Divisions and subdivisions of the human digestive system
Food initially enters the oral cavity. This is the beginning of the digestive tract, which is not always correctly called the gastrointestinal tract in everyday life, identifying the concepts. Metabolic products ultimately enter the rectum. This is the terminal section of the digestive tube.
Diagram of human digestive physiology
| Gastrointestinal Department | Functions performed |
| Oral cavity | Mechanical processing, grinding of food, participation in the elementary breakdown of complex carbohydrate foods |
| Pharynx | Bolus propulsion and swallowing |
| Esophagus | Transit of food, esophageal phase of swallowing. |
| Stomach | Mechanical impact, protein hydrolysis |
| Small intestine | Participation in all types of metabolism, absorption of oligosaccharides, fatty acids and oligopeptides, water |
| Colon | Absorption of water, vitamins, bacterial digestion |
| Rectum | Formation of feces |
| Pancreas | Participation in hydrolysis, lipolysis |
| Liver | enzyme “factory” |
At all stages of transit of the food bolus, mechanical or chemical transformation occurs. Each section of the gastrointestinal tract has its own function and task in this complex, multi-stage process.
Oral cavity
It has two important sections: the vestibule of the mouth and the oropharynx. This is where a food bolus begins to form. Incoming products cause stimulation of the tongue receptors. Information enters the brain through the olfactory and gustatory pathways.
The volume of saliva reflexively increases or decreases depending on the quality of the product. Under the influence of these impulses, the ground is prepared for the further process of digesting food in the human body: the secretion of other digestive juices increases.
The tongue and teeth take part in grinding food components. This is an important stage, because mechanical processing precedes chemical processing, which begins in the mouth.
Here, under the influence of saliva, complex carbohydrate components are broken down. Saliva contains two important enzymes: maltase and alpha-amylase. Simpler disaccharides and oligosaccharides are formed, which then become easier to digest.
Pharynx
The oral cavity is responsible not only for the formation of the bolus, but also for its further propulsion and movement along the tube.
It does not stay in the oropharynx for long. At the stage when food enters the area of the tongue root, the oral phase of swallowing ends. Next comes the pharyngeal or oropharyngeal. Within about 1 second, a whole cascade of muscle contractions occurs, as a result of which the muscles of the pharynx contract, and the sphincter apparatus of the esophagus - the next section of the gastrointestinal tract - relaxes.
Esophagus
The third stage of swallowing, the esophageal stage, takes place in the cavity of this long curved tube. Due to the secretion of glandular cells of the organ mucosa and muscle contractions, food moves towards the stomach.
This is where it gets after contraction of the lower esophageal sphincter. More complex chemical breakdown processes begin.
Stomach
The physiology of human digestion provides that the process of processing food after passing through the esophagus continues in the stomach. This is a very important organ. Consists of several anatomical and functional sections. From the esophagus, its contents enter the cardiac region. There are practically no digestive enzymes here. The pH value does not reach the optimum for their normal operation.
From the cardia, food enters the body of the stomach. There are a large number of parietal or so-called parietal cells. They are responsible for the production of chlorine anions and hydrogen cations. The resulting hydrochloric acid is responsible for the high acidity of gastric juice. The optimal pH for the normal functioning of enzymes is from 1.5 to 2.5.
Gastric juice also performs the following functions:
- participation in the obturator mechanism of the pyloric part of the stomach, since acidic food will not be able to enter the duodenum;
- disinfecting: the presence of a sufficient amount of acid provides protection against bacteria that cause rotting and fermentation;
- creates conditions for autocatalysis of pepsin - a whole cascade of reactions.
The proenzyme (inactive form) is formed in the main cells of the gastric mucosa. Their maximum also occurs in the body area. In an acidic environment, pepsinogen is converted into an active protein, which activates and accelerates protein breakdown processes. It is transformed into simpler oligo- and polypeptide chains.
Gastric juice and its components do not participate in the hydrolysis of carbohydrates. An acidic environment is harmful to them.
The fat component is also not broken down chemically. But here the acidic environment of the stomach creates conditions for their emulsification. In this form, lipids in the lower parts of the gastrointestinal tract break down more easily and with less energy consumption.
Small intestine
It consists of the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. They differ in their structure and functions.
From the pyloric region of the stomach, food passes directly into the duodenum. This is a relatively small area of the intestine, but an extremely important one. After all, it is here that catabolic reactions of all types of metabolism take place, as well as the absorption of nutritional components.
The gruel that gets here from the stomach undergoes further propulsive movements, as a result of which the mechanical processing of the food bolus continues. The pH value here is alkaline - from 7.5 to 8.4. When acidified, enzymatic processes become slower and less efficient.
