Gallbladder cholesterosis - what is it? To put it simply, this is a disease associated with a malfunction in fat metabolism.
The pathology is quite rare, but it interferes with a full life due to the accumulation of cholesterol in the gallbladder and disruption of important functions of the organ. No inflammation is observed.
Women 40-45 years old who already have problems with lipid metabolism and high cholesterol levels are most at risk of developing cholesterosis. Also, those people who have been diagnosed with atherosclerosis (problems with the arteries that lead to their narrowing and obstruction of blood flow) are at risk of the disease.
In rare cases, cholesterosis can be a consequence of cholelithiasis or cholestatic syndrome, which causes problems with bile or its patency.
Gallbladder cholesterosis - what is it?
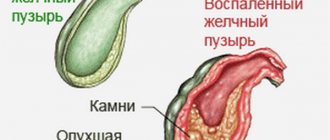
Gallbladder cholesterosis is an accumulation of fatty molecules on the inner surface of the organ. They stick to its walls from the inside and prevent it from functioning fully. Congestion develops, causing severe complications. They will be discussed below.
When the disease occurs, the functioning of the entire digestive tract is disrupted, the patient suffers from dyspeptic (digestive) disorders, and in rare cases severe pain develops. Treatment is effective only in the early stages of the disease; in advanced cases, the patient’s life can only be saved by surgery to remove the gallbladder. It's called cholecystectomy. Today, the equipment allows the procedure to be performed using a minimally invasive laparoscopy method. The patient quickly goes through the rehabilitation period and returns to his usual lifestyle.
The gallbladder (GB) is a small, hollow sac that temporarily stores bile produced in the liver.
Bile is directly involved in the process of digesting food, so the slightest disruption of the gallbladder leads to dangerous complications. One of the serious but rather rare diseases is cholesterosis or lipoid cholecystitis (lipodiasis).
The cause of the disease is abnormal lipid metabolism, as a result of which the walls of the gallbladder are covered with a layer of harmful cholesterol.
Cholesterosis can develop as an independent disease or as the initial stage of gallstone disease. Lipodiasis is extremely rare (about 5% of cases), and the risk group mainly includes women over 40 years of age.
The disease was identified and described back in the 1800s, but it has only begun to be studied in more detail in the last 15 years. Thanks to this, new methods for diagnosing and treating cholesterosis have emerged.
What kind of examination do you need to undergo?
The earlier specialists detect gallbladder diseases, the sooner they will begin treatment, including surgery. Many people are afraid of surgery and postpone it, despite constant colic and severe pain. Without treatment, cholesterosis of the gallbladder, especially the calculous type, can lead not only to disruption of the functionality of the biliary system, but also to tissue malignancy.
The main diagnostic method for cholesterosis is ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder. This method is affordable and absolutely safe for health. Anyone who has chronic gallbladder disease is recommended to undergo an ultrasound examination several times a year in order not to miss the worsening of their condition.
Often people first learn about gallbladder cholesterosis on an ultrasound scan. The method allows viewing mainly the anterior side wall of the organ. Cholesterosis is detected in the form of uneven thickenings of the mucous membrane. In polyposis and focal forms, the diagnostician detects noticeable parietal formations, which are difficult to confuse with other diseases and tumors.
Other diagnostic methods are not very informative. Pathological changes in blood biochemistry occur only when cholesterosis is combined with calculous cholecystitis. In this case, the level of alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin increases.
https://youtu.be/Htl7kRokwnA
Cholesterosis and cholesterol polyp
Gallbladder cholesterosis is a rare pathology that is diagnosed more often in women (ICD10 code - (K82)). The disease manifests itself in the accumulation of cholesterol in the organ, as a result of which its membrane suffers, then its functionality. The walls of the bladder are especially affected, so the disease is often called cholesterosis of the walls of the gallbladder.
Cholesterol esters are deposited on the surface of the organ in the mucous membrane. In photographs, these deposits appear as yellowish stripes, resembling a scaly structure. There is no inflammatory process, so the symptoms of the disease do not appear immediately, which is the greatest danger.
