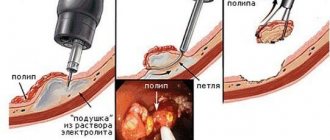
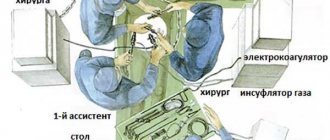
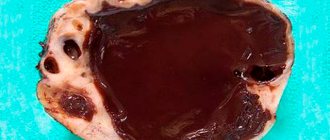
In case of severe inflammatory process, malignant neoplasms in the organs of the reproductive system, conservative therapy does not always give a positive result. The persistence of problematic elements can lead to infection of neighboring areas, the spread of metastases, and the growth of tumor cells into adjacent tissues. The optimal solution if indicated: laparoscopy or laparotomy, removal of the ovaries in women.
The consequences of resection of important glands have both a positive and negative side: a factor that negatively affects a woman’s health disappears, but at the same time problems with hormonal levels arise due to estrogen deficiency. It is important to know for what diseases the ovaries are removed, how to smooth out the consequences of the operation, and how HRT works.
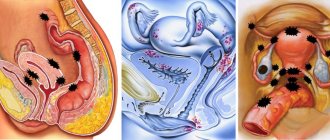
Types of ovarian cysts
In modern medicine, the following types of ovarian cysts are distinguished:
- Follicular;
- Corpus luteum cyst;
- Mucinous;
- Paraovarian;
- Dermoid;
- Endometrioid;
- Hemorrhagic.
Follicular cyst and corpus luteum cyst
Follicular cyst and corpus luteum cyst
Such cysts are formed during the normal functioning of the ovaries of a healthy woman. That is why cysts of this type are called functional. In young girls and women, in 90% of cases when a cyst is detected, it is the functional form that is diagnosed.
Functional cysts, as a rule, form on the left or right ovary and disappear on their own within a period of several weeks to several months. No treatment required. Follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts can reach sizes of 5 cm or more.
Mucinous cyst
most often consists of several chambers filled with mucous fluid. In some cases, they can reach large sizes and degenerate into a malignant ovarian tumor.
Paraovarian cyst
appears from the appendage, located above the ovary and representing a single-chamber formation of a round or oval shape, which is filled with a clear liquid. Quite often, this tumor is diagnosed in women aged 20 to 40 years. In most cases, the ovary is not related to the pathological process.
Dermoid cyst
contains various derivatives of connective tissue (fat, nails, hair, teeth, etc.), parts of embryonic layers.
Endometrioid cyst (endometriotic)
is a blister filled with blood that forms on the ovary during endometriosis. In addition to the formation of ovarian cysts, endometriosis can also manifest itself as prolonged nagging or aching pain in the lower abdomen, extremely painful periods, and infertility.
Hemorrhagic cyst
formed through hemorrhage into a functional cyst. The main symptom by which this type of cyst is distinguished is a nagging, dull pain in the lower abdomen. If the cyst is in the left ovary, then the pain in the lower abdomen on the left side is more pronounced
https://youtu.be/Koq58mkDnN0
Reasons for spay removal in women
Removal of the ovaries is carried out for the following indications:
- uterine fibroids;
- ovarian cysts;
- endometriotic cysts in combination with adenomyosis;
- ovarian abscess;
- ovarian apoplexy;
- ectopic pregnancy in the organ;
- malignant tumors in the ovaries;
- polycystic ovary syndrome with severe sclerosis;
- massive endometriosis;
- purulent and inflammatory diseases of the ovaries without a tendency to improve with conservative treatment.
After 50 years, the indications for removal expand, as menopause has set in and the risk of malignancy of various tumors in the ovaries has increased.
Is it possible to remove ovaries at will?
It is impossible to remove the ovaries only at your own request. Technically, this operation fits the definition of sterilization, which is permitted in the Russian Federation for women over 35 years of age with at least two healthy children. But in these cases, tubal ligation is performed, preserving the ovaries. Removing an organ is a rather mutilating operation, which doctors cannot do only at the request of the woman.
