Ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy is a serious life-threatening pathology in which the fertilized egg implants and begins to develop outside the uterus. In gynecological practice, the attachment and division of a zygote, an egg fertilized by a sperm, is most often observed in the fallopian tube, but there are cases of its implantation to the wall of the ovary, the epithelium of the cervical canal or in its rudimentary horn. After IVF, it is possible that the fertilized egg may become fixed in the abdominal cavity, where it is attached to the intestines or any other organ. The causes of ectopic pregnancy are well known to obstetricians and gynecologists, but it is difficult to predict in advance where the egg fertilized by sperm will be fixed and to prevent the pathology.
It is very important to register and be observed by a gynecologist from the first weeks of gestation. Regular scheduled examinations and modern informative diagnostic methods, such as ultrasound, laparoscopy, make it possible to detect the presence of this pathology with high reliability and immediately perform surgery.
- Pathology of the structure or disease of the fallopian tubes
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
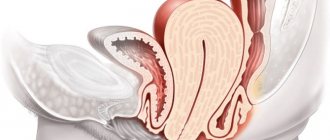
Every woman needs to know what an ectopic pregnancy is. This is the incorrect location of the fertilized egg when it does not develop in the wall of the uterus. The embryo attaches to the fallopian tube or penetrates the ovary and abdominal cavity. Less often, it descends from the uterus to its cervix.
Ectopic pregnancy
How is it happening?
Fertilization of the egg occurs in the fallopian tube. A zygote is formed, the product of the fusion of male and female reproductive cells, which is then, due to muscular contractions of the tube, transported to the uterus and implanted into its wall.
How an ectopic pregnancy occurs depends on the pathology that caused it. If the function of the fallopian tubes is impaired, the movement of the zygote becomes difficult or occurs in the direction of the abdominal cavity. In such cases, the fertilized egg grows in the tube, ovary, abdominal wall, liver or spleen.
When the uterus is diseased, the embryo does not implant into its wall and ends up in the cervix. With congenital anomalies of the female genital organs, an ectopic pregnancy develops in the uterine horn.
Duplication of the uterine body is a developmental defect in which this organ consists of two cavities resembling horns. Women for a long time do not realize that they have such an anomaly.
The fertilized egg actively produces enzymes that destroy the tissue around it. It grows into the affected organ and over time leads to irreversible changes in it.
Causes
The most common causes of ectopic pregnancy are:
- genitourinary inflammatory diseases;
- long-term use of intrauterine and oral contraceptives;
- previous operations;
- tumors of the uterus and appendages.
- endometriosis;
- congenital anomalies of the genital organs;
- smoking;
- mental trauma.
Inflammatory diseases cause disturbances in the normal structure of the uterine wall, which makes it difficult for the embryo to attach to it. Sexually transmitted infections also play a role. When they are chronic, adhesions occur that prevent the movement of the zygote.
The risk of developing pathology increases with long-term use of intrauterine devices and oral contraceptives. When used, the structure of the uterine mucosa changes over time and the motor function of the fallopian tubes decreases.
Surgical interventions on the uterus and appendages lead to changes in their anatomy. Tubal ligation operations play an important role. After them, the risk of developing the disease increases to 50%.
Tumors also change the anatomical location of organs. Another direction of their influence is a change in the endocrine activity of the body. Ovarian tumors exhibit metabolic activity and synthesize hormones.
Endometriosis is a disease in which the endometrium, which normally lines the inner layer of the uterus, grows abnormally. More often it affects the genitals.
Endometriosis leads to mechanical damage to the fallopian tubes, changes hormonal activity and is often accompanied by inflammatory diseases.
Smoking is dangerous due to the nicotine content in cigarettes, which leads to delayed ovulation and a decrease in the contractile function of the internal genital organs.
Severe stress is the cause of the development of many diseases. It changes the activity of the cerebral cortex, which affects the activity of the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is the main endocrine gland. It coordinates the activities of all human endocrine organs. Under stress, its function is disrupted, the ratio of hormones produced changes, and the fallopian tubes stop contracting normally.
It is believed that the egg itself leads to an ectopic pregnancy. For some unknown reason, it is implanted before moving into the uterus. The hypothesis arose due to the fact that the disease is rarely detected in healthy patients without risk factors.
