Pain in the lower abdomen in men is one of the most common clinical manifestations that trouble representatives of the stronger half of humanity. Ignoring the symptom can lead to irreparable complications. Pain syndrome most often indicates the presence of a pathological process in the human body. Usually the condition is associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system, but clinicians also identify a number of other provocateurs.
- Etiology
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention and prognosis
Pain often becomes the first symptom, against which a large number of other external manifestations develop. The most common include nausea and vomiting, constipation and diarrhea, belching and heartburn, frequent urination and general malaise.
The correct diagnosis is established only by the clinician, who conducts a thorough physical examination and other primary diagnostic measures, prescribes laboratory and instrumental examinations, and, if necessary, refers the patient for consultation with other specialists.
Pain in the lower abdomen in men is eliminated using conservative methods of therapy, but the tactics for treating the underlying disease are selected on an individual basis.
Etiology
Clinicians know many causes of pain in the lower abdomen: all causes are divided into several categories.
The first is represented by diseases that negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract:
- intestinal obstruction;
- inguinal hernias;
- Crohn's disease;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- oncological or benign tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular in the large intestine;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- acute inflammation of the cecal appendage;
- diverticulosis and intestinal dysbiosis;
- chronic constipation;
- sigmoiditis;
- polyposis;
- gastritis of any nature;
- gastroduodenitis;
- ileitis;
- inflammatory process in the pancreas;
- ulcerative lesion of the stomach.
Stomach ulcer in men
The second most common cause is pathological causes involving the genitourinary system. In such situations, the occurrence of pain is provoked by the following factors:
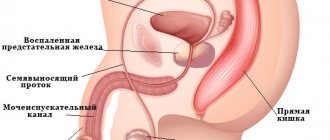
- inflammation of the prostate gland;
- priapism - acute pain in the lower abdomen caused by prolonged erection;
- adenoma and prostate cancer;
- pyelonephritis and cystitis;
- an inflammatory process in the testicles, which is medically known as orchitis;
- renal colic caused by urolithiasis;
- inflammatory lesion of the penis;
- vesiculitis and epididymitis;
- urethritis;
- cavernitis and colliculitis;
- inflammatory or oncological lesions of the bladder;
- balanitis and fasting;
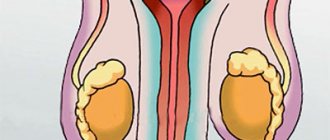
- varicocele or testicular hydrocele;
- testicular torsion.
Less common predisposing factors that cause lower abdominal pain in men include:
- disruption of the functioning of the endocrine system (adrenal glands, pituitary gland and thyroid gland);
- cystitis;
- radiculitis;
- STD;
- kidney disease;
- infarction or volvulus of the spleen;
- intervertebral disc herniation.
Cutting pain, in addition to the indicated pathological provocateurs, can be caused by the prolonged influence of such physiological sources:
- lack of physical activity;
- addiction to bad habits, for example, drinking alcoholic beverages in large quantities;
- hypothermia of the body;
- lack of diet;
- presence of obesity;
- interrupted sexual intercourse;
- hormonal imbalance;
- failure of the immune system.
What to do?
If pain or burning occurs in the lower abdomen, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor who can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate and resort to traditional methods of therapy without first consulting with your doctor. During the therapeutic course you should:
By following all these rules, you can avoid the occurrence of pathology.
Symptoms
Regardless of the cause of pain in the lower abdomen in a man, discomfort always acts as the first, but not the only clinical manifestation.
The symptomatic picture may include a large number of signs characteristic of the underlying disease, which is why the complaints of each patient will be strictly individual.
There is a group of symptoms that develop most often.
Additional clinical manifestations:
- bloating;
- increased gas formation;
- frequent urge to urinate - some may be false;
- nausea ending in vomiting - vomiting does not always bring relief;
- temperature increase;
- fluctuations in blood tone indicators;
- disruption of the bowel movement process - constipation and diarrhea, their alternation;
- the presence of pathological impurities in feces, urine and vomit;
- premature ejaculation;
- erectile disfunction;
- decreased physical activity and mental performance;
- aversion to food;
- irritability and weakness;
- tendency to depression;
- itching and burning in the anal area;
- irradiation of pain - more often the pain spreads to the lower limbs, scrotum and groin area, the entire anterior wall of the abdominal cavity and lower back;
- profuse sweating;
- headaches and dizziness;
- causeless weight loss;
- pain when urinating;
- decreased duration of sexual intercourse;
- chills and belching;
- discharge from the urethra;
- heartburn and hiccups;
- pale skin;
- infertility.
The main symptom can be either constant or periodic. Increased pain is most often observed at night, during or after eating food, during sexual intercourse and visiting the toilet.
All external signs that may be accompanied by aching pain in the lower abdomen should be attributed to males of any age category.
Why is this dangerous?
If you experience pain and a burning sensation in the lower abdomen, you must consult a doctor and start treatment on time, otherwise there is a possibility of complications that depend on the type of disease that caused these symptoms:
Diagnostics
When the lower abdomen hurts in men and there are one or more additional symptoms, you should contact a urologist or gastroenterologist for an initial consultation. In most situations, the sources of pain are pathological conditions of the digestive and genitourinary systems.
