Today, doctors diagnose many people with the development of an acute form of cholecystopancreatic pathology. Symptoms of cholecystopancreatitis have a similar clinical picture to the development of other diseases of the digestive system, which is caused by exposure to environmental factors, food products that include GMO elements, as well as the persistence of stressful situations. According to medical statistics, this disease is quite widespread among the fair sex. In this article we will look in more detail at what is called chronic cholecystopancreatitis, the causes and mechanism of its development, as well as the symptoms and treatment of cholecystopancreatitis, which occurs in both acute and chronic forms.
General information
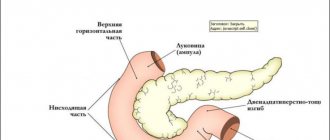
The occurrence of cholecystopancreatitis is due to the anatomical proximity and functional interaction of the pancreas (PG) and gallbladder. Failure of self-regulation of the sphincter system of the nipple of Vater in the event of disease in one of the organs sooner or later leads to pathological changes in the other. According to research in the field of clinical gastroenterology, in 69-70% of patients with acute cholecystitis, the parenchyma of the gland is pathologically altered; in chronic cholecystitis, the figure reaches 85-88%.
In 38-39% of people suffering from acute pancreatitis, cholecystitis is diagnosed; with chronic inflammation of the pancreas, the gallbladder is affected in 62-63% of cases. In a disease such as acute cholecystopancreatitis, the liver is often involved in the process - it becomes inflamed, and dystrophic and necrotic changes occur in it.
Features in women
The number of sick women has increased sharply. If recently the highest prevalence of cholecystopancreatitis was among people 45-50 years old, now inflammation is most often detected at 30-35 years old. The acute form of the disease is more often diagnosed in women than in men. There is a theory that acute inflammation is caused by changes in hormonal levels.
Specifics in men
In men, this pathology is caused by alcoholism in more than half of the cases. In this case, experience is of great importance. In men, smoking is a risk factor. In them, cholecystopancreatitis often leads to complications.
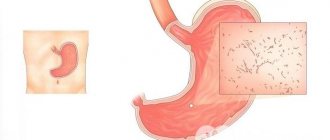
What is cholecystopancreatitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder and pancreas does not differ by gender, social status, or age. All people are susceptible to pathology, since these organs are located the same anatomically in everyone. And if the pancreas fails, then the gallbladder is often involved in the process.
ICD-10 classifies cholecystopancreatitis in the eleventh class along with other diseases of the digestive system. In total, the document identifies 22 classes. The latter, codes for special purposes, begins with the letter U. The approach is very similar to a library catalog, in which each book has its own letter and number so that the librarian can easily find it on the shelf.
Among many diseases, chronic and acute cholecystopancreatitis also have their own ICD-10 code. In the classification, diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract are listed under codes K80 to K87; other pancreatic diseases are recorded under K86. But for chronic cholecystopancreatitis, the ICD-10 code is marked K86.8.2*.
This classification helps doctors more accurately diagnose and prescribe appropriate treatment. The marker for diseases of the digestive system is the letter K. In general, the ICD begins with the letter A, under which infectious and parasitic diseases are encrypted.
If acute or chronic cholecystopancreatitis develops, the features of its course are such that they can lead to irreversible damage to the pancreas. Cholecystitis according to ICD-10 and pancreatitis are assigned different codes, but if the disease has spread to the pancreas and gallbladder, they are treated comprehensively.
https://youtu.be/u2d6m-mB3Io
Causes
The occurrence of combined inflammation of the pancreas and gallbladder is associated with a primary lesion of one of these organs. In 85% of patients, the initial stage of the disease is cholecystitis associated with cholelithiasis. In 15% of cases, the inflammatory process develops in the pancreas and is complicated by secondary enzymatic cholecystitis. The leading role of cholelithiasis in the development of cholecystopancreatitis is due to the influence of factors such as:
Mechanical obturation of the papilla of Vater. When the pathways for the secretion of pancreatic juice and bile are blocked, biliary stagnation occurs, which provokes the accumulation of a critical amount of intestinal flora inside the gallbladder, causing inflammation of the organ. A simultaneous increase in intraductal pressure in the pancreatic gland leads to the entry of its own enzymes into the tissues of the organ and the onset of inflammatory-destructive changes.
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Constant irritation by small stones causes dyskinesia of the smooth muscles of the papilla of Vater. The resulting biliary-pancreatic and pancreato-biliary refluxes contribute to the entry of bile, including infected, into the pancreas, and pancreatic enzymes into the bile ducts. An aggravating factor is intraductal hypertension against the background of hypertonicity of the sphincter of Oddi.
In addition, the reasons may be:
- infectious diseases;
- diabetes;
- stomach ulcer;
- metabolic disorders;
- cholelithiasis;
- inflammation in the gallbladder;
- oncological pathologies;
- the presence of parasites in the body.
Of course, poor diet and bad habits can also often trigger the occurrence of this disease. In addition, people who abuse alcoholic beverages and smoke a lot often suffer from pathology such as cholecystopancreatitis. Inflammatory changes in the gallbladder and pancreas can also be caused by various medications that people take uncontrollably, without taking into account side effects.
Stress and excessive emotional stress are also a provoking factor for this disease, and since today all segments of society are exposed to stress, the disease is quite common, and the number of cases is growing every year. If a person has pockets of bacterial infection in the body, for example, untreated caries, or sinusitis, etc., then these pockets can also trigger the development of acute cholecystopancreatitis.
Causes of cholecystopancreatitis in adults
Unlike most inflammations that can occur in other parts of the body, cholecystopancreatitis is not always the result of an infection.
Stones in the bile ducts and the bladder itself are one of the main causes of cholecystopancreatitis.
If the gallbladder fails to empty properly (for example, due to scarring, injury, or obstruction), bile accumulates and stones form.
Stones block the duct partially or completely, which leads to the development of an inflammatory process.
