Bile plays an important role in the human body, as it participates in the digestion process. Thanks to this substance, many fat-containing vitamins are broken down and absorbed. Kinking of the gallbladder is a fairly common pathology not only in adults, but also in newborns. The disease is accompanied by pain, nausea and vomiting, and general malaise. If the pathology is not treated, serious health consequences may occur in the form of diabetes and obesity.
Causes
Excesses of the gallbladder are congenital and acquired. The first type of bend is often formed during the intrauterine development of the embryo, mainly at the 5th or 6th week of embryo formation. It is during this important period that the formation of the liver, as well as the gall bladder, occurs.
The causes of intrauterine development of pathology are external and internal factors:
- taking various medications by a pregnant woman (up to 12 weeks);
- diseases of pregnant women caused by viruses and infections;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages and tobacco during pregnancy;
- bad ecology;
- the presence of chronic diseases before and during pregnancy.
Acquired bending of the gallbladder appears due to the following reasons:
- obesity of any degree;
- poor quality nutrition (consumption of large quantities of spicy, fried and smoked foods);
- frequent strict dieting;
- impaired metabolism;
- cholecystitis;
- lifting weights;
- cholelithiasis;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- surgical interventions on the liver, gall bladder;
- long-term use of various medications;
- pregnancy period;
- diseases of the liver, duodenum, and pancreas.
In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision or ICD-10, gallbladder inflection is classified under “other specified pathologies of the gallbladder” and is listed under code K82.8.
Who to contact? If you suspect a bend in the gallbladder, you should contact the nearest clinic. First of all, you need to get an appointment with a therapist, who, based on the patient’s complaints, will conduct an external examination of the patient. For a more objective diagnosis, the therapist will issue directions for stool and urine tests, general and biochemical blood tests, and ultrasound. Based on the test results, the therapist will prescribe the necessary treatment. If there are significant deviations in the tests, consultation with a gastroenterologist may be required.
The gastroenterologist will conduct a more detailed examination of the patient and may prescribe duodenal intubation. If there are concomitant liver diseases (hepatitis, cholelithiasis), the help of a hepatologist will be required. If treatment is only possible through surgery, a consultation with a surgeon is scheduled.
https://youtu.be/Yn4JSCX7luY
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of signs of pathology, it is worth reviewing your usual lifestyle and making some adjustments:
- Add more physical activity and play sports.
- Women during pregnancy are advised to take more walks - the disease worsens during pregnancy.
- Review your gastronomic habits and develop a meal schedule.
- The grocery basket should include healthy ingredients rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Control your weight. Avoid excess or deficiency.
- Do not perform excessive physical activity.
- For preventive purposes, undergo examination by a gastroenterologist.
- Eliminate bad habits (alcohol, nicotine).
- Treat inflammatory processes in the body in a timely manner.
- Replace caffeine-containing drinks with medicinal herbal teas.
It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it, therefore, you should not ignore the body’s signals. A feeling of discomfort is a reason to be examined by a doctor.
How dangerous is the pathology?
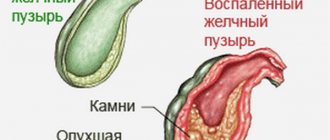
A bend in the gallbladder is a dangerous condition, because the deformed organ is unable to perform its necessary functions, which leads to stagnation of bile, the formation of stones and a strong inflammatory process. Due to pathology, diseases such as cholelithiasis, chronic and calculous cholecystitis often develop. The most dangerous condition is considered to be a bend in the neck of the organ, especially if it is accompanied by cholelithiasis. As a result, the stone can become an obstacle to the exit of bile from the bladder.
Consequences resulting from bladder pathology:
- Poor outflow of bile substances, resulting in the appearance of stones and disruption of the digestion process.
- Diabetes mellitus develops.
- Blood circulation in the bladder is disrupted, resulting in destruction of the walls of the organ.
- Stomach ulcers, gastritis and pancreatitis develop.
- Poor absorption of fat-containing vitamins. As a result, vision deteriorates and heart problems appear.