In what cases are a woman’s ovaries removed for prevention?
Women's ovaries are removed as a preventive measure for cancer in cases where the woman is at increased risk of developing them. Currently, preventative spay removal is a controversial issue.
Many gynecologists advise women to do a genetic test for the BRCA-1 and BRCA-2 genes, which are associated with a high risk of developing breast and ovarian cancer. If these genes are detected, it is recommended to remove the ovaries and tubes, which will reduce the risk of developing pathology.
This must be done in the premenopausal period, 5 years before a close relative developed such a pathology. In the case of prophylactic ectomy, one must also take into account family history: it is usually aggravated in individuals from a high-risk group. For breast cancer, the ovaries are also removed as a preventative measure.
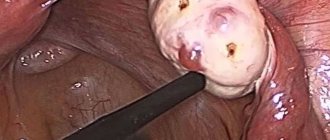
Therapeutic laparoscopic surgery
Therapeutic laparoscopic surgery is a gentle option for oophorectomy. The surgical technique is quite simple. In this case, the woman is put under anesthesia, and several small incisions are made on the anterior surface of the abdominal wall. Through them, all the instruments for removing the ovaries are inserted into the abdominal cavity.
The operation is performed under video endoscopic control. All vessels immediately coagulate, and the contents of the ovaries are sucked into the instruments and released out. This operation is suitable for removing cysts and benign formations. In the case of extensive inflammatory lesions, purulent foci and the presence of a malignant tumor, preference is given to open surgery.
When to remove in children and adolescents
Most often, the reason to remove an ovary in a child or adolescent is a malignant tumor of the ovary or surrounding tissues involving the ovary; this method is also indicated for purulent melting of organ tissue. Sometimes cysts develop, which leads to severe dysfunction that cannot be restored. In this case, an oophorectomy is also performed.
But such issues are always resolved collectively and taking into account all the risks and indications, since this will lead to a sharp disruption of puberty and the ability to give birth to a child.
Contraindications for carrying out
Contraindications for spay removal are:
- severe renal failure;
- decompensation of liver diseases;
- severe cardiovascular and respiratory failure;
- state of shock;
- bleeding disorders;
- pregnancy in the second trimester.
These restrictions apply mainly to open total operations with entry into the abdominal cavity through an incision. When it comes to laparoscopic operations, the contraindications include:
- severe obesity;
- a large number of adhesions in the abdominal cavity;
- hemophilia and other blood diseases;
- beginning peritonitis;
- acute salpingoophoritis;
- infectious diseases that developed less than two months before surgery.
If the patient has acute pathologies that threaten her life, for example, ovarian torsion or rupture of a tube/cyst, then emergency open surgery is resorted to, despite most restrictions. In the preoperative period, they try to stabilize all vital functions, but the operation is performed according to vital indications.
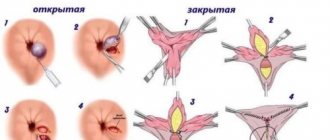
Operating technique: laparoscopy, laparotomy
Laparoscopy is performed on any day of the cycle, except for menstruation itself. The woman is given endotracheal anesthesia, the area around the navel is treated with an antiseptic on the operating table, the first incision is made and a trocar is inserted, then the abdominal cavity is penetrated. Then carbon dioxide is injected there to create an overview and allow manipulation. After this, a video laparoscope is inserted, which will transmit the image to the screen.
An incision for instruments is made in the right and left iliac regions. A scalpel and a coagulator will be inserted there and the removed organ will be removed through these holes. In the pelvic area, the ovary is grabbed, cut at the site of the intended ectomy and the stump is coagulated, and the ovary itself is sucked into the instrument tube. The entire operation is observed on the screen. Once the organ is removed, the entire cavity is examined, instruments are removed, and the incisions are removed.