A cholesterol polyp of the gallbladder occurs as a complication of long-term cholesterol. The cells of the mucous membrane of the organ are degenerated, and a rounded growth appears. It is easy to notice during diagnostic testing. Tissues with cholesterol deposits grow rapidly and therefore require urgent treatment. Polypous cholesterosis requires surgical intervention.
There are three main types of gallbladder cholesterosis:
- focal (individual cholesterol plaques are determined);
- polypous (cholesterol plaques protrude strongly into the lumen of the bladder);
- diffuse or mesh (the wall of the bladder is completely affected, cholesterol deposits are distributed evenly over the entire area or in the form of a dense network).
In addition, calculous and acalculous forms of gallbladder cholesterosis are distinguished. Very often, treatment tactics depend on the presence or absence of stones.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of gallbladder cholesterosis resemble symptoms that are characteristic of most pathologies of the biliary system. The severity of clinical manifestations depends on the severity of the pathology and the prevalence of the pathological process.
The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium. The pain syndrome is aching in nature and intensifies after errors in the diet (consumption of fatty, spicy, smoked foods). Soreness usually occurs in the evening;
- Nausea after eating fatty foods;
- Dryness and bitter taste in the mouth;
- Diarrhea gives way to constipation.
Important! 25% of patients with gallbladder cholesterosis have no symptoms of the disease.
When cholesterol polyps appear in the gallbladder, an attack of biliary colic often develops, which is characterized by:
- Sudden sharp pain in the right hypochondrium;
- Repeated vomiting that does not bring relief;
- General weakness, sweating;
- Bitterness in the mouth;
- Dizziness;
- Severe nausea;
- One-time diarrhea.
With the development of inflammatory processes, the following signs develop:
- Sudden development of pain on the right side of the abdomen;
- Sharp bitterness in the mouth;
- Repeated diarrhea;
- Severe nausea and vomiting that does not relieve the condition;
- Temperature increase up to 390 C;
- Apathy, weakness, increased fatigue.
Causes and mechanism of formation of cholesterol stones in the gall bladder
Cholesterol accumulates in large quantities in the gallbladder always against the background of lipid metabolism disorders. These disorders can develop for the following reasons:
- obesity;
- metabolic disease;
- overeating, eating unhealthy foods;
- hypothyroidism (thyroid deficiency). Metabolism throughout the body slows down with this disease. Fats are poorly absorbed by tissues; their excess remains in the blood and does not have time to be processed. Cholesterol settles on blood vessels or organs;
- endocrine gland tumors;
- congenital genetic diseases (familial hypercholesterolemia - a defect in the chromosome responsible for fat metabolism);
- liver diseases;
- hormonal dysfunction.
Cholesterol penetrates the bloodstream into the gallbladder and is partially absorbed by its tissues. An excess amount remains in the organ cavity. It is this residual fat that causes cholesterosis.
The gallbladder is a cavity for storing bile; it is formed in the liver. When food enters the digestive tract, the gallbladder reflexively begins to contract and releases part of the bile into the small intestine. There it performs its function - breaking down dietary fats. When cholesterol accumulates in the gallbladder, this process is disrupted.
First, excess fat settles on the inner surface of the organ in the form of individual molecules. They begin to be absorbed by special cells of the gallbladder tissue - macrophages. These are functional units responsible for removing foreign substances from the body. They “absorb” molecules and digest them internally with the help of enzymes. Excess cholesterol in the gallbladder is perceived by the body as something foreign.
Due to the abundance of fatty molecules, macrophages do not have time to process them and become filled with fatty contents. In this form, cholesterol penetrates deep into the tissues. When tissues are thoroughly “saturated” with fatty contents, excess cholesterol begins to settle on the internal walls of the organ. Plaques and growths form, which over time (as the walls contract) come off and settle in the form of cholesterol stones. This is the last stage of cholesterosis.
