In the clinic of neurotic conditions, patients often complain of an unpleasant taste in the mouth, including a sensation of iron taste, bitterness, and acidity. The reason for such discomfort is the poor mental state in which the person is. And quite often without even noticing it.
Some patients who have physical symptoms of restlessness, anxiety, and nervous agitation realize that they are worried. And they worry chronically. Others either do not notice their nervous state at all.
Or they notice it, but call it VSD - vegetative-vascular dystonia. Or they claim that they are worried about their failing health. They say that if it weren't for some bodily ailment, such as a bad taste, they would be calm and optimistic.
This is usually not the case.
Every disease has its own taste. How to determine your diagnosis by the taste in your mouth
Sweet
After dessert, the sweetness remains in your mouth for some time. But there are situations when that sweetness is felt, regardless of what the person has eaten. So, the possible causes of an obsessive sweet taste:
Poisoning by poisons. Toxins in the body affect several organ systems at the same time, so poisoning is often accompanied by a change in taste. Therefore, if you have a memory of contact with pesticides, phosgene or other poisons, it is better to immediately contact the toxicology department of the hospital for a quick diagnosis of the disease;
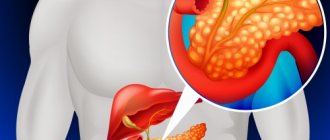
Impaired production of the hormone insulin. The cause of obsessive sweetness in the mouth may be an excessive amount of sugar in the blood, caused by disorders of the pancreas. The mechanism of the phenomenon is quite simple: sugar from the lymphatic system enters saliva, sweetening it. Therefore, it is better to immediately visit an endocrinologist to determine your blood sugar level, so as not to provoke the development of diabetes. Pancreatic dysfunction can also cause a sweet and sour taste in the mouth, which is often accompanied by heartburn. This is the first suspicion of pancreatitis;
Problems with the nervous system . If nerve fibers are damaged, the brain cannot properly process the information received, which leads to a sweetish sensation in the mouth. The cause may be common bacterial and viral infections. In this case, you need to take a general blood test and take it to a therapist;
Prolonged stress. The stress hormone tends to increase blood glucose levels. Therefore, during periods of depression, people can often feel a sweetness on the tongue that appears immediately after a stressful situation occurs;
Diseases caused by exposure to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Such a bacterium, affecting the lungs or oral cavity, also provokes a sweetish taste. It's all about the metabolic products of the microorganism;
To give up smoking. At first, when a person quits smoking, a sweetness is felt in the mouth after eating.
Sour
This item is accompanied not only by a sour taste in the mouth. Often a person is bothered by heartburn and belching. Let's consider the possible causes of these phenomena:
Gastrointestinal diseases. G astritis, ulcers, reflux and other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract often have symptoms of high acidity. These diseases can be indicated by accompanying symptoms such as pain in the upper abdomen, problems with stool, general weakening of the body and periodic nausea. In this case, you need to contact a gastroenterologist as soon as possible;
Dental diseases. As you might guess, oral problems almost always change the taste in your mouth. Caries, periodontitis and other dental problems cause increased acidity in the mouth. If accompanying symptoms are toothache and swelling, you should contact a dental clinic;
Pregnancy . An increase in the size of the uterus causes pressure in the abdominal cavity;
Night glutton. If you eat a lot of food at night, you will have an unpleasant taste in the morning.
Bitter
Bitterness in the mouth is the most unpleasant symptom. There may be several reasons for this, namely:
Diseases of the liver and biliary system. Bile has a bitter taste, and in case of diseases of these organs, it enters the oral cavity, causing a burning bitterness. This may be cholecystitis, gallstones and other diseases. Associated symptoms: nausea, acute pain in the upper right corner of the abdomen. It is necessary to contact a gastroenterologist;
Abuse of fatty foods . It also causes excessive bile secretion;
Love for alcohol. A similar principle for the appearance of bitterness;
Frequent use of anti-allergy medications. This is due to the impact on the immune system, which causes general disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary system.
Salty
This problem is usually caused by minor factors. But still, the problem can also be infectious diseases.
Possible reasons are:
Bacterial and fungal diseases of the nasopharynx. If such diseases are accompanied by the secretion of mucus, a salty taste may be felt, which is caused directly by the substance entering the oral cavity;
Diseases of the salivary glands. Many pathogenic microorganisms disrupt the functioning of the salivary glands. It is necessary to contact a dentist;
Abuse of alcohol, tobacco products and sweet water . Damage to the oral mucosa is to blame;
Lack of oral hygiene. In this case, you need to brush your teeth more often and drink up to 2 liters of water every day.
