Polyps in the gallbladder are benign neoplasms that can greatly ruin your health and even develop into cancer. They are detected using ultrasound. Not everyone knows exactly what it is, what the dangers are and why polyposis should be taken seriously. Despite the benign nature of the growths, which may be round, teardrop-shaped or irregular in shape, they must be dealt with. Any growth under certain circumstances can quickly turn into a cancerous tumor. Each type of polyp has its own symptoms and treatment.
Classification of polyps in the gallbladder
Women over 35 years of age are at particular risk. The share of such cases is 80%. Sometimes a polyp in the gallbladder is diagnosed in a child under 10 years of age. The reason for this phenomenon is frequent examinations of this category of patients. Formations localized in the gall bladder are divided into several types:
- An adenomatous polyp is called true. In this case, there is a proliferation of glandular tissue located in the thickness of the epithelium. It is characterized by a very high risk of malignancy: in 30% of cases the tumor degenerates into cancer. After diagnosing this polyp, it is necessary to see a doctor regularly. Without treatment, the chance of avoiding complications is minimal.
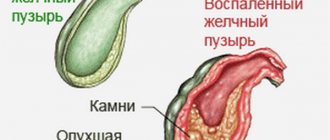
- An inflammatory polyp is classified as a pseudotumor. It provokes constant irritation of the gall mucosa. The result of advanced inflammation is the abnormal growth of its granulation tissue. Frequent culprits of inflammatory polyps are pancreatitis, biliary dyskinesia, calculi (stones in the bladder) or parasites.
- A cholesterol polyp is also a pseudo-formation. It belongs to those types of growths that can be successfully treated with conservative treatment. The difficulty here is the accuracy of diagnosis. When examined by ultrasound, they are mistaken for the adenomatous or inflammatory variety. The reason for the misdiagnosis is calcified inclusions in places where cholesterol accumulates in the gallbladder.
- It is not entirely correct to call papillomas polyps. These benign tumors are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV). Papillary growths are small in size, but they can also suddenly develop into malignant neoplasms. They also need to be treated.
The growths in the bladder come in different sizes - 2 mm, 3 or more. Diameter from 5 mm to 10 does not require surgery, but if further growth of the polyp is observed, surgery is necessary. It is impossible to avoid it when the size exceeds 10 mm, since conservative treatment will not bring results.
Reviews
Samara, Katya. An ultrasound revealed six polyps. Ursosan was prescribed. After two months, the polyps decreased by two, which I was very happy about. But I couldn’t drink Ursosan for the entire three months because I felt discomfort in the pancreas. After a five-month break, I will start drinking Ursosan again.
Khabarovsk, Marina. After giving birth, my right side began to hurt. This went on for three years. It was scary to go to the hospital. I read on the Internet that this could be liver decay. In the winter of 2013, I finally decided to go for an ultrasound. We discovered a polyp in the gallbladder measuring 7x4. It's all because of my diet after childbirth. I thought that in order to have fatty milk, you had to eat fatty milk. This is what it all led to.
Tyumen. Olga. My daughter was diagnosed with a gallbladder polyp. Watched in dynamics. My daughter is already 30 years old. She adheres to proper nutrition. Limits himself to fatty and fried foods. A friend had a polyp removed along with her gall bladder. She feels great, although she was very afraid. Even the puncture sites are almost invisible after laparoscopy.
https://youtu.be/ApP0St1xWkk
Causes of growths
It has not yet been precisely established which factor is responsible for the occurrence of growths in the gallbladder.
Polyps are more common in women, especially after the age of 35, and only in 20% of cases in men.
There are three possible causes that lead to pathology in both men and women.
Heredity
Genetic predisposition plays an important role in the case of benign tumors. Therefore, heredity is called the most important reason for the occurrence of papillomas and adenomatous neoplasms in the gallbladder. Tumors in other organs that are present in one of the relatives increase the risk of polyp formation in the gallbladder and other places. A connection has been established between a hereditary factor and biliary dyskinesia, a possible provocateur for the appearance of these growths.
Metabolic disorders
Improper metabolism is to blame for the occurrence of pseudopolyps, especially the cholesterol variety, since it is the result of stagnation of bile in the bladder, liver, and ducts. Impaired fat metabolism leads to the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of the gallbladder. As time goes by, calcium salts are deposited in these deposits. Due to the absence of obvious symptoms, the patient is not even aware of the disease that has settled in the bladder. Unpunished polyps continue to grow.
