Causes of pathology
The exact cause of endometrial polyps in the uterus has been established. It has only been reliably revealed that hormonal imbalances contribute to the appearance of endometrial hyperplasia. In sick women, an increased level of estrogen and a lack of progesterone are detected.
Predisposing factors for the formation of an endometrial polyp are:
- Ovulation disorders: anovulation, irregular, early or late ovulation.
- Multiple ovarian cyst or tumor.
- Chronic inflammatory processes of the genital organs: vulvitis, cervicitis, adnexitis, endometritis.
- Obesity.
- Endometrial trauma during abortion, curettage, and surgical interventions.
- Diseases of the endocrine system: disturbances in the functioning of the hypothalamus or pituitary gland.
- Premenopausal period.
- Sexually transmitted diseases: gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, syphilis, genital herpes.
Obesity is a possible cause of endometrial polyp in the uterus.
It is also believed that long-term use of oral contraceptives can lead to the development of endometrial polyp. Combination drugs that contain an estrogen component are especially dangerous. Under the influence of these hormones, local thickening of the endometrium and polyp formation occurs.
Types of endometrial polyps
Endometrial polyps vary in type of location. They can be located in the fundus, walls or cervix. There is also a classification based on histological structure. Such polyps are:
- Ferrous. They develop from the basal layer of the uterus. In this case, the glandular component predominates in the body of the polyp.
- Fibrous. Consist of connective tissue. Single glands are rarely found in their structure.
- Glandular - fibrous. Neoplasms of this type consist in equal proportions of connective tissue and glandular tissue.
- Adenomatous. They have a tendency to quickly degenerate into a malignant tumor.
All types of polyps can occur at any age. However, they are more common in women in their reproductive years.
Symptoms of appearance
Endometrial polyp in the uterus does not have pathognomonic symptoms. With small growths, there are no signs.
The growth of these formations contributes to the occurrence of the following manifestations:
- Infertility.
- Irregular menstrual cycle.
- Pain during menstruation.
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
- Intermenstrual bleeding.
Sometimes patients experience pain in the lumbar region, bleeding after sexual intercourse, and vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Is it possible to understand for yourself that such a neoplasm is located in the uterus?
Polyps themselves are small in size, so often their formation and development are not accompanied by any symptoms.
Often a woman may not even know for quite a long time that she has become the owner of this disease.
But after a certain time has passed, the woman will be able to suspect something is wrong, as some symptoms will make themselves felt. But this only happens when the disease has already fully come into its own. It is not possible to understand this on your own, since this disease has no clear symptoms. Most often, the disease is detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist or during an ultrasound procedure of the pelvic organs.
Diagnostics
Before diagnosing an endometrial polyp, the doctor interviews the woman. Patients usually complain of vaginal bleeding or spotting from the vagina.
Then the internal and external genitalia are examined. Vaginal examination reveals hyperemic mucosa and cone-shaped formations with clear boundaries.
Instrumental examination methods play an important role in the diagnosis of uterine endometrial polyp. They include:
- Ultrasonography. Doppler or three-dimensional ultrasound is more often performed. Using this method, even small polyps can be detected.
- Hysteroscopy. During this procedure, the condition of the endometrium can be examined and the presence of a neoplasm can be detected. A piece of the polyp is also taken for research (biopsy).
- Hysterosalpingography. This is the name for x-ray diagnostics of the condition of the internal cavity of the uterus. A special contrast agent is injected into the uterus. An x-ray is then taken. This method of diagnosing polyps is auxiliary. More often it is used to determine the patency of the fallopian tubes.
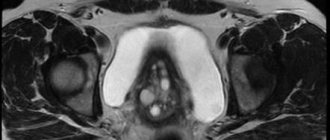
- CT or MRI of the uterus. These studies are expensive. But with their help, you can effectively determine the presence or absence of an endometrial polyp.
- Diagnostic curettage. Currently, the effectiveness of such manipulation is less than 50%, so it is extremely rarely used for diagnosing polyps.
Ultrasound examination is a method for diagnosing endometrial polyp in the uterus.
When a tumor in the uterus is present, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with cervical polyp, uterine cancer, myometrial hyperplasia and submucosal uterine fibroids.
With a cervical polyp, a cone-shaped formation with a smooth surface is detected, located in the cervical canal.
With hyperplastic processes, a thickened folded surface of the endometrium is observed.
With uterine cancer, the formation does not have clear contours. Nonspecific changes in the uterine cavity are observed. You can identify the presence of a single myomatous node or a conglomerate of nodes, a significant enlargement of the uterus.
