Rehabilitation after an ectopic pregnancy is a complex and lengthy process. It is aimed at restoring not only the general health of a woman, but also her reproductive function.
- 1 What is ectopic pregnancy and what are the causes of its occurrence?
- 2 Therapeutic measures after termination of an ectopic pregnancy 2.1 Recommendations depending on the cause of the pathology
- 2.2 General recommendations
The duration of the recovery process and the effectiveness of the entire complex of rehabilitation measures will ultimately depend on how correctly the treatment is chosen and how accurately the patient follows the doctor’s instructions.
https://youtu.be/KIZ7_1pFgZc
Probability of subsequent pregnancies
Subsequent pregnancies are possible if you follow the recommendations during the recovery period. It is important to follow hygiene rules and take into account general recommendations:
- do not swim in open sources (staves, sea) for the first 3 months;
- Bathing is prohibited (shower only for the first month);
- physical activity is unacceptable;
- taking intravaginal medications without a doctor’s prescription;
- use tampons for the first 3–4 cycles.
If you follow all the recommendations, then if you have a second healthy tube, pregnancy will occur. The main thing is not to plan it before 9 months, ideally after 1.5 years.
The general prognosis for women who have undergone organ removal but have a second part is positive: this will not affect the likelihood of motherhood and quality of life. However, in most cases, the question is about preserving the life of a woman who could die at any moment from rupture and sepsis. Therefore, there is no choice.
Often, removal of the fallopian tube is the only chance to save life. In order to also preserve the ability to bear a child, it is necessary to contact an antenatal clinic at the first signs of pregnancy. In the early stages, ectopic pregnancy is a pathology that can be easily eliminated without removing the fallopian tube.
- hormonal levels have improved;
- the previous cyclicity of menstruation resumed;
- an ovary with a healthy tube was again able to release healthy eggs for fertilization.
If there is no fallopian tube, where does the egg go?
When both fallopian tubes are in place, they use fimbriae to capture the egg released from the ovary into the abdominal cavity and gradually move it into the uterus. It is also possible for a sperm to meet an egg in the tube and fertilize it. In the peritoneal cavity, the egg can exist for two days, after which it dies.
When a woman has one tube missing, the following options are possible:
- Ovulation will not occur, the follicles will begin their reverse development. This situation is most often observed against the background of hormonal imbalance.
- The egg will be released into the abdominal cavity, and after 2 days it will die and be destroyed in it.
- The egg will float around the abdominal cavity, can reach the tube that remains intact, and pass through it to the uterus.
Of course, it is much easier for fimbriae to capture the egg that is released by the ovary from the side of the healthy tube. If a woman has both appendages removed, the ovaries either undergo reverse development, or the egg will constantly die in the peritoneal cavity.
Complication after laparoscopy, ectopic pregnancy
To remove an incorrectly implanted fertilized egg, laparoscopy is used. This operation is performed using several punctures in the abdominal cavity, under the full supervision of a laparoscope. The surgeon sees the entire operation process on the monitor. For good visibility and the possibility of manipulation during the operation, gas is injected into the peritoneum. The surgeon cuts the fallopian tube, removes and removes the embryo, and cauterizes the vessels to stop bleeding. In such cases, the fallopian tube can be preserved; it will again restore all its functions. But there are cases that an ectopic pregnancy develops again after laparoscopy.
Contraindications to tubal laparoscopy
The fallopian tubes cannot be removed using the laparoscopic method if there are the following contraindications:
- Peritonitis.
- Rupture of the fallopian tube, accompanied by severe bleeding.
- Myocardial infarction, stroke.
- Cancer of the uterus and appendages.
- Obesity 3 and 4 degrees.
- Diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation.
If these contraindications are present, the woman undergoes laparotomy removal of the appendages.
Ectopic pregnancy after surgery
After laparoscopy, an ectopic pregnancy can develop if irreversible changes occur in the structure of the fallopian tube, hemorrhage or some other pathological processes. These processes can provoke ectopic pregnancy again after laparoscopy. In case of repeated ectopic pregnancy after laparoscopy, the fallopian tube is removed. The operation itself is low-traumatic; during the operation, the abdominal cavity is sanitized and cysts are removed, if any are found during examination. An ectopic pregnancy may recur after surgery. About fifty percent of women who had an ectopic pregnancy received a verdict after the operation - infertility. Compliance with all the doctor’s requirements and timely treatment gives a great chance of having a baby.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
The main cause of ectopic pregnancy is a change in the fallopian tubes caused by various inflammatory processes or their congenital underdevelopment (infantilism).
The first place among other diseases that disrupt the normal course of all processes associated with the onset of pregnancy is given to chronic salpingitis. This disease is nothing more than the process of formation of adhesions in the oviducts. And it is provoked by infections transmitted through sexual contact. The situation can be aggravated by artificial termination of pregnancy, surgical interventions previously performed in the pelvic organs, as well as various types of diseases of the reproductive system.
As for congenital malformations of the tubes, these include:
- Duplication of the fallopian tubes (this pathology can be observed on both sides or only on one);
- Underdevelopment of the fallopian tube;
- Agenesis (absence) of the fallopian tube;
- Pipe asymmetry;
- Excessive shortening/lengthening of pipes;
- The presence of additional blind passages in the fallopian tubes;
- Splitting of the lumen of the fallopian tube;
- Congenital obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
Read more Angioedema how to treat
Various tubal anomalies develop in girls even in the prenatal period and almost always through the indirect fault of the mother, who took medications prohibited for pregnant women during pregnancy, was exposed to the negative effects of harmful factors (for example, radiation exposure), suffered infectious diseases of the reproductive system, etc.
