The lack of timely diagnosis and proper treatment is the basis on which, without any doubt, complications of appendicitis will arise. Timely medical care and properly selected treatment will stop the development of appendicitis, otherwise the consequences will be severe and sometimes extremely life-threatening. The picture of complications can be very diverse, it all depends on how much time has passed from the onset of inflammation to the diagnosis and the adoption of measures to stop and eliminate the disease.
Appendicitis clinical picture
It is quite difficult to diagnose appendicitis on your own. Particular difficulties arise when identifying inflammation in women, the elderly and young children. The pain that accompanies appendicitis is not immediately localized in a typical place, so the disease is often ignored and confused with other, less dangerous ailments. For example, women may mistake pain for menstrual pain. This often leads to the patient delaying seeing a doctor, which puts him at great risk.
The causes of inflammation of the appendix can be different. Most often, acute appendicitis is caused by blockage of the lumen between the appendix and the cecum, damage to the mucous membrane, and the entry of food particles and fecal stones into the appendix.
Appendicitis: causes and factors provoking development
The absolutely exact causes of the occurrence and development of the inflammatory process in the appendix have not yet been established. There is an opinion that the disease can be triggered by eating sunflower seeds and watermelon with peel, eating grapes with seeds, and poor chewing of food.
In fact, this version is not confirmed by anything or anyone, but doctors and scientists have identified certain factors that can still provoke an inflammatory process in the appendix of the cecum:
- Changes in the immune system that occur for no apparent reason. With this condition, the walls of the appendix become more susceptible to irritation and infection.
- Blockage of the lumen of the appendix of the cecum. The cause of blockage may be:
- formation of fecal stones;
- helminthic infestations;
- tumor diseases (benign and malignant).
- Inflammatory processes in the walls of blood vessels - vasculitis.
- Infectious diseases of a general nature - for example, tuberculosis, typhoid fever.
Please note: no one will ever be able to predict in advance the development of the inflammatory process in the vermiform appendix of the cecum. Even if a person undergoes regular examinations, it is impossible to prevent the development of acute inflammation.
Probable causes of inflammation
There are a number of reasons that can cause appendicitis. The most common is an infectious factor that can cause the development of inflammation in the presence of certain conditions:
- Blockage of the lumen of the appendix, which causes congestion to form inside the organ.
- Disorders of the vascular system, due to which the blood circulation of the appendix is weakened, vascular thrombosis.
- Disturbances leading to increased peristalsis and microcirculation failure.
Fears that poorly chewed food can cause appendicitis are not without merit. One of the reasons for inflammation of the appendix is its blockage with undigested particles (most often seeds), hard fecal formations, and foreign bodies.
It is believed that in the process of evolution the appendix ceased to perform its digestive functions, but still the digestive process affects the condition of the appendix.
The cause of inflammation of the appendix may be an infection of other organs, such as the intestines or respiratory tract. In addition, there are favorable factors for the development of appendicitis, such as immunodeficiency, the presence of an infectious focus in the body, and a tendency to allergic reactions.
The features of the appendix have not been fully studied by specialists, so it is difficult to identify a clear mechanism for the development of inflammation. However, it is important to know what specific causes can cause appendicitis in order to reduce the risk of the disease.
- Inflammation caused by infections.
- Chronic constipation.
- Pathological curvature of the process.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Consumption of meat in large quantities.
- Bad habits, stressful situations.
- Diseases of the abdominal organs.
Making an accurate diagnosis can be quite difficult even in a hospital setting, let alone diagnosing it at home.
Therefore, if you experience pain in the right lower abdomen, you should be wary and consult a doctor, because inflammation of the appendix is always an indication for its removal.
Diagnosis of appendicitis
At the very beginning of diagnosing appendicitis, a thorough interview and examination of the patient is important. In many cases, patients complain of high body temperature, as well as pain of varying intensity when pressing on the right side of the lower abdomen. With the inflammatory process of the peritoneum, other signs of appendicitis appear. So, when pressing on the abdomen, the patient feels the so-called “ricochet” pain. That is, when you press on the stomach, after which the doctor very sharply removes your hand, a sudden, short-lived pain appears.
When making a diagnosis, the specialist must take into account the number of white blood cells. If an infectious process develops in the body, the analysis shows an increased number of white blood cells . At first after the onset of the disease, the number of white blood cells may remain normal, but a slight increase in their number, as a rule, occurs already in the very early stages of the disease. But it is important to take into account that such a sign is characteristic of almost any infectious process that develops in the body. Because of this, a high level of white blood cells in the blood is not considered as direct evidence of appendicitis. During the diagnostic process, a microscopic examination of the patient’s urine is also performed.
coprolite (a hardened piece of feces that blocks the exit from the appendix) as the cause of appendicitis This phenomenon most often occurs in children.