Secondary common causes:
- infection with bacteria that penetrate the liver and blood;
- endocrine diseases such as diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2 and HIV can cause swelling of the bile and pancreas;
- Cancer diseases can also affect the development of a simultaneous inflammatory reaction in the pancreas and gall bladder. In these cases, the pathology is formed due to the blocking of the bile ducts by the tumor;
- stomach ulcer and the presence of parasites in the body.
Classification
The following types of inflammation exist:
- acute and chronic;
- infectious and non-infectious;
- calculous and stoneless;
- with reduced or increased motility of the gallbladder;
- complicated and uncomplicated;
- primary and secondary;
- hyperenzyme (with increased production of pancreatic enzymes) and hypoenzyme;
- mild, moderate and severe.
When systematizing the forms of the disease, the peculiarities of its course and the nature of histological changes are taken into account.
Taking into account the main morphological changes, the following forms of cholecystopancreatitis are determined:
- purulent;
- exudative;
- necrotic-destructive;
- atrophic.
According to the nature of the flow, they are distinguished:
- Acute cholecystopancreatitis. As a rule, it occurs suddenly in the presence of mechanical obstruction or gross errors in nutrition. It is characterized by severe pain and regurgitation syndromes. In the absence of adequate therapy, mortality is 31.5-55.5%.
- Chronic cholecystopancreatitis. The disease develops gradually and is usually associated with cholelithiasis. Dyspeptic symptoms, discomfort in the epigastric and subcostal areas, and progressive disruption of digestive processes due to pancreatic degeneration predominate.
- Chronic recurrent cholecystopancreatitis. More often it is the outcome of an acute form of pathology, less often observed with a previous persistent course. Relapses are often provoked by nutritional disorders. The mortality rate during exacerbations reaches 3.5-7%.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis of cholecystopancreatitis is made after the doctor examines the patient and sends him for laboratory tests and hardware diagnostics. Since many diseases of the digestive system have similar symptoms, it is necessary to conduct research as thoroughly as possible. For example, ultrasound and MRI give excellent results.
The doctor will definitely order blood, stool and urine tests, a biochemical blood test, and you may need duodenal intubation and fluoroscopy. These measures will help determine how much inflammation has affected the organs, what their size is, and how they perform their functions.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of development of cholecystopancreatitis is based on a violation of the physiological passage of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum. Under normal conditions, the own sphincters of the pancreatic and common bile ducts prevent the return of secretions. With intraductal hypertension, resulting from mechanical obstruction of the papilla of Vater or dyskinesia of the sphincter of Oddi, it becomes possible for bile to enter the pancreatic duct.
This leads to the activation of phospholipase and other pancreatic enzymes, and the formation of highly toxic substances from bile components that destroy the organ. Less often, against the background of existing pancreatitis, a reflux of enzymes into the biliary tract occurs, provoking the development of cholecystitis. An additional factor is reflux, hematogenous and lymphogenous spread of pathogenic flora. In acute forms of cholecystopancreatitis, inflammation is catarrhal or purulent-necrotic; in chronic forms, fibrous-degenerative processes predominate.
Treatment of chronic cholecystopancreatitis
The characteristic symptoms that appear and treatment of the chronic form of cholecystopancreatitis should be carried out comprehensively, including therapeutic methods of conservative treatment, folk remedies, adherence to a special dietary diet, physiotherapeutic procedures and, if necessary, surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment
Conservative therapy consists of prescribing the following types of medications to the patient:
- antibiotic,
- analgesic drugs, in the form of Baralgin or analgin,
- metabolic spectrum drugs, one of which is Methiuracil tablets,
- enzymatic preparations, in the form of Festal or Pancreatin,
- drugs that inhibit the secretion of gastric juice, such as Omeprazole and its generics.
Surgery
Chronic cholecystitis, against the background of which simultaneous damage to the pancreas by ulcerative neoplasms develops, as well as the presence of gastritis or ulcerative lesions of the stomach, provided there is no proper effect over a long period of treatment of these pathologies with conservative methods, is the reason for surgical intervention.
The operation is prescribed to eliminate the root cause of the pathology, relieve pain, and also to normalize the process of outflow of bile and pancreatic juice into the intestinal cavity.
Folk remedies
The use of folk remedies is prescribed as an additional therapy that has an auxiliary effect during drug treatment.
One of the most effective infusions that are recommended to eliminate symptoms and treat acute cholecystopancreatitis is an infusion of aloe leaf blades. In order to prepare this infusion, you need:
- chop the leaves and place in a glass container,
- pour the chopped aloe with a glass of cold water and leave to infuse for 5-6 hours,
- Strain the prepared infusion and consume 1 tablespoon three times a day 30-40 minutes before meals.
Also, for preparing medicinal infusions and decoctions at home, the following types of herbs are used:
- wormwood,
- immortelle,
- ginseng,
- basil,
- peppermint,
- St. John's wort.
Symptoms
Cholecystopancreatitis has symptoms similar to those of other gastrointestinal diseases. In particular, these are dyspeptic disorders, nausea (and sometimes vomiting) after eating, a feeling of heaviness or even pain in the right hypochondrium. There are acute and chronic cholecystopancreatitis. The acute form occurs immediately after eating, when a person eats fried or fatty foods.
Patients complain of girdling pain, painful vomiting, bloating, belching and bitterness in the mouth. Insomnia may occur due to constant pain, and diarrhea or constipation may develop. In a person diagnosed with chronic cholecystopancreatitis, the disease occurs with periods of exacerbations and remissions. During the period of exacerbation, the symptoms of the disease are similar to those described above, and during the period of remission, the doctor determines an enlargement of the liver, which is painful on palpation, and pain in the area of the gallbladder.
The course of a disease such as chronic cholecystopancreatitis is long-term and treatment requires an integrated approach, which includes drug therapy, physiotherapy, traditional methods and diet. Sometimes cholecystopancreatitis takes a severe form - obstructive. With this form of the disease, the pancreatic ducts are clogged, which leads to disruption of digestive processes and the development of inflammatory phenomena in other organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
There are also rare symptoms of this disease that appear in some people:
- development of ascites;
- yellowing of the skin;
- damage to small joints;
- the occurrence of false cysts.
