotence,
- nausea and vomiting;
- increase in temperature (very high up to 40).
By the evening, all symptoms may disappear, the temperature may return to normal, and diarrhea may stop, but this deceptive condition is better to consult a doctor.
Diagnosis of botulism
Diagnosis of botulism begins with a thorough medical history. If a person is suspected of having botulism, the foods he ate the day before should be carefully checked for botulinum toxin content.
Of particular importance in the diagnosis of botulism is the characteristic clinical picture: absence of intoxication, damage to the nervous system like pseudoparalysis, gradual involvement of new organs in the process.
The key to diagnosing botulism is to detect a dangerous toxin in the patient’s bloodstream - the culprit of all problems. It is important to take blood for this test before treating the patient with antitoxic serum. In addition to blood, other biological fluids of the body can be examined for botulinum toxin content.
Diagnosis of botulism also includes detection of the bacterium itself. To identify the pathogen that causes botulism in mushrooms and other homemade products, it is necessary to inoculate these products on certain nutrient media. In addition to examining suspicious jars for the causative agent of botulism, you can examine cultures of feces and stomach contents.
If wound botulism occurs, then discharge from the wound and pieces of dead tissue should be examined. To confirm botulism in infants, their blood and stool must be tested.
Clinical manifestations of the disease
There are simple and wound botulism. In the latter case, microbes enter the body through contact. This is a disease caused by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. With botulism, the causes are few. This pathology is difficult. The maximum incubation period is 10 days. The first signs of botulism appear within a few minutes or hours from the moment the body is infected. In most cases, complaints arise within the first 24 hours.
Mostly young people under 30 years of age are affected. Botulism poisoning is increasingly occurring at home. The reason is the consumption of home-made canned foods. The susceptibility is very high. Signs of the disease appear even when a small amount of botulinum toxin enters the blood.
Treatment of botulism
Treatment for botulism should be started immediately from the moment a doctor or paramedic suspects this infection. Timely seeking help provides more guarantees that the illness will end favorably for the person.
Treatment at home
There is no home treatment for botulism. As soon as botulism is suspected, the patient is urgently hospitalized in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit.
Before hospitalization, the patient needs to rinse the stomach to remove the remaining toxin from the body. After gastric lavage, intestinal sorbents (Activated carbon, Smecta, Filtrum, etc.) are given orally. Sometimes medications are given to stimulate diuresis (urine output).
Hospitalization for botulism
It is necessary to hospitalize a patient in a hospital for botulism. It is recommended to lie in bed as much as possible; some patients are allowed to sit up.
- Diet
Table 10 is prescribed: it is intended for nutrition of cardiac patients. The diet excludes foods that have a stimulating effect on the nervous system, heart and blood vessels. Liquid and salt are limited. Foods that can cause flatulence and indigestion are undesirable. Food is given boiled. Vegetables, fruits and dairy products are allowed.
If the patient has difficulties with swallowing and digestion, food is given through a tube in the form of special nutritional mixtures or parenterally (intravenously) in the form of concentrated solutions of fats, amino acids and glucose.
- Drug therapy
All patients require administration of antitoxic botulinum serum. This medicine is given intravenously. To prevent serious allergic reactions to it, it is necessary to administer prednisolone to the patient in advance. Serums can be monovalent (against a specific type of toxin) or polyvalent (against different toxins). In the case where the type of toxin is not established, either a mixture of monovalent serums or one polyvalent one is introduced.
In addition to serum, human anti-botulinum immunoglobulin is used to treat botulism.
Treatment of botulism in its severe form cannot occur without intensive therapy aimed at supporting vital functions and restoring them.
- Care must be taken to prevent aspiration of gastric contents into the respiratory tract. To do this, a permanent tube is installed in the patient, going through the nose into the stomach. Sometimes airway intubation is used.
- Ventilatory support for the patient depending on his condition.
- Taking medications that reduce the acidity of gastric contents (ranitidine, omeprazole, etc.).
- Prescribing medications that enhance the motor function of the digestive tract (Cerucal, Domperidone).
