1701
0
Parasites will come out like scalded ones if you drink in one gulp...
Mountains of parasites will come out of you if you drink the usual gulp on an empty stomach...
Go to website
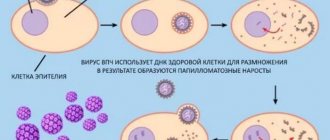
Many types of helminths inhabit the human body. According to scientists, about 80% of the population are carriers of parasites. Most people don't even realize it because there are no symptoms. Worms provoke various diseases, and the proliferation of helminthic colonies leads to chronic forms. Helminths can choose any organ as a place of settlement. Their waste products cause intoxication of the body, taking away vitality and weakening the immune system. The pattern of human infection is very simple and therefore dangerous. Let's consider the general characteristics and classification of helminths.
Over 300 species of worms have been discovered and classified.
According to their location in the body, parasites are divided into:
- Fabric
The habitat of helminths and larvae is the subcutaneous fat layer.
- Translucent
Concentrated mainly in the intestines and other internal organs.
- Extraintestinal
They are able to move through blood vessels, bile ducts, and settle in muscles, liver, brain tissue and lungs.
Classification
In parasitology, there are three main classes of helminth worms that can exist in the human body :
- Nematodes (round);
- Cestodes (tape);
- Trematodes (liver, pulmonary, lanceolate fluke, etc.)
Nematodes have a characteristic filamentous body configuration, round in cross section. They appear in humans after consuming unwashed gardening products. Symptoms of roundworm infestation are similar to other types of intoxication and require an integrated approach to treatment . In addition to the intestines, some nematodes are able to migrate and exist successfully in various parts of the human body. For example, female pinworms penetrate the genitals, causing inflammation, and Trichinella are often localized in the muscles, causing swelling of the limbs and pain in the muscles.
Flat nematodes are characterized by a ribbon-like configuration consisting of individual proglottids. They are attached with specific suction cups and hooks to the tissues of the small and large intestines, sucking out ready-made nutrients. The sizes of formed individuals vary from a few millimeters to 15-18 meters. In most cases, infection occurs through fresh and lightly salted fish and insufficiently processed cattle meat.
Tapeworms, depending on the location, give rise to various clinical pictures, but most often the first symptoms in a person are weakness, abnormal bowel movements, nausea, and pain in the lower abdomen. Frequent signs of infection in the later stages are: sleep disturbance, decreased visual acuity, excessive yellowness of the skin, and headaches. Alveococci and pork tapeworms are especially dangerous; when parasitized, they can cause brain damage and, in the absence of the necessary measures, lead to death.
Trematodes parasitize various tissues of the human body, affecting the liver, lungs, gall bladder, blood vessels, and brain. Infection with fluke parasites occurs when eating fish products that are not sufficiently cooked. You can also accidentally ingest eggs by consuming garden crops that have been watered with water from rivers and lakes. In this case, signals of the presence of helminth worms become noticeable only after a long period of intoxication. The early stages of infection are practically asymptomatic, and the treatment process requires referral to specialists and the use of specialized medications.
Attention!
Helminthiasis is a fairly serious problem that causes many complications.
The waste products of worms are toxic and often provoke allergic reactions.
The larvae of some helminths can penetrate through the walls of blood vessels into the circulatory system and travel through the bloodstream throughout the body, affecting the liver, lungs, brain, and eyes.
In advanced cases, vitamin deficiency and even protein deficiency develop, which can lead to delayed development of motor skills, mental and speech development.
Under the influence of helminthiasis, immunological reactivity decreases, which often leads to insufficient production of antibodies during vaccination. This makes the prevention of polio, measles, diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus and other infectious diseases less effective.
If there are a lot of worms, they can clog the intestinal lumen, causing obstruction.
What do the statistics say?
According to the World Health Organization, every year approximately half of the people on the planet become infected with parasitic worms, which leads to trichuriasis, hookworm and other complex forms. The most common in Russia are roundworms, which are found in 90% of infected people. Every year, about 800 million cases are recorded worldwide, mainly through poorly washed fruits and vegetables. In this case, the main signs of the presence of parasitic forms are noted: loss of appetite, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, general weakness, itching.
