Today we will talk about the reasons why the lower abdomen hurts in women; there are many reasons for this of varying degrees of severity.
Almost every woman has experienced unpleasant aching and pulling sensations in the lower abdomen at least once in her life.
Physical and strength exercises, hard sexual intercourse, lifting heavy objects - any of the above actions can cause a feeling of pain in the lower abdominal cavity.
If we do not take into account physiological causes (before and during the menstrual cycle), which do not require treatment, acute pain in a woman in the lower abdomen on the right or left may be associated with organic causes (inflammatory processes, damage to the pelvic organs and peritoneum) and be an alarming signal development of inflammatory and neurological pathologies.
Plus, diseases of the digestive system, kidney problems, infectious gynecological diseases - all this can be a consequence of a woman experiencing pain of various types (pulsating, sharp, pulling) in the lower abdomen.
Possible causes of nagging pain in women
Nagging pain in the lower abdomen occurs very often in women for various reasons.
But, unfortunately, while they are not clearly expressed, patients are in no hurry to see a doctor. And this is wrong, because many gynecological diseases develop secretly for a long time. This means that their treatment may be more difficult in the future. Nagging pain in the lower abdomen is usually associated with pathologies of the pelvic organs. First of all, this applies to the uterus and ovaries. In addition, such pain can occur for physiological reasons.
The main pathologies that can lead to the development of serious consequences without timely and proper treatment:
- Diseases of the uterus and ovaries - uterine fibroids, endometriosis and ovarian cysts.
- Sexual infections.
- Scars after surgical interventions.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary system, in particular pathologies of the kidneys and bladder.
- Diseases of the large intestine.
It is very dangerous if the nagging pain is caused by the intrauterine device. This may indicate the development of complications that, without timely treatment, will require surgical intervention in the future. Pathologies that occur during pregnancy are also dangerous.
Functional reasons that pose a threat to a woman’s health are the following:
- Algodysmenorrhea
, if it occurs against the background of abnormal position of the uterus or its underdevelopment. - Bend of the uterus
, which leads to stagnation of menstrual blood in the organ cavity. - Ovulatory syndrome
. Due to certain individual characteristics of the female body, every time ovulation occurs, aching pain occurs in the lower abdomen, which disappears within a short time and is not a dangerous sign.
Treatment of lower abdominal pain
Having diagnosed the pathology, no one deals with pain treatment as such. A certain course of painkillers is prescribed, and at the same time additional symptoms (inflammation, spasms) are eliminated. All together, the patient’s condition is alleviated, after which:
- an operation is prescribed to eliminate the underlying factor;
- taking hormonal drugs, suppressing ovarian activity to stop ovulation;
- a psychologist can work with a woman;
- immune correction is performed.
Unpleasant pain symptoms will subside as the underlying provoking disease is treated. Usually, the treatment of such pathologies is successful and does not entail health consequences, subject to timely intervention by doctors, correct diagnosis of the disease, effectiveness, and selected treatment methods.
Dangerous pathologies of the internal genital organs are most often eliminated surgically, under anesthesia, due to the fact that one cannot hesitate. Sometimes doctors fail to recognize the causes of the phenomenon; it is attributed to mental factors; in this case, psychotherapists work with the patient for a long time.
When mental and physical causes cannot be found, the problem is justified by the individual characteristics of the body, increased sensitivity, and the intersection of some nerve fibers is prescribed, thereby reducing the frequency of pain impulses entering the nervous system.
Symptomatic therapy may also include physiotherapeutic treatment to help eliminate provoking factors, and antidepressants are prescribed. Rarely can a doctor approve the additional “connection” of traditional medicine, and then only if the pathology does not cause serious danger and does not threaten complications.
Prevention and advice on what to pay attention to
Most often, it is difficult to treat diseases that cause pain in women in the lower abdomen. It is best to try to prevent their occurrence. For prevention purposes it is necessary:
- eat right, drink enough fluids daily;
- monitor your weight;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- avoid promiscuity;
- do not overcool;
- keep the body in good shape by periodically taking vitamins, training, playing sports, leading a healthy lifestyle;
- do not have abortions, especially underground ones;
- if the intrauterine device is not suitable, refuse this type of contraceptives;
- knowing about painful periods, together with your supervising doctor, consider taking certain medications to alleviate the condition;
- if any pathology develops “like a woman”, do not self-medicate, but immediately go to the hospital;
- When deciding to give birth to a child, you first need to prepare the body, stimulate the immune system, which the gynecologist observing you will help with. During pregnancy, strictly follow your doctor’s recommendations and monitor your condition.