- Monitoring the acid-base composition of the blood, cardiac output, hemoglobin levels and other important parameters.
- If bacterial complications develop, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed.
- Immunoglobulins (Octagam, Pentaglobin, etc.) have a good effect.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is effective in combating hypoxia in the body.
If a person suffers from wound botulism, then surgical treatment of the wound and antibacterial therapy are used.
Discharge of patients home is allowed only after the disappearance of clinical symptoms of the disease. After the illness, the patient is under follow-up care by an ophthalmologist, neurologist and cardiologist.
Diagnostic methods
Unfortunately, in order to make a correct diagnosis, specific clinical diagnostic methods will not help the doctor if botulism is suspected. There are no characteristic changes in general blood, urine and stool tests.
Serological tests (detection of typical antibodies and antigens) are not carried out in conventional laboratories, since the disease is not accompanied by the production of characteristic antibodies. The dosage of the toxin is too small to detect, but sufficient to cause clinical manifestations.
Research at the bacteriological level is possible only in specialized laboratories where it is possible to work in an oxygen-free chamber. Toxins are released from feces and vomit obtained during gastric and intestinal lavage, the contents of wounds, and food products consumed by the sick person.
The analysis is carried out on experimental mice and guinea pigs. They are injected intraperitoneally with a solution obtained by mixing the patient’s blood with anti-botulinum serum (types A, B, E) followed by centrifugation. The entire study takes 4 days.
As a result, mice that are not protected by the antitoxin die, while those individuals who were injected with a serum similar to the toxin remain alive.
The specific type of toxin can be clarified by performing an indirect hemagglutination reaction, enzyme-labeled antibodies, and gel precipitation. The causative agent of botulism is isolated by inoculating the contents of the stomach and intestines on special nutrient media for anaerobes.
Hotinger's casein-mushroom medium is used for crops.
The existing hardware electromyographic study makes it possible to detect specific disturbances at the level of synaptic signal transmission in botulism.
Prognosis of the disease "botulism"
Botulism is very dangerous for humans. Severe forms of the disease claim human lives every year. In case of severe botulism infection, the causes of an unfavorable (deadly) outcome may be the following:
- Acute respiratory failure due to paresis of the muscles involved in the act of breathing;
- Acute cardiovascular failure due to dangerous arrhythmias;
- Multiple organ failure caused by impaired innervation of internal organs;
- Secondary bacterial complications.
Patients who have recovered from a severe form of botulism may experience shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat for a long time. They have pathological changes on the ECG for a long time.
If a person survives a severe form of botulism, all his lost functions of the nervous system and internal organs are gradually restored completely, no matter how severe they may be.
After suffering from botulism, a weak immune system is developed, so re-infection is possible in the future.
Symptoms that occur with this disease
Botulism, like all diseases, has its own main symptoms. They are divided into three types: arising in the digestive tract (most common), visual impairment, problems with the bronchopulmonary and respiratory systems.
The first signs of poisoning and botulism infection, which usually appear in the digestive system.
They are very easy to confuse with ordinary poisoning:
- nausea and vomiting (may occur several times a day);
- attacks of pain in the stomach;
- diarrhea (loose or watery stools);
- feeling of dryness in the mouth (for no reason).
Plus, your body temperature may rise, and while eating you may feel a “lump” in your throat (difficult to swallow).
Visual impairment is very rare at the first symptoms, the following changes occur:
- sharpness of vision decreases;
- a person does not see clear objects, everything seems to be blurred;
- a feeling as if “stars” and “flies” are moving before the eyes;
- the patient sees objects that are far away well, but sees objects that are close poorly.
Problems related to the respiratory system:
- a sick person breathes very heavily (often or, on the contrary, rarely);
- pale skin (sometimes even blue);
- very fast pulse;
- severe causeless shortness of breath.
When the disease begins to progress, there may be a combination of several types of symptoms.
The patient experiences the following difficulties with swallowing:
- At first it is difficult to swallow solid food, then liquid food;
- the tongue becomes wooden and clumsy;
- the small tongue is motionless.