During an ultrasound examination, the presence of an abscess or an enlarged appendix can be detected. But in patients with appendicitis, the appendix can be seen only in half of the cases. In view of this, the inability to examine the appendix during ultrasound does not exclude appendicitis. However, when conducting this study, it becomes possible to exclude pathology of the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, that is, a number of conditions that could simulate appendicitis.
During a computed tomography scan of the appendix area, appendicitis or a periappendiceal abscess can be diagnosed. This excludes a number of diseases inside the abdominal cavity and pelvis, the symptoms of which resemble appendicitis.
Also, to establish the diagnosis of appendicitis, the laparoscopy . This is a surgical procedure that involves inserting a thin tube with a camera into the abdomen through a small hole in the abdominal wall. During this procedure, you can see the appendix and a number of other organs. And if appendicitis is detected, the appendix is immediately removed.
To date, only laparoscopy can accurately diagnose appendicitis. In view of this, if appendicitis is suspected, complex studies are carried out or surgery is performed.
Diagnosing appendicitis in some cases is very difficult. After all, the vermiform appendix in the abdominal cavity can be in different positions. Sometimes it is difficult for a specialist to determine which side the appendicitis is on. Most often, the appendix is located in the lower abdomen on the right. However, it does have a mesentery , a sheet-like membrane that attaches the appendix to other structures in the abdomen. And in the presence of a long mesentery, the vermiform appendix sometimes moves to another place. In this case, the vermiform appendix itself can be long. Therefore, with this combination, the appendix can descend into the pelvic cavity and be located behind the colon. In this case, the symptoms of appendicitis may coincide with the symptoms of inflammation of other organs. Due to these characteristics, a patient with suspected appendicitis is observed for a certain period of time in order to anticipate whether signs of appendicitis or another disease will appear.
In the process of diagnosing appendicitis, it is very important to remember a number of other diseases that have symptoms similar to appendicitis. Thus, it is necessary to differentiate appendicitis from Meckel's diverticulum (protrusion of the intestinal wall, which is located next to the appendix), pelvic inflammation , inflammatory processes in the upper right part of the abdomen , right-sided diverticulitis , kidney disease .
Signs and first symptoms of appendicitis
It is very difficult to accurately diagnose appendicitis at home, but it can be determined by the presence of both general and specific symptoms.
- Almost always the inflammatory process is accompanied by pain. In the case of appendicitis, pain occurs in the central part of the abdomen, in the navel area, which eventually migrates to the lower right part of the abdominal cavity. When coughing, sneezing, or taking a deep breath, the pain intensifies. If you lay the patient on the right side, bending the legs to the chest, the pain will decrease, while turning to the left side will increase the symptom. Such a manipulation will help determine appendicitis at home. The pain syndrome may subside a little, then increase, but if the pain has completely disappeared, this is a very alarming sign. It may indicate a ruptured appendix and blood poisoning. This condition is considered dangerous and leads to death.
- A patient who experiences severe pain due to appendicitis cannot straighten his back. Staying upright becomes an unbearable challenge for him, so he tends to lie on his side (preferably on the right) and tuck his legs in, imitating the fetal position.
- One of the signs of inflammation of the appendix is nausea and vomiting.
- An increase in temperature, as one of the main signs of inflammation, is characteristic of acute appendicitis. If in an adult patient the thermometer mark rises to 37 or 38, then for a small child the thermometer reading can rise to 40 degrees.
- For young patients, bowel movements are common. Often appendicitis is accompanied by diarrhea, which makes it possible to confuse the disease with an upset stomach or poisoning. However, one should be wary of the fact that with appendicitis there is no relief after bowel movement. Urination is accompanied by discomfort.
- White coating on the tongue and dry mouth also indicate inflammation of the appendix.
If several of the above symptoms are present at the same time, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance to avoid peritonitis and other complications. In this case, the victim should not be given any medications. A big risk arises when appendicitis is confused with another disease, trying to eliminate false symptoms with medications.
Diagnostic measures
To diagnose appendicitis, you will need to conduct a number of examinations:
- General examination with identification of syndromes:
- Kochera - intermittent pain from the upper abdomen to the right side;
- Mendel - when tapping the anterior wall of the abdomen, the patient complains of pain in the right iliac region;
- Shchetkin-Blumberg - the right hand is inserted into the right iliac region and then sharply removed - the patient experiences severe pain;
- Sitkovsky - when the patient tries to turn on his left side, the pain syndrome becomes as intense as possible.