Diseases of the liver and gall
The cause of the appearance of such polyps is also diseases of the hepatobiliary system. Insufficient or excessive amounts of bile greatly complicate digestion, and the result is various gastrointestinal pathologies that are directly related to the occurrence of polyps. This category includes acute or chronic cholecystitis, pancreatitis, dyskinesia (impaired motility) of the biliary tract, and cholelithiasis.
Symptoms
The presence and intensity of clinical manifestations of the disease will depend on the nature of the neoplasms and their location. For example, cholesterol polyps are asymptomatic or cause minimal discomfort to a person. These are the factors that cause patients to seek qualified help late.
The most dangerous polyps are those located in the neck of the bladder or its duct. Such formations cause unpleasant symptoms. This is explained by the fact that there is a disruption in the process of bile outflow into the intestines. When the polyp is localized in another area of the organ, the symptoms of the pathology are erased and mild in nature.
A polyp in the gallbladder is expressed in the following symptoms:
- the appearance of pain of varying intensity. The more the organ walls are overstretched, the more painful the pain will be. The location of pain is the projection of the gallbladder. The nature of the pain is dull and cramping. The intensification of this symptom can also be facilitated by eating large amounts of fatty foods, frequent overeating, drinking alcohol and stress;
- yellowness of the skin and sclera - this manifestation is most typical for true polyps, as well as in situations where stagnation occurs in the bladder. Such factors lead to bile leaking into the bloodstream;
- change in the shade of urine, it becomes darker, almost brown, and stool - it becomes discolored - this occurs against the background of the previous symptom;
- severe itching of the skin – also associated with the appearance of jaundice;
- increase in body temperature;
- attacks of nausea, which may result in vomiting. Nausea is often observed in the morning, immediately after sleep;
- a feeling of bitter taste in the mouth, which is a consequence of the reflux of bile into the stomach;
- muscle and joint pain;
- hepatic colic is a syndrome characterized by the sudden onset of severe and cramping pain in the area under the right ribs. This symptom is a consequence of the fact that the outflow of bile is completely disrupted. When such a disease occurs, such a sign appears extremely rarely, only in cases where the presence of a polyp on a very long stalk is diagnosed. Located in the neck of this organ, the long leg of the polyp can be pinched and cause sharp pain, increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, pale skin and cold sweat. It is also worth distinguishing hepatic colic from simple pain - a patient with colic cannot find a position in which the intensity of the expression of pain will decrease.
It is worth noting that polyps in the bladder can lead to the formation of other diseases, the symptoms of which will complement the clinical picture of the main disease. Such pathologies include:
- dyskinesia or spasm of the bladder duct;
- housing and communal services;
- acute or chronic form of pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis.
The appearance of such ailments is due to the fact that polyposis often acts as a source of infection.
Symptoms of gallbladder polyp
Insidious growths often grow quietly, without disturbing the patient. This asymptomaticity does not make it possible to detect their appearance in the early stages. The first signs of the presence of tumors in the gallbladder may be:
- Dull or cramp-like pain (colic) in the area of the right hypochondrium after eating fatty foods, eating a large amount of food, or drinking alcohol. These feelings are sometimes triggered by stress.
- Yellowness of the skin, sclera, mucous membranes. It is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and itching. Signs such as darkening of urine and increased temperature are also possible.
- Bitter taste in the mouth, which indicates a bile deficiency.
These symptoms are often attributed to normal illness and are considered signs of other diseases (for example, ulcers or gastritis). This reaction allows the tumor to develop further.
Why are polyps in the gallbladder dangerous?
An advanced disease can have unpredictable consequences. The worst of them is the degeneration of a polyp into a malignant tumor of the gall bladder. This fate befalls 10-30% of patients. If such a development of events was avoided, then the patient may face equally dangerous consequences:
- liver abscess;
- hepatitis;
- osteoporosis;
- peritonitis;
- cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts);
- chronic cholecystitis;
- cirrhosis.
The risk of contracting these diseases can be reduced. To do this, you need to learn not to ignore regular examinations, especially if you have a history of gall and liver diseases.
Diagnostics
Typically, patients come to a medical facility when they are constantly bothered by unpleasant, painful sensations that arise in the right hypochondrium.
For successful diagnosis, one ultrasound examination is not enough, so several methods are used in combination:
- Ultrasound. The examination allows you to detect neoplasms located on the walls of the gallbladder. At the same time, the disease is differentiated, excluding another possible diagnosis - stones. When the patient's body position changes, gallstones move, but the tumors remain in place.
- Ultrasonography. Refers to precise endoscopic methods for studying tumors. It is carried out using an ultrasound probe inserted into the duodenum. Thanks to this, it is possible to visualize the gallbladder located in close proximity. The method provides a high-quality image of polyps.