The likelihood of developing a pathological condition increases after 24 years in women who have given birth. After IVF the probability is also high. You need to know what causes ectopic pregnancy in order to treat these conditions before in vitro fertilization.
Types of ectopic pregnancy and their frequency of occurrence
What are the consequences of this danger?
The germination of fetal tissue into the organ causes its gradual destruction. Rupture of the affected organ is what makes an ectopic pregnancy dangerous.
A ruptured fallopian tube or ovary causes significant blood loss. Patients often lose consciousness from a rapid drop in pressure.
Blood pouring into the abdominal cavity irritates it. This manifests itself as intense pain radiating to the perineum and thigh. If this clinical picture occurs, urgent hospitalization with emergency surgery is necessary.
Infertility is another complication that can result from ectopic pregnancy. Its consequences are associated with irreversible damage to the structure of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, which reduces the likelihood of becoming pregnant in the future.
Preventive measures
An ectopic pregnancy cannot be predicted - there are too many factors that can lead to such a development. But doctors have developed specific preventive measures:
- from the moment of sexual activity, regularly visit a gynecologist for preventive examinations and early diagnosis of inflammatory/infectious diseases;
- keep a calendar of the menstrual cycle and, in case of minor irregularities, consult a gynecologist;
- promptly and fully treat any pathologies of the reproductive system, including inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- plan your pregnancy - for example, before conceiving, undergo a full examination by general and specialized doctors.
Ectopic pregnancy is considered a rather complex and dangerous pathology. But if medical measures were carried out at an early stage of the pathology or competent measures were taken when the fallopian tube ruptured, then the prognosis will be favorable. Modern advances in medicine make it possible not only to save a woman’s life, but also to provide her with the opportunity to have children in the future.
More details about ectopic pregnancy in the video review:
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category.
25, total, today
( 55 votes, average: 4.31 out of 5)
11th week of pregnancy: how mother and baby feel
Chorionic centesis (chorionic villus biopsy): what is it during pregnancy, indications and consequences.
Related Posts
How to determine early at home?
With timely diagnosis, it is possible to perform organ-preserving operations, after which the likelihood of developing infertility is less. It is important to know how to determine an ectopic pregnancy at home, so that if suspicious sensations arise, contact a specialist.
When can it be recognized?
The location of the attachment of the fertilized egg determines how long the disease can be determined. As the fetus grows in the fallopian tube and ovary, clear symptoms appear after the first month. With cervical localization, symptoms occur earlier, since the cervix is not able to hold the fertilized egg for a long time.
As the fetus grows in the uterine horn, the disease manifests itself at 2-4 months. At what time the pathological condition is determined also depends on whether the patient went to the antenatal clinic when signs of pregnancy appeared. Ultrasound reveals improper attachment of the fetus as early as 3 weeks.
What signs does it show?
It is impossible to say exactly how to determine an ectopic pregnancy. There are many signs of it, and they are non-specific. Often the clinical picture mimics diseases of the digestive tract. Sometimes the disease manifests itself with sudden bleeding, and the diagnosis is made already during surgery.
You should consult a specialist if you have any unusual sensations, as ectopic pregnancy is felt differently in different women.
How an ectopic pregnancy manifests depends on where the embryo develops. Common symptoms for all variants of pathology are as follows:
- delay of menstruation;
- abdominal pain;
- bloody issues.
In the first 2-3 weeks, such manifestations are rare. It is impossible to say exactly how to recognize a pathological condition in the early stages, since the disease is accompanied by symptoms characteristic of any pregnancy: nausea, engorgement of the mammary glands, altered appetite.
Every woman needs to know how to identify early signs of any pregnancy, not just an ectopic pregnancy, in order to register with an antenatal clinic as early as possible.
Basal temperature
Basal temperature is the temperature in the rectum, measured in the morning over 5-7 minutes. In the first half of the cycle, due to the saturation of the blood with estrogen, the temperature decreases. On the day of ovulation and after it, the temperature rises by 0.3-0.6 degrees.
Basal temperature during ectopic pregnancy, as well as during physiological pregnancy, is increased to the level of 37.0-37.3 degrees. This is due to the appearance in the ovary of the corpus luteum - a formation that produces progesterone and prepares the uterus for bearing a fetus.
The method of studying basal temperature for diagnosing pathology is ineffective, since it does not help to recognize an ectopic pregnancy. When the embryo dies, the basal temperature decreases, but this sometimes happens with the normal attachment of the fertilized egg.
