Causes and development of pathology
The main causes of cholecystitis during pregnancy are:
- congestion in the gallbladder;
- violation of the principles of healthy eating;
- infectious lesion of the mucous membrane of the gallbladder.
Congestion in the gallbladder in a pregnant woman occurs primarily for reasons such as:
- pressure from the enlarged uterus;
- the presence of stones in it;
- scars, adhesions;
- tumors.
The uterus does not put pressure on the gallbladder directly - it literally props up the intestines, which already puts pressure on the bladder.
Scars that appear in the wall of the gallbladder play a role in the disruption of the outflow of bile and, as a result, the occurrence of cholecystitis. As for adhesions, this is a manifestation of adhesive disease, which usually occurs after surgical interventions even before pregnancy.
note
Tumors, both benign and malignant, usually from the liver and intestines, can lead to congestion in the gallbladder. If the tumor arose in the wall of the uterus, then when this organ enlarges in late pregnancy, the neoplasm will also put pressure on the gallbladder, thereby disrupting the outflow of bile and therefore provoking an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the bladder.
Cholecystitis, both under normal conditions and during pregnancy, can be aseptic and infectious. In the latter case, it develops when there is an infection in the gallbladder.
As for violations of the principles of healthy eating, the occurrence of cholecystitis can be provoked by the abuse of fried and fatty foods.
The pathological process in case of development of cholecystitis during pregnancy can be:
- according to the course – acute and chronic;
- according to the presence of stones - stoneless and calculous;
- by severity - mild, moderate and severe.
Nutrition rules
Therapy begins with dietary adjustments. The patient should eat food often (4–6 times a day), but in small portions (about 300 g). This is necessary so that the gallbladder is emptied regularly.
With cholecystitis, the expectant mother should follow a diet
The patient should give up fatty, fried, spicy foods, soda, wine, beer and other alcoholic beverages. Egg yolks, nuts, baked goods, cold foods, fresh vegetables and fruits are excluded from the diet. The expectant mother who has been diagnosed with cholecystitis must adhere to the rules of table No. 5.
When the symptoms of the disease become less pronounced, the diet can be supplemented with vegetable purees, vinaigrette, watermelons, melons, raisins, prunes, dried apricots, etc. Adhering to these rules, the patient will speed up the restoration of the functionality of the gallbladder, and also get rid of constipation.
When gallbladder motility decreases, it is recommended to consume “cholecystokinetic” products: light broths from meat or fish (low-fat varieties), low-fat sour cream, soft-boiled eggs. It is allowed to include cottage cheese, protein omelettes, and cod (boiled or baked) in the menu, as they contain a large amount of lipotropic substances.
If the biliary contraction is too active, the patient can drink warm mineral waters with a low degree of mineralization (Essentuki 17, Arzni, Batalinskaya). In the last months of pregnancy, liquid is recommended to be consumed in moderation.
Symptoms of cholecystitis during pregnancy
Symptoms that indicate the occurrence of this pathology are:
- pain;
- dyspepsia.
The characteristics of pain will be as follows:
- by location - in the right hypochondrium;
- by distribution - can radiate to the right half of the chest and neck, arm, collarbone, scapula;
- by nature - aching or acute, like hepatic colic;
- in terms of severity - when the pain is aching, it is usually tolerable, when it is acute, it is often intolerable;
- by occurrence - may occur against the background of provocation by spicy or fried foods.
The most common dyspeptic disorders associated with cholecystitis in pregnant women are:
- belching with bitterness - the longer the pregnancy, the more pronounced it is;
- nausea;
- vomiting that does not bring relief.
Characteristic symptoms
The disease can appear at any time. However, more often the exacerbation occurs in the third trimester. The provoking factor is the abuse of spicy, fatty, fried foods, as well as overeating. Often the disease is combined with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, duodenitis).
Symptoms of acute cholecystitis:
- acute colicky pain radiating to the shoulder, shoulder blade, and neck on the right side;
- nausea and vomiting with bile;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- increase in body temperature up to 38 ° C;
- spontaneous inhalation delay when pressing on the right hypochondrium;
- pain when inhaling when palpating the hypochondrium on the right;
- jaundice (yellowing of the mucous membranes and skin).
Symptoms of chronic cholecystitis:
- moderate pain in the hypochondrium on the right;
- feeling of heaviness after eating in the epigastric area;
- nausea, vomiting;
- belching with bitterness or a persistent bitter taste in the mouth.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of cholecystitis during pregnancy is made taking into account the patient’s complaints, medical history (history of development) of the disease, and the results of additional examination methods (physical, instrumental, laboratory).
The following details will be revealed from the anamnesis:
- when did the first symptoms occur - before or during pregnancy;
- how the patient’s condition changed as the pathology developed;
- whether jaundice was observed.
A physical examination reveals the following:
Doctor examining pregnant woman
during examination - the general condition in case of a chronic process is satisfactory, in case of an acute process - moderate, and in case of advanced condition - severe;- on palpation (palpation) – there is pain in the right hypochondrium, in acute and/or calculous process – severe pain. Even an enlarged gallbladder usually cannot be palpated due to the fact that the enlarged uterus literally pushes it under the liver.
Of the instrumental methods in diagnosing cholecystitis during pregnancy, the most optimal is ultrasound examination, since its use has no negative consequences for the fetus. During it, the condition of the gallbladder wall, the presence of stones and other possible inclusions, as well as the condition of the surrounding tissues are determined.