The second most common type of helminthiasis in Russia and Europe is pinworms, which are localized in the lower intestines and cause enterobiasis. Among the main manifestations: nausea and pain in the abdomen, loose stools. These reactions are pronounced in severe cases of the disease, and in the first stages the presence of a worm can be detected in the stool or by characteristic nighttime itching in the rectal area.
In the Russian Federation, cases of infection are recorded annually throughout the territory. The main foci are the areas of the Ob, Irtysh, Volga, Kama, Yenisei, Lena, Neva, Pechora river basins, as well as the southern regions of the country.
Symptoms of infection
Manifestations of helminthiasis depend on the type of worm that has settled in a person, but there are general signs:
- constipation;
- weakness;
- painful sensations in the joints;
- loss of appetite;
- increased fatigue;
- weight loss.
Additional symptoms of infestation by various worms:
- round: itching in the anus, insomnia, distracted attention, dizziness, headache, swelling, fever;
- tapeworms: cracks and painful spots on the tongue, abdominal pain, diarrhea;
- flukes: fever, malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
Evolution of helminthiases
The widespread distribution of parasitic worms on the planet and the annual registration of cases of infection are the result of their high degree of adaptability to various conditions in the process of evolution. Modern parasitology allows us to trace the development and changes in the localization of human worms using the example of trematodes, cestodes and nematodes.
Trematodes
The most ancient species are helminths of mollusks and fish, the biological development cycle of which was ensured by the fish eating crustaceans and the corresponding change in the stages of “egg” - “worm”. Gradually they adapted to warm-blooded organisms, the first of which are presumably waterfowl, beavers and seals. The first introductions into the internal organs of primitive people occurred randomly, through the consumption of water and fish from open reservoirs.
During the transition of Homo sapiens to sedentism, polygostal representatives of the class increasingly entered the food tract of domesticated animals feeding on raw fish, creating new epizootic chains. Some of them have successfully adapted to new cycles and carnivorous hosts, changing depending on specific natural relationships. Even then, signals of invasive influences could be detected everywhere, although trematodes did not become an exclusively human invasion, having chosen more accessible animals.
For example, fascioliasis and plagiorchiasis circulate according to the following scheme: animals - entry of fecal particles into water bodies - infection of shellfish - release of larvae into the water - infection of livestock at watering places. In addition, most helminth worms have adapted to the conditions of development of larvae outside the aquatic environment and have mastered new methods of ecological connections, which has contributed to their wider distribution.
Diagnosis and treatment
To establish the presence of parasites and determine their type, several methods are used. The most common is a stool test for worm eggs, but it does not always give a reliable answer the first time, since the results depend on the life cycle of the parasites and their number in the body.
A more reliable answer is provided by an immunological blood test for the presence of antibodies to parasite antigens - enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). This method makes it possible to determine the type of parasites and their number.
When helminths penetrate tissues, diagnosis is difficult, since eggs or larvae are not detected when analyzing stool. In this case, a serological blood test, ultrasound of internal organs, computed tomography, endoscopy, as well as examination of material taken during a biopsy are performed.
Antiparasitic agents and sorbents are used for treatment. After anthelmintic therapy, doctors, as a rule, prescribe sorbents, the purpose of which is to remove from the body the waste products of parasites that poison the body from the inside. It absorbs toxins released by helminths and removes them naturally, cleansing the body and restoring normal intestinal microflora.
Cestodoses
Parasitic tapeworms are characterized by a complex development pattern with a succession of several intermediate host organisms. They evolved along a similar path to trematodes, and therefore also belong to fish helminths. The most ancient cestodes are considered to be the causative agents of multiceptosis, which affects domesticated dogs and sheep. You can find indicators of cestodoses in people with invasive infection by tapeworms (Pseudophyllidea) or tapeworms (Gyclophyllidea).
Separation of worms by structure
All types of parasites are divided into three types.
So, roundworms have another name - nematodes. There are about 20 thousand species. In terms of their structure, they are all quite small. In addition, all nematodes have different sexes, which allows them to create symbioses.
Tapeworms, or flatworms, have a scientific name - cestodes. There are only about 3 thousand species, and all parasites of this group belong to worms. They do not have a digestive system, but they have unusually developed genital appendages. They reach a length of up to 30 meters and have the ability to plant a huge number of eggs.