In addition, the following can lead to pathology:
- Diseases of the endocrine system, as a result of which the peristalsis of the tubes is disrupted;
- Taking separate contraceptives;
- In vitro fertilization: according to statistics, approximately every twentieth patient who has undergone the procedure of artificially introducing a fertilized egg into the uterine cavity is subsequently diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy due to the fact that the egg could penetrate slightly further than required;
- Disturbance of normal hormonal levels.
Factors that increase the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy are:
- Smoking (since it can impair the peristalsis of the fallopian tubes and disrupt the process of normal movement of the fertilized egg through them);
- Wearing too tight and synthetic underwear;
- Frequent hypothermia;
- Age (in women over 35 years of age, cases of ectopic pregnancy are diagnosed more often than in younger patients);
- The presence of tumors in the uterus or its appendages.
Discharge after ectopic pregnancy
Discharge with blood after an ectopic pregnancy indicates the onset of menstruation if twenty-five to thirty days have passed after the operation. If discharge after an ectopic pregnancy begins earlier, this indicates the onset of uterine bleeding. If there is no discharge after an ectopic pregnancy for more than a month, then a hormonal imbalance is possible. In these cases, an urgent visit to the doctor is required. If the discharge after an ectopic pregnancy has an unpleasant odor, a pasty state is an indicator of the presence of infection and examination is required.
Prognosis for future pregnancies
After removing one tube, the chance of getting pregnant is 80%. The presence of the following factors reduces the likelihood of pregnancy:
- inflammation;
- endometritis;
- adhesions;
- low muscle activity of the uterus;
- infantile cilia in the uterus (poor movement);
- hormonal imbalance;
- stress;
- active physical activity in the first 6 months;
- non-compliance with recovery recommendations.
If you follow the rules of rehabilitation, then even after an ectopic pregnancy the probability of conceiving a child is high, since the egg will be released by a healthy organ during ovulation.
The consequences of removing an ectopic pregnancy partly depend on the woman herself, who understands the importance of such a process as rehabilitation and complies with all recovery requirements. If a pathology of fetal development is detected in the early stages, the zygote can be evacuated without removing part of the reproductive organ.
Sex after an ectopic pregnancy
Sex after an ectopic pregnancy is contraindicated for several weeks after surgery. This is the time during which a woman’s body must recover after surgery and hormonal levels normalize. If sex after an ectopic pregnancy causes pain in a woman, then she should go to the clinic for examination. Pain may indicate postoperative complications or an inflammatory process. Rehabilitation after an ectopic pregnancy requires not only a responsible attitude towards oneself on the part of the woman, but also a reverent attitude of the man towards the woman. After a while, sex after an ectopic pregnancy will not give the woman any unpleasant sensations, and the body’s previous state will be restored. Sex after an ectopic pregnancy may be allowed earlier, it all depends on your state of health and the complexity of the operation.
When can you plan to conceive after surgery?
After removal of one fallopian tube, a woman will be able to become pregnant on her own in 56-61% of cases. Moreover, this does not depend on the type of surgical intervention. Doctors indicate that you need to plan a pregnancy no earlier than six months after the operation. A number of experts recommend that a woman wait 1-2 years while taking oral contraceptives. During this time, it will be possible to normalize the functioning of the neuroendocrine system and the body will be ready to bear a child.
After removal of the fallopian tubes, 42% of patients develop infertility, and in 40% of cases, the ovaries stop working with their previous strength. Moreover, the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy increases 10 times. Therefore, IVF is the only method that allows a woman to conceive a child after removal of the fallopian tubes.
Is it possible to give birth after an ectopic pregnancy?
It is possible to give birth after an ectopic pregnancy. Rehabilitation after an ectopic pregnancy involves preparing the woman’s body for the next pregnancy. Before a woman can give birth again after an ectopic pregnancy, she must be examined after surgery to determine the cause of this complication. The woman will be prescribed to undergo examination for infections, a study to detect adhesions and inflammatory processes of internal organs after an ectopic pregnancy. It is possible to give birth after an ectopic pregnancy if there are no serious complications, subject to the doctor’s recommendations and certain rules. Pregnancy after surgery should be planned within a year. It is possible to give birth after an ectopic pregnancy using IVF. If a woman had her fallopian tubes removed during surgery or had an ovarian resection, or pregnancy does not occur in the usual way, IVF is a solution for such women.
Rehabilitation after an ectopic pregnancy can be lengthy, depending on the cause of the complicated pregnancy. Very often, fibroids and endometrial diseases become the cause of ectopic ectopia. One of the causes of ectopic pregnancy may be untreated sexually transmitted infections, hepatitis and viruses. Rehabilitation after an ectopic pregnancy is a process of finding the cause of the complication, its treatment and overall restoration of health.
Sex after an ectopic pregnancy is contraindicated for several weeks after surgery. This is the time during which a woman’s body must recover after surgery and hormonal levels normalize. If sex after an ectopic pregnancy causes pain in a woman, then she should go to the clinic for examination. Pain may indicate postoperative complications or an inflammatory process. Rehabilitation after an ectopic pregnancy requires not only a responsible attitude towards oneself on the part of the woman, but also a reverent attitude of the man towards the woman. After a while, sex after an ectopic pregnancy will not give the woman any unpleasant sensations, and the body’s previous state will be restored. Sex after an ectopic pregnancy may be allowed earlier, it all depends on your state of health and the complexity of the operation.
Rehabilitation
The general recovery period includes a time period that is determined after the operation and until the patient’s complete recovery. And it can be conditionally divided into several stages:
Primary rehabilitation after an ectopic pregnancy can last from several days to two weeks. This period includes stopping bleeding, relieving pain syndromes, preventing the development of infections and disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, and the beginning of scarring of the suture.
After this, the patient is discharged, and further recovery at home, the prohibitions and recommendations of the doctor will need to be strictly followed, which will allow for a faster recovery.