Laboratory methods used in the diagnosis of this pathology are:
- general blood test - detects an increase in the number of leukocytes (leukocytosis) and ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate);
- biochemical blood test - determine the amount of bilirubin, alanine and aspartate aminotransferase;
- stool analysis - it determines bile pigments.
Diagnostic measures
Detection of cholecystitis is carried out in a medical institution. To determine deviations, it is recommended to do a series of laboratory tests. Clinical and biochemical blood tests can determine the level of leukocytes and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. When the norm changes, it is customary to diagnose an inflammatory process in the body.
Additional examination methods during pregnancy are instrumental methods. These include ultrasound and duodenal intubation. The first procedure is aimed at studying the condition of the abdominal organs. An ultrasound can detect changes in the size of the gallbladder and the presence of stones in it.
Duodenal sounding is a more informative procedure. It allows you to assess the condition of the gallbladder, the amount of bile and the presence of additional pathologies. It is carried out exclusively in the early stages of pregnancy.
Differential diagnosis
Differential (distinctive) diagnosis of cholecystitis during pregnancy is most often carried out with diseases such as:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum - the occurrence of deep defects in the wall of these organs;
- gastritis – inflammation of the gastric mucosa;
- duodenitis – inflammatory lesion of the duodenal mucosa;
- pancreatitis – inflammation of the pancreas.
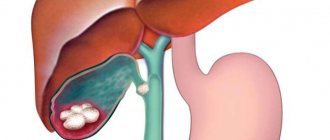
What is cholecystitis
This is a pathology that is characterized by inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder. The cause of cholecystitis is stagnation of bile masses, sand or stones formed in the gallbladder.
Important! Cholecystitis is accompanied by gallstone disease in 95% of cases. If the doctor is not going to conduct a test for the presence of stones or sand in the gallbladder, request it yourself so that, if necessary, you can undergo comprehensive treatment.
Sometimes inflammation occurs against the background of an infectious pathogen that has entered the bile ducts. Pathology occurs against the background of compression of the digestive system by the growing fetus.
Treatment of cholecystitis during pregnancy
Treatment of cholecystitis during pregnancy depends on its form.
Important
In case of an acute process (especially purulent), cholecystectomy is urgently performed. If cholecystitis was provoked by the presence of stones, but there are no acute symptoms, then they try to stop its manifestations using conservative methods, and removal of the gallbladder with stones is carried out routinely after delivery.
If cholecystitis develops during pregnancy, diet No. 5 according to Pevzner is prescribed. Compliance means the following:
- Fatty meats, animal fats, legumes, garlic and onions, cocoa are prohibited;
- Fried and spicy foods are excluded from the diet;
- food intake should be fractional - 5-6 times a day.
There are no medications recommended for use in the event of cholecystitis developing specifically during pregnancy (there is no approved list) - they somehow negatively affect the intrauterine development of the fetus. Therefore, drug therapy is used only in cases where the risk to the mother’s health outweighs the risk to the fetus. Appointed:
- antispasmodics – No-Shpa, Papaverine, Platiphylline;
- analgesics – Analgin;
- antibacterial drugs - Ampicillin, Rifampicin (they reach the highest concentration in bile);
- choleretic agents. In addition to pharmaceutical drugs, these can be herbal products (for example, a decoction of corn silk), which can reduce risks to the fetus.
Traditional treatment
It is best to give preference to medicines that can be made at home. For this, plant raw materials are usually used. For example, corn silk, peppermint, rose hips, dill and immortelle. These ingredients are poured into a glass of boiled water and carefully filtered. You need to take a third of a glass half an hour before meals.
In the second trimester, a pregnant woman has to keep a special record of all the liquid that was drunk. That is why during these months it is recommended to choose Flamin tablets, consisting of sandy immortelle extract. Take 1-2 pieces, preferably shortly before meals. If a herbal decoction is prescribed to remove bile, this will have a positive effect on diuresis. After all, such components are considered diuretics.
If desired and there are no contraindications, you can perform probing or tubing using 40 ml of vegetable oil. Corn and olive are quite suitable. This procedure is also carried out using Barbara salt, and only 1 dessert spoon should be placed per glass of liquid. Don't forget about mineral water, but it should be at room temperature. The last option is suitable only for those women who do not have edema. Tubage is performed in the morning, before meals. First, the prepared remedy is drunk, then the expectant mother lies on her right side and remains in this position for several hours. If acute pain is felt on the right side, then you are allowed to take a No-Shpy or Baralgina tablet.
Cholecystitis during pregnancy and its effect on the fetus
The prognosis for this pathology is different. Mild manifestations of cholecystitis during pregnancy can be controlled with dietary nutrition; more pronounced and complicated manifestations require more radical measures with a risk to the fetus.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
just today
( 60 votes, average: 4.03 out of 5)
Chorionic centesis (chorionic villus biopsy): what is it during pregnancy, indications and consequences.
Water birth
Related Posts
a brief description of
Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder (GB). The disease is one of the most common. According to statistics, about 10 percent of the world's population suffers from it. In economically developed countries this figure is higher.
Women suffer from cholecystitis three to five times more often than men. The disease can appear at any age, but most cases of this gallbladder pathology are registered in middle age. Despite this, cholecystitis is not uncommon during pregnancy.
Human biliary system