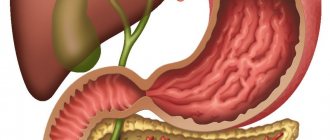
Location and communication
Patients who are faced with gastrointestinal diseases are often interested in whether the gallbladder and pancreas are the same thing? The localization of the bubble is formed in the anterior part of the right longitudinal groove of the liver. The bubble has the shape of a pear or a cone. The size of the gallbladder is compared to an egg. It looks like an oval bag.
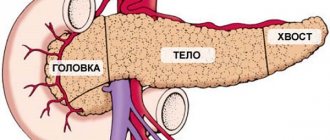
The pancreas is a glandular organ that performs an endocrine exocrine role. The gland is localized in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach in the epigastric zone near the spleen. Its left section is located under the left rib. The omental bursa divides the stomach and pancreas. At the back it borders with the veins and aorta.
The pancreas and gallbladder are connected in an anatomical and functional manner.
A special connection is visible in the initial form of the channel structure, when they are connected into a single common ampoule, into which secretion and bile arrive at one moment. Such a structure often leads to the development of the disease, because the common canal can become obstructed:
- excrement;
- tumor formation;
- be blocked by a polyp, preventing the contents from exiting into the intestines.
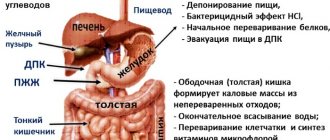
There is also a close relationship between the gallbladder and the gland. The breakdown of food products is carried out with the participation of a secretion that contains enzymes. It is they who break down carbohydrates, fats and proteins into fairly simple components that are absorbed into the blood and participate in subsequent life processes. The bile acids present in bile also stimulate the digestive juice. Thus, the excretion of bile into the intestinal passage is regulated by humoral and nervous means.
Pathologies of the pancreas are often associated with an inflammatory reaction, tumor phenomena, the formation of cysts and the occurrence of stones in tissues. An inflammatory disease of the gland is pancreatitis, which manifests itself in acute and chronic forms.
Biliary pancreatitis is referred to as damage to the pancreas. Since the enzymes of the organ are not able to penetrate into the intestinal area, they begin to linger, having a destructive effect on the pancreas. Toxins penetrate into the blood vessels, so the damage can spread to neighboring organs.
The disease can appear due to a number of reasons.
- With an incorrect diet and lifestyle, excessive drinking of alcohol, soda, and intake of prohibited foods.
- In case of genetic predisposition to the pathology.
- When the patient takes potent drugs for a long time, which include antibacterial drugs - tetracyclines, drugs containing estrogen and corticosteroids.
- Due to changes with age, which causes a disruption in the blood supply to organs.
- When an advanced chronic type of pathology of the digestive system is observed.
The following reasons can also cause damage in the gallbladder area:
- penetration of bacteria;
- increased cholesterol levels and plaque formation;
- changes in the chemical composition of bile;
- change in the relationship between the bladder and the nervous system;
- the presence of anomalies in the structure of the bubble.
This disease is often observed in women over 40. This is associated with an increase and decrease in body weight and destructive habits. Patients who have had 3-4 or more pregnancies are also at risk.
https://youtu.be/_50qy28qWx8
Symptoms of inflammation of the gallbladder and pancreas
The pancreas and gallbladder, although they perform different jobs in the digestive tract, can have a strong impact on each other. The pancreas is ensured by the productivity of secretions, which contain enzymes and hormones. When the inflammatory process develops in the pancreas, a change in the waste of produced enzymes is observed. Their excess enters the passage of the gallbladder, which leads to a divergence of the painful course to this organ.
Symptoms for inflammation of the gallbladder and pancreas are quite similar. At the same time, cholecystitis and pancreatitis often occur together, so the pathologies complement and irritate each other. In addition, the diseases are considered unsafe and lead to the development of severe outcomes if pancreatitis and cholecystitis are not treated immediately. When initial signs of gallbladder and pancreas disease appear, you must immediately go to the doctor to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Cholelithiasis is characterized by the development of the formation of stones in the canals or bladder. Stones are solid crystals that are formed from calcium salts and cholesterol, bound by the bile component - bilirubin. Symptoms of gallbladder pathologies develop based on the volume and size of the stones. They may not bother the patient for a long period of time. At the initial stage of their progress, the patient feels:
- colic in the liver, which will be strong, sharp under the rib and radiate under the right shoulder blade, limb;
- nausea occurs;
- vomiting bile;
- there is a bitterness in the mouth;
- dry mouth;
- weakness.
The patient’s temperature also rises, appetite decreases, and a food allergy is possible.
Cholecystitis manifests itself in 2 types - acute and chronic. Due to the acute course of the disease, the following develops:
- vomit;
- the patient is chilling;
- temperature increases;
- symptoms of jaundice appear;
- skin itches.
