All articles by the author
Author of the article: Ekaterina Sergeevna Churaeva
Practicing obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound diagnostics doctor
A general urine test is part of a complex of primary laboratory examinations both at the initial stage of development of any pathology and during preventive examinations. If, when reading the result, it is determined that leukocytes in the urine of women are elevated, the doctor will prescribe a series of laboratory tests to identify the cause of the disorders.
How do white blood cells get into the urine?
White blood cells, the main function of which is to protect the human body from the pathogenic influence of foreign microbes and harmful toxins, are always sent to places where pathological processes form and develop.
White blood cells come in several varieties, differing in their shape and functional abilities, which allows them to perform different roles at certain stages of the immune response. Some of the subspecies of white bodies are distinguished by their ability to actively move, others by phagocytosis, which, penetrating through the capillary walls, enter the intercellular space and perform their function.
Meeting alien agents on their way, they devour them, which is why they increase in size. As a result of phagocytosis, leukocytes are destroyed, which, in turn, causes an inflammatory reaction in the surrounding tissues. Externally, this manifests itself in the form of a painful compaction with hyperemia (redness) and the formation of pus-like accumulations.
This property of leukocytes explains the mechanism by which they enter the urine. When an infectious focus forms in the urinary or reproductive system, white cells rush to it to attack the invading microorganisms or ingested toxins.
They are located on the mucous membranes, and when urinating, the fluid filtered by the kidneys, accumulating in the bladder, washes away leukocytes from the walls of the urinary tract. In this case, white blood cells are detected in urine tests and are one of the main laboratory signs of diseases of the genitourinary system.
What to do if there is a high level of leukocytes in the urine?
An increased level of leukocytes in the urine is usually treated with medications, folk recipes and changes in the patient’s diet.
Drugs
Treatment of diseases that cause leukocyturia is carried out using antibiotics of different groups, as well as symptomatic drugs.
The antibiotic Ampicillin is prescribed for the treatment of leukocyturia
| Group of drugs | Impact on pathology | Examples of funds |
| Penicillins | Antibacterial agents are used to destroy the cause of genitourinary tract infection, which provokes an increase in the level of white blood cells. | Ampicillin, Amoxiclav |
| Nitrofurans | Furazidin, Nifuratel | |
| Sulfanalamides | Streptocide, Sulfazin | |
| Quinolines | Ciprofloxacin, Negram | |
| Antifungal drugs | Used to treat mycotic infections such as thrush in women. | Fluconazole, Flucostat, Mycoflucan |
| Local antiseptics | Locally destroy pathogenic bacteria and prevent the development of infection. | Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Hexoral |
| NSAIDs | They reduce the inflammatory process, relieve fever when the temperature rises due to infection, and reduce pain. | Nurofen, Ketanov, Dicrofenac |
| GKS | Glucocorticosteroid drugs are used for inflammatory processes that are not controlled by NSAIDs. | Hydrocortisone, Cyclesonide, Prednisolone |
| Antispasmodics | They help with spasmodic abdominal pain that occurs due to infectious diseases of the genitourinary system. | Papaverine, No-Shpa, Drotaverine |
| Diuretics | They prevent urine from stagnating in the bladder, eliminating infectious agents from the genitourinary organs. | Diacarb, Indapamide, Furosemide |
| Immunosuppressants | They are used for increased levels of leukocytes in the urine caused by autoimmune pathologies. | Entyvio, Supresta, Xolar |
| Antihistamines | Used for leukocyturia caused by chronic allergic reactions. | Diazolin, Suprastin, Claritin |
| Probiotics | They consist of natural bacteria, normalize the microflora after taking antibiotics. | Linex, Lactobacterin, Bifidumbacterin |
| Prebiotics | They contain nutrients for bacteria and restore microflora. | Hilak forte, Baktistatin, Lactofiltrum |
| Immune system modulators | Strengthen the immune system, stimulate natural resistance to infections and inflammation in the body. | Ingavirin, Eleutherococcus, Echinacea |
| Vitamins | Supradin, Alphabet |
Folk remedies
Herbs, berries and seeds with a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect are used as traditional methods for treating leukocyturia.
Herb tea
Add knotweed to herbal tea and take before meals
To prepare this drink you will need herbs:
- knotweed;
- motherwort;
- field ivy.
The herbs must be crushed and mixed in equal proportions, and then diluted in a ratio of 1 tsp. mixture per 200 ml of water. The drink is infused for 10-15 minutes, after which it is taken before or during meals.
Also 1 tsp. the mixture can be added to a serving of soup or main dish.
Birch juice
Birch sap contains natural antibiotics and microelements that remove decay products of pathogenic microorganisms. It effectively relieves inflammation in the urinary tract and genitals.
Treatment is carried out using fresh juice, taken in the morning on an empty stomach. 1 serving of juice is 100-200 ml.
Green beans
Green beans have a strong antimicrobial effect
Green beans, a strong antimicrobial agent, will help get rid of leukocyturia.
- Wash and peel 100g beans.
- Squeeze the juice out of them by hand or using a juicer.
- Drink 1 tsp on an empty stomach. for the reception.
Treatment with bean juice lasts 1-2 weeks.
Cranberry tea with lemon balm
Cranberry, lemon balm and tea leaves have strong anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects. The drink is prepared as follows:
- Peel, rinse, and mash 30 g cranberries in a deep container.
- Add the resulting puree to the teapot, mix with 2 tbsp. l. tea leaves.
- Pour the mixture with water, let it brew and consume internally.
Melissa leaves are added to tea before ingestion. The recipe can also be supplemented with raspberry leaves or berries.
Wormwood infusion
Wormwood infusion will help cope with infections in the body
Wormwood is an effective herb that fights inflammation and infection. The infusion is prepared as follows:
- Wash the grass, dry it, chop it finely.
- Mix 3 teaspoons of wormwood with 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave for 1 hour.