Later symptoms
Obvious signs of an ectopic pregnancy appear after at least 4-8 weeks. Before this, the embryo can develop in the “wrong place” without causing inconvenience to the woman.
When the growth of the fertilized egg leads to stretching of the walls of the fallopian tube or ovary, the following symptoms appear:
- Bloody issues. They can often be confused with menstruation. But if the discharge is scanty, comes late and continues for a long time, this is a reason to seek medical help. Menstruation that does not occur as usual should always alarm a woman.
- Pain. Acute pain during an ectopic pregnancy is felt in the area where the embryo is attached. In case of tubal and ovarian pregnancy - on the side in the lower abdomen, in case of abdominal pregnancy - above, maybe in the center of the peritoneum or shifted to the side. It usually hurts when changing body position, sudden movements, there may be shootings in the shoulder blade or rectum.
This is what worries a woman when the embryo, during the process of growth, has not yet damaged the walls of the internal organs. When this happens, additional symptoms appear that cannot be ignored. It is best, of course, not to wait for them and, at the slightest suspicion of ectopic pregnancy, contact a gynecologist for examination.
Here are the latest symptoms of a ruptured fallopian tube or ovary:
- dizziness, loss of consciousness;
- increased body temperature;
- low pressure;
- cold sweat;
- pallor of the skin.
When a rupture occurs, internal bleeding opens, which is life-threatening and requires immediate medical intervention.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy begins with a thorough medical examination. Unilateral enlargement of the uterine appendages is an important symptom, as it manifests itself early in the disease. There is also pain when the cervix is displaced.
The size of the uterus in pathology is smaller than what is normal at a given period. Laboratory and instrumental research methods can confirm the diagnosis.
HCG for ectopic
Human chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone secreted by the tissues of the fertilized egg. Its function is to regulate the activity of the uterus and maintain the normal functioning of the entire female body during pregnancy.
Its content is determined in the blood from 7-8 days after conception. With an ectopic pregnancy, the concentration is lower.
What does a pregnancy test show?
A pregnancy test detects the presence of hCG in the urine from day 14-15. With an ectopic pregnancy, the test is positive, but sometimes the second strip is less intensely colored.
Signs on ultrasound
Ultrasound is the main diagnostic method that allows early detection of the disease. An ectopic pregnancy on ultrasound shows the following signs:
- absence of an embryo in the uterus and its abnormal location in another location;
- heterogeneous structure of appendages;
- fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- thickened endometrium;
- the uterine cavity is closed or dilated, filled with coagulated blood.
With the cervical variant of the pathology, ultrasound reveals a change in the shape of the uterus. It takes on an hourglass shape.
Types of ultrasound used for diagnosis
Artificial insemination (IVF, ICSI)
It would seem that when conceiving in this way, all risks should be minimized. However, as the practice of obstetrics and gynecology proves, every 20th couple who undergo the procedure ends up with an ectopic pregnancy. Of course, the embryo itself is implanted directly into the uterine cavity, but by chance it can begin to move further.
The IVF procedure becomes the only chance for many couples to become parents. But even despite all the high costs, the experience of doctors and other factors, no one is immune from the improper development of pregnancy. That is why doctors advise getting a test tube baby only in severe cases. Everyone else should initially try to conceive on their own, having first undergone a comprehensive examination and treated all existing diseases.
In Vitro Fertilization
What to do?
Suspicion of abnormal attachment of the embryo is an indication for hospitalization in a gynecological hospital. Only the operating doctor knows exactly what to do for this condition. Blood for transfusion is prepared in advance for the patient due to the increased risk of bleeding.
Is there a treatment?
The main method of treatment is surgical. It is carried out regardless of the period at which the ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed. The operation involves removing the fallopian tube or cutting it and extracting the fetal tissue.
When the embryo is localized to the ovary, removal of the ovary is often performed. In case of cervical location, curettage is performed followed by stopping the bleeding.
If the fetus grows in an abdominal organ, the affected organ is usually preserved by removing only the changed tissue.
There is drug therapy with the antitumor drug methotrexate. This treatment for ectopic pregnancy is carried out if:
- gestational sac less than 35 mm;
- no fetal heartbeat detected;
- the patient has no significant pain;
- hCG level in the blood is less than 5000 IU;
- there is no concomitant intrauterine pregnancy.