Conservative treatment of polyp in the uterus during menopause
Conservative treatment of tumors in the uterus during menopause is relevant and promising for two reasons:
- Restoration of hormonal levels;
- Stabilization of the polypous lesion at the current moment.
The following groups of medications are prescribed::
- Hormonal phytoestrogenic drugs : Klimadinon, Remens. The remedies are effective in the first 6 months after menopause.
- Bioidentical hormones : Janine, Femoston, Duphaston. Drugs are prescribed to maintain the balance of hormones, prevention, and malignancy of tumors in the uterine cavity.
- Products with estrogen : Klimonorm, Premarin, Ovestin. The drugs are indicated to prevent tumor formation and damage to bone and joint tissue.
For existing or removed polyps, cytostatic drugs are prescribed to prevent the growth of tumors or relapse. Be sure to monitor the condition of the vaginal microflora, preventing infectious processes.
Doctors no longer need to preserve reproductive function. The goal of drug treatment is to reduce symptoms, stabilize hormonal levels, and prevent the growth and spread of polyps.
Should I remove a polyp in the uterus during menopause or not?
Oncologists recommend immediately removing tumors of any location. Surgeons evaluate other criteria: growth tendency, heredity, provoking factors, general condition of the woman.
If a woman is diagnosed with one hyperplastic polyp of about 0.5 mm, then the patient is registered with a dispensary and examined at least once a year (ultrasound, hysteroscopy, MRI).
If the polyp is large (or several of them), has clear echo signs on ultrasound, and differs in growth dynamics, then it must be removed. A pedunculated polyp protruding into the cervical canal can become strangulated, contribute to necrotic changes in the mucous membranes, and the development of intrauterine bleeding.
Another danger is endometrial cancer. Unfortunately, almost all women with endometrial cancer had uterine polyps. To prevent cancer, it is recommended to conduct histology of suspicious tissues for atypical cells.
Therapy methods
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the type of polyp and its location. The main goal of therapy is to relieve the symptoms of the disease and remove the benign tumor.
Currently, several methods of treating this pathology are used:
- Conservative.
- Operational.
- Traditional methods.
Sometimes complex or combination therapy is used. The choice of the necessary method depends on the size and type of polyp, the cause that caused it, the woman’s age, and the presence of concomitant chronic diseases.
Medication
Drug therapy is an auxiliary method of treating polyps. Medicines are more often used in the postoperative period or to prevent relapses of the disease.
For conservative treatment, the following is prescribed:
- Oral contraceptives: Zhanin, Novinet, Yarina.
- Medicines that regulate progesterone levels: duphaston, utrozhestan.
- Installation of an intrauterine hormonal device.
- Analogs of gonadotropin-releasing hormone: zoladex, buserelin.
The course of treatment lasts from 3 to 6 months. Patients are also recommended to take general restoratives, homeopathic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Surgery
The main method of therapy is surgical removal of endometrial polyps in the uterus. Radical treatment of this disease without surgery is impossible.
The following types of operations are distinguished:
- Hysteroscopy. The polyp is removed using an endoscopic device (hysteroscope). It is inserted into the uterine cavity and the tumor is excised.
- Cryodestruction. This method involves exposing the polyp to low temperatures. They cause tumor necrosis with subsequent rejection.
- Laser ablation or cauterization. Only small polyps can be treated with laser.
- Hysterectomy or removal of the uterus. Endometrial polyps are often removed in this way for postmenopausal or menopausal women.
- Diathermocoagulation. They use special tools that are supplied with high frequency current. A crust forms at the site of the polyp, which then comes out of the uterus on its own. The mucous membrane is restored naturally.
Surgery is a method of treating an endometrial polyp in the uterus.
Before removing an endometrial polyp in the uterus, a histological examination is required. The extent of the operation and the choice of treatment method depend on this.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine methods are also used to treat endometrial polyps in the uterus.
The most effective include:
- Infusion of celandine. 1 tbsp. dry herbs pour 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for 2 hours. Then apply 1 tsp. x 3 times a day after meals.
- Viburnum. You need to eat frozen or fresh berries. You should eat 2 tbsp per day. viburnum. The course of such treatment lasts 1 month.
- Sea buckthorn oil You can buy it at the pharmacy or prepare it yourself. To do this you need to take sea buckthorn and sunflower oil. The berries are crushed in a blender and mixed with oil in a 1:2 ratio. The resulting mixture is recommended to be applied to a tampon and inserted into the vagina. The procedure must be repeated every day for 2 weeks.