The infusion is taken orally, 15 drops before each meal.
Flax seed infusion
Flax cleanses the kidneys, fights infection, restores tissue and mucous membranes of the genitourinary organs. An infusion of it is made according to the following recipe:
- Pour 30 g of dry flax seeds into 200 ml of hot water.
- Infuse the drink for 2-3 hours in a cold, dark place.
- Dilute the mixture with 200 ml of cold water and consume internally.
The drink is drunk 4-5 times a day, 50 ml at a time.
Norms and deviations in women
Reference values for the presence of white bodies in the urine of women may vary slightly, due to the age and condition of the subject. So in girls and young girls under 18 years of age (not pregnant), the number of leukocytes in urine should not exceed 7 pieces in the field of view. Over 18 years of age, not pregnant – 5 cells. Pregnant women under 18 years of age normally have no more than 12 cells in their field of vision, and pregnant women over 18 years of age have no more than 10 cells.
Attention! Higher values may be evidence of a developing pathology, and the patient will need to undergo a full range of diagnostic procedures to determine the cause of their increase.
Depending on the quantitative content of white blood cells that are detected in the laboratory technician’s field of view during a urine test, two degrees of their increase are distinguished:
- Leukocyturia is diagnosed if the number of detected cells fluctuates in the range of 7-60 pieces.
- Pyuria (pus in the urine) is indicated on the analysis form if more than 60 leukocytes are detected in the field of view.
The presence of the latter described condition can often be suspected before laboratory tests, since the urine becomes cloudy and has an unpleasant odor. And patients complain about symptoms characteristic of inflammatory processes in the urinary system or other internal organs. As a rule, such manifestations indicate a serious illness, which in no case should be left without proper medical care.
Nagging pain in the lower back is one of the main signs of inflammatory processes in the kidneys
White blood cells are higher than normal
When receiving the results of a general urine test, it is possible that you will find that the white blood cell count (WBC) will be elevated (that is, white blood cells in the urine 4 or more in men and 6 or more in women). Let's figure out what elevated white blood cells in the urine mean, why this happens and what to do about it. In medical terminology, an increased level of white blood cells in the urine is called leukocyturia. There are several classifications of leukocyturia. Let's look at some of them:
- Types of leukocyturia:
- True - when the causes of elevated leukocytes in the urine are pathologies and diseases of the urinary system
- False - in case of leukocytes entering the urine from the genital organs, due to poor hygiene of the external genital organs, or inflammation of the genital organs (balanitis or balanoposthitis in men and vulvovaginitis in women)
According to the severity of leukocyturia, there are:
- Severity of leukocyturia:
- Minor is a situation when leukocytes in the urine are increased above normal to 35-40 cells in the field of view
- Moderate - leukocytes from 40 to 60
- Severe (pyuria) - white blood cells from 60-70 and above, while pus and flakes of sediment appear in the urine, and the urine itself becomes cloudy with an unpleasant odor.
Pyuria suggests the presence of an acute infection in the body.
Also in the form of results of a general urine test, in addition to numerical ones, there are also verbal interpretations of the level of leukocytes in the urine. Doctors use special verbal designations for various results, and it is difficult for an untrained person to understand what “leukocytes in the urine 10-12” or “30-40” means, or how “all leukocytes” differs from “accumulation of leukocytes.” Below are possible entries in the analysis results and their interpretation.
- White blood cells in urine (possible results):
- “Leukocytes 10-12”, or 10-15, 15-20, 20-25, 30-40 or 40-50 - here the numbers indicate the number of cells (leukocytes) in the test sample. All these records indicate that there are high white blood cells in the urine (increased to the indicated level)
- “Accumulation of leukocytes” - this means that in the sample of urine being tested, leukocytes accumulate in a certain way, forming groups (this information is used by attending physicians to determine the characteristics of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment)
- “Leukocytes completely” or “cover the entire field of view” - when analyzing there are so many leukocytes in the urine that they cannot be counted, they fill the entire field of view of the microscope
Reasons leading to the increase in the indicator
An increased content of leukocytes in the urine of women can be observed under the influence of both physiological and pathological, that is, disease-related factors. The first causes of leukocyturia include pregnancy and breastfeeding.
During pregnancy, the body perceives the fetus as a half (due to the father’s biomaterial) foreign object and the number of leukocytes may increase slightly in the blood, which accordingly leads to their growth in the urine.
When feeding a baby, an increase in leukocytes in the mother's urine can be caused by hormonal changes in the body. Most often, such changes are not pronounced and disappear at the end of lactation.
An increase in the rate is sometimes caused by taking a certain number of medications, such as diuretics, immunosuppressants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and anti-tuberculosis drugs. In such situations, the values of white cells return to normal when the drugs are discontinued or replaced with their analogues.
There are much more pathological reasons for the appearance of an increased number of leukocytes in the urine of women than physiological ones, but as mentioned above, a significant part of them are diseases of the genitourinary system. This list includes the following diseases.
Kidney infections
Glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidney glomeruli). With this disease, leukocyturia is mainly diagnosed, and its indicators most often do not exceed 25-30 leukocytes in the field of view, which is a moderate severity of the condition.
Pyelonephritis (inflammation of the renal pelvis) is characterized by pyuria, which often reaches more than 250 cells or higher in the field of view. This is a very serious disease, which without adequate treatment can lead to complications that can pose a threat to human life.
Kidney abscess is a purulent inflammation with a clearly defined cavity. This is one of the most dangerous pathologies developing in the kidneys. The disease may be accompanied by pyuria with a very high content of leukocytes in the urine, and requires immediate medical intervention.
Hydronephrosis of the kidney is a pathology caused by the expansion of the collecting apparatus, which leads to stagnation and accumulation of urine. As a result of such disturbances, pathogenic bacteria multiply in the urine, which manifests itself in the form of leukocyturia. As the disease progresses, the number of white blood cells may also increase.
