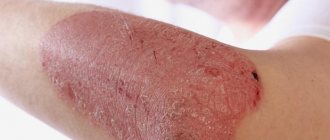
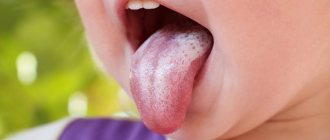
Uric acid (UA) is one of the most important markers of the state of purine metabolism in the body.
In healthy people, its level can normally increase with increased consumption of foods containing purine nucleotides (fatty meat, offal, beer, etc.). A pathological increase may be associated with the breakdown of cellular deoxyribonucleic acid after taking cytotoxic drugs, widespread malignant tissue damage, severe atherosclerosis, cardiovascular pathologies, etc.
If uric acid in the blood is elevated, the risk of developing a common pathology, which is also called “the disease of kings” (due to the consumption of expensive fatty foods) increases significantly - this is gout.
That same bump on the foot in the area of the big toe. For reference. The level of uric acid is one of the most important markers in the initial diagnosis of gout and subsequent monitoring of the course of the disease.
What is uric acid
The substance is formed in the body as a result of the exchange of purine bases. The latter are compounds of organic nature, components of deoxy- and ribonucleic acids. They can be of endo- and exogenous origin (that is, come from outside or form inside the body). Without purines, a macroorganism cannot exist, since the bases are involved in the encoding of genetic information and its implementation for the synthesis of proteins.
Purine bases are constantly broken down and synthesized anew. Uric acid is formed from the degradation of purines. The compound is produced by the liver under the action of the enzyme xanthine oxidase. The plasma concentration of uric acid depends on the rate of its elimination (removal), the amount of purines, and the rate of their processing. The human body produces from 570 to 1000 mg of uric acid per day.
About a third reaches the intestines, where it is consumed by bacteria. Microorganisms process it to form ammonia and carbon dioxide. The remainder travels through the bloodstream to the kidneys. After passing through the filtration system, a significant amount of the substance is reabsorbed back. About a quarter of all filtered uric acid ends up in the urine (some sources say only 10%).
There are 2 forms in the blood: dissociated and non-dissociated. The second form is poorly soluble, can penetrate into body tissues (articular, muscle, subcutaneous, brain) and form crystals. Such phenomena occur more often at night when the concentration of urates (uric acid salts) increases.
Means and preparations for normalizing uric acid levels
What to do when you find elevated uric acid levels? In many cases, it is enough to use natural remedies or follow dietary recommendations.
When hyperuricemia is associated with pathology, diet or herbal medicine will not be enough to reduce the level of uric acid in the blood and urine and drug therapy will be required.
Natural remedies to normalize uric acid levels
Two plants are used to reduce the concentration of uric acid:
Ash: This plant contains many active substances, including phrasins, coumarins, flavonoids, malic acid, tannins and polyphenols. They help metabolize purines and therefore stimulate the excretion of uric acid.
The bark and leaves are used in the form of:
- capsules, dosage is two capsules twice a day
- tincture, dosage – 30 drops three times a day
- infusion, simply brew about 8 g of ash leaves in a cup of hot water, strain and drink.
Birch: The active compounds in birch, including hyperosides, tannins, caffeic acid and triterpene alcohols, help against hyperuricemia.
Birch leaves and bark are used in the form of:
- capsules, it is recommended to take two capsules after meals, twice a day
- juice concentrate, recommended to take 40 drops twice a day
- infusion, brew two tablespoons of dried birch leaves in warm water, leave to infuse for a quarter of an hour, and then strain and drink when you want.
Diet: What to Eat and Avoid for High Uric Acid Levels
Proper nutrition is important to prevent the buildup of uric acid in the blood. Some foods help clear the body of uric acid buildup, while other foods promote the buildup.
Foods to Avoid: All foods that are high in purines. This includes offal, meat broths and extracts, herring, mackerel, caviar, eggs, shellfish, mussels, and game. All alcoholic drinks are prohibited.
Foods to limit: These are foods that have a medium purine content, i.e. white meat, sea bass, halibut, trout and hake. You should limit some types of vegetables, such as bell peppers, peas, asparagus, cauliflower and lentils, and some types of fruits, such as watermelon, chestnuts, loquats and almonds.
Preferred foods: those that are low in purines. Among them we have milk and dairy products, eggs, pasta, rice, cheeses (mozzarella, ricotta and scamorza), vegetables such as beets, potatoes, tomatoes, turnips, lettuce and endive, and fruits such as apricots, apples, peaches, pears and cherries.
Drug therapy for elevated uric acid levels
Drug therapy is used only in cases where elevated uric acid levels determine the onset of diseases such as gout, or when it is a consequence of another pathology.
The most commonly used medications are:
- Allopurinol: It affects the synthesis of uric acid, blocking its production and therefore helping to reduce concentrations.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: medications that are used to treat acute inflammatory conditions, including those caused by the deposition of uric acid crystals. However, they have many side effects, in particular, a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
- Paracetamol: is an effective pain reliever that can counteract pain caused by inflammation.
The role of uric acid in the body
The substance is an important product of metabolism, thanks to which excess purines can be successfully removed from the bloodstream. Its main task is to remove ammonia, which is toxic to all living cells.
The circulation of the compound in the blood is also not wasted. In tissues, uric acid stimulates the sensitivity of cells to neurotransmitters and prolongs the effect of certain hormones. The antioxidant property of the substance was confirmed by research. It can be a “trap” for free radicals, prevent the degeneration of cells into malignant ones and, thus, inhibit the development of serious pathologies. Moreover, there is a theory about the role of the compound in protecting the brain from multiple sclerosis.
The negative properties of uric acid are associated with its poor solubility. Only 70 mg of the substance can be dissolved in 1 liter of liquid, and much more is formed in the body. This means that the less urine a person produces, the higher the risk of acid levels rising above normal. This process is dangerous due to the deposition of urates in tissues.
The immune system perceives microscopic salt crystals as bacteria, activating phagocytes and other protective cells against them. As a result, chronic inflammatory processes develop. The most famous and common disease associated with disorders of purine metabolism is gout (read more about the disease in the article “Gout”).
Serum creatinine
Changes in the amount of creatinine produced by the kidneys occur only in cases of advanced pathology. Normally, its concentration remains virtually unchanged and is 0.044-0.100 mmol/l for healthy men and 0.044-0.088 mmol/l for women. A persistent increase in blood creatinine levels, like elevated urea levels, indicates kidney dysfunction and can be assessed as an early sign of kidney failure. Also, the creatinine content increases with the pathologies listed for urea - with the exception of prostatitis. A decrease in creatinine levels in the blood has no diagnostic value.