In cases where the disease is not treated in a timely manner, the likelihood of complications increases. Among the most common complications of this pathology are bile duct obstruction, vein thrombosis, diseases of the endocrine system, as well as damage to peripheral nerves and peritonitis.
Symptoms of cholecystopancreatitis
Clinical symptoms of chronic cholecystopancreatitis can be very diverse and manifest themselves as signs of inflammation of the pancreatic gland and inflammation of the gallbladder. Like the acute type of the disease, chronic cholecystopancreatitis is manifested by pain in the abdomen, which is localized in the epigastric region or hypochondrium. In the acute form, the pain intensifies after a person eats fatty foods or drinks alcohol. Repeated vomiting is also likely, in which bile impurities are detected. But it does not bring relief to the patient.
Also, as the disease develops, the following symptoms appear:
- dyspeptic manifestations - nausea, belching, bitterness in the mouth, feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- bowel dysfunction - stool becomes discolored, contains undigested food, bowel movements become more frequent up to several times a day;
- urine becomes dark in color;
- The sclera, skin and mucous membranes may turn yellow;
- Insomnia may occur due to constant pain ;
- During an exacerbation, fever , decreased blood pressure and a feeling of general weakness are observed.
In general, the symptoms of this disease are similar to those of other diseases of the digestive system. In the chronic form, periods of remission and exacerbations are observed. During exacerbations of the disease, the liver is enlarged, which the doctor determines during palpation.
In the obstructive form of the disease, which is very severe, the pancreatic ducts are blocked and digestive processes are disrupted. As a result, other organs of the gastrointestinal tract become inflamed.
Some patients experience rare symptoms of this disease. These include:
- ascites;
- damage to small vessels;
- false cysts.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of cholecystopancreatitis is made based on patient complaints and visual examination.
Cholecystopancreatitis can be suspected in the presence of typical complaints and physical symptoms (Kera, Murphy, Mayo-Robson, Mussi-Georgievsky). To confirm the diagnosis, a comprehensive examination using laboratory and instrumental studies is necessary.
The most informative diagnostic methods are:
- Blood chemistry. Characteristic signs of the disease are a significant increase in alkaline phosphatase and direct bilirubin; with pancreatic necrosis, the levels of AST and ALT increase. Hypoalbuminemia and dysproteinemia are also detected, which is associated with digestive insufficiency.
- Microscopic analysis of stool. In the case of cholecystopancreatitis, the remains of undigested food, a large number of unstriated muscle fibers and starch grains are determined in the coprogram. Additionally, stool ELISA is performed for alpha-amylase - an increase in the enzyme level by 3-4 times allows you to confirm the diagnosis.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. Ultrasound of the gallbladder and pancreas reveals signs of organ damage. Characteristic features include thickening of the walls and swelling of the gallbladder, the presence of stones in its cavity and bile ducts, heterogeneity of the pancreatic parenchyma, and deformation of its contours.
- Tomography. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography is used when the information content of other methods is insufficient and helps to study in detail the structure of the pancreas and biliary system. The method is necessary for detecting cysts and areas of necrosis, diagnosing pathologies of the liver and head of the pancreas.
- RCP. Retrograde cholangiopancreatography is used to visualize the condition of the biliary tract and pancreatic ducts. The method allows you to identify X-ray negative stones, assess the diameter of the bile ducts, and the condition of the sphincter of Oddi. According to indications, papillosphincterotomy can be performed.
In a general blood test, during exacerbation of cholecystopancreatitis, slight leukocytosis and an increase in ESR are noted. A biochemical urine test may contain bilirubin and urobilin. If helminthiasis is suspected, enzyme immunoassay blood tests are performed. In order to exclude pathologies of other organs of the gastrointestinal tract, plain radiographs and X-ray examination with oral contrast are performed.
First of all, acute or aggravated chronic cholecystopancreatitis is differentiated from acute appendicitis. The main diagnostic criteria are localization of pain in the epigastrium or left hypochondrium, ultrasound signs of damage to the pancreas and biliary tract, positive Mayo-Robson and Kehr symptoms. Pay attention to the history and duration of the disease - a rapid increase in symptoms against the background of general well-being indicates an acute surgical pathology. A gastroenterologist, hepatologist and surgeon are involved in examining the patient.
Inflammation of the gallbladder and pancreas
The patient quickly learns about the presence of the disease thanks to obvious symptoms, but the final diagnosis can only be made by a doctor after diagnosis.
Acute symptoms
In the acute form, the symptoms of cholecystopancreatitis are pronounced. The patient experiences:
- severe pain under the ribs on the right side of the body, it can spread to the back and become girdling;
- nausea and vomiting;
- flatulence and bloating;
- weight loss;
- constipation and loose stools alternately;
- belching, dryness and bitterness in the mouth;
- skin rashes and itching;
- dehydration;
- blue skin around the umbilical fossa.
Signs of a chronic process
In the absence of treatment, the acute form gradually turns into chronic cholecystopancreatitis, characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission. An exacerbation is manifested by signs characteristic of acute cholecystopancreatitis.
During the period of remission, symptoms disappear and the patient feels relatively healthy. But at the same time, negative changes occur in the body, manifested in the form of:
- yellowness of the skin;
- pain in the hypochondrium after eating certain foods;
- the appearance of a white coating on the tongue;
- formation of arthritic nodules on the hands;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- dryness and peeling of the skin.
ICD code
Chronic cholecystopancreatitis has a code according to ICD 10 - K86.8.2. The disease belongs to class 11, which includes pathologies of the digestive system and is designated by the letter K. ICD 10 codes are written using letters (from A to U) and numbers.
The designations K80-K87 encrypt diseases of the biliary tract and gall bladder. In particular, K86 stands for other diseases of the pancreas.
Sonographic picture
The diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a doctor. He examines the patient, listens to complaints and prescribes tests. The most important way to detect the disease is an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. When performing it, a specialist can detect signs of cholecystopancreatitis in the form of diffuse changes in the walls of the liver and bile ducts:
- grain;
- heterogeneity;
- density;
- scarring;
- sclerosis;
- hemorrhages;
- accumulation of metabolic products and other changes in tissues.