The effect of food on enzyme production
Enzymes that are synthesized as inactive compounds (such as trypsinogen) are activated when they enter the small intestine thanks to the duodenal contents. They begin to be released as soon as food enters the duodenum. This process lasts 12 hours. The food consumed is important, affecting the enzymatic composition of the juice. The largest amount of pancreatic juice is produced for the incoming carbohydrate food. Its composition is dominated by enzymes from the amylase group. But bread and bakery products produce the maximum amount of pancreatic secretion, and less when eating meat products. A minimal amount of juice is produced in response to dairy products. If bread is cut into a thick piece and swallowed in large quantities, poorly chewed, this affects the condition of the pancreas - its work intensifies.
The specific amount of enzymes contained in the juice also depends on the food: 3 times more lipase is produced for fatty foods than protease for digesting meat. Therefore, during inflammation of the pancreas, fatty foods are prohibited: to break them down, the gland has to synthesize a huge amount of enzymes, which is a significant functional load for the organ and enhances the pathological process.
The foods consumed also affect the chemical properties of the pancreatic fluid: in response to the intake of meat, a more alkaline environment is formed than to other dishes.
Diagnosis and differences of pathologies
The symptoms of the gallbladder and pancreatitis have much in common. Both with pancreatitis and with damage to the pancreas, the patient feels pain under the rib on the right. Painful discomfort increases when dietary nutrition is disrupted, fatty, spicy, fried foods, and alcohol are consumed.
Manifestations of pancreatitis and cholecystitis include:
- diarrhea – oily consistency, gray in color, stools are frequent and foul-smelling, have remnants of undigested foods;
- numerous vomiting that does not bring relief;
- pain in different places.
In addition to the listed manifestations, gallbladder diseases are manifested by biliary hypertension, which is caused by stagnation of bile.
- The mucous membranes and skin are yellow.
- Skin itching.
- Enlarged spleen, followed by anemia, leukopenia.
- Ascites in severe situations without therapy.
Clinical signs are not enough, so the gallbladder and pancreas are checked in more detail.
Modern methods include:
- laparoscopy - the method involves inserting microchambers through a puncture into the peritoneum, which are attached to a tube;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy - an endoscope is inserted into the esophagus and the gastrointestinal mucosa is examined;
- duodenal intubation - the study involves taking material for analysis. A rubber probe is inserted into the intestinal area. Bile is collected to perform visual, microbiological analysis and identify inflammation.
Instrumental diagnostic methods.
- Assessing the position of the gastrointestinal mucosa is carried out using gastroscopy. A probe with a camera attached is swallowed. The doctor examines the intestines, canals, and stomach in this way.
- To detect pancreatic calcification and stones, radiography is used.
- To obtain a three-dimensional image of the pancreas, the examination is performed using computed tomography, including a laparoscopy.
To obtain complete information about the position of internal organs, blood tests are used. The patient also needs to give urine.
Treatment
When suspicious signs associated with the gallbladder or pancreas occur, it is forbidden to treat yourself. The gastroenterologist will conduct a complete diagnosis, make the correct diagnosis and select medications so that the patient’s condition improves.
Carrying out therapeutic manipulations includes several stages. Initially, the patient needs to change the menu and include a healing diet. It is important to completely treat the disease so that chronic pancreatitis and cholecystitis do not develop. Diseases are cured systematically, without interruption, even when the patient’s well-being improves.
In case of changes in the activity of the gallbladder and biliary pancreatitis, the attending physician will prescribe the following drugs for the treatment of the pancreas and gallbladder:
- inhibitors Kontrikal, Gordox - drugs for the pancreas and gall bladder catalyze the production of enzymes;
- Pentoxyl, Methyluracil - to improve metabolism;
- pain-relieving tablets for the gallbladder and pancreas that will relieve pain;
- Cimetine, Omeprazole - will help suppress secretion productivity;
- Pancreatin, Festal are enzyme agents.
In the presence of cholelithiasis, which is detected during diagnosis, the gallstones are removed and the bile ducts are cleared.
The chronic form of the disease is effectively treated with traditional methods. Healing herbs that have an anti-inflammatory effect are used. If there are stones in the bladder, then take a decoction of medicinal plants, which changes the composition of bile.
After the required time has passed, a pause is made, after which the therapy is repeated three to four times.
In the case of cholecystitis and inflammation of the gallbladder, dietary recommendations for illness are followed. In addition to drug treatment, it is necessary to organize the diet correctly. It is contraindicated to heat food; it is contraindicated to eat hot and cold foods. Eat little by little 6 times a day. Include only permitted foods in your diet.
What to do
In order for the pancreas to resume its work and function normally, it is regularly cleansed. For example, for two weeks, every morning after 6-10 hours, eat 15 dates on an empty stomach. You can wash it down, but only with boiled water or spring water, if available. After half an hour they start eating.
We also recommend viewing: Pancreatic cancer: treatment methods
In the absence of dates, cleansing can be replaced by taking buckwheat for ten days. This procedure is done as follows: a glass of buckwheat is washed and filled with kefir in a volume of 500 grams per glass of buckwheat. In the morning, divide the resulting porridge into two parts: eat one instead of breakfast, and the second a couple of hours before bed.