Oh, how sad I am!
Constant bitterness in the mouth occurs in those who eat too much fatty and fried foods or abuse alcohol, as well as in those who take antibiotics and allergy medications for a long time. But, if a strong bitterness in the mouth constantly bothers you, you need to rush to a gastroenterologist and do an ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver and gall bladder). Causes of a bitter taste in the mouth:
pathologies of the liver, gallbladder and biliary tract - bitter bile enters the esophagus and mouth;
chronic cholecystitis and cholelithiasis - this may also cause pain under the right rib, nausea and vomiting.
“Express” diagnosis: what tests are done at Health Centers
Read more
Taste buds
A violation of the sense of taste is a condition when it is difficult, and in some cases impossible, for a person to determine the taste of a substance using receptor cells. The disease can occur when taste buds or nerves that are responsible for transmitting impulses to the brain are damaged; if there are problems in the cerebral cortex, taste sensations often disappear due to the lack of smell.
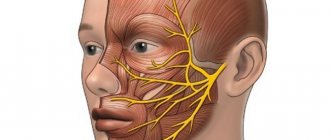
Taste is the feeling that appears when exposed to the taste buds located in the oral cavity of various substances, which, with the help of the facial, glossopharyngeal or vagus nerves, transmit information to the cerebral cortex, where it, after analyzing the information and combining it with data received from the olfactory organ and with other sensations, produces the result.
Taste buds can distinguish only four (according to another classification - five) tastes: sour, salty, bitter, sweet, and umami. Taste acquires its hue when basic sensations are combined with the density, temperature, acidity, and spiciness of food, which are perceived by the oral cavity, primarily the tongue, and also the olfactory organ.
Of the twelve thousand taste buds that are in the oral cavity, ten thousand are located on the tongue, the rest are on the cheeks, palate, larynx, epiglottis, and pharynx.
They are neuroepithelial cells collected in papillae (from several pieces in small bulbs, to five hundred in large bulbs). Most of the bulbs are concentrated at the tip of the tongue; as they approach the root of the tongue, their number decreases.
A hole is formed in the center of the bulb, through which each receptor located in it brings out the finest villi, which, when in contact with a chemical substance, are responsible for identifying taste. A single receptor is capable of recognizing only one taste (sweet, salty, bitter, sour), so they are collected into one bulb only with those receptors that are capable of perceiving the same sensations as them.
The lifespan of the receptor is short: it lives no longer than fourteen days, and after it dies, it is replaced by another, which is the reason that with age a person’s taste preferences often change (in this case, the sense of smell also plays an important role).
Each taste bud is connected to the central nervous system by nerve fibers that send information about the identified taste. First, the impulses enter the brain stem, after which they go to the thalamus, the part of the brain where the final processing of information occurs and taste and its shade are determined.
How did menthol appear in mint?
According to biologist and chemist Paul Wise, the ancestors of the modern mint plant (of which there are 42 species in the world today) developed the ability to synthesize menthol and use it as a defense mechanism. Mint is known to have a very strong cooling effect and odor, which may be off-putting and repellent to animals. In other words, those plant species that were able to adapt to external threats, as well as pass on their genes to subsequent generations, were eventually able to survive to this day.
Today, mint is widely used in a wide variety of products. Starting from food and ending with cosmetics. Due to its properties, mint is also used in medicine.
Impaired sense of taste
A person is not able to identify taste until the analyzer located in the cerebral cortex detects it. Therefore, a change in taste sensations can signal quite serious problems. These could be neurological disorders, a brain tumor, cranial nerve disease, head injury, or cerebrovascular accident. Sometimes the taste is partially lost and restored after some time, sometimes completely and irreversibly.
When they talk about problems in the perception of taste, they mean the following types of diseases:
- Ageusia – taste is completely absent;
- Hypogeusia – taste is felt, but weaker than usual;
- Dissociated hypogeusia - receptors determine taste sensations, but not all;
- Dysgeusia is a change in the sense of taste, often manifested as a metallic or sour taste in the mouth, sometimes a burning sensation is felt;
- Parageusia - when one sensation is replaced by another (sour is confused with bitter);
- Fantageusia - a non-existent taste is felt.