Considering that painful symptoms can be associated not only with female organs, prevent diseases of the intestines and musculoskeletal system, avoid stressful situations, and worry less. Every year, or even twice a year, you need to see specialists who are “important” for you, so as not to trigger and monitor the developing pathology. If any disease is detected, immediately begin treatment.
Diseases that cause nagging pain in the lower abdomen
A symptom of many serious diseases is aching pain in the lower abdomen in women.
These may be the following diseases of the reproductive organs:
- Adnexitis or salpingoophoritis
. This pathology is characterized by inflammation of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries due to infection. Aching pain occurs when the disease becomes chronic. Either one ovary or both may be affected. This determines the location of the pain. Additionally, vaginal discharge with purulent patches may appear and the temperature may periodically rise. Pathology without timely treatment leads to tubal obstruction and, as a consequence, to infertility. In addition, the risk of ectopic pregnancy increases. - Endometritis
. In this case, inflammation of the uterine mucosa occurs. The pathological process most likely spreads to the appendages without treatment. In this case, pain is constantly present.
- Endometriosis
. The disease is associated with the proliferation of the uterine mucosa. This process can affect the ovaries and even the intestines. The causes are usually hormonal imbalances. In addition to aching pain, irregular, painful menstruation occurs. With further development of the disease, amenorrhea occurs. In severe cases, the fallopian tubes may become blocked, leading to infertility.
- Ovarian apoplexy
. Pathology often occurs against the background of the formation of a cystic cavity in the ovary. Hemorrhage can be triggered by rough sexual intercourse or physical activity. In this case, bleeding occurs into the abdominal cavity, which can be life-threatening.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
. Many cysts that form can disrupt the functioning of the ovaries and cause aching pain in the lower abdomen. Often this causes menstrual irregularities.
- Colpitis
, which is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervix. Pathology is provoked by various infectious agents: streptococci, gonococci, fungi, etc. Colpitis can develop as a consequence of vaginitis. Itching occurs in the vagina and there is a discharge of profuse leucorrhoea.
- Myoma
, which is a benign tumor. Such formations can appear both inside the uterus and outside the organ. The resulting tumor puts pressure on the vessels and disrupts blood supply, which provokes nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
Malignant neoplasms
Malignant tumors localized in various parts of the reproductive system are one of the most common causes of cutting pain in the pelvic area. A growing tumor causes ruptures of healthy tissue and sharp discomfort in the lower abdomen. In the initial stages, the pathology is quite difficult to diagnose, since it does not manifest itself with pronounced clinical symptoms. Depending on the location of the carcinoma, the patient may experience bleeding from the genital tract, menstrual irregularities, and pain during sexual intercourse. As the pathological process develops, the woman develops the following signs of the disease:
- feeling of bloating and heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- bowel dysfunction, constipation;
- intense pain during coitus;
- ascites – accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- loss of body weight up to cachexia - complete exhaustion;
- lack of appetite;
- fatigue;
- anemia;
- intestinal obstruction, intoxication with waste products.
Ovarian cancer
Attention! Ovarian cancer is one of the most difficult to diagnose malignant pathologies of the reproductive system. In order to promptly identify this disease, it is necessary to undergo regular preventive examinations by a gynecologist.
In the treatment of malignant tumors, two main treatment methods are used: surgery and the use of cytostatics. At the initial stage of the disease, in the absence of metastases, it is possible to remove only the affected organ; in more severe cases, more extensive surgery is required. After surgery, in most cases, courses of therapy with Cisplatin, Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate and other drugs are indicated to destroy malignant cells.
The drug Cyclophosphamide
What to do if you have frequent pain
If nagging pain is associated with functional causes, in particular when it occurs before or during menstruation, then you can cope on your own. With a mild, nagging pain syndrome, you can simply endure the discomfort. To quickly stabilize the condition, you can take a painkiller or antispasmodic drug. You can also apply a heating pad. In addition, it should be understood that in such cases rest is indicated. It is necessary to avoid any physical activity that can increase pain.