For each woman, recovery occurs differently; if there were no complications, then this period may take about a month, otherwise up to one and a half.
The first few days of the postoperative period are considered the most important, as it includes: drug therapy, pain relief, normalization of blood circulation and restoration of intestinal motility. During this period, an important component is proper nutrition, which includes light broths, pureed vegetables and non-carbonated drinks.
After discharge, restorative procedures should be continued according to the recommendations of the attending physician. This should include:
- It is mandatory to wear a bandage that will provide abdominal support. It should be selected in such a way that it covers the seam on all sides by at least 15 mm.
- You should not lift weights or perform physical activity for 60 days after surgery.
- It is prohibited to visit baths, saunas, or swim in open water.
This should also include the rhetorical question of many women when it is possible to have sex after an ectopic pregnancy; on the advice of doctors, this is allowed only after two months after the operation.
The main reason for this ban is the possibility of infection, since not only the general immunity of the body is reduced, but also at the local level. Therefore, only the doctor is able to make his verdict on this matter, after the suture has completely healed.
Features of pregnancy planning after an ectopic pregnancy with tube removal
Pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy (if surgery was performed and one fallopian tube was removed) most often does not occur on the first or even on the second attempt. Still, the chances of becoming a mother after such an operation are halved, but the statistics do not apply to some women. Much depends on the woman’s health, preparation for subsequent pregnancy, and the patency of the remaining tube. But first things first.
Features of preparation for pregnancy after VB
The first thing doctors recommend to all women who have survived surgery is to protect themselves from pregnancy for about six months. Moreover, it is recommended to use birth control pills - oral contraceptives - as protection. Firstly, this guarantees almost a 100th result (pregnancy will not occur; today oral contraceptives are the most reliable means of contraception, except for the Mirena coil, but you should not use the coil). Secondly, there is evidence that after “rest” the ovaries begin to work with redoubled force - pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy and the removal of one tube can occur sooner. And you can take modern low-dose oral contraceptives without interruptions for as long as you need, of course, if there are no contraindications to taking them.
Different birth control pills may be prescribed to different women. There is a myth that the choice depends on the individual hormonal background of the woman. However, it is not. The first choice drugs are combined oral contraceptives with a dosage of ethinyl estradiol - 20-30 mcg. These include Logest, Novinet, Janine, Lindenet 20 (and 30), Yarina, etc. You can choose depending on your financial capabilities. The price of tablets can vary quite a lot. Let's say, a pack of Lindenet 20 (30) costs about 300 rubles, and its analogue Logest (the composition is the same, but the manufacturers are different) is 2-2.5 times more expensive. It is recommended to start taking the pills at the beginning of the next menstrual cycle after the operation (you cannot make love for 1 month after the operation).
Those planning a pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy should undergo a full examination. There is only one fallopian tube left, which means everything needs to be done to prevent the situation from happening again. This means that before active planning, it is necessary for both partners to undergo all tests in order to detect possible sexually transmitted infections. Everyone needs to do this. Even those who have previously undergone similar tests or are confident that they are healthy. There are many so-called hidden infections that are not always detected the first time by tests. Meanwhile, pathogenic bacteria provoke inflammatory processes in the pipes, which leads to the formation of adhesions. And adhesions in the tubes in many cases prevent the fertilized egg from moving into the uterus for implantation, and it is forced to implant right there, in the tube, ovary or in the abdominal cavity. Thus, an ectopic pregnancy may occur again after an ectopic pregnancy and removal of one tube.
In addition, it is necessary to undergo another important examination - to check the patency of the fallopian tubes, or rather the one remaining one. This procedure is familiar to many women and is called hysterosalpingography (HSG). The procedure is not very pleasant, but it is not painful either, but some sensitive or simply restless women may require pain relief. A thin flexible cannula is inserted into the cervix, through which a special aqueous solution is injected. It fills the uterus and fallopian tubes, after which the doctor takes several x-rays. This way you can clearly see whether there are adhesions in the pipe or not, whether it is passable or not. If yes, then intrauterine pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy is quite possible. If not, your doctor may recommend laparoscopy, a simple operation without incisions to cut through adhesions. But let's return to the HSG procedure. Many women notice after this procedure the appearance of such unpleasant things as thrush, and inflammatory processes in the area of the internal genital organs may occur, so HSG is not done without special indications. Most often, the surgeon who performed the operation for VD can tell you about the condition of the second fallopian tube. If he said that her condition is not important, you can immediately go for laparoscopy.
How to speed up conception with one fallopian tube
Many doctors claim that ovulation in healthy women occurs alternately in one ovary and then in the other. In reality, it turns out differently, one ovary “leads”. And the woman will be very lucky if this ovary is on the side where she still has the fallopian tube. Then pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy can occur without problems and very quickly, especially if the woman is still young - under 30 years old. If not, then you need to try to find out the day of ovulation in order to be sure to hit it, and thereby increase the chances of conception. There are several ways to track ovulation. We'll look at them briefly.
1. Ovulation tests.
This method is suitable for those who are not too burdened with material resources, since one cycle of tests will require at least 5 pieces and it is not at all a fact that everything will work out right away. Ovulation test strips are very similar to pregnancy tests. As a rule, ovulation (the only day when conception can occur) occurs in the middle of the cycle. The most optimal days for the test can be determined as follows: you need to subtract 17 from the number of days in the cycle. For example, the cycle is 28 days. We subtract 17 and get 11. This means that tests need to be performed from 11 to 15 days of the MC, on average. But if, for example, the test turns out to be positive on the 12th day, then, as you understand, there is no point in continuing to be tested. The second stripe appears due to an increase in the content of luteinizing hormone. The test remains positive for up to 36 hours, and during this period, sexual intercourse in terms of possible conception will be most successful. It is advisable to perform the test at the same time, and it is even more reliable if it is done 2 times a day.