Reference! About 90% of pregnant women experience hydronephrosis in the third trimester, which is why they are prescribed regular urine tests - the most effective method of monitoring the development of kidney disease.
Inflammation of the urinary tract
Cystitis (inflammation of the bladder) in most cases is not a serious disease, but its symptoms bring significant discomfort to the patient. Drawing and sharp pain when urinating, heaviness in the lower abdomen, groin, the appearance of blood in the urine - all this makes it impossible to postpone a visit to the hospital.
Urethritis (inflammation of the urethra (urethra)) is also not considered a serious pathology and causes discomfort (itching, pain during and after urination, pain, etc.). These two diseases are often accompanied by mild leukocyturia, and a urine test reveals no more than 15-20 cells per field of view.
Microorganisms that can cause inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system
Reproductive system infections
There are a great many pathogens that cause infectious diseases of the reproductive system, and each of them is accompanied by leukocyturia to varying degrees of severity, and sometimes pyuria. Just a few of them are listed here.
Herpes is a recurrent disease characterized by the appearance of peculiar rashes on the skin or mucous membranes, caused by a special type of virus and can spread over all surfaces of the body. But what causes the most problems is their appearance on the genitals.
Trichomoniasis is a pathology caused by the entry into the body of the simplest microorganism - Trichomonas. The disease responds well to treatment and is not severe. Leukocyturia with it is insignificant.
Gonorrhea is a disease that is caused by the appearance of gonococcus in the genitals and the further proliferation of its population. With prolonged avoidance of therapy, the pathology can reach leukocyturia of high severity and lead to various complications, such as adnexitis (inflammation of the ovarian appendages, etc.)
Ureaplasmosis and chlamydia are caused by pathogens of the same name, and are serious diseases that, in the absence of proper therapy, can lead to infertility and other complications. Leukocyturia with them does not reach too high values, but this does not mean that treatment should be delayed.
Candidiasis is a fungal infection of the vaginal mucosa. During the analysis, not only an increase in leukocytes is noted in the field of view, but also a large number of yeast fungi of the Candida species, as well as white impurities in the sample.
Inflammation of the genital organs
Almost all inflammatory processes that develop in the genital organs of women are caused by the presence of some pathogen. Therefore, with them there is also an excess of white cells in the fluid secreted by the kidneys.
Vulvitis - inflammation of the vulva (external female genitalia) is not a complex pathology, and is not in all cases accompanied by leukocyturia. If there is an increase in the indicator, it is quite insignificant. Sometimes it develops in girls and is non-infectious.
Colpitis (vaginitis) - inflammation of the vagina is not a very dangerous disease, but women feel quite severe discomfort with it. Leukocyturia, if it occurs, is not very pronounced.
Cervicitis is inflammation of the cervix. It can be infectious or non-infectious in nature. Without timely treatment, it can spread to the uterus and neighboring organs, leading to various complications.
A large number of leukocytes in the urine may be observed during a control test after recent recovery from genitourinary infections, since their level has not yet returned to normal. In this case, it is recommended to repeat the examination after a while.
Other causes of leukocyturia
An increase in white blood cells is observed in several other diseases, some of which are not directly related to the organs of the genitourinary system. This includes the following:
- oncological neoplasms in the genitourinary system;
- the presence of various parasites in the body;
- urolithiasis disease;
- systemic allergy.
Also, poor adherence to intimate hygiene rules can lead to a false increase in the white blood cell count. As a result, the microflora present in the vagina changes, acidity changes, and white blood cells appear. When collecting a sample for analysis, particles of vaginal discharge fall into the container, and as a result, leukocyturia is determined.
During pregnancy, an increase in the content of leukocytes in the urine is very often observed.
Types of urine analysis
A clinical study (or general) requires the collection of up to 100 ml of urine (morning), involves the assessment of organoleptic indicators (color, smell, transparency), physicochemical (acidity, thickness), microbiological (presence of protein, glucose, blood cells, bacteria) . This is the most accessible and widespread method of urine analysis, used by almost all medical institutions as diagnostic and preventive.
If necessary, other tests are performed. A three-glass test involves studying urine divided into 3 portions (initial, middle, final), which is important for assessing the localization of inflammation in the urological tract. With a two-glass sample, only the first and last portions of urine are studied.
Using the Nechiporenko method, the concentration of bodies in 1 ml of urine sediment obtained by centrifugation is determined. The Kakovsky-Addis analysis requires collecting urine for 24 hours, followed by counting leukocytes in the sediment (which is important for latent leukocyturia). To determine the quantitative ratio of protective cells of different types, supravital staining of the biomaterial is performed.
High white blood cells during pregnancy and after childbirth
When carrying a child, a woman’s hormonal system undergoes many different transformations, which affects the functioning of almost all organs. This may also affect the formation and concentration of leukocytes in certain places, including in the genitourinary system, as a result of which their levels will be increased.
White flakes in urine during pregnancy
If leukocyturia is observed for a short time and does not reach high values, then it will only be enough to keep it under regular monitoring, which includes taking urine and blood tests, as well as assessing the general condition of the woman.
If high leukocytes in the urine are observed for a long period, then it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient, and this is especially important in the presence of pathological symptoms, albeit mildly expressed.
Since such changes may indicate the appearance and development of an inflammatory focus, the most common pathology found in pregnant women is pyelonephritis.
In addition, we should not forget about possible postpartum leukocyturia - a physiological manifestation that, as a rule, is not characterized by a significant increase. In this case, urine taken for analysis after childbirth may include vaginal discharge containing not only leukocytes, but also red blood cells.