If the pain occurred once and disappeared within a couple of hours, and after that it did not arise again, then you can do nothing. More dangerous are constant nagging pains in the lower abdomen. In such cases, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Types of pain, nature of occurrence
The pelvic area sends weak impulses to the nervous system due to the small number of nerve ganglia. Pain impulses are perceived differently; a distinction is made between radiating and phantom pain.
Sensations of varying intensity of the pain threshold, different in duration, arising in the lower abdomen and not associated with the source of true origin are called radiating pain. The phenomenon occurs taking into account the individual sensitivity of the body and the uniqueness of physiological processes.
Pain felt after the causes of its occurrence have been eliminated is called phantom pain. Doctors consider this phenomenon unstudied and associate it with impaired perception of nerve endings.
According to the nature of their occurrence, pain sensations can differ significantly and be associated with the true source of their occurrence. This is how pain happens:
- acute;
- aching;
- piercing;
- dull;
- pulling;
- weak;
- cramping;
- pulsating;
- sharp;
- constant.
The nature of the pain and frequency make it possible to understand what pathological process caused it. Hence they distinguish between acute (lasting no more than two days) and chronic pain.
Which doctor should I contact?
To speed up the diagnosis, it is recommended that if you experience nagging pain in the lower abdomen, you should first consult a gynecologist. If the examinations exclude any pathologies of the organs of the reproductive system, then you should undergo an examination by a therapist. He will prescribe all the necessary laboratory tests and instrumental studies. Based on the results obtained, a referral to another specialist (urologist, nephrologist) will be given.
You should definitely contact a gynecologist if you have the following additional symptoms:
- Bloody or other discharge that occurs at any time and is not related to the menstrual cycle. Such signs are always evidence of the development of inflammation of the internal genital organs.
- Copious yellowish discharge with an unpleasant odor, which indicates the development of infectious diseases of the genital organs. At the same time, the temperature may rise.
If nagging pain in the lower abdomen occurs in combination with a burning sensation in the genital area and frequent urination, this indicates the development of pathologies of the urinary system. In such cases, you need to contact a urologist.
When additional symptoms include nausea, vomiting, bloating, flatulence and digestive disorders, then, most likely, nagging pain in the lower abdomen is associated with intestinal pathologies. A gastroenterologist treats such diseases.
Pathologies of the urinary system
When there is an inflammatory process affecting the bladder (cystitis), the patient first experiences aching pain in the area of the affected organ. Very soon the unpleasant sensations become cutting and acute. Localized mainly above the pubis. Become more pronounced during urination.
Cholecystitis, cystitis - localization of pain
A disease such as pyelonephritis can be included in this category. It is characterized by the occurrence of painful sensations in the lumbar region. The process is accompanied by an increase in temperature, disturbances in urination processes, etc.
Pyelonephritis
To treat the diseases considered, drugs from the group of antibiotics and nitrofurans are traditionally used.
Treatment with medications and folk remedies
Treatment of nagging pain in the lower abdomen in women depends entirely on the diagnosis. In this case, both conservative and radical methods can be used. For conservative treatment, medications are selected on an individual basis.
Various types of drugs are used to relieve pain, for example:
- for severe pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or analgesics are prescribed;
- for spasms, antispasmodics and muscle relaxants are indicated;
- for swelling caused by allergic reactions, antihistamines are prescribed.
If the disease is caused by viruses, then the course of treatment will be carried out with antiviral drugs; For bacterial infections, antibiotic therapy is indicated. For successful treatment, it is recommended to try to improve the emotional background and eliminate stress. If necessary, physiotherapeutic methods are used, as well as folk and homeopathic remedies.
It should be understood that to treat nagging pain in the lower abdomen in women, it is not recommended to take any medications on their own. Initially, the cause of the pain must be determined and a diagnosis made. If you use any medicine without understanding the cause of the pain, there is a risk of worsening the condition. Many medications have side effects and can lead to intoxication of the body if used incorrectly or overdosed.
Most often, No-shpu is prescribed to relieve pain in the lower abdomen. This drug has a minimum of side effects. It is recommended to take 1-2 tablets. 2-3 times a day for nagging pain.
Ketonal is a stronger remedy, but this drug is recommended to be taken only once, in case of urgent need. Sometimes nagging pain can be associated with allergic reactions. In this case, pain can be reduced by taking Suprastin or Loratadine. For pain in the lower abdomen, Papaverine is also considered effective. The product eliminates spasms and relaxes smooth muscles.
