Infertility is a violation of the reproductive function of the body associated with the inability to reproduce offspring.
According to WHO, the frequency of infertile marriages in the world ranges from 8 to 17% and does not tend to decrease.
If the frequency of infertility exceeds the threshold of 15%, this becomes not only a medical, but also a socio-demographic problem.
It is customary to talk about infertility if, with active sexual life of partners without the use of contraceptives, natural conception does not occur within a year.
The cause of an infertile marriage can be female, male infertility, common factors, as well as incompatibility of partners.
The female factor accounts for 45% of infertility cases, the male factor accounts for 40%, and common factors are present in 15%.
What is infertility?
Infertility is a pathological condition that develops as a result of the inability to develop pregnancy in a couple subject to regular sexual activity without the use of barrier methods.
In this case, it should be taken into account that such a diagnosis is established if pregnancy does not develop for a year or more.
A shorter period of time is not legitimately taken into account for such a diagnosis, unless a thorough examination of the couple has been carried out and the impossibility of independent fertilization of one of the spouses or the reasons why pregnancy will not occur in this couple have been identified.
Details about inability to conceive
Infertility in women can be diagnosed at a very young age. When a girl visits a gynecologist and undergoes a series of tests, the doctor may notice an anatomical feature of the genital and reproductive organs, in which pregnancy will never occur. Some congenital pathologies of internal organs are amenable to surgical treatment. However, the absence of one or two ovaries, fallopian tubes or the baby's place itself are signs of infertility in women. When medical personnel establish a diagnosis after an examination, two types of pathology are distinguished:
- Primary. When a woman cannot have children and has never become pregnant in her life. If at any age a girl’s egg was fertilized and moved through the tubes to the uterus, then she will not be diagnosed with infertility, but will be prescribed treatment that will help her get pregnant and preserve the embryo.
- Secondary. In this case, signs of infertility are considered when a woman already has one or more children, but she is unable to become pregnant again. The cause of the pathology can be trauma, surgery to remove the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Statistics
Unfortunately, according to medical statistics, one in ten married couples suffers from the inability to have children. Moreover, in 45% of cases, the causes are diagnosed in men. They manifest themselves in sperm inactivity, impotence or impaired sperm output. In the remaining 55% of cases, signs of infertility are diagnosed in girls. If the desired pregnancy does not occur, both partners must be examined at a family planning center.
In addition to the anatomical and physical characteristics of sexual partners, the reasons may be psychological and emotional disorders in a married couple. In order to establish a final diagnosis and prescribe treatment, it is necessary to find out why a woman has infertility and its causes.
Main reasons
There are many reasons for infertility.
In the primary process, this is most often:
- Hereditary disorders.
- Hormonal imbalances manifested by an irregular menstrual cycle.
- Also in this case, organic pathologies associated with developmental defects of both external and internal genital organs should be excluded.
- With the development of secondary infertility, this is predominantly a process of chronic inflammation.
Physiological disorders
The second type of deviation occurs in various diseases of the female reproductive system. Each of the disorders has its own underlying causes and symptomatic signs.
Abnormalities in the fallopian tubes
Complete or partial obstruction of the fallopian tubes interferes with normal fertilization. In a healthy woman, the egg unites with the male reproductive cells in them, after the first one leaves the body of the ovary. Fallopian tube damage is often the result of:
- inflammatory processes in their body;
- existing viral and bacterial diseases;
- diseases transmitted through sexual contact;
- complications after surgical procedures;
- with formed adhesions and tissue scars.
Endometriosis
The inner lining of the uterine body is lined with endometrium; as abnormalities develop, the mucous membrane begins to grow inside and outside the reproductive tract. The main causes of endometriosis are considered to be genetic abnormalities in the body.
Excess tissue can block the exits of the fallopian tubes, causing ovulation problems and subsequent infertility. The disease is recognized by its symptomatic manifestations:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- increased amount of discharge;
- pain during menstruation.
Benign neoplasms
An increase in the quantitative indicators of estrogen can lead to the appearance of fibroids in the uterine body. The benign type of tumor consists of muscle tissue and manifests itself with existing abnormalities:
- hereditary predisposition - if there are cases of fibroids in the uterine body in the family, there is a high percentage of occurrence in subsequent generations;
- various deviations in normal metabolism;
- constant stress, psycho-emotional stress;
- medical and criminal abortions.
Presumable symptoms of its appearance:
- excessively heavy menstruation;
- menstrual irregularities;
- painful sensations during menstruation.
In complex cases, it can cause childlessness, spontaneous abortions, or complicated conditions during pregnancy that threaten the life of the fetus.
Uterine abnormalities
After inflammatory processes, trauma and endometriosis, adhesive processes occur in the body of the uterus, changing and merging the walls of the organ. The pathological structure of the uterus is caused by disorders of intrauterine development of genetic etiology:
- uterine infantilism - underdevelopment of the female organ, which remains the size of a child;
- the presence of an additional partition that is not present in normal development;
- unicornuate or bicornuate uterus.
With existing pathologies, any pregnancy ends in spontaneous abortion in the early stages. The fertilized egg cannot attach to the wall of the organ, which causes abortion.
Changes in the cervix
After surgery or against the background of infectious processes, after healing, various adhesions and scars form on the cervix. Artificial narrowing interferes with the normal passage of male reproductive cells into the fallopian tubes, causing infertility. Congenital or acquired deformation of the organ, various deviations in the composition of the cervical mucous secretion complicate the process of penetration of sperm into the body of the uterus.
Inflammatory processes in the pelvis
They occur when pathogenic microflora penetrates the organs of the reproductive system. A significant number are diseases transmitted through sexual contact and provoked by:
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasma;
- gonococci;
- Trichomonas, etc.
The risk of infection increases if the rules of safe contact are violated - intercourse without using condoms, frequent change of sexual partners. Pathogenic microorganisms may also appear:
- during intrauterine operations, in violation of the rules of septic and antiseptic;
- during menstruation – insufficient hygiene;
- in the postpartum period.
Infectious processes cause various diseases:
- salpingoophoritis - a process of inflammation in the ovaries and fallopian tubes;
- endormetritis - an inflammatory process in the uterus;
- cervicitis – inflammation of the cervix.
Symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- non-standard discharge;
- untimely menstruation;
- feeling of constant itching;
- pain in the genital area.
During a gynecological examination, specialists record the formation of spots and ulcerations on the mucous membranes.
Types of infertility in women
Primary and secondary
- Primary infertility is a type in which a woman does not become pregnant at all. In this case, it should be taken into account that pregnancies should include not only cases of the birth of a child, but also all cases in which conception occurred, but pregnancy did not develop until the moment of birth.
- Secondary infertility is a pathological condition in which pregnancy does not occur for a year or more, but before that the woman had a history of egg fertilization. These cases do not always end in childbirth; these are miscarriages, frozen and ectopic pregnancies.
Absolute and relative
You should also distinguish between absolute and relative infertility:
- In the first case, pregnancy cannot occur. These are genetic pathologies, organ underdevelopment, etc. In this situation, treatment will be futile.
- While in the case of relative, various treatment methods can be undertaken. Usually this is the prescription of hormonal drugs, anti-inflammatory therapy, as well as surgical methods.
Immunological
Immunological. This is one of the most severe and difficult to eliminate types of inability to get pregnant.
It can occur in both men and women. Among female representatives, this problem occurs much more often. This type is formed due to a disorder in the immune system in which specific antibodies are produced that prevent fertilization.
This substance is called antisperm. It can be contained in various biological fluids, not only in sperm and vaginal secretions, but also in blood serum and the vas deferens.
With the development of new research methods, it has been proven that this problem occurs in more than a fifth of all couples. But not everyone is considered infertile.
It all depends on the concentration of antibodies, and they can act on any stages necessary for fertilization:
- First of all, on the part of the male body, they violate the integrity, structure and functionality of sperm.
- Having already penetrated the female body, antibodies can attach to them against the background of their good quality and make it difficult for sperm to penetrate through the secretion of cervical mucus, as well as disrupt the processes of catapultation into the egg and prevent the process of fertilization.
Even with the development of the fertilization process, the further development of pregnancy is disrupted, so difficulties arise with the implantation of the embryo to the uterine wall and the formation of a full-fledged fetal membrane.
The quality of the formed embryo is much lower in the presence of antisperm antibodies in the body, its viability is reduced. Any provoking pathological factor provokes the development of spontaneous miscarriage. This type is formed due to disturbances in immune response processes.