Actively dividing cells are most sensitive to methotrexate. Tissues of tumors and the ovum are among these. Drug treatment is effective, but is rarely used in Russia. The decision on methotrexate therapy is made by a committee of doctors.
Surgery using laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a method of surgical access to the affected organ through a small opening, for example through an incision in the navel.
Its advantages over the classical surgical approach:
- absence of postoperative scar;
- low blood loss;
- rapid recovery of the patient after the procedure;
- rare formation of adhesions.
This operation is no less effective than the classic one, since the embryo is removed at an early stage. Laparoscopy is also performed for diagnostic purposes in unclear cases.
Laparoscopy
Causes and pathogenesis
Normally, at the end of the second week of the menstrual cycle, a woman ovulates - the release of a mature egg from the ovary into the free cavity of the peritoneum.
Next, with the help of special villi, the female reproductive cell penetrates the fallopian tube, where it merges with the sperm and forms a zygote. After 1 week, the embryo reaches the uterine cavity, where implantation occurs. If these processes are disrupted, the embryo does not enter it on time, which leads to the development of ectopic pregnancy. The causes of ectopic pregnancy are extremely varied, and they cannot always be identified. The etiology of this pathology is the slow movement of the embryo through the fallopian tube or increased activity of the trophoblast (layer of cells of the embryo), which leads to premature implantation. The most common predictive factors for ectopic pregnancy include 6 diseases and situations:
- Inflammation of the fallopian tube. Due to this disease, the cilia that move the egg to the uterine cavity die. Also, adhesions can form in the fallopian tubes.
- Sexual infantilism. This disease is accompanied by the presence of long and tortuous fallopian tubes; the egg does not have time to reach the uterine cavity in time.
- IVF and treatment with hormonal drugs. Excessive concentration of progesterone in the blood slows down the movement of the egg through the tubes.
- Surgical interventions on the fallopian tubes. Lead to the formation of scars and adhesions on them.
- Tumors of the female genital organs. This group of diseases can lead to anatomical changes in the fallopian tubes.
- Endometriosis. This pathology causes a decrease in the activity of the tubal villi.
In a tubal pregnancy, the embryo is implanted into the fallopian tube, in which bleeding occurs, dissecting its wall.
The embryo begins to increase in size, but this happens more slowly than during physiological gestation. Changes characteristic of normal pregnancy are noticeable in the uterus: a slight increase in size, softening of the cervix and isthmus. After some time, the embryo grows to a large size and ruptures the tube; sometimes it is spontaneously expelled into the peritoneal cavity (tubal abortion). The period during which these processes occur depends on the location of implantation; it ranges from 4 weeks to 4 months. Ovarian pregnancy is rare and occurs as a result of migration of the zygote from the tube to the ovary. Some doctors believe that with such a gestation, fertilization of the egg occurs in the follicle, that is, before ovulation. Abdominal pregnancy is an even rarer pathology; it can occur primarily - with a perverted localization of fertilization, or as a result of a tubal abortion.
Can abnormal attachment of the fertilized egg occur during IVF?
Infertile women using reproductive technologies are wondering whether there can be an ectopic pregnancy with IVF?
Statistics say that the likelihood of abnormal embryo implantation during in vitro fertilization is twice as high as during physiological conception. Due to the high risk, the patient should be carefully examined for the presence of inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs, endocrine pathology and endometriosis. All identified pathologies must be treated in advance.
Ectopic pregnancy during IVF often occurs due to the same reason that caused infertility.
Congenital malformations
It also happens that before planning a pregnancy, a woman is not even aware of the peculiarities of the internal organs. And after the terrible diagnosis of “ectopic pregnancy,” trying to understand the causes of the pathology, she learns that her tubes are either too short, or, conversely, too long and tortuous. Often this is a congenital anomaly, inherent in intrauterine development. The reasons for this may lie in the poor lifestyle of the woman’s mother: drinking alcohol after conception, working in hazardous industries, and exposure to radiation.
It is worth noting that even taking certain medications and intrauterine infections can lead to abnormal development of fetal organs.
How to exclude an ectopic pregnancy?
Even healthy women are likely to have it. It is impossible to give definite advice on how to avoid an ectopic pregnancy. You can only reduce the risk of its occurrence.