Among physiotherapeutic procedures, electrophoresis is often used, which can accelerate the penetration of drugs into tissues. This allows you to quickly reduce pain.
There are also many folk remedies that can help fight nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Of course, they can only be an additional means of treatment. If the pain syndrome is associated with disorders of the digestive system, then a decoction of chamomile is effective. To prepare it, you need to pour 2-3 tablespoons of dried chamomile flowers with half a liter of boiling water and leave for 2-3 hours. It is recommended to take the drink 5-6 times a day, half a glass. It is allowed to brew chamomile flowers along with regular tea. You can drink this drink as many times a day as you wish.
Medicinal herbs have long been used to treat pathologies, the symptom of which is nagging pain in the lower abdomen. For women, mint tea is recommended as a sedative that effectively relieves neurological disorders. But men are not recommended to drink this drink, as it promotes the production of female hormones.
For severe spasms, you can prepare a tincture of wormwood, which helps relax smooth muscles. But at the same time, it is important to take this remedy with caution against the background of hypertension, since wormwood helps to increase blood pressure. To prepare, you need to pour 2 teaspoons of wormwood into 250 ml of alcohol. It is recommended to drink the tincture 3 times a day, one teaspoon.
Pain during pregnancy
Such discomfort is far from uncommon for expectant mothers. Unpleasant symptoms accompany the first trimester, when the body adapts to the new status and undergoes global hormonal changes. Pain is also a concern in the later stages, which can be regarded as a normal physiological process in the form of uterine tone, changes in the ligamentous apparatus, lack of calcium, or a sign of a threat to pregnancy due to increased pressure on the cervix.
A reliable remedy for illness is relaxing the body and changing its position. Some doctors recommend resorting to moderate physical activity, but only if there are no contraindications.
When, in the later stages, there is sharp pain in the lower abdomen, dizziness is noted, you need to immediately seek medical help due to the risk of placental abruption, which can lead to dangerous intrauterine death of the baby.
Starting from the 36th week, recurring spasms with tension in the uterine muscles - training contractions - may occur from time to time. Although this phenomenon is considered normal, consultation with a gynecologist should not be neglected.
Prevention
Since the most common nagging pain in the lower abdomen in women occurs due to the development of gynecological pathologies, it is necessary to regularly visit the doctor. Preventive examinations in a gynecological office once a year will detect diseases at the initial stage of development. This means that it will be possible to carry out timely treatment, and, therefore, eliminate the occurrence of nagging pain.
To minimize the risk of developing diseases of the genitourinary system, it is important to follow simple rules:
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Avoid hypothermia of the body.
- Keep your immune system in good condition.
You can reduce the risk of developing various intestinal pathologies that cause nagging pain in the lower abdomen by normalizing your diet. In addition, you should give up a sedentary lifestyle and play sports.
It should be understood: if any pathology is diagnosed in a timely manner, then modern treatment methods give a positive prognosis in most cases. Only in an advanced state can pathologies that cause nagging pain in the lower abdomen pose a threat to health. That is why, when such a symptom appears, it is imperative to find time to conduct an examination in order to establish a diagnosis.
What complications can there be?
Pelvic inflammatory disease, in which there is no treatment, can negatively affect reproductive function. There is a detrimental effect on the fallopian tubes and damage to the ovaries occurs. As a result, infertility cannot be ruled out.
Gynecological problems can cause infertility
Attacks of pain and severe pain significantly affect the emotional state of a woman, she refuses sexual relations. In parallel, infections that have become chronic (were not treated in a timely manner or were not fully treated) can cause premature delivery, and then infection of the child during passage through the birth canal (for example, with vaginitis).
Premature birth may occur due to gynecological diseases
Cystitis, which was not treated in a timely manner and became chronic, is dangerous for the development of pyelonephritis, that is, kidney damage. Thus, a prolonged inflammatory process leads to necrosis of nephrons. As a consequence of this, patients become eternal hostages of hemodialysis.
Pyelonephritis
Cramps can warn of an exacerbation of urolithiasis. If therapy is not applied in a timely manner, the stones will be directed to the urinary canals. When stones block the urinary canals, the outcome is unfavorable - the patient’s death.