Fresh parsley juice is also useful for restoring the functioning of the gland. To do this, several bunches of green parsley are chopped in a mixer with the addition of lemon. The crushed mass is transferred to a fine sieve and a container is placed under it. Then pour the mixture into a sieve with one and a half liters of clean boiled water. The resulting liquid is poured into another container and consumed throughout the day; honey can be added to taste. You need to drink up to three liters of fluid per day. During this period, it is recommended to avoid drinking coffee and black tea. These drinks can be replaced with mineral, boiled or spring water. A variety of dried fruit compotes or natural vegetable and fruit juices are also suitable. In the morning, switch to drinking herbal tea, to which you can add a small amount of green tea, rose hips or hibiscus tea.
To stimulate the glands, include a variety of spices in the diet, onions, garlic, ginger and horseradish; it should also contain legumes and sprouted grains. Daily consumption of raspberries, sorrel, barberry and pomegranate has a good effect on improving the functioning of the pancreas. Taking infusions of string, linden blossom and wild strawberry also has a beneficial effect.
To restore the functioning of the gland, you must stop eating fatty, fried, smoked foods and reduce alcohol consumption to a minimum. You can give up sugar for a while and eat more plant-based foods.
Complications
Any disruption in the activity of the pancreas and gall bladder leads to the formation of other pathological systems. So, with acute manifestations of the disease, complications develop:
- disturbance of blood supply;
- vascular thrombosis;
- internal blood loss due to the presence of an ulcer in the stomach or duodenum;
- pneumonia;
- tachycardia and others.
When there is a deviation in the gallbladder, the following occurs:
- formation of pus;
- peritonitis;
- sepsis;
- acute inflammatory process in the pancreas.
Both diseases provoke the development of cancer, and the functioning of nearby organs will change. This leads to tissue death and disruption of chemical reactions throughout the body.
Pancreatic diseases
The pathology in the organ that causes its illness can be caused by various reasons. For example, a frequent danger awaits the pancreas from its “neighbor” - the gallbladder, especially if it is burdened with stones.
The gallbladder is an organ that stores bile produced by the liver. Bile is a colloid with a balanced content of phospholipids, acids, cholesterol, bilirubin and salts. Bile is essential for the digestion and absorption of both fats and fat-soluble vitamins. Fats, if there is insufficient amount of bile, are not digested, remaining in the gastrointestinal tract, they are attacked by bacteria living there. This leads to diarrhea, flatulence, and pain in the abdomen.
With prolonged acholia (lack of bile in the intestines), there are signs of deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins K, D, A, which can lead to serious health problems - night blindness, brittle bones, poor blood clotting. Bile produced by the liver removes excess cholesterol from the body and prevents the occurrence of fermentation and putrefactive processes in the intestines, as it can exhibit antibacterial properties.
Gallstone disease is the most common cause of inflammatory processes in the pancreas. Cholestopancreatitis or biliary inflammation of the gland is a diagnosis that in most cases is given to women.
Doctors strongly recommend routinely getting rid of stones, the presence of which in the gallbladder resembles the effect of a time bomb. Large stones can form bedsores and further rupture of the gallbladder wall. As a result, high concentrations of bile enter the pancreatic parenchyma, causing irreparable damage to it. Small specimens, clogging the ducts, disrupt its outflow. Obstructive jaundice occurs, the level of bilirubin in the blood increases, and pancreatitis occurs. In both cases, immediate medical attention is required.
Diabetes
Not everyone realizes that the pancreas has another function besides producing enzymes. This is an endocrine function. The gland produces the hormone insulin, which is responsible for regulating blood glucose levels. When the amount of insulin produced by the pancreas decreases, diabetes mellitus develops.
The main reasons for the development of diabetes are eating foods rich in complex carbohydrates, excess body weight, eating large amounts of sweets containing sugar, lack of physical activity and movement in general, and overwork. It also provokes the development of diabetes and the presence of vascular atherosclerosis, hyperthyroidism, and the use of synthetic hormones.
Attention! Diabetes often develops against the background of pancreatitis, if the latter is not treated.
If a person has diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin, which is why hyperglycemic syndromes periodically occur. Signs: dry skin, headaches, chilly hands and feet, thirst, deterioration in the quality of vision. To avoid such conditions, insulin must be administered regularly.
Insulin itself helps glucose to be absorbed from the blood, but in its absence or shortage, glucose from the blood cannot escape anywhere, its level rises, resulting in diabetes. If there is too much glucose in the blood, then the biochemical balance between cells and the environment around them is seriously disturbed, and damage to proteins, nucleic acids, and fats occurs. And glucose itself begins to actively combine with proteins. This process is called glycation. And when it goes too fast, it can cause harm to the tissues surrounding the blood. By the way, glycation occurs in healthy people, but very slowly.
An increase in glucose levels, in turn, has a negative effect on the pancreas. Thus, the cells that are responsible for the production of insulin in this organ quickly die and can no longer restore their numbers, which is why the situation only gets worse.