It is necessary to limit the number of sexual partners in order to avoid infection with sexually transmitted diseases, give up bad habits, and, if possible, avoid stress before the planned conception.
Since it is impossible to completely exclude an ectopic pregnancy, you should reduce the risk of its development by leading a healthy lifestyle and promptly contacting the clinic about any illness.
Other reasons
A woman’s hormonal background plays a huge role in her well-being, her monthly cycle, her ability to conceive and the course of pregnancy. If one of the hormones, progesterone, is in insufficient quantities in the body, this reduces the likelihood of conception to a minimum, and if successful, seriously complicates the development of the fetus. It also provokes ectopic pregnancy, since due to low rates the fallopian tubes contract poorly, retaining the fertilized egg.
Smoking can also be a cause of abnormal attachment, since nicotine works in a woman’s body on the same principle as a lack of progesterone.
Paradoxically, even douching done at the wrong time can ruin plans for a happy pregnancy.
Age is another unfavorable factor. The American lifestyle, actively imposed on us from television screens, encourages women to initially build a career, build a family nest, and only then give birth. As a result, conception occurs after 30 years of age, which automatically puts the expectant mother in the category of “old mothers” by our doctors and forces us to carefully monitor the development of pregnancy and the condition of the woman’s body. From this same age, the risk of improper implantation of a fertilized egg in the body increases significantly.
It is worth noting that those women who have experienced an ectopic pregnancy before are 12 times more likely to have it again than those who have not had one.
Is it possible to get pregnant after?
Not all women know whether it is possible to become pregnant after an ectopic pregnancy. Many people think that after it they become infertile.
In order to preserve fertility, an incision is made into the fallopian tube to remove fetal tissue. Conditions for manipulation:
- fertilized egg up to 5 cm;
- no pipe rupture;
- HCG up to 15 thousand international units.
After the operation, the tube is sutured, and pregnancy becomes possible again. In case of rupture, the affected organ is removed. Even after such an intervention, a healthy fallopian tube remains on the opposite side.
Infertility occurs after hysterectomy in order to eliminate massive bleeding, but the need for this arises mainly when the embryo is located in the cervical region.
Treatment options
Common treatment methods are surgical. They are based on surgical intervention to remove the fertilized egg from its place of attachment. There are several surgical methods, and it is worth considering each of them in detail.
Laparoscopy
A safe and effective type of surgery. Laparoscopy with reliable accuracy allows you to determine the place of attachment of the fertilized egg, as well as timely diagnose complications that have arisen. The exclusion of ectopic pregnancy is carried out using four ports - a video camera, a clamp and working tools.
In case of complications, the fallopian tubes along with the ovaries are also removed. Using the laparoscopic method, in case of a pipe rupture, you can provide emergency assistance, stop the bleeding and remove the burst organ.
Contraindication to surgery is hemorrhagic shock in women. Adhesions in the pelvic area can be an obstacle, but experienced doctors usually take on such cases.
There are two options for laparoscopy: conservative and radical. Conservative treatment involves making an incision on the surface of the fallopian tube and removing the embryo; radical treatment involves partial or complete removal of the tube. The latter type of operation is performed if it is necessary to preserve the woman’s life and completely excludes further reproductive activity.
Laparotomy
This surgical method is an operation with an incision in the abdominal cavity along the line from the navel to the pubic region. In particular, the laparotomy method is used for caesarean section. In the early stages of ectopic pregnancy, laparotomy is performed when there are contraindications to other treatment methods.
Main indications for laparotomy:
- If the embryo was located outside the fallopian tubes;
- Fertilized egg implanted in the cervical area of the uterus;
- Frozen ectopic pregnancy.
Significant disadvantages of the operation: a high risk of blood loss and long rehabilitation.
Salpingotomy
This type of surgical operation is performed for a number of indications:
- Early pregnancy;
- The size of the embryo is up to 5 cm;
- The fetus is implanted in the intact fallopian tube;
- Hemodynamic stability.
The algorithm of surgical actions is as follows: an incision is made on the uterus to exclude the fetus, then after removal, a suture is placed at the site of the incision. This is a safe method that allows the patient to subsequently become a mother.
Types of pathology
In 95% of cases, the fertilized egg remains in the fallopian tube. But sometimes rare pathologies develop - implantation in the cervix, ovaries or abdominal cavity.