Prevention
If you already have any gallbladder diseases (dyskinesia, chronic cholecystitis, polyposis), even if they occur without pronounced symptoms, you must radically change your diet and completely abandon, first of all, fatty and fried foods. Avoid trans fats that are created during frying.
Replace animal fat with vegetable fat: to prevent the formation of cholesterol, atherosclerosis, cholesterosis and other pathologies associated with the synthesis of low molecular weight cholesterol, it is useful to consume olive, flaxseed, and cottonseed oils. They enrich the body with high-density lipoproteins. Olive oil also relieves inflammation of the vascular walls. Many experts consider the development of the inflammatory process in the vascular endothelium to be the root cause of atherosclerosis.
To prevent biliary cholesterosis, it is recommended to combine reasonable dietary restrictions with an active lifestyle. Regular physical activity helps empty the bladder of bile and maintain a high metabolic rate. Remember to eat small portions, but every 3-4 hours. This will allow bile to leave the bladder in a timely manner, preventing its thickening, inflammation of the mucous walls and the formation of stones.
In this video you can learn something new about the work of the bile, liver and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract, about ways to prevent and treat diseases of the biliary system. Many of the tips are easy to put into practice and will help you prevent gastrointestinal problems in the future.
Gallbladder cholesterosis is a disease that occurs against the background of impaired fat metabolism in the body. This process causes the accumulation of cholesterol in the wall of the gallbladder. As a result, an inflammatory process occurs.
In modern medical practice, the disease does not occur so often, mainly in women with atherosclerosis. Sometimes difficulties arise in making a complex diagnosis, then additional instrumental diagnostics are required. The disease code according to ICD-10 is K82.4.
Forms of the disease
The disease is classified according to two criteria. According to the nature of the disease, two types of cholesterosis are distinguished:
- Calculous (with the formation of gallstones).
- Non-calculous (without the formation of stones).
Another classification is based on the nature of the damage to the walls of the organ. The following types of cholesterosis are distinguished:
- focal - cholesterol settles locally on the walls of the bladder, forming plaques in one or several places;
- diffuse - the walls of the organ are completely covered with a cholesterol layer, its contractile activity is atrophied;
- polyposis - cholesterol builds up on existing plaques in the form of growths. On ultrasound they look like polyps or cysts;
- reticular - cholesterol covers the entire surface of the organ with a thin layer. On ultrasound, the coating looks like a mesh.
It is the polypoid form of gallbladder cholesterosis that leads to the formation of stones.
Causes
Cholesterosis is considered a disease that is not fully understood; experts are researching its causes. It is known that the basis for the development of pathology is a violation of fat metabolism. Cholesterol, which is “bad” or “excess”, is deposited on the walls of the organ as a failure in metabolic processes occurs.
The main reasons are:
- dyslipidemia – eating too much fat, which leads to impaired fat metabolism;
- diabetes;
- disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland and the entire endocrine system;
- fatty liver disease (non-alcoholic);
- fatty liver;
- formation of stones in the gall bladder (cholelithiasis).
The causes of cholesterosis are still being studied by specialists from different countries.
Symptoms and signs
Cholesterosis progresses slowly and does not cause any symptoms. The patient may occasionally feel slightly unwell, and dyspeptic disorders may appear (vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, belching with bile, bad breath). But these symptoms are mild; in most cases, people associate them with poisoning or simple indigestion.
When excess cholesterol affects the walls of the gallbladder deeply, so that they lose their contractility, more striking symptoms appear:
- diarrhea with undigested pieces of food and fatty traces;
- spasmodic pain in the right side of the abdomen (night attacks);
- vomiting with bile;
- temperature increase;
- weakness, pallor, drowsiness.
Common symptoms of cholesterosis
Identifying cholesterosis is often difficult. At first, the disease usually passes without pronounced symptoms; the person is not aware of the problem brewing in the body. There are no special signs of cholesterosis at the initial stage, so it is impossible to determine the pathology.