- Peritonitis may occur (in case of rupture or cracks in the walls of the bladder). In this case, bile enters the abdominal cavity.
A bend in the gallbladder is considered a very dangerous pathology that requires immediate assistance from a specialist.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosing the inflection of the gallbladder neck is only possible using equipment. At the initial stage of the study, the gastroenterologist conducts a survey of the patient to clarify the clinical picture, the severity of the disease, and determine the severity of symptoms. The doctor studies the patient’s medical history, lifestyle, and finds out hereditary factors. Afterwards, a physical examination is carried out by palpating the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, in particular the area under the right hypochondrium, and examining the condition of the skin and sclera.
The patient is prescribed laboratory tests: blood, urine and feces.
An ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is performed to determine the degree of deformation of the gallbladder. In some cases, the patient may be recommended a CT scan in order to obtain a more accurate picture of the pathology.
Therapeutic tactics are selected based on the diagnosis, form and severity of the disease
Types of bend
Doctors distinguish 2 types of inflection development: temporary and permanent. According to the degree of localization, kinks can be divided into the following types:
- bends of the bladder neck;
- body organ;
- bottom;
- ducts
It is often the bending of the organ neck that is observed; pathologies of the body or fundus are rare, but they are considered the most dangerous conditions, as they lead to rupture of the walls of the organ. The bend occurs in the shape of a hook, an arc, or sometimes an hourglass. Sometimes a double bend of the organ is observed; it has an S-shape. It is rare to see a bend in several places at once; this pathology is mainly caused by a congenital anomaly of the bladder (when it has a spiral shape).
Symptoms
The severity of the signs of manifestation directly depends on the reason for which the bend formed and where it was localized. Congenital pathology of the gallbladder often occurs without visible symptoms and is sometimes recognized completely by accident during an ultrasound examination.
Clear signs of excesses are:
- severe pain in the area of the right rib. Pain is sometimes felt in the back, collarbone, and rarely in the spine;
- there is a constant feeling of nausea, attacks of vomiting;
- salivation increases;
- the frequency of breaths increases;
- there is a strong heartbeat;
- there is a bitter taste in the mouth;
- increased sweating;
- facial skin becomes gray;
- body temperature rises.
When the neck of the bladder is twisted, the pain can spread throughout the body, and after eating, the patient experiences severe bloating.
Kink in children
For congenital pathology, which is detected only by ultrasound examination, treatment, as a rule, is not prescribed, but it is important for the child to follow a diet. Otherwise, with age, various complications may appear in the form of poor functionality of various organs. In case of acquired inflection of the bladder, mandatory treatment is prescribed, which is very labor-intensive.
The causes of acquired pathology can be:
- obesity;
- excessive physical activity of the child;
- frequent fasting;
- psychoemotional disorders.
Also, cholecystitis, excessive prolapse of the peritoneal organs, or an enlargement of one of the organs of the biliary system can also often provoke an inflection.
Acquired bending of the bladder in children is accompanied by exactly the same symptoms as in an adult, while congenital bending in most cases occurs without any symptoms. Only acquired pathologies are dangerous; in this case, children may experience complications such as:
- liver enlargement;
- liver tissue dysfunction;
- developmental delays in children;
- the appearance of jaundice;
- the occurrence of chronic diseases of the digestive system.
Diagnostics
The most accurate picture of the pathology is provided by an ultrasound examination of the patient.
Ultrasound is able to determine exactly where the localization of the inflection occurred, find out the degree, as well as the type of pathology. For a reliable result, the examination is first carried out on an empty stomach, and a second examination can be carried out half an hour after breakfast. For breakfast, before the re-examination, you need to eat choleretic products (butter, egg yolk). If the bend is congenital, the shape of the organ after loading with breakfast will remain the same (deformed).
Treatment
In the event that the bend of the gallbladder is congenital (in a small child), treatment is practically not prescribed. In most cases, as the child’s body grows and develops, the pathology disappears. Acquired inflection requires medication therapy and various physical procedures.
- If the bending of the gallbladder is caused by an infectious disease, the doctor will prescribe antimicrobial drugs.