The protective functions of sperm are disrupted and they lose their ability to mimic. Any organism, especially a woman’s, begins to perceive it as a foreign substance that gets inside and forms pathogenicity factors. The formation of suppressive bodies and a smaller number of helpers occurs.
Sperm begin to come into direct contact with substances that are part of the immune system. In order for the male body to produce substances against its own cells, exposure to an unfavorable factor is necessary.
These can be traumatic effects, surgical interventions, inflammation, infectious processes caused by both specific and nonspecific pathogens, various anomalies in the structure of the organ of the reproductive system, as well as a malignant process.
Tubal infertility
Tubal infertility. This is one of the options for the impossibility of pregnancy associated with the development of the inability of sperm to penetrate the egg.
At the same time, about half of all women who are diagnosed with the impossibility of fertilization suffer from this problem. It can be both primary and secondary. Most often this is secondary infertility in mature women.
Occurs due to many reasons:
- The main one is inflammation caused by specific pathogens, such as Trichomonas, chlamydia, gonococci.
- It can also be hormonal dysfunction, a local increase in smooth muscle tone, as well as anatomical defects that create an obstacle to passage. Mostly, an adhesive process is detected, creating obliteration of the passage of the fallopian tube. This problem is quite easy to diagnose and there are many methods to eliminate it.
Currently, the most popular and effective way to make a diagnosis is hysterosalpingography, in which a contrast agent is injected through the uterine cavity and its passage through the fallopian tubes is checked.
In some cases, the process can only be one-sided, most often this is associated with pelvic masses, as well as previous operations on the fallopian tubes (for example, ectopic pregnancy).
Treatment is predominantly surgical; if the cause is identified as an infection, then anti-inflammatory treatment is also prescribed.
Royal
Uterine type of infertility. This is another type of infertility that is caused by pathology of the main reproductive organ of a woman.
It is the uterus that plays one of the main roles in childbirth; it is the receptacle for the fruit. In this case, fertilization may occur, but the implantation process does not occur.
Most often these are anatomical defects in the cavity . This is a less common type, occurring mainly in women as a variant of the primary one.
Young women deal with this problem; in most cases, this problem can be associated with other pathologies of the reproductive sphere:
- First of all, these are birth defects such as impaired organ development, these include bicornuate and saddle-shaped uteruses, hypoplasia, duplication, etc.
- These are also pathological formations in the cavity , for example, synechiae and intrauterine septa; polyps can also occur that occupy all the free space.
- Sometimes implantation processes are disrupted by myomatous nodes , which grow into the cavity or deform the organ. They are not always large; sometimes they are quite small in size, which will disrupt the process of implantation into the mucous membrane. This problem is predominantly faced by women with secondary infertility, in whom myomatous nodes are formed after a previous intrauterine intervention.
Endocrine
Endocrine infertility. This is one of the most difficult to treat types of infertility, which is formed due to disruption of the glands, mainly internal secretion.
Causes:
- In this case, there is almost always a disorder of the menstrual cycle, in which not only inadequate preparation of the mucous membrane for implantation occurs, but also a disruption in the maturation of the egg.
- The most dangerous case of this type is hermaphroditism , in which the glands and genital organs are formed incorrectly relative to the sex in which the external genitalia were formed.
- This group also includes insufficient functioning of the ovaries , with the lack of formation of maturation of follicles and eggs, as well as the production of estrogens.
- Infertility does not always develop due to dysfunction of the gonads; it can also be changes in the production of hormones by the thyroid gland, hypothalamus, pituitary gland and adrenal glands. The functioning of the thyroid gland is often assessed, especially paying attention to insufficient activity.
- In some cases, it is necessary to look for hormonally active tumors in the body , which can change the endocrine background of a woman.
- This group also includes metabolic diseases , such as diabetes.
Polycystic
Polycystic. This condition is multifactorial and reflects pathology on the part of the ovaries. In this case, most often this is a manifestation of a genetic defect.
It occurs in no more than a fifth of all women who turn to reproductive specialists or gynecologists with problems of not getting pregnant.
Polycystic disease is usually considered an endocrine cause of infertility. The pathology is characterized by an increased content of androgens, which are male sex hormones, in the bloodstream, as well as changes in the regularity
menstrual cycle, lack of egg maturation and, consequently, ovulatory processes. Other metabolic changes also appear.
There are several types of ovarian changes:
- The first one is central. It is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the female genital organs associated with hypothalamic-pituitary malfunctions, as well as tumor processes, accompanied by increased hormonal activity.
- Ovarian. Violation directly at the ovarian level.
- Mixed. Associated with impaired functioning of both the ovaries and adrenal glands. Currently, this problem is regarded as a congenital genetic defect in which there is a change in the production of estrogen and testosterone. In women, this problem is expressed not only by disruption of the process of egg maturation due to changes in the menstrual cycle, but also by skin manifestations and metabolic changes. The woman notices pronounced androgenization, manifested by increased hair formation, seborrhea, increased activity of the sebaceous glands and acanthus of the skin. Also, women who have this problem face the problem of excess weight. Adipose tissue is concentrated mainly in the abdominal area. Such symptoms are most often associated with insulin resistance.
Endometriosis
This is a common pathology, which is accompanied by the release of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity - the endometrium - beyond its anatomical boundaries.
Normally, this layer is also called functional, since it changes depending on hormonal levels and is exfoliated during menstruation.
In addition, it is the site where implantation of the fertilized egg occurs during pregnancy.
With endometriosis, tissue spreads not only to the area of the uterus, but also to any other organ of both the reproductive system and those located in the abdominal cavity. As a result of serious dyshormonal disorders, the formation of an egg does not occur and ovulation does not occur.
As a result of the above factors, the process of pregnancy is impossible. With the development of endometriosis, localized in the body of the uterus, even in the initial stages, fertilization of a mature egg is possible, but due to disturbances in the structure of the organ, the process of implantation of the fertilized egg does not occur.
The cause of the development of endometriosis is still poorly understood. Quite a lot of theories have been put forward, in some cases it is the transfer of menstrual blood with endometrial cells to other areas, or a genetic predisposition.
Genetic
This is the rarest form of this disease.
It manifests itself as a congenital pathology, which can be associated with mutational processes in chromosomes. They can occur equally in both male and female organisms. It is either a disease transmitted by inheritance or a pathology that develops during pregnancy.
This may be the impact of harmful factors that caused mutations, as well as diseases of the mother or father, which led to inferior formation of the egg or sperm.
This type of infertility is incurable. If it is associated with partial underdevelopment of the reproductive system, in some cases it can be corrected. But in cases of gene mutations or the complete absence of some genes, the situation is irreversible.
In cases of severe abnormalities in the genetic apparatus, clinical changes can be seen. But in most cases, infertility is diagnosed after lengthy examinations and exclusion of all possible causes.
Psychological
This type is quite rare and is associated with changes at the mental level.
This problem occurs in women. The age group that is susceptible to it can be completely different; most of the identified cases are young women planning pregnancy for the first time.
It is expressed by disorders that arise at the subconscious level, when a woman preparing to become a mother does not want to realize it, or is not yet ready for this step.
Internal conflicts are formed, as well as unconscious fears associated with the difficulties of motherhood and the subsequent birth of a child.
They arise against the background of complete physical health; after a complete diagnosis of the body, no objective reasons for the formation of infertility are found. But nevertheless, with prolonged exposure to the factor, disruption of the endocrine system can occur.
This picture is reversible; in most cases, working with a professional psychologist is enough.
The most common type of infertility is primary. The reasons leading to its development include endocrine and uterine reasons.
Types of female infertility
There are the following forms of female infertility:
- Primary infertility, when a woman has not had a single pregnancy. The causes are abnormalities in the development of the female genital organs and disorders of the neuroendocrine regulation of the reproductive system.
- Secondary, when there was at least one pregnancy in the past. Factors that cause secondary infertility include spontaneous miscarriages, abortions, adhesions after operations on the pelvic organs or against the background of chronic inflammation of the uterus and fallopian tubes.
- Absolute infertility is when a woman is unable to become pregnant naturally. This, as a rule, occurs with congenital anomalies of the development of the female reproductive system: the absence of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes and other structural elements of the reproductive system.
- Relative infertility, when it is possible to restore reproductive functions.
From a clinical point of view, the greatest importance is attached to the classification of female infertility by pathogenetic factor.
Tubal and peritoneal infertility
Tubal infertility occurs when functional or organic disorders of the patency of the fallopian tubes occur against the background of adhesions in the pelvis or without it.
Changes in the function of the fallopian tubes occur under stress, with hormonal imbalance, when a high concentration of androgens is observed at low estrogen levels.