- Oak bark, sage and yarrow. All herbs are taken in different proportions, crushed and mixed. Then pour boiling water over it. For 1 tbsp. mixture you need to take 1 glass of water. The resulting decoction is drunk 1 tbsp. daily.
- The grass is boron matka. A decoction is prepared from it and drunk twice a day, morning and evening.
Herbal treatment for endometrial polyps has a positive effect on the general condition of the body and normalizes hormonal levels. However, it must be remembered that such folk methods have a number of contraindications. Therefore, they should be used only after consultation with your doctor.
Treatment methods for polyps during menopause
Treatment of endometrial polyps is carried out only under the guidance of the attending physician. The polyp treatment method is selected based on the following individual indicators:
- How seriously is the woman sick?
- What do the test results and preliminary research say?
- How long has she been going through menopause, at what age did she enter it, how difficult was it?
- What is the reason for the growth of the endometrium and the formation of a polyp in the uterine area?
- How long ago did the patient suspect something was wrong and decide to see a doctor about the problem?
- How was she treated before, and was such treatment successful?
Attention! There are cases when polyps in the cervical canal do not require special treatment. This happens because when hormone levels return to normal, such a formation resolves on its own.
If polyps negatively affect the condition of the female reproductive system, then you need to immediately decide on treatment and start it.
The most common treatment for this problem is surgery. There is no need to be afraid of such an intervention, since it is done through the cervical canal of the uterus. There are no incisions, so there are no stitches. The rehabilitation period after such an operation is also minimal.
Attention! When performing a surgical operation, you do not have to worry about your reproductive function. If during menopause you are still planning a child, this operation will not affect fertility at all, and endometrial polyps will disappear without a trace.
In addition to treatment with surgery, there is also a conservative method of getting rid of such growths during menopause. And this is a conservative treatment carried out with the help of medications. This type of treatment is suitable for a woman when for some reason she refuses surgery or is afraid to have it.
- Treatment of polyps in the uterine area, which is carried out using oral contraceptives of the most diverse spectrum of action. It is suitable only when the doctor has diagnosed you with either a glandular polyp or a glandular-cystic growth. These drugs can stop the growth of the polyp and stop hemorrhages in the uterine area. This saves the woman from curettage procedures, which she must constantly attend during uterine bleeding. Treatment with oral contraceptives takes only 3 weeks. After this, you will need to undergo a second course of examination of the pelvic organs in order to make sure that the treatment really has a result, and such a disease of the cervix will no longer bother you.
- Treatment with hormonal drugs. Treatment with hormones is carried out only with drugs that contain progesterone. These medications allow you to bring hormonal levels back to normal, as well as stop uterine bleeding, if any. Treatment of this type will last a little longer - about six months. Unfortunately, today it can hardly be called the most effective, since there are cases when polyps of the cervical canal recur. That is, such treatment will not make sense. However, this situation does not always arise. Some, with the help of hormones, managed to completely get rid of polypous formations of the reproductive organs.
- Treatment with hormone agonists. This treatment is effective only for those women who are at the age of menopause.
Possible complications
The consequences of an endometrial polyp in the uterus include:
- Anemia. This complication develops with prolonged, heavy bleeding.
- Infertility. Occurs with large polyps or anovulatory cycles.
- Malignancy of the polyp. Characteristic of adenomatous forms of the disease.
When asked by a patient whether it is possible to become pregnant if there is an endometrial polyp in the uterus, doctors answer differently. Some believe that pregnancy is quite possible with this disease. Other experts say that single or multiple (polyposis) endometrial tumors are the cause of infertility. Thus, there is no clear answer to the question of whether it is possible to get pregnant with a polyp in the uterus.
If a woman still manages to become pregnant with endometrial hyperplasia, then her risk of miscarriage or various abnormalities of fetal development increases. Therefore, the polyp must be removed before pregnancy.
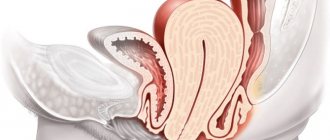
What are polyps?
An endometrial polyp that arises in the uterine cavity is considered one of the types of pathological proliferation of endometrial layers, which is an oval body connected to the mucous surface of the uterine cavity by a characteristic stalk.
This neoplasm has a benign habitat, resulting from changes in hormonal levels in the female body.
The size of the growth can vary within different limits. In one case, its size may not exceed a couple of millimeters, and in another, it can occupy the entire uterine cavity, causing serious consequences.
Therefore, the formation of a polyp, regardless of its size and manifested symptoms, requires a competent approach to treatment, since with the prolonged existence of a polyp in the uterus, the risk of its malignancy and degeneration into a cancerous tumor increases.