Analysis for uric acid and its interpretation
The level of the substance can be determined as part of a biochemical blood test. The test is prescribed for diagnostic and preventive purposes, during medical examination. Biochemistry reflects not only the level of uric acid, but also other important characteristics of the blood. Separately, the concentration of the substance is determined in individuals with gout. Indications for regular blood tests are:
- diabetes;
- thyroid diseases;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- kidney disease;
- failure of internal organs (heart, kidneys, liver).
The level of uric acid can vary widely, depending on gender, age, diet, metabolic activity, the presence of chronic diseases, and also on the time of day (higher in the morning than in the evening). The generally accepted limits of normal are indicated below.
Table - Physiological indicators of uric acid in the blood
| Population category | Norm, µmol/l |
| Children under 14 years old | 120‒320 |
| Adult women | 150‒350 |
| Adult men | 210‒430 |
| Women over 60 | 210‒430 |
| Men over 60 | 250‒480 |
| Women over 90 | 130‒460 |
| Men over 90 | 210‒490 |
An increase in the concentration of uric acid above the permissible norm is considered a sign of metabolic disorders. The term hyperuricemia is used to refer to the condition.
In order for the results of a biochemical test to be accurate, you need to prepare for the analysis. You should come to the laboratory in the morning. For the study, venous blood (up to 10 ml) is taken using a sterile syringe or vacutainer. Preparation conditions:
- medications are stopped a week in advance (except for vital ones);
- for 3 days, adhere to the usual diet, but do not abuse meat, fish, mushrooms, legumes, or alcohol;
- during the day you need to avoid stress and excessive physical activity;
- 9-12 hours in advance you must stop consuming any food and drinks except clean water;
- In the morning, only water is also allowed;
- It is better not to smoke half an hour before donating blood.
It is important to note that uric acid levels may be falsely elevated. The prerequisites for this are psycho-emotional and physical stress, abuse of sources of purine bases (legumes, meat, fish, broths, mushrooms), and alcohol. Incorrect test results may be obtained due to the use of medications:
- NSAIDs (Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, Piroxicam);
- diuretics;
- beta blockers;
- anabolic steroids;
- ethacrynic acid;
- Isoniazid;
- Cyclosporine;
- Caffeine;
- Ascorbic acid;
- Aspirin.
The biochemical test takes about a day. Some laboratories provide results within a few hours. It is better to entrust the study of the study protocol to a doctor, because not only the fact of the presence of deviations from the norm in the level of uric acid is important, but also the combination with other disorders of blood characteristics.
If you have signs of hyperuricemia, you should see a physician. The child needs to be shown to a pediatrician. Pregnant women should pay special attention to their uric acid levels. An increase can be a sign of preeclampsia, so you should not hesitate to consult a doctor.
Symptoms of increase
The condition of elevated blood uric acid is called hyperuricemia. The main manifestations of this phenomenon are associated with the cause that caused the growth of acid - a symptom complex typical of the “main” disease is observed.
But uric acid metabolism disorders also have some of their own symptoms:
- The appearance of tartar.
- Chronic fatigue syndrome.
- Weakness, very easy fatigue.
- Skin problems.
- Joint pain.
- Digestive disorders.
- Muscle spasms, myalgia.
- Sleep disorders.
- Neuroses, nervous breakdowns.
- Stroke.
- Varicose veins.
- Rheumatism.
- Headache.
- Decline in cognitive abilities due to brain dysfunction.
Gout is considered a very clear sign of hyperuricemia. With it, uric acid crystals settle in the bones and joints. In children, excess uric acid manifests itself as diathesis - red spots on the hands and skin of the cheeks.
If the patient does not pay attention to these phenomena, then a further increase in the concentration of acid molecules contained in the blood will lead to damage to the central nervous system due to general intoxication of the body, and if help is still not provided, there is a possibility of death of the patient.
In addition to negative manifestations, this condition also has a positive effect, no matter how strange it may seem.
Products of purine metabolism that enter the blood in increased quantities can have beneficial effects:
- uric acid is chemically similar to one of the caffeine compounds, due to which patients in the acute stage of hyperuricemia can experience a state of increased performance. In the 60-70s, large-scale studies were conducted, the results of which showed an increase in reaction speed and intellectual abilities in such patients;
- the compound is a natural antioxidant;
- It also has a powerful neuroprotective effect, due to which in some cases it can even reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
However, it is important to understand: the positive effect appears only against the background of acute hyperuricemia, which was compensated in a timely manner. A chronic state of increased acidity causes severe negative consequences.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/yuRX8Q4eStA
What symptoms might there be?
Hyperuricemia is a laboratory concept and not an independent disease. When the level of uric acid in the body increases, 10% of patients have no symptoms at all, and disorders are discovered by chance. Initial deviations do not have obvious symptoms. Metabolic changes occur due to the adverse effects of urate deposition in the body. Signs may be:
- general weakness, drowsiness, fatigue;
- joint pain, feeling of stiffness in the morning;
- decreased range of motion of the limbs;
- hyperemia (redness) of the skin over the affected areas;
- changes in blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- decreased volume of urine excreted;
- sediment in urine;
- plaque on teeth;
- muscle pain;
- spots and sores on the skin.
Manifestations of hyperuricemia are often complemented by symptoms of a disease that has led to the accumulation of uric acid in the body.
Uric acid levels are normal for men and women
Normally, the content of uric acid in the body is determined at the genetic level, that is, it is transmitted from parents. It is believed that individuals whose concentration is relatively high are characterized by greater activity.
Normal analysis numbers (in µmol/l):
- men – 200-420;
- women – 160-320;
- elderly people (after 65 years) – up to 500;
- newborn babies –140-340;
- young children – 120-300;
- children under 15 years old - 140-340.
On average, about 1 g of uric acid is constantly present in the body of a healthy adult, and one and a half times more is released every day! It is able to bind acidic radicals, providing cell protection from these toxic compounds. Thanks to antioxidant activity, malignant degeneration of cellular elements is prevented. Uric acid activates adrenaline and norepinephrine, which helps stimulate the activity of the central nervous system.
Reasons for the increase
An increase in the concentration of uric acid means its excessive formation (with active metabolism of purine bases) or impaired utilization (the kidneys cannot cope with such an amount). The reasons may be the characteristics of a person’s lifestyle:
- constant stress, prolonged depression, psycho-emotional exhaustion;
- hunger, adherence to strict diets (mainly protein);
- regular meals with fatty meat and fish dishes;
- alcoholism;
- excessive physical activity (for example, among professional athletes).