- Laboratory research:
- Clinical blood test;
- biochemical blood test;
- coprogram;
- stool test for the presence of occult blood;
- general urine test;
- examination of stool for the presence of worm eggs;
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of the abdominal organs;
- electrocardiogram (ECG).
Please note: interviewing the patient and collecting anamnesis of life and illness is carried out only in the initial stage of development of inflammation in the vermiform appendix of the cecum.
In case of an acute attack, emergency surgery is indicated when the diagnosis is confirmed using the syndromes described above. Detailed information about the causes, signs of acute appendicitis, as well as treatment methods is in the video review:
Accurate diagnosis
Recognizing appendicitis at home is not easy, as symptoms can often indicate other pathologies. But there are some manipulations that allow you to suspect inflammation of the appendix.
- If you ask the patient to stand up straight and take several steps with a straight back and high knees, the pain syndrome will intensify. This indicates an exacerbation of inflammation.
- The patient lies on his back and tries to completely relax. With appendicitis, the stomach will be swollen, the muscles will be tense, and light pressure on the stomach will lead to increased pain.
- If you lightly press on the area near the navel and then suddenly remove your hand, you will experience a sharp pain radiating to the navel. From this we can conclude that appendicitis has worsened.
Inflammation of the appendix can only be accurately determined with the help of a doctor. A number of diagnostic methods are used for this.
- Ultrasound examination is considered the most popular way to determine appendicitis. It can be used to study other internal organs. Ultrasound is considered a safe and inexpensive diagnostic method, but the accuracy of the diagnosis largely depends on the competence of the specialist.
- Medical thermography – examination with a thermal imager. Due to the fact that pathological processes in the body affect the distribution of heat, appendicitis can be diagnosed using this method very simply and with high reliability.
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging methods are often used to determine inflammation of the appendix. MRI is considered a safer method, and it is prescribed to diagnose the disease in children and pregnant women.
- Laparoscopy has the highest accuracy in determining appendicitis. The test involves inserting an optical tube with a small video camera into the abdominal cavity through an incision. Using this method, the doctor can accurately diagnose appendicitis and immediately begin surgery. The disadvantages of this method are that it is actually a surgical intervention and is performed under general anesthesia.
Features of the manifestation of pathology
Painful sensations in the epigastric region are one of the harbingers of purulent appendicitis. Gradually, the pain syndrome changes localization, moving to the area of the right ilium.
As the pathological process progresses, other symptoms join the pain:
- increase in body temperature to febrile values;
- general intoxication of the body;
- diarrhea;
- nausea.
But these symptoms are characteristic of all types of acute appendicitis. Purulent appendicitis can be diagnosed only during diagnostic laparoscopy or when examining the appendix during surgery. In this case, the surgeon may note the following abnormalities:
- the formation of fibrinous layers on the surface of the diseased organ;
- pronounced swelling and friability of the appendix;
- thickening of the walls of the organ and their tension;
- purulent contents in the lumen.
Important! If you do not seek help in a timely manner or if surgical intervention is delayed for a long time, the course of the disease worsens. The patient experiences the development of concomitant complications in the form of further purulent tissue melting or the formation of an appendiceal abscess.
First aid
If you suspect inflammation of the appendix, it is very important to provide the patient with competent pre-medical care.
- As soon as it becomes clear that the patient has worsened appendicitis, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
- Providing peace to the patient is the first thing to do in this situation.
- You cannot resort to self-medication, give the patient medications, or use traditional medicine without a doctor’s prescription, as this will only worsen the situation.
- To relieve pain, you can apply ice to your stomach. Under no circumstances should you use a warm heating pad.
- Until a definitive diagnosis is established, you should refrain from eating and drinking water.
Treatment of acute appendicitis
If symptoms of acute appendicitis appear at the stage of prehospital care, the patient is advised to rest in bed, apply an ice pack to the stomach, and refuse to eat. Applying a heating pad to the stomach is strictly contraindicated, as this may lead to the development of complications of acute appendicitis. You should seek medical help even if the acute pain subsides spontaneously. Before diagnosis, the patient should not take painkillers, antispasmodics or any other medications, as this may complicate the diagnosis of the disease.
After a diagnosis of acute appendicitis is made, an urgent surgical intervention is performed - appendectomy (removal of the appendix). Surgical treatment of acute appendicitis can be performed using an open (laparotomy) or closed (laparoscopy) method. In uncomplicated cases of the disease, laparoscopic appendectomy is usually used. A laparoscope is inserted through a small hole in the abdominal wall; to provide surgical space, the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide (pneumoperitoneum), after which the appendix is removed under visual control (the laparoscope is equipped with a cold light source and a microcamera that transmits a scaled image of the surgical field to a monitor in the operating room). This method allows you to avoid unnecessary trauma and blood loss; the advantages of laparoscopic appendectomy also include a reduction in the postoperative period and a good cosmetic effect.