The most important enzymes involved in the breakdown of protein structures are tryspin and chymotrypsin. They are produced in the brush border of intestinal cells. They are also synthesized in an inactive form and activated by enterokinase.
Trypsinogen, transformed into trypsin, breaks down the remaining polypeptides into shorter amino acid chains and oligopeptides. The resulting mixture is subjected to more thorough hydrolysis using chymotrypsin.
This is not the end of protein breakdown. Terminal carboxy groups are cleaved from peptide chains by elastase and carboxypeptidase. As a result, oligopeptides and amino acids enter the distal parts of the intestine.
Fat metabolism in the duodenum occurs under the action of lipase. This enzyme breaks down various groups of lipids. As a result, glycerol and fatty acids appear.
From carbohydrate components, under the action of maltase and amylase, sugars are broken down and monosaccharides are formed. They are further used in anabolic reactions.
The physiology of human digestion continues in the jejunum and ileum. Absorption of oligo- and monosaccharides, fatty acids, and amino acids occurs here. Parietal digestion is responsible for this. Water is absorbed along with them. These metabolites enter the lymphoid apparatus through microvilli. Next, the path lies through the systemic bloodstream and the liver filter.
Colon
Water absorption continues in this part of the digestive tract. At the same time, the formation of feces begins.
The large intestine has the following sections:
- cecum;
- ascending and descending colon;
- transverse colon;
- sigmoid colon.
Within the proximal parts of the tract, absorption of water, vitamins, as well as the remaining chlorine, potassium, and magnesium ions occurs. In addition, the cecum and colon are colonized by various bacteria. They participate in the processing of the remaining masses. This process is called bacterial digestion. Fermentation and rotting may occur here.
The large intestine is a reservoir, a kind of depot for future feces. They are deprived of excess water. And they act lower.
Rectum
The physiology of human digestion does not end with the absorption of elements. The rectum is the final section of the digestive tube. This is where feces are finally formed.
Excess water is absorbed by the mucous membrane of the organ. It is abundantly supplied with blood. There is a peculiarity - this is where the hemorrhoidal blood flow originates, through which the blood goes directly to the portal vein through the portocaval anastomosis. Therefore, substances dissolved in water can still be absorbed into the bloodstream from here.
Anal hole
It does not participate in the digestion process in any way. The role of the anus is in the process of defecation.
Muscle sphincters are subject to the cerebral cortex, which allows a person to control the process. The final products of digestion leave the body through the anus.
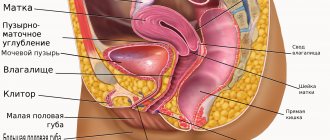
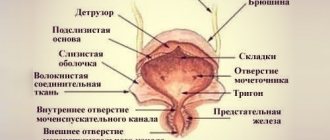
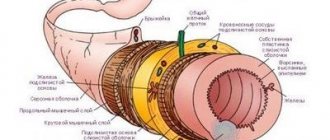
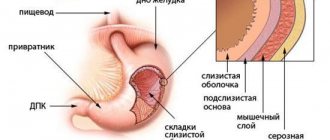
Structure of the stomach
The stomach is located in the upper abdomen, and is slightly displaced to the left hypochondrium. In the medical literature, the upper part of the abdomen, located under the lower edge of the sternum and ribs, is called the epigastric region, or epigastrium.
The shape of the stomach is not constant and depends on its filling, body position, the condition of surrounding organs and the constitution of the person.
The stomach is a hollow muscular organ, the maximum volume of which is individual for each person and is 1.5-2.5 liters.
The stomach has two sphincters (ring muscles) that regulate the entry of food from the esophagus and its exit after processing into the duodenum. These are the esophageal and pyloric sphincter (or pylorus).
The stomach is conventionally divided into 4 sections: Cardiac section, fundus or fornix, body and pyloric section.
Structure of the stomach:
Other organs involved in digestion
Physiology is structured so adequately and uniquely that the process of digestion in the human body involves organs that are not part of the digestive tract.
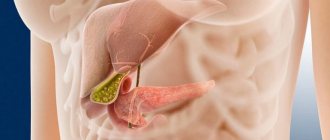
Pancreas (otherwise called Albarran's gland). It synthesizes hormones involved in carbohydrate metabolism, as well as enzymes that are directly involved in the digestion of food.
Pancreatic lipase is an important enzyme necessary to break down fats. That is why the secretion of pancreatic juice is maximum when eating fatty foods.
In addition, pancreatic secretions contain deoxyribonuclease, chymotrypsin and trypsin.
The role of the liver in digestion is very difficult to overestimate. After all, this organ is a storehouse of enzymes. It is he who is responsible for the synthesis of proteins involved in the breakdown of products from complex to simple, ready to enter the bloodstream.