Only after the amount of cholesterol deposits increases along with the area of affected tissue will the diagnosis be effective.
The focal form of cholesterosis may not be accompanied by obvious pathologies at all. But after a while, cholesterol formations begin to spread to the submucosal layer of the gallbladder. Then the first alarming symptoms appear:
- feeling of heaviness on the right under the ribs;
- increased discomfort after poor-quality or heavy food;
- the occurrence of pain in the right side in the late afternoon or night;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- belching with a bad odor;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea;
- itching;
- problems with bowel movements.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out in several stages. It includes the following activities:
- Collecting anamnesis (data about lifestyle, previous diseases, medications taken).
- Examination of the patient: palpation, visual assessment of his condition.
- Laboratory research methods: general blood test (detects the presence of an inflammatory process and the state of immunity in general), biochemical blood test (assesses the function of the gallbladder and the functioning of other organs), urine analysis and stool analysis. The latter shows the presence of undigested food residues and traces of fat.
- Instrumental methods. Ultrasound is considered the most reliable way to examine the gallbladder. On examination, the screen shows the size of the organ, thickening on the walls, and the presence of stones.
Indications for treatment
There are no specific indications for treatment of CVD. There are two reasons:
- It is difficult to assess using ultrasound how effectively treatment is being performed in patients with various types of gallbladder lesions.
- There is little clinical experience confirming the effectiveness of conservative methods when using different treatment tactics and for different forms of CP.
The main indications for therapeutic treatment are polyposis reticularis and polyposis forms.
There are no strict criteria for selecting patients depending on the number of polyps and their size. Some authors say that the number is not so important, only the size matters, others believe that the number of polyps should be no more than 5.
Contraindications to therapy:
- Polypous form with a large number of polyps and an extensive process involving all the walls.
- It is impossible to exclude a malignant disease of the gallbladder.
- The presence of formations larger than 1 cm in diameter.
- The gallbladder is emptied less than 30%, that is, its contractile function is reduced.
Classification
The disease is classified on several grounds. Based on the presence of stones in the organ, the following forms are distinguished:
- stoneless,
- with cholesterol stones.
The first type is common and is not accompanied by the formation of deposits.
Depending on the specific course of the disease, the following types are distinguished:
- Focal. Small areas of lipid accumulation occur. In some cases, not only the wall is affected, but also the tissue itself.
- Total. It affects the entire organ, including the extrahepatic ducts.
- Polypous. Characterized by the formation of fatty protrusions of the wall. This type requires a thorough examination, since it is necessary to exclude the possibility of development of formations.
- Reticulate. Leads to thickening of the wall. It is a prerequisite for the development of polyposis.
Microscopically, a latent form is identified; it has no symptoms, it is combined. In the latter case, a combination occurs with:
It is classified by function based on the results of the diagnostics performed. An ultrasound is performed using a test breakfast rich in fat. Depending on the results, the doctor may talk about a slight, moderate, or pronounced decrease in the evacuation function of the gallbladder.
Complications and consequences if left untreated
Today, the disease in most cases is detected in the early stages during a routine examination of the digestive organs or a blood test. In the early stages, the condition is easily corrected, the gallbladder is completely cleansed.
In the absence of timely diagnosis and treatment, cholesterosis leads to serious complications:
Cholesterol stones in the organ block the bile ducts. The patient develops obstructive jaundice. The level of bilirubin in the blood rises sharply. This is the main pigment of bile, it gives it its characteristic golden color. Externally, the condition is manifested by yellowing of the skin, eyeball and mucous membranes.
When there is stagnation in the gallbladder, when the walls lose their ability to contract, favorable soil for the proliferation of bacteria is formed inside. The infection covers the entire gallbladder, and in severe cases spreads to other organs and peritoneal tissue. Peritonitis develops. This is a life-threatening condition.
