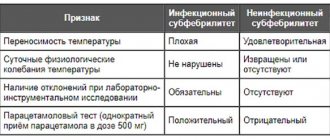
In adults, body temperature is a sensitive indicator of many natural and pathological conditions. Thermoreceptors located in different parts of the body are responsible for its change. They are under the general control of the cerebral cortex.
As soon as they transmit signals to the center about changes in the properties of the internal or external environment, it responds by changing the temperature regime. They are provided by a variety of reactions, for which the immune, circulatory, vascular, endocrine, nervous and other systems are responsible.
Therefore, a fibrous temperature of 38.4 and above can pass quite quickly when the mechanisms of regulation of the body’s activity are turned on or when a pathogenic agent is destroyed.
Classification
Generally accepted classification of fever:
- over 37.0, but not more than 37.9 ℃ is called subfebrile hyperthermia;
- if the temperature reaction values are in the range of 38.0-38.9 ℃, then they speak of febrility;
- hectic fever is characterized by the following figures: over 39.0 ℃.
To find out the cause of an elevated temperature without symptoms, you need to know its nature. This is done using a weekly temperature curve graph consisting of morning and evening indicators.
- inverse, that is, the increase occurs not in the evening, but in the morning;
- recurrent or recurring. It is established when, after a febrile period, remission occurs followed by the resumption of hyperthermia;
- wavy - characterized by a gradual increase to high numbers and a subsequent decrease with the repeated formation of individual peaks of increase;
- intermittent - set if daily fluctuations in the numbers on the thermometer exceed 1.0 ℃; atypical - it is quite difficult to follow the patterns of rise and fall of hyperthermia;
- laxative – when fluctuations in values during the day also exceed 1 ℃, but never reach normal values;
- constant - recorded if hyperthermia during the day remains above 38.0 ℃, and fluctuations do not exceed 1.0 ℃.
Thus, the nature and type of fever can help the doctor make a diagnosis. Therefore, with hyperthermic syndrome, it is extremely important to regularly record the level of fever in the morning and evening using a thermometer and write it down on a separate piece of paper.
Temperature norm
During the day, the temperature of a healthy person fluctuates in the range of + 35.5 oC - +37.4 oC. The thyroid gland and hypothalamus are responsible for these changes. Both endocrine glands are involved in the regulation of metabolism. The metabolic rate in the body is not constant at different times of the day. A slowdown in metabolism causes a drop in temperature.
Minimum body temperature in the morning, immediately after waking up. Blood flow is slow at this time and metabolic rate is reduced. At this time, a healthy person’s temperature can be 35.5 °C when measured in the armpit. In the evening, the temperature rises and normally can reach 37°C-37.4°C.
The average body temperature is the temperature measured in the middle of the day at rest; it is 36.6 °C.
- Temperature below 35.2 °C - very low, corresponds to general hypothermia;
- Below 35.8 °C to 35.2 °C – moderately low, characteristic of impaired liver function, decreased muscle tone;
- Subfebrile – range of values from 37 oC to 37.8 oC;
- Febrile – values above 38 °C–38.9 °C;
- Pyretic – 39 oC–40.9 oC;
- Hyperpyretic – above 41 oC.
Temperatures above 38°C are considered high.
Physiological reasons
The temperature may rise as a result of changes in the external environment or for other natural reasons. In the presence of unfavorable conditions, the body makes every effort to return metabolism to the most comfortable state for it. Therefore, in order to quickly establish metabolic processes, he sometimes turns on the hyperthermia mode.
A temperature of 38 - 38.5 without symptoms may jump due to the fact that an adult:
- overheated in the sun;
- dressed too warmly;
- drank too much alcohol;
- intensively engaged in physical education;
- put on synthetic clothes;
- experienced severe nervous tension;
- is in the period of ovulation;
- suffers from vegetative-vascular dystonia; took a steam bath;
- experiencing menstruation;
- takes certain medications;
- drank hot tea or ate an overheated dish, etc.