During laparotomy, larger abdominal incisions are made in the lower abdomen, through which the ovaries are removed. With this method, there is more blood loss and the scale of the operation as a whole, but it is the method of choice for large formations in the ovaries or a suspected malignant process. During laparotomy, the woman is given spinal anesthesia or endotracheal anesthesia.
How long does it last
On average, laparoscopic surgery lasts about half an hour from the moment of immersion in anesthesia. Laparotomy may take longer - from an hour to an hour and a half. If other elements are found in the cavity, or there is a need to perform resection of the lesser omentum, the operation time may increase to several hours.
Watch this video about the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer:
Is it possible to avoid
Removal of the ovary can be avoided if the identified cyst or benign tumor can be removed or resected separately from the organ. Sometimes such tissue separation cannot be carried out, and they switch to complete removal.
Also, the ovary is not always removed for endometriosis and ectopic pregnancy. But the risk of oophorectomy is still present.
Diagnosis of ovarian cyst
When diagnosing an ovarian cyst, the following methods are used:
- determination of tumor markers-antigens (antigen-125);
- gynecological examination, during which the doctor can easily identify enlarged appendages;
- Ultrasound;
- a general blood and urine test to determine the presence of blood loss and inflammation;
- computed tomography gives a clearer picture of the tumor;
- Laparoscopy, in addition to diagnostics, makes it possible to perform surgery; it is used if a cyst rupture or torsion of the cyst stalk is suspected;
- pregnancy test to exclude ectopic pregnancy;
- puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix, through which the presence of blood or fluid in the abdominal cavity can be detected.
Indications for removal of an ovarian cyst
How to prepare for surgery
After confirming the diagnosis, the gynecologist gives a referral for laparoscopy or traditional surgery. The patient should know why the surgery is performed, what risks are associated with ovarian resection, and how the rehabilitation period goes. An important point is possible complications and side effects in the short postoperative period, during the first two years and throughout life.
When preparing for surgery, tests and studies are needed:
- blood type and Rh factor,
- exclusion of syphilis, AIDS,
- tomography, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity,
- X-rays of light,
- blood chemistry,
- test for tolerability of an anesthetic drug.
After studying the test data and ultrasound results, the gynecologist, together with the surgeon, decides whether surgery is necessary. It is important to choose the optimal method: laparotomy (open access to the affected organs) or laparoscopy (minimally invasive intervention). Doctors determine whether uterine resection is necessary or whether an important organ can be treated conservatively.
Indications for removal of an ovarian cyst
· Large cysts. The large size of the tumor provokes the risk of rupture of the cyst or ovary, which threatens the development of intra-abdominal bleeding and the formation of adhesions.
· Formation of a pedunculated cyst, which can cause torsion or rupture of the cyst, including removal of the ovary.
· Development of a cyst deep in the ovary, which can lead to disruption of its functions.
· Risk of degeneration of the cyst into a malignant formation.
· Formation of an endometrioid cyst (often develops against the background of endometriosis).
Complications after ovarian resection
Possible complications after ovarian resection include:
- complications associated with the use of anesthesia;
- accidental injury to internal organs when trocars were inserted;
- injury to blood vessels;
- influencing the body by the injected gas;
- the occurrence of infectious complications;
- development of hematoma or seroma;
- the occurrence of transient fever;
- the occurrence of adhesions in the pelvis;
- development of postoperative hernia.
Consequences of removing an ovarian cyst
are limited to two weeks of rehabilitation to a working condition and restoration of physical activity. Problems may arise with anesthesia, since everyone may have a nonspecific reaction to an anesthetic drug, so before surgery it is advisable to take tests to determine the optimal anesthetic.
The most harmful, but also rare, after laparoscopy are adhesions. Without the necessary supervision, adhesions that develop uncontrollably can lead to a number of diseases of the genital organs, and even infertility. This is a fairly common problem after any surgery, which once again prompts you to follow all the doctors’ instructions and undergo a course of drug treatment during rehabilitation.