Previous inflammatory diseases of the genital organs (gonorrhea, chlamydia, tuberculosis), operations on the pelvic organs, endometriosis cause organic damage to the fallopian tubes, which leads to their obstruction.
Peritoneal infertility is associated with an adhesive process that develops in the area of the uterine appendages after surgical interventions on the abdominal organs.
Both of these pathologies are closely related to each other, often have a common etiology, similar developmental mechanisms, therefore they are united under the general term - tubo-peritoneal infertility.
Read more about the pipe factor >>>
Endocrine infertility
The main role in the development of this type of infertility is played by disruption of the normal functioning of the ovaries with ovulation disorder.
The reasons are:
- Hypothalamic-pituitary dysfunction, in which due to inhibition of the production of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, ovarian function is suppressed.
- Hyperandrogenism occurs as a result of increased synthesis of male sex hormones (androgens) by the adrenal glands or ovaries.
- Lack of luteal phase of the menstrual cycle - deficiency of female estrogens does not allow the endometrium of the uterus to prepare for embryo implantation, which leads to spontaneous abortion.
- Exhausted ovarian syndrome is the absence of normal menstrual cycles already at the age of 35–38 years.
Read more about endocrine forms of infertility >>>
Uterine infertility
This form of female infertility is caused by congenital anatomical abnormalities or acquired diseases of the uterus.
Uterine factor (15%) ranks 3rd in the structure of causes of female infertility.
Causes of uterine infertility:
- Congenital developmental anomalies: absence of the uterus, duplication, saddle shape, retroflexion of the uterus (improper position): rotation around the axis, bending of the uterus, displacement of the organ upward or to the sides.
- Myomas and fibromyomas are benign tumors.
- Endometriosis.
- Hyperplasia of the inner layer of the uterus - endometrium (polyps).
- Intrauterine adhesions (synechias), cicatricial deformities of the uterine cavity, consequences of tuberculous endometritis.
- Foreign bodies in the cavity in the uterine cavity: intrauterine devices, remnants of suture material after surgery.
One of the variants of uterine infertility is the cervical factor, which is formed due to structural, biochemical and functional transformations of the cervix. These changes interfere with the movement of sperm or even lead to their death.
Causes:
- Adhesions and cicatricial changes in the cervix, most often the internal os as a result of infection, abortion, or surgery.
- Anomalies in the structure of the cervix.
- Cervical canal stenosis.
- Cysts and tumors in the internal os or cervical canal.
- Presence of antisperm antibodies (ASAT) in cervical mucus.
Psychogenic factors of infertility
Observed in various forms of disorders in the psycho-emotional sphere of a woman. Constant conflict situations in the family, at work, dissatisfaction with sexual life, the “anticipation of pregnancy” syndrome, feelings of inferiority, and depression cause menstrual irregularities, incoordination of the smooth muscle fibers of the fallopian tubes, which leads to functional tubal obstruction.
In 48% of infertile women, one cause of infertility is found, in the rest - a combination of two or more factors.
Diagnosis of infertility
This is a rather complex process that begins with interviewing the patient and finding out the exact complaints. Great importance is given to clarifying the possible causes leading to this pathology, as well as the medical history.
You should ask if there have been any cases of infertility in the family. In most cases, the doctor is interested in determining menstrual function, symptoms of hormonal disorders, as well as drawing up a general impression of the woman’s development.
After this, an inspection is carried out, both external and specialized. It is necessary to assess the condition of the genital organs, exclude organic pathologies, as well as inflammatory processes.
After this, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods begin to be used by exclusion:
- Functional diagnostic tests are one of the most labor-intensive, but at the same time effective methods for assessing the reproductive system. They are used to exclude possible organic reasons for the absence of pregnancy, as well as the male factor. Tests are of the following types: Among them, the most popular is the method of assessing basal temperature . It is based on the fluctuation of body temperature depending on the day of the menstrual cycle. This dependence occurs due to the production of progesterone, which increases body temperature. When measuring rectal temperature daily, a graph is built. During ovulation and the process of formation of the corpus luteum, an increase in temperature occurs, which is expressed by a rise in the graph. If the follicle does not mature, then the temperature will not rise.
- The next test is the pupil sign . In this case, the condition of the cervical canal is assessed. The size of its opening will depend on the effect of estrogen on hormonally dependent organs, one of them is the cervix. It promotes sperm penetration. So, under the influence of estrogen, it expands, reaching a peak at the time of ovulation. The assessment is made during a gynecological examination of the cervix in the mirrors at various phases of the menstrual cycle. Symptom for assessing the extensibility of cervical mucus. In this case, the work of the estrogen component is also assessed. Since the mucus in the cervix performs several functions at once, its composition changes depending on the day of the menstrual cycle. During the period of maximum estrogen content, that is, during ovulation, its extensibility increases. As a result, the mucus obtained from the cervical canal does not rupture, but remains elastic.
- The fern symptom is also an assessment of the condition of the cervical mucus for the content of estrogen in it. When their content is sufficient, a large branching of the pattern formed on the glass slide occurs. The method does not take much time and economic costs, since it is enough to apply mucus and wait for it to dry completely. After which an assessment is made. In this case, you cannot use only one method. To fully assess the menstrual cycle and hormonal levels, it is necessary to carry out several methods characterizing the various hormones responsible for the onset of egg maturation, as well as the ovulation process. The advantage of their use is their relatively low cost and low energy consumption.
- To determine the hormonal background, the level of Prolactin is examined, and follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones are also assessed, and estradiol is checked if necessary.
Surgical and instrumental methods for diagnosing infertility
In addition to medication, treatment of infertility in women is carried out using surgical methods. These include:
- Hysteroscopy. This is an examination of the uterine cavity using a surgical endoscope. Diagnosis is carried out by inserting a flexible tube into the cervix with a video camera at the end, the image from which is displayed on the monitor screen. The gynecologist sees the entire uterine cavity from the inside, changes in it, the presence of tumors and other pathologies. Indications for diagnosis are:
- frequent spontaneous miscarriages;
- suspicion of intrauterine tumors.
- Laparoscopy. In this case, female infertility is diagnosed by inserting a flexible tube of an endoscope through an incision in the woman’s anterior abdominal wall. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia in the hospital department. Indications for this are:
- stagnation of the fallopian tubes,
- infertility,
- cystic growths on the internal organs of the pelvis in women.
The examination is carried out when there is a change in the menstrual cycle, frequent in vitro fertilizations that end in miscarriages.
Diagnosis in the form of laparoscopy has been proven to be highly effective. This method helps specialists understand how to treat infertility. During surgery, the patient does not lose much blood. After laparoscopy, the rehabilitation period is easy and an invisible scar remains after the incision.
Treatment
Treatment of tubal infertility
The main ways to eliminate this problem are surgical methods. The method will depend on the specific reason for the development of this type of infertility.
- The fimbryolysis procedure is the separation of the fused fimbriae necessary for the capture of sperm, as well as the transfer of the egg into the fallopian tube.
- Methods of salpingolysis include the elimination of anatomical defects in the area of the fallopian tube, as well as the separation of formed adhesions.
- Plastic surgeries that help create a new hole in the obliterated area.
- As well as the processes of transplanting the tubal section into the uterine cavity.
Treatment of endocrine infertility
It begins with possible compensation of endocrine pathologies, possible replacement therapy.
If necessary, it is possible to begin stimulating the ovulatory process and the maturation of a morphologically functional egg.
In addition to Clomiphene citrate, it is possible to prescribe agents that regulate the overlying sections.
For large formations that are hormonally active and contribute to the development of endocrine infertility, surgical removal is possible.
In addition, other hormonal medications may be used for other types of endocrine problems.
Treatment of uterine and cervical infertility
In cases where problems such as uterine fibroids are identified, hormonal medications and surgical methods can be used.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a form of infertility in which the only way to eliminate it is a hormonal course or continuous treatment.
One of the latest ways to eliminate anatomical defects of the uterine cavity is laser reconstruction of the uterine cavity.
In the case of an inflammatory process, medications are prescribed to eliminate the lesion or reduce its activity.
Treatment of immunological infertility
Condom therapy
Provides for the complete exclusion of any contact of sperm with the female body.
Therefore, all sexual acts must be protected.
The duration of this treatment should be at least six months.
This increases sensitivity to sperm. And in the future, the couple has a high probability of conceiving a child.
Hyposensitization
This group of drugs helps reduce the sensitivity of the immune system. As a result of these mechanisms, less and reduced antibody production occurs. The course is prescribed for a week on the date of expected ovulation.
