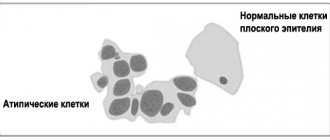
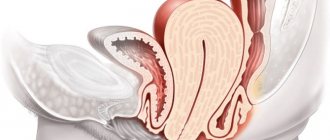
What is a polyp in the cervix? A cervical polyp (cervical) is a benign abnormal growth from the tissue of the endocervix (the mucous lining of the cervical canal). When multiple nodules on the cervix are diagnosed, the pathology is referred to as cervical polyposis.
What does a cervical polyp look like and what are the features of its development?
Causes of cervical polyps
The final cause of the formation of cervical polyps has not been clarified, however, there are a number of provoking factors for the development of pathology, and we will now talk about them.
Chronic infectious and inflammatory processes
The appearance of polyps on the cervix can be caused by:
- cervicitis;
- endometritis;
- adnexitis;
- human papilloma virus.
Hormonal disorders
A provoking factor for the occurrence of cervical polyps can be disruption of the functioning of the ovaries, an increase in the amount of estrogen and a decrease in progesterone levels.
Traumatic effects on the cervix
The development of polyps can be provoked by frequent abortions and diagnostic curettage of the cervical canal, because there is a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane. The addition of sexually transmitted infections leads to the appearance of formations.
Causes of neoplasms
The formation of polyps occurs due to the proliferation (growth) of epithelial cells in the cervix. Benign formations look like growths on a wide or thin stalk. They grow into the lumen of the cervical cavity or extend beyond it through the external os.
The true causes of polyps in the cervix have not yet been determined. In 8 out of 10 cases they are detected in patients after 40-45 years of age. Oncologists and gynecologists identify factors that provoke the proliferation of columnar epithelium in the cervical canal:
- hormonal imbalance;
- immune failures;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- cervical injury;
- adnexitis;
- pregnancy;
- abuse of hormonal drugs;
- frequent abortions;
- chronic endocervicitis;
- diabetes;
- menopause period;
- ovarian pathologies;
- cervical injuries received during childbirth;
- hysteroscopy.
In the structure of benign pathologies of the genital organs, cervical polyps are found in 25% of cases.
Along with condylomas and erosions, they are considered background diseases that increase the likelihood of cervical cancer. In 75% of cases, growths formed in the cervix are combined with endometriosis, atrophic colpitis, uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, and endometrial polyps. The formations provoke disturbances in the vaginal microflora and the risk of contracting STDs - chlamydia, ureplasma, urogenital candidiasis, genital herpes, etc.
Signs and symptoms
Single polyps do not lead to the appearance of abnormal signs; they are diagnosed more often during routine examinations by a gynecologist. When the growth becomes inflamed or its integrity is damaged, the following may appear:
- pulling pain in the lower abdomen;
- leucorrhoea;
- increase in the duration of menstruation;
- discomfort during sexual relations;
- bloody issues.
Women of childbearing age may experience problems with fertilization and menstrual irregularities.
Why is growth dangerous?
Typically, polyps are background in nature and arise as a result of other pathological processes.
But if they are not treated in a timely manner, the polyps can become malignant and cause cancer.
Among the most common dangers lurking in polypous processes, experts highlight:
- Severe anemic processes caused by heavy bleeding;
- Infringement of the formation by the walls of the cervical canal, the elimination of which requires urgent surgical assistance;
- An even greater imbalance in hormonal status;
- High risk of miscarriage;
- Problems with conception, infertility;
- A high percentage of the probability of degeneration of growths into cancerous tumors.
The greatest danger for a woman is the risk of oncology, since in such a situation not only the outgrowth, but also the uterine body is usually removed.
Types of cervical polyps
Polypous formations of the cervix are:
- Glandular or mucous. They are localized in the area where the nabothian glands are located, their size usually does not exceed 15 mm. Most often, such polyps are diagnosed in women of reproductive age; they respond well to treatment, do not lead to complications and do not have a tendency to relapse.