List of factors that cause strange taste sensations
A strange taste is a nonspecific symptom detected in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and oral cavity, liver failure, cerebrovascular accident, and localization of infectious agents in the upper respiratory tract.
Additional reasons that contribute to the appearance of an unpleasant taste in the mouth include:
- Taking medications, mainly antibiotics. The side effect of most antimicrobial drugs is a disruption of the natural microflora of the body, the development of dysbacteriosis and candidiasis of the mucous membranes. The negative effects of medications are accompanied by the appearance of a strange aftertaste. Discomfort can also be caused by the presence of individual intolerance to the components of the tablets, the death of pathogens, and exacerbation of chronic ailments.
- Dehydration. An unpleasant taste that periodically appears in the mouth may be a consequence of a lack of fluid in the tissues of the organs. Water deficiency occurs when you abuse carbonated drinks, alcohol, tea, and coffee.
- Metal poisoning: mercury, arsenic.
- Incorrect oral care. Poor hygiene is one of the reasons that causes an unpleasant taste in the mouth in the morning and increases discomfort after eating.
- Tobacco smoking.
- Oncology. Malignant tumors localized in various organs can cause the appearance of an unusual taste and bad odor. Among such neoplasms are cancer of the lungs, liver, and soft tissues of the mouth.
- Dietary features: constant overeating, unbalanced menu, eating at night.
Bad taste that appears in the mouth may be accompanied by a number of additional symptoms: fetid odor, the formation of deposits on the tongue, dry mucous membranes, belching, discomfort in the stomach, flatulence.
The reactions of receptor zones to the development of anomalies in the body are differentiated into several types. The most common ones include the appearance of sour, sweet, metallic, salty or bitter tastes. Sometimes patients in medical clinics complain of the appearance of a taste of mold, pus or soda, localized in the throat, tongue and lips.
If the strange taste that appears in the mouth is transient, then you can eliminate the symptom yourself. The development of special physiological conditions accompanied by the appearance of the discomfort in question (menopause, heavy menstruation) requires the supervision of a specialist. If an abnormal taste occurs that is permanent, you should immediately consult a doctor.
https://youtu.be/FkxsBpNhpMc
Causes
One of the main causes of loss of taste is a cold or flu: a severe runny nose often dulls or even completely deprives the sense of taste. This happens because the viruses that cause a runny nose also infect the taste buds, causing them to lose the ability to perceive the necessary feeling.
Also, one of the reasons for changes in taste sensations is allergies, which stuff up the nose and interfere with the full perception of taste, depriving food of aroma.
Why does the sweet taste occur?
The first thought of the average person when there is a constant sweet taste in the mouth is diabetes. A doctor would rather assess the cause of a sweet taste in the mouth as the development of pancreatitis.
Additional symptoms of the condition:
- The sweetness is felt most strongly in the morning, on an empty stomach;
- a burning sensation is felt in the epigastric area;
- Heartburn often occurs.
Stable insulin production is disrupted, resulting in poor metabolism. Glucose combines with gastric juice in an unsplit state.
If treatment is not started at this stage, diabetes may develop in the future. Can we give another answer to the question why there is a sweet taste in the mouth? Disorders of the nervous system, leading to its functional disorders, disrupt impulses.
They are first transmitted in a distorted form to the brain, then - incorrectly perceived - they go back to the taste buds. The taste sensations change so much that sour and bitter things are mistaken for sweet, but not when eating - at this time the concentration of food is high - but after, when the aftertaste remains.
The setback can linger for quite a long time.
A sweet taste in the mouth in the morning may be due to the presence of a purulent-inflammatory process in the oral cavity. During the day, people constantly chew or drink something; if there is a small amount of pus in the tonsils or dental cavity, it is constantly washed off.
During the night, while a person is sleeping, it accumulates to a significant extent, and its taste is felt. Pathogenic flora “hidden” in the nasal passages, ear canals and oral cavity changes the taste of saliva. Carbohydrate metabolism is also disrupted during intoxication. Once their source is eliminated, the condition will return to normal.
An adult with a strong immune system may not suspect for a long time that a particular product is not suitable for him. The body is already producing antibodies, preparing the “soil” for the manifestation of an allergic reaction, and apart from a sweetish taste, the increasing intoxication does not manifest itself in anything.
If you analyze your own feelings and remove the allergen from your diet, your health will immediately improve. After quitting a bad habit, smokers may experience a feeling of constant sweetness.