This is due to the fact that after the birth of a child, bloody discharge occurs from the mother’s genital tract for several days or weeks. If postpartum leukocyturia is accompanied by symptoms such as:
- headache,
- malaise, weakness,
- pain in the groin and lower back,
- increase in body temperature,
- frequent and/or painful urge to go to the toilet and others,
then this indicates the emergence of a pathological process that requires immediate medical intervention - diagnosis and further treatment. A condition in which leukocytes in the urine are low is not considered in medical practice, since an analysis in which these cells are completely absent is considered ideal.
Types of leukocyturia
Depending on the presence of bacteria in the urine, aseptic leukocyturia is distinguished (accompanied by an increase in the level of lymphocytes and eosinophils with a small number of bacteria) and septic (neutrophils predominate, over 100 thousand microorganisms are detected). Based on the type of protective cells present in the urine, neutrophilic, lymphocytic, eosinophilic or mononuclear leukocyturia is determined (which helps in determining the localization of the inflammatory process).
The concentration of white bodies can be:
- insignificant (up to 50 units/p.z.), which indicates a small focus of inflammation;
- moderate (from 50 to 100 units/p.z.), indicates 1 large or several small pathological foci, chronic disorders;
- pronounced (over 100 units/p.z.), accompanies complications of infectious diseases, the presence of purulent-necrotic lesions.
Based on the localization of the inflammatory process, leukocyturia is divided into renal and extrarenal (affects the urinary tract, genitals, and other systems). By origin, the disorder can be true (diseases of the urinary structures) or false (when the urological tract is not damaged).
Therapeutic approach
Treatment and correction of leukocyturia directly depends on the cause that led to it. Only a specialist can determine it and develop appropriate therapeutic tactics, so in no case should you self-medicate.
Attention! Ignoring the problem and postponing a visit to the hospital in many situations accompanied by an increase in the level of leukocytes can lead to a significant deterioration in the patient’s condition.
The very first thing to do is a comprehensive examination that will help establish a diagnosis. This may include both laboratory and instrumental techniques. If a bacterial infection is determined, then antibiotics are prescribed in the form of tablets (in severe cases in injection form), such as Ampicillin, Tetracycline, Ceftriaxone, etc. If necessary, vaginal suppositories or bladder lavage are prescribed.
If a viral infection is detected, antiviral drugs are used. In addition, symptomatic treatment is prescribed. The allergic reaction is relieved by using antihistamines - Diphenhydramine, Suprastin.
In case of reduced immunity, it is recommended to take medications to stabilize it or adjust the diet. Identified neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature are treated with surgery and subsequent radiation or chemotherapy.
If, based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis, no pathological processes were diagnosed, then therapy is not prescribed, and the woman is recommended to undergo further examinations over time in order to monitor her condition.
If an infection is detected in the genitourinary tract, antibiotics are prescribed in most cases.
It should be noted that minor leukocyturia diagnosed during pregnancy and after delivery does not require specialized therapy, and the doctor, as well as the woman herself, is only required to monitor the state of health. Otherwise, there is always a chance of missing the onset of the development of any pathology.
If the increase in the indicator is caused by taking medications, then you need to notify the doctor about this, and he will prescribe analogues that do not affect the composition of urine or reduce the dosage of the drug.
How to prepare for analysis
Correct urine test results are no less important than blood tests. Therefore, you need to prepare for the delivery of biomaterial. 2-3 days before the test, stop taking medications from the group of diuretics, antiplatelet agents, antibiotics, and hormones. Before stopping medications, you should consult your doctor. The day before the test, you should avoid foods that can change the physical and chemical qualities of urine (red wine, beets, sorrel, chocolate, game meat). Excessive physical exertion or psycho-emotional shocks are undesirable.
Urine collection must be approached responsibly. It is better to purchase a special sterile container at the pharmacy (for children - a urinal). It is not advisable to take tests in a previously used and washed jar.
For general examination, morning urine is collected. Before the procedure, you need to wash yourself with soap and wipe your genitals with a clean towel (preferably paper). The entire morning portion is collected in a separate container, and then the container is filled. For the Nechiporenko test, you need to give only mid-sized urine, and for three-glass urine, each portion of urine separately.
The biomaterial must be transported to the laboratory within 1.5 hours. It is allowed to store urine in a cool place, but at above-zero temperatures. Frost may cause precipitation.
Prevention
So, given that in the vast majority of cases, an increase in the number of leukocytes in the urine of women is a clear sign of a developing inflammatory process of internal (mainly genitourinary) organs, it is worth paying attention to the following.
It is very important to take care of the prevention of infectious diseases, and first of all, strengthen your immunity. The rules for maintaining a healthy immune system are quite simple, but require strict adherence. To prevent the occurrence of the disease, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and, if possible, harden the body.
Hypothermia should be avoided (dress appropriately for the weather, do not spend long periods of time in the cold and walk in wet shoes). It is also important to follow all rules regarding personal and intimate hygiene. Eat well, do not burden the body, and in particular the kidneys, with junk food, alcohol, and toxic drugs.
Do not neglect visits to the hospital for routine check-ups, and be sure to promptly treat acute and chronic diseases. It should be remembered that only with the strictest and most careful care of her body will a woman always feel good, which, of course, will certainly affect her appearance and desire to live a full life.
Diagnostics
To find out why leukocytes in the urine are elevated, a number of diagnostic procedures are carried out taking into account the accompanying symptoms, namely: additional studies of urine, microflora of the genital organs and the condition of the urinary system.
Analysis according to Nechiporenko
Microscopic examination of sediment in the urine, which is prescribed to detect infections and to monitor the treatment of inflammatory diseases of bacterial origin. The table shows the quantitative indicators of leukocytes, erythrocytes and cylinders in 1 milliliter of urine.
| Indicators | Normal, cells |
| Leukocytes | Until 2000 |
| Red blood cells | Up to 1000 |
| Cylinders | Up to 20 |
Three-glass or two-glass test method
Analysis by dividing urine into several portions allows you to determine the exact location of inflammation and consists of sequential collection of material into three or two separate sterile containers with precise order marking.