Sex and sports after laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
are considered unacceptable loads. With regard to sexual intercourse and sports, the period of complete abstinence lasts one month. When restoring training, of course, you need to start with the least load in order to gradually master lost skills and control the limit of permissible stress. In particular, doctors prohibit lifting weights over three kilograms for the first three months after surgery, and in the next three months - no more than five.
Six months is the postoperative period, after which you need to return to your doctor for examination for complications. And if the doctor allows it, it will be possible to return to normal loads - for most women, such requirements, in principle, do not change their lifestyle, although athletes and workers in various industries or trade will have to limit themselves.
How is surgery performed?
In most cases, laparoscopic surgery is prescribed to remove the ovaries. The minimally invasive technique reduces the risk of blood loss and reduces the likelihood of infection. To insert miniature instruments into the pelvic cavity and peritoneum, small incisions are sufficient, each no more than 2 cm long. With this approach to oophorectomy, a woman is spared unsightly scars at the site of long incisions during traditional removal of the gonads. An important point: the postoperative period is less painful, shorter than with laparotomy, which allows the woman to quickly return to her normal life.
If, for medical reasons (malignant tumor process, organ prolapse, extensive endometriosis, numerous large fibroids), it is necessary to remove not only the ovaries, but also the uterus, then doctors choose the method of organ resection. Taking into account many factors, doctors perform laparoscopy or open abdominal surgery. Hysterectomy (resection of the uterus) is performed only if the woman’s life is at risk.
When removing the ovaries, general anesthesia is used. The organs are removed through a large abdominal incision or small incisions during laparoscopy.
Pregnancy after laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
is not only a safe solution - the operation itself is often performed to treat infertility. As mentioned above, a follicular cyst can cause infertility, since persistent cysts, despite regression and the absence of symptoms, prevent the development of new follicles with eggs inside them.
After laparoscopy, 85% of patients treated for infertility in this way become pregnant in the first year after surgery (20% in the first month, 20% in the period from three to five months, 30% after six months, and the remaining 15% wait nine months). months to a year).
Judging by how evenly the periods are distributed, it is clear that the period of pregnancy after infertility treatment is purely individual. If laparoscopy is done by dissecting adhesions, then the patient has a whole year to conceive, which is safe in terms of complications. If laparoscopy revealed other disorders besides the cyst, and treatment for gynecological problems was carried out, then the long-awaited pregnancy will most likely occur in the first few months.
Menstruation after laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
should occur on schedule, since the integrity of healthy tissue is not compromised during laparoscopy. However, any operation on the ovary can shift the menstrual cycle - this phenomenon is within the physiological norm.
After laparoscopy, mucous discharge may also appear. Such discharge sometimes occurs even immediately after surgery, and does not mean anything bad. There will be cause for alarm if this discharge turns yellow-green or brown-green - this means that an infection has appeared in the body. Usually this symptom is accompanied by characteristic weakness, drowsiness, fever, and discomfort.
In addition, white discharge may also be detected, which appears as a result of laparoscopy while taking antibiotics. They may be talking about developing thrush, or about another infection, to identify which they do a smear. In any case, medical supervision and timely medical assistance help to quickly cure diseases in the early stages.
Changes in the body
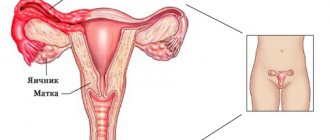
The importance of the ovaries for a woman’s body is very difficult to overestimate.
They are responsible for several vital functions:
- Vegetative. It is thanks to the ovaries that during puberty a girl acquires characteristic feminine features - roundness of shape, softness of skin, lack of hair on the face and body, and a gentle voice. The ovaries begin their work during the adolescent’s first menstruation and end after the onset of menopause.
- Hormonal. The ovaries produce in a certain mode two hormones necessary for the maturation of the egg and the subsequent maintenance of pregnancy - estrogen and progesterone.
- Childbearing. It is the ovaries that produce eggs ready for fertilization.