Fluke worms are also called trematodes and reach up to 1.5 meters in length. They have well-developed suckers. For the most part, trematodes belong to individuals with double genital appendages.
Nematodes
The ancestors of modern nematodes, the most numerous class of parasitic helminths, are free-growing forms of Rhabditata. Some of them remained unchanged in the process of evolution, but most developed to primary enterohelminths living in the intestines. Under the influence of a number of factors, individual families lead a migratory lifestyle, penetrating into the bloodstream of the victim, and from there into other systems.
How to recognize helminthiasis
Most often, it is not easy to find specific signs without testing. The task is complicated by the fact that the symptoms are similar to many chronic diseases. As a result, the cause remains unchanged, and symptomatic prescriptions do not produce a lasting effect. It is important to know how to detect uninvited guests in order to take action in time and avoid destructive consequences in tissues, organs and systems.
You can recognize that parasitic forms of worms are present in your organs yourself by carefully studying the most characteristic indicators:
- Digestive problems. Toxins produced by mature individuals lead to loss of sodium, which in turn provokes the disorder. With significant sizes of helminth worms settled in the intestines, the likelihood of
- Constipation, bloating, and prolonged pain in the stomach. Against the background of the life activity of parasites, appetite decreases and metabolism deteriorates.
- Anal itching , intensifying at night, is the consequence of the migration of female pinworms to lay eggs, which cause noticeable irritation of the skin.
- Chronic fatigue is also a signal of the possible presence of helminthic infection, manifested by severe daytime sleepiness, general weakness, and decreased cognitive abilities.
- Irritability , causeless anxiety, depressive states - all these are the results of the effects of toxins from helminth activity on the central nervous system.
- Bruxism (involuntary teeth grinding) often indicates the presence of heartworms. Under the influence of the toxins they secrete, the synthesis of vitamin B12 decreases, leading to excessive tension in the jaw muscles. Bruxism is not the main symptom and can only be considered as an indirect confirmation when making a diagnosis.
- Dermatological problems , including rashes, acne, peeling skin, baldness. The activity of most parasitic life forms is based on sucking nutritional masses from intestinal tissues, as a result of which their lack in the “host” is manifested.
- Muscle and joint pain of various localizations, caused by the migration of adults and the release of large amounts of toxins.
Depending on the type of invasion, location and extent of damage, other signals are observed: insomnia, hemorrhoids, allergies, enlarged lymph nodes, weight loss, nausea, coughing attacks. At the same time, each of these symptoms individually may indicate an infectious or chronic disease, so it is necessary to undergo laboratory tests to determine their cause.
How to remove parasites forever
If factors of worm damage are identified, comprehensive treatment must be started immediately. Modern approaches to getting rid of human helminthiasis parasites and a number of effective medications make it possible to quickly get rid of worms, restoring the normal functioning of internal systems and organs. The means used in antiparasitic programs are:
- Anthelmintic substances, the action of which is aimed at destroying parasitic worms;
- Enterosorbents that remove harmful toxins;
- Antihistamines , which help minimize the allergic response to products of helminthic origin;
- Vitamin complexes containing B12, iron, folic acid - to replenish their deficiency in the blood;
- Hepatoprotectors , restoring liver function;
- Probiotics for improving intestinal functions.
The modern pharmaceutical market offers many medications aimed at the prevention and removal of helminthiases. It is important not only to determine which phenomena indicate the disease, but also to choose the right program taking into account the diagnosis and the individual characteristics of the patient. The selection of domestically produced antiparasitic drugs includes chemical, complex and herbal tablets, solutions, drops, and teas. The most popular of them are helmindazole, decaris, pyrantel, piperazine adipate and additional herbal remedies.
Domestic anthelmintics
Helmindazole
Enterobiasis, strongyloidiasis, taeniasis, ascariasis, trichocephalosis, hookworm disease, echinococcosis, trichinosis
The active component mebendazole provokes irreversible disruption of the functioning of parasitic worms, leading to their death. It has a number of contraindications and possible side effects, so it should not be taken unless prescribed by a specialist.