When the sphincter of Oddi is blocked by stones, pancreatitis develops. Through this passage, bile and pancreatic enzymes enter the small intestine. If the sphincter is completely blocked, all pancreatic enzymes accumulate inside it and begin to digest the organ tissue. An acute form of the disease occurs. Manifested by severe abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. If the sphincter of Oddi is partially blocked, pancreatitis becomes chronic. It is practically asymptomatic, with only occasional heaviness in the abdomen and nausea.
When there is stagnation in the bladder, its walls become inflamed. Cholecystitis develops - inflammation of the gallbladder and its ducts.
It is extremely rare for organ tissues affected by cholesterol to degenerate into cancer cells. The oncological process begins.
All complications can be avoided if you take good care of your health and visit your doctor in a timely manner.
Complex treatment of gallbladder cholesterosis
If the disease is detected at an early stage, then the only treatment method will be diet. A healthy diet helps the patient to improve their lipid balance and eliminate excess cholesterol and its consequences.
Deposits on the walls of the gallbladder dissolve on their own, and the organ gradually regains its former performance. During the entire diet period, the doctor monitors the condition of the gallbladder walls and conducts regular ultrasounds. The slightest change is monitored, and if necessary, medications are added to treatment if the process worsens.
The following groups of medications are used:
- antispasmodics (painkillers);
- choleretic;
- antimicrobial agents (if an infectious process has joined);
- digestive enzymes.
The operation is prescribed in extreme cases when:
- lack of effect from drug treatment or deterioration of the patient’s condition;
- active spread of cholesterol deposits throughout the organ, formation of polyps;
- reduction in contractile activity of the gallbladder up to 30%;
- the addition of a purulent infection;
- formation of large diameter stones.
Diagnostic measures
In the absence of stones and inflammation in the gallbladder, cholesterosis is asymptomatic. In such cases, the disease is diagnosed accidentally as part of a routine medical examination, ultrasound of the biliary system, or cholecystectomy. If the development of cholesterosis is suspected, patients are prescribed the following types of examination:
- Biochemical blood test. Characterized by an increase in cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins;
- Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system. During the procedure, the doctor notes thickening of the walls of the organ. With the diffuse type, individual echo-positive areas are visualized. If a polypous or focal form is diagnosed, the specialist notes parietal formations or local thickening of the wall. To increase the accuracy of diagnosis, the patient is given choleretic products during the procedure;
- MRI and CT. Studies can determine thickening of the walls of the gallbladder, the appearance of biliary sludge, and polypoid growths;
- Cholecystography. The method is used to diagnose polypous forms of the disease. However, the procedure allows only in 40% of cases to differentiate a cholesterol polyp from tumors and parietal stones.
Principles of nutrition and diet
If you have cholesterosis, following a diet is mandatory. Patients are prescribed food according to the fifth diet. This is a restriction regime intended for patients with pancreatitis and cholecystitis. Basic principles of nutrition:
- eating small portions of food;
- you need to eat 5-6 times a day, plus include snacks in the form of a glass of yogurt or kefir;
- exclude fried, fatty, smoked, spicy and sour foods;
- include low-fat meats, fish, cereals, vegetables and fruits in your diet. Vegetables are best consumed boiled;
- completely eliminate alcoholic drinks and smoking.
Vegetable oils are not prohibited, but they should also be consumed in moderation. For drinks, give preference to green tea and herbal infusions. Avoid coffee, strong black tea, and carbonated drinks. The consumption of sweets should also be limited. It prevents the complete consumption of cholesterol by tissues, as it is easily absorbed as an energy source. The need for lipids disappears.
Medications
Medicines are used for significant disturbances in the functioning of the gallbladder and for active growth of the lipid layer in the cavity of the organ. The following groups of medications are used.
- Antispasmodics. These are substances that relieve spasms from the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract. They are used for painful attacks, which are always spastic in nature. Medicines are also used to relieve spasms in the bile ducts when they are blocked by stones or viscous bile secretions. It thickens when there is a lot of cholesterol in the composition. Names of tested drugs:
- Duspatalin capsules 200 mg 30 pcs.