If no pathological symptoms are observed, then such a situation does not pose the slightest danger and will soon go away on its own. But it also happens that an increase in temperature above 38.1 - 38.5 degrees is not accompanied by pronounced painful signs, but at the same time, if you carefully observe the person, You can notice a certain amount of trouble. Do not forget that there may be more unpleasant causes of fever.
When a fever without cold symptoms is not dangerous
Despite the danger of the situation, in some cases you can do without consulting a doctor even with a high body temperature. If we talk about adult patients, then there is no need to worry in the following cases :
- Recently there has been regular overwork or stress has been experienced in the recent past;
- were exposed to the sun for a long time or in a stuffy room - the temperature will indicate overheating;
- there is a history of diagnosed dystonia of a vegetative-vascular nature - this disease is manifested by sudden hyperthermia.
Please note: adolescence itself is considered to be the cause of a spontaneous increase in temperature - this occurs due to active growth. In the process, hormones are intensively produced, too much energy is splashed out, which causes hyperthermia. In adolescence, asymptomatic fever is characterized by a sudden onset and short duration.
If we talk about childhood, parents should know the following:
- Overheating of a child can occur in summer and winter due to improper selection of clothing - in this case, medical attention will not be needed. Pay attention to the child's behavior - when overheated, he is apathetic and sleepy.
- Teething. This process can last for many months and the baby’s temperature does not necessarily rise. But if, against the background of hyperthermia, the child’s anxiety and increased salivation are noted, then you don’t have to go to the doctor - most likely, after 2-3 days the baby’s condition will normalize.
- Children's infections. If the temperature stabilizes quickly and for a long time after taking antipyretic medications, then you can take a wait-and-see approach and dynamically monitor the child’s condition. Often the simplest childhood infections (colds) are mild and the body copes with them without the help of medications.
Possible diseases
The causes of temperature 38 without symptoms in an adult may be associated with diseases such as:
- Inflammatory diseases of bacterial origin: endocarditis, pyelonephritis, osteomyelitis, pneumonia, tonsillitis, andexitis, sinusitis, meningitis, prostatitis, inflammation of the uterine appendages, sepsis;
- Infectious diseases: tuberculosis, typhus and relapsing fever, brucellosis, Lyme disease, HIV infection;
- Diseases of viral, parasitic or fungal etiology: malaria, infectious mononucleosis, candidiasis, toxoplasmosis, syphilis;
- Oncological diseases: leukemia, lymphoma, tumors of the lungs or bronchi, kidneys, liver, stomach (with and without metastases);
- Systemic inflammations, including autoimmune ones: polyarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, allergic vasculitis, periarthritis nodosa, systemic lupus erythematosus, Crohn's disease;
- Endocrine diseases: thyrotoxicosis.
In these cases, an increase in temperature is one of the main symptoms of a malfunction of the body. It lasts quite a long time. It may be caused by severe infection, active cell death, or multiple destruction of blood cells.
general information
Temperature is a kind of indicator of the body's functioning.
Normally, its indicators should not exceed 37 degrees. Throughout the day they can deviate up or down. The minimum values usually occur in the early morning, and they reach their peak at approximately 17:00. Changes in temperature indicators can be a consequence of both physiological processes in the child’s body and pathological ones. It is these two criteria that determine the reasons for the sharp jumps. Let's consider each of the cases in more detail.
Increased performance when taking medications
A sudden increase in indicators can be triggered by the use of certain medications. This usually occurs after five days. The main provoking drugs include:
- Cardiovascular drugs.
- Antihistamines.
- Iodide medicines.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Antibiotics.
Of the cardiovascular drugs, an increase in temperature is caused by Hindin and Alpha methyldol. Anti-inflammatory drugs – Ibuprofen, Tolmetin. Antibiotics: Isoniazid, Cephalosporin, Penicillin, Tetracycline.
How to help the baby?