2.
A more budget-friendly option to speed up pregnancy after an ectopic and removal of one tube is
measuring basal temperature
. Mountains of literature have already been written about this. And although many modern doctors consider this method to be outdated, that is, uninformative, it is still worth a try. This method can be used not only as an independent method, but also as a supplement to existing ones. For example, you can very accurately determine the onset of ovulation using an ultrasound examination. But you will have to do it for several days in a row, which is not financially feasible for everyone. Therefore, you can use basal temperature to identify the desired day, and use an ultrasound to confirm or refute your doubts. But you can do without an ultrasound if the diagnosis of infertility has not yet been made, and there is a chance that pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy will occur quickly and easily.
3. Observation of your own feelings.
During ovulation, a woman may experience mild, aching pain in the area of the ovary where the egg has matured. Sometimes pain is felt in the lower abdomen. Clear, “stretchy”, odorless vaginal discharge appears. Many women note an increase in sexual desire.
There are many folk ways to help the egg mature. For example, after sexual intercourse, stand in the “birch tree” position so that the sperm reaches the uterus faster. You shouldn’t get up immediately after an act of love; it’s better to lie down with your pelvis raised, and you definitely shouldn’t take a bath. Some women claim that some herbal infusions also help to become a mother faster, for example, sage infusion. But all this has not been scientifically proven.
Many people fail to conceive a child due to a serious psychological barrier. This is understandable, because there is at least a 5% chance that a pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy will again be pathological, and if the tube has to be removed again, then there will be no chance of becoming a mother in a “natural” way, without medical intervention. An experienced psychologist with a medical education can help get rid of fears. Hope should also be given by the fact that if the fallopian tube is preserved, the likelihood of VD occurring is higher. And for those who have one fallopian tube, but it is definitely passable, the chances of a repetition of the situation are negligible. You can read the stories of women who have already experienced a similar situation and after that successfully became mothers. It wouldn't hurt to go on a relaxing vacation. The main thing is to set yourself up for the good and not even think about the fact that you may fail again.
If you can't get pregnant on your own
No matter how good everything is, a certain proportion of women who have undergone this operation cannot get pregnant on their own. You need to start looking for other solutions after a year of unprotected sexual activity, if conception has not occurred. In this case, a diagnosis of infertility is already made.
But the female gender is not always “to blame” for the absence of children. And this must be taken into account. The spouse must also be examined. And if conception does not occur due to some “male” pathology, such as too few live sperm capable of fertilization, the ICSI procedure can be performed. What it is? In short, the procedure is similar to IVF, but with ICSI, active sperm can be isolated from a man’s sperm, even if they are present in minimal quantities. Both IVF and ICSI are practically the only ways (not counting surrogacy) to continue the birth for infertile couples. The presence or absence of fallopian tubes no longer plays any role here. The eggs are taken directly from the woman's ovary and fertilized in vitro.
As you can see, it's not all bad. And pregnancy after an ectopic and removal of one tube is possible. You just need to be thoroughly examined, follow all the doctor’s instructions, monitor your health and well-being, and just that. believe that everything will definitely work out.
2.
A more budget-friendly option to speed up pregnancy after an ectopic and removal of one tube is
measuring basal temperature
. Mountains of literature have already been written about this. And although many modern doctors consider this method to be outdated, that is, uninformative, it is still worth a try. This method can be used not only as an independent method, but also as a supplement to existing ones. For example, you can very accurately determine the onset of ovulation using an ultrasound examination. But you will have to do it for several days in a row, which is not financially feasible for everyone. Therefore, you can use basal temperature to identify the desired day, and use an ultrasound to confirm or refute your doubts. But you can do without an ultrasound if the diagnosis of infertility has not yet been made, and there is a chance that pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy will occur quickly and easily.
Ectopic pregnancy: symptoms and consequences
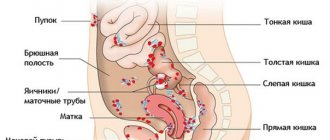
The uterus is the only organ in which bearing a child is possible. If the fertilized egg is attached outside its cavity (in the fallopian tube, on the cervix, in the abdominal cavity or ovaries), a successful completion of the pregnancy is excluded, and the child cannot be saved.
Moreover, the woman’s life and health are at risk, because the consequences of the pathology are:
- rupture of the tissue of the tube or other organ into which the egg was implanted;
- internal bleeding;
- peritonitis;
- development of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs with the formation of adhesions and scars;
- infertility;
- in the worst case scenario, death.
Sometimes, in order to save a woman’s life if an ectopic pregnancy is detected late, doctors have to remove the fallopian tube, which reduces the chances of conception in the future.
This is why every woman should be attentive to her condition after the test showed 2 coveted stripes. This is especially true for expectant mothers who have already encountered a dangerous diagnosis in the past - the chances of the pathology reoccurring are very high.
Can I get my period during an ectopic pregnancy? The answer is negative, since even when the fertilized egg is implanted outside the uterine cavity, characteristic changes occur in the body designed to create optimal conditions for the development of the embryo.
First of all, the active production of progesterone begins, inhibiting the cycle. However, with an ectopic pregnancy, there may be a discharge similar to menstruation.
They are one of the signs of a dangerous pathology and cause particular concern in combination with the following symptoms:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, intensifying when walking and turning the body;
- weakness, fainting;
- dizziness;
- faint second line on the test.