In all of these cases, uric acid is formed in large quantities, and the kidneys do not have time to remove it. The substance is also actively synthesized against the background of excessive destruction and formation of purine bases, which is observed with massive death of body cells. Such disorders are based on tissue destruction and an increased need to recreate the genetic material of cells. When purines are transformed, uric acid is released. Hyperuricemia accompanies:
- malignant diseases (leukemia, myeloma, lymphoma, tumors of internal organs, metastatic cancer);
- chemo- and radiation therapy of intractable pathologies;
- psoriasis and eczema in the acute phase;
- pneumonia;
- tuberculosis;
- extensive burns and purulent-necrotic processes;
- hemolytic and B12-deficiency anemia.
Endocrine diseases, in which specific types of metabolism or metabolism in general are affected, can provoke the accumulation of uric acid. Serious disorders in the body are caused by diabetes mellitus, obesity and hyperlipidemia (cholesterol metabolism disorders, atherosclerosis), hypoparathyroidism and hypothyroidism (decreased function of the thyroid and parathyroid glands), Down and Lesch-Nyhan syndromes, pathologies of the liver and gall bladder.
Disturbances specifically in purine metabolism are observed in gout, and an increase in the concentration of uric acid acts as a mechanism for the development of gouty arthritis. Pathology is more often observed in men than in women.
Useful information: Urobilinogen in urine is increased: what does this mean, reasons, norms for adults and children. What is the danger of the condition
Kidney pathologies can also cause hyperuricemia. Actually, doctors try to exclude them first if deviations of uric acid from the norm are detected. Failure of kidney function is caused by:
- acute alcohol poisoning;
- intoxication with salts of heavy metals (lead, arsenic);
- polycystic kidney disease;
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- acute and chronic renal failure;
- arterial hypertension, starting from stage 2;
- urolithiasis (and hyperuricemia is its cause and consequence).
When the rate of blood filtration through the kidneys decreases, uric acid is released in small quantities. Given significant reabsorption and poor solubility, its concentrations in the blood increase significantly.
What are the dangers of excess uric acid?
During the reaction of acid with water and sodium, poorly soluble compounds are formed - urates. They tend to precipitate when the temperature decreases and the environment becomes acidic. Their accumulation in joint tissues provokes the development of gouty arthritis. The “trigger” of this process is often local or general hypothermia. Urates are perceived by the immune system as foreign particles, and it tries to destroy them. But at the same time, the own joint tissues are damaged, resulting in the development of an inflammatory process with alternating phases of remission and exacerbation.
Sodium salts enter the kidney tubules, where over time urate stones form, which can obstruct the ureters and cause renal colic. Salt deposits can also form in the gastrointestinal tract and muscle tissue.
In the kidneys, uric acid is actively formed due to alcohol abuse, so binge drinking provokes exacerbations of gouty arthritis. This compound can also be synthesized in the liver during the metabolism of individual sugars.
A decrease in the pH of the body is observed in patients with diabetes, as well as in athletes (active physical exercise causes an increase in the level of lactic acid - lactic acidosis).
note
Hyperuricemia is often detected in girls who are overly addicted to restrictive diets.
How to remove uric acid
Treatment of hyperuricemia depends entirely on the underlying disease. As the pathology is eliminated, its symptoms will subside and laboratory tests will return to normal. Therapy aimed specifically at reducing uric acid levels will be required for metabolic disorders, when the concentration of the substance increases due to metabolic failures, poor nutrition or poor lifestyle, as well as endocrinopathy. To normalize the patient’s blood composition, an integrated approach is required. It includes:
- dietary nutrition;
- lifestyle correction;
- drinking enough liquid;
- taking medications.
Doctors resort to medications as a last resort when other measures do not have an effect or hyperuricemia is provoked by serious diseases. Alternative methods can also be used as part of complex therapy.
Diet
Correction of uric acid levels in the blood begins with reducing the level of intake from outside. If the patient is overweight, the Pevzner diet 8 is indicated; if the patient is of normal body weight, diet table 5 is prescribed. The diet should be balanced, with normal or reduced calorie content and a minimum content of purine bases. Their main sources were mentioned above, but other dangerous foods will also need to be excluded from the diet:
- offal (liver, brains, stomach, kidneys);
- canned food (fish and meat);
- fatty fish (river and sea);
- salted, smoked fish, caviar;
- beef, pork, lamb, chicken, duck, goose;
- sausages (any smoked meats, boiled sausage, frankfurters, ham);
- marinades and pickles;
- sauces, spices, pepper;
- mushrooms in any form;
- alcohol, coffee, strong tea, sweet soda;
- chocolate and cocoa;
- salted cheeses;
- legumes (chickpeas, peas, beans, beans, lentils);
- sweet and puff pastry;
- spinach, cauliflower, sorrel, tomatoes, rhubarb, horseradish;
- raspberries, figs
The diet is based on low-fat dairy products, vegetables, fruits, and a moderate amount of cereals. It is preferable to prepare dishes by boiling or steaming; vegetables can be grilled or baked. Meat (turkey, rabbit), fish (perch, pike perch) and seafood are consumed exclusively in boiled form (can be baked after boiling), no more than 3 times a week.
You can eat eggs (1 per day), fermented baked milk, sour cream, cottage cheese, kefir, low-fat and unsalted cheeses. Salt is added in a minimal amount. Among the vegetables, carrots, beets, pumpkin, cucumbers, potatoes, zucchini, dill, broccoli, and avocado will be especially useful. Among the fruits you should prefer are citrus fruits, apples and pears, currants, gooseberries, watermelon, apricots, and cherries. Marmalade, natural marshmallows, jelly, and jelly are allowed as desserts.
Drinks allowed include herbal teas, rosehip infusion, and compotes without added sugar. Doctors recommend creating a menu based on liquid and semi-liquid dishes (vegetarian soups, slimy porridges) of raw and cooked vegetables. It is important to drink enough water. With normal kidney function, the daily volume of fluid is increased to 3 liters.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine recipes should be discussed with your doctor. If uric acid metabolism disorders are caused by serious diseases, herbal medicines can only serve as an auxiliary method for correcting blood composition. Diet and medications will have the main effect. However, when the level of the substance is elevated due to diet or poor lifestyle, alcohol abuse, medicinal plants will help to quickly remove urate from the body.