Intrauterine insemination
This method eliminates the contact of sperm with cervical mucus. There is a preliminary purification of the liquid from antigens and its direct introduction into the uterine cavity.
ECO
If the above methods are ineffective, IVF (in vitro fertilization) begins to be used.
In this case, an artificial fusion of a previously obtained egg and sperm is carried out.
Which, after being grown in the laboratory under artificial conditions to a certain size, are transplanted into the already prepared cavity of the woman’s uterus.
Hormonal disorders
For the timely maturation of the egg and its release from the body of the ovary, the body produces various types of sex hormones:
- estrogen;
- progesterone;
- follicle-stimulating;
- luteinizing.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
It occurs due to an excess amount of male sex hormones, with parallel large-scale production of insulin. Against the background of their increased number, a large number of follicles are formed in the body of the ovaries, none of which fully mature.
The mechanism for releasing the egg does not occur, nor does the process of ovulation. The body of the ovary increases in volume two to six times, the duration of the menstrual cycle lengthens in time, and regulative omissions occur. Most females with polycystic disease experience increased body weight.
Insulin resistance
Resistance of the female body to the hormone is often recorded in polycystic ovary syndrome. Produced by the pancreas, it is responsible for delivering glucose from the bloodstream to cellular structures.
When cellular metabolism is disrupted, glucose levels increase sharply, and insulin production increases accordingly. Factors that lead to the development of the process:
- incorrect diet, with a large intake of carbohydrates and sugars;
- frequent stress;
- sedentary lifestyle, excluding any physical activity.
Excess of male hormones
Unstable menstruation or its absence indicates hyperandrogenism. The functionality of the ovaries is suppressed by an excessive amount of male hormones, the cycle is disrupted to the point of complete absence. With severe development of the pathology, infertility occurs. The presence of hyperandrogenism can be determined by certain signs:
- increased body hair growth;
- acne;
- lowering the tone of the voice closer to a man’s;
- change in figure according to the characteristics of the opposite sex.
Pituitary gland disorders
Deviations in the functionality and normal performance of the gland appear against the background of various disorders:
- problems with local blood circulation;
- reasons of genetic origin;
- previous injuries;
- taking medications;
- available in the anamnestic data of meningitis.
As the disease develops, a number of characteristic signs develop:
- the presence of milk-like contents in the mammary glands;
- disruption of the normal menstrual cycle;
- mastopathy;
- untimely enlargement of the mammary glands;
- increased fragility of bone tissue;
- decreased desire for a sexual partner.
Prolactin, produced by the pituitary gland, is considered a hormone of nursing mothers. Due to its appearance in the body, ovulation and the menstrual cycle stop. An increased amount of it in the body of nulliparous women is associated with a malfunction of the thyroid gland - hypothyroidism.
Early menopause
Average statistical data indicate that the onset of menopause occurs at the age of 50 years. Certain factors contribute to a reduction in the functionality of the reproductive system:
- autoimmune diseases;
- disorders of genetic etiology;
- various diseases of the genital organs;
- wrong lifestyle;
- chronic nicotine addiction.
All of the above reasons cause the onset of menopausal changes in women who are forty years old. A decrease in the production of female sex hormones and loss of ovarian function are recorded in 1% of females. Opportunities for childbearing fade and infertility sets in.
Lack of corpus luteum
At the site of the follicle that released the egg, a corpus luteum appears. This is a temporary gland responsible for the production of prolactin, the main hormone of the corpus luteum. Prolactin stimulates the preparation of the walls of the uterus for the implantation of a fertilized egg in them.
If its quantity is insufficient, consolidation does not occur and the desired pregnancy does not occur. In some cases, consolidation occurs, but then spontaneous abortion develops. For the occurrence of a pathological condition, the following prerequisites are necessary:
- congenital genetic abnormalities;
- pathological disruptions in the functionality of the ovaries - polycystic syndrome, malignant neoplasms;
- dysfunction of the pituitary gland.
Assisted reproductive technologies
The following reproductive technologies can be used:
- ICSI. This is the process of intracytoplasmic injection of sperm into the egg. It is one of the necessary methods in preparation for in vitro fertilization. In this case, the egg is taken from the woman’s own, which matures using a natural method. The advantage of in vitro fertilization is the careful selection of germ cells. Preference is given to the most viable ones, with a good morphological structure. The fertilized oolite is placed for further maturation in a container with a specialized medium. It is used when antisperm antibodies are detected in a woman, as well as other variants of immunological infertility, pathology of egg development, as well as unsuccessful previous attempts.
- Transfer of embryos into the fallopian tubes. This is a type of in vitro fertilization. Can be prescribed for various types of infertility. In most cases, these are inflammatory processes or developmental defects or post-traumatic changes in the fallopian tubes. In this case, the woman first eliminates the cause of infertility, and also takes medications that prepare the endometrium for the attachment of the embryo.
- Insemination with husband's sperm. This is a fairly commonly used method, but in most cases it is a way to eliminate the male factor in infertility. Women are prescribed artificial insemination for psychological, cervical, and other factors in the development of infertility, when the cause is not always clearly established. The procedure is performed during expected ovulation to increase the chance of pregnancy. In some cases, additional preparation with the use of medications may be required. Its advantage against the background of infertility is its simplicity and painlessness, as well as the absence of the involvement of material devices. The method is the most economically profitable.
- Surrogacy. This is a fairly new method of being able to give birth to a child. Those couples who cannot give birth to a child in the event of a uterine factor, in most cases this is a history of uterine amputation, resort to it. Moreover, this method is established by law, therefore it is currently regulated to the maximum extent possible legally. In this case, the genetic material of a married couple can be used, but gestation will take place in the body of another woman. Sometimes a close relative can act as a surrogate mother, since there is no transfer of chromosomal tissue from this person to the fetus. The limitation in its use is the difficult psychological attitude towards such a decision.
General information
Health problems and psychological factors interfere with conception and subsequent pregnancy. Infertility is registered in both sexes, but more often the cause in childless marriages is abnormalities in the woman.
The reason for the lack of long-awaited conception is determined in a clinical setting, using specialized diagnostics. In some cases, the pathology can be corrected with medications or surgery, but sometimes doctors cannot determine the root causes of infertility.
Folk remedies for the treatment of infertility in women
There are no specific remedies aimed at treating female infertility. Therefore, in most cases, women who cannot get pregnant resort to using universal remedies that are effective for diseases of the reproductive organs.
Such means include:
- Sagebrush. This is a universal and effective plant that is used for hormonal, inflammatory and other diseases. Since these pathologies can lead to infertility, a decoction of wormwood will help, in combination with medications, to cope with the problem. To use it, you need to pour boiling water over the dry wormwood herb and leave it to infuse for an hour or until the solution has completely cooled; if necessary, it can be boiled from the moment it boils. The resulting mixture is consumed in a volume of 100 ml twice a day.
- Upland uterus, wintergreen, wintergreen are those plants that are used by women for infertility at various stages of the process; in the case of undeveloped stages, in most cases three courses are enough. They are consumed in the form of tinctures. When preparing, the herb is poured into vodka at the rate of 50 grams per 1500 ml. The mixture is infused for two or more weeks in a place inaccessible to sunlight. Use the mixture for a month in the amount of one teaspoon three times.
Infertility treatment depending on the type and cause of the pathology
Infertility in women causes various symptoms. A specialist can make a final diagnosis and prescribe complete treatment based on the results of laboratory and clinical studies. Women are anxiously wondering: Is it possible to cure infertility? Experts assure that with such a diagnosis, pregnancy can occur, but not very soon. During infertility, treatment at the initial stage is aimed at normalizing the functioning of the woman’s genital organs. If endocrinology is disrupted, hormonal levels are normalized. Doctors can put a woman on a diet if she is overweight. When hormones are normalized, follicle maturation is monitored. If you eliminate the main problems of infertility and the causes, then in most cases, with the normalization of hormonal levels, women experience a long-awaited pregnancy. How to cure pathology in case of obstruction of the fallopian tubes? The doctor prescribes laparoscopy to clean them and normalize their work. If the surgical intervention is insufficiently effective, the couple is put on a waiting list for in vitro fertilization, but a long-awaited pregnancy can occur without IVF. If the uterus develops abnormally, infertility can be cured through surgery. In 30% of cases, women become pregnant after a long rehabilitation period. If the diagnosis reveals a complete absence of an organ, then the family is offered to find a woman who, for a large fee, will carry and give birth to a child and give him to his parents to raise.
Preventive methods of infertility
Prevention of infertility should be carried out from the moment a girl reaches maturity. It includes:
- Avoid promiscuous sexual intercourse and frequent changes of sexual partners.