For women, a two-glass test is used, the breakdown of the leukocyte content in which is indicated in the table.
| Portions | What does a high white blood cell count mean? |
| First | Inflammation in the urethra |
| Second | Bladder diseases |
| In both | Pyelonephritis or cystitis |
If elevated white blood cells in the urine of women are combined with symptoms of an infectious lesion of the external genitalia, then additional tests are prescribed to determine the type of bacterial infection:
- bacterial culture for flora - used to detect the content of bacteria in urine and to monitor treatment;
- a smear from the vagina, urethra and vulva - necessary for microflora analysis;
- urocytogram - examination of urine sediment for the presence of bacterial cells.
If the development of non-communicable diseases is suspected, investigations should be carried out to determine the cause (presence of stones or possible changes in the shape, position, size and functioning of the kidneys, ureter and bladder) using the following procedures:
- Ultrasound;
- radiograph;
- urography;
- cystoscopy;
- kidney biopsy.
How to increase white blood cells at home
There are a variety of ways to increase the level of white blood cells in the blood, but diet plays a fundamental role in the treatment process. As practice shows, it is almost impossible to increase the number of leukocytes without following a diet, even if you take special medications. This diet is prescribed by your doctor. Typically, the amount of carbohydrates consumed is limited; instead, the diet is enriched with protein foods and vitamins, especially ascorbic and folic acid. You also need to eat foods high in choline and the amino acid lysine.
The main products in the treatment of leukopenia - increasing leukocytes at home:
- Eat more citrus fruits and various berries.
- It is useful to consume royal jelly to increase the level of leukocytes. Its amount should not be too large, depending on the doctor's recommendations.
- You are allowed to drink large amounts of milk and other fermented milk products.
- Eat more vegetables and legumes, cooked or raw, which are high in fiber.
- As additional vitamins, you can use vitamin C, B9 - they effectively increase white blood cells.
- A decoction of barley, which is infused for half an hour on fire to increase the concentration of grain, is useful. To do this, you need to pour one and a half glasses of barley into a two-liter container and add water. Boil over a fire until the water is half boiled away, and then drink the strained liquid 200 grams twice a day.
If a low white blood cell count is detected, it is recommended to seek treatment from a hematologist - a specialist in the treatment of blood diseases. The hematologist must find the cause of leukopenia and prescribe treatment. In some cases, consultation with an oncologist, infectious disease specialist or immunologist is necessary.
The human body constantly contains leukocytes that are able to fight foreign agents that come into their field of vision. The tasks and abilities of each particle are individual. Some are able to recognize the enemy and report a threat to their fellow humans, others are able to give commands to action, others are able to train young cells to remember dangerous elements, and hard-working killer cells are able to destroy microorganisms. It would seem that the more smart cells, the more protected the body is. However, an increased number of white particles indicates the presence of unnatural processes in the body. In such a situation, it is urgent to find out the cause of the anomaly, which will determine how to lower leukocytes in the blood.
The level of white particles in the blood can change under the influence of natural physiological processes. In this case, the process is almost imperceptible to humans. In rare cases, dizziness and slight changes in temperature may occur.
If the level of leukocytes is affected by diseases and the process is pathological in nature, symptoms characteristic of the underlying disease are first monitored.
With leukocytosis – – unnatural conditions may be observed in the form of:
- weaknesses in the body;
- increased sweating;
- fatigue;
- weakened appetite;
- dizziness;
- elevated temperature;
- impaired vision;
- hematomas and bruises;
- weight loss;
- bleeding from mucous membranes;
- pain in the abdomen.
It is possible to confirm assumptions about changes in the quantitative indicators of white particles only by conducting a blood test.
Decoding the results
When examining urine, laboratory assistants check:
- Color normally ranges from yellow to straw. Darkening can cause infections and liver damage.
- smell . In healthy people, the smell of urine is specific, but not pungent. A change to ammonia is evidence of the development of cystitis and other infections, fecal - with E. coli, putrefactive - with the decomposition of organ tissues.
- foam . When shaking the urine of a healthy person, a small foam appears, which quickly settles. Strong foaminess is evidence of the presence of protein.
- transparency . A sediment may fall due to the presence of impurities, an increase in quantitative indicators: red blood cells, pus, salts, which normally should not be in the urine.
- density . Variant of the norm from 1.01 to 1.022 g/l. An excess is associated with a lack of fluid in the body, a decrease is a sign of kidney dysfunction.
- acidity is normal from 4 to 7 pH. Exceeding the indicator may indicate the presence of diabetes, fasting or excessive consumption of meat. With kidney dysfunction, the indicator may be lower than normal.
- protein from 0 to 0.033 g/l. Exceeding the indicator is possible with exacerbation of kidney disease or overwork.
- sugar up to 0.8 mmol/l. An increase above this value may occur with diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands, diabetes mellitus.
- bile pigments , ketone bodies, bacteria, salts, parasites are not found in the urine of a healthy person.
- slime . Normally it is not found in urine, being a sign of the development of a sexually transmitted infection.
- red blood cells . From 0 to 3 should be in the analysis of a healthy woman.
- leukocytes . From 3 to 6 per field of view in the analysis of a healthy woman.
How are protein and leukocytes determined?
Urine is a liquid that is constantly formed in the kidneys and flows down the ureters into the bladder. After filling the organ, it is removed by the act of urination. The human body produces up to 2 liters of urine per day. Its composition is a variety of organic and inorganic compounds dissolved in water (mineral salts, amino acids, enzymes, etc.).
Urine is the optimal material that makes it possible to determine the presence of diseases of the prostate, kidneys and their tracts, and other systems of the human body. Therefore, urine analysis is used as an object to obtain diagnostic information.
To obtain objective data on the composition of urine and the presence of traces of protein and leukocytes in it, several methods are used. Often, the indicators of such studies are the basis for making a diagnosis, determining the severity of the patient’s condition, and based on them, a treatment regimen is determined.