When examining the bile ducts, their increased echogenicity is noted, and the location and condition of the blood vessels is poorly visible.
Treatment
The drugs that are prescribed to the patient for this disease are: antibiotics; painkillers (baralgin, analgin); metabolic drugs (methyluracil); enzymatic agents (pancreatin, festal); means of suppressing juice secretion (cimetidine, omeprazole). Nutrition for illness should be normalized, and certain categories of foods should be excluded. Therefore, nutrition for this disease requires a careful approach - a person needs to completely rebuild his diet in order to avoid repeated exacerbations of the disease.
Folk remedies have a good effect on the digestive organs, so treatment with them is quite justified, but only in combination with diet and drug therapy. As for physiotherapy, it is prescribed purely individually, depending on the severity of the process and the form of the disease. Moreover, in the acute stage it is contraindicated, and in chronic cholecystopancreatitis it is carried out only in the remission stage. Sometimes the only possible method of eliminating pathology is surgical treatment.
Drug treatment
For chronic cholecystitis and pancreatitis, medications are prescribed: antibiotics, painkillers, metabolic agents and enzymatic:
- To relieve pain and improve the functioning of the gallbladder, antispasmodics are prescribed. This is Papaverine, Analgin.
- To improve digestion and produce a sufficient amount of enzymes - Creon, Pancreatin.
- To reduce the production of glandular secretions - Omeprazole.
- Antibacterial drugs – Metronidazole.
- To restore intestinal microflora - Hilak.
All these remedies cannot be used independently; they must be agreed upon in advance with a doctor.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is often used in the treatment of cholecystopancreatitis.
The most effective:
- medicinal electrophoresis;
- reflexology (impact on active points);
- exposure to alternating current;
- magnetotherapy.
Physiotherapy procedures are carried out after the disappearance of pain in the remission phase. For inflammation of the gallbladder and pancreas, mud therapy, hydrotherapy and sanatorium treatment are useful.
Surgical intervention
In case of repeated inflammation, surgery is advisable. This means that gallbladder surgery must be performed within 24 hours of hospitalization.
Acute inflammation of the gallbladder can be cured without surgery. However, complications often occur after conservative therapy. In 30% of cases of treatment of chronic cholecystopancreatitis, the doctor prescribes surgery.
After removing the organ, the abdominal cavity is washed to completely remove the leaked bile.
For older people or those at increased surgical risk due to concomitant diseases, surgery may be postponed to a later date.
Diet therapy for cholecystopancreatitis
Adults should definitely follow proper nutrition. With the pathology of chronic cholecystopancreatitis, diet is a way of life.
In the acute form of the disease, doctors sometimes allow you to deviate from the rules they have established in terms of nutrition, but this should not be abused.
What does following a diet mean? First of all, this is the exclusion of harmful products. To create a diet, contact your doctor. Here it is important to take into account the course of the disease, the presence of concomitant ailments, test results and the patient’s taste qualities.
Diet is an important stage of treatment. However, this method cannot act as monotherapy. Diet alone will not help cure cholecystopancreatitis.
The meal schedule should be calculated immediately. It is recommended to eat every 2.5–3 hours. For example, breakfast should be 30% of the daily diet, second breakfast - 10%, lunch - 30%, afternoon snack - 15%, dinner - 10%.
Following a diet helps not to overeat, eat well, do not burden the stomach and stop the inflammatory process.
Approximate diet menu:
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday |
| 3 egg whites, oatmeal with water, weak tea, crackers or biscuits | oatmeal, crackers and chamomile infusion | potato omelette, steamed cutlet, soft-boiled egg, tea | soft-boiled egg, macaroni and cheese, tea with milk | steam omelette with vegetable salad, buckwheat porridge with milk, a glass of warm tea with lemon | semolina porridge, green tea, cheesecakes in honey sauce | a portion of oatmeal, cottage cheese and crackers, jelly |
| a glass of kefir or low-fat cottage cheese | marshmallow and mint tea | rosehip decoction with caramel | chamomile tea with dry biscuit | biscuits and low-fat milk | fruits | vegetable salad, meringue |
| vegetable soup, a piece of rabbit or other lean meat, semolina | carrot puree, beef cutlet, rosehip infusion | meatball soup, baked fish in lemon sauce, green tea | baked apples, vegetarian soup, milk | jelly or crackers with kefir, mashed potatoes with butter, yogurt | celery soup, steamed fish, buckwheat porridge and vegetable salad | pumpkin puree soup, compote, meringue |
| glass of kefir with biscuit | jam from non-acidic berries with a piece of yesterday's bread and tea | afternoon snack - baked apples | cottage cheese casserole | curd soufflé, jelly | tea with lemon and steam omelette | apples baked with cottage cheese |
| dried fruit compote, not sweet jam | a glass of low-fat homemade yogurt, biscuits | 200 ml low-fat kefir or milk | vegetable salad of tomatoes and cucumbers, tea with lemon | cup of kefir | curdled milk and baked meat pie | low-fat cottage cheese, tea with lemon |
To create a weekly diet, you need to know what foods are prohibited to use and in what form the food is prepared.
Patients with cholecystopancreatitis are recommended to take pureed food. Steam, bake, boil. It is not advisable to use meat broths.
Spicy foods, smoked meats, pickles, and ready-made store-bought foods (soups in briquettes, instant porridges) are not allowed. It is forbidden to eat fresh bread, fatty meat, cream, legumes, drink coffee and alcohol.
The list of prohibited foods also includes pickled foods, animal fats, baked goods and mushrooms.
Traditional methods
Treatment of chronic cholecystitis and pancreatitis using traditional methods will help.
The most common of them are:
- Infusions of wormwood and yarrow. To do this, take 1 tsp. each of the herbs is poured with a glass of boiling water. You need to infuse the decoction for about 30 minutes, then strain and take half of it 3-4 times a day.