- Abortion protection.
- Compliance with barrier contraception.
- Genital care.
- Annual visit to the gynecologist.
To prevent infertility, prophylaxis must be carried out continuously. From an early age, parents should talk with their children about the existence of such pathology and methods of combating it.
Video: Causes of female infertility – It is possible for a woman with infertility to become pregnant
Prevention of infertility
It must be remembered that absolute infertility is difficult to prevent, since this problem is irreparable. Therefore, it makes no sense to resort to various procedures.
But the prevention of primary and secondary infertility, which are relative, occupies a special place in gynecology:
- So, women or girls who have any complaints from the reproductive system need to seek help from specialists as soon as possible , without waiting for complications to develop.
- This is also control over menstrual function ; if there are disturbances, then it is necessary to find out the cause and eliminate it.
- Some anatomical defects , such as septum or synechiae, can be corrected.
- Regularly diagnose infectious diseases , especially those associated with specific pathogens. The risk group will include women with a non-regular sexual partner.
- Also, when the inflammatory process develops in the acute stage, it is necessary to carry out timely and complete treatment ; when transitioning to the chronic stage, it is recommended to carry out anti-relapse treatment, as well as follow a set of measures aimed at eliminating exacerbations.
- A woman should pay attention to her diet ; it should be complete and balanced. Include sufficient amounts of protein and fats necessary for the functioning of the ovaries.
- Great importance is also paid to the daily routine. Sleep should be at least 8 hours. Work must be selected excluding heavy physical activity and emotional stress.
Symptoms of infertility
Often, the absence of pregnancy is the only sign of trouble in the reproductive system, but there are a number of symptoms that indicate the presence of a particular disease that is an obstacle to pregnancy.
| Types of infertility | Symptoms |
| Trubnoye | There are no specific symptoms. |
| Peritoneal | Aching pain in the lower abdomen associated with menstruation intensifies after physical activity or during sex. |
| Endocrine | Disruption of the menstrual cycle, prolongation of intermenstrual intervals, decrease in the amount of blood released, bleeding outside of menstruation. Acne, tendency to obesity, engorgement of the mammary glands, male pattern hair growth. Periodic pain in the abdomen and lower back. |
| Royal | Endometrial hyperplasia: intermenstrual spotting, anovular bleeding. Uterine fibroids - prolonged bleeding leading to anemia, dysuria, constipation, abdominal pain radiating to the groin. Intrauterine synechiae: hypomenstrual syndrome or amenorrhea. |
| Psychogenic | Anxiety-depressive state, pregnancy anticipation syndrome, hysteroid reactions, oligomenorrhea, sometimes cessation of menstruation. |
Reviews
Reviews from women about infertility and its treatment:
Whatever the cause of infertility, your doctor must diagnose you. Numerous forums on the Internet dedicated to the question “How to get pregnant if you can’t?” can be a good source of moral support, but nothing more.
You should not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication using traditional methods, or make dubious conclusions based on the experience of others.
You need to come to an appointment with a fertility specialist, who will conduct the necessary diagnostics, order tests, help determine the type and extent of the problem and prescribe appropriate treatment.
General recommendations
To prevent the formation of infertility in a timely manner, you must follow several simple rules:
- Visit a gynecologist in a timely manner - any infectious and inflammatory diseases are easier to treat in the initial stages of occurrence. Delaying a visit to the doctor will lead to structural changes in the reproductive organs (adhesions, scars, narrowing).
- Medical and criminal abortions often serve as prerequisites for the development of conception disorders - any surgical interventions leave marks on the mucous membranes of the uterus and its cervix. A serious attitude towards contraception will eliminate the appearance of secondary or primary infertility.
- Self-medication and uncontrolled use of medications can cause complications. At the first signs of illness, you should immediately contact a medical facility.
Disorders of the ovarian-menstrual cycle
The regularity of menstruation is an important indicator of women's health. Any delays, changes in the duration of menstruation, or increased pain indicate a problem. Girls are recommended to keep a calendar of menstruation, which will mark the dates of their beginning and end. If the regularity and cyclicity of menstruation is disrupted, you should immediately contact a gynecologist for consultation.
The physiological norm for the duration of the menstrual cycle is 28 days. The onset of menstruation is the first day of a new cycle. The next menstruation should begin in 28 days. This schedule is observed in approximately 60% of women of reproductive age.
Due to the individual characteristics of the female body, the duration of the ovarian-menstrual cycle may differ from the generally accepted norm. But it should not be shorter than 21 days and longer than 42 days. These are the extreme points of the range of a non-pathological cycle, provided that it is constant. You must inform your gynecologist about any deviations from the physiological norm.
How to determine the disease
Infertility in women is determined by the absence of pregnancy during open sexual intercourse, contact with ejaculation inside for one and a half to two years.
At the same time, doctors divide the diagnosis of infertility into 2 categories:
- Absolute infertility. This disease indicates that there are irreversible pathological changes in the female body (abnormal development of the female organs), due to which the fair sex cannot become pregnant, and never.
- Relative infertility. This category is more comforting than the first option, since such infertility is treatable and subsequently the woman has considerable chances of having a baby.
Primary and secondary infertility
- primary - the spouses were never able to conceive and give birth to a child
- secondary - the couple already has children or has become pregnant
Primary female infertility is often associated with some congenital pathology, for example, the absence or insufficient development of the uterus. Secondary female infertility can be caused by various factors: infectious processes, changes in hormonal levels, the development of endometriosis and many other reasons. Moreover, absolute female infertility involves pathological changes that cannot be corrected, while relative female infertility is reversible.
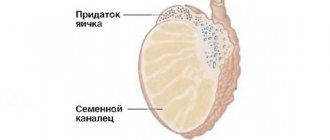
In men, primary infertility is also often based on genetic pathologies, and the secondary form can be associated with previous STIs, varicocele, and testicular injuries.
Traditional methods of treatment
The effectiveness of traditional treatment for infertility has not been proven, but doctors allow the use of herbal medicine as an addition to the main method of treatment. For tubo-peritoneal infertility, the following preparations are recommended:
- Collection No. 1
Mix and grind 100 gr. dill seeds, 50 gr. anise seeds, 50 gr. celery and the same amount of stinging nettle. Add half a liter of honey, stir and take 3 tbsp three times a day. spoons.
- Collection No. 2
For 20 minutes in a liter of water, boil 10 tablespoons of plantain leaves over low heat, then add a glass of honey and boil for another 10 minutes, cool the broth and then strain, drink 1 tablespoon three times a day.
- Collection No. 3
Three times a day, drink a tablespoon of plantain syrup (collection No. 2), and after 10 minutes, drink 75 ml of herbal decoction: geranium leaves, epiploin root, hair-like ossicle, shepherd's purse, hop cones, flowers and leaves of the cuff . To prepare the decoction 2 tbsp. spoons, pour half a liter of water, boil for 15 minutes over low heat and strain.
It is also allowed to take herbs for infertility in the form of decoctions and teas that are rich in phytohormones, but under the supervision of a doctor: sage leaves and plantain seeds, knotweed and St. John's wort, marin root, ramshia herb. A large number of phytohormones are contained in black cumin oil and ginger, and in the herbs boron uterus and red brush.
Why shouldn’t you delay your visit to the gynecologist?
According to statistics, the longer infertility lasts, the more difficult it is to cure. Therefore, if there are unsuccessful attempts to get pregnant throughout the year, with constant sexual intercourse without birth control, if male factor infertility is excluded, a woman must consult a gynecologist to identify the causes of this condition, and if problems are identified, begin therapy immediately.
This is especially true for women after 30 years of age, because the number of eggs in reserve becomes smaller and smaller over time, and ovulation with age, even in healthy women, does not occur in every cycle. A timely visit to specialists regarding infertility often subsequently ends with the childless couple having a long-awaited, beloved baby.
Male infertility: causes, diagnosis and treatment
The choice of the optimal treatment regimen directly depends on the reasons underlying the decrease in the fertilizing ability of sperm. The main diagnostic method is a spermogram. In addition, you will need to undergo an ultrasound examination of the scrotum and prostate gland, and take tests for infections and hormones. The doctor will be able to tell you how to treat male infertility in each specific case only after conducting an examination. As a rule, surgical intervention is effective for the obstructive form. For the secretory form, drug or surgical treatment may be prescribed, as well as the use of ART methods. We briefly talked about male infertility, the causes and treatment of this pathology, however, more detailed information about the problem can only be obtained during a face-to-face consultation with a specialist.