How to find out what type of frozen pregnancy has occurred and exclude other pathologies? You cannot do this on your own; the entire examination must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Pipe
If the fertilized egg is located in a narrow canal of the tube, rupture occurs at 6–7 weeks, this is accompanied by severe pain and significant blood loss. The condition is life-threatening for a woman, so it is important to pay attention to the signs of an ectopic pregnancy.
Ovarian
One of the dangerous conditions, the symptoms resemble the development of acute ovarian pathologies. It occurs extremely rarely and ends with the rupture of an internal organ. Severe pain and bleeding in the abdominal cavity appear.
Abdominal
May form as a result of an unsuccessful tubal abortion. The development of a fertilized egg traumatizes internal organs and tissues.
More often, pathology is detected late, when bleeding occurs or damage to the organ into which the embryo is attached.
Heterotopic
An extremely dangerous condition in which two fertilized eggs develop. One is located in the uterus, as it should be, the other is outside it.
This is an abnormal and rare phenomenon; an accurate diagnosis can be made in the first trimester. At the same time, there are cases of successful elimination of pathology and bearing a child born in the uterine cavity.
Consequences of inattention
Unpleasant result:
- Rupture of the genital internal organs: tubes, abdominal area.
- Self-termination of pregnancy.
- Serious bleeding from the vaginal opening. Internal bleeding.
- Peritonitis, inflammatory processes.
- Death.
Provided that a woman still has at least one tube with good functionality, the likelihood of having a child in the future is high. Quick professional intervention by doctors will allow the body to become pregnant again in 1 year.
Pregnancy after ectopic
After an ectopic pregnancy, a physiological pregnancy is possible if the tubes were not removed or only one of them was excised. If a woman has both of them removed during surgery, pregnancy is only possible with the help of IVF; she will not be able to conceive a child on her own. Difficulties with conception may also occur if only one tube is removed: the fertilized egg may need to travel twice as far (if it comes out from the side where there is no tube).
After the operation, great importance should be given to methods of contraception and protection from pregnancy in the near future. It is preferable to use combined contraceptives for oral use. Before the next attempts to conceive, the duration of contraception should be at least six months; sometimes it is even recommended to refrain from trying to conceive a child for a year. A gynecologist who constantly monitors the woman will give precise recommendations on this matter. In some cases, the doctor may allow the couple to try to get pregnant as early as 3 months after the VB.
Surgical intervention
Once both spontaneously aborted and progressive VB are identified, surgical intervention is performed on an emergency basis - this assumes the standard of care for ectopic pregnancy. Hemorrhagic shock is also an indication for surgery. Most often, with VB, the fallopian tube is removed, but in some cases conservative plastic interventions are performed:
- Squeezing out a fertilized egg.
- Incision of the tube and subsequent removal of the fertilized egg (if the egg is small).
- Resection of a segment of the tube (partial removal).
Treatment after an ectopic pregnancy with removal of the tube is carried out if there has already been an ectopic pregnancy, during which conservative intervention was performed. Also indications are:
- spontaneous pipe rupture;
- large egg sizes (more than 3 cm in diameter);
- reluctance to become pregnant in the future;
- cicatricial changes in the tube.
When performing organ-preserving surgery (that is, when squeezing out the fertilized egg or removing it through a small incision), the risk of recurrent VD increases in the future.
How to identify houses yourself
It is easy to determine intrauterine pregnancy yourself with a special test that reacts to the level of a certain hormone. With the development of an ectopic pregnancy, this hormone is also present, however, its amount will be less.
A regular test will show pregnancy regardless of the location of the embryo, but the second line will be barely noticeable.
It is impossible to accurately determine a dangerous condition at home - only to suspect it, since the symptoms are identical to those that occur during a non-pathological pregnancy. A clear sign will be severe pain.
As the pathological process develops, the symptoms progress every day. Symptoms of concern:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, rectal area;
- nausea, vomiting, weakness;
- bleeding from the vagina;
- increased heart rate;
- blood after sexual intercourse.
The fallopian tube ruptures at 7 weeks, causing internal bleeding. The woman will die from blood loss and painful shock if medical assistance is provided late.
In 5–10% of cases, the result of untimely treatment is infertility.
Pregnancy tests
If a sufficient amount of the hCG hormone is present in the urine, a reaction occurs on the surface of the test - the result is positive.