- Fibrous. The development of formations occurs from connective tissue cells. They are detected more often in women over 30 years of age. There is a high risk of degeneration into a malignant form.
- Glandular-fibrous. They are formed from cells of glandular and connective tissue; their sizes can reach 25 mm. The pathology requires surgical treatment, after which hormonal drugs are prescribed. There is a need for constant monitoring by a gynecologist (to reduce the risk of relapses).
- Adenomatous. Formations of this type can be up to 40 mm; they require surgical removal and a course of chemotherapy. There is a high risk of transformation into cancer cells.
Peculiarities
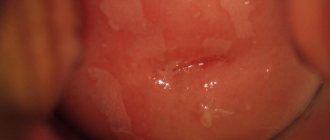
- The growth is a dense, round, oval or elongated formation, similar to a pink wart, ranging from 2 to 40 mm in length. The thickness can reach 4 – 5 mm in diameter.
- It is formed both on a thin ligament stalk and on a wide base.
- Unlike a cyst, inside of which there is a cavity with exudate, a polyp is considered as a tissue formation with a homogeneous structure.
- The outer layer consists of epithelial cells of the mucous membrane of the uterine cervix.
- The growth in the cervix may be single, but more often the processes are grouped.
- When several cervical polyps grow together, their shape resembles a bunch or inflorescence of cauliflower.
- In gynecological practice, polyps of the uterus and cervix are more often diagnosed in women after 40 years of age, usually during menopause.
- Although such growths are not malignant, they can be dangerous, since without treatment of a cervical polyp, in 1 to 2 patients out of a hundred, there is a possibility of developing a cancerous process in the cells.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, it is important to carry out the correct diagnosis. We will now talk about what methods are used to detect cervical polyps.
Visual inspection of the vaginal walls and cervical canal
During a gynecological examination, the doctor can visualize an enlargement and thickening of the cervix and pink growths of a dense, elastic or soft structure on its surface.
They can be round in shape or resemble a bunch of grapes. Polyps are white in color - with a tendency to keratinization. If the color of the polyps is dark cherry, this indicates a violation of their blood supply.
Cervicoscopy
During the study, a video camera is used, thanks to which it is possible to identify small polyps, their structure, the presence of an inflammatory process and ulcers on the surface of the cervical canal.
Ultrasound
Using an ultrasound examination, it is possible to determine the location of polyps, their size, structure, as well as the presence of inflammation and growths on the walls of the uterus.
Analyzes
The most informative laboratory methods for diagnosing cervical polyps are the following examinations:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood biochemistry;
- pap smear;
- hormonal panel;
- analysis for tumor markers.
Prevention of relapse
If you are prone to polyp formation, it is recommended to be examined by a gynecologist at least 2 times a year. To avoid relapses, you should:
- treat sexually transmitted infections in a timely manner;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- exclude casual sexual relationships;
- avoid abortion;
- strengthen immunity;
- control hormonal levels.
Benign cervical growths are more common in women with diabetes, thyroid or ovarian dysfunction. But when hormonal levels and metabolism are normalized, the re-formation of polyps does not occur.
Removal of cervical polyp
Conservative treatment in the vast majority of cases does not bring the desired result, especially for large polyps. That is why surgery is considered an effective way to combat the disease.
Can be carried out:
- hysteroscopy;
- diathermocoagulation;
- cryodestruction;
- radio waves;
- polypectomy;
- complete removal of the cervix.
Should I delete
It is possible to completely get rid of polyps only through surgical treatment. If the tumor is small and there is no risk of malignant degeneration, conservative therapy can be used.
The choice of treatment method should be made by a doctor, he takes into account the following factors:
- size of polyps;
- type;
- stage;
- woman's age;
- individual characteristics of the patient.