In acute appendicitis, surgery is indicated - appendectomy
In the event of complications of general appendicitis, in particular diffuse peritonitis, a laparotomy is performed with a thorough examination of the abdominal organs. In this case, the Volkovich-Dyakonov approach to the appendix is usually used (an incision in the right iliac fossa is made parallel to the inguinal ligament).
Postoperative complications develop in 5–10% of patients with acute appendicitis, mortality is 0.1–0.3%.
For catarrhal acute appendicitis, antibiotic therapy is not required. Antibacterial drugs are prescribed, as a rule, in the presence of an inflammatory effusion in the pelvis, as well as in the phlegmonous form of the disease. When acute appendicitis is complicated by diffuse peritonitis, antibiotics are used at the stage of preoperative preparation and in the postoperative period.
Treatment
For acute appendicitis, there is only one treatment option - surgery to remove the inflamed appendix. There are no other ways. It is impossible to refuse the operation, since the inflamed appendix can rupture, and this can be fatal. This is a simple operation, after which recovery occurs quite quickly.
The doctor prescribes a diet in which you need to eat often, but in small portions.
Treatment of chronic appendicitis with mild symptoms can be done conservatively. In this case, antispasmodics, physiotherapeutic procedures, and preventive medications for intestinal disorders are prescribed. This suggests that modern medicine tends to use surgical treatment only as a last resort, since a healthy appendix is not a useless organ, as was previously thought.
Classification of appendicitis
The forms are divided into acute appendicitis and chronic appendicitis. In the first case, the symptoms will be pronounced, the patient’s condition is very serious, and emergency medical care is required. Chronic appendicitis is a condition after suffering an acute inflammatory process with no symptoms.
Doctors distinguish three types of the disease in question:
- catarrhal appendicitis - penetration of leukocytes into the mucous membrane of the appendix occurs;
- phlegmonous - leukocytes are found not only in the mucous membrane, but also in the deeper layers of the tissue of the appendix;
- gangrenous - the wall of the appendix affected by leukocytes becomes dead, inflammation of the peritoneum develops (peritonitis);
- perforated - the walls of the inflamed appendix rupture.
Doctors' opinion
Doctors consider appendicitis a dangerous disease only if the patient did not seek the help of specialists in time and tried to deal with the problem on his own at home. This is strictly prohibited. Even a doctor using special diagnostic devices cannot always accurately determine inflammation of the appendix.
It is better to immediately call an ambulance if similar symptoms occur, because ignoring the problem and self-medicating can cost the patient his life.
Preventive actions
There is no specific prevention of appendicitis, but to reduce the risk of developing an inflammatory process in the appendix of the cecum, you can adhere to the following recommendations:
- Correction of diet. This concept includes limiting the consumption of greens, hard vegetables and fruits, seeds, smoked and too fatty foods.
- Timely treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases - there have been cases when inflammation of the appendix of the cecum began due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms from diseased tonsils (with decompensated tonsillitis).
- Detection and treatment of helminthic infestations.
Appendicitis is considered not a dangerous disease - even the probability of complications after surgery does not exceed 5% of the total number of operations performed. But such a statement is appropriate only if medical care was provided to the patient in a timely manner and at a professional level.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category.
14, total, today
( 62 votes, average: 4.55 out of 5)
Autoimmune pancreatitis: why it occurs, how to treat it
Stomach pain: causes, characteristics, treatment
Related Posts
Results
Appendicitis is considered a very common surgical disease, and operations to remove the appendix are not particularly difficult. Ignoring symptoms and self-medication can lead to dangerous complications. It is very important to seek medical help in time to avoid consequences that can be fatal.
See
Prevention of complications of acute appendicitis Why the scar from appendicitis hurts On what day are sutures removed after appendicitis Is it possible to eat seeds after removal of appendicitis
Postoperative period and diet after appendicitis
After surgery to remove appendicitis, the recovery period involves following diet No. 5.
It includes:
- soups with vegetable broth;
- compotes;
- lean boiled beef;
- fruits (non-acidic and soft);
- legumes;
- crumbly porridge.
Lard, baked goods, fatty meat and fish, black coffee, chocolate, hot spices and sauces, milk and fermented milk products are excluded from the diet.