Table - Folk remedies against hyperuricemia
| What to use | How to cook | How to use |
| Lingonberry leaves | Pour 200 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of raw materials and leave covered for 35 minutes. | Drink the entire prepared volume at once, three times a day, half an hour before meals. |
| Apple | Get the juice, quickly fry the slices in butter, add to the liquid | Drink in small sips, then eat slices |
| Nettle | Pluck the tops of the shoots, pass through a meat grinder, extract the juice from the mass | Take 5 ml three times a day, before meals |
| Grape shoots | Collect the “whiskers”, chop finely, pour a teaspoon of the mixture with a glass of hot water, simmer over low heat for 7 minutes, leave for 30 minutes | Take 50 ml 4 times a day, before meals |
| Wild carrots | Pour 1 glass of boiling water over 1 umbrella, leave for an hour | Take ¼ cup 4 times a day |
| Birch leaves | Pour 20 g of raw material with a cup of boiling water, simmer for 20 minutes in a water bath, leave for half an hour | Drink 50 ml 4 times a day |
Drug treatment
A doctor should prescribe medications to correct purine metabolism after understanding the mechanism of origin of the abnormalities. The names below are provided for informational purposes only. Each drug has a list of contraindications and side effects, and if used incorrectly, it can cause harm to health. Drug treatment of hyperuricemia is carried out using:
- medications that inhibit xanthine oxidase (Allopurinol, Uriprin, Apurin, Uridoside);
- blockers of purine metabolism enzymes (Benzobromarone, Dizurik, Urinorm);
- stimulators of uric acid excretion by the kidneys (Sulfinpyrazone, Pirocard, Sulfazon);
- reabsorption blockers (Etamide).
Doses are selected individually, focusing on the causes, degree of deviation, weight and age of the patient.
How to treat hyperuricemia?
The main way to combat high uric acid levels is through a restrictive diet.
It is advisable to exclude the following products from the diet:
smoked meats (both meat and fish);
- fatty meat (especially lamb);
- salo;
- liver;
- kidneys;
- canned food;
- sausages;
- marinades and pickles;
- strong broths;
- seasonings and spices;
- mushrooms;
- beans;
- peas;
- sorrel;
- cream cakes;
- store-bought juices;
- sweet sodas;
- chocolate.
The following products are allowed:
- eggs (soft-boiled, and no more than 1 piece per day);
- boiled chicken;
- weak broths;
- vegetable oils (preferably olive);
- green tea;
- any vegetables;
- fruits;
- rye bread with bran;
- dry biscuits (biscuits);
- hard cheese;
- cottage cheese;
- kefir;
- rosehip decoction;
- fresh juices;
- weak coffee with milk.
Once a week, it is advisable to arrange fasting days, consuming only kefir + cottage cheese or fruit.
If the diet is ineffective, and exacerbations of gout periodically make themselves felt, pharmacotherapy is prescribed.
The most effective drugs against hyperuricemia are:
- Allopurinol;
- Colchicine;
- Benzobromarone;
- Sulfinpyrazone;
- Blemaren.
note
The drug Blemaren optimizes the process of dissolving uric acid stones in the kidneys and urinary tract. The dosage and duration of course therapy are determined by the attending physician. During the treatment period, periodic monitoring of the acid-base status of urine is required. The delivery set of the drug includes an indicator for its determination. Absolute contraindications to taking Blemaren are circulatory failure and chronic renal failure.
The listed drugs must be taken in long courses. Dosages are determined individually by the attending physician.
note
The level of uric acid falls while taking birth control pills, the antibiotic Azathioprine, antilipemic drugs (Fenofibrate and Clofibrate) and the antipsychotic Chlorprothixene. Probenetsi is also capable of reducing its concentration (by stimulating the excretion of the substance by the kidneys).
Traditional medicine recommends decoctions and infusions of strawberry and currant leaves, knotweed herb and blueberry fruits (berries).
Plisov Vladimir, doctor, medical observer
16, total, today
( 38 votes, average: 4.71 out of 5)
Monoblastic leukemia: symptoms and treatment
Increased hemoglobin in women: what does it mean and what to do
Related Posts
FAQ
Question: Are uric acid and urea the same thing?
Answer: No, these are different products of protein metabolism. Both serve to remove nitrogenous substances from the body. However, urea does not perform any functions in the body, is easily excreted, and does not cause harm even with a significant increase in concentration above the norm.
Question: Why is gout called the “disease of kings”?
Answer: Because representatives of high society were previously predisposed to this disease, who did not deny themselves tasty food (in particular, meat and fish), and regularly drank alcohol. Another popular name for gout is “the disease of the well-fed and intoxicated.”
Question: If there are abnormalities only in uric acid, but everything else is normal, should I go to the doctor?
Answer: It all depends on the degree of deviation. If the indicator significantly exceeds the norm, you need to contact a specialist. If it is several units, the culprit may be stress or a morning run.
Question: Why are men more prone to gout than women?
Answer: Metabolism in the female body is slower than in the male body, and therefore more stable. It is largely controlled by hormones. The male half of humanity exposes itself to significant stress, more often violates the diet and drinks alcohol, hence the predisposition to gout. But we must not delude ourselves. A woman who likes to drink a couple of liters of beer, eats herring and fried meat, and eats rolls for dessert has a similar risk of developing obesity and other metabolic disorders.
Question: What drugs can quickly remove uric acid if I am sure that the reason for the increase is diet?
Answer: It is better to switch to a balanced diet. You can take a diuretic (Trifas, Hydrochlorothiazide, Indapamide). At the same time, we must not forget about drinking a large amount of liquid, with which the metabolic product will come out.
When does uricosuria occur?
You should not immediately panic when you detect elevated uric acid. It is necessary to understand the temporary causes of uricosuria, and only after ruling them out, think about possible diseases.
Diet
In addition to pathological conditions, the cause of uricosuria most often lies in the patient’s diet. This is facilitated by the consumption of high-protein foods that contain many purine compounds. These include:
- meat, especially young animals;
- offal (kidneys, liver, brains);
- tomatoes;
- legumes;
- fish, especially canned fish;
- greens, especially spinach;
- mushrooms;
- seafood;
- smoked products, marinades;
- pickles;
- chocolate, cocoa;
- coffee and black tea;
- alcohol.
Physiological factors
In addition to diet, there are a number of physiological prerequisites for uricosuria:
- male gender;
- Negroid race;
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating);
- starvation;
- regular strong physical activity.
Such uricosuria disappears after lifestyle correction.
Taking medications
Increased excretion of urate in the urine can result from taking certain medications:
- cytostatics;
- beta blockers;
- thiazide diuretics;
- Theophylline;
- some antibiotics.
If the patient is taking any medications and his uric acid concentration is elevated, you need to tell the doctor about it. Perhaps he will recommend canceling the appointment and retaking the test for uric acid levels.
Diseases that lead to uricosuria
The pathological causes of increased uric acid are as follows:
- Pathology leading to dehydration of the body contributes to the concentration of urine and, accordingly, the occurrence of uricosuria. This is prolonged diarrhea, persistent vomiting, febrile temperature, as symptoms of infectious diseases, preeclampsia in the second half of pregnancy.
- Disturbance of renal blood flow due to abnormalities in the development of blood vessels, their atherosclerosis, thrombosis, embolism, kinking of the arteries during nephroptosis.
- Gout is a metabolic disorder that is characterized by persistent hyperuricemia, uricosuria, as well as damage to the joints, kidneys, and soft tissues, where urates are deposited, causing inflammation.