It is one of the effective ways to combat worms . A short course of administration allows you to quickly remove cestodes and roundworms.
Solution "9 stoprasite"
Cestodoses, nematodes, trematodes, mixed invasions (including ascariasis, opisthorchiasis, enterobiasis)
It is used to prevent invasions , including those occurring in a latent form. The solution contains only natural components that have anthelmintic, bactericidal, antiprotozoal and antifungal activity.
Due to the absence of synthetic components in the formula and an optimally balanced herbal base , the solution has no contraindications or side effects. Can be used at any age, as well as during pregnancy. Positively affects the immune system, increasing resistance to repeated invasive risk.
Troychatka premium
Support gastrointestinal functions during parasite elimination
Consists of plant components with anthelmintic properties: cloves, oat and walnut extract, ginger, oat fiber. It is not accompanied by undesirable effects from the digestive system.
Ensures complete removal of toxins produced by worms from the body. Eliminates all signs of parasites, improving the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. It is recommended to be taken as an auxiliary tool in complex anthelmintic therapy.
Herbal tea “The Power of Russian Herbs”
Has antihelminthic, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic effects
A biologically active food supplement that contains an optimal ratio of hypericin, flavonoids and tanning components.
The herbal medicine has no contraindications , so it can be used without consulting a doctor. Helps ensure the prevention of helminth infections. Helps normalize digestion when performing an antiparasitic program.
Pomogusha, children's syrup
Preventive antiparasitic product for children over 3 years old, a source of vitamins C, B1, PP, B6, BC, B12.
The natural composition , enriched with vitamins, is specially designed for children from three years of age. Contraindicated in case of individual intolerance to the components contained in the product.
It has antihelminthic properties due to optimal proportions of herbal infusions. Does not cause allergic or other unwanted reactions.
Dekaris
Antimicrobial and antiparasitic agent that gets rid of roundworms, American necator and duodenal crooked head.
The medication destroys parasite cells, causing their death, blocks succinate-ubiquinone oxidoreductase, and inhibits the production of fumaric acid. Often accompanied by side effects such as nausea, bad breath, vestibular disorders.
Despite frequent cases of concomitant negative microreactions, the medication has proven itself to be an effective method against ascariasis. Easy to use, the course of therapy lasts 3 days.
Troychatka Evalar
Prevention and comprehensive treatment of a wide range of helminthic infestations in children
The plant complex has antiparasitic properties , reduces fermentation processes in the intestines, getting rid of larvae and individuals, leveling the consequences of their presence.
It is an effective herbal remedy with a pronounced anthelmintic, choleretic and socogonal effect.
Piperazine adipate
Ascariasis and enterobiasis
It exhibits a pronounced deworming property , paralyzing the muscles of nematodes. With a single use, the effectiveness reaches 90-95%, and with repeated use – 100%.
Inexpensive and effective tablets that quickly relieve painful conditions that accompany the activity of helminths. Requires caution in use due to a number of possible associated phenomena.
Pirantel
Ascariasis, nekotoriasis, enterobiasis, trichuriasis
It is used for preventive measures , blocks the effects of parasitic organisms, and is suitable for the treatment of specific and mixed infestations.
When used, there is a low level of toxicity and a lasting effect in destroying roundworms, pinworms, etc.
Among the disadvantages are low absorption, possible reactions in the form of diarrhea, vomiting, temporary hearing loss, and headaches.
If you know what worms are, then the main question when treating a parasitic invasion is finding the optimal medicine . It is important to make a choice based on specific symptoms, because most medications have a narrowly targeted effect. Many patients who have experienced anthelmintic prescriptions themselves note the high effectiveness of imported drugs.
What are roundworms?