- Infusions of violet, mint, linden, St. John's wort, chamomile. To do this you will need to take 1 tsp. each of them and pour 500 ml of boiled water. Leave for half an hour, strain and take 1 glass 3 times a day before meals.
- Infusions of wormwood, St. John's wort and mint. These herbs have high medicinal properties. They have proven themselves excellent in the treatment of cholecystopancreatitis. To do this you will need to take 1 tsp. each herb and pour all 0.5 liters of boiling water. Leave for 20 minutes, strain and take 1 glass 2 times a day on an empty stomach.
- Leaves of the Golden Whisker. Grind 2-3 leaves of the plant, pour 500 ml of boiling water, boil over medium heat for 10-15 minutes. Leave for 8 hours. It is recommended to drink warm tincture 3 times a day before meals, 50 ml. Course 30 days. This treatment helps relieve inflammation of the biliary tract and is used for gallbladder diseases.
- Strawberries. Pour boiling water (250 ml) over wild strawberry roots (1 tablespoon). Let it brew for 1 hour. Drink 100 ml morning and evening. Used for cholecystitis, gastritis, and pancreatitis.
- Dill. Dill water is used for problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Pour boiling water over the dill seeds and let it brew. Drink 100 ml 3 times a day. Ready-made dill water can be purchased at the pharmacy.
In addition to drug treatment of chronic cholecystopancreatitis, rose hip decoction, flaxseed oil, and a mixture of castor oil with any freshly squeezed juice are used. All this must be taken 30 minutes before meals. To cleanse the gastrointestinal tract, ginseng, nutmeg and basil are added to food.
How to treat pathology
Treatment of chronic cholecystitis consists of taking medications and a strict diet.
The complex of medicines includes the following drugs:
- Painkillers that relieve pain.
- Enzyme products help with digestion.
- Drugs are needed to inhibit the formation of pancreatic secretions.
- Antibiotics will most likely be required.
- Mineral water will remove toxins from the body.
- Probiotics should introduce beneficial microorganisms into the intestines that will reduce fermentation and gas formation.
- Prokinetics will improve stomach function.
For any form of illness - acute or chronic - you must adhere to diet No. 5. A diet for pancreatitis is a whole nutritional system aimed at restoring the functions of the pancreas and gall bladder. The patient is prescribed stewed, boiled, baked dishes. Sweet, baked, spicy, salty foods will have to be excluded. Food should not be allowed to provoke an increased secretion of enzymes and juices.
https://youtu.be/by7UNc4PKr8
Many familiar products are banned. This forced measure is designed to prolong a person’s life. Among the main recommendations are the following:
- Only yesterday's bread is allowed;
- vegetables – after heat treatment;
- soups – pureed vegetable soups without frying;
- eggs in any form other than hard-boiled are prohibited;
- You can’t drink sweet soda at all, it’s better to minimize strong teas and coffee;
- It is better to consume carbohydrates in the form of liquid porridges - buckwheat, oatmeal, rice;
- meat and fish dishes should be prepared from low-fat varieties, without a fried crust;
- fermented milk products – only low-fat ones;
- You will have to master jelly, compotes, and decoctions of healthy herbs.
Various marinades, dishes with spices, and fibrous vegetables without heat treatment are harmful to a diseased pancreas, and therefore should be completely excluded from the diet.
The diet is regulated by the attending physician, and it must be strictly followed even during remission. You need to eat small portions 5-6 times a day. This way, there will be no unnecessary stress on the pancreas and gallbladder.
There are a lot of prescriptions, you need to get used to the diet. But this is the only way to stay healthy.
Complications
With cholecystopancreatitis, severe digestive insufficiency is formed, associated with impaired bile secretion and the lack of necessary pancreatic enzymes. Patients experience steatorrhea and lienterea, and significant weight loss is observed. Due to the involvement of the islets of Langerhans in the pathological process, pancreatogenic diabetes mellitus can develop. Infection of adjacent areas of the small intestine leads to duodenitis.
A severe complication of cholecystopancreatitis is pancreatic necrosis, which is detected when enzymes are activated inside the pancreatic ducts. Patients often exhibit gallbladder damage in the form of pericholecystitis and empyema. Without treatment, perforation of the organ and release of infected contents into the free abdominal cavity may occur. There is a risk of bile peritonitis. During exacerbation, multiple organ failure can develop, which sometimes leads to death.
Symptoms of acute and chronic cholecystopancreatitis
The first symptom of the disease will be severe pain on the right side of the abdomen, under the ribs. As the inflammatory process spreads, the pain will spread to the back and become girdling, which is characteristic of pancreatitis. The man feels unwell and vomits. If urgent measures are not taken, the most undesirable consequences are possible. Cholecytopancreatitis, unfortunately, has a fairly high mortality rate.
Lack of medical care can lead to damage to nerve fibers, blockage of the bile ducts, and vein thrombosis. All these complications are fraught with an extremely serious condition – peritonitis.
The gastroenterologist reveals the following clinical picture:
- bloated stomach;
- constipation and loose stools alternately;
- belching;
- dryness and bitterness in the mouth;
- skin itching;
- dehydration.
Recommendations for symptom relief
To relieve the symptoms of chronic pancreatitis and cholecystitis, follow these recommendations:
- Drink at least 2 liters of water per day.
- Include in your diet: garlic, ginseng, nutmeg. They will help improve the functioning of the gallbladder and remove harmful substances from there.
- Reduce your intake of fatty meats, chicken eggs, potatoes and anything else that greatly increases cholesterol.
- More often include foods rich in vitamin C in your diet, as they contain a lot of ascorbic acid. These products include: cauliflower and broccoli, kiwi, citrus fruits, strawberries, horseradish, spinach, garlic, black currants.
- A great way to cleanse your gallbladder is to take castor oil with any freshly squeezed juice.
Nutritional Features
When asked how to treat cholecystopancreatitis, the gastroenterologist will answer - with proper nutrition. No matter how effective the medications are, they will not help without following a special diet necessary for cholecystopancreatitis.