First of all, parents should try to understand why their child’s temperature is fluctuating. Whether he is 3 years old or already 13 years old, there is practically no difference. If the reasons are physiological in nature, there is no need to fight them. In rare cases, it is necessary to adjust the child’s lifestyle, change the situation or his environment. If temperature fluctuations are caused by allergies, it is necessary to exclude the provoking factor.
If a pathological nature of the disorder is suspected, qualified assistance is required. In this case, parents should immediately call a team of medical professionals. The doctor came to the house, what next?
Temperature 39 without symptoms in an adult
In most cases, a sharp rise in temperature below 39 ℃ indicates a serious and severe infectious process:
- endocarditis – damage to the inner lining of the heart;
- meningococcemia – a systemic infection caused by meningococcus. If not treated promptly, it can lead to death;
- sepsis – massive penetration of toxins into the systemic bloodstream with the formation of separate purulent foci in the internal organs;
- acute pyelonephritis – severe diffuse inflammation of kidney tissue;
- atypical pneumonia, which can occur only with fever;
- malaria, which is characterized by 2 days of fever up to 39.5 ℃ with a decline on the third day or 2 days of fever with a decline on the fourth day.
A rise in body temperature to such numbers is a direct reason to go to the hospital to receive adequate medical care.
High temperature without symptoms. Bad sign!
Body temperature above normal indicates health problems, which are mainly associated with inflammatory processes within the body.
The main sources of inflammation are infections, bacteria, fungi and viruses.
Problems with thermoregulation can also be associated with factors of non-microbial origin - stress, overheating or hypothermia, age-related weakness, etc.
If a person knows what causes hyperthermia - an increase in body temperature above 37 degrees, it is enough to simply organize the correct treatment, and the condition will soon be restored.
But, unfortunately, against the background of high indicators of the body’s thermal state, there are often no other additional symptoms at all, so that one can independently determine the disease. This complicates the situation significantly.
When the temperature rises steadily over several days for no apparent reason, a sick person urgently needs to be examined by a doctor in order to promptly identify hidden pathogenesis and prevent its progression.
Causes of asymptomatic high temperature
Diseases of viral and infectious etiology may not manifest themselves in any way at the initial stage except for high fever.
In addition to common colds and flu, there are a large number of infectious viral pathologies, which are also accompanied for a certain time by the only symptom – hyperthermia.
High temperature without other symptoms (the clinical manifestations appear on the 3rd day or more) is also characteristic of many diseases caused by fungi and bacteria rickettsia. Therefore, it is important not to delay your visit to the doctor, since you can only make an assumption of a febrile phenomenon on your own and nothing more.
- Tuberculosis and abscess pneumonia - an increase in body temperature constantly fluctuates from high to normal values, while a decrease in the heat index occurs on its own - without the use of fever pills.
Typhoid and epidemic typhus
– these are pathologies caused by anthropogenic infections, which are characterized by a long prodromal period (without pronounced symptoms). For several days before the appearance of clinical signs, the temperature is stably maintained at high values.- Sodoku - fever lasts 4-10 days, after which the high temperature drops sharply, and after a few days another attack of hyperthermia develops, which is already accompanied by dermatological signs (polymorphic rash). The causative agents of the disease are streptobacilli and spirochetes, and the carriers of the infection are rats.
- Tropical malaria - infectious carriers are female malaria mosquitoes that live in Africa, so you can catch the disease after a vacation in the hot countries of this continent. A characteristic sign is the complete absence of a typical clinical picture for malaria, with general malaise and high temperature occurring for 1-2 days, after which it decreases without sweating or taking medications. Some cerebral and respiratory symptoms then develop.
- Traumatic injuries - dislocations, blows to the head, mechanical or thermal damage to the integrity of organs, as well as elementary scratches, splinters or sprains, can provoke hyperthermia due to the resulting inflammatory process in the affected tissues.
- Infectious pathogenesis in the genitourinary organs is characterized by instability of temperature values, which either rise extremely or drop to normal values over a long time. Also, the temperature can constantly remain within subfebrile limits. Such pathologies include chronic pyelonephritis, cystitis, and urethritis.