Please note: in the first 2 days after surgery, the diet can only include chicken broths, still water with lemon, and weak tea. From day 3 you can gradually introduce permitted foods. You can return to the normal menu only 10 days after removal of the inflamed appendix of the cecum. To maintain immunity in the postoperative period, you need to take vitamin complexes, as well as preparations containing iron and folic acid.
A surgeon talks about proper nutrition after appendicitis removal:
Appendicitis in pregnant women
Appendicitis in pregnant women is a common occurrence that occurs during the second trimester of embryonic development. Pain during the pathological process of the patient is confused with the characteristic pain syndrome from constipation or fetal movements. Against the background of the inflammatory process, a woman’s heart rate increases, shortness of breath appears, and her temperature increases. Nausea and vomiting in this case are not specific signs of damage to the rectal appendage, because they may be signs of toxicosis.
The severity and localization of pain depend on the force of pressure of the uterus on the inflamed appendix. The longer the pregnancy, the more the uterine endometrium begins to put pressure on the appendix. As a result, the appendage of the cecum begins to rise upward, changing the location of the pain.
This increases the risk of premature birth, intestinal failure, placental abruption and peritonitis. Therefore, if appendicitis is suspected, a woman should immediately consult a doctor in order to protect her life and ensure the normal embryonic development of the unborn child.
Pylephlebitis
Pylephlebitis is an acute inflammation followed by suppuration of the portal vein, which leads to severe intoxication of the body. The prognosis of treatment leaves much to be desired, since in 9 out of 10 cases death occurs due to sepsis of all organs and tissues. The disease can be lightning fast, in which case death occurs within a few hours, or it can be protracted, in which case the person suffers for a month.
Causes
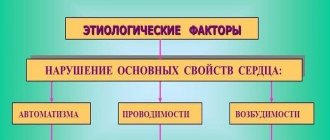
Why does this disease appear? The causes can be divided into 4 groups: mechanical, infectious, vascular and endocrine.
In most cases, purulent appendicitis occurs when the lumen of the cecum is blocked by fecal stones, a tumor, parasites, lymphatic follicles or a foreign body. As a result, blood circulation worsens, pathogenic microflora multiplies and inflammation intensifies.
Against the background of these processes, tissue death occurs, followed by perforation of the walls of the appendix. This etiology of the origin of appendicitis corresponds to the mechanical theory. The reasons are as follows:
- structural features of the appendicular process;
- formation of fecal stones in the intestines;
- tumors;
- lack of high-fiber foods in the diet, insufficient fluid intake;
- entry of a foreign object into the cecum;
- formation of lymphoid follicles;
- action of parasites.
According to the infectious theory of the occurrence of the appendix, the causes may be tuberculosis, typhoid fever, amoebiasis and others.
Vascular and endocrine theories are rarely taken into account. According to the first, the cause of the appendix may be vasculitis, the second considers the appendix as the place where the inflammatory hormone is produced.
Most often, purulent appendicitis occurs in patients aged 20 to 45 years.
Appendicitis in a child
The most difficult task for a doctor is to determine appendicitis in a small child. If children constantly cry and complain of persistent pain, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Up to 2 years of age, the pathological process develops extremely rarely, which is due to the digestive system being unprepared for complete digestion.
Therefore, in 90% of cases, teenagers are admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of acute inflammation of the appendix.
The clinical picture in children over 7 years of age coincides with the classic manifestations of appendicitis in adult patients. The difficulty in determining pathology arises due to the immature psychological state of the child. He may be capricious and cry from fatigue, and not from pain. Children cannot tell exactly how the pain manifests itself and where it is strongest. Therefore, doctors have identified several distinctive symptoms that are characteristic of a child with inflammation of intestinal atavism:
- when he squats, he holds his stomach;
- curls up in a fetal position and does not allow touching or changing body position;
- after the pain appears, the child will periodically wake up;
- in children, body temperature can rise to +40°C;
- the pain intensifies when bending to the right side and in the process of changing clothes;
- constant nausea and uncontrolled vomiting.
After the first day from the onset of inflammation, the child’s condition worsens sharply. Lethargy develops, there is no appetite and strength for physical activity. When the stomach is touched, children begin to scream and cry.
When visiting the hospital, you should remember that the consequences of surgery greatly affect the child’s body. Therefore, it is important to prevent the development of appendicitis and know in advance for what reasons pathology may appear in childhood:
- Weak immunity. Frequent colds and viral diseases of the respiratory system, flu, infections can lead to depletion of the immune system. The condition can be aggravated by taking antibiotics, which are necessary in the fight against pathogenic microorganisms.
- Parasites and ingestion of foreign objects. Children can eat the seeds with the husk, eat orange peels, or eat the berries with the bone. Indigestible debris can lead to a blockage of the appendix.