The absence of hCG or low concentration does not give a reaction - there is only one strip on the test. The average sensitivity of the test is 25 mUI; two weeks after intercourse you can find out whether pregnancy has occurred or not.
Prevention
Prevention of ectopic pregnancy consists of the following measures:
- avoidance of casual sex and associated sexually transmitted diseases;
- timely detection and treatment of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- medical examination at the stage of pregnancy planning;
- prevention of abortions (use of contraception);
- after an ectopic pregnancy, a long course of rehabilitation with planning a new pregnancy no earlier than 6, and preferably 12 months.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Possible complications
The most important and dangerous complication of an ectopic pregnancy is large internal bleeding, which can lead to the death of a woman in just a few hours or even tens of minutes. It is also possible that an ectopic pregnancy may recur in the future or that infertility may develop due to damage to the fallopian tubes. In addition, shock due to internal bleeding can impair the functions of other internal organs, not just the reproductive system.
Due to the fact that an ectopic pregnancy can develop in organs with a rich blood supply, which in particular include the ovaries and the areas where the fallopian tubes enter the uterus, surgery to remove the embryo can result in the removal of one of the fallopian tubes, the removal of one of the ovaries and even the removal of the uterus with both fallopian tubes. But even if all internal organs are preserved, an ectopic pregnancy still reduces a woman’s chances of further conception and normal childbearing. Sometimes, after the operation, an inflammatory process and intestinal obstruction develop, and seals form in the pelvis.
In order to minimize the negative consequences of ectopic pregnancy as much as possible, after the operation it is necessary to undergo anti-inflammatory and restorative therapy. The hormonal background and protective resources of the woman’s body must be fully restored before the next pregnancy, otherwise the risk of recurrence of the pathology or the development of secondary infertility will be too great. From a medical point of view, you can plan your next pregnancy no earlier than six months to a year after the operation.
Run to the doctor at the first symptoms! An ectopic pregnancy is an extremely dangerous condition for a woman’s health and life, therefore, if any suspicious symptoms and especially acute abdominal pain appear, it is necessary to consult a doctor or call an ambulance as soon as possible. And if the diagnosis is confirmed, you will either be prescribed an termination of this pregnancy, or an operation will be performed to eliminate the consequences of the tubal abortion that has occurred. Today, both surgical and medical methods are used to treat ectopic pregnancy. The specific method is determined by the attending physician based on the patient’s condition and the severity of the disease.
Clinic and diagnosis of pipe rupture
In the event of a pipe rupture, the symptoms are quite bright, so that they do not create any problems during diagnosis. Signs of rupture are due to abdominal bleeding. Symptoms of rupture include:
- pain from the side of the tube in which the fertilized egg is attached;
- loose stools, burning, cutting pain in the rectum without excretion of feces;
- pain radiates to the right collarbone and rectum;
- severe weakness, fainting, dizziness, nausea and vomiting;
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- cold sweat, shortness of breath;
- sharp pain in the abdomen when palpated;
- symptoms of peritonitis;
- apathy, slow reaction in the patient;
- weak pulse, decreased blood pressure;
- bloating, noticeable tension in the lower part;
- all other signs of hemorrhagic shock.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor may detect cyanosis of the vaginal mucosa. Increased size and excessive mobility of the uterus, pain, overhang of the posterior vaginal vault, and bloody discharge from the uterus are usually absent. The clinical picture is usually so clear that there is no need for additional diagnostics.
The clinical picture of rare forms of VD is usually similar to the manifestations of a pipe rupture. The final diagnosis in this case is established during the surgical treatment of ectopic pregnancy.
Progressive pregnancy
A very important diagnosis of an ongoing ectopic pregnancy. The timing of treatment must not be missed, otherwise there is a risk of death. Progressive pathological pregnancy is complicated by the fact that there are no symptoms of an “acute abdomen”, and the patient’s condition repeats the signs of physiologically normal attachment and further development of the fertilized egg. The patients have all the signs of a normal pregnancy, but upon examination, a discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the expected period, the presence of soft formations in the area of the appendages, and pain on palpation are revealed. With a short period of time, it is not possible to determine the enlargement of the fallopian tube due to its small size. For timely diagnosis, the previously listed methods are crucial: ultrasound, blood test, laparoscopy, determination of the amount of hCG in the blood.