Most often, the formation of endometrial polyps occurs in postmenopausal women. Also, this pathology can occur in younger females, up to adolescence. Only regular routine examinations and a responsible attitude towards their reproductive health will allow a woman at any age to promptly detect any pathology that has arisen and take all necessary measures to eliminate it.
Preventive measures
Nonspecific prevention of endometrial polyps includes:
- Regular observation by a gynecologist.
- Systematic ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages, hormonal studies.
- Treatment of existing chronic diseases of the genital organs.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, having a regular sexual partner, no abortions.
- Use of individual protective measures during sexual intercourse.
Early detection of polyps will help quickly get rid of the disease in the initial stages.
The tactics for managing patients with an endometrial polyp depends on its size, type and severity of clinical manifestations. The gold standard of treatment is polypectomy (removal of tumors). This eliminates all clinical manifestations and increases the likelihood of pregnancy in case of secondary infertility.
Removal of a polyp in the uterus during menopause
Indications for removal of uterine polyps during menopause are:
- atypical discharge from the cervical canal,
- addition of purulent and bloody impurities in the mucous component,
- high risks of malignancy,
- soreness,
- heavy bleeding.
Various methods are used to remove polyps in the uterus.
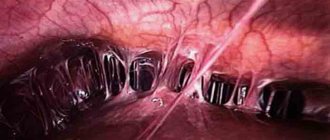
Hysteroscopic removal
Hysteroscopy is an endoscopic method of treating polyps using hysteroscope equipment. The device is equipped with optics and lighting, and has ways for introducing surgical instruments. During endoscopic removal, there is no significant damage to the endometrium. The manipulation is performed under general or local anesthesia.
During the manipulation, access to the polyp is made through natural pathways, a probe and special instruments are inserted. Pedicled polyps are removed with a metal loop, and the vessels are coagulated with a laser or electric current (polyp hysteroresectoscopy).
New growths on a wide base, as well as in case of risks of malignancy, excision of altered tissues is carried out within the healthy membranes with a scalpel.
The entire course of the manipulation is controlled by a doctor; early rehabilitation takes several days. Read more about the consequences of removing an endometrial polyp by hysteroscopy in this article. After the manipulation, the woman is sent home based on her health.
Hysterectomy
In case of malignancy of tumor cells, as well as in case of metastases or total uterine polyposis, a hysterectomy is performed - complete removal of the uterus.
During menopause, women do not necessarily need to preserve the organ. After surgery, women receive lifelong hormonal treatment.
Polypectomy
Removal of polyps from the uterine cavity is carried out using endoscopic equipment. The manipulation is performed under general anesthesia. After access to the polyps, they are cut with a loop, forceps, or cut out with a scalpel. The wound surface is coagulated using electric current.
Polypectomy is a classic loop method of excision of pedunculated polyposis lesions. If it is absent, an artificial leg is formed, after which the neoplasm is removed in any way.
Scraping
The most “ancient” method of removing the upper layer of the endometrium along with neoplasms and other structural changes. Indicated for total polyposis, when the number of growths cannot be determined, as well as for women with realized motherhood. Curettage or curettage is not used for polycystic uterine disease.
The algorithm is as follows:
- Introduction of general anesthesia;
- Administration of drugs to dilate the cervix;
- Insertion of dilators into the uterus;
- Curettage of the uterus with a curette;
- Introduction of antiseptics.
The operation is quite traumatic and lasts up to 40-50 minutes. Despite the duration and thoroughness of the manipulations, the risks of relapse are the highest - up to 35%.
Curettage is often combined with vacuum aspiration, when the curette only cuts off the growths, and a special vacuum sucks the contents out. Vacuum aspiration is not used as an independent method. This is due to the fact that during the manipulation it is almost impossible to remove the root of the growth, so the risk of relapse increases several times.
Laser removal
The modern method of removing polyposis lesions in the uterine cavity is laser excision.
The advantages of the method are:
- high impact accuracy,
- control over beam intensity,
- minimizing the risks of complications.
More complete information about removing a polyp from the uterus with a laser is here.
However, during the procedure there is strong smoke, which makes visibility difficult and increases the risk of developing healthy tissue burns and perforation.
There is another way to remove tumors with a high oncogenic risk - ablation. The method involves excision of the endometrial layer while preserving the function of the organ.
The rehabilitation period is determined by the volume of surgical intervention and the risks of postoperative complications. The larger the surgical volume, the longer the recovery.
Rehabilitation includes:
- protective regime,
- sexual rest,
- long-term drug correction.