The doctor definitely recommends an examination of both spouses, since only in this way can all existing pathologies be detected and an optimal treatment regimen be developed to achieve pregnancy. Nova Clinic has all the capabilities to quickly find out the cause of infertility in a particular couple and offer effective ways to overcome it.
Other reasons
- Age. By the time of puberty, a woman’s ovaries contain about 300 thousand eggs. Over time, they age - the DNA is damaged, since the system for its restoration works less well with age. Accordingly, their quality decreases—suitability for fertilization and embryo development. This process becomes noticeable after 30 years, and when a woman turns 35-40, aging accelerates.
- Overweight or underweight. Excessive amount of adipose tissue in the body threatens hormonal imbalances - an increase in the amount of estrogen and testosterone, which threatens gynecological diseases, including infertility. Under the influence of medications, obese women can become pregnant, but problems often arise with the bearing and development of the child. Lack of weight (BMI less than 18.5) also leads to dysfunction of the endocrine system, but less hormones are produced than necessary for the normal functioning of the reproductive system, and eggs stop maturing.
- Stress, nervous exhaustion, chronic fatigue. Stress is the cause of hyperprolactinemia and a decrease in estrogen levels in the blood, which affects the ability of the egg to mature and attach to the uterine wall. Another consequence of emotional overload is spasms and muscle contractions, which leads to hypertonicity of the uterus and fallopian tubes, which prevents conception.
- Congenital disorders. Stein-Leventhal syndrome (provokes polycystic ovary syndrome), adrenogenital syndrome (impaired functioning of the adrenal glands and increased levels of androgens), Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome (absence of menstruation), blood clotting disorders and some other disorders are of a genetic nature and interfere with conception or cause early miscarriages.
- Immunological factors . The presence of antibodies to sperm in cervical mucus can lead to infertility. In other cases, the mother's immune system prevents the embryo from attaching to the wall of the uterus and thus causes a miscarriage.
- Psychological reasons. In some cases, a woman subconsciously perceives pregnancy as a danger. This may be caused by moral trauma, fear of changes in life or appearance, or fear of childbirth. The brain controls all processes in the body, so a negative psychological attitude leads to infertility.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic procedures include: medical history, external and gynecological examination, full examination of partners, referral for tests (blood, urine), various functional tests (postcoital, immunological compatibility, cervical index, basal temperature curve), study of hormone levels, spermogram, determination of fallopian tube patency.
Patients often have to undergo many examinations, since usually both male and female infertility have a complex of causes and provoking factors.
List of examinations and tests
You may be prescribed: ultrasound, hysterosalpingography, x-ray of the skull (if a pituitary tumor is suspected), colposcopy, hysteroscopy, laparoscopy (some techniques can be simultaneously used for treatment). Examinations will help to assess the structure and condition of the pelvic organs, detect foci of erosion and cervicitis, find possible neoplasms, adhesions, determine the patency of the fallopian tubes, and evaluate the process of ovulation.
Popular tests: determination of hormonal levels (levels of testosterone, prolactin, cortisol, progesterone), STDs (sexually transmitted infections), immunogram, compatibility analysis, genetic analysis for chromosomal abnormalities.
How does fertilization occur?
During fertilization, a male reproductive cell (sperm) merges with a female reproductive cell (ovum). In a healthy woman, almost every month, approximately in the middle of the cycle, one egg matures. This is called ovulation. During sexual intercourse, namely during ejaculation, millions of sperm move towards the goal - one egg. At this time, the egg leaves the ovary and moves through the fallopian tubes, where fertilization occurs.
How does the female reproductive cell move, since it does not have a tail, unlike the sperm? On the surface of the fallopian tubes there are cilia that direct the egg towards the uterus, and the fallopian tubes themselves have a muscular layer and are able to contract slightly, which also facilitates the advancement of the egg.
Implantation of the embryo into the uterine cavity
Next, the fertilized egg moves into the uterine cavity to penetrate its mucous membrane for further formation. If at any of these stages of fertilization a failure occurs and it is repeated cycle after cycle, with constant sexual activity, conception becomes impossible, which is manifested by infertility.
Barren marriage
In 2000, WHO formulated the following definition of an infertile marriage: a marriage in which, with regular sexual intercourse without the use of contraceptives, pregnancy does not occur for 12 months.
A couple may be infertile due to fertility problems in one or even both partners at the same time. According to statistics, in 40% of cases the inability to conceive a child is associated with male infertility, in 45% - with female infertility. And finally, 15% of infertile couples have a combination of both factors.
As for the statistics on the number of infertile couples in the Russian Federation, this figure varies depending on the region and reaches 8-19%. Most infertile marriages are observed in industrial centers and megacities. Due to the increasing number of such marriages, the demographic situation is becoming unfavorable and poses a serious problem for health care and modern society as a whole.
Sexually transmitted infections play a major role in the spread of infertility (primarily tubo-peritoneal infertility - TPI). More and more cases of infection with such infections have been recorded in recent years. This trend is explained by an earlier age at the onset of sexual activity, low awareness of the population, family and social instability, when, due to labor migration, partners are forced to live away from each other for a long time.
In many cases, the cause of infertility is common gynecological problems (ovarian cyst, long-term inflammation of the appendages and uterus, endometriosis, uterine fibroids). Termination of pregnancy (both artificial and spontaneous), illiterate use of contraceptives and hormonal drugs can lead to serious consequences. Also, the ability to conceive is negatively affected by bad habits (alcoholism, drug addiction, smoking).
The environment also has a certain impact on male and female fertility. The influence of negative external factors explains the higher percentage of infertile couples in industrial regions. Intensive urbanization processes have the most negative impact on human health. Moreover, the effect of environmental factors is aggravated by constant stress loads, which, unfortunately, are impossible for residents of large cities to avoid. A state of chronic stress and nervous overstrain leads to disturbances in the hypothalamic-pituitary regulation of the reproductive system, which causes endocrine infertility.
Another serious problem in our time is age. Modern women often plan to start a family and have children after 30, when they manage to make a career and firmly establish themselves in society. However, they do not take into account that the influence of many negative factors increases over the years and the risk of infertility increases. Moreover, mature age in itself is a factor that limits a woman’s reproductive capabilities and causes additional difficulties in infertility treatment (this is especially true for women over 37 years old).
The serious medical and biological consequences of an infertile marriage include, first of all, psychological problems associated with the unrealized maternal and paternal potential. This dissatisfaction greatly affects the quality of life of the couple, forming an inferiority complex in the spouses, leading to severe neuroses and psychosexual disorders.
Prolonged psychological stress, which often accompanies infertility, is dangerous not only because it can further worsen the condition of the reproductive system. A stressful situation creates additional risks for human health in general - it provokes the occurrence of many diseases (primarily metabolic-endocrine and cardiovascular), and also worsens the course of existing chronic diseases.
Also, an infertile marriage has certain social consequences. These include:
— A decrease in labor and social activity of the most productive category of people due to psychological problems that result from the inability to realize parental potential.
— A significant increase in cases of divorce, which undermines the institution of the family.
— Deterioration of the demographic situation in the state.
The effectiveness of treatment for infertile couples in the Russian Federation is not very effective. This can be explained by the following reasons:
— Lack of qualified specialists.
— Incomplete awareness of medical workers about all existing methods and programs for treating infertility.
— Insufficient interaction between doctors working in antenatal clinics, family planning centers and gynecological hospitals on the one hand and doctors working in the field of Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) on the other hand.
— To diagnose infertility in women, many have to travel from the regions to large cities.
In addition, the results of infertility treatment are greatly influenced by factors such as the duration of the infertile marriage and the woman’s age. According to medical statistics, in women under 30 years of age, pregnancy occurs within 12 months of regular sexual intercourse without contraception in 80% of cases. In the age group under 40, this figure is much lower – 25%. And among women over 40 years old - only 10%.
Hormonal imbalance
Due to hormonal imbalance, several problems arise in a woman’s body, which can cause, including infertility. Hormones play an important role in the maturation of eggs inside follicles, the formation of the endometrium, embryo transplantation, and the course of pregnancy. To exclude a hormonal factor in infertility, it is necessary to do a hormone test. The list of necessary tests is compiled by the gynecologist individually. The fact is that a woman’s hormonal background constantly changes throughout the menstrual cycle. Therefore, in order to have a complete picture of the hormonal profile, it is necessary to take the test at certain phases of the menstrual cycle.
Hyperprolactinemia is one of the main diseases that causes hormonal imbalances and reduces a woman’s fertility. High concentrations of prolactin in the blood lead to menstrual irregularities, anovulation (lack of ovulation), contractions of the luteal phase, and infertility.