Along with these signs, a woman may experience all the symptoms of a normal pregnancy:
- swelling of the mammary glands;
- soreness and darkening of the nipples;
- change in taste preferences;
- reaction to odors, etc. Read more about the first signs of pregnancy→
Doctors detect ectopic pregnancy through ultrasound examination (at 6-7 weeks, the egg in the uterus is visualized through the abdominal wall, at 4-5 weeks - using a vaginal sensor) and tests for the content of hCG in the blood (concerns are caused by the discrepancy between the indicators and the period being too slow). their height).
If you notice drops of blood on your underwear in the first trimester of pregnancy, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Often, discharge that resembles menstruation is not a sign of an ectopic pregnancy, but is a variant of the norm or indicates less serious pathologies, such as:
- Implantation bleeding is scanty discharge that occurs 10-14 days after conception and lasts a maximum of 1-2 days. Their cause is slight damage to the vessels of the uterus as a result of the fertilized egg being fixed in its mucosa.
- Erosion that existed before conception or formed under the influence of hormonal changes. During pregnancy, it may bleed, which is sometimes a symptom of its enlargement or the development of an inflammatory process in the pelvis - in any case, a doctor’s examination is necessary, but the prognosis for a successful outcome is great. Read more about erosion during pregnancy and planning→
- Trauma to the vagina - for example, as a result of sexual intercourse or examination in a gynecological chair.
- Menstrual-like discharge in the first months, associated with the habit of the body: there are known cases of “red pregnancy”, when in the first trimester, on the usual days of the cycle, women experience bleeding (most often, this is an inherited feature). The phenomenon is explained by the body’s peculiar adjustment to a decrease in the amount of hormones produced after fertilization of the egg has not occurred, and in rare cases, every 4 weeks after conception, out of habit, the hormonal background changes slightly, but this is not the norm, but a threat of miscarriage.
Mechanism of development of the condition
The main difference between an ectopic and a normal pregnancy is the incorrect location of the embryo. It determines all other non-compliances with the norm. But at first everything happens as always:
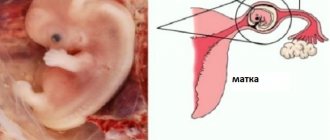
Embryo in the fallopian tube during ectopic pregnancy
A delay in menstruation during an ectopic pregnancy can be up to 14 days. If we consider that all other manifestations are similar to the signs of the usual development of this position, a woman can independently determine it. The only thing that is not available at the moment is identifying the location of the fertilized egg.
The only thing that can be seen clearly and differs from the normally proceeding process is a delay in menstruation, the test is negative, an ectopic pregnancy at this stage can “deceive” him. HCG, on the basis of which the pharmaceutical product works, will appear in the blood a week later than if the condition develops correctly. And its level can be reduced compared to normal.
But you cannot rely on these signs, since they exist even in the absence of an “interesting situation.” And yet, a barely visible second line on the test should convince a woman to listen more carefully to what is happening in her body.
Treatment
Rehabilitation after termination of an ectopic pregnancy is long and requires restoration of body processes due to removal of the tube. You need to see a doctor regularly. He will issue a sick leave certificate, tell you what medications are prescribed and what you can eat.
Antibiotic therapy
Treatment after termination of an ectopic pregnancy includes the use of medications. They are necessary because surgical interventions are fraught with inflammation and bacterial infections. Medicines will help the body recover in the postoperative period after an ectopic pregnancy and prevent complications during rehabilitation.
A wide range of medications are used - Metronidazole, Cefuroxime, Tienam. Drugs after tube removal for ectopic pregnancy should only be prescribed by a gynecologist. Self-medication will harm the body or be useless.
The duration of the course is determined after the test results. Antibiotics will prevent the development of infectious and inflammatory pathologies in the pelvic organs. The intensity of treatment depends on your health status and complications.
Hydrotubation of the fallopian tubes
Hydrotubation during rehabilitation
The procedure involves introducing a special liquid into the pipes. Hydrotubation during recovery after an ectopic pregnancy allows you to determine the patency of the tubal lumens. Using manipulations, the doctor identifies the presence of inflammation or adhesions.
Hydrotubation during rehabilitation is allowed to be done only after vaginal smears to ensure the absence of pathogenic microflora. In addition to liquid, medications are injected into the penis to prevent bacterial infection. But after the procedure, it is possible that the pipes will become overstretched, which will reduce their performance.
Ectopic and menstruation: does this happen?
Since no woman is immune from such a development of events after conception, everyone should know whether menstruation can occur during an ectopic pregnancy. After all, it is thanks to this sign that it is detected at an early stage, without waiting for complications that could pose a danger to life or reduce subsequent chances of conception.
The threat is created by severe bleeding, which opens after a fallopian tube ruptures. And difficulties with a new pregnancy arise after its forced removal, which is necessary to save a life.
Whether menstruation occurs during an ectopic pregnancy is determined by the processes occurring in connection with its presence. The amount of progesterone that holds the lining of the uterus in place is quite high. But since its cavity is empty, some endometrial cells can separate and come out.
Whether menstruation occurs during an ectopic pregnancy also depends on the woman’s general condition. Hormone deficiency, often observed during its normal course, also occurs with tubal. It is also capable of causing discharge when it should not occur.
Menstruation during ectopic pregnancy
Removal of fallopian tubes: progress of the operation, consequences for the body and rehabilitation
Quite often, young women, for one reason or another, undergo removal of one fallopian tube and, somewhat less frequently, both. The total number of such patients ranges from 3 to 12%. Among many, including doctors, there is an opinion that the fallopian tubes serve only as a “conductor” for the egg, and therefore their removal in no way can affect the general condition of the body.
At the same time, in various scientific and practical works, attention is increasingly drawn to the fact that among women with various menstrual cycle disorders and other disorders, a large number of those who have undergone such surgical treatment are identified.