The patient should eat 5-6 times a day in small portions. Food should be easily digestible, contain a large amount of proteins and minimal sugars. Stewed, boiled, baked dishes are consumed. Yesterday bread, dishes that do not cause excessive secretion of pancreatic juices.
The diet for chronic cholecystopancreatitis excludes:
- spicy, salty and smoked foods;
- sausages and semi-finished products;
- spices, marinades;
- fatty foods;
- raw vegetables;
- chocolate and cocoa;
- alcohol;
- legumes;
- carbonated drinks;
- citrus juice;
- strong tea and coffee.
List of required products
Nutrition for cholecystopancreatitis involves consuming:
- yesterday's bread;
- boiled or stewed vegetables (tomatoes are limited);
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- eggs in various forms, except hard-boiled;
- lean meat and fish;
- porridges, especially those with increased stickiness, such as oatmeal;
- soups without frying, preferably pureed;
- herbal decoctions, jelly and compotes.
These products should form the basis of the diet. Salty foods or raw vegetables may be included in small quantities during periods of remission.
Diet during an exacerbation
The diet for cholecystopancreatitis during an exacerbation is aimed at minimizing the load on the liver and pancreas. The list of food products is reduced to a minimum and includes:
- slimy soups;
- light pureed food without oil, cooked in water;
- yesterday's wheat bread and crackers;
- pureed liquid porridge, optionally with a small amount of milk;
- jelly, compotes, herbal decoctions.
When the first symptoms go away, lean meat, fish and cottage cheese are gradually introduced into the menu.
During an exacerbation, liquid porridges are useful
Features of treatment of the disease
Cholecystopancreatitis - treatment
Most often, the disease is treated surgically. Symptomatic therapy is prescribed for a long time. Medications are used to improve digestion. Such products are artificial analogues of digestive enzymes and are intended to eliminate steatorrhea, normalize digestion and prevent the formation of elastase in feces.
The entire treatment procedure is based on the following principles:
- stabilization of pancreatic functionality;
- improving the patient’s quality of life;
- neutralization of possible complications;
- elimination of inflammatory processes.
Intoxication is eliminated by prescribing mineral waters containing chlorides and bicarbonates (one glass five times a day).
Mineral water analysis
A special diet food has also been developed (we are talking about diet No. 5P), which excludes fatty, spicy and sour foods, and carbonated drinks.
Diet No. 5P
Below are the medications that are prescribed for the treatment of cholecystopancreatitis.
Delicious recipes
So that life with inflammatory diseases of the pancreas and gall bladder does not seem so gray and boring, it is necessary to diversify it somewhat. We offer the following recipes for pancreatitis and cholecystitis.
- Potato cutlets . We take 7 medium potatoes, peel them, cook them, and when they cool down, grate them. To this mass add finely chopped 250 g of milk or doctor's sausage, as well as 200 g of grated hard cheese. Mix in 3 raw eggs, herbs and green onions to taste, salt, 2 tablespoons of flour. You should get a mass from which cutlets are made (they need to be breaded in flour). Prepare the dish in a double boiler.
- Vegetable soup with cheese meatballs. Take 2.5 liters of either water or vegetable broth and put it on fire. Prepare the meatball mixture: grate 100 g of mild hard cheese, mix with softened butter, 100 g of flour and 1 raw egg, herbs and a small amount of salt. Stir and place in the refrigerator for 30 minutes. For the broth: coarsely grate 1 carrot, cut 1 bell pepper into strips, and cut an onion and 5 potatoes into cubes. Cook for about 15 minutes in boiling water. Next, throw in bean-sized meatballs, formed from the cheese mass that was in the refrigerator.
- Pumpkin – a very useful product. You can prepare many dishes from it. For example, pumpkin casserole with apples.
Pumpkin casserole with apples - both a tasty and very healthy dish
You need to take 600 g of pumpkin, peel and grate it. Do the same with 200 g of raw apples. Then simmer the pumpkin and apples in a frying pan with 10 g of butter and rub with a fork. Add 100 ml of milk to the resulting puree, bring to a boil, add a little (about 60 g) semolina, cook for 8 minutes over low heat. Next, remove from heat, cool to 60°C, add a tablespoon of sugar and 1 egg, mix . This mass should be placed on a baking sheet greased and sprinkled with breadcrumbs, and baked in the oven. Serve with sour cream.
https://youtu.be/BOVLqyHQmeY
Reasons for development
The anatomical connection of the entire digestive system leads to the fact that if one organ of the gastrointestinal tract is affected, then other organs of this system are also drawn into the inflammatory process. The second reason for the appearance of simultaneous inflammation of all organs of the gastrointestinal tract is the common causes of the disease - irregular nutrition, alcohol intake, imbalance of food.
The main factors, the presence of which provoke the development of cholecystitis and pancreatitis:
- Irregular eating;
- Unbalanced diet high in fats and easily digestible carbohydrates;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Chronic stress;
- Other concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diseases such as cholecystitis, pancreatitis and cholecystopancreatitis are considered autoimmune inflammatory processes of an aggressive nature. In practice, this means that most often their trigger is infection.
If there are permanent foci of bacterial damage in the body, for example, untreated caries, this becomes a factor in the development of the disease.
Chronic and acute cholecystopancreatitis develops for various reasons. The following etiological factors are of greatest importance:
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- poor nutrition;
- autoimmune disorders;
- obesity;
- taking medications;
- parasitic diseases;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- hepatitis;
- gastroduodenitis;
- cystic fibrosis.
Types of disease
There are acute and chronic cholecystopancreatitis.
The acute form always develops suddenly. The attack is preceded by nausea. Often a spasm occurs after excessive consumption of fatty foods. The disease manifests itself after the formation of stones and blockage of the bile ducts or after acute dilatation of the bile duct.
The main distinguishing sign of cholecystitis-pancreatitis is pain localized on the right side or in the navel area. The nature of the pain syndrome is sharp, cutting.
Signs of chronic cholecystopancreatitis are smoothed out. Their exacerbation is associated with poor nutrition and consumption of alcoholic beverages . Provided that a person adheres to a diet and does not allow stress or bad habits, it is possible to achieve stable remission.