Prices
The cost of infertility therapy in Moscow and St. Petersburg, as well as other cities of the Russian Federation, depends on the severity, form of the disease, the presence of complications, concomitant pathologies and negative factors, the prestige of the clinic, the choice of medications or surgical techniques.
So, IVF will cost about 100 thousand rubles. The state allocates the same amount if there is evidence.
In private clinics you will have to pay for all procedures: from consultations (1000 - 5000 rubles) to diagnostic procedures (for example, colposcopy costs 2000 - 3000 rubles, smear - about 500 rubles, hysterosonography - 10,000 rubles, etc.) and operations (for example, uterine plastic surgery will cost from 5 to 12 – 13 thousand rubles). You will need to pay separately for medications and consumables.
Abroad (Israel, Germany) diagnostic procedures will cost from $3,500, treatment – $4,000 – 5,000, IVF – about $13,000.
Drawing conclusions
Did you have a misfire? Judging by the fact that you are reading this article, victory is not on your side.
And of course, you know firsthand that impaired potency is:
- Low self-esteem
- Women remember your every failure, tell their girlfriends and your friends
- Prostate disease
- Developing depression, which negatively affects your health
Now answer the question: ARE YOU HAPPY WITH THIS? Can this be tolerated? Do you remember that feeling when you look at a naked woman and can’t do anything? Enough is enough - it's time to get rid of potency problems, once and for all! Do you agree?
We have studied a huge amount of materials and, most importantly, tested most potency products in practice. So, it turned out that a 100% working drug without any side effects is Predstanol. This drug consists of natural ingredients that completely eliminate chemicals.
ATTENTION! PROMOTION! You can try the drug for free
, place your order using the link or filling out the form below:
In the modern world, the problem of infertility has blurred the line between the medical and social components of this diagnosis. Indeed, due to the lack of a desired pregnancy, a large number of marriages are dissolved. In this article we will tell you why infertility occurs, consider the main types, types and causes of infertility, present the diagnosis of infertility, as well as ways to treat this problem.
Uterine and cervical infertility
Patients who cannot become pregnant due to hyperplastic processes of the endometrium (hyperplasia and polyps) and who do not have other factors of infertility are given treatment aimed at eliminating the pathologically altered uterine mucosa and normalizing hormonal and metabolic processes in the body. In the case of glandular cystic hyperplasia, curettage of the uterine cavity is carried out, followed by the administration of estrogen-gestagen drugs (3 - 4 months), and in case of relapse of the disease, hormonal treatment continues for 6 - 8 months. Uterine polyps are removed using hysteroscopy and then the endometrium is scraped out. Hormonal therapy is prescribed when polyps are combined with endometrial hyperplasia.
The choice of treatment method for patients with uterine fibroids depends on the location and size of the node. The submucosal myomatous node is removed hysteroscopically (hysteroresectoscopy), interstitial and subserous nodes no more than 10 cm are removed laparoscopically. Laparotomy is indicated for large uterine sizes (12 weeks or more) and atypical location of the nodes (cervical, isthmus). After conservative myomectomy, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (Zoladex) are prescribed for 3 cycles. If a woman does not become pregnant within 2 years after myomectomy, she is referred for IVF. During the waiting period, ovulation is stimulated.
Treatment of patients with intrauterine synechiae consists of their hysteroscopic dissection and the administration of cyclic hormone therapy after the intervention for a period of 3 to 6 months. To reduce the chances of re-formation of adhesions in the uterine cavity, an IUD is inserted for at least a month. The prognosis for this disease is quite complex and is directly proportional to the degree and depth of damage to the basal layer of the endometrium.
In case of malformations of the uterus, plastic surgery is performed (dissection of the intrauterine septum or metroplasty of a bicornuate uterus or existing two uteruses).
Treatment of cervical infertility depends on the cause that caused it. In the case of anatomical defects, reconstructive plastic surgery is performed on the cervix; if polyps of the cervical canal are identified, they are removed, followed by curettage of the canal mucosa. When underlying diseases and endometrioid heterotopias are identified, anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed, followed by laser or cryodestruction. At the same time, ovarian function is normalized with the help of hormonal drugs.
Reasons that interfere with conception or pregnancy
There are many reasons for infertility. Some are so primitive that if the spouse had known about them earlier, problems could have been avoided. Others may be so serious that the baby can only be delivered through IVF. It also happens that couples remain infertile even after treatment - the causes in this case cannot be eliminated.
According to statistics, most often the reason for non-occurrence of pregnancy lies in the female body, but it is still worth starting the examination with a man. This is due to the fact that first he needs to take only one test - a spermogram, while a woman will have to undergo different procedures.
Let's look at the main causes of female infertility.
How to detect infertility?
Female infertility can be detected using general and special methods. The purpose of general methods is to assess the woman's condition. This can be done through an initial examination (condition of the skin, chest, physique, mucous membranes, hair), palpation of the glands and abdomen, and measurement of pressure and temperature.
Special diagnostic methods involve conducting various tests: instrumental, laboratory, functional. They give doctors the opportunity to evaluate features in the structure of the genital organs and examine discharge from the genitals.
The most effective functional tests are:
- Periodic changes in basal temperature and, based on the data obtained, determination of the degree of deviation of hormonal activity from normal limits, as well as the characteristics of the ovulation period and menstrual cycle. This is a very labor-intensive process that requires regularity and care. In addition, errors are possible, because a person’s body temperature can change under the influence of different conditions.
- Measuring the level of hormones - estrogen by taking a smear of discharge from the cervix.
- Postcoital study of sperm activity and analysis for the presence of antisperm bodies.
Laboratory tests include testing urine and blood for hormones, testing smears and blood for infections, etc.
The most important examination for infertility is ultrasound. There are several techniques that allow you to fully examine the reproductive organs. For example, you can do a transvaginal ultrasound and get a complete picture of the condition of the uterus. Ultrasound with contrast helps to find adhesions and determine the degree of their patency. Doppler ultrasound shows how the blood flow functions. And folliculometry will show how and when follicles mature, their number, etc.
These examinations are inexpensive, safe, but very effective. Another plus is that they are painless.
Female and male infertility
- female infertility - the problems of an infertile marriage are associated only with problems in the health of the female body. The structure of infertility is approximately 50%.
- male infertility - a couple’s infertility problems are associated with abnormalities in the man’s health - about 50%
- combined - poor health of both women and men becomes the cause of their problems with conception and occurs statistically in more than half of all married couples.
Main pathologies of the female reproductive system
What causes infertility? Classification according to pathologies of the female reproductive system:
- Pathology of the endocrine system;
- Bilateral tubal obstruction;
- Inflammatory diseases;
- Pathologies of the uterus;
- Endometrial proliferation;
- Immunosuppression;
- Hypergonadotropic amenorrhea;
- Underweight or overweight;
- Problems of the cervical canal;
- Genetic mutations;
- Psychogenic disorders;
- Infertility for unknown reasons.
Let's look at infertility diseases in more detail.
Endocrine infertility
How to treat endocrine infertility depends on the type and location of the pathological process. Women with anovulatory infertility and concomitant obesity can normalize their weight by prescribing a low-calorie diet, exercise, and orlistat for 3 to 4 months. You can also take sibutramine, and if glucose intolerance is impaired, metmorphine is recommended. If pregnancy does not occur within a specified period of time, ovulation stimulants are prescribed.
In the case of diagnosed scleropolycystic ovarian disease (PCOS), the treatment algorithm includes:
- drug correction of hormonal disorders (hyperandrogenism and hyperprolactinemia), as well as therapy for excess weight and impaired glucose tolerance;
- if pregnancy does not occur during treatment, ovulation inducers are prescribed;
- if conservative treatment has not had an effect within 12 months, laparoscopy is indicated (resection or cauterization of the ovaries, exclusion of tuboperitoneal infertility).
If the patient has regular menstruation, normally developed genital organs, and the levels of prolactin and androgens are normal (endometriosis is excluded), the following therapy is carried out:
- single-phase COCs are prescribed according to a contraceptive scheme, in a course of 3 months and breaks between courses of 3 months (total number - 3 courses, duration of treatment 15 months) - the method is based on the rebound effect - stimulation of the production of own hormones by the ovaries after discontinuation of COCs and restoration of ovulation ( if there is no effect, ovulation inducers are prescribed);
- stimulation of ovulation is carried out with clostilbegit, human chorionic gonadotropin and progesterone (clostilbegit is taken 50 mg once a day during the first 5 days of the cycle, and to consolidate the effect, human chorionic gonadotropin is prescribed intramuscularly on the 14th day of the cycle) - the duration of treatment is 6 cycles in a row;
- stimulation of ovulation with FSH preparations (Metrodin, Gonal-F) from the first day of the cycle for 7–12 days until the maturation of the main follicle (ultrasound monitoring is required), the course is 3 months;
- stimulation of ovulation with FSH and LH drugs (pergonal, humegon) and the administration of human chorionic gonadotropin (pregnyl).