The participation of the liver in carbohydrate metabolism is very high. If the function of this organ is impaired, severe metabolic disorders develop, including the formation of diabetes mellitus.
Bile is formed in the liver. It contains bile acids - a necessary participant in digestion. This makes fat molecules available for further biochemical transformations. In other words, bile acids are responsible for the emulsification of fats. In addition, they create the necessary level of acidity in the duodenum.
The bile ducts and gallbladder are reservoirs for bile synthesized in the liver. There it is deposited “on demand”. With inflammation and systematic violation of the diet, there is a tendency to form stones in the gall bladder.
The secretions of the pancreas, liver and gall bladder enter the duodenum and there they realize their action and participation in digestion.
When to see a doctor
If you experience problems with the digestive tract, it is recommended not to delay your visit to the doctor. Such diseases are treated by a gastroenterologist, but in the absence of such a specialist in the locality, the treatment is carried out by a general practitioner.
If the patient shows signs of gastrointestinal bleeding, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance, which will take the patient to the surgical department. You should not postpone a visit to a specialist, even if there are no acute symptoms of the disease.
Total length of the gastrointestinal tract
In the human body, the intestines are enormous. After all, this increases the area of contact with food. This fact is important for intensive absorption of electrolytes, metabolites, vitamins and water.
The small intestine is the longest section of the gastrointestinal tract. This is 6.5 - 7.0 m. It is in this section that the maximum intensity of absorption and biochemical transformation of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates is provided.
The large intestine is about 2 meters. The digestion processes here are less intense, since the main function is to deposit the forming feces and the final absorption of residual nutrients.
Surgeries to reduce stomach volume as a way to combat obesity
As many years of experience in performing operations on the stomach suggest, a person can easily live without part of it without experiencing any particular discomfort. There are situations when, for certain indications, in order to preserve the life and health of the patient, it is necessary to perform one of the operations to reduce the volume of the stomach.
One such indication is obesity. People whose body mass index (BMI) is above 40 kg/m2 can undergo surgery to ensure guaranteed weight loss. The fact is that the volume of the stomach affects our weight. Firstly, the feeling of fullness occurs only when the stomach is full, otherwise our baroreceptors will not be able to send the corresponding signal to the brain. Secondly, the amount of hormones that are secreted by the stomach also directly depends on its volume.
Nowadays, there are several options for gastric reduction surgery – gastric banding and gastroplasty. Banding is a more gentle method that involves placing a cuff on the upper third of the stomach. Thus, it is conditionally divided into small and large stomachs. The volume of the small one is no more than 15 ml, and it fills quickly, giving the patient a feeling of satiety. In addition, the volume of the bandage can be adjusted if necessary.
Gastroplasty is a radical method in which most of the stomach is excised. There are different gastroplasty techniques, which depend on the anatomical characteristics of the patient.
Of course, surgery is always associated with certain risks, and not everyone can decide to do it. Scientists are looking for ways to “deceive” the brain, because it is the brain that controls the processes of hunger and satiety. To do this, it is recommended to drink more water, because the centers of hunger and thirst are located nearby in the brain. The only condition is not to wash down your food with water, as this leads to dilution of gastric juice and poor processing of food. In addition to water, you need to drink green tea, eat foods with Omega 3 fatty acids and fiber - such food dulls the feeling of hunger, gives volume, which allows you to get full faster. Proper rest and sleep are also important, as chronic fatigue causes uncontrollable appetite.
Watch your diet and take care of your stomach so as not to think about surgery!
https://youtu.be/KiL02a0UNxk
10 November 2020, 10:37 0 7,824
The human muscular digestive organ is considered fundamental in the digestion process. Where is the stomach located, what is its task and features of its morphological structure? You need to know the answers to these and other questions in order to understand what happens at the initial stage of digestion and what its role is in the life of the body.
Digestion and excretion
The process begins in the mouth and oropharynx. With the help of the tongue, lips, and muscles of the palate, a lump of food is formed. The tongue carries out taste perception. The pharynx takes part in moving food to the esophagus, from where food enters the stomach almost unchanged.
In this department, mechanical processing continues and emulsification of fats begins. Proteins are hydrolyzed by pepsin into simpler polypeptide chains. Fats are not subject to biochemical transformation in this segment.
In the small intestine, namely in the duodenal cavity, under the influence of pancreatic juice, liver secretions and gall bladder, fats, proteins and carbohydrates are broken down. Fats break down especially intensively.
In parallel, wall absorption of simple metabolic products and water occurs here. Next, only water and vitamins are absorbed in the colon. What is not absorbed earlier is exposed to bacterial flora and their enzymes. As a result, bacterial digestion occurs.
Feces are formed in the rectum, and the last remaining water is absorbed. Excretion is carried out through the anus.