- Obesity, frequent overeating and excess protein in the diet.
The appearance of symptoms characteristic of appendicitis cannot be ignored. To exclude the disease, you need to seek medical help.
Treatment in hospital
Having diagnosed the pathology, the surgeon prescribes intracavitary surgery.
Treatment is carried out using two methods:
- A standard appendectomy is amputation of the appendix through an incision in the abdominal cavity. Carried out in 85% of all established cases.
- The laparoscopic method is less traumatic, consisting in removing the damaged area through 3-4 incisions of 4-7 cm in diameter. This is done using a computer monitor. Does not injure the abdominal cavity. Not allowed for peritonitis.
Progress of the procedure:
- The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Before administering drugs to the patient, possible risks and complications are explained, and written consent for surgical intervention is taken.
- The abdominal cavity is toileted, treated with an antiseptic, and the perineum is shaved.
- The surgeon cuts the peritoneum. The appendix is removed and drainage is placed. In case of peritonitis, the pus is removed, the internal organs are washed, and a tube is inserted to drain the ichor and purulent discharge.
- The incision is sutured. In most cases, a cosmetic suture is installed, no more than 10 cm in size.
- The entire process for uncomplicated pathology takes 30-60 minutes. After the operation, the patient is transferred to intensive care until she awakens from anesthesia. If you feel well, after 12 hours you are transferred to a regular ward.
- Antibiotics are prescribed to prevent inflammation and infection. Body temperature is measured 2 times a day. At the end of 1 day, the doctor may prescribe a cleansing enema. Medical personnel treat the wound daily.
- On the 2nd day the woman is forced to stand up. From 3 – you should start walking slowly.
- In the normal course of the postoperative process, the patient spends no more than 7-8 days in the hospital; on the 10th day the stitches are removed.
In pregnant women, surgical treatment is best performed laparoscopically under general anesthesia. For anesthesia, drugs that are harmless to the fetus are selected. In the postoperative period, gentle antibacterial therapy is carried out.
Until the end of the 9-month period, after discharge from the hospital, the patient is under the supervision of a gynecologist due to the risk of premature birth. When an appendectomy is performed in the 3rd trimester, the woman is admitted to the hospital before the onset of labor.
How many days is sick leave given after appendicitis?
The period for which sick leave can be issued directly depends on the legislation of the country in which it was issued, the characteristics of the surgical intervention, the presence or absence of complications, as well as the general condition of the body.
In some cases, primarily with laparoscopic removal, without abdominal surgery, a certificate of incapacity for work may be issued for three days. In the absence of complications, the patient’s good condition and his desire, sick leave can be so short.
In the case of uncomplicated appendicitis and laparoscopic surgery (also without complications), sick leave can be issued for a period of five to ten days - with this type of intervention, trauma is minimal and recovery is as fast as possible.
Complicated variants such as purulent, phlegmonous, gangrenous appendicitis require full abdominal surgery, and the period of disability in such a case can reach up to thirty days.
If there are complications or the patient’s serious condition persists, the duration of sick leave can be extended to more than thirty days by a medical commission.
Complications of appendectomy
The most common complication in this case is infection of the surgical wound. A mild complication may occur - redness, soreness. However, very severe lesions also occur, in which the use of surgical treatment is mandatory. In some severe cases, the surgeon may not close the incision completely after surgery. This occurs with very severe inflammation and infection, when the incision becomes dirty immediately after making it. It will be stitched up in a few days.
Also, an abscess in the area of the appendix becomes of appendectomy After surgery, the development of adhesions may also occur.
Until today, there is no exact information about the functions of the appendix. But after its removal, a person generally does not experience health problems.
Diet
You are allowed to drink water for the first time after surgery.
Dietary nutrition is an important part of the treatment of appendicitis and the recovery period after surgery.
At first, you are only allowed to drink water and weak tea. The dietary menu should take into account the patient's preferences. The patient can eat liquid porridges, broths and soups, fish dishes and thermally processed vegetables, cottage cheese and butter. You can eat liquid food after 3 days.
It is forbidden to eat salty, sour, fatty, fried and peppered foods. Meals should be fractional, you need to eat in small portions many times a day. If a patient has complicated appendicitis, he must adhere to a strict diet (vegetable soups and cereal porridges) for several months. Drinking coffee and soda is prohibited.
Nutrition for appendicitis should be developed by the attending physician.
The temperature of the food consumed should be average. Eating cold or hot food is prohibited.
Possible complications
The most dangerous consequence of purulent abscessed appendicitis is peritonitis. It can form when the appendix ruptures, the presence of which passes into the peritoneum. Signs of peritonitis may be: severe abdominal pain, increased temperature, vomiting, stool upset, renal colic, tachycardia, difficulty urinating.