- CT. The tomography method is optional. The study allows you to determine the exact location of polyps, their structure, and identify abnormalities of the biliary tract. The main advantage of the study is its high resolution, which makes it possible to detect the smallest single tumors and correctly assess the possibility of their further transformation into a malignant tumor.
In addition to instrumental studies, laboratory tests are carried out. These include blood tests (general, biochemical), feces, and urine. If polyps are detected on an ultrasound, you need to know which doctor to contact with the results. Such conditions are treated by gastroenterologists, and they make a verdict on whether bladder surgery is necessary. When diagnosing small tumors, a conservative approach is preferred.
Main types
There are several types that differ in composition, shape, and mechanism of formation:
- adenomatous are tumors of a benign type, the only ones that are considered true. In 10% of all cases, they transform into malignant cancerous growths due to tissue proliferation. This species requires constant monitoring by doctors;
- papillomas are also tumors of non-malignant origin. They resemble multiple papillae, which eventually become cancerous tumors;
- inflammatory – pseudotumors that arise due to inflammation in the mucous membranes of the gallbladder. Bile tissue grows due to irritation of the membrane by stones or parasites;
- cholesterol polyps are false formations that resolve under the influence of drug therapy. During an ultrasound examination, specialists often mistake them for true ones. These are growths consisting of cholesterol due to a failure in fat metabolism. Over time, calcium salts are added, which allows them to be diagnosed as stones.
How to treat polyps in the gallbladder without surgery
Single or multiple polyps in the bladder can be treated only if they are cholesterol formations. Sometimes, to achieve the goal, it is enough to prescribe certain medications and adjust your diet.
If the polyps belong to other species, and their size does not exceed 1 cm, then at first no drastic measures are taken: only observation is carried out. The patient is periodically referred for ultrasound or CT. When tumor growth is not observed, they prefer not to be touched.
Pharmacy medicines
One of the main drugs is usually prescribed, since getting rid of polyps in the gallbladder is not too difficult: it is enough to take measures to destroy cholesterol deposits. The following dissolution agents are used:
- Ukrliv, Ursosan, Ursofalk. The active component is ursodeoxycholic acid, bear bile.
- To lower cholesterol: Ovencor, Simvastatin, Simvastol.
- Choleretic: Allohol or Holiver.
- Gepabene, Gepatrin are hepatoprotective drugs.
- Drotaverine, No-shpa, Spazmalgon relieve spasm of the smooth muscles of the bladder.
- Vitamins: ascorbic acid, group B, rutin.
Treatment takes from 3 months to 2 years, depending on the size of the tumors.
Folk remedies
You can also stop the growth of tumors in the gallbladder using folk methods. But the best result will be if herbal medicines are considered only as an additional method. Use the following recipes:
- 15 g of mature crushed raincoats are poured with 100 g of vodka, put away for a week in a dark, warm place. For further preparation, the alcohol is drained, the mushrooms are chopped, mixed with 50 g of honey and 500 g of butter. Take the composition three times a day for 2 months strictly after meals. Dose - tablespoon.
- Fresh aloe leaves are placed in the refrigerator for 2 weeks, then crushed, honey (100 g) and 500 g of butter are added. Take in the same way as the product with raincoats.
- Dry celandine herb (1 tbsp) is placed in a thermos, a glass of boiling water is added, and left for at least 2 hours. Drink a tablespoon three times a day half an hour before meals. After a month's course, take a break for 10 days.
Physiotherapy
Treatment of gallbladder polyps without surgery involves a combination of physiotherapeutic methods. Contraindications are chronic cholecystitis, multiple polyposis.
As for heredity and genetic abnormalities, scientists have proven that polyps can be inherited. Even if other tumors have been identified in blood relatives, the risk of gall bladder polyposis increases significantly.
The necessary procedures include:
- mineral baths and internal intake of mineral waters;
- colon hydrotherapy;
- hydromassage;
- magnetotherapy:
- laser therapy;
- ozokerite or paraffin applications;
- ultrasound treatment;
- electrophoresis.
Patients are especially recommended complex sanatorium treatment to strengthen the immune system and restore the bile-forming function of the liver.
Exercise therapy
Therapy for gallbladder polyposis is often supplemented with therapeutic exercises aimed at eliminating bile stagnation. Exercises must be performed regularly.
- Take a horizontal position, bend your knees, clasp them with your hands. For several minutes, rock back and forth, then left and right.
- Standing, spread your legs shoulder-width apart, rotate your upper body clockwise, then counterclockwise.