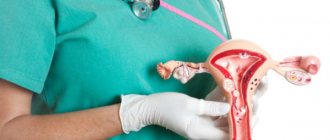
Salpingectomy (or tubectomy) is an operation that involves the complete removal of the fallopian tube. It can be one or two-sided and carried out on an emergency or planned basis. Salpingectomy is indicated:
- For ectopic pregnancy, accompanied by rupture of the fallopian tube and intra-abdominal bleeding.
- In case of undisturbed tubal pregnancy, which cannot be resolved conservatively when the diameter of the ovum is more than 30 mm. Conservative methods are used if a woman wants to maintain the possibility of natural conception and pregnancy in the future. They involve pushing the fertilized egg into the ampullary part or applying a salpingostomy (communication with the abdominal cavity).
- In cases of bleeding after unsuccessful salpingostomy.
- With an undisturbed but repeated ectopic pregnancy in the same fallopian tube.
- In cases of long-term salpingitis and/or salpingoophoritis (adnexitis) that is not amenable to conservative treatment, leading to significant changes in the tube, as a result of which it becomes functionally unpromising.
- For purulent inflammation (pyosalpinx).
- In the presence of one- or two-sided hydrosalpinx (accumulation of a significant amount of fluid). Infertility is often a consequence of this disease. Liquid accumulates in the pipes, as a rule, due to a chronic, periodically worsening inflammatory process in them.
- In cases of planning in vitro fertilization (IVF). Removal of the fallopian tubes before IVF is due to the fact that otherwise there is a high risk of its ineffectiveness. This is explained by the possibility of reverse flow of inflammatory fluid from them into the uterine cavity and mechanical “washing away” of the embryo during implantation. In addition, hydrosalpinx fluid containing microorganisms, products of their decay and vital activity, inflammatory components, especially during the period of exacerbation of salpingitis at the stage of embryo transfer, have a toxic effect on the endometrium and the embryo. Even when a fertilized egg is implanted and pregnancy develops, there remains a very high risk of spontaneous abortion. Therefore, if a woman has hydrosalpinx of significant size, existing for more than six months, it is recommended to undergo IVF after removal of the fallopian tubes.
- In case of significant adhesions in the pelvis involving the fallopian tube.
- During hysterectomy for tumors - multiple fibroids, uterine fibroids of significant size, malignant tumor of the ovary, body or cervix.
Diagnostic laparoscopy provides great assistance in deciding on the choice of treatment method and the need for salpingectomy.
Laparoscopic method of removal of fallopian tubes
Surgical treatment is carried out laparoscopically or laparotomically. Laparoscopic salpingectomy can be performed in all cases (except for intra-abdominal bleeding) if the appropriate equipment is available and the gynecological surgeon is familiar with this method.
The advantages of laparoscopic surgery compared to laparotomy are small incisions (up to 1.5 cm) and less trauma. In addition, the postoperative period is easier, and rehabilitation after removal of the fallopian tubes using the laparoscopic method is much shorter in duration.
An ectopic pregnancy that occurs as a rupture is usually accompanied by heavy bleeding into the pelvic cavity. Blood loss can reach a significant volume, leading to hemorrhagic shock and other serious negative consequences.
This pregnancy complication requires emergency surgery. The only surgical method in this case is laparotomy salpingectomy with simultaneous intensive infusion-transfusion therapy. Often only such emergency measures can save a woman’s life.
The operation is performed under anesthesia in several main stages:
- Providing access. Access to the pelvic organs is provided by a transverse above the pubis (according to Pfannenstiel) or a longitudinal inferomedian (below the navel) incision of the anterior abdominal wall (laparotomy).
- Evacuation into special vials of blood spilled into the abdominal cavity (in the absence of foci of infection), for the anesthesiologist to perform a blood transfusion (blood transfusion) during the operation.
- Removal of the uterus with appendages into the wound and identification of the source of bleeding.
- Applying several clamps to the isthmic region (at the very corner of the uterus) and to the mesosalpinx (mesentery), after which the bleeding stops.
- Isolating and cutting off the pipe.
- Carrying out sanitation of the abdominal cavity and layer-by-layer suturing.
The principles of surgical treatment using the laparoscopic method are the same, with the exception of collecting blood in the abdominal cavity and transfusing it to the patient.
For certain indications, instead of salpingectomy, resection of the fallopian tubes is performed, that is, their partial (segmental) removal. This is possible with:
- adhesive process in the pelvis involving the latter, but in a very limited area;
- with a developing but undisturbed ectopic pregnancy (without rupture of the fallopian tube);
- in the presence of a benign tumor formation localized in one of the uterine angles, as well as in cases of technical difficulty in performing salpingectomy.
How to suspect a tubal pregnancy?
Despite the initial similarity with the usual “interesting situation,” differences appear soon enough. So, the condition is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Menstruation or similar discharge appears intermittently, with varying intensity, color and consistency;
- The hCG volume is lower than usual at this time;
- Feeling dizzy, low blood pressure;
- The stomach hurts in the lateral part, the sensations increase;
- Body temperature may be elevated.
It is useful to learn how to distinguish an ectopic pregnancy from a period, keeping in mind the problems it brings:
- Menstrual pain gradually subsides, but with abnormal localization of the fertilized egg, this sensation increases. An ectopic pregnancy makes it stronger in the area where the embryo is stuck;
- Discharge during menstruation is more uniform and comparable to that observed in the previous cycle. They last 3-7 days. Discharge during an ectopic pregnancy is often brown, spotting or with clots, and may look like coffee grounds. They are characterized by intermittency, a longer duration, even when there is not so much daub;
- Unpleasant sensations in the chest disappear with the onset of menstruation, the tissues become soft, and soreness goes away. With tubal pregnancy, all signs remain and may intensify;
- On critical days, appetite usually does not suffer, but a craving for sweets appears. Menstruation during an ectopic pregnancy is accompanied by an aversion to food and sometimes the inability to take a sip of water. Or there is another extreme - you want to try something that is not eaten;
- Menstruation comes on schedule. For discharge caused by ectopic pregnancy, there is sometimes no periodicity; it may occur with a delay. But sometimes they begin according to the schedule of menstruation, which makes it difficult to understand what is happening.