- Urolithiasis and dysmetabolic urate nephropathy.
- Inflammatory kidney diseases such as glomerulonephritis. Urinary tract infections (pyelonephritis, cystitis), the symptoms of which are fever, chills, frequent and painful urination, vomiting, changed color and odor of urine.
- Renal failure (end stage), when the kidneys become unable to maintain urine pH at normal levels. Acidification of urine leads to precipitation of urate crystals.
- Diabetes.
- Leukemia.
- Malignant neoplasms of different localizations.
- Chronic purulent diseases: abscess, osteomyelitis.
- Viral hepatitis.
- Down syndrome.
- Cystinosis.
- Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
- Sickle cell anemia.
The list of diseases is quite large, so if you detect an increased level of uric acid in the urine, you should immediately consult a doctor to determine the cause.
conclusions
- Uric acid is the end product of purine base metabolism, enters the body with food and is formed internally.
- The substance is formed under the action of a liver enzyme.
- The main reasons for the increase in the concentration of the compound: rapid purine metabolism and delayed excretion of metabolites by the kidneys.
- The average level of uric acid in the blood is 160‒400 µmol/l.
- If the indicator is high, then there is a risk of developing gout or urolithiasis.
- To reduce uric acid levels, you need to adjust your diet and drink enough clean water. Serious diseases are treated by a doctor using special medications.
Excessive formation and subsequent deposition of uric acid in the joints leads to gout. The disease has a hereditary predisposition and is more common in men. A characteristic symptom is unbearable pain in the joints, especially the first toe. Read more about symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and diet in the article “Gout.”
Diet for hyperuricemia
Low-calorie diet (table No. 5 is best if the patient is okay with his weight), meat and fish - without fanaticism, 300 grams per week and no more. This will help the patient reduce uric acid in the blood, live a full life, without suffering from attacks of gouty arthritis. Patients with signs of this disease who are overweight are recommended to use table No. 8, remembering to unload every week, but remember that complete fasting is prohibited. Lack of food at the very beginning of the diet will quickly raise the level of sUA and exacerbate the process. But you should seriously think about additional intake of ascorbic acid and B vitamins.
All days while the exacerbation of the disease lasts should proceed without eating meat and fish dishes. Food should not be solid, however, it is better to consume it in liquid form (milk, fruit jellies and compotes, juices from fruits and vegetables, soups with vegetable broth, porridge “smear”). In addition, the patient should drink a lot (at least 2 liters per day).
It should be borne in mind that a significant amount of purine bases is found in such delicacies as:
- Brains, thymus gland;
- Liver (primarily beef);
- Tongue and kidneys (also taken from cattle);
- “Young” meat (veal, chicken);
- Fatty meat (regardless of the type of animal);
- Smoked meats of any kind;
- Canned food in oil (sprats, sardines, herring);
- Cool rich fish and meat broths.
- Fresh peas, lentils, beans;
- Mushrooms, especially dried ones;
- Spinach, sorrel;
- Brussels sprouts;
- Coffee and cocoa.
On the contrary, the minimum concentration of purines is observed in:
- All dairy products, starting with milk itself;
- Poultry eggs;
- Caviar (oddly enough);
- Potatoes, salad, carrots, cucumbers;
- Bread products;
- Cereals of all types;
- Any nuts;
- Oranges, plums, apricots;
- Pears and apples.
This is a short list of foods that are prohibited or allowed for patients who detect the first signs of gout and elevated uric acid in a blood test. The second part of the list (milk, vegetables and fruits) will help reduce uric acid in the blood.
Primary hyperuricemia
Primary hyperuricemia is a congenital, or idiopathic, form. Approximately 1% of patients with primary hyperuricemia have a fermentation defect in purine metabolism. This leads to excess synthesis of uric acid.
Most often, primary hyperuricemia is congenital and can be associated with conditions such as:
- Kelly-Siegmiller syndrome;
- Lesch-Negan syndrome;
- increased synthesis of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase (inborn error of metabolism).
It should be noted that the congenital form of hyperuricemia is rare.
Elevated uric acid: treatment with medications
Treatment with drugs should only be carried out as prescribed by a doctor. The drug method of removing uric acid is carried out under the supervision of a specialist who will regularly prescribe appropriate tests.
To cleanse the body, the doctor prescribes diuretics that remove uric acid. Next, medications are prescribed that inhibit the synthesis of this product, usually Allopurinol or its analogues. To achieve the effect, strict adherence to the medication regimen is required for four weeks or more. The doctor may also consider it necessary to prescribe preventative medications, for example, Koltsikhin.
Normal blood content
Depending on the gender and age of a person, the normal level of uric acid in the blood is calculated. So, in children under 14 years of age, this figure should be in the range of 120-320 µmol/l.
For men under 60 years old - from 250 to 400 µmol/l, from 60 years old - from 250 to 480.
The indicator for women under 60 years old is from 200 to 300 µmol/l, from 60 years old – from 210 to 430.
It is worth noting that not only high uric acid is harmful to health, but also its low level.
Traditional methods of treatment
How to reduce the level of uric acid in the blood with gout? This is the main goal of complex treatment, since it is not enough to relieve the clinical manifestations of the disease with the help of symptomatic medications. An increase in uric acid levels over time leads to the deposition of urate salts and progression of the disease.
In order to quickly and effectively achieve normalization of hyperuricemia, it is necessary to establish the reasons that provoked the development of pathological accumulation of uric acid in the body. After all, salts can accumulate for two main reasons - their increased synthesis and diseases of the kidneys and other organs, as a result of which they are poorly excreted.
To reduce uric acid levels, 2 groups of drugs are used:
- Preparations that promote the rapid removal of salts from the human body. The most commonly used are Probenecid, Sulfinpyrazone, Benzobromarone, etc. A correctly prescribed dose of medication will help stabilize the level of uric acid in the blood plasma.
- Drugs that affect the process of urate production. They slow down the breakdown of purine compounds to final breakdown products, as a result of which its level in the blood plasma decreases. This reduces the likelihood of its accumulation in tissues, joints, and other organs in the form of salts. These drugs include Allopurinol, Allomaton, etc.
The goal of treatment is to reduce the level of uric acid in the blood plasma to no more than 310 µmol/l in women, 420 µmol in men and 350 µmol in children.
The development of the disease is often provoked by hyperuricemia. Treatment for gout is aimed at restoring fluid levels to normal.
The changes that occur in the body during hyperuricemia do not occur asymptomatically. The patient is recommended to consult a doctor who will prescribe a diagnosis.
You can reduce the level of uric acid in the blood using folk remedies. Many medicinal plants have shown sufficient effectiveness in the fight against this pathological condition.