- Malignant or benign tumors - the possibility cannot be ruled out that the cause of the high temperature was neoplasia in a specific organ or system. It is the neoplasms that often occur over a long period, which often stretches for months and even years, without pronounced symptoms. If you discover that you have causeless problems with thermoregulation, undergo a full medical examination in order to promptly detect the formation of tumors in the body or confirm the absence of tumors.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism, goiter) and hormonal imbalance - many endocrinological diseases affect the disturbance of thermoregulation in the body, while other signs may not be observed for a long time. In cases of unexplained increases in body temperature with inconsistent frequency, it would not hurt to check with an endocrinologist.
- Red blood cell hemolysis is a disease characterized by severe destruction of red blood cells in the blood, which leads to a high concentration of bilirubin in the bloodstream. Pathogenesis often occurs in an unnoticed form. But one of the clinical signs is sometimes an increase in body temperature, and later yellowing of the skin, hair loss and other symptoms are added to it. A person usually finds out about a blood problem by accident - after undergoing tests.
- Lymphoma and leukemia are hematological pathologies of the oncological group. At the initial stage, clinical symptoms are often absent or manifested by general ailments similar to influenza: febrile syndrome, without catarrhal signs.
- Myocardial infarction and coronary artery disease - ischemic necrosis in individual cases occurs without the pain symptoms characteristic of a heart attack. So, for example, in some patients with diabetes mellitus, painful chest discomfort may not be observed, but a high body temperature will be noted.
Allergies of various types
- an allergic process caused by the invasion of the body by any antigen to which there is hypersensitivity, in particular cases it follows along with a temperature reaction. To relieve a high temperature, you will simply need to prevent human interaction with the irritant and take an antihistamine.- Hypothalamic disorders - thermoregulation disorders occur due to damage to the frontal hypothalamus. With impaired functions of the diencephalon, a person for the most part does not worry about anything except a high temperature, which constantly remains at low-grade levels with acute periods of its increase to critical levels - up to 38-40 degrees. Unfortunately, no cure has yet been created for hypothalamic disorders, so patients are forced to accept and live with elevated body temperature while taking sedative medications.
- Inflammation of the endocardium occurs as a result of improper treatment of a sore throat or flu, which causes one of the pathologies to develop into a more complicated form with a severe course. The complication occurs in the inner lining of the heart. Inflammatory processes in the endocardium are accompanied by high temperature fluctuations in the range of 37.5-40 degrees. This disease requires urgent qualified drug therapy, which can only be selected by a specialist in cardiology.
- Meningococcal meningitis is a severe disease caused by meningococcal infection. What is especially dangerous is that it is usually detected already at critical stages, since it is typical for pathology not to manifest itself at all or to give mild symptoms. And the first clinical sign that appears at the very peak of pathogenesis is a sudden and rapid rise in body temperature to the highest possible values - up to 40 degrees. With the help of antipyretic medications, the temperature decreases, but not for long, after which it quickly increases again. In this case, you should immediately call an ambulance.
- Mental illnesses - most mental disorders are accompanied by damage to the thermoregulatory center of the brain, which is why people with various forms of psychosis often experience episodic “jumps” in body temperature.
How to bring down the temperature?
What to do if an adult has a temperature of 38°C and there are no other symptoms? Doctors do not recommend taking antipyretics from the first day if a person tolerates the temperature relatively well, as this can reduce the body’s natural defenses and increase the duration of the disease.
To alleviate the condition, bed rest and plenty of fluid intake are recommended in the form of:
- green tea;
- fruit drink;
- compote;
- milk with honey;
- mineral water without gas.
If there are any concomitant chronic diseases, or if an adult has a hard time tolerating an elevated temperature, then it is recommended to bring it down. You can reduce your temperature with paracetamol, which is available in tablets, syrup and rectal suppositories. You can also use Ibuprofen or Aspirin.