In addition, purulent inflammation is dangerous due to the following complications:
- pleurisy, pylephlebitis;
- the appearance of adhesions, intestinal obstruction;
- abscesses;
- pneumonia, endometritis;
- liver inflammation, sepsis disease;
- septic thrombophlebitis;
- fistula formation.
After surgery, the wound may become inflamed and the stitches may come apart.
Already a day after the onset of the pathology, dangerous complications that threaten a person’s life can appear.
Diagnostics in the hospital
After delivering the patient, doctors will need a urine and blood test. As a rule, tests are taken in the hospital to rule out other potential diseases that cause similar symptoms.
The condition of the abdominal area is checked using an ultrasound. Carrying out ultrasound analysis makes it possible to accurately determine the occurrence of inflammatory processes inside the human body. With the help of the examination, the location of the organ is determined.
If the previous examination did not make it possible to diagnose the disease, it is not possible to make a clinical diagnosis, an additional study is carried out using a CT scanner. Difficulty arises when the patient is overweight. The presence of a large amount of fat makes it impossible to see on an ultrasound the exact picture of what is happening in the abdomen.
Symptoms of a ruptured appendix
Sooner or later, purulent appendicitis necessarily bursts, after which there is an outpouring of pus into the abdominal cavity. This condition cannot be missed, as it is accompanied by severe, sharp pain.
A ruptured appendix is accompanied by:
- pains throughout the entire abdominal area, which are subsequently localized in the right and its parts;
- rapid increase in body temperature;
- the patient experiences general symptoms of intoxication (nausea, vomiting, weakness, loss of sleep and appetite);
- the patient may experience tachycardia, dizziness, or even loss of consciousness.
After quickly carrying out all diagnostic procedures, the victim is sent for surgery. In any case, such a complication of appendicitis as its rupture does not pass without leaving a trace on the body. However, the quality of medical care can minimize all further problems.
Purulent peritonitis after a ruptured appendix is the most common complication. Intoxication of the body due to the release of pus into the abdominal cavity occurs rapidly; several stages of this disease are distinguished.
- Immediately after the appendix ruptures and pus comes out, all adjacent tissues are irritated. The pain becomes constant, spreading to all parts of the abdomen. A person is worried about bloating, nausea, and may experience uncontrollable vomiting.
- In the second stage, the patient's condition begins to improve. This occurs due to atrophy of the nerve endings, which are affected by pus. The victim may feel almost healthy, the pain goes away completely, and he is no longer bothered by bloating. The only thing is that sticky sweat may appear on the skin, increased heart rate and intestinal obstruction are observed.
- The third stage is characterized by a rapid increase in symptoms of intoxication. There are all the signs of purulent peritonitis and various dyspeptic disorders. The body temperature rises to high levels, the pain is not sharp, but constant. A person is worried about gas formation and severe bloating.
- The fourth stage, also called terminal, often leads to death. It is characterized by uncontrollable vomiting, complete intestinal obstruction and severe signs of intoxication. Vital organs (such as the liver, heart, kidneys and pulmonary system) begin to suffer. Often at this stage there is no help for the patient.
In any case, peritonitis is easier to prevent than to treat it later. This is why it is so important to seek help from doctors in a timely manner. However, not a single stage of this disease passes without a trace for the body.
Complications due to peritonitis
In addition to death, which is quite rare with modern medicine, peritonitis can become a catalyst for the development of other unpleasant diseases that are also dangerous in terms of mortality.
Patients with this disease are diagnosed with:
- purulent-septic lesions of nearby organs;
- various abscesses;
- gangrene;
- renal and liver failure.
To prevent such troubles, it is necessary to remember that you need to be attentive to the body, especially if you have a complicated medical history. Only high-quality treatment of appendicitis can prevent necrosis of appendix tissue.
Preoperative pathologies
Preoperative complications of acute appendicitis include:
- peritonitis;
- perforation;
- pylephlebitis;
- appendicular abscesses;
- appendicular infiltrate.
In destructive forms of the disease, perforation usually occurs 2-3 days after the onset of the disease. When an organ ruptures, the pain suddenly intensifies, severe peritoneal symptoms, clinical manifestations of local peritonitis occur, and leukocytosis increases.
If in the early stages the pain syndrome was not very pronounced, then perforation is perceived by patients as the beginning of the disease. The mortality rate for perforation reaches 9%. Rupture of appendicitis occurs in 2.7% of patients who applied in the early stages of the pathology and in 6.3% of patients who saw a doctor in the later stages.