Stones in the kidneys
As it has already turned out, pain on the side can warn of inflammation of appendicitis. If you do not react in a timely manner, the appendix bursts and the purulent contents infect the abdominal cavity, causing peritonitis.
Symptoms of peritonitis
Therefore, in order to preserve not only women’s health, but also life, you should go for a diagnosis when cramps appear. Thus, the doctor will be able to promptly identify the pathology and prescribe the necessary therapy.
Causes of abdominal discomfort
The most common factors affecting the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and the appearance of discomfort are poor nutrition. Abuse of salty, fatty and spicy foods, eating foods that do not combine well with each other at one time, as well as regular drinking of alcoholic beverages leads to disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract. You can also identify reasons such as following too strict diets and eating on the go, overeating.
Common diseases that cause discomfort include:
- gastritis – accompanied by acute pain in the epigastric region;
- gastroduodenitis - characterized by damage to the upper loop of the intestine and the pylorus of the stomach, symptoms are similar to gastritis;
- disorders in the intestines - dysbiosis, celiac disease, intestinal obstruction are often accompanied by bloating, gas formation and heaviness;
- ulcerative lesions - characterized by very acute pain that deprives a person of the ability to move;
- diseases of the liver and gall bladder - heartburn appears, belching with bitterness, the color of urine changes to darker, heaviness appears from the right hypochondrium.
A rapidly developing disease - appendicitis - can also be accompanied by slight discomfort, which is constantly increasing. At the same time, the temperature rises, acute pain occurs, and vomiting is possible. You can consider in more detail severe autoimmune and oncological processes, which are difficult to treat and often do not manifest themselves at all.
Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease affects the intestines and is accompanied by regular tingling in the lower abdomen and acute pain during the period of activation of the disease. It is found in both men and women. Symptoms during an exacerbation can be confused with signs of appendicitis. Bloody diarrhea often occurs. Crohn's disease is an autoimmune disease that cannot be cured; it can only be contained.
Tumor processes
Periodic aching, tingling pains are companions of intestinal tumors, as well as other neoplasms - polyps. Symptoms can be very different: slight pain, diarrhea, constipation, nausea, weight loss, loss of appetite. With tumors, blood is sometimes observed in the stool, which indicates malignant processes.
Intestinal diverticulitis
Symptoms of diverticulitis are the same as other diseases: tingling, sharp pain from time to time. A characteristic symptom is constant constipation and discomfort in the left side of the abdomen.
Irritable bowel syndrome
The pathology is associated with an emotional state and can last up to 3 months and then recede. Physiological causes of the disease are not detected during examination. The sensations are accompanied by pain, constipation or diarrhea, relief after bowel movement.
Urinary tract diseases
Symptoms extending to the abdominal area in men are often associated with diseases of the urinary system. The reason for this is the special structure of the body. The pain will be paroxysmal, radiating to the groin and thigh. Cystitis in women often causes discomfort, but it is difficult to confuse it with other diseases.
Specific gastrointestinal diseases, poor nutrition, and symptoms associated with the urinary system are equally common in men and women. A broad picture of disease symptoms makes it difficult to diagnose at home. But there is another group of causes of discomfort, often found only in women.
Intestinal problems
Pain in the lower abdomen (in the middle) in women can occur due to intestinal pathologies. So, most often it is fecal retention or frequent bowel movements. Usually such symptoms appear due to poor nutrition. However, they can also be caused by more serious problems, such as inflammation or dysbiosis.
If discomfort arises due to problems in the intestines, then the fairer sex often notices other symptoms. These include increased gas formation, lack of appetite, nausea, and so on. If you have problems with your intestines, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible and get qualified help.
Other reasons
In addition to the above diseases, the following conditions can cause this symptom.
- Lower lobe pneumonia. With inflammation of the lungs in the lower sections, pain may be felt in the abdominal area. The patient is concerned about fever, cough with sputum and symptoms of intoxication.
- Atypical form of myocardial infarction. This pathology is accompanied by epigastric pain, hiccups, bloating and vomiting. This clinical form makes timely diagnosis of a heart attack difficult and often leads to the development of complications.
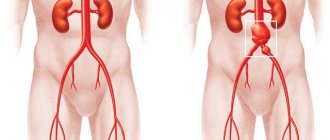
- Rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm. The patient is worried about pain in the abdomen and lower back, collapse (sharp drop in pressure), and pulsation of a vessel in the abdominal cavity can be detected.