We recommend reading the article that talks about the possibility of menstruation during pregnancy. You will learn about the dangers of spotting, when there is a threat of miscarriage and if necessary, see a doctor.
What is menstruation like?
Strictly speaking, this discharge during an ectopic pregnancy is not menstruation. But leaving the genital tract can lead to an erroneous interpretation of what is happening, which can waste time. And this is fraught with more complex and traumatic treatment.
If you know what periods are like during pregnancy, measures to eliminate it can be taken on time, preserving all organs, and therefore the opportunity to give birth in the future. Modern doctors have the means to clean out the fertilized egg, leaving the fallopian tube intact.
Menstruation can have different appearances. At the same time, they have a certain set of characteristics that distinguish them:
- Scanty discharge. They are observed when the fertilized egg is separated from the walls of the fallopian tube. This is the best outcome in this situation, but it does not happen in all cases. The same is true for menstruation in early ectopic pregnancy, when the embryo is still implanting in the tube. Its walls are injured, blood vessels burst, which causes a slight bruise with pain.
- Intense discharge. Heavy periods during an ectopic pregnancy are caused by the implantation of the fertilized egg in the area of the cervix of the organ. There are many blood vessels there that are damaged. The discharge literally pours out as the embryo grows, injuring an increasingly wider area of the organ. They last for a long time, causing pain in the suprapubic part of the abdomen and side, and rapid loss of strength.
- Uneven discharge. Ectopic pregnancy and periods with clots are also often observed phenomena. Along with the blood, endometrial tissue, particles of the walls of the fallopian tube or fertilized egg may come out.
Here it is no longer possible to do without an operation to remove the tube, but the danger to life remains after it, since blood entering the abdominal cavity can cause sepsis.
Considering all the threats, there is no need to doubt whether menstruation is possible during an ectopic pregnancy. If there are all the signs, including discharge, you need to hurry to the gynecologist, and not wait for them to intensify.
Do menstruation occur during an ectopic pregnancy: the nature of the discharge
So, it turned out that during an ectopic pregnancy, menstruation can occur - more precisely, discharge, which can be mistaken for menstruation.
How to recognize an alarming symptom? And what can cause such bleeding? Every woman should know about this - no one is immune from the occurrence of pathology.
There are a number of reasons why menstruation may occur during an ectopic pregnancy:
- Independent rejection of the fertilized egg is the most successful option for the development of pathology, characterized by scanty discharge and nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which can radiate to the rectum.
- Implantation of a fertilized egg into the cervical part of the uterus - this segment of the organ is penetrated by a huge number of blood vessels that are damaged during the implantation of the fertilized egg, usually provoking heavy bleeding, which sometimes in itself poses a threat to the woman’s life and simply cannot go unnoticed.
- Rupture of the fallopian tube - such bleeding, in the absence of timely treatment, is guaranteed to occur by the end of the first trimester or earlier, with a tubal ectopic pregnancy; the pathology is accompanied by increasing sharp pain and discharge. At this point, the clock is ticking, and the woman needs emergency medical care.
- Stretching and rupture of tissues of an organ not intended for bearing a child - discharge in this case is easy to distinguish from regular menstruation. They occur at uncharacteristic times and are usually dark brownish in color and have an atypical consistency.
- Rupture of the wall of the fertilized egg with its subsequent release is also a fairly favorable outcome of the pathology, accompanied by dark brown discharge and nagging pain in the lower abdomen. To prevent the development of complications, curettage in a hospital setting is required.
It is important to remember: whether menstruation occurs during an ectopic pregnancy or not, a woman needs monitoring and intervention from specialists.
Menstruation after treatment
An ectopic pregnancy does not resolve on its own. Depending on the degree of its development, it is possible to remove the fertilized egg laparoscopically or using a special drug; in the worst case, the woman loses one of the fallopian tubes.
Naturally, she is worried about what and when her periods will be after an ectopic pregnancy. After all, doctors try to preserve the chance of becoming a mother whenever possible.
Cycle recovery
Laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy
The most burning question: when will your period start after an ectopic pregnancy? Many are in a hurry to try again, because they are sure that time is working against them in this regard. This is a big mistake, the body needs rest and time to recover.
It is also necessary to find out the reasons for improper attachment of the fertilized egg, so that in the future they do not interfere and do not cause a similar situation again. The second tubal localization of the embryo will reduce the chances of having a child.
For some, the first period after an ectopic pregnancy occurs immediately after surgery, within a day or two. This can be regarded in two ways, as it is caused by different reasons:
- Rapid restoration of the reproductive system;
- Hormonal imbalance that provoked uterine bleeding.
The last option is the most likely. Doctors do not consider it something dangerous; rather, they perceive it as cleansing the uterus from an overgrown layer of mucous cells. But the process is always monitored, and if necessary, hemostatic drugs are prescribed.
For the majority of those operated on, menstruation occurs 25-30 days after the intervention. This is the standard cycle size, indicating the good ability of the reproductive organs to recover.
At the rehabilitation stage, the woman’s behavior is important; she needs to monitor her own regimen, minimize physical activity, avoid taking a bath, limiting herself to a shower. Sex should also be moderate and accompanied by protection.