This is explained as follows: under the influence of nicotine and various tars, the perception of taste buds was disrupted, and, having lost the “drug,” they were “confused.” It’s not without reason that when quitting smoking, people are advised to suck on candy. Sweets can suppress the craving for smoking, since the desire to eat something tasty is similar to the desire to smoke a cigarette.
If adapting the taste buds of your tongue to a healthy life causes discomfort, you can chew a couple of coffee beans.
This will instantly cause the receptors to switch and change the impulses sent to the brain.
Treatment
If you lose your sense of taste, you should take into account that this problem is not so much a dental problem as a general medical one, so if such a disease occurs, you should consult a therapist and it is advisable not to hesitate.
Any taste disorder, especially one that occurs suddenly, without any apparent reason, is a reason to undergo a comprehensive examination, especially if after the first tests the doctor finds it difficult to make a diagnosis. https://youtu.be/-yNP32GzglY
The doctor will be able to prescribe treatment only after the cause of the loss of taste has been determined. When the underlying disease is cured, the sense of taste usually returns. To restore taste sensations, doctors often conduct a psychological assessment of the patient, while giving several important tips:
- First of all, the patient is explained how taste recognition occurs and how this is affected by temperature, density, and spiciness of food. This knowledge often contributes to improving the perception of taste.
- The patient is also advised to learn to enjoy the aroma of food: this affects the sense of smell, which has a direct interaction with the taste analyzer.
- The basic rule that must be followed is the need to eat only fresh, high-quality food and ensure that it does not spoil during storage in the refrigerator. Otherwise, if the taste is impaired, you can eat a spoiled product and become poisoned by it.
Throughout life, every person periodically faces such an unpleasant phenomenon as loss of taste. This condition can be temporary, after a person has damaged the mucous membrane of the tongue with hot or open food, or it can last for a long time. In the latter case, a full examination is necessary to exclude serious diseases .
Unpleasant taste in pregnant women
Since a woman’s body undergoes restructuring during pregnancy, she often notices a metallic or some other taste in her mouth. Basically, there is nothing wrong with this.
Bitterness is sometimes a harbinger of minor disruptions in the functioning of the liver and biliary tract, and sourness in combination with heartburn makes itself felt more often in the second trimester of pregnancy. As a rule, all this does not pose any threat, but if there is persistent discomfort, you should consult your doctor
https://youtu.be/T1_TFyUUEi0
Causes of loss of taste
The diagnosis of “hypogeusia” is made to the patient if he experiences a change in taste sensations. Changes in taste can be of different nature:
- Injuries to the taste buds on the tongue. Occurs with burns of the mucous membrane and mechanical damage. Experts equate this ailment to transport losses.
- Damage to receptor cells. This phenomenon already applies to sensory disorders.
- Diseases of a neurological nature in which there is atrophy of the afferent nerve or dysfunction of the taste analyzer.
The reasons for the loss of taste in food can be completely different. This phenomenon can be provoked by serious diseases and a lack of certain substances in the body:
- Facial nerve paralysis. With this pathology, there is a violation of the sensitivity of the very tip of the tongue.
- Traumatic brain injury. In this case, a person cannot identify complex taste compositions. At the same time, it distinguishes sweet, salty, bitter and sour tastes well.
- Colds. In this case, it may happen that senses such as smell are lost, which is associated with severe swelling of the nasopharynx.
- Cancers of the tongue. Most often, the tumor develops closer to the base of the tongue, on the side. This leads to the death of taste buds. The disease is accompanied by pain and bad breath.
- Geographical language. This original name characterizes inflammation of the papillae of the tongue. With this disease, spots of different sizes and shapes appear on the surface of the tongue.
- Oral candidiasis. It is manifested by the appearance of a cheesy layer on the tongue and oral mucosa. When the plaque is removed, bleeding ulcers appear. The disease occurs with a disturbance in the sense of taste.
- Sjögren's disease. This is a genetic disease in which the functioning of the glands is disrupted. Due to a lack of saliva, the oral mucosa dries out and becomes susceptible to infections. With this syndrome, patients cannot taste food.
- Hepatitis. In the acute course of the disease, dyspeptic symptoms are observed, which are accompanied by a change in taste perception.
- Side effects from radiation therapy. After treating oncology with this method, patients experience a lack of taste.
- Deficiency of certain vitamins and minerals. It has been revealed that problems with taste can be caused by a deficiency of zinc and vitamin B.