What to do if you have a low-grade fever after the flu
If a low-grade fever appears after an acute respiratory viral infection, then before visiting a doctor you can take a number of measures to normalize it:
- Maintain bed rest and complete rest.
- Including various fruit juices in your diet.
- Drinking large amounts of liquid.
- Taking vitamin and mineral complexes during the cold season.
In a situation where low-grade fever persists for more than four days, you need to consult a doctor. Then it will be carried out:
- A complete examination of the respiratory system to identify inflammatory processes in them.
- Laboratory examination of blood and urine.
After the diagnosis, the doctor may recommend:
- Taking pharmaceutical drugs.
- Rinsing the nasopharynx and removing sputum.
- Using traditional medicine recipes.
Low-grade fever should not be ignored, as it may be a symptom of dangerous secondary infections. Some of them may threaten the patient's life. Pneumonia, sepsis, meningitis, and renal pathologies are similar to other infectious diseases; it is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own. Only doctors can carry out differentiated diagnostics.
What should you not do if you have a fever?
If an adult’s temperature reaches 38.5 – 39.5 degrees, the following activities are prohibited:
- vinegar and alcohol rubbing: such actions lead to even greater heating of the body and worsen the situation;
- wrapping yourself in warm clothes and blankets;
- take carbonated and sweet drinks (only warm teas with lemon, dried fruit compotes);
- open vents and windows in the room.
A high temperature without symptoms in an adult can be a sign of serious pathological processes, without diagnosis and treatment of which a person’s life is threatened.
Possible causes of temperature changes
There are other reasons when an adult’s body temperature jumps, such as:
- heart attacks;
- purulent and infectious processes;
- development of tumor formations;
- the occurrence of inflammatory processes;
- the appearance of an autoimmune condition;
- injury to joint or bone structures;
- manifestations of allergic reactions;
- development of endocrine disorders;
- the appearance of hypothalamic syndrome.
With abscess and tuberculosis, temperature jumps from 36 to 38 degrees are often observed. This phenomenon is inexplicable, but experts say that the body periodically perceives the infection as a foreign phenomenon.
When tuberculosis occurs, temperature fluctuations may vary by several degrees throughout the day. If we are talking about a severe form of the disease, then you can see a curve on the graph.
This phenomenon is also typical for purulent processes. Temperatures can rise to 38 degrees. After opening the infiltrate, the temperature returns to normal.
The temperature in the evening may increase in the presence of chronic processes in the form of:
- adnexitis;
- sinusitis;
- pharyngitis;
- pyelonephritis.
Hyperthermia in such situations is manifested by additional symptoms. Therefore, it requires therapeutic therapy. Antibacterial medications are prescribed, but only after a detailed examination.
If temperature fluctuations are caused by the appearance of a tumor-like formation, then the course of the disease and treatment will depend on its location. In most cases, surgery is performed, after which the indicators return to normal.
If there are disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, the patient may complain:
- for weight loss;
- to increased irritability;
- to sudden mood swings;
- for tachycardia;
- for interruptions in the heart muscle.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, the patient needs to undergo an examination, which includes:
- donating blood for general and biochemical analysis;
- donating urine;
- performing ultrasound diagnostics;
- performing electrocardiography;
- blood donation for the amount of hormones.
After this, a treatment regimen is prescribed.
Why is a temperature of 38 dangerous?
Elevated body temperature promotes the production of interferons, special substances that protect the body from viruses, bacteria, as well as from their waste products. Also, increased body temperature prevents the proliferation of pathogens and contributes to their death.
Therefore, when answering the question of whether it is worth lowering the temperature to 38°C, experts do not recommend immediately taking antipyretics. The exceptions are patients with cardiovascular and pulmonary pathologies, neuropsychiatric disorders, immune system disorders, and the elderly. In this category of patients, it is recommended to reduce the temperature above 38°C.