Depending on the predominance of destructive processes, there are:
- pancreatic necrosis and catarrhal chronic pancreatitis;
- destructive cholecystitis with pancreas edema;
- catarrhal cholecystitis together with chronic pancreatitis;
- total destructive cholecystopancreatitis.
Diagnosis and treatment
The diagnosis of cholecystopancreatitis is made based on patient complaints and visual examination. Laboratory diagnostic data (blood and urine tests) are also taken into account.
When it is not possible to accurately diagnose the disease, ultrasound of the gallbladder and pancreas, as well as MRI, are indicated.
Treatment of this disease must be comprehensive. This means that drug treatment is complemented by diet and physical therapy. The drugs that are prescribed to the patient for this disease are:
- antibiotics;
- painkillers (baralgin, analgin);
- metabolic drugs (methyluracil);
- enzymatic agents (pancreatin, festal);
- means of suppressing juice secretion (cimetidine, omeprazole).
Nutrition for illness should be normalized, and certain categories of foods should be excluded. In particular, the diet provides for a complete abstinence from pickles, marinades, smoked meats, preserves and alcoholic beverages. Meals should be small and frequent, and the diet should be followed for a long time, and not only during the period of exacerbation of the disease.
There are many other foods that the diet for cholecystopancreatitis does not allow for consumption. In particular, these are baked goods, ice cream and chocolate, green onions, strong tea, radishes, sorrel, sour juices, lean meat and fish broths, as well as some other products. Therefore, nutrition for this disease requires a careful approach - a person needs to completely rebuild his diet in order to avoid repeated exacerbations of the disease.
Patients are allowed diet No. 5, and all the products that it includes, for example, boiled meat, fish, vegetable soups, semi-liquid cereals, fresh dairy products and much more. A full description of what diet No. 5 consists of will be written by the attending physician after confirmation of the diagnosis.
Folk remedies have a good effect on the digestive organs, so treatment with them is quite justified, but only in combination with diet and drug therapy.
As for physiotherapy, it is prescribed purely individually, depending on the severity of the process and the form of the disease. Moreover, in the acute stage it is contraindicated, and in chronic cholecystopancreatitis it is carried out only in the remission stage. Sometimes the only possible method of eliminating pathology is surgical treatment.
Preventive measures
The main principle of preventing cholecystopancreatitis is considered to be the cessation of alcoholic beverages and smoking.
Quitting smoking, drugs and alcohol
In addition, attacks of the disease are accompanied by severe pain in the upper abdomen after each meal, so the diet should be designed in such a way that the amount of provoking foods in it is minimal. You should eat fractionally (no more than 60 g at a time), with frequent repetitions, the amount of fats should be limited, and, on the contrary, vitamins should be increased.
Fractional meals
https://youtu.be/Y96AmKe3eoE
Signs of the disease
During the period when chronic cholecystopancreatitis has entered the acute stage, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pain after eating;
- weight loss;
- flatulence;
- the presence of fats in stool;
- pain or discomfort in the area under the right rib;
- the skin in the navel area may acquire a bluish tint;
- the presence of a seal in the area where the pancreas is located;
- presence of a rash near the navel;
- a decrease in the volume of the abdominal muscles, combined with a thinning of the layer of subcutaneous fat.
If pancreatitis and cholecystitis are not treated for a long time, this can lead to pancreatic insufficiency. In this case, a lack of digestive enzymes can cause the following symptoms:
- fats are not digested;
- pancreatic lipase is produced in small quantities;
- feces become liquid and acquire a whitish color;
- the presence of undigested muscle fibers in the feces is observed.
In some cases, the disease can take on a special form - chronic obstructive cholecystopancreatitis. It is characterized by blockage of the excretory ducts of the duodenum.
In many ways, the symptoms of the disease may depend on its form. Thus, pain in the area of the right lower rib can be observed with cholecystopancreatitis in a chronic form or an acute stage.
In the presence of inflammatory processes in the pancreas or gallbladder, pain tends to intensify after eating. These sensations may decrease if the patient sits and leans forward slightly.
Severe nausea and vomiting are the main signs of alcoholic cholecystopancreatitis. In this case, the pathology develops, as a rule, as a result of damage to the epithelium of the pancreas.
Nausea and vomiting may also indicate severe poisoning of the body with ethyl alcohol. The latter is processed in the liver, after which it enters the bloodstream. With prolonged accumulation of it in the body in large quantities in cells, disruption of biochemical processes can occur, the production of digestive enzymes decreases, and the release of biologically active substances decreases. These are the main causes of nausea, vomiting, and digestive disorders.
Diet for the treatment of cholecysto-pancreatitis
The success of treatment of cholecystic pancreatitis largely depends on adherence to diet, since proper nutrition contributes to the patient’s rapid recovery. The basic principles of rational nutrition for this disease are:
- frequent and fractional meals in small portions;
- eating food at the same time;
- exclusion of cold and hot foods from the diet;
- consumption of boiled and stewed foods;
- exclusion from the diet of spicy, fatty and fried foods;
- reducing the amount of coffee and tea consumed.
Authorized products:
- black and white bread, biscuits;
- lean meat, fish, poultry;
- cereal porridges and side dishes, especially buckwheat and oatmeal;
- vegetable, cereal, milk soups;
- fresh and steamed vegetables, herbs;
- low-fat dairy products, including hard cheese;
- butter and vegetable oil;
- honey, sugar, jam in small quantities.
Prohibited products:
- freshly baked bread and pastries;
- fish, poultry, fatty meats;
- canned food, marinades, smoked meats, caviar;
- rich broths of mushrooms, meat and fish;
- horseradish, mustard, hot seasonings;
- alcohol, strong tea, coffee;
- fatty ice cream, cream, chocolate.
The treatment diet is compiled individually for each patient with cholecysto-pancreatitis, taking into account the body’s reaction to certain foods, and the food must be high enough in calories to provide the body with all useful elements and vitamins.