Other diseases can be provocateurs, so doctors from other fields of medicine should take part in the process of identifying the cause of pain:
- endocrinologist;
- nephrologist;
- neurologist;
- traumatologist;
- vertebrologist;
- oncologist;
- pediatrician;
- therapist.
To make a correct diagnosis, you need an integrated approach. First of all, the clinician must independently perform a number of manipulations:
- studying the medical history and life history of the patient - to identify the most likely pathological or physiological predisposing factor;
- urological examination with mandatory digital examination of the prostate;
- palpation and percussion of the abdomen - a description of the sensations when pressed will help to establish not only the place where the nagging pain is localized, but also the area of irradiation;
- measurement of temperature, heart rate, pulse and blood pressure;
- a detailed survey of the patient - to draw up a complete symptomatic picture, which will enable the doctor to understand the nature and severity of pain.
The most informative laboratory and instrumental examinations:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- blood biochemistry;
- taking a smear from the urethra;
- microscopic examination of feces;
- gastroscopy;
- puncture - to obtain secretions from the prostate gland;
- ultrasonography of the pelvic area and peritoneum;
- radiography;
- colonoscopy;
- anorectal and colonic manometry;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- biopsy;
- CT;
- MRI.
Colonoscopy
Only after studying the results of diagnostic procedures and establishing the cause of sharp pain in the lower abdomen in men, treatment will be prescribed, selected on an individual basis.
Other reasons
Pain in the groin area can also be caused by:
- Inguinal hernia. In this disease, due to a defect in the abdominal muscles, a section of the intestine prolapses into the inguinal canal in the form of a pouch-shaped diverticulum (loop). In men, the symptoms of an inguinal hernia are nagging pain at the site of diverticulum formation. Upon examination, the hernial protrusion can be seen; it increases with the vertical position of the body.
Important! If the hernia is large, it may become strangulated, and the pain syndrome increases sharply. The blood supply to the pinched area of the intestine is disrupted, and its tissues may become necrotic, which can lead to the development of peritonitis. In such a situation, emergency surgery is indicated.
- Appendicitis. All known signs of inflammation of the appendix are attacks of colic that cover the right side of the groin. They can radiate to the leg or perineum; palpation reveals tension in the peritoneal muscles. An acute attack of appendicitis is often accompanied by nausea, stool retention, and low-grade fever.
- Tumors in the pelvic area. The phenomenon of synalgia, when pain radiates to other areas of the body, in particular the groin and perineum, is typical for most neoplasms localized in the pelvic area. The source of the pain signal in such cases is identified during examination using laboratory and instrumental methods.
- Varicose veins Pain in the groin can be caused by pathologies of the valves of the veins located in the perineum. In particular, this is how varicocele manifests itself - varicose veins of the vessels of the spermatic cord.
- Injuries . When the muscles or tendons of the groin are damaged, pain usually occurs when moving. There may also be slight inflammation or swelling of the soft tissue.
- Pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. People with diseases of the skeletal system often complain of discomfort in the groin. With osteochondrosis, arthritis or coxarthrosis, compression of the nerve fibers occurs, some of which extend to the lower edge of the peritoneum.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes. Enlarged lymph nodes located in this area can cause pain in the lower abdomen. Catarrhal phenomena in the lymph nodes can develop due to diseases of the internal organs, as well as as a result of infection or injury.
Treatment
The tactics of neutralizing pain syndrome are conservative. Treatment of discomfort involves taking medications:
- antibacterial substances - in cases of any inflammatory process;
- analgesics and antispasmodics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- immunomodulators;
- prebiotics and probiotics;
- mineral and vitamin complexes.
Severe pain in the lower abdomen in men can be eliminated using physiotherapeutic procedures:
- ultrasound;
- medicinal electrophoresis;
- warming up;
- acupuncture;
- magnetic therapy;
- diadynamic therapy;
- darsonvalization;
- inductothermy;
- UHF.
Conservative treatment may include:
- diet therapy - a gentle menu is compiled only by the attending physician;
- massotherapy;
- folk remedies - used only after consultation with a clinician;
- Exercise therapy.
All methods will help relieve pain, but do not affect the treatment of the underlying disease. To eliminate the disease that caused the pain, both conservative methods and surgical intervention may be required.
If stabbing pain appears in the lower abdomen in men, indications for surgery are:
- testicular torsion;
- neoplasms of any nature;
- appendicitis;
- varicocele;
- cholelithiasis.
Prevention and prognosis
To avoid pain in the lower abdomen in men, you just need to follow general simple preventive rules:
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- avoiding physical and emotional fatigue;
- healthy and balanced diet;
- constant strengthening of the immune system;
- weight loss (if necessary);
- prevention of hypothermia;
- engaging in protected sex only;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- timely detection and treatment of any pathological conditions that may lead to pain;
- visiting a medical facility several times a year to undergo a full examination.
Dull pain in the lower abdomen in men is not life-threatening. If discomfort is ignored and there is a complete lack of treatment, the underlying disease will progress, which is fraught with consequences that can lead to death and the inability to have children.