- Also, to stimulate the secretion of bile, you need to take choleretic drugs (“Flamin” costs from 247 to 310 rubles, “Ursofalk” costs from 209 to 1,739 rubles, “Allohol” costs from 8 to 43 rubles).
- If pain and spasms occur, the use of antispasmodics and painkillers is indicated.
- The most effective herbal remedy that has a choleretic effect is choleretic herbal collection No. 3. It contains such medicinal herbs as:
- calendula flowers;
- peppermint leaves;
- chamomile;
- tansy;
- yarrow.
The decoction should be brewed in a water bath for about 10 minutes (2 tablespoons of herbs per 200 ml of boiling water). Take the product 1/3 cup per 30 minutes. before meals 3 times a day. Treat with a decoction for 1 month. Please note that young children, pregnant and lactating women, as well as patients with calculous cholecystitis are prohibited from taking this collection.
In especially severe cases, when therapy with medications and herbs does not bring a positive effect, surgical intervention is prescribed to eliminate the kinks in the bladder.
Reviews
Dear readers, your opinion is very important to us - therefore, we will be glad to hear your feedback about the inflection of the gallbladder neck in the comments, this will also be useful to other users of the site.
Laura
As a result of chronic cholecystitis, a bend in the neck of the gallbladder appeared. The defect was discovered during an ultrasound when the abdominal cavity was examined. Treatment was prescribed. She took choleretic drugs and underwent a physiotherapeutic procedure - electrophoresis with novocaine.
Eve
My daughter had a gall bladder problem until she was 3 years old. The disease appeared after she began to eat adult food. Doctors, based on the results of the examination and examinations, said that the condition does not require intervention and will correct itself, since it arose as a result of underdevelopment of the gallbladder. And so it was.
https://youtu.be/BYB053lfhi4
Diet
In case of congenital pathology of the gallbladder, a therapeutic diet should accompany the patient throughout his life. With acquired inflection, a diet is necessary to reduce the symptoms of the disease. You should eat in small portions, 5 times a day with an interval of about 4 hours. The following foods should be removed from the main diet:
- fatty, fried, smoked and spicy foods;
- legumes;
- chips and crackers;
- canned food;
- sweet drinks;
- alcoholic products;
- seasonings and spices;
- apricots, raisins, grapes and dried apricots.
It is necessary to reduce to a minimum the consumption of salt, coffee drinks, butter, chocolate and cocoa, jam, sugar, and honey. You should eat lean varieties of meat and poultry, eat fish and seafood, eat more vegetables and fruits (but not sour ones), cereals, pasta, dairy products, and vegetable oils. Dishes must be boiled, steamed and baked.
A bend in the gallbladder must be examined by a doctor. Even with congenital pathology, you should carefully monitor the patient’s well-being and, in case of any deviations, contact a specialist. Timely treatment can completely eliminate the problem and help avoid serious health consequences.
You can also watch a video where they talk about several options for traditional treatment of a bend in the gallbladder.
Signs and symptoms of a kinked gallbladder
Characteristic clinical symptoms of gallbladder inflection are:
- Constant bitterness in the mouth;
- Nausea;
- The appearance of bad breath;
- Gray or yellowish coating on the tongue;
- Belching;
- Bloating and increased gas formation;
- Heartburn;
- Feeling of heaviness in the stomach, especially after eating;
- Vomiting when eating fatty, fried, smoked foods;
- Stool disorders (diarrhea followed by prolonged constipation).
When stones form in the ducts of the bladder against the background of constant stagnation of bile, the patient sometimes experiences yellowness of the skin and visible mucous membranes.
Periodically, the organ itself and the bile ducts become inflamed, as a result of which the patient develops cholangitis or cholecystitis, the symptoms of which are:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Diarrhea;
- Increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees;
- Refusal to eat;
- Yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes;
- Attacks of biliary colic.
A bend in the gallbladder in an infant before the introduction of complementary foods may not manifest itself clinically, however, after the inclusion of adult food in the diet, constant regurgitation and stool disturbances are possible. The S-shaped bend of this organ in a young child is in most cases the main cause of a common pathology - biliary dyskinesia.