The patient also develops vision problems:
- he sees not one object, but two;
- there is strabismus;
- it is very difficult for the patient to concentrate on one subject;
- eyelids droop involuntarily.
Added to these symptoms are problems with pronunciation. Here are some of them:
- the voice is completely inaudible, this is due to disturbances in the vocal cords;
- the timbre changes and the pronunciation of sounds changes;
- hoarseness;
- discomfort in the throat and dryness in the oral mucosa.
If the disease is in progress, it is difficult not to notice these signs:
- change in gait;
- muscles are very weak;
- the presence of stool disorders, namely constipation;
- urinary disturbance;
- pale complexion;
- cardiopalmus.
Very rarely, the following signs of illness occur: a person cannot smile with all his teeth, stiff facial muscles, a convulsive sensation in the face. But for some reason the patient hears well, thinks clearly, and his body temperature is normal.
If the disease has reached the final stage, a change occurs in the bronchopulmonary and respiratory systems, there is absolutely not enough oxygen, and additional diseases such as pneumonia may develop.
At the last stage of the disease, the motor, muscular and skeletal systems are disrupted, the person becomes like “dough”. He absolutely cannot hold his head straight (it falls), he moves very little. Perhaps clear memory and consciousness will be preserved, but the patient stops moving and an attack of suffocation occurs, and this all ends in death.
What can happen to a person who has been poisoned by botulism, and if he was not prescribed proper treatment or did not seek help from the hospital in time:
- very often additional diseases (or complications due to a viral infection) are added to the main disease: pneumonia, sepsis and inflammation of the bronchopulmonary tract;
- the development of complications of other vital organs is possible: cardiovascular system, musculoskeletal system;
- complications after treatment, digestive tract disorders and other diseases occur.
Experts have calculated and found that this disease lasts about a month or a little less if the patient receives the right medications and procedures. All disorders in the human body are restored.
Some symptoms are very difficult to get rid of, for example, the voice is restored in about a month and a half. If treatment is prescribed correctly and on time, you do not have to worry about any complications.
How to eliminate symptoms
After a preliminary diagnosis has been made, hospitalization of the patient is required. Before calling an ambulance, you can provide first aid to the person. You need to do the following:
- rinse the stomach;
- perform a siphon enema;
- take enterosorbent;
- put in an IV.
To neutralize botulinum toxin, you need to rinse your stomach with a soda solution. This must be done on the first day. After the first symptoms of botulism are identified, a siphon enema is performed. This will require up to 10 liters of warm water, soda, a funnel, a jug and a container for washing water. The enema is given with the person lying on his left side.
Enterosorbent - activated carbon
To prevent complications, you need to take enterosorbent (activated carbon or Polysorb). To eliminate the symptoms, the person is hospitalized in the infectious diseases department. If necessary, a ventilator is connected. After first aid for botulism has been provided, treatment includes the administration of serum. This must be done in the first 3 days. Otherwise, its effectiveness is reduced.
Botulism is a food poisoning that can be severe. Depending on the patient’s condition, polyvalent serum is administered 1, 2 or more times. Skin tests are required beforehand. Treatment for botulism often involves the use of immunoglobulin. This is a modern method of therapy. Antibiotics are often prescribed.
During botulism infection, they help suppress the activity of vegetative forms of clostridia. In case of respiratory failure, hyperbaric oxygen therapy is performed. Antipyretic drugs are used to eliminate fever. Treatment of botulism involves the use of homologous plasma. An important aspect of therapy is proper nutrition.
Infection manifested by dysphagia is an indication for parenteral nutrition. If necessary, a probe is used. With the development of myocarditis, cytoprotectors are prescribed. If blood pressure increases during botulism disease, then taking antihypertensive drugs is indicated. Corticosteroids are prescribed to prevent anaphylactic shock.