The normal functioning of all body systems gives a woman health, beauty, emotional stability and the ability to conceive and bear a healthy baby.
Reference.
When even one ovary is removed, the production of hormones is sharply disrupted, the number of ovulations decreases, appearance deteriorates and sudden mood swings appear.
If the doctor decides to remove the ovaries on both sides, the woman is completely deprived of the required estrogenic influence. She experiences early post-operative menopause, also called post-castration syndrome.
For women over 50 years of age who are already approaching the natural end of their menstrual cycles, the operation does not have such severe consequences as for young girls of childbearing age.
With the onset of natural, age-related menopause, the body gradually adapts to a decrease in hormone production and the cessation of egg ripening. After the operation, artificial menopause in women is usually extremely difficult.
Hormonal background
If only one ovary is removed, the body adapts after some time, transferring all functions to the second appendage, and the woman will experience only a short-term decrease in the amount of hormones released.
After some time, the background, supported by drug therapy, will be restored, and the woman will even be able to plan a pregnancy.
If both ovaries are removed, the production of estrogen either sharply decreases or disappears altogether, since the organ that produces them no longer exists.
Also, due to the removal of organs and the extinction of estrogen and progesterone production, unpleasant symptoms may appear such as:
- roughening of the skin, deterioration of hair condition;
- the appearance of acne and pimples on the face;
- sudden weight gain or loss;
- male pattern hair growth - the appearance of hairs on the chest, chin, cheeks;
- dryness of the mucous membrane, including the vagina;
- frequent colds.
To reduce the consequences of the operation, the patient must strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations, take prescribed hormonal medications (sometimes they can be replaced with herbal medicine and homeopathy), carefully monitor her appearance and pay great attention to nutrition and drinking regimen.
Psycho-emotional state
Hormonal deficiency leads to “post-castration syndrome” a few weeks after surgery.
Psychological instability appears - nervous breakdowns, tearfulness, increased anxiety and suspicion. Also, due to physiological reasons, there is a sharp decrease in sexual desire. If sexual intercourse does occur, it only gives the woman unpleasant sensations (pain, burning sensation and vaginal dryness). Against this background, even a slight disgust towards a previously loved partner may arise.
Against the background of hormonal disorders, aggravated by the difficult recovery period after the operation itself, depressive states, a complete lack of interest in life and constant breakdowns with loved ones may appear.
Reference.
Depression is exacerbated by the inability to quickly return to usual work or favorite activities, as a woman’s memory may sharply deteriorate, she becomes absent-minded and inattentive. Very often, after the operation, women refuse to drive a car or work with complex documents because they do not feel confident.
The consequences of removing one ovary are not so critical - as a rule, after a maximum of two months, the woman returns to a stable emotional state.
Diet after laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
should make the rehabilitation process as easy as possible for the reproductive system. Due to the fact that the ovaries are in close proximity to the intestines, their condition also depends on the well-being of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, the food consumed in the first three months should contain more fiber, which improves peristalsis and normalizes glucose levels. Accordingly, you should refrain from eating fatty, fried, very spicy and salty foods. Such food is too difficult to digest and, moreover, severely irritates the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
A special requirement for the diet after laparoscopy is a ban on drinking alcoholic beverages of any kind for one and a half months.
The diet consists of eating foods that are easy for the digestive tract (vegetables, fruits, boiled, stewed dietary meat) in small portions 10-12 times a day. When healing internal wounds, the body will greatly benefit from freshly squeezed juices full of vitamins, low-fat dairy products (kefir, milk), and cereal products (porridge). We remind you that, in connection with the likely prescription of a course of antibiotics, you must also forget about drinking alcohol for the first month and a half.
When should you worry?
Recommendations after removal of an ovarian cyst
- The temperature after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is more than 38⁰C and lasts longer than a day,
- There is severe pain in the lower abdomen,
- Pain in the suture area, especially accompanied by redness,
- Severe weakness, confusion, although more than 6 hours have passed since anesthesia.