- 1 General characteristics
- 2 Types
- 3 Routes of infection
- 4 The structure of the roundworm body
- 5 Reproduction
- 6 Development life cycle
- 7 Migration and localization
- 8 Symptoms of ascariasis in humans
- 9 Diagnostics
- 10 Treatment of invasion
- 11 Prevention
The human roundworm is a detritivorous worm (at the initial stages of development, it lives in the soil and feeds on decaying organic matter) belongs to the genus of Nematoda roundworms. The habitat of the mature human roundworm is the gastrointestinal tract. Ascaris and humans are a parasitic type of relationship between two organisms. These roundworms, settling in the intestines, disrupt the digestive tract and cause painful symptoms in the abdominal area. Children are at high risk of infection.
general characteristics
The parasite is a geohelminth: before entering the human body, the maturation of roundworm eggs occurs in the soil, since the full development cycle of the human roundworm includes contact with the soil. The disease is caused by ascariasis. Roundworms in humans do not attach to the intestinal walls, but move freely in the lumens. This lifestyle of the human roundworm allows the worms not to be excreted in feces during bowel movements, but to remain in the intestines, which complicates the diagnostic procedure.
Return to contents
Kinds
The Nematoda class includes more than 24 thousand species of parasitic varieties of roundworms. Scientists have developed a special table, which includes the most common types of parasites living in the human body. Among the roundworms, the most famous are roundworms and pinworms. The helminths Guinea worm and hookworm often infect people, which are slightly less common than pinworms and roundworms. Pinworm worms are also a type of roundworm, but they differ in that they exist in the human body for a long time without causing obvious signs of disease.
Return to contents
Routes of infection
By adhering to basic hygiene, you can reduce the risk of infection with worms.
They usually become infected when basic rules of personal hygiene are not followed. Invasion is also possible when drinking unboiled water from contaminated sources. Flies and other insects carry eggs on their legs. When they land on food or a table, they transmit helminth eggs. Often the carriers are domestic animals - cats, dogs. The route of transmission of roundworm eggs to humans is oral.
Return to contents
The structure of the roundworm's body
Contrary to popular belief that this parasite is a hermaphrodite, this is not the case. Human roundworms are dioecious. The body of the human roundworm is elongated, round, and quite large in size. The external form of the roundworm looks like an earthworm. The size of the female reaches a length of up to 40 centimeters, the length of the males is much smaller - up to 25 centimeters.
Structural features: the end of the male’s body is pointed, which makes it easy to identify the sex of the worms. The digestive system of the human roundworm is not fully developed. The body contains light-sensitive cells. Biohelminths have a multi-layered cuticle. The hypodermis, or cuticle, creates the outer layer that protects against damage. Underneath it are muscle fibers that are responsible for the activity of movement. The internal cavity of the roundworm's body is filled with a liquid substance. This body structure preserves the elastic forms of the parasite.
Return to contents
Reproduction
A female roundworm can lay more than 200 thousand eggs in just one day.
The reproductive organs are very well adapted for maximum reproduction of offspring. Helminths have a special type of relationship, thanks to which one individual reproduces once a day, laying several hundred thousand eggs. The female has 2 ovaries and 2 uteri, and the male is endowed with a long testis. The eggs laid by the females are released along with feces and a new life cycle of the human roundworm begins. The reproduction of roundworms depends on the characteristics of the human body.
Return to contents
Development life cycle
The life cycle scheme is quite complex: initially, helminth eggs enter the soil, then into the human body. From the intestines, roundworm larvae penetrate the blood and migrate to the respiratory tract. By irritating the pulmonary membrane, the larval forms of the parasite cause coughing, are coughed up into the oral cavity and are re-swallowed by a person. The roundworm begins to develop into a sexually mature individual.
Helminth eggs have a durable shell that protects the embryo from mechanical damage and even ultraviolet radiation. Before entering a living organism, eggs go through a certain sequence of stages in the development cycle in the soil. Geohelminth fully develops at a temperature of +24 degrees Celsius. If conditions are favorable enough, eggs can live in the soil in the suspended animation stage for more than 10 years. They do not require an intermediate host; the larvae hatch from the eggs in the small intestine of the main host and parasitize its body.
The life of roundworms does not have a typical cycle.
Once in the intestine, the roundworm egg shell dissolves and the immature larval form of the worm enters the intestine. Then, by boring through the intestinal walls, the roundworm larva penetrates the blood and migrates along with the bloodstream. In the intestines, roundworm worms reach sexual maturity and begin producing eggs. Together with feces, the eggs are released into the external environment and the life cycle begins all over again.