What is the price
In public medical institutions, surgical removal of cervical polyps is performed free of charge. In private clinics, the price can range from 5,000 to 20,000 rubles, everything will depend on the type of surgical intervention.
How to prepare properly
Before the procedure for removing polyps, it is necessary to undergo an ECG, ultrasound and hysteroscopic diagnostics of the cervical canal, take a general blood test, urine test, and be tested for HIV, hepatitis and HPV.
If you have problems with the veins, you will need to consult a phlebologist. It is forbidden to eat or drink 12 hours before surgery; it is recommended to do a cleansing enema.
Polypectomy
The essence of the procedure is to twist out the cervical polyps and cauterize the base with an electric current. If the growth is localized at the edges of the external pharynx, it is removed and the wound surface is sutured with catgut. If the pathological process is located higher, the procedure is performed under the control of a hysteroscope.
List of sources
- Kustarov V.N., Linde V.A. — Pathology of the cervix. - St. Petersburg, 2002;
- Rusakevich P.S. Diseases of the cervix: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention. -Minsk: Higher School, 2000;
- Diseases of the cervix: Clinical lectures. Ed. V.N. Prilepskaya. M. 2005;
- Practical gynecology (clinical lectures). Ed. IN AND. Kulakova and V.N. Prilepskaya. M.2001;
- Barinov V.V., Blumenberg A.G., Bogatyrev V.N. Tumors of the female reproductive system / Ed. M. I. Davydova, V. P. Letyagina, V. V. Kuznetsova - M: MIA, 2007.
Drug treatment
With the help of conservative treatment, it is impossible to get rid of polyps; only a dulling of their growth is observed, as well as the disappearance of pathological symptoms. For cervical polyps, the following is considered justified:
- hormonal drugs;
- antibiotic therapy;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- vitamins
Treatment with folk remedies
Recipes from folk sources can be used as an additional method of therapy, in combination with drug therapy or surgery. Treatment with folk remedies for cervical polyps is not a panacea.
Nettle
Nettle is used to make tea, douches and make medicinal tampons.
To prepare tea you need 1 tsp. pour 250 ml of boiling water over the raw material and leave for 5 minutes. Take these medications 1-2 glasses a day.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of polypous formations includes the following:
- examination in a gynecological chair using mirrors;
- colposcopy;
- hysteroscopy;
- Ultrasound;
- metrography;
- microflora smear;
- clinical blood test for hormones, as well as blood test for hormones;
- clinical urine analysis;
- biopsy.
Below is how a colposcopy is done.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Does it hurt to remove
It all depends on the individual characteristics of the woman and the method of polyp removal. Discomfort may occur during the procedure and for some time after it.
Is it possible to have an intimate life?
After the operation, sexual intercourse is prohibited for 14 days.
Is it possible to cure a uterine polyp without surgery?
The main method of permanently getting rid of growths is surgical removal of the tumor.
Is it possible to get pregnant after surgery to remove
The onset of pregnancy after removal of cervical polyps (if desired) can be observed after 3-6 months.
Removal operation
Surgery to remove polyps is called a polypectomy. It is performed using a hysteroscope, which visualizes all the doctor’s actions inside the vagina and cervix.
Hysteroscopic surgery to remove the growth is considered the most common method of treatment today.
More recently, the most common method of treatment has been curettage. But this technique has a number of negative aspects.
The procedure is carried out blindly; the specialist may not completely remove the polyp, which will lead to relapse in the future. In addition, curettage is considered a rather traumatic method, so it is gradually becoming a thing of the past.
Removal can also be carried out using a laser method, which is considered minimally invasive and the most modern. The laser beam is directed at the polyp and it is precisely removed.
The procedure is safe, does not damage surrounding tissues and does not affect reproductive functions. Removal by cryodestruction, radio wave therapy, diathermocoagulation, etc. is possible.