Expert advice
To protect yourself from the disease, you need to know which foods cause botulism. Based on this, you can follow simple rules for prevention:
- You should not preserve meat, fish products, fruits and vegetables in hermetically sealed jars if it is not possible to wash them well from the soil (for example, beets, carrots, etc.);
- It is not recommended to eat smoked or dried home-made products due to the possible risk of spores in the intestines and other parts of animals;
- It is strictly forbidden to buy home-canned goods from strangers;
- It is best to use nylon covers that allow oxygen to pass through. The products will not be stored as long as we would like, but in this way the risk of botulism infection can be reduced to zero;
- If, however, it is still not possible to refuse home-cooked food, then be sure to boil such products after opening the jar for at least 20–25 minutes. With such actions, the toxin is completely destroyed and does not pose a health hazard.
Cloudiness of the brine is one of the signs of food contamination
Please note that contaminated jars often become cloudy and break open. Under no circumstances should they be used for food. Even boiling will not help restore the product to its previous appearance and quality.
Consequences of botulism
Untimely treatment of botulism can cause a number of complications.
Consequences of the disease:
- Botulinum toxin blocks the impulses of the central nervous system and causes paralysis.
- Dysfunction of the visual organs: double vision, the appearance of fog and spots before the eyes, strabismus.
- Impairment of the motor system: the patient’s body becomes sluggish, it is difficult for him to hold his head upright.
- The appearance of problems with respiratory and swallowing function: the victim can hardly swallow food, breathing becomes shallow and frequent.
- Gastroenteric syndrome: nausea, vomiting, loose stools.
Timely first aid and further treatment in a hospital under the supervision of doctors will help avoid serious consequences of intoxication.
To protect yourself and your family from botulism, you need to know which products cause botulinum toxin poisoning and how to properly preserve and store homemade preparations.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of botulism is determined based on:
- information about what canned foods the victim ate;
- evidence of characteristic disturbances in vision, speech, swallowing, and so on;
- laboratory data.
When infected with botulism, diagnosis includes differential and laboratory data.
Differential is carried out in order to exclude:
- food poisoning;
- late complications of diphtheria;
- acute respiratory infections;
- complications of blood circulation in the brain.
Botulism is diagnosed in the laboratory
Laboratory diagnostics consists of:
- studies of vomit, food;
- determination of ESR in order to identify secondary infection;
- lymphopenia in order to identify possible disorders in the process of hematopoiesis;
- NB assay to determine the degree of leukocytes.
What foods cause botulism?
Food products contaminated with botulism bacteria cause the development of this disease in 90 percent of cases. Most often, the toxin enters the human body with products that undergo special processing to increase their shelf life. Such products include various canned food, sausages, dried, salted or smoked meat and fish. If the rules for preparation, preparation and storage of such products are not followed, botulism bacteria penetrate into them. Subsequently, when favorable conditions are formed, microbes begin their activity, resulting in the formation of botulinum toxin in products. Products that may contain the causative agent of botulism are:
- mushrooms;
- cucumbers and tomatoes;
- sausage, ham;
- stew;
- fish;
- caviar;
- milk;
- store preserved food.
Moreover, mushrooms are one of the most common foods that cause infection with this toxin. They account for about 50 percent of all cases of botulism. This is because when cooking mushrooms, it is quite difficult to completely remove the soil from them.
Botulism: incubation period
On average, the incubation period of the disease can last from several hours to one day. Its duration is determined by the amount of infection in the body. The period from poisoning to the appearance of the first signs of botulism can reach up to 2-3 days and even up to 10 days, but such cases are quite rare. There have been cases where the duration of the incubation period increased due to the patient's consumption of alcohol.
Manifestations of the disease most often have a sudden nature, strongly reminiscent of the symptoms of food poisoning. The toxin from contaminated foods is rapidly absorbed into the intestines, enters the bloodstream and instantly spreads throughout the body. In this case, vital organs become targets of damage.
The sooner botulism makes itself felt, the more severe the course of the disease turns out to be.
Forecasts
For botulism, hospitalization lasts from 14 days
Knowing how to protect yourself from botulism and with timely medical intervention, in case of infection, the prognosis is favorable. If proper treatment is not followed, the probability of death is 30-60%. Patients who have recovered may experience residual effects after paralysis for another 1-2 months. Complications in the form of sepsis, pneumonia or myocardium may also appear.