For correct analysis results, the starting material must be correctly collected from the patient.
Treatment
After diagnosis, depending on the cause of the development of leukocyturia and proteinuria, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
For urolithiasis, medications are prescribed that dissolve stones (Blemaren, Asparkam, Cyston, Canephron, Urolesan, Gortex). If there are indications, surgical crushing of stones is prescribed. In case of inflammatory pathologies of infectious etiology, a course of antibacterial therapy is prescribed, which is active against the identified pathogen (Ceftriaxone, Bisiptol, Flemoxin Solutab, Levofloxacin). For fungal diseases, antifungal drugs are used (Fluconazole, Flucytosine, Amphotericin). To increase the body's resistance, immunomodulators (Interferon, Kagocel, Ergoferon, Arbidol, Viferon) are used. To reduce pain and facilitate the passage of stones through the urinary tract, antispasmodic and painkillers are prescribed (No-shpa, Papaverine, Baralgin, Spazmalgon, Analgin). If leukocyturia and proteinuria are accompanied by hyperthermia, antipyretic medications (Paracetamol) are used, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nurofen, Ibuprofen), which not only reduce body temperature, but also have a pronounced analgesic and antiphlogistic effect
An important place during treatment is occupied by diet, which can reduce the load on the urinary system and speed up the healing process. For renal pathologies, treatment table No. 7 and its modifications a and b are prescribed, according to which you should avoid eating fatty, fried, spicy, smoked, salty, canned, sweet foods
According to the diet, you should strictly limit your salt intake - no more than 3-5 g per day. You should also give up fatty meats (pork, lamb) in favor of lean varieties (chicken, turkey, veal). The basis of the diet should be fresh or steamed vegetables and fruits, dairy products. It is important to drink a lot of water daily - more than 2 liters, unless there are contraindications. Diuretics (Lasix, Furosemide, Oksodolin, Veroshpiron) and traditional medicine, among which cranberry, currant, lingonberry, bearberry, chamomile, horsetail, flax seeds, birch leaves and buds are considered the most effective, help restore the impaired outflow of urine. To prepare decoctions and teas, you should purchase ready-to-use herbs at the pharmacy and prepare them according to the instructions on the package.
It is also important to give up drinking alcohol and other bad habits that negatively affect the functioning of the kidneys and vascular system. Increased levels of protein and leukocytes in the urine of a child and an adult often indicate improper collection of biological material for research or are a symptom of a disease of the urinary system, vascular pathologies
To identify the cause of proteinuria and leukocyturia, additional diagnostics should be performed using instrumental methods. Treatment is prescribed in accordance with the cause of deviation from the norm
An increased level of protein and leukocytes in the urine of a child and an adult often indicates improper collection of biological material for research or is a symptom of a disease of the urinary system or vascular pathologies. To identify the cause of proteinuria and leukocyturia, additional diagnostics should be performed using instrumental methods. Treatment is prescribed in accordance with the cause of deviation from the norm.
Kidney infections
UTI diseases include:
- Inflammation of the bladder (cystitis) and its forms: acute uncomplicated cystitis, chronic and recurrent cystitis.
- UTI with complications.
- Prostatitis in men.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Infections during insertion of a urinary catheter.
A more general division is into lower urinary tract infections (urethra, bladder and prostate) and upper urinary tract infections (kidneys and ureters). Kidney damage is especially dangerous, because complications of the pathology include destructive changes in the tissues of the organ or blood poisoning (sepsis).
If the infection spreads to the kidneys, pyelonephritis occurs. The name of this disease speaks for itself. It is formed from two roots - “pus” and “kidney”. As you know, the main component of pus is dead leukocytes, which, dying, adhered to the pathogen and formed pus. With pyelonephritis, protein is also released into the urine.
Kidney infections can occur at any age, so it is possible that white blood cells are found in a child’s urine. The chances of a kidney infection are especially high in a female child.
The causes of this disease are bacteria that have gained access to the urinary tract. They usually get there from the anus, vagina, or skin. Risk factors for pyelonephritis include pregnancy, frequent UTIs, kidney stones, use of urinary catheters, diabetes, and surgery. Kidney infections are not contagious.
Pyelonephritis makes itself felt by symptoms of fever, chills, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. There is pain during urination, frequent urge to go to the toilet.
Acute and purulent inflammation of the kidneys
Acute nephritis is the main cause of increased proteins and leukocytes in the urine. This is an intense inflammation of the parenchyma of the paired organ, glomerular vessels and tubules. The etiology of acute nephritis is associated with the penetration of bacteria into the kidneys. Most often, the causative agent is streptococcus, which initially causes a sore throat or flu, and then affects the urinary organs.
Sometimes the infection comes from neighboring areas due to cystitis or urethritis. Less commonly, the cause is pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases and bacteria of the genus pneumococcus and staphylococcus. Foreign flora destroys the structure of the renal tissue, increases vascular permeability and promotes the formation of purulent foci. This explains the penetration of protein and leukocytes into the urine. Purulent lesions can also develop due to urolithiasis. In this case, treatment is only surgical.
On a note! Acute nephritis predominantly affects young patients under 30 years of age and children.
Clinical manifestations
An acute form of inflammation in the kidneys develops over several days, and sometimes hours. Symptoms are always striking and are accompanied by a decrease in the amount of urine excreted.
Among the main clinical manifestations:
- fever up to high levels;
- unbearable pain in the lumbar back;
- swelling;
- chills;
- tachycardia;
- headache.
Urine takes on an unnatural color. May be cloudy, whitish, brown, or contain flakes or streaks of blood. The number of leukocytes increases as it progresses, and the daily loss of protein exceeds 150 mg. With prolonged failure to provide assistance due to the toxic effects of bacteria, symptoms of heart failure (shortness of breath, cyanosis of the lips, pain in the heart) appear.