- Side effects from medications. Some antibiotics, antidepressants, antihistamines and vasoconstrictor nasal drops can lead to this unpleasant phenomenon.
- Long-term smoking. We are talking not only about cigarettes, but also about a pipe. Tobacco smoke is a toxic compound and leads to atrophy of the taste buds on the tongue.
Taste of salt in mouth
Experts identify 2 main reasons for the formation of the anomaly in question - non-compliance with the basic rules of oral hygiene and prolonged dehydration, which provokes the accumulation of salts. The described change in taste perception may indicate the latent course of some ailments:
- sinusitis;
- failure of the kidneys;
- sinusitis;
- pathologies of the salivary glands.
The secondary cause of salty taste in the mouth is injury to the nose, gums, tongue, teeth, soft palate, accompanied by bleeding. Blood plasma contains sodium chloride, so its contact with the microvilli of taste analyzers causes the appearance of a salty taste.
In addition to the above, a strange taste sensation can occur when using a number of medications (injections, tablets) used in cancer treatment regimens, as well as with the onset of menopause.
Clinical picture
Ageusia can be general, selective and specific. With general ageusia, the patient does not feel taste at all; with the selective form, the person feels only some tastes. With a specific form, a change in taste is possible only when consuming certain products.
In addition, dysgeusia may develop under the influence of negative factors. With this disease, certain taste qualities are incorrectly perceived. Most often, sour and bitter tastes are confused.
If a person has lost his taste, then at the same time he may experience a loss of smell and a feeling of nasal congestion. In some people, ageusia is accompanied by weakness and irritability.
If the cause of a change in taste sensations is a traumatic brain injury, then headache, dizziness and impaired coordination of movements may simultaneously occur.
How to get rid of metallic taste?
If the iron taste appears regularly and is accompanied by additional symptoms, you need to consult a therapist and undergo a comprehensive examination.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, you will also need to consult a dentist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, or otolaryngologist. If the taste of iron is a temporary phenomenon and is not associated with pathologies, you can get rid of it with the help of:
- Rinse with acidified water.
- Eating foods that increase saliva production: tomatoes, oranges, lemons.
- Adding cardamom, cinnamon, ginger to the diet.
- Drink purified, non-mineral water. You can add juice or a slice of lemon to it.
- Cooking acidic foods in ceramic or glass containers.
- Quitting bad habits: smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Thorough oral hygiene: brushing your teeth, flossing, cleaning your tongue, using rinses.
- Inclusion in the diet of foods containing vitamins B, E, C: greens, lettuce, apples, citrus fruits, liver, red meat, bran.
- Replacement of metal dental prostheses with ceramic ones.
- Sucking on mint candies.
https://youtu.be/w8XYzZbGzp8
The taste of iron in the mouth occurs when the taste buds are not functioning correctly. It is associated with the entry of heavy elements into the body, diseases of various etiologies and the use of certain medications. To establish the cause of the symptom, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis in a medical institution.
Causes of a metallic taste in the mouth may include: reflux, dehydration, mouth breathing, smoking, dry mouth, pregnancy, sinus disease, hyperparathyroidism, untreated diabetes, upper respiratory tract infection, dementia, side effects of certain medications, poor oral hygiene mouth
In most cases, metallic taste in the mouth can be easily eliminated with home remedies and certain lifestyle changes. We offer you 10 of the most effective ways to eliminate metallic taste in the mouth at home.
To get rid of dysgeusia, you need to drink water regularly. This helps remove toxins from the body. In addition, drinking water reduces the acidity of gastric juice.
- Drink up to 8-10 glasses of water per day.
- Include high water content fruits and vegetables in your diet.
To know if you're drinking enough, pay attention to the color of your urine. If it is light, it means your body is getting the amount of water it needs.
To get rid of the sour taste in the mouth, you need to approach the problem comprehensively. In most cases, with timely treatment, the symptom can be eliminated in the shortest possible time. At the same time, it will be possible to get rid of the concomitant disease. However, first of all, you should consult a doctor for advice.
Diagnostics
Although loss of taste is not considered a critical condition, it requires mandatory consultation with a doctor . Initially, the doctor determines the patient’s level of sensitivity to certain tastes. The patient is asked to determine the taste of different substances one by one. Based on the results of this testing, the doctor determines the nature of the damage to the taste buds.