Causes of temperature fluctuations in women
Most often, sudden changes in temperature are recorded in pregnant women. This phenomenon is caused by the transformation of hormonal levels, a significant increase in the concentration of the hormone progesterone in the blood. Typically, during pregnancy, body temperature rises and falls from 36.0 to 37.3°C.
Moreover, temperature fluctuations do not in any way affect the well-being of expectant mothers. They are observed mainly during the first two or three months of gestation, when the mother’s body gets used to its interesting position. But for some women, the temperature fluctuates until the very birth.
Article on the topic - how long does it take for the temperature to drop after antibiotics.
Sharp temperature fluctuations pose a danger to the health of young mothers only if they are accompanied by a profuse rash on the skin, painful sensations in the abdomen, disruption of the urination process and other symptoms. Not only the pregnant woman herself, but also the baby in the womb can be seriously harmed. Therefore, if you experience the slightest discomfort due to temperature fluctuations during pregnancy, you should immediately go to the doctor.
Sharp jumps in body temperature are often noticed at the beginning of ovulation. At this time, temperatures jump from 36.0 to 37.3°C. In addition to temperature fluctuations, signs of ovulation include the following symptoms that appear in a woman:
- weakness, powerlessness;
- nervousness, irritability;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- improved appetite;
- swelling.
By the time menstruation arrives, the above symptoms disappear and body temperature stops jumping. Deterioration in the condition of a woman’s body during ovulation is not considered a pathology; in this case, there is no need to consult a doctor.
For the vast majority of older women, the temperature fluctuates during the initial stages of menopause. This phenomenon occurs due to a sharp decrease in the concentration of sex hormones in the blood. Almost all representatives of the fairer sex, when entering menopause, in addition to temperature fluctuations, experience the following symptoms:
- hot flashes;
- excessive sweating;
- increased blood pressure;
- minor disturbance of heart function.
Fluctuations in body temperature during menopause are not harmful to health. But if a woman feels very bad, then it is better for her to consult her doctor. The healthcare professional may need to prescribe hormone therapy for the patient.
Treatment of fever without signs of a cold
So, let us remind you that treatment of fever without signs of a cold must begin with finding out the true cause of this problem. And for this you should contact a doctor - and without delay. Only a qualified doctor (and often more than one) will be able to answer the question of why you have a high temperature without signs of a cold, and prescribe comprehensive treatment.
If the identified disease turns out to be infectious-inflammatory, then antibiotics will be prescribed. And, for example, for lesions of fungal etiology, polyene antibiotics, triazole drugs and a number of other medicinal treatments are prescribed.
In general, as you yourself understand, the treatment of arthritis requires certain drugs, while the treatment of thyrotoxicosis or, say, syphilis requires completely different ones. When the temperature rises without signs of a cold - when this single symptom combines diseases so different in etiology - only a qualified doctor can determine which medications should be taken in each specific case. So, for detoxification, that is, to reduce the level of toxins in the blood, they resort to intravenous drip administration of special solutions, but only in a clinical setting.
Therefore, curing fever without symptoms is not just about taking antipyretic tablets at home like paracetomol or aspirin.
Any doctor will tell you that if the diagnosis has not yet been established, the use of antipyretic drugs can not only prevent the cause of the disease from being identified, but also aggravate its course. So a temperature without signs of a cold is really a serious cause for concern. Bronchitis in adults: how to treat, what symptoms, list of antibiotics Epilepsy: symptoms, causes and treatment Bronchial asthma: symptoms, treatment, emergency care at home Chickenpox: symptoms and treatment in children at home
Why do you have a fever after the flu?
The temperature after ARVI may remain for some time at around 37 degrees or slightly higher. This situation occurs in several cases:
- The change in temperature is due to residual effects after the disease. In this case, doctors talk about a temperature tail, that is, the infectious process has been stopped, but the weakened body needs time to recover. This is one of the normal variants; it does not pose any threat to humans. The duration of the period of maintaining low-grade fever is considered acceptable when the indicator is 37 degrees for no more than seven days, and in some situations up to 10 days. This time is enough for the patient’s weakened body to begin to function normally.