What white blood cell count is considered elevated?
Normally, no more than 5 leukocytes per field of view should be detected in the sediment.
If there are more than 8 cells, but less than 40, this is weak leukocyturia.
Moderate is diagnosed when the number of cells is up to 100 pieces per cell.
If there are so many leukocytes that they cannot even be counted, this is severe leukocyturia or pyuria (discharge of pus in the urine).
Additional methods (Kakovsky-Addis, Nechiporenko, Amburge) make it possible not only to confirm the presence of this syndrome, but also to find out which cells are secreted.
There are many types of leukocytes.
Their different types appear in various diseases:
- neutrophils – for tuberculosis, pyelonephritis
- mononuclear cells – against the background of glomerulonephritis or interstitial nephritis
- lymphocytes – for autoimmune diseases (lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis)
- eosinophils – for allergic inflammation
Diagnosis of the problem
As a rule, the pathological condition is detected by TAM. If the analysis reveals an increase in leukocytes, then the woman is given a referral for a clarifying urine examination according to Nechiporenko.
If deviations from the norm are detected in the control analysis, then further diagnostic measures will be aimed at identifying the cause of the disease.
- Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky. The technique is necessary for diagnosing developing pyelonephritis.
- Bacterial culture of urine. The analysis helps to select the appropriate drug to combat the pathogen.
- CBC and blood for biochemistry. Allows you to evaluate ESR, the number of leukocytes and hemoglobin in the body. Indicators suggest the presence of certain diseases.
If there are no pathogenic microorganisms in the urine, then the woman is given a referral for a vaginal smear. In sexually transmitted diseases, germs are not sown in the urine.
Symptoms of leukocyturia
An increase in the level of protective cells in the urine does not manifest itself with specific signs; it is always a consequence of some pathology. The patient is concerned about phenomena associated with the disease that provoked leukocyturia. Most often, these are signs of malfunction of the urinary organs:
- nagging pain in the lower back and lower abdomen;
- urge to go to the toilet;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- pain and spasms during the passage of urine;
- uncharacteristic color of discharge (“meat slop”, yellow-green, brown);
- impurities (mucus, flakes, pus, blood clots).
Nonspecific symptoms include fatigue, drowsiness, apathy, fever, chills.
Useful information: Increased prolactin in women: more than 6 causes, 9 main symptoms, treatment (3 drugs) and consequences for the body
Treatment of leukocyturia
Therapy is not aimed at normalizing the results of urine analysis, but at eliminating the causes that led to deviations. Since an increased number of white blood cells most often accompanies urinary tract infections, the main task is to neutralize pathogens and relieve inflammation. For this, complex therapy is prescribed:
- antibiotics (Monural, Ciprofloxacin, Amoxicillin) or antimicrobials (Nitroxoline, Furadonin, Furamag);
- antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Spazmalgon, Buscopan);
- herbal anti-inflammatory drugs (Canephron, Urolesan);
- means to reduce the acidity of urine (Kataria, alkaline waters).
The dosage of drugs and the course of treatment are determined by the doctor. If the inflammation is caused by kidney stones, surgical assistance or the prescription of special medications to dissolve the stones (Urolit, Fitolit) is required.
Phytotherapy can be used in complex treatment. The use of herbal infusions helps to “wash out” microbes from the excretory organs and provides astringent and anti-inflammatory effects. At home, you can infuse corn silk, horsetail, and bearberry leaves. All these herbs are sold in pharmacies without a prescription.
During treatment of leukocyturia, it is important to follow a diet. You need to give up:
- fatty, fried, smoked foods;
- spices and herbs;
- sweets, chocolate, coffee;
- mushrooms, broths;
- vegetables with purine bases in their composition (tomatoes, eggplants, sorrel, spinach, celery).
The menu should include cereals, dairy products, and a lot of green vegetables (broccoli, zucchini, cucumbers). It is very important to normalize your drinking regime. If you have inflammation of the urinary system, you need to drink at least 2 liters of water per day, not counting other liquids. Doctors recommend eating berries - sea buckthorn, cranberries, viburnum. They have a general strengthening effect, supply the body with vitamins, and promote the removal of fluid.
The mechanism of protein appearance in urine
So, let’s figure out when there are elevated leukocytes and protein in the urine.
Normally, the vast majority of proteins do not penetrate through the glomerular basal membrane. This is due to the large size of the protein units, as well as their charge and shape. If there is even a slight defect in the membrane, then albumin without leukocytes first comes into the urine; if the defect is more significant, the molecules are larger. Epithelial tubular tissue, even in a healthy person, forms a certain proportion of proteins, some of which penetrates from the ureters and urethra.
When do protein and leukocytes appear in the urine?
What to do with “bad” tests
The results of any study must be read by a doctor. In most cases, he prescribes it. If you take the test yourself and are not pleased with the results, you should consult a therapist. Pregnant women must make an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist; their children are shown to a pediatrician. If necessary, the doctor will refer you to a specialized specialist (venereologist, nephrologist, urologist, andrologist).
If the urine test result is unsatisfactory, a repeat test is performed. If its outcome is similar, a Zimnitsky analysis and bacterial culture are prescribed. To determine what caused the deviations, general and biochemical blood tests are performed. Women are prescribed microscopy of a vaginal smear. To assess the condition of the kidneys, it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound.
Until the reasons for the deviations are clarified, it is better for the patient to abstain from alcohol and the use of any medications. It is important to avoid overwork and stress. It is necessary to eat rationally, balance the amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates coming from food.
Role of leukocytes
Leukocytes make up a group of blood cells along with red blood cells and platelets. These uncolored blood cells are responsible for immunity. They are able to detect pathogens penetrating from the outside and destroy them, as well as fight internal pathological processes.
The leukocyte group consists of five types of cells: lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, basophils and eosinophils.