If there are no complications within 14 days, the patient is discharged. In case of complications:
- for myocardium – incapacity for work for at least 10 days, as well as treatment by a cardiologist with examination at least once every six months;
- for neuralgic symptoms - incapacity to work for at least 14 days with further observation by a neurologist and infectious disease specialist.
Botulism is a complex disease, and although it is quite rare, its danger should never be ignored. If you follow all precautions, you will minimize the risk of “catching” this problem.
In case of illness, you should immediately seek medical help, which guarantees a quick cure without serious consequences. Remember that you are unlikely to help yourself with botulism, so do not delay calling a doctor.
Neurological manifestations of the disease
With botulism, the first signs are soon complemented by neurological symptoms. This is due to the affinity of the toxin for the medulla oblongata and motor neurons of the spinal cord, as well as damage to the muscular system. The following signs of the disease are possible:
- grid before eyes;
- difficulty seeing near;
- drooping eyelids;
- doubling of objects;
- strabismus;
- uneven pupil size;
- involuntary eye movements;
- mydriasis
Strabismus
The appearance of these signs of botulism poisoning indicates paresis of the ciliary muscles and disruption of the innervation of the organ of vision. These symptoms are combined into ophthalmoplegic syndrome. In some people, exposure to botulism toxin causes severe farsightedness. Strabismus is most often convergent. Nystagmus is vertical. Toxins cause the development of bulbar syndrome.
It includes dysphagia and aphonia. In the first case, a person’s speech becomes slurred. First, the timbre of the voice changes. Hoarseness is observed. The reason is dryness of the pharyngeal mucosa. Then paresis of the soft palate and tongue develops. This manifests itself as dysarthria and nasality. The coughing impulse becomes stronger. If a foreign object or mucus gets into the patient's respiratory tract, asphyxia is possible.
Botulism toxin causes difficulty swallowing food. In severe cases, the person is unable to drink water. The cause is paresis of the muscles of the pharynx and palate. Bilateral damage to the facial nerve often occurs. This is manifested by facial asymmetry and impaired facial expressions. The bacterium with the toxin often causes damage to the glossopharyngeal, vagus and hypoglossal nerves.
Reasons for appearance
Botulism in canned food
The reasons for the first complaints are few. The following etiological factors are known:
- consumption of foods contaminated with bacterial spores;
- accumulation of toxin in products;
- improper preparation of canned food.
Bacteria with toxins enter the body through food and household contact. Anoxic conditions are optimal for the growth and reproduction of clostridia. Manifestations of botulism are possible when consuming canned mushrooms, vegetables and meat. The greatest danger is presented by products from jars with bulging lids.
Sometimes botulism bacteria enter the human body through wounds. The following changes play the most important role in the development of the disease:
- absorption of botulinum toxin in the mouth, stomach and small intestine;
- distribution of the toxin through the blood throughout the body;
- binding it to nerve cells;
- disruption of impulse transmission to muscles;
- damage to the spinal cord and brain;
- suppression of leukocyte activity;
- metabolic disorders in red blood cells;
- respiratory depression;
- disruption of oxygen transport to tissues.
Botulinum toxin is one of the most dangerous substances.
Symptoms during the development of complications
Bronchitis
When first aid for botulism is not provided in a timely manner, there is a risk of developing dangerous consequences. Mortality is high. The following complications of botulism are possible:
- pneumonia;
- tracheitis;
- bronchitis;
- acute respiratory failure;
- respiratory arrest as a result of paralysis of the diaphragm;
- acute heart failure;
- myositis;
- mumps;
- dehydration;
- acute urinary retention;
- involuntary urination;
- myocarditis.
In case of botulism, diagnosis allows one to determine pneumonia. Pneumonia causes symptoms such as cough and chest pain. Prolonged vomiting and inability to drink water lead to dehydration. It is manifested by dry skin and mucous membranes, confusion, drop in blood pressure and apathy. Botulinum toxin often causes acute intestinal obstruction.