- An increase in temperature is associated with a developing complication of the disease. This situation is typical for those cases when the patient was self-medicating and did not notice the development of a bacterial infection. People are especially negligent about colds of the upper respiratory tract. Many people do not consider nasal congestion, sore throat, and superficial cough to be serious pathologies and treat them themselves or not treat them at all. And at this time, an inflammatory process develops in the body in the respiratory system and spreads to neighboring organs. The body's first reaction is to increase body temperature.
In any case, only a doctor can carry out a differentiated diagnosis. and find out why after ARVI the temperature of 37 lasts for a week or more.
Stages of fever development
A painful condition with hyperthermia, fever, and chills is called fever. There are three periods of fever: increase, retention at an elevated level, decrease. As fever increases, a restructuring of the body's thermoregulation is observed: heat energy increases, heat transfer decreases. Against the background of a decrease in heat transfer, vasoconstriction occurs, sweating is inhibited, and goose bumps appear. Thermal energy occurs due to increased muscle tone and muscle tremors. A rise in fever is accompanied by chills, fever, and trembling.
The retention of fever is associated with the establishment of constant hyperthermia, which lasts for several days. The duration depends on the type, severity of the causative virus and the ability of the immune system to resist it. The stage is accompanied by skin that is hot to the touch, pale, and feeling hot. If there is a sharp jump to 39 degrees or more, or vomiting or severe headache occurs, you must call an ambulance.
- Symptoms of poisoning
- Temperature with hemorrhoids: can there be an increase?
- Symptoms of pneumonia in adults - pneumonia
A decrease in fever is accompanied by profuse sweating, dilation of peripheral vessels, and frequent breathing. The temperature decreases due to increased heat transfer and decreased thermal induction. At this stage, the body completely destroys pathogenic, toxic substances, viruses, gradually normalizes the temperature, restores strength and appetite.
Possible reasons for the increase
If you notice that your temperature has been above normal for a very long time and you cannot understand what is happening on your own, then the smartest decision in this case would be to see a doctor. Only a long-term and professional examination by specialists will make it clear whether you should worry, try to treat some disease, or whether such a condition is a safe norm for your body. But, it will also be useful to familiarize yourself with the possible causes that cause uncomfortable symptoms:
- this may be a variant of the norm;
- changes in the body of a woman who is carrying a child (hormonal levels);
- thermoneurosis;
- temperature trace of already suffered diseases;
- development of a tumor or other cancer;
- tuberculosis;
- different types of infection;
- AIDS;
- intestinal diseases.
Basic principles of treatment
To bring down a high fever, children are usually given Ibuprofen or Paracetamol. Infants who do not yet know how to eat on their own are given an injection with an antipyretic drug. It is worth noting that you should not self-medicate under any circumstances. Many drugs prescribed for adults are strictly prohibited for children. These include medications with metamizole sodium, as well as Aspirin and Analgin.
After this, the child is usually hospitalized or given an appointment with a local pediatrician. To find out the cause of sudden changes in temperature, you will need to undergo a full examination. It usually includes blood and urine tests, ECG, and ultrasound of organs. After receiving a complete clinical picture of the little patient’s condition, the pediatrician prescribes therapy and gives recommendations for care. Depending on the situation, the specialist prescribes antibiotics, hormonal drugs, antihistamines or anti-inflammatory drugs.
Degrees of temperature rise
It is customary to systematize the temperature at the stage of hyperthermia according to thermometer readings. According to this medical classification, body temperature is divided into the following categories:
- reduced – less than 35°C;
- normal – from 35°C to 37°C;
- subfebrile – from 37°C to 38°C;
- febrile – from 38°C to 39°C;
- pyretic – from 39°C to 41°C;
- hyperpyretic – more than 41°C.
At what temperature do viruses die?