- Thrombosis of mesenteric vessels. The clinic depends on the size and location of the blocked vessel. Unbearable pain in the abdomen is often disturbing; it can be cramping, but more often it is constant. Vomiting mixed with bile and blood, later blood appears in the stool. Painful shock develops with a sharp drop in pressure, and later signs of peritonitis appear.
There are many reasons and conditions leading to pain in this area. In order not to guess why this happened and what may cause pain, you should contact a specialist and undergo the necessary tests.
Principles and approaches to the treatment of such pain
Treatment for this symptom depends on the cause that caused it. The most correct decision would be to visit a specialist who will clarify the nature of the pain and offer a competent treatment regimen. If abdominal pain is associated with cramps, then antispasmodics (Drotaverine, etc.) will help eliminate it. In cases of severe severe pain, it is better not to take painkillers and antispasmodics before the doctor arrives, so as not to blur the clinical symptoms.
For any cause of pain, before consulting a specialist, you can play it safe and provide the body with hunger, cold and rest to make it easier to endure this condition. Heat or heating pads on the abdominal area can only be used in cases of spastic pain. If the patient is not sure, then it is better not to do this.
Acute stabbing and girdle pains, vomiting blood or bleeding from the genitals are a reason to immediately seek medical help. It’s better to play it safe than to deal with serious complications in the future.
Diagnosis and treatment
The success of treatment depends on correct identification of the root cause of the disease. Diagnostics include:
- General and clinical blood tests, as well as ESR.
- Conducting laboratory smear tests.
- Ultrasonography.
- Laparoscopy and other procedures.
Treatment depends on the identified disease. Depending on the severity, they resort to therapeutic treatment or surgical intervention.
Cystitis and pyelonephritis are treated with antibacterial drugs (Fosfomycin, Nitrofurantoin, Cephalexin). They use folk remedies. It is very important to maintain a proper hygiene regime.
Endometritis is treated with antibacterial drugs ( Sparfloxacin ), the patient is prescribed electrophoresis and magnetic wave therapy.
To relieve pain during salpingitis, it is advisable to take Norfloxacin and Ofloxacin, painkillers.
Cervicitis is treated with Acyclovir , Ofloxacin . The genital tract is treated with medicinal disinfectants (chlorophyllipt solution, dimethyl sulfacid).
Malignant neoplasms are eliminated either therapeutically or lipo through surgical intervention. These diseases require immediate diagnosis and treatment.
Appendicitis is eliminated through surgery. Removing the vermiform appendix.
It is very important to seek medical help if you experience pain during pregnancy. Extreme measures to eliminate the symptom would be forced abortion and uterine surgery.
Pathology of the digestive tract
One of the common causes of pain in this area is gastrointestinal pathology. Let's list the most common diseases and conditions.
- Appendicitis (inflammation of the appendix of the cecum). In the first hours/days, the pain is localized in the middle of the abdomen, then the right side in the lower abdomen begins to hurt. In addition, this acute surgical pathology is characterized by nausea, vomiting, digestive disorders and general condition. Check for characteristic symptoms of peritoneal irritation: muscle tension in the right iliac region, Voskresensky, Shchetkin-Blumberg, Sitkovsky, etc. symptom.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases (colitis, enteritis). These diseases are accompanied by disorders of the digestive tract: nausea, bloating, stool disorders, mucus or bloody discharge in the stool. They are characterized by bursting pain in the abdominal area.
- Acute and chronic intestinal obstruction. The pathology is caused by a violation of the movement of contents along the digestive tract. Accompanied by abdominal pain, vomiting, retention of stool and gas, bloating and asymmetry.
- Diseases of the biliary tract. Problems with the biliary tract (stones, stricture, cholecystitis) lead to discomfort in the lower abdomen on the right and indigestion due to insufficient flow of bile into the intestines. In addition to pain, the patient complains of nausea, heaviness in the stomach, belching, heartburn and other dyspeptic disorders. With severe obstruction of the biliary tract, the patient may develop jaundice. Hepatic colic develops due to blockage of the bile ducts by a stone. It is characterized by paroxysmal stabbing pain in the right hypochondrium, which spreads to the shoulder, shoulder blade and abdomen. The pain can be cramping or constant and is often accompanied by frequent vomiting, which does not improve the patient’s well-being.