Symptoms
When one of the gastrointestinal diseases develops, the patient may be bothered by various symptoms, which depends on the specific disease and the degree of its neglect.
The most common manifestations will be the following:
- Nausea and bouts of vomiting, which in most cases alleviate the patient’s condition. As bleeding develops, the vomit becomes dark brown or even black.
- Heartburn and belching.
- Indigestion, heaviness after eating.
- Spasms of smooth muscles of the intestines and stomach.
- Pain in the epigastric region, navel.
- Constipation or loose stools. Often these conditions alternate, which further weakens the patient.
- Decreased appetite.
- Increased gas formation, flatulence.
- Loss of body weight.
Among the external manifestations of diseases are deterioration of the skin, dryness and flaking. With a long course of the disease, the patient experiences brittle nails and hair, and the appearance of a rash on the face. Sometimes the skin becomes jaundiced, since pathologies of the stomach and intestines often provoke complications from the liver and gall bladder.
The patient's abdomen may be swollen, and when touched, he feels sharp pain. If the condition is associated with bleeding, the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall are tense, the patient becomes pale, and the skin is moist. The patient is in a lying position; when trying to palpate the stomach and intestines, severe and sharp pain is noted.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5_3-QTvWYtI{amp}amp;modestbranding=0{amp}amp;controls=1{amp}amp;rel=0{amp}amp;showinfo=1{ amp}amp;enablejsapi=1{amp}amp;origin=
When bleeding, loose stools are also noted, which in medicine are called “coffee grounds.” This phrase very accurately describes stool, which in color and consistency really resembles coffee grounds. An additional symptom of bleeding will be a sharp decrease in blood pressure to critical levels.
Motility and innervation of the digestive tract
The walls of the hollow organs of the digestive system contain numerous plexuses of autonomic nerve fibers. But each department has its own innervation characteristics.
Sympathetic innervation of the pharynx is carried out by the laryngopharyngeal branches of the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion. And the vagus nerve is responsible for parasympathy.
In the mucous membrane of the esophagus, muscle fibers are oriented longitudinally for better movement of the food bolus in the craniocaudal direction. Plexuses also form around the organ. They consist of fibers of the vagus nerve, which is responsible for parasympathetic innervation, as well as branches of the cervical and thoracic nodes of the sympathetic trunk.
The muscle mass of the stomach consists of multidirectional and oriented muscle fibers. This is due to the fact that food is actively mixed in this organ, and the most intense mechanical effect on the food bolus occurs.
The innervation of the organ comes from the fibers of the celiac plexus and the vagus nerve. Their branches form numerous plexuses, among which the anterior and posterior gastric plexuses are powerfully expressed.
A similar principle of innervation occurs in the small intestine. Only instead of the celiac plexus, the mesenteric plexus takes part.
The large intestine is structured differently. The muscle layer consists almost entirely of the circular layer. This causes the predominance of pendulum-like and mixing movements in the transverse, ascending and descending colon, as well as pendulum movements in the sigmoid and rectum.
The physiology of human digestion is not simple. The sympathetic department is represented differently in the upper and lower levels of the large intestine. The same goes for the parasympathetic nerves. The sympathetic is formed from branches of the existing pancreatic and mesenteric plexuses. The branches of the nervus vagus (10th pair of cranial nerves) and the pelvic nerves are responsible for parasympathetic innervation.
The physiology of the digestive process in the human body allows us to maintain consistency within the digestive tract. This is important in the constantly changing conditions of its functioning.
Article design: Mila Friedan
Possible complications
Without treatment, complications will certainly develop. The most common is peptic ulcer disease, when the patient does not consult a doctor when symptoms of gastritis appear. In addition, peritonitis may develop when the ulcer perforates and the contents of the stomach escape into the abdominal cavity.
Peptic ulcer is the most common gastrointestinal disease
The condition is life-threatening for the patient. In addition, any disease can become chronic. A common consequence is patient exhaustion, asthenia, anemia as a result of regular blood loss. The most dangerous complication is death.
Gastrointestinal disorders are considered a fairly common problem among patients of different genders and ages. Diseases require timely treatment to prevent complications.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
- Body drying for girls: fat burning without damaging muscles
How to avoid problems?
When there is a disorder in a complex mechanism, nutrients are not absorbed, which leads to disruption of vital functions. It is important to know what means to support a healthy digestive process:
- avoid injuries to the abdominal area;
- do not drink tap water;
- monitor the health of the oral cavity;
- maintain the required time for sleep and daily walks;
- taking medications only after consulting a doctor.
Nutrition plays an important role in the prevention of functional disorders. It is important to remember and know how nutritious food affects health protection. In any case, food should be healthy, varied, and regular. Only by following these simple rules can every person maintain their health, preventing pathological failures.