- Lying on your back, lift your legs one by one, bend them, and bring them close to your chest.
- In the same position, alternately retract and relax the abdominal muscles.
It is recommended to add yoga asanas for beginners, as well as breathing exercises, to this complex.
Nutrition rules
Successful treatment of a polyp is impossible without nutritional adjustments. The habit of splitting food, that is, eating in small portions, but often, must become a law. The patient must completely forget about the following products:
- legumes;
- fatty fish and meats;
- all hot and sour vegetables (sorrel, radish, tomato);
- canned food, marinades, pickles;
- fatty dairy products;
- baked goods, pies;
- chocolate;
- alcohol;
- carbonated drinks.
It is recommended to limit the amount of hard-to-digest fiber. The basis of the diet should be vegetables, fish, meat, cooked in a gentle way - steamed or baked. Jelly, compotes, pureed vegetables or fruits, and cottage cheese should be included in the diet daily.
Treatment
The method of eliminating such a disease is determined by the nature of its course, for example, drug therapy can be aimed not only at eliminating symptoms, but is also used to treat cholesterol polyps, which can be gotten rid of without surgery.
Drug therapy is aimed at:
- drugs that stimulate bile secretion and peristalsis of the affected organ. Such substances are strictly prohibited if the bladder duct is completely blocked by a polyp;
- means for normalizing bile secretion;
- medications that lower cholesterol levels in the blood, as well as to destroy cholesterol deposits;
- medications to relax the smooth muscles of the affected organ.
Another effective way to eliminate polyps of cholesterol origin without surgery is alternative medicine recipes. Treatment of polyps in the gallbladder with folk remedies involves the use of:
- rose hips and strawberries;
- knotweed and wormwood;
- coltsfoot;
- St. John's wort and shepherd's purse;
- dill seeds and immortelle leaves;
- honey and celandine;
- chamomile and mint;
- pumpkin seeds and corn silk;
- tansy and aloe;
- black radish juice and chaga mushrooms;
- bee products, in particular honey and propolis.
For other types of polyps, the only treatment option is surgery. Indications for such treatment of gallbladder polyposis include:
- polyp volumes greater than one centimeter;
- situations in which the etiological factor of the disease was any chronic disease;
- constant growth of tumors;
- multiple polyps;
- diagnosing cholelithiasis;
- transition of the disease to the oncological process;
- significant deterioration in bile outflow;
- inflammation of the walls of the affected organ.
Regardless of the indications, complete removal of the gallbladder will be required, which can be done in several ways:
- laparoscopic cholecystectomy - endoscopic instruments are inserted through several small incisions in the abdomen;
- open cholecystectomy - excision of this organ through a large incision on the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity.
The basis of postoperative recovery is the diet for polyps in the gallbladder. The list of permitted and prohibited foods, recommendations for preparing dishes, as well as a sample menu are provided to the patient only by the attending physician.
How to treat a gallbladder polyp surgically
There are situations when polyposis cannot be cured or the risk of tumors degenerating into malignant ones is high. Only then do they resort to the last resort - surgical intervention. Gentle laparoscopic cholecystectomy is most often used. During the operation, the entire bladder is removed without large tissue dissection - through small punctures for the endoscope and instruments.
At the first alarm bells, it is necessary to undergo an examination to prevent the development of cancer. Then the prognosis for a successful recovery will be extremely positive.
In some cases, open surgery is performed - traditional. The basis for the decision is growths that degenerate into a cancerous tumor with metastases that have spread to regional lymph nodes. The disadvantage of this method is that it is highly traumatic, since the incision is 15 to 20 cm long.
Endoscopic bladder-sparing polypectomy is used less frequently. In this operation, the instrument is a diathermic loop, which is placed over the stem of the growth, then it is cut off. The bleeding is stopped by an electrical discharge passed through the loop. The outcome of the operation cannot be predicted.
Diagnosis
It needs to be diagnosed using special equipment. It is impossible to make a diagnosis without examination and listening to the symptoms. The following types of diagnostics are distinguished:
- Ultrasonic. On examination, the organ appears as a dark spot, and polyps look like small round formations growing from the wall of the bile organ. Ultrasound may provide inaccurate information about the disease. To clarify the details, it is better to go through it in combination with other types.
Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder
- Endoscopic diagnostics. Compared to ultrasound, it provides more accurate data on the location of the growth and its structure.
- CT scan. This form of examination has a minus - high cost, and a plus - the ability to detect small polyps.
- MRCP (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography) is the most advanced method for detecting polyps.
The described methods can provide information about the disease in full or in part, depending on the choice of the first.