Lack of menstruation
A delay in menstruation after a problem is also a likely occurrence. It can be caused by several circumstances:
- Hormonal disorders. They can be observed even before pregnancy and cause its incorrect development. After treatment, the problem can worsen, as other factors come into play (nervous tension, anesthesia, medications);
- Stress. The very fact of the ectopic location of the ovum can be a serious shock for a woman who wants to become a mother. There is also increased anxiety associated with surgical intervention and fear of the inability to have a child in the future;
- The complexity of the treatment. The level of trauma to the reproductive organs, and therefore the speed of restoration of their functions, depends on it. The more severe the intervention, the more likely and longer the delay will be.
Absence of menstruation for the above reasons is considered acceptable for up to 2 months. Further delay requires targeted elimination, that is, drug therapy.
We advise you to read the article about signs of pregnancy before your missed period. You will learn about the first symptoms, such as breast sensitivity, pain in the sacral area, problems with the digestive system, toxicosis and others.
Character of menstruation
Menstruation after surgery may change compared to what was recorded before. Since the “memory” of the reproductive system is long, it can be expressed in the nature of menstrual flow. However, difficulties with the cycle and the characteristics of menstruation are not always to blame for the operation.
The causes of problems of all kinds can be the same factors that led to the localization of the embryo in the fallopian tube or other inappropriate place in the abdominal cavity. These are chronic inflammation, hormonal deficiency, constant stress and gynecological diseases.
The first period after an ectopic pregnancy can provoke very noticeable sensations. This:
- Pain in the abdominal area. Its intensity depends on the level of intervention and the woman's ability to tolerate cramps. The pain is caused by the normal contractions of the uterus during menstruation, which radiate to the area of the fallopian tube. If it persists, adhesions may form in the tissues, adding to the discomfort. If the tube is removed, painful periods occur due to insufficiently restored tissues, to which vibrations are transmitted from the contraction of the smooth muscles of the organ;
- General weakness. The intervention takes place under anesthesia, which is necessary, but does not add strength to the woman. During menstruation, immunity decreases, due to hormonal imbalance, lethargy and drowsiness appear. After surgery and great emotional upheaval, they may intensify.
Even medical removal of the fertilized egg, which is possible in the early stages, requires “quarantine” for at least six months. For this purpose, oral contraceptives are prescribed, which are selected by a specialist.
Consequences of the operation
The uterus and fallopian tubes share common nerve fibers, blood and lymphatic vessels. In addition, the condition of the mammary glands and the neuroendocrine system as a whole depends on their work. Therefore, disruption of these connections negatively affects the functioning of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
Hormonal imbalance is one of the consequences of surgery to remove the fallopian tubes.
Women complain of symptoms such as:
- Headache and dizziness;
- Nervousness, irritability, tearfulness;
- Painful sensations in the heart area;
- Increased sweating;
- Rush of blood to the upper half of the body.
Symptoms tend to intensify before the next menstruation, and they do not bother all women (observed in approximately 42% of cases).
About 35% of patients notice menstrual irregularities 2-3 months after removal of the appendage. During an ultrasound, they are diagnosed with an enlarged ovary on the side where the fallopian tube was removed. Over time, it undergoes sclerotic changes, which is caused by disruption of the flow of lymph and blood.
At what stage does an ectopic pregnancy occur?
Approximately on the 13-15th day of the menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs - the release of a mature egg from the follicle, ovary and its entry into the fallopian tube, where fertilization often occurs within 1-2 days. Next, the egg moves towards the uterus within 4 days, which is facilitated by the following factors:
- contraction of the smooth muscles of the fallopian tube, occurring in one direction - towards the uterine cavity;
- movement of the cilia of the fallopian tube epithelium: they direct the fluid contained in the fallopian tubes, and with its current the egg is sent to the uterus;
- relaxation of the sphincter located at the border of the oviduct and uterus: normally it prevents the premature entry of the egg into the uterine cavity.
All these processes are stimulated under the influence of estrogens and progesterones. If the balance of these hormones in the blood is disturbed, premature release of the egg into the uterine cavity may occur.
At the same time, it is not able to penetrate the endometrium and dies, after which it leaves the mother’s body along with menstruation. If the movement of the fertilized egg slows down or certain obstacles appear on its path (adhesions prevent it, the sphincter does not work), it reaches a relatively large size while still inside the fallopian tube and, requiring nutrition, is implanted into its wall.
In this case, an ectopic or tubal pregnancy occurs, which occurs 2–6 days after fertilization of the egg or approximately 16–20 days of the menstrual cycle. In 95 out of 100 cases, an ectopic pregnancy is tubal, with the fertilized egg implanted in the wall of the oviduct. Much less often, it develops inside the ovary or in the abdominal cavity. Organs that are not intended for rapid enlargement (ovary, fallopian tube) are not able to withstand the active development and growth of the fertilized egg, as a result of which they begin to deform and bleed. During this period, a woman may observe bloody discharge from the genital tract.
Ovulation occurs approximately on days 13–15 of the menstrual cycle.
Further, if the pathology of conception is not identified and eliminated in time, a rupture of the fallopian tube occurs, followed by hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity. The condition is fraught with large blood losses and, in the absence of urgent treatment, the death of the woman. In some cases, it is not the fallopian tube that ruptures, but the membrane of the fertilized egg. In this case, the fertilized egg can be expelled either from the uterine cavity and leave the body naturally, or through the end of the fallopian tube enter the abdominal cavity. Both cases are called tubal abortion . Often, the process of rupture of the membrane of the fertilized egg is accompanied by pain and weakness, then the woman’s condition returns to normal. If the fertilized egg enters the uterine cavity, there is a risk of developing infectious diseases, so in most cases the woman undergoes curettage to remove the remnants of the fertilized egg from the uterus. In the abdominal cavity, internal bleeding and inflammation of the peritoneum are possible, to avoid which the fertilized egg is removed surgically.