Myocarditis
The cause is muscle paresis. Obstruction is characterized by stool retention, flatulence and abdominal pain. Unlike many other diseases, botulism can lead to myocarditis. It manifests itself as pain in the heart area, shortness of breath during exercise, sweating and a feeling of irregular rhythm.
Causes of death from botulism
The main cause of death in botulism is respiratory failure. The reason for this is paralysis of the respiratory muscles due to blockade of neuromuscular transmission and mucus stagnation.
The main respiratory muscles are:
- diaphragm;
- intercostal muscles;
- intercartilaginous muscles.
Paresis and paralysis of these structures lead to ventilation failure, with the development of hypoxia and acidosis (a shift in the acid-base balance of the blood). This happens because due to the lack of movement in these structures, the acts of inhalation and exhalation cease to occur. Thus, the phenomenon of plegia of the respiratory muscles is noted. Plegia (or paresis) is a state of complete absence of movement. With botulism, plegia is observed in all muscle groups, but the most dangerous is plegia of the respiratory muscles.
Respiratory failure with botulism has its own characteristics. Since it occurs against the background of complete muscle plegia, it is not accompanied by characteristic shortness of breath. Thus, in other pathologies, the main symptom of respiratory failure is severe shortness of breath, which is visually visible when examining the patient, or psychomotor agitation (the feeling of lack of air makes the patient anxious). However, this is not observed with botulism due to muscle paralysis. The only symptom of respiratory failure is an increasing bluish coloration of the skin (cyanosis). Breathing becomes almost unnoticeable. The respiratory rate is constantly increasing and reaches 40 – 50 breaths per minute. Such frequent breathing is explained by the fact that the body is trying to compensate for the access of oxygen. Since shallow breathing does not provide the necessary gas exchange, the body tries to breathe more often. But despite this, due to paralysis of the respiratory muscles, breathing remains ineffective.
Sometimes respiratory failure can develop gradually. But botulism is no less characterized by the phenomenon of acute respiratory failure. Acute respiratory failure can develop as a result of paralysis of the epiglottis. In this case, the access of oxygen to the lungs is completely stopped and cerebral edema develops.
Visible signs of acute respiratory failure are:
- the patient’s skin becomes moist, which is a sign of increasing concentrations of carbon dioxide;
- the color of the skin becomes cyanotic (blue) or purple;
- convulsions may occur.
Pneumonia and purulent tracheobronchitis can also cause death due to botulism. They develop due to stagnation and infection of mucus in the bronchi. The difference between such pneumonia is that the prescription of antibiotics is practically ineffective in this case. Purulent secretions continue to accumulate in the lungs due to the lack of effective breathing movements.
Other symptoms of botulism
The greatest danger is posed by a disease with severe respiratory disorders. Botulinum toxin leads to paresis of the diaphragm and accessory muscles. This is manifested by a feeling of heaviness in the chest, pressing pain, a feeling of lack of air, frequent and shallow breathing. Symptoms progress, and if not treated properly, breathing may stop (apnea).
Dry skin
If botulism is present, signs include dry skin, decreased saliva production, constipation, dysuria, pallor, and bloating. The cause is damage to the parasympathetic nervous system. Impaired muscle metabolism leads to myasthenia gravis. The botulism bacillus and toxin cause cardiac dysfunction.
The following symptoms are possible:
- dyspnea;
- increased blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart;
- skin cyanosis.
Botulinum toxin negatively affects almost all organs. There are 3 degrees of severity of the disease. In mild forms of botulism, the clinical picture is blurred. Slight muscle weakness, visual disturbances and eyelid ptosis are observed. Symptoms persist for 1-3 days. There is no risk to life. Not everyone knows how moderate botulism manifests itself.
These people have specific symptoms, but swallowing is not difficult. The voice does not change. There are no life-threatening movement disorders. The disease lasts 2-3 weeks. In severe forms of botulism, respiratory, motor and circulatory disorders are pronounced. If treatment is not carried out, death is possible within 3-4 days.