- Whitish or yellowish-reddish discharge.
- In all these cases, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Pain after removal of appendages: vaginal prolapse
The cause of pain after removal of the appendages may also be vaginal prolapse. This condition is especially common in those patients who have had their uterus amputated. Then the painful sensations are weak, aching, reminiscent of discomfort from a foreign object inside. Accompanying symptoms include constipation or problems with urination.
Hormone replacement therapy, the dosage of which is calculated by the gynecologist, will help get rid of the feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. A woman must strictly adhere to the regimen, perform daily exercises that strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, and, if necessary, wear a medical pessary.
Feeling pain after removal of appendages can indicate both natural healing processes and the development of postoperative complications. Therefore, you should pay attention to the accompanying symptoms and accurately describe them when consulting a doctor. Following the instructions and recommendations of the rehabilitation period will help the body cope with the stress of surgery and maintain health and well-being for a long time.
source
Recommendations after removal of an ovarian cyst
Before discharge from the hospital, the attending physician must give recommendations after removal of the ovarian cyst. As a rule, they are as follows:
- You should not take a bath for fifteen days after surgery;
- After taking a shower, it is necessary to treat the seams with disinfectants;
- In the first month after surgery, it is not recommended to consume alcoholic beverages and heavy foods;
- Sexual rest during the first month after surgery;
- Planning pregnancy no earlier than three months after removal of the cyst;
- Periodic observation by a gynecologist until complete recovery.
Sex after surgery
Doctors recommend abstaining from intimacy for at least a week after laparoscopic surgery and two after laparotomy. Ideally, you should wait 3-4 weeks to avoid unwanted reactions such as infection, inflammation or bleeding.
In the future, after removal of both ovaries, you should pay close attention to the sensations: dry mucous membranes and pain often occur. You should use lubricants and periodically undergo vaginal swabs. It is also worth remembering that after such operations a woman’s natural protection decreases, so during unprotected sexual intercourse the risk of contracting an infection is much higher.
We recommend reading about how a cervical biopsy is performed for erosion. From the article you will learn why a biopsy of cervical erosion is prescribed, types of procedures, contraindications, and biopsy results. And here is more information about what you should know about hysteroresectoscopy of an endometrial polyp.
Spay removal always affects a woman's quality of life and causes many health consequences. This operation is performed according to strict indications and improves the prognosis for a woman’s life in a number of pathologies. It can also be performed in childhood if there are appropriate indications.
To compensate for the effect of oophorectomy in the postoperative period, women are offered hormone replacement therapy, as well as complex symptomatic treatment. After removal of the ovaries, many women give up and become depressed, which requires the attention and sensitivity of loved ones to help restore health and support the body.
Removal of an ovarian cyst during pregnancy
Removal of an ovarian cyst during pregnancy is carried out only in emergency cases: if there is a rupture or torsion of the cyst. Even in the presence of a benign formation, there is a certain risk for a pregnant woman: if the cyst grows to a large size, it may rupture or twist, which causes bleeding and poses a danger to bearing a child. Removal of a cyst during pregnancy is carried out using laparoscopy, and in cases where this is not possible, a lower-middle incision is made to create the most gentle conditions for the fetus. As for anesthesia, during pregnancy, for safety reasons, it is preferable to use local anesthesia. If this is not possible, then the operation is performed under regional anesthesia, and only as a last resort general anesthesia is used.
Pregnancy
After removing one of the ovaries, while fully maintaining all the functions of the second, it is quite possible to become pregnant naturally.
The eggs continue to mature, hormonal function weakens, but remains intact.
In some cases, in order to successfully conceive or maintain an existing pregnancy, the patient will be prescribed additional hormonal medications.
Reference.
After removal of two ovaries, natural pregnancy is impossible - the woman has no eggs.
But if the uterus and tubes are preserved, the patient may be offered to undergo an IVF procedure with the participation of a donor egg and partner’s sperm.
https://youtu.be/6NN7v5ykQAI