Artichoke is one of the best foods to reduce uric acid. The vegetable has a pronounced diuretic effect. Artichokes are eaten boiled and the remaining vegetable broth is drunk.
Apples are also considered a fruit that is beneficial for gout. The fruits contain a large amount of pectins, which bind and remove uric acid from the intestines.
Diet can rightfully be considered the basic basis of this treatment.
Its specificity lies in the following points:
- it is necessary to avoid foods containing purine;
- limit the amount of smoked food;
- Avoid eating salty foods in large quantities;
- stop drinking alcoholic beverages.
Diet rules are important aspects for treating high uric acid in the blood. In combination with a diet, you should take medications that remove uric acid from the body; this approach will allow you to achieve the most effective result. Drug therapy is prescribed for any manifestations of the disease, based on the results of a complete diagnostic examination.
Its action should be aimed at achieving the following goals:
- getting rid of symptoms and manifestations of the disease;
- treatment of different stages of gout;
- treatment of chronic disease states.
Drug therapy is prescribed by the treating doctor. Throughout the treatment, it is necessary to be observed by a specialist and adjust the direction of treatment.
After a diagnostic examination and diagnosis, the attending physician prescribes drug therapy, taking into account all the individual characteristics and specific manifestations of the disease. Medicines for high uric acid are aimed at relieving symptoms, treating the root cause and using preventive measures. An important factor is also the correction of possible pathologies.
Gout has periods of exacerbation, during which time anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, which are aimed at relieving acute manifestations and symptoms. For this, the following drugs are prescribed: Diclofenac, Voltaren, Butadione. Additionally, gels and ointments are used to reduce pain.
Basic principles of the influence of drug treatment during acute attacks of gout:
- Non-steroidal drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect are prescribed.
- Additional folk remedies that have a natural basis and have a beneficial effect on the body.
- You should take medications that reduce the level of uric acid in the blood, with their help you can prevent relapses of the disease.
Medicines and their dosages are prescribed by a specialist and take into account all the characteristics of the body.
A medicine or medication that lowers uric acid in the blood can either help or harm the body. It is important to control the level of uric acid, otherwise needle-like crystals will form in the tissues, which bring severe discomfort and acute pain. Their accumulation and proliferation leads to serious pathologies and changes.
Uncontrolled uric acid levels can lead to the following pathological manifestations:
- formation of tophi;
- acquisition of chronic forms of the disease;
- damage to blood vessels and capillaries;
- modification of joints;
- blood pressure surges;
- deformation of connective tissues;
Failure to treat this disease can lead to various pathologies, as well as render vital systems unusable. That is why it is so important to follow all the specialist’s recommendations and follow all the basic rules of treatment.
The disease can be prevented if you follow the following main recommendations:
- Adjust your diet and include a complex of vitamins and microelements in your daily menu.
- Include light physical activity in your daily plan, which helps increase vitality.
- Drink plenty of liquids and decoctions of medicinal herbs.
- Massage and self-massage are an effective technique for complete recovery. Joints need careful care, so devoting 10-15 minutes a day to your body can achieve good results.
- Avoid unnecessary worries and stressful situations, lead a calm, measured lifestyle.
Comprehensive and timely therapy, as well as taking preventive measures, will save the body from unpleasant diseases.
Experts say gout can be cured. Excessive amounts of uric acid can be removed from the body using medications and traditional medicine methods.
Complex therapy can restore lost strength and return the functioning of all vital systems to normal. Achieving effective reduction of uric acid levels is the main goal of gout treatment.
Decoding the analysis results
Normally, the content of uric acid in the body is determined at the genetic level, that is, it is transmitted from parents. It is believed that individuals whose concentration is relatively high are characterized by greater activity.
Normal analysis numbers (in µmol/l):
- men – 200-420;
- women – 160-320;
- elderly people (after 65 years) – up to 500;
- newborn babies –140-340;
- young children – 120-300;
- children under 15 years old - 140-340.
On average, about 1 g of uric acid is constantly present in the body of a healthy adult, and one and a half times more is released every day! It is able to bind acidic radicals, providing cell protection from these toxic compounds. Thanks to antioxidant activity, malignant degeneration of cellular elements is prevented. Uric acid activates adrenaline and norepinephrine, which helps stimulate the activity of the central nervous system.
Direct causes of increased uric acid concentrations include:
- high level of dietary protein intake (source of purines);
- decreased excretory activity of the kidneys;
- increased synthesis of the substance in the liver;
- pneumonia;
- rhabdomyolysis;
- polycythemia vera;
- hemolytic anemia;
- psoriasis.
note
Diseases that cause hepatic and renal dysfunction include pyelonephritis, nephrosis; hepatitis, cirrhosis and diabetes.
Indirect causes of hyperuricemia;
- leukemia;
- hypovitaminosis of group B (especially B12);
- metabolic disorders (overweight, obesity);
- hypofunction of the parathyroid glands;
- metabolic acidosis (including with gestosis in pregnant women);
- carbon monoxide, ammonia or lead poisoning;
- long-term use of certain pharmacological agents (diuretics, salicylates, antitumor and antituberculosis drugs);
Uricemia increases with smoking (which is caused by tissue hypoxia), as well as with insolation (cells need additional protection from free radicals formed under the influence of ultraviolet radiation).
In expectant mothers, the level of the substance decreases in the first and second trimesters, and increases in the third.
It is noted that hyperuricemia is typical for individuals with blood group 3 (B).
During the reaction of acid with water and sodium, poorly soluble compounds are formed - urates. They tend to precipitate when the temperature decreases and the environment becomes acidic. Their accumulation in joint tissues provokes the development of gouty arthritis. The “trigger” of this process is often local or general hypothermia. Urates are perceived by the immune system as foreign particles, and it tries to destroy them. But at the same time, the own joint tissues are damaged, resulting in the development of an inflammatory process with alternating phases of remission and exacerbation.
Sodium salts enter the kidney tubules, where over time urate stones form, which can obstruct the ureters and cause renal colic. Salt deposits can also form in the gastrointestinal tract and muscle tissue.
In the kidneys, uric acid is actively formed due to alcohol abuse, so binge drinking provokes exacerbations of gouty arthritis. This compound can also be synthesized in the liver during the metabolism of individual sugars.
A decrease in the pH of the body is observed in patients with diabetes, as well as in athletes (active physical exercise causes an increase in the level of lactic acid - lactic acidosis).
note
Hyperuricemia is often detected in girls who are overly addicted to restrictive diets.
The main way to combat high uric acid levels is through a restrictive diet.