In acute appendicitis, complications develop due to the destruction of the appendix and the spread of pus
Peritonitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the peritoneum, which is accompanied by local or general symptoms of the disease. Secondary peritonitis occurs when bacterial microflora penetrates from the inflamed organ into the abdominal cavity.
The clinic distinguishes 3 stages:
Removal of appendicitis using laparoscopic method
- reactive (pain, nausea, gas and stool retention, abdominal wall tension, body temperature rises);
- toxic (shortness of breath, coffee vomiting appears, the general condition worsens, the abdomen is swollen, the abdominal wall is tense, intestinal motility disappears, gas and stool are retained);
- terminal (with treatment by the 3-6th day of the disease, the inflammatory process can be limited and the intoxication syndrome can be reduced, due to which the patient’s condition improves. In the absence of therapy, an imaginary improvement occurs on the 4-5th day, abdominal pain decreases, the eyes become sunken, vomiting of greenish or brown liquid continues, breathing is shallow. Death usually occurs within 4-7 days.).
When treating peritonitis, it is necessary to eliminate the source of infection, perform sanitation of the abdominal cavity, drainage, and adequate antibacterial, detoxification and infusion therapy. Appendiceal infiltrate is called internal organs (omentum, intestines) that have grown together around the appendix and are changed by inflammation. According to various statistics, pathology occurs in 0.3-4.6 to 12.5 cases.
Rarely are such changes detected in the initial stages of the disease; sometimes they are discovered only during surgery. A complication develops on the 3-4th day of illness, sometimes after perforation. It is distinguished by the presence in the iliac region of a dense formation similar to a tumor, which is moderately painful when palpated.
Peritoneal symptoms subside, since the pathological process is limited, the abdomen becomes soft, and this makes it possible to palpate the infiltrate. The patient's body temperature is usually subfebrile, leukocytosis and stool retention are noted. If the location of the process is uncharacteristic, the infiltrate is palpated in the place where it is located; if it is located low, then it can be felt through the rectum or vagina.
An ultrasound examination can confirm the diagnosis. In difficult cases, a diagnostic operation (laparoscopy) is performed.
The presence of infiltrate is the only circumstance under which surgery is not performed. Surgical intervention cannot be performed until the infiltrate has abscessed, since there is a high risk that when trying to separate the appendix from the conglomerate, the fused organs (mesentery, intestines, omentum) will be damaged, and this can lead to serious consequences.
Therapy for infiltration is conservative and carried out in a hospital setting. Cold on the abdomen, a course of antibiotics, bilateral perinephric blockade, taking enzymes, diet therapy and other measures that help reduce inflammation are indicated. The infiltrate resolves in the vast majority of cases, usually within 7-19 or 45 days.
If the infiltrate does not disappear, then a tumor is suspected. Before discharge, the patient must undergo irrigoscopy to exclude a tumor process in the cecum. If the infiltrate was detected only on the operating table, then the appendage is not removed. Drainage is done and antibiotics are injected into the abdominal cavity.
Pylephlebitis is thrombosis of the portal vein with inflammation of its wall and the formation of a blood clot that closes the lumen of the vessel. The complication develops as a result of the spread of the pathological process from the mesenteric veins of the appendix through the mesenteric veins. The complication is extremely severe and usually ends in death after a few days.
It leads to high temperature with large daily fluctuations (3-4 C), cyanosis and jaundice appear. The patient has severe acute pain throughout the abdomen. Multiple liver abscesses develop. Treatment involves taking anticoagulants, broad-spectrum antibiotics, which are administered through the umbilical vein or spleen.
Appendiceal abscesses appear in the late period, before surgery, mainly as a consequence of suppuration of the infiltrate, and after surgery as a result of peritonitis. Complications appear 8-12 days after the onset of the disease. By location they are distinguished:
- ileocecal (paraappendicular) abscess;
- pelvic abscess;
- subhepatic abscess;
- subphrenic abscess;
- interintestinal abscess.
Diagnostics
There are no difficulties in making a diagnosis; palpation and observation of the patient for 2-3 hours is sufficient. Among laboratory tests, only a general blood and urine test is informative. An increased number of leukocytes and protein indicates an inflammatory process.
Women are examined by a gynecologist to identify gynecological pathologies.
To differentiate purulent appendicitis from other diseases, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Ultrasound;
- radiograph;
- ECG.
In some cases, laparoscopy cannot be avoided.
Purulent appendicitis is differentiated from renal colic, pyelonephritis, cholecystitis, pleurisy, pneumonia, Meckel's diverticulum, diseases of the small and large intestines, as well as ectopic pregnancy, pathologies of the right ovary.