- Trimedat tablets 100 mg 10 pcs.
- No-shpa forte tablets 80 mg 24 pcs.
The course of using antispasmodics is long - up to several months.
- Substances that enhance the contractile activity of the gallbladder. They are needed to prevent stagnation of bile inside the organ. The following tools are used:
- Magnesium sulfate solution 250 mg/ml 5 ml 10 pcs.
- Hepabene capsules 30 pcs.
- Substances that normalize the composition of bile and prevent its thickening. Names of medications:
- Ursosan capsules 250 mg 10 pcs.
- Hofitol tablets 60 pcs.
They are used for a long time - in courses of up to six months.
- Enzyme agents. These are medications containing digestive enzymes. They are needed to stabilize the digestion process. If the gallbladder is not functioning properly, digestion of food in the small intestine becomes difficult. These drugs are used to compensate for the lack of digestive juices. They help nutrients to be fully absorbed. This is very important for a sick body.
- Antibiotics. Used if the gallbladder is affected by infection or purulent inflammation. The following drugs are used: Bactrim, Tetracycline, Signicef. These are broad-spectrum medications. If a purulent infection is detected in its rudimentary form, they can protect a person from having the gallbladder removed. Bactrim is used primarily in children.
Application of mineral water
Mineral waters with low salt content are used to treat cholesterosis. The course of therapy should be prescribed by a doctor, because some waters may be contraindicated for the patient.
For cholesterosis, it is useful to perform tubage. To carry it out, you need to drink 0.5 liters of still warm mineral water in the morning before meals, and then lie on your right side, placing a heating pad under it.
You should lie in this position for at least half an hour. It is recommended to add a small amount of sorbitol to the mineral water you drink, but you can do without it.
Diet
For problems with the gallbladder, an important part of therapy is the patient’s lifestyle and diet. You should definitely discuss with your doctor what is and is not allowed to eat. Especially with early manifestations of cholesterosis, such an adjustment will not only avoid complex and lengthy treatment, but also completely cure gallbladder disease.
Below are nutritional principles recommended by doctors to support the functioning of the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts:
- eat frequently (5-7 times a day) in small portions;
- spend enough time eating and chew food thoroughly;
- try to take a meal break at the same time every day;
- give up fatty foods, smoked foods, avoid foods that are too salty, sour and spiced;
- give up alcoholic beverages;
- eat mostly cereals, fresh or stewed vegetables, lean meat;
- eat low-fat dairy products.
You will have to follow this diet for the rest of your life. Treatment with folk remedies can also support the health of the gallbladder and restore its function. Usually, choleretic herbs are used, which must be brewed according to the instructions and consumed several times a day.
Is it possible to dissolve cholesterol stones in the gallbladder using folk remedies?
There are a large number of traditional medicine recipes for dissolving cholesterol stones. The effectiveness of the methods has not been clinically proven, but judging by patient reviews, some of them are highly effective:
- chicken bile;
- bay leaf decoction;
- black radish;
- dill infusion;
- corn silk.
Most of these substances have choleretic activity. Bile liquefies, moves easily through the bile ducts and copes well with the function of digesting food.
The digestive system is restored as a whole, which helps dissolve cholesterol stones.
Recipes based on medicinal plants can effectively cleanse the gallbladder, normalize the functioning of the digestive organ, and eliminate unpleasant symptoms of the disease. For this purpose, use:
- Beetroot juice. To normalize the flow of bile, it is recommended to take 50 ml of freshly squeezed juice before each meal;
- Dandelion rhizome. Raw materials must be collected in April - May during flowering. The rhizome must be thoroughly washed, peeled, and chopped. Next, 100 g of raw material is poured with 200 ml of boiling water, the composition is brought to a boil. The chilled decoction should be taken 30 ml before each meal;
- Herbal teas based on calendula, parsley, immortelle, birch buds, corn silk, mint, chamomile flowers, rose hips. The listed plants can be used individually or in combination.