The doctor collects anamnesis, asking the patient whether he has had traumatic brain injuries and whether he suffers from neurological diseases. Oncological diseases treated with radiation therapy are also taken into account.
The specialist pays attention to the medications the patient is taking. Taking some of them is accompanied by side effects in the form of impaired taste.
If necessary, a computed tomography scan is prescribed. It reflects the state of the brain and nasal appendages. The patient may be referred for consultation to a dentist if there are signs of stomatitis.
A detailed blood test and allergy tests are prescribed. They allow you to determine the inflammatory process in the body and identify susceptibility to irritants. If it is not possible to determine the cause of the violations, then a re-diagnosis is carried out after a couple of weeks.
Taste sensations can change during pregnancy, during menopause and in other cases when hormonal balance is disturbed.
Taste of iodine in the mouth
- If an excess of iodine has accumulated in the body, in addition to this unpleasant taste, vomiting will also appear and the temperature will rise. The same applies to iodine poisoning. It is imperative to rinse and then cleanse the body.
- With diseases of the thyroid gland, there are often cases of the appearance of an iodine taste.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Liver diseases can cause almost any taste in the mouth, including the taste of iodine. We have already talked about the importance of the work of this largest gland in the body - the liver. But pain in the liver appears when it is 70% affected. Therefore, you should not ignore such a symptom.
- A taste of iodine in the mouth is possible with prolonged use of hormonal drugs and other medications. Moreover, it often appears some time after the end of their intake.
- Dental problems can also cause the taste of iodine in the mouth.
Treatment
The treatment regimen is determined after the diagnosis has been made. Depending on the cause of the change in taste sensations, the following medications may be prescribed:
- For dry mucous membranes caused by insufficient saliva production, it is advisable to prescribe artificial saliva preparations. These include Salivart.
- The patient is advised to frequently rinse his mouth with a soda solution or Chlorophyllipt solution.
- For stomatitis and other fungal diseases, antifungal agents are prescribed - Clotrimazole or Nystatin.
- If there is a lack of vitamins and minerals, a course of multivitamin complexes is prescribed.
- For neurological disorders, it is enough to drink decoctions of medicinal herbs. Suitable herbs with a sedative effect are mint, motherwort, hops and valerian.
- To improve the taste of food, add cinnamon, cloves, mustard and ground pepper.
To prevent disturbances in taste perception, you should regularly clean the surface of your tongue with a brush or special device.
Loss of taste may be associated with neurological disorders and diseases of the oropharynx. Fungal infections and a lack of minerals in the body often provoke the problem.
Briefly about diagnosis and treatment
Detection of most of the described signs requires contacting a medical facility. To exclude the possible development of dangerous illnesses, the patient will need to visit a general practitioner, an infectious disease specialist, a gastroenterologist and a number of highly specialized doctors.
Diagnosis and treatment are made after interviewing and examining the patient and obtaining the results of additional studies. Among the latest:
- general and biochemical blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- MRI;
- radiography;
- PCR diagnostics.
Having found out why the discomfort appeared, the doctor develops a treatment regimen for the disease. Relief of ailments that bother the patient is carried out by using anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and hormonal drugs. Treatment is carried out taking into account the patient’s age, his condition, and the presence of a history of chronic ailments. Recovery time varies depending on the form and type of pathology.
A favorable outcome of the identified disease is possible only if you consult a doctor early, do not self-medicate, and follow all the recommendations of the clinic employee.
https://youtu.be/GIOls2IRWDA
stomaget.ru
Acetone odor from the mouth due to poor diet
The level of ketone bodies also increases significantly during fasting or an unbalanced, monotonous diet. As a rule, for this reason, it often appears in women who adhere to strict diets that involve a sharp restriction of the calorie content of food consumed, as well as in those who are overly keen on various hunger strikes.
Low-carbohydrate diets have a similar effect on humans. When carbohydrates do not enter the body, the active process of breaking down accumulated fat begins, but such weight loss is not at all beneficial. With this breakdown, ketone substances are formed, which accumulate in the blood and poison the body from the inside. Such diets primarily affect the kidneys, stomach and intestines, and liver.
Diets and food interruptions
The causes of an acetone taste in the mouth in women often lie in fasting or a low-carbohydrate diet.
During fasting, the body does not receive enough energy necessary for life, and begins to draw it from its own reserves of adipose tissue.
It should be noted that a passion for such diets does not lead to weight loss, but to serious health problems - ketone bodies poison the body, which causes dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys and liver.