- Liver diseases (hepatitis, jaundice). Problems with the liver occur with unpleasant sensations in the area of the right hypochondrium. With cirrhosis of the liver, in addition to pain, the patient experiences many other symptoms: nose and gum bleeding, jaundice, appetite and digestive disorders, swelling, change in the color of stool, telangiectasia, spider veins, redness of the palms, change in the color of the tongue.
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. Outside of an exacerbation, the patient only experiences digestive dysfunction. During an exacerbation, sharp pain in the abdomen is disturbing, usually in the upper part, but it can also move lower.
- Poisoning. Food poisoning is accompanied by abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Vomiting brings noticeable relief. The duration of the disease depends on the reactivity of the body and the damaging agent.
- Helminthiases (enterobiasis, etc.). The presence of parasites in the body can manifest as unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen. With enterobiasis, the patient is concerned about itching of the anus, loss of appetite, weight loss and changes in the character of stool.
- Complications of peptic ulcer and duodenum (bleeding, penetration, perforation). These complications are accompanied by a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition, abdominal pain and other symptoms: vomiting mixed with blood, signs of peritoneal irritation, etc.
- Acute pancreatitis. It is suspected if the left side in the lower abdomen hurts. The disease is accompanied by nausea, bloating, repeated vomiting and dehydration.
Bladder diseases
The bladder is an unpaired pelvic organ and is located in the lower abdomen just behind the pubic bone. In women, the organ borders the uterus, so diseases always affect reproductive health. Pain in the bladder area indicates diseases of other organs, for example, the kidneys or urethra. They can occur even in young women.
Cystitis, urethritis
This is a disease of the bladder mucosa that occurs due to inflammation due to decreased immunity, hypothermia, hormonal disorders or poor hygiene. The pain is sharp, stabbing, urination becomes difficult, all this is accompanied by high fever. Cystitis develops against the background of physical inactivity and rare emptying of the bladder. Urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra, often provoked by the proliferation of pathogenic microflora (streptococci, staphylococci, E. coli).
Bladder stones
They appear as a result of metabolic disorders with the subsequent formation of salts (urates, phosphates, oxalates) in the bladder. They are characterized by pain when urinating, and the lower part of the lumbar region suffers, and renal colic. The cause of stones is anatomical features or consequences after surgery, when stones grow on the suture threads. The formation of stones is promoted by eating a large amount of spicy or sour foods and drinking hard water.
Oncological neoplasms in the organ
Determining the presence of cancer is not easy due to the long asymptomatic course of the disease. When the outflow of urine is disrupted, a process of accumulation of dead cells occurs. This gradually leads to irreversible consequences in the form of tumors. In the later stages, pain occurs when urinating, up to an acute burning sensation. The following factors contribute to this:
- Bad habits (alcohol and especially nicotine);
- The presence of hereditary diseases;
- Chemotherapy (other organs);
- Chemical contamination of the body (paint and varnish work, arsenic).
Conditions in which you need to urgently consult a doctor
If strange sensations in the abdomen are combined with additional symptoms, you should consult a doctor. Here are the most dangerous conditions for which it is recommended to call an ambulance:
- intense pain;
- nausea and vomiting;
- high or increasing temperature over several days;
- the presence of discharge from the genital organs in women with an unnatural color and odor, or bleeding;
- profuse diarrhea mixed with blood and mucus;
- absence of stool for 3 or more days.
Women need to go to the doctor if swelling of the mammary glands appears after menstruation. Normally, this condition is permissible only before menstruation.
Treatment
Basic therapy will depend on the diagnosis and the underlying factor. In general, drug treatment may include the following:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- means for improving gastric motility;
- painkillers;
- antibiotics.
Diet therapy is required, which excludes the consumption of fatty, spicy, too salty and alcohol.
If the pathological process cannot be eliminated through conservative methods of therapy, then a surgical method is selected. In some cases, this is the only rational method of eliminating the disease.
Diagnostics
If you have such a symptom, you should consult a therapist, gastroenterologist or gynecologist. In this case, it all depends on the current symptoms. The diagnostic program may include the following:
Irrigoscopy procedure
- blood sampling for general and biochemical analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- coprogram;
- PCR for latent infections;
- urine culture;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs;
- colposcopy;
- cystoscopy;
- irrigoscopy.
Additional diagnostic methods will depend on the current clinical picture.