Chronic cholecystopancreatitis is a disease in which a complex of symptoms occurs that are characteristic of a condition when the process of digesting fats and carbohydrates is disrupted as a result of a failure in the production of bile and intestinal digestive enzymes.
Among the factors that provoke the development of this pathology are the following:
- abnormally close located organs of the hepatopancreatic system, as a result of which bile may flow back into the duodenum;
- the presence of scar tissue in the duodenal duct, as a result of which it narrows;
- the presence of chronic cholecystitis, combined with the occurrence of stones that block the ducts;
- lack of normal tone of the sphincter of Oddi, which can lead to duodenopancreatic reflux;
- too much pressure on the liver and duodenum due to flatulence.
The following pathogenetic mechanisms can cause inflammation of the pancreas and gallbladder:
- the presence of swelling in the area of the nipple of Vater due to the fact that digestive enzymes cannot move normally;
- high acidity of the stomach, which is combined with stimulation of the sphincter of Oddi, which leads to its contraction due to an excess amount of hydrochloric acid;
- the presence of stones in the gall bladder;
- ulcerative lesions of the stomach lining;
- malignant neoplasms on organs of the hepatobiliary system;
- tumor processes of the pancreas.
Treatment with folk remedies
Treatment only with folk remedies is pointless, since it will not bring the proper result. Treatment according to “grandmother’s recipes” must necessarily be combined with medication. The result of the use of pharmacological agents is relief of the patient’s general condition and reduction of pronounced symptoms of the disease.
Traditional methods of combating the disease only seem harmless, but in fact they can be dangerous for people with cholecystopancreatitis.
Therefore, the use of any folk remedy must be agreed with the attending physician.
How to prevent cholecystopancreatitis?
Is it possible to avoid exacerbation? Of course yes. However, this depends on the patient. Stagnation of bile in the bile ducts plays a special role in the development of cholecystitis. This means that a person needs to move more, not sit on one spot for several hours, but lead an active lifestyle.
If you don’t move much because of your work, then you should carve out at least 30 minutes every day for gymnastics. However, those who suffer from calculous cholecystitis, which usually develops against the background of the formation of stones in the gallbladder, should avoid any sudden movements, as this can simply provoke attacks of hepatic colic.
Many patients suffering from a similar disease place high hopes on modern pharmacological drugs, while ignoring the necessary diet and rules of nutrition.
It is worth remembering that bile is excreted only in response to food intake. Therefore, you should eat very often, about 5 times a day strictly at a certain time. It is frequent meals that help normalize the release of bile, as well as all the microorganisms contained in it, which can also provoke the inflammatory process and its exacerbation.
https://youtu.be/YJC0KABotqI
Juice therapy
Take fresh juice of aloe, black radish, red beets, half a liter of vodka and honey. It is worth noting that the aloe plant must be more than three years old. Pour everything into a three-liter jar. Stir and cover with a nylon lid. Wrap the jar in a plastic bag and bury it in the ground for several weeks. You should bury it so that the jar is up to the lid or completely in the ground.
After two weeks, remove the jar from the ground and place it in a cool and dark place. For more convenient use, the mixture can be poured into a bottle. Take one tablespoon 30 minutes before meals. You should drink the entire prepared mixture. At the same time, all fried, spicy, fatty foods, as well as alcohol, should be removed from the diet.
Herbal treatment
Folk remedies prepared from medicinal herbs should be taken longer than any pills. But the effect will be the same. To prepare the drug, take one part of celandine, two parts each of peppermint leaves, tansy and toadflax flowers, 4 parts each of erect cinquefoil rhizomes and medicinal dandelion roots.
After this, pour the resulting mixture with hot water. One spoon of herbal mixture requires a glass of water. Let the infusion stand for half an hour. After this, strain the medicine through a strainer. Take herbal infusion before meals. Preferably within 20 minutes. You need to drink the infusion three times a day, 1/4 or 1/3 cup.
One course – 21 days. Treatment with this infusion should be repeated every 6 months or a year. As a result of this treatment, you can forget about attacks of pain. However, while taking this drug, you should follow a strict diet. Otherwise, the bile will still stagnate and cause discomfort.
Corn silk tea is also considered a good folk remedy against cholecystopancreatitis. As for meals, there should be 6 of them, and the portions should be small.
The peculiar diet of modern man, which consists mainly of fatty and carbohydrate foods, contributes to the development of inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. Often the pancreas and gallbladder suffer from an improper diet. Special medications are used to treat cholecystopancreatitis, but during the recovery period you can also use traditional medicine.
To begin with, you should adhere to a special diet that excludes the consumption of alcohol, spicy and fatty foods. We should also not forget about moderate physical activity, but do not overdo it, so as not to provoke an exacerbation of the pathology. Infusions and decoctions of medicines relieve inflammation and prevent relapses of the disease.
If the disease is caused by Giardia
One folk method will help cure such a disease. To prepare the medicine, it is necessary to collect and dry young leaves, or rather the first ones, of birch. The leaves should be sticky. After this, pour a tablespoon of dried raw material with a glass of hot water and leave to infuse for 24 hours. Take the product for a month.
In parallel with the infusion of birch leaves, it is worth taking an infusion of May wormwood. The course is 14 days. Wormwood is simply poured with boiling water. Take the infusion three times a day, half a glass.
Before starting treatment of any disease with traditional medicine, be sure to consult with specialists. Self-medication without the supervision of a doctor can lead to complications that will not give anything good. In addition, common herbs can also harm your body if overdosed or used inappropriately.
Home » Bladder diseases » Chronic cholecystopancreatitis - symptoms, treatment with diet, medications and folk remedies
Chronic cholecystopancreatitis is currently one of the most common digestive problems.
The disease is manifested by the development of a chronic inflammatory process simultaneously in the gallbladder and pancreas, followed by dysfunction of these organs.
As a result of this disease, an insufficient amount of enzymes and bile enters the human intestine, which complicates the breakdown of fats and carbohydrates and causes a number of pathological symptoms.
Pathology is a pathogenetically complex disease process that is diagnosed with equal frequency in both men and women.