The first two belong to agrunolocytes, that is, they do not have granules in the cytoplasm. The rest are granular and are called granulocytes.
Each type performs specific functions:
- Neutrophils are the most numerous group (from 47 to 72%). In the blood of a healthy person, mainly mature forms (segmented) and very few young forms (band) circulate. Their main purpose is to fight harmful bacteria. They immediately respond to bacterial infection, which is expressed by an increase in the number of young forms in the blood. Neutrophils have the ability to quickly move through the body, accumulate in affected tissues, capture pathogenic microbes and destroy them.
- Basophils are the largest granulocytes. Their content in the blood normally ranges from 0.5 to 1%. They perform different functions, but the main one is participation in the formation of inflammation and immediate allergic reactions (for example, anaphylactic shock). This is possible due to the fact that their granules contain many bioactive chemicals - mediators of inflammation and allergies. These are serotonin, histamine, heparin, prostaglandins, leukotrienes and others.
- Eosinophils are able to move quickly, penetrate beyond the vascular wall and carry out phagocytosis, but their main property is cytotoxic. They take an active part in the fight against parasitic infections and in the formation of antiparasitic immunity. In addition, they can both absorb and release allergy mediators, that is, they can both suppress an allergic reaction and cause it.
- Lymphocytes are the main immune cells of the body, which make up from 25 to 40% of the total number of leukocytes. They are responsible for cellular and humoral immunity. Lymphocytes produce antibodies against harmful agents. These are the main fighters against viral infections and cancer cells.
- Monocytes are the largest white cells, the content of which in healthy people ranges from 3 to 11%. These macrophages perform several functions, but the main one is phagocytic defense against microbes.
Classification of proteinuria
There are 2 classifications of this pathology.
Proteinuria is divided into:
- prerenal (associated with increased tissue breakdown);
- renal (due to kidney disease);
- postrenal (the pathological process is located in the urinary tract).
There are two types of renal proteinuria:
- tubular (based on a change in the normal process of reuptake of low molecular weight protein units);
- glomerular (if the filtration system of the glomerulus of the kidney is damaged).
Urine analysis during pregnancy
The health and well-being of the expectant mother and her child directly depends on the frequency of laboratory tests and examinations in pregnant women. If the levels of proteins and leukocytes are increased, salts are present in the urine, perhaps we are talking about a dangerous inflammatory process that must be eliminated in order to avoid negative consequences for the pregnant woman and the fetus.
Submitting urine for analysis during pregnancy is a mandatory procedure.
During pregnancy, the risk of developing pathologies of the genitourinary system is significantly increased due to the growing uterus, which puts pressure on the pelvic organs and makes them especially vulnerable to infection. With pronounced leukocyturia, bacteriuria (the appearance of harmful bacteria in the urine) can often be diagnosed. Red blood cells in the urine of a pregnant woman are characteristic of the same diseases as in an ordinary person. An increase in protein in pregnant women may be associated with a dangerous pathology called gestosis. This disease can be diagnosed without preliminary laboratory tests: the pregnant woman develops excessive swelling, fatigue syndrome, general malaise, and hypertension. This condition requires hospitalization and round-the-clock monitoring of the patient’s condition by medical personnel, since there are high risks of miscarriage.
Features of treatment of pyelonephritis
The most important component of any treatment for kidney infections, as with any other bacterial infections, is the use of antibiotics under the supervision of your doctor. If the diagnosis of pyelonephritis is confirmed, a broad-spectrum antibiotic is prescribed that fights all possible bacteria that could be its cause. After bacterial culture, which determines the type of bacteria, broad-spectrum antibiotics are replaced with antibiotics whose action is aimed at this type of microorganism.
Successful treatment of uncomplicated kidney infections and UTIs usually requires antibiotics in tablet form, as well as adequate fluid intake . But in case of severe symptoms, such as uncontrollable nausea and vomiting, for which the tablets are ineffective, hospitalization of the patient is necessary. In a clinical setting, treatment is prescribed with intravenous antibiotics, intravenous hydration, and other types of aggressive therapy aimed at eliminating symptoms. In cases of complicated pyelonephritis, hospitalization is also required.
To reduce the risk of developing infections, it is necessary to take plenty of fluids daily and maintain good hygiene. For chronic illness, or for people at increased risk of kidney infections, your doctor may prescribe small doses of antibiotics for prophylactic purposes. If pyelonephritis is treated early and correctly, therapy has a high chance of success.
How the urinary system works
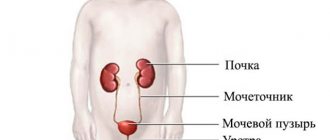
The kidneys are a paired organ located on the sides of the spine, under the diaphragm, in the lumbar region. Each kidney is connected to the bladder in the pelvis by ureters (long, narrow tubes) that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Urine accumulates in the bladder and leaves the body through the urethra. Together, this system forms the urinary tract, and the kidneys play an important role here.
The kidneys perform many important functions for the human body. The main thing is the filtration of the blood and the removal of waste from it, which is eliminated from the plasma as the blood circulates through the capillaries of the kidneys. In addition, the kidneys regulate blood pressure, maintain a constant balance of electrolytes (calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium and chlorine ions), and participate in the production of red blood cells. Therefore, if malfunctions occur in the urinary system, this will affect health in the most detrimental way.
Urine analysis allows you to find out whether pathologies are developing in the urinary system, for which its composition is studied in detail. In this case, leukocytes and red blood cells, protein and bacteria are measured.
Urine, like other fluids of the human body, in a healthy state does not contain bacteria, proteins, leukocytes, or red blood cells. True, doctors take into account that a person will collect material for analysis incorrectly, eat a certain type of food before collecting urine, or attend a training session. Therefore, the presence of these elements in urine is allowed in small quantities. For example, the norm of leukocytes and erythrocytes should not exceed 3-5 units. in the field of view, protein – 0.033 g/l.