Return to contents
Migration and localization
The parasite is localized in any organs, provoking the development of an inflammatory process. The migration of larvae along with the bloodstream is directed to large vessels and parts of the heart. From these, the larvae penetrate into smaller vessels and then into the lungs, causing a cough. During a cough, roundworm larvae enter the oral cavity and are swallowed by a person, penetrating a second time into the gastrointestinal tract, where the stage of development of a sexually mature individual begins. The roundworm larva develops in the human body on average 2 weeks. Parasites live for several years.
Return to contents
Symptoms of ascariasis in humans
In most cases, ascariasis first causes a feeling of chronic fatigue.
Ascariasis is characterized by the appearance of signs of invasion in a short period of time. The first typical symptom is often malaise. The weakening of the body caused by the vital activity of parasites is similar to the first signs of a cold. The affected organs begin to perform their functions poorly. Parasitic manifestations that are characteristic of invasion look like severe intoxication and allergic rashes. The main symptoms signaling ascariasis:
- the skin becomes pale;
- lack of appetite;
- problems with stool;
- sudden weight loss;
- labored breathing;
- pain in the abdominal area;
- nausea after eating;
- exposure to ARVI;
- respiratory tract diseases;
- temperature increase;
- sweating;
- depression;
- allergic manifestations;
- chronic fatigue.
Return to contents
Diagnostics
Modern laboratory tests accurately determine the type of parasite.
Blood test for antibodies When starting a diagnosis, one must take into account that it is much more difficult to detect larvae in the migration stage. Differential analysis will be very important in such cases. After the research, the difference between ascariasis and other helminth infections will be obvious. Several types of research are carried out:
- hematological;
- immunological;
- X-ray.
During diagnosis, migrating roundworm larvae are detected during lung sputum tests. A blood test shows the presence of eosinophils, and an eosinophilic infiltrate is detected in the respiratory organs. Often the diagnosis is based on the analysis of stool, which contains eggs of human roundworms. The most reliable method is considered to be vegetative resonance diagnostics, with the help of which the specific type of helminth and the place where it parasitizes is determined.
You will be surprised how many parasites will come out if you drink a glass of regular...
Parasites will leave the body in 3 days! You just need to drink on an empty stomach...
A parasitic infection caused by roundworms can be completely cured without complications or consequences for human health.
Return to contents
Treatment of infestation
Drug therapy is carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment. How long the treatment will last, which drugs are best to use and what dosage to use will be prescribed by the doctor, based on the clinical picture of the disease. It must be taken into account that if roundworm is detected in a person’s body, the whole family must undergo therapy. To get rid of parasites, the following drugs are used:
- "Vormil";
- "Vermox";
- "Dekaris."
About 24 hours after taking these drugs, you need to take a laxative so that the dead biohelminths leave the body and do not lead to general intoxication with decomposition products. Herbal medicine has been successfully used to combat worms. An excellent anthelmintic is the herbal mixture from which a decoction is made. It includes the following plants:
- St. John's wort;
- wild rosemary;
- strawberry leaves;
- lovage stems;
- common elecampane.
Mix equal parts of herbs, pour 1 tablespoon of the mixture with boiling water (250 grams). Cook for 15 minutes. Leave for several hours. Take 100 grams in the morning and evening, for children - 50 grams. During and after treatment, nutritious nutrition is very important in recovery. The patient should adhere to a light and nutritious diet.
Return to contents
Prevention
To avoid infection, follow the rules of personal hygiene: wash your hands with soap after visiting the street, playing with animals and before eating. It is not recommended to drink raw, unboiled water. Children should not put their fingers in their mouth. Fingernails are cut short, since helminth eggs trapped under them are difficult to wash out. Vegetables and fruits should be thoroughly washed and doused with boiling water before consumption. Food should not be left open, especially in areas where flies have access. Since roundworm initially lives in the soil, after contact with the soil you must thoroughly wash your hands and treat them with an antiseptic.
Imported anthelmintic drugs
Nemozol (India)
Intestinal nematodes, larval stages of cestodes, Giardia, mixed infestations
The active substance albendazole disrupts the functioning of parasitic individuals , causing irreversible damage. Destroys adult worms and blocks the development of larvae.
Requires caution in patients with various disorders of the liver and hematopoietic system.