When a pathogenic microorganism enters the area of the mucous membranes of the throat and nose, a local immune reaction occurs. If the barriers are not developed enough, the virus enters the blood. There it releases toxic substances that spread throughout organs and tissues. As a result, body aches, dizziness, and headache occur. In response to these symptoms, immune system cells migrate to the lesion, that is, into the blood. They cause fever.
Fever is regulated by the thermoregulation center, which is located in the brain. In order for the viruses to be destroyed, it is necessary to reach values up to 38.5 degrees. This is the optimal environment in which most pathogenic microorganisms die.
If the rate rises higher, this does not mean that more viruses will die. But at this moment negative reactions for the body may occur. Therefore, if the parameter exceeds 38.5 degrees, the use of antipyretic drugs is recommended, each of which depends on the age of the patient.
The following types of viruses die during fever:
- influenza, parainfluenza;
- adenovirus;
- rotavirus;
- rhinovirus.
These are just some of the types of viruses that attack the human body. Every year they mutate and create new strains. But this does not affect the effects of fever. With it, most of them will die.
On a note! A high temperature during ARVI in children is brought down only after 38.5 degrees. Some parents give antipyretics at bedtime if the readings are lower. This is mistake.
Which doctor should I contact?
In the case of a relatively satisfactory condition, it is recommended to first contact your family doctor or local physician at the clinic at your place of residence.
The therapist will decide on the breadth of the examination and the need for consultations with other specialists (infectious disease specialist, neurologist, surgeon, urologist).
If the hyperthermia is quite high, and the general state of health is equivalent to severe, then it is advisable to call an ambulance at home, who, after examination, will hospitalize you in the necessary department or solve the problem at home.
For the flu
In adults, the first symptom of a typical flu is hyperthermia up to 37–38°C, which is not recommended to be brought down. The temperature can last up to 2-5 days, this is relatively short. If the pathogen is atypical, then hyperthermia may not begin at all. In children, the flu is much more severe. Fever reaches 39–40°C and lasts 3-5 days. In most cases, influenza in children is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea and other symptoms of intoxication. A repeated increase in temperature serves as a signal of the onset of a complication, for example, pneumonia.
Mechanism of body temperature rise
Body temperature is controlled by the preoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus of the brain. There is a biological thermostat there. If the temperature is too low relative to the accepted target, the hypothalamus sends signals to increase the temperature through the process of thermogenesis.
It involves the muscles in which, at first glance, chaotic convulsions occur - in fact, this is of a deliberate nature - at the same time, the same thing happens in the antagonistic muscles, which leads to the formation of heat.
At such moments, we observe a characteristic trembling, which is familiar to us from cold days when our body was trying to warm up. At the same time, so-called tremorless thermogenesis occurs in adipose tissue, as a result of which the accumulated energy is converted into heat. If the temperature is too high, the hypothalamus causes the blood vessels to dilate and increases sweat production.
Pathogenic microorganisms responsible for infections produce compounds called pyrogens. It is these substances that stimulate the hypothalamus to increase body temperature . Interestingly, most exogenous pyrogens have molecules too large to penetrate the blood-brain barrier and therefore cannot directly stimulate the hypothalamus.
Instead, the body produces its pyrogens in response to the presence of toxins. These are mainly interleukins, substances secreted by lymphocytes and macrophages, which simultaneously stimulate the rapid production of T-lymphocytes, thus launching two directions of fight against the source of infection.
The body can mistake not only metabolic products of bacteria or fungi for pyrogens, but also some medications or toxins. For example, as a result of poisoning, an increase in body temperature can also occur, which has an unfavorable effect on the process.
Diagnostics
The examination is complicated by the absence of symptoms.
To find out the reasons, the doctor will suggest you undergo the following laboratory tests:
- detailed blood test;
- general urine analysis, according to Nechiporenko;
- blood culture for sterility;
- HIV testing;
- tumor markers.
To diagnose the causes of temperature, a urine test is performed according to Nechiporenko
To identify the source of the disease, instrumental methods include chest X-ray and ultrasound of the digestive and pelvic organs. Examination of the uterus and appendages in women, prostate in men.