To lose weight and not harm the body, you need to give up so-called fast carbohydrates, which are found in baked goods, sweets, processed foods, mayonnaise, and fast food. Slow carbohydrates (cereals, wholemeal bread and pasta, legumes, vegetables) must be present in the diet.
Fishy breath: causes and treatments
Halitosis can appear regardless of age category. The nature of the unpleasant odor from the mouth can tell you whether any changes or pathologies are occurring in the internal organs. The smell of fish from the mouth may also indicate the development of diseases or disorders in the body. Therefore, you should not ignore such a symptom; consult a doctor who will prescribe a diagnosis and, if necessary, treatment.
Trimethylaminuria as a cause of fishy breath
Why does my breath smell fishy? In some cases, the appearance of a fishy odor is associated with the development of trimethylaminuria. This is a rare disease that develops as a result of liver dysfunction. It is characterized by the inability of the organ to break down the specific enzyme trimethylamine. Typically, such disorders are congenital and genetically determined. Less commonly, they are acquired, in which case the cause is the consumption of foods such as eggs, offal, fish, sprouted wheat.
Also, this disease can be triggered by long-term use of nutritional supplements, for example, L-carnitine by athletes. A key symptom of trimethylaminuria is an unpleasant fishy odor from the mouth. The appearance of bad breath may be associated with taking certain medications, in particular antiparasitic drugs and antidepressants.
Also, the appearance of bad breath indicates health problems - metabolic disorders. Often, people suffering from such a disorder may not even realize that diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or metabolic disorders cause such halitosis and other symptoms.
The cause is alcohol abuse and smoking. But there are also more serious clinical cases. The smell of fish from the mouth may be one of the signs of a chronic metabolic disorder.
Other reasons for this scent
If your breath smells like fish, the reasons may lie in the following factors:
- Diseases of the liver and pancreas. Various pathologies of internal organs develop under the influence of pathogens, namely bacteria - a common cause of halitosis.
- Abuse of ethanol-containing drinks, after which the breath has an unpleasant odor.
- Such problems may be associated with the accumulation of bacteria in the oral cavity due to poor hygiene. As a result, putrefactive bacteria begin to decompose and plaque accumulates.
- Wearing dentures can also cause halitosis, especially if they are not properly cleaned of food debris and plaque.
- Dental diseases - caries, gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, stomatitis or candidiasis.
- The problem associated with fishy breath is often caused by the development of dysbiosis in the intestinal tract.
- If such a symptom appears in a child, the cause may be helminth infection. Therefore, in this case, it is necessary to undergo timely treatment of helminthiasis.
How to determine the presence of odor
In some cases, it is not only diseases that cause unpleasant odors. This condition is also observed when consuming certain foods (fermented milk products, eggs). Therefore, if your breath smells bad, you should pay attention to the duration of such a symptom. If it smells like this for a short time, it may be the food. If such a smell constantly accompanies a person, there is no need to ignore it. It is recommended to seek help from a doctor, determine the cause and, if necessary, undergo therapy.
To check your breathing, you need to bend your palm into a boat, sharply exhale air into it, and smell it. You can also lick your wrist, lick a spoon. Then smell it. Using such procedures, you can evaluate not only the nature of the odor, but also its severity.
Who to contact
If an unpleasant fishy odor appears from the mouth of an adult, you should first consult a dentist. This condition can be concomitant with the development of many dental diseases.
If the dentist does not find pathologies, you should contact a therapist or gastroenterologist. Such breathing can be caused by stomach diseases or associated with endocrine disorders. Therefore, an additional examination of the endocrine system organs will be required.
Ways to eliminate fishy breath
How to get rid of fish smell? To kill this aroma, you can use pharmaceutical and folk remedies. To stop the smell of fish, you can fight off the smell by carrying out thorough hygiene: after every meal, clean your teeth and tongue. To do this, use a toothbrush and toothpaste, floss, and irrigators. Pharmacy rinses, special sprays, and chewing gums help remove halitosis.
To get rid of unpleasant aroma in the mouth, rinsing with herbal decoctions is also used. To prepare them, use sage, calendula, nettle, chamomile, St. John's wort, and yarrow. We also get rid of the problem with the help of tea tree oil, which we add to the water for rinsing the mouth. It effectively combats halitosis, removes bacteria and plaque.
If it’s all about diseases of the internal organs, before you remove the smell yourself, you should definitely visit a doctor, find out the cause, eliminate it, and at the same time take measures to eliminate the problem.