At the same time, immunomodulators (levamisole, methyluracil), antioxidants (vitamin E, unithiol) and enzymes (Wobenzym, Serta) are prescribed.
For regular periods and underdevelopment of the genital organs, the following treatment regimen is prescribed:
- cyclic hormone therapy with estrogens (microfollin) and gestagens (pregnin, norkolut) for a course of 6–8 months;
- vitamin therapy according to the phases of the menstrual cycle for the same period (in the first phase, vitamins B1 and B6, folic acid, in the second phase, vitamins A and E, and throughout the course of rutin and vitamin C);
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis with copper in the first phase and with zinc in the second);
- gynecological massage (up to 40 procedures);
- stimulation of ovulation with clostilbegit and human chorionic gonadotropin.
Women who cannot get pregnant due to hyperprolactinemia are prescribed drugs that suppress prolactin synthesis, restore the cycle (eliminating anovulation and increasing estrogen levels) and fertility, and reduce the symptoms of hypoestrogenism and hyperandrogenism. Such medications include parlodel, abergin, quinagomide and cabergoline. It is also recommended to take a homeopathic remedy - mastodinon.
Hyperandrogenism of ovarian and adrenal origin is treated for six months with dexamethasone, and if ovulation is restored, then ovulation is stimulated (clostilbegit, human chorionic gonadotropin, FSH and hCG or FSH, LH and hCG).
Treatment of infertility in patients with hypergonadotropic amenorrhea (resistant ovarian syndrome and exhausted ovarian syndrome) is unpromising. The prognosis for other forms of endocrine infertility is quite favorable; in approximately half of the cases, patients become pregnant within six months of ovulation-stimulating treatment (in the absence of other infertility factors).
Frequency of occurrence
According to statistics, the incidence of certain forms of infertility has been determined:
- hormonal infertility (anovulatory) reaches 35 – 40%;
- infertility caused by tubal factors is 20–30% (according to some data, reaches 74%);
- the share of various gynecological pathologies accounts for 15–25%;
- immunological infertility is 2%.
But it is not always possible to establish the cause of infertility even with the use of modern examination methods, therefore the percentage of so-called unexplained infertility is 15–20.
Metabolic disorders
The problem of excess weight and its deficiency negatively affects the fertility of women. Moreover, deviations from the physiological norm of BMI 18-24 indicate existing problems with metabolism in the body. It cannot be said that all overweight girls are infertile. But obesity is one of the factors that causes hormonal imbalances, which result in diseases such as diabetes mellitus, polycystic ovary syndrome, and endometrial hyperplasia. It can cause disruption of menstrual cycles; the risk of disruption of the endocrine system increases and may even subsequently contribute to the development of cancer.
Lack of weight is also considered as a factor that can potentially cause infertility. A woman's adipose tissue plays an important role in the metabolism of a number of hormones and produces more than twenty bioactive substances involved in metabolic processes. Like severe obesity, lack of body weight often becomes one of the causes of anovulation (lack of release of an egg), which makes pregnancy impossible.
Metabolism is closely related to the endocrine system. To restore normal body weight and stabilize metabolic processes, sometimes it is not enough to adjust nutrition and physical activity. It is necessary to establish the cause of the imbalance and undergo a course of treatment.
Medical diagnosis
At the first visit to the doctor, he conducts a survey (history). The survey consists of finding out the following details:
- The specialist listens to the patient’s complaints;
- Establishes heredity;
- Past illnesses;
- Regularity of menstruation;
- Partner constancy and frequency of sexual intercourse.
After the history, a physical examination is carried out, that is, body weight, type of hair growth and examination of the genital organs are characterized.
At the third stage, functional tests are carried out:
- A basal temperature graph is created, with the help of which the presence of ovulation and ovarian function are determined;
- Measurement of hormonal activity - estrogen;
- Postcoital test (presence of antibodies against sperm).
Laboratory tests:
- Blood tests for hormone levels;
- Antibody content towards spermatozoa;
- Presence of infectious diseases.
Instrumental tests:
- Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland and pelvic structure;
- Tomography of the skull to detect pituitary gland disorders;
- Colposcopy;
- Radiography.
Surgical tests:
- Hysteroscopy for the purpose of examining the uterus and uterine uteruses is carried out using a special device that is inserted through the uterine pharynx. This method effectively diagnoses infertility.
- Laparoscopy is performed by introducing an optical device through the uterine os.
In rare cases, the causes of infertility are not determined even after tests have been performed.
Immunological causes of infertility
Sometimes, although rarely, the presence of antisperm antibodies to sperm in the cervical mucus can lead to infertility; in other words, a woman develops specific immunity against male germ cells.
For this type of infertility, modern reproductology offers artificial insemination, in which sperm are artificially introduced directly into the uterine cavity, without contacting the cervical mucus.
In other cases, specific immunity can be developed even against an embryo that has already attached, resulting in pregnancy ending in spontaneous miscarriage.
Age - after 35 years, the chances of conceiving decrease!
Nowadays, so-called “late births” have become popular, when the first child appears after 30 or even 35 years. However, at this age the possibility of getting pregnant is significantly reduced. The risk of having a baby with chromosomal abnormalities also increases. From a material point of view, it may not be bad that a woman gives birth when she is already mature. But nature has established the optimal age for the birth of the first child - 19-25 years. It is during this age period that strong, healthy children are most often born, and a woman quickly recovers after childbirth.
There are 3 reasons for age-related infertility:
- Decreased ovarian reserve
. At birth, a woman is given a certain number of eggs; when the reserve is exhausted, she becomes infertile. - High risk of recurrent miscarriages
. With age, toxins accumulate in the body, the immune system weakens, metabolism is disrupted, all this leads to disturbances in the formation of germ cells. Nature has laid down a program in which most of the embryos with abnormalities die in the very first stages and are born as miscarriages. The patient may not even know that heavy periods mean an early miscarriage. - Possibility of early menopause
. Every 10th woman experiences menopause before the age of 40.
Infertility treatment - tubo-peritoneal infertility
Therapy begins with the prescription of conservative methods, and treatment should be comprehensive and step-by-step. If there is functional tubal infertility, psychotherapy, sedative and antispasmodic drugs and anti-inflammatory treatment are indicated. At the same time, correction of hormonal changes is carried out. If an STI is detected, the prescription of antibiotics is indicated, taking into account the sensitivity of the identified pathogens to them, immunotherapy, as well as absorbable treatment: local in the form of tampons and hydrotubations and the prescription of biostimulants and enzymes (lidase, trypsin, Wobenzym), corticosteroids. Hydrotubation can be performed with antibiotics, enzymes and corticosteroids (hydrocortisone).
After a course of anti-inflammatory treatment, physiotherapeutic methods are prescribed:
- electrophoresis with iodine, magnesium and calcium, enzymes and biostimulants;
- ultraphonophoresis (using lidase, hyaluronidase, vitamin E in an oil solution);
- electrical stimulation of the uterus and appendages;
- irrigation of the vagina and cervix with hydrogen sulfide, radon, arsenic waters;
- massage of the uterus and appendages;
- mud applications.
3 months after the course of treatment, hysterosalpingography is repeated and the condition of the tubes is assessed. If obstruction of tubes or adhesions is detected, therapeutic laparoscopy is indicated, which in the postoperative period is supplemented with physiotherapeutic methods and drugs to stimulate ovulation. The following microsurgical operations are performed using laparoscopy:
- salpigolysis – eliminate kinks and curvatures of the tubes by separating the adhesions around them;
- fimbryolysis – the fimbriae of the tube are freed from adhesions;
- salpingostomatoplasty – a new hole is created in a tube with a closed ampullary end;
- salpignosalpingoanastamosis - removal of part of an obstructed tube followed by end-to-end stitching;
- transplantation of a tube if it is obstructed in the interstitial region into the uterus.
If peritoneal infertility (adhesive process) is detected, separation and coagulation of adhesions is performed. If concomitant pathology is detected (endometrioid lesions, subserous and interstitial myomatous nodes, ovarian cysts), it is eliminated. The chances of pregnancy after microsurgical treatment are 30–60%.
If fertility has not been restored within two years after conservative and surgical treatment, IVF is recommended.