A broad antiparasitic medicine helps to recover in a short time.
It has a number of side effects, so it should be taken under the supervision of a doctor.
Vermox (Romania/Hungary)
Enterobiasis, hookworm, echinococcosis, capillariasis, taeniasis, strongyloidiasis, trichocephalosis, trichinosis, ascariasis, mixed variations of helminthiases.
After administration, it is only slightly absorbed , leading to the death of worms in adults and children over 2 years of age. Simultaneously with the use of tablets, disinfection measures are required (processing furniture, washing and ironing bed linen, clothes)
One of the most effective medications at an affordable cost.
Sanoxal (India)
Larval forms of tapeworm, mixed helminthiasis, echinococcosis, nematodosis, protozoal infections such as giardiasis and microsporidiosis.
The principle of action of chewable tablets is based on the destruction of the intestinal tract of parasites, suppression of glucose utilization, and blocking the circulation of organelles in roundworm cells. Upon admission, laboratory monitoring of blood composition is recommended.
A good combination of effectiveness and safety. Reviews from patients indicate that all manifestations of parasites disappear the next day after taking Sanoxal tablets. At the same time, accompanying negative reactions are observed extremely rarely.
Biltricide (Germany)
Schistosomiasis, trematodiasis, cestodiasis, neurocysticercosis (except for ocular localization), pulmonary flukes, liver flukes, broad tapeworms, bovine and pork tapeworms.
Therapy with the active substance praziquantel effectively fights against a number of invasions , but requires an individual approach to determining the dosage.
Contraindications include: pregnancy, lactation, children under 4 years of age, cysticercosis in the eye area, liver dysfunction, cardiac dysfunction, kidney disease.
Biltricide is toxic and should only be used under the supervision of a competent specialist . Patients note good results in the treatment of opisthorchiasis, but complain of noticeable concomitant reactions.
Niclosamide (Germany)
Teniarinhoz, taeniasis, diphyllobothriasis, hymenolepiasis.
The parasitocidal effect is due to a direct contact effect on the pathogen, which inhibits oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria of cestodes. Almost complete absence of negative effects when taken in recommended daily doses.
Well tolerated, characterized by high anthelmintic properties. In some cases, it requires a second course of treatment. Quickly relieves symptoms of parasitic infection that were observed before taking niclosamide.
In cases where a person has severe symptoms, complex therapy is necessary. Most traditional medicines with antiparasitic properties include artificial chemical elements and hormones that provoke negative manifestations in the digestive system and central nervous system. Leading parasitologists recommend paying attention not only to synthetic medications, but also to natural complexes. Herbal infusions, herbal teas and other natural products can cope with parasitic worms without any negative health effects.
Many people do not know what to do if they test positive for eggworm in a laboratory test. Regardless of what symptoms appear, it is necessary to choose anthelmintic and anti-inflammatory spectrum therapy, taking into account contraindications and possible negative reactions.
Do not neglect preventive measures aimed at minimizing possible parasitic infestations. Among the main preventive measures: compliance with personal hygiene rules, proper food processing, caution when contacting animals. At the first suspicion of infection with parasites, it is recommended to take preventive herbal herbal remedies, as well as correct nutrition with the introduction of anthelmintic products (pumpkin seeds, garlic, thyme, cloves).
Prevention
- Mandatory heat treatment of raw fish and meat used as food (or for pet food), especially of unknown origin (imported Japanese sushi, crabs, squid)
- It is advisable to refrain from swimming in polluted fresh water bodies located near pastures, animal watering places, etc. Avoiding kebabs, barbecues and picnics in such places
- Regular examination and timely treatment of helminth infections will help to avoid conditions that threaten health and life.
- Timely attention to the health and deworming of your pets will also reduce the risks of your infection
- Thorough sanitary treatment of children's household items, nurseries, toys, playgrounds and street animals (yard cats, dogs)
- Fighting street and wild animals (certain precautions when going into the forest, while hunting and fishing)
- Extermination of domestic insects
- Combating wastewater emissions in small towns, polluted water bodies, and old landfills
- Thorough sanitary and hygienic treatment of hands, food before consumption, places of residence and work (especially for culinary workers) and kitchen utensils.