Preventive actions
To prevent oral problems, you should carefully monitor your hygiene and eat right. Quitting smoking and alcohol is mandatory. If any diseases of the liver, kidneys, or digestive system are detected, it is important to follow all medical prescriptions and undergo timely treatment.
Good nutrition will help prevent metabolic disorders. You should also undergo timely preventive examinations at the dentist, treat diseases of the oral cavity that cause the accumulation of bacteria and halitosis. If any alarming symptoms appear, do not hesitate to consult a doctor. The same activities apply to children. Only timely contact with specialists will help prevent the development of various complications.
https://youtu.be/RAHvsvJ8q4A
tvoyzubnoy.ru
Taste of rot
This is a common companion to diseases of the mucous membrane of the mouth and throat. So, periodontitis, tonsillitis, adenoiditis, laryngitis, etc. can lead to such an unpleasant symptom. Therefore, it is worth carefully examining the likely areas of damage and starting treatment before complications begin.
News
Fear of candy and white spots: signs of caries in children named
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
The prognosis of treatment depends entirely on the disease, the manifestation of which is the acetone taste. An increase in ketone bodies associated with malnutrition can be eliminated without drug therapy, only by correcting the diet. In this case, the prognosis is favorable.
If the causes of ketoacidosis are endocrine disorders (diabetes, thyrotoxicosis) or severe infectious diseases, then the prognosis depends entirely on timely treatment. If the patient is not provided with qualified assistance, severe complications may develop, including coma:
- acetone irritates the vomiting center, causing uncontrollable vomiting, threatening severe dehydration;
- cardiovascular failure develops;
- brain cells are affected.
Etiology
An unpleasant taste in the mouth can be caused either by a pathological process or simply by non-compliance with basic rules of oral hygiene.
The following pathological processes are identified that can lead to the manifestation of this symptom:
Predisposing etiological factors include the following:
- poor oral hygiene;
- poor nutrition;
- food poisoning;
- a consequence of taking certain medications;
- dehydration;
- smoking, alcohol abuse.
It is also quite common to experience an unpleasant taste in the mouth during pregnancy. In this case, this symptom cannot always be regarded as a manifestation of a pathological process, since it may be caused by hormonal changes in the body of the expectant mother.
In any case, if you experience an unpleasant taste in the mouth that extends to the nose, throat, and is accompanied by additional symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Preventive actions
Preventive measures for the occurrence of acetone taste are based on proper nutrition with the obligatory presence of complex carbohydrates in the diet. In addition, you need to follow a daily routine, maintain physical activity - take daily walks in the fresh air and do morning exercises. Sleep should be at least 8 hours a day, stress and prolonged exposure to the sun should be avoided. Reappearance of the symptom requires regular anti-relapse therapy of the primary disease.
How to determine the cause
To find out what a metallic taste in the mouth means, you need to pay attention to the conditions under which it arose. For example, if the sensation appears after drinking water, you need to check the condition of the pipes. A sharp change in the composition of the diet or taking medications can also affect the perception of receptors.
If the cause lies in the development of any disease, this will be indicated by a number of accompanying symptoms:
- skin itching, thirst in the morning, blurred vision accompany diabetes mellitus;
- dry throat, cough, white plaque on the tonsils – pharyngitis and tonsillitis;
- abdominal cramps, heartburn, belching – stomach ulcers;
- nausea, weight loss, lack of appetite - liver disease;
- pain in the right side, bitterness, alternating diarrhea and constipation - gallbladder pathologies;
- drowsiness, weakness, pallor, dizziness and arrhythmia - anemia.
We suggest you read: Symptoms of a stone in the salivary gland and its treatment
Tip #5: Take Treatment Seriously
Naturally, treatment must be prescribed by a doctor. The set of therapeutic measures for each patient will be determined individually and according to the clinical situation, but first of all, the doctor will prescribe medications and liquids that will help stop intoxication of the body and remove harmful substances from it.
Then you will have to go for treatment and observation to a highly specialized specialist, for example, a gastroenterologist or endocrinologist. You will also additionally need to follow a plant-based diet, exclude fatty and heavy foods, and no fasting is allowed.
Rate this article:
( 4 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
prevention
Consulting specialist
Soblirova Alena Maksimovna
Doctor rating: 9.7 out of 10 (3) Specialization: Dentist-therapist Experience: 10 years