It is advisable to exclude the following products from the diet:
- smoked meats (both meat and fish);
- fatty meat (especially lamb);
- salo;
- liver;
- kidneys;
- canned food;
- sausages;
- marinades and pickles;
- strong broths;
- seasonings and spices;
- mushrooms;
- beans;
- peas;
- sorrel;
- cream cakes;
- store-bought juices;
- sweet sodas;
- chocolate.
The following products are allowed:
- eggs (soft-boiled, and no more than 1 piece per day);
- boiled chicken;
- weak broths;
- vegetable oils (preferably olive);
- green tea;
- any vegetables;
- fruits;
- rye bread with bran;
- dry biscuits (biscuits);
- hard cheese;
- cottage cheese;
- kefir;
- rosehip decoction;
- fresh juices;
- weak coffee with milk.
Once a week, it is advisable to arrange fasting days, consuming only kefir, cottage cheese or fruit.
If the diet is ineffective, and exacerbations of gout periodically make themselves felt, pharmacotherapy is prescribed.
The most effective drugs against hyperuricemia are:
- Allopurinol;
- Colchicine;
- Benzobromarone;
- Sulfinpyrazone;
- Blemaren.
note
The drug Blemaren optimizes the process of dissolving uric acid stones in the kidneys and urinary tract. The dosage and duration of course therapy are determined by the attending physician. During the treatment period, periodic monitoring of the acid-base status of urine is required. The delivery set of the drug includes an indicator for its determination. Absolute contraindications to taking Blemaren are circulatory failure and chronic renal failure.
The listed drugs must be taken in long courses. Dosages are determined individually by the attending physician.
note
The level of uric acid falls while taking birth control pills, the antibiotic Azathioprine, antilipemic drugs (Fenofibrate and Clofibrate) and the antipsychotic Chlorprothixene. Probenetsi is also capable of reducing its concentration (by stimulating the excretion of the substance by the kidneys).
Traditional medicine recommends decoctions and infusions of strawberry and currant leaves, knotweed herb and blueberry fruits (berries).
Plisov Vladimir, doctor, medical observer
The rate of this indicator directly depends on the gender and age of the person.
In children, the norm for this indicator is 120-330 µmol/l.
In men under 60 years of age, uric acid should range from 250 to 400 µmol/L, and in men over 60 years of age - from 250-480 µmol/L.
The norm for women is slightly lower than for men. For persons under 60 years of age, it should not go beyond 200 to 300 µmol/l, and for persons over 60 – from 210 to 430 µmol/l.
In medicine, an increase in the level of uric acid in the blood is called hyperuricemia.
A test for uric acid is carried out both for healthy individuals for the purpose of medical examination, and for patients with diseases that lead to a delay in the excretion of uric acid from the body. These include diabetes mellitus, diseases of the cardiovascular system, gout and others.
In order for the test results to be objective, you should properly prepare for donating blood. To do this, 24 hours before the blood draw procedure, you need to remove fruit and vegetable juices, caffeine-containing and alcoholic drinks, chewing gum from your daily diet, and also reduce physical and mental stress.
Blood sampling is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach, so the last meal should be no later than 12 hours before the procedure. You should also not smoke 1 hour before the test.
For analysis, venous blood is taken from the vessels that pass through the cubital fossa.
The submitted tests are processed within 24 hours and issued the next day. But in emergency cases, a biochemical blood test can be performed urgently (in cito) within 2-3 hours.
Elevated uric acid levels can be caused by the following conditions:
- hypertonic disease. With a constant increase in blood pressure, the kidneys are damaged, resulting in hyperuricemia. In this case, a cardiologist or general practitioner gives patients recommendations on how to reduce the level of uric acid in the body, which consists of taking medications that lower blood pressure and diet;
- gout. The cause of this disease is increased synthesis of purines. The target organ for gout is the kidneys, as a result of which their failure develops. Gout also affects the joints, so-called gouty arthritis. In addition, with this pathology, uric acid crystals settle under the skin. Such deposits are called tophi. All patients must be prescribed a diet for high uric acid in the blood and drug therapy to help remove urate from the body. We will talk in more detail about the treatment of gout and drugs that remove uric acid from the body;
- diseases of the endocrine system. Hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands leads to an increase in the concentration of calcium in the blood, and this in turn leads to hyperuricemia. Diabetes mellitus is accompanied by a violation of almost all types of metabolism in the body, including purine;
- overweight and obesity. These conditions do not directly affect purine metabolism, but increase the risk of hypertension, gout and diabetes;
- increased cholesterol levels in the body and atherosclerosis. Hyperuricemia often appears against the background of high cholesterol and atherosclerosis;
- pathology of the urinary system. In this case, we can talk about a vicious circle, since uric acid is a component of stones. In turn, urolithiasis contributes to nephropathy, polycystic disease, renal failure, that is, conditions that cause hyperuricemia;
- blood pathology. Polycythemia, anemia, hemolysis of erythrocytes, leukemia and others can lead to hyperuricemia. Hyperuricemia in blood diseases is explained by the fact that tissues are actively breaking down and purine bases, from which uric acid is synthesized, are released into the blood.
Also, an increased amount of uric acid in the body can be formed due to massive burns, Down syndrome, unbalanced diet, alcohol abuse, long-term protein diets, excessive physical activity, taking Furosemide, Aspirin, Theophylline and other medications.
If uric acid in the blood is low, then they speak of hypouricemia. The following pathological conditions can be the causes of hypouricemia:
- deficiency in the body of enzymes such as xanthine oxidase and phosphorylase, which are involved in purine metabolism. Such conditions can be either congenital or acquired;
- mutations of the URAT1 and GLUT9 genes, since they are responsible for regulating the reabsorption of uric acid in the proximal tubules of the kidneys;
- polydipsia;
- large introduction of fluid into the body during infusion therapy;
- hyponatremia;
- intravenous nutrition;
- HIV infection and AIDS;
- cancer of various localizations, which leads to depletion of the body;
- diseases of the small and large intestines, in which the supply of proteins is disrupted, and others.
The main reasons why a uric acid test is taken
| Uric acid level | μmmol/l |
| Men | 200-420 |
| Women | 160-320 |
| Elderly people over 65 years of age | Not higher than 500 |
| Newborns | 140-340 |
| Children from 1 year to 7 years | 120-300 |
| Children from 8 to 15 years old | 140-340 |
| Category | Norm, µmol/l |
| Children under 12 years old | 120-330 |
| Women under 60 years old | 200-300 |
| Men under 60 years old | 250-400 |
| Women over 60 years old | 210-430 |
| Men over 60 years old | 250-480 |
| Normal for women over 90 years of age | 130-460 |
| Normal for men over 90 years old | 210-490 |
- The use of a number of drugs - Furosemide, Aspirin, Phenothiazines, Theophylline, Adrenaline, etc.