Each treatment method has its own disadvantages and advantages. Therefore, the choice of therapy method should be approached more seriously, having discussed all the details with a specialist.
SDA second faction against the disease
ASD fraction 2 – a drug that quickly increases immunity.
Its main component is an adaptogen - a substance released by a cell before death. When it enters the human body, the adaptogen transmits a signal to damaged cells about the need for restoration, thus mobilizing protective mechanisms .
The drug should be taken orally twice a day, dissolving one cube of ASD-2 in 50 ml of water.
After a course of five days, take a break for three days, then repeat the course three more times and take a break for a month, after which the entire cycle is repeated.
For best results, it is recommended to douche every evening with a 1% solution of ASD-2.
Folk remedies
As mentioned above, treatment with folk remedies is prescribed as symptomatic therapy.
Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs and beekeeping products are widely used. The products can be intended for douching and tamponation, as well as for oral administration.
The most commonly used medicinal plants are:
- viburnum bark;
- angelica;
- hog uterus;
- aloe;
- cinnamon;
- nettle;
- bloodroot;
- caraway;
- chamomile;
- St. John's wort;
- currant leaf;
- dandelion;
- sage;
- yarrow;
- knotweed and many others.
Types and course of surgical intervention
The essence of the operation
The choice of anesthesia depends on the size of the polyp. For large tumors, general anesthesia is preferred (painkiller is delivered by injection into a vein, the patient is conscious) and hospitalization. Small polyps are removed under local anesthesia; using low-traumatic techniques, the operation can be performed on an outpatient basis.
hysteroscopy
A woman sits on a gynecological chair. A hysteroscope is inserted into the cervix - this is a tube with a light source and a camera. It allows you to accurately see the location of the polyp. Sometimes a hysteroresoscope equipped with an attachment with a cutting surface is used.
The doctor unscrews the polyp , completely removing it; if necessary, the pedicle is excised, which may be located in the thickness of the epithelial tissue (this should be visible on an ultrasound). Multiple tumors are excised. After this, curettage is performed - complete cleansing of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal and uterus. It is performed using a special instrument - a curette.
Note. A curette is a medical spoon, which is a rod with an attachment resembling a spatula or a loop with a pointed edge.
Some doctors have a negative attitude towards this practice because it is aphysiological, but most are inclined to use it because it reduces the risk of relapse. With low-traumatic removal methods and a small polyp, curettage can be abandoned.
The removed tissue and polyp are examined. It is necessary to confirm the benign nature of the tumor. Tests are prepared within 1 to 10 days.
Types of surgical treatment of polyp
Despite the same essence of the operation, technologies may differ in the method used for removal.
Main types of surgical intervention:
- Polypectomy. The neoplasm is twisted until it is completely detached from the wall of the cervical canal or truncated using a special conchotome instrument. The operation is indicated for the removal of polyps up to 3 cm in size. The bed is cauterized.
- Laser coagulation. The stalk of the polyp is excised using radiation. This method allows the vessels feeding the neoplasm to be coagulated, which minimizes the risk of bleeding. Laser coagulation is effective for removing polyps of any size.
- Cryodestruction. This way you can get rid of small polyps. The stem is frozen with liquid nitrogen, after which the polyp is removed. The method is considered low-traumatic; after its use there are no scars left.
- Diathermoexcision. This method involves destroying the base of the polyp using a loop through which an electric current is passed. There is a risk of formation of adhesions and erosions. The method is used for deformation of the cervix and dysplasia of its walls.
- Radio wave coagulation using the Sugitron apparatus. The doctor touches the leg of the polyp with an electrode; when the wave passes through the cellular structures, the latter heat up and are destroyed. When using a Sugitron generator, thermal damage is reduced by three times compared to the action of a loop with electric current.
Video: polyp of the cervical canal. Radio wave, loop polypectomy
How are polyps detected?
Neoplasms can be detected in several ways:
- During a routine gynecological examination of the vagina. This procedure is carried out using mirrors. In this case, the gynecologist is able to see any protruding formations. They are usually distinguished by color; both pink and bright red growths can appear. The shape of polypous formations can be either grape-shaped or round. When the polyp becomes keratinized (thickened and covered with stratified epithelium), its color may become white. If it is colored burgundy or purple, this may indicate a violation of blood circulation in it. Usually the structure of such a neoplasm is soft to the touch, and it itself is elastic.
- Colposcopy or cervicoscopy. Cervicoscopy is performed using a hysteroscope. The presence of a video camera makes it possible to examine even the smallest neoplasms, the focus of inflammation that has arisen near them, or, especially, ulcers around the growths. In order to exclude the presence of degeneration of the polyp into a low-quality neoplasm, a biopsy is performed during the procedure. Moreover, if the growth is small in size, then it is possible to remove it at the same time. Colposcopy is performed using a special binocular with built-in lighting.
- Diagnostics using ultrasound. If a polyp is detected in the cervical area, then its appearance is possible in the endometrium. Using ultrasound, you can obtain information not only about the thickness of the endometrium, but also about the structure of this layer. In addition, data will be obtained on the condition of both the ovaries and tubes.
Using tinctures
- Propolis. This remedy has no contraindications and can be used even during pregnancy. The tincture is diluted with water, a tampon is soaked in it and inserted into the vagina. This recipe will also help with erosion, fibroids and endometriosis . In addition, it is recommended to chew a small piece of propolis on an empty stomach.
- Golden mustache. Pour 500 ml of vodka into 50 joints of the plant and leave for 10 days, shaking occasionally. On the first day, take 10 drops of tincture per three tablespoons of water half an hour before meals, twice a day. On the second day - 11 drops, on the third day - 12 and so on up to 25 drops per three tablespoons of water. After this, the number of drops should be reduced by one daily and so reach 10 drops twice a day . Then you need to take a break for 10 days and repeat the course. In total you need to take five such courses .
- Borovaya uterus. Borovaya uterus can also be used in the form of a tincture. To do this, 30 g of dry grass is poured into 300 ml of vodka and left for a month. Take one teaspoon three times a day before meals, diluting the medicine with water. Course – month .
What should not be done after the intervention?
To ensure that the recovery process after removal of the tumor is quick and without complications, it is recommended:
- For 2 months, refrain from visiting baths and saunas, and also avoid any overheating in every possible way, as this can lead to the formation of cracks in the postoperative crust.
- Lifting heavy objects, playing sports or exercising is strictly prohibited.
- Do not use tampons - only pads.
- Planning a pregnancy should be postponed for at least 3-4 months.
- Sexual relations should be excluded for a period of 2 months.
Decidual polyp and pregnancy
The expectant mother, anxiously awaiting the birth of her baby, is very worried about the progress of her pregnancy, so any changes in the reproductive system cause well-founded concern. Polyps “do not bypass” this category of women either. During pregnancy, a very special type of formation occurs - a decidual polyp, which is nothing more than a growth of decidual tissue into which the uterine mucosa turns during pregnancy.
The powerful hormonal changes that occur after conception cause the growth of the endometrium, which will then serve as a bed for the embryo and a source of its nutrition. An excessive amount of decidual tissue can lead to its protrusion into the cervical canal, which then creates the appearance of a polypous formation. In fact, it is not a polyp itself, since it lacks a vascular pedicle (pseudopolyp), but it can cause a lot of problems for the expectant mother.
Since the tissue of the developing chorion is rich in blood vessels, any irritation, be it a doctor’s examination or physical activity, can cause bleeding, which cannot but frighten the expectant mother. In addition, such a polyp can become infected, and then inflammation and microorganisms can penetrate into the uterine cavity, where the embryo grows.
Having left the doctor with such a conclusion, there is no need to panic, because a decidual polyp is most often detected at the beginning of its appearance, of course, subject to regular visits to an obstetrician-gynecologist. Considering the possible consequences (risk of miscarriage, inflammation, bleeding), doctors prefer to get rid of such pseudopolyps without waiting for the end of pregnancy to ensure the successful formation of the fetus and childbirth later.
Preventive measures
To prevent cancer caused by the degeneration of polyps, it is necessary to undergo a gynecological examination in a timely manner. An antenatal clinic should be visited at least twice a year. Timely diagnosis will help avoid not only infertility, but also cancer.
If you experience any discharge or blood clots, you should consult a doctor. Any inflammation that occurs must be cured completely. Mechanical damage to the genital organs should be avoided when performing douching and washing. Injury can also occur during curettage or abortion.
In case of endocrine diseases, hormonal levels must be corrected with prescribed special medications. If ruptures or cracks occur during childbirth, they must be healed immediately and thoroughly.
Frequent abortions can cause growths to appear. Because of this, you should use contraception during sex. It will also allow you not to get sick during sexual intercourse with a new partner.
Menstruation should occur at a time known to the woman. If the cycle is disrupted, its normalization must be carried out immediately.
It must also be remembered that long-term use of hormonal contraception leads to various imbalances in the body.
If you are overweight, you should take care of yourself. This requires diet and exercise.
If you follow these recommendations, the appearance of polyps can be avoided.
Treatment with herbs
- Celandine. One of the most effective remedies for treating this disease. It can be used both internally and for douching, or a combination of both methods. To do this, fresh celandine grass is crushed, placed in a jar and poured with two liters of boiling water. The jar should be wrapped to keep it warm for as long as possible . The infusion is left for 10-12 hours, filtered and placed in the refrigerator. The course of treatment lasts six weeks . The first week you should take half a teaspoon daily in the morning. The second week, celandine is taken a whole teaspoon, in the third week - one tablespoon, in the fourth - two. Then the dosage is reduced back to one teaspoon per day . If necessary, the course is repeated after two to three weeks. Strictly follow the indicated dosage, since celandine is a poisonous plant .
- Geranium flatifolia. Pour two tablespoons of geranium herb into a glass of water, bring to a boil and cook covered for five minutes. Then turn off the fire and keep it covered for another half hour . Drink one glass of decoction twice a day.
- Upland uterus. A well-known remedy for all female diseases, a decoction of this plant has proven itself to be an effective way to combat polyps. Pour one tablespoon of dried herb into a glass of boiling water, cool, strain and take half a glass twice a day before meals.
- Wintergreen. In addition to treating the tumors themselves, wintergreen restores the tissue of the uterine mucosa, relieves inflammation and treats erosion. Brew two teaspoons of the herb in a thermos with a glass of boiling water and leave for 2-3 hours . During the day you need to drink the resulting decoction in small portions. Strictly observe the dosage, as in the case of celandine.
Herbal mixture, which includes:
- chamomile – 100 g;
- St. John's wort – 50 g;
- mint leaves – 50 g;
- calendula flowers – 20 g;
- hop cones – 20 g;
- white nettle flowers – 100 g;
- yarrow – 50 g;
- shepherd's purse grass – 50 g.
Pour one teaspoon of the mixture into a glass of boiling water, leave covered for half an hour, strain.
Take hot before bed every day.
Possible dangers
When polyps are detected in the uterus, it becomes necessary to remove them due to the fact that they are dangerous to the woman’s health.
Among the possible troubles that a woman may encounter are:
- Uterine bleeding. If therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, the polyp develops internal small vessels. But due to the fact that its walls do not have a dense structure, there is a possibility of injury. Because of this, bleeding may occur even in the middle of the menstrual cycle. They are completely insignificant and the woman will not notice it. But even small blood losses, when repeated systematically, “threaten” to manifest as anemia. However, large polyps when injured lead to quite heavy bleeding. It will not stop on its own.
- The possibility of conception becomes difficult. The larger the tumors, the more serious the possible problems. A fertilized egg will not be able to penetrate inside the uterus and, naturally, gain a foothold there. On its way there will be a polyp, which is a mechanical obstacle.
- Complications may also arise when carrying a child. If there are polyps, miscarriages and placental abruption may occur. The pregnancy itself may be ectopic.
- The polyp may appear as a source of infection. If a pathological agent enters the uterine cavity, then it will “begin” its destructive effect near the polyp. This effect occurs due to the fact that the polyp shell is not able to resist infection.
These possible complications can lead to major health problems for the woman. Because of this, there is a recommendation from gynecologists to remove detected formations immediately after their identification.
Possible complications
In rare cases, complications such as these may occur after polyp removal:
- Recurrence of polyposis;
- Discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse;
- Long delay of menstruation (more than 3 months);
- Copious bleeding;
- Infectious lesion of the endometrium;
- Uterine perforation (can occur after blind curettage);
- Scarring and adhesions that make conception difficult or even lead to infertility;
- Development of cancer processes (these are extremely rare cases and occur due to incomplete removal of polypous growths).
After surgery, you must regularly visit your gynecologist. Any alarming symptoms should prompt an unscheduled visit to the doctor. If complications occur, the specialist will take the correct treatment tactics. Repeated hysteroscopy is often performed, then antibacterial, hormonal and detoxification agents are prescribed.
A month after the intervention, the inner surface of the uterus is restored and endometrial regeneration occurs.
It is important to know that in the first 2-3 days after surgery, a woman’s temperature may rise. There is no need to panic, since this is a natural exacerbation of the inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes.
Often, after removal of polyps, microbial-free inflammation is observed, which is also a natural reaction of the body aimed at restoring the mucous membrane.
An additional useful video about uterine curettage and possible complications after surgery:
Removal of polyps is a radical treatment method that many patients are afraid of. But innovative methods of polypectomy are nothing more than a quick and painless mini operation. However, for isolated small formations that do not cause discomfort, it is recommended to choose a wait-and-see approach. The most important thing for a woman is to find a specialist whom she can trust with her health.
You can make an appointment with a doctor directly on our website.
Contraindications
Polyp removal is not carried out in the following cases:
- Inflammatory and infectious processes in the reproductive organs. To do this, before the operation, the woman undergoes examinations, and if inflammation is detected, the ailment that provoked it is treated, and only after that the timing of the surgical intervention can be set.
- Pregnancy - polyps are removed after childbirth and the end of the lactation period.
- Menstruation - the optimal time for removing a tumor is considered to be the 7-8th day of the menstrual cycle, although in some cases doctors recommend doing this on the 4-6th day.
- Malignant formation.
- Bleeding, including menopausal bleeding.
In some cases, the operation is limited by chronic diseases - hemophilia, diabetes, renal failure, and so on..
Tampon therapy
- Tampons with milk. To prepare such tampons, you need to take milk that has begun to sour. The milk should be heated, and when it curdles, add a little honey and crushed aloe leaves to its flakes . Place the mixture in clean gauze and form a tampon.
- Tampons with propolis. Dissolve 5 g of propolis in 100 ml of boiling water. Let it sit until it reaches a comfortable temperature, moisten the tampon with the resulting liquid, and then insert it into the vagina.
- Tampons with garlic. Chop a large clove of garlic, wrap in two layers of gauze and tie tightly. This tampon is inserted deep into the vagina before bed and left there until the morning. The procedure should be repeated every day for a month .
- A course of different tampons. On the first day in the morning, insert a tampon with baked onion gruel. In the evening, change to a mixture of finely grated fresh onions and laundry soap. The second day - in the morning and evening, insert tampons with onions and soap. The third day - in the morning - a tampon with cottage cheese, a spoonful of honey and a spoonful of aloe pulp. Repeat day and evening . The fourth day is the same as on the third.