- A diet rich in purine bases. It is known that the second name for gout is a disease of aristocrats with excess meat, fish, red wine, and offal in the diet, i.e. foods containing large amounts of purines.
- Drinking alcohol, especially beer and red wines rich in purines. In addition, alcohol negatively affects kidney and liver function, which also contributes to hyperuricemia.
- Long-term diets, as a result of which the excretory function of the kidneys is impaired.
- Excessive physical activity leads to hyperuricemia due to increased protein consumption, i.e. its collapse.
- Hereditary deficiency of xanthine oxidase, in which uric acid is not formed and is excreted by the kidneys in the form of an intermediate metabolic product - xanthine. Xanthine is not completely eliminated, being partially deposited in skeletal muscles and kidneys.
- Hereditary deficiency of purine nucleoside phosphorylase is a disease in which purine bases are not formed.
- Acquired xanthine oxidase deficiency associated with allopurinol use and liver disease.
- Renal hypouricemia due to mutation of the URAT1 and GLUT9 genes, which control proteins responsible for the reabsorption of acid in the proximal renal tubules.
- An increase in the volume of extracellular fluid with large doses of intravenously infused drugs, as well as against the background of polydipsia - severe thirst.
- Cerebral syndrome, in which hyponatremia is observed, leading to hyperuricemia.
- Parenteral nutrition - specific nutrition is aimed at maintaining vital functions and, naturally, does not contain purines.
- HIV infection, in which uric acid deficiency occurs due to brain damage.
- Oncological diseases due to protein and purine base deficiency.
- Enterocolitis due to impaired protein absorption by the intestinal epithelium.
- During early pregnancy, when the total volume of circulating blood increases, uric acid is diluted by an increased volume of the aqueous part of the blood.
- Low-purine diet with limited meat and fish. This situation can occur among low-income people or those who deliberately comply with such restrictions.
- Abuse of tea and coffee, which have a diuretic effect and help remove acid from the body.
- Taking medications: losartan, salicylates, estrogen hormones, trimethoprim, glucose, etc.
- Loss of skin sensitivity;
- Visual impairment, hearing loss;
- Asthenia - mood swings, tearfulness, increased fatigue, uncertainty, memory impairment;
- In severe cases - paralysis with possible death due to suffocation, multiple sclerosis with multiple damage to nervous tissue.
Preparing for analysis
To determine the level of uric acid in the blood, it is necessary to submit it for a general analysis. But in order to have reliable results, it is necessary to prepare for this process in advance.
The day before the biochemical analysis, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Drinking water should be ordinary, without gas.
- Avoid chewing gum.
- Do not smoke or drink alcohol.
- Avoid stress and other emotional turmoil.
Within a few days, the body needs to be prepared for analysis as follows:
- Avoid food for 8-10 hours before taking the test. It is advisable to donate blood in the morning, before meals.
- The day before the analysis, exclude fatty, fried, salty and smoked foods.
- The same is done with sweets, chocolate, pastries, strong tea and coffee.
- Two days before the test, a complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages is required.
- Don’t be nervous on the eve of the test and don’t exhaust yourself with physical exercise.
- On the day of the test, cancel your trip to the X-ray machine or solarium.
- If you take tests in one laboratory and the results do not disappoint you, then you should not change it during the next analysis.
- Immediately before donating blood, calm down, normalize your pulse, only then the results will be reliable.
How to properly prepare for testing is described in the video:
Diet
The cause of hyperuricemia is a violation of the diet, consumption of large amounts of protein foods. Treatment must be accompanied by a special diet. The diet for gout and high uric acid consists of excluding from the diet:
- pickled;
- fat;
- smoked;
- highly salted;
- fried;
- canned.
Diet for hyperuricemia
The patient should limit salt intake to 7 g per day.
Sausage, internal organs of animals, and fish (fried) are contraindicated. Chocolate is harmful. Baking is not recommended. The restriction applies to some vegetables and herbs.
Alcohol is dangerous. Alcohol disrupts liver function and provokes the development of hyperuricemia. It is better to replace it with green tea, which helps the body cleanse itself of toxins.
Preference should be given to fermented milk products. Do not get carried away with eggs; one boiled egg per day is allowed.
Cook by steaming or boiling. This food is ideal for the recommended diet. Doctors do not recommend getting involved in a raw food diet.
Products that act as diuretics promote the release of excess enzymes.
The greatest effect of the diet will be if once a week you drink only kefir, water, and eat nothing. Pure water helps cleanse the intestines. If metabolic processes are normalized, the effectiveness of the diet will speed up the healing process.
We must not forget about the risk of an allergic reaction and the possible presence of other diseases. It is not recommended to change your diet or determine your daily menu on your own; it is better to consult a doctor who takes into account the nuances of your health condition.
If you have hyperuricemia, you need to normalize your diet and, in future, not return to old eating habits. During treatment, you should completely exclude the following foods from your diet:
- beef
- any fatty meat
- liver, kidneys, brains
- salo
- smoked fish and meat products, sausages
- semi-finished products
- rich broths
- chocolate
- coffee
- confectionery with cream
- alcohol
Uricosuria in children
In pediatrics, there is the concept of uric acid or neuro-arthritic diathesis - this is a constitutional anomaly, which is characterized by the tendency of the child’s body to metabolic disorders: the formation of uric acid in excess of the norm, ketoacidosis, eating disorders. Such children are usually thin, nervous, and capricious. In adulthood, they are prone to developing gout and urolithiasis. Despite the fact that they are physically less developed than their peers, in mental development they are often much stronger. When the diet is violated, episodes of vomiting often occur as a result of an increase in ketone bodies in the blood. By adolescence, in most children, the symptoms of uric acid diathesis go away on their own.
Why are tests for this compound performed?
In men after 40 years of age, there is a sharp increase in acidity. Therefore, it is recommended to periodically donate blood to determine the indicator.
To get the right data from a study, you need to prepare for it. Patients should follow the rules for preparing and taking the test:
- a few days before the test, you should not include fatty, spicy, fried, salty, smoked foods in your diet, and limit protein intake;
- 2 days before the test you should not drink alcoholic beverages;
- 1 week before the study, you cannot use new medications that the doctor has not been warned about;
- the last meal should be 8 hours before the test;
- testing is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach.
For analysis, the doctor takes a small amount of venous blood from the patient. An anticoagulant is added to the test tube to prevent clot formation. The blood is immediately sent to the laboratory to determine the indicator. The study is carried out using a semi-automatic analyzer, which independently calculates the indicators. This eliminates the risk of medical error.
Determining the level of uric acid allows you to objectively assess the state of purine metabolism, and, accordingly, obtain information about the functional activity of the kidneys and liver, as well as the state of the hematopoietic system and skeletal muscles.
Monitoring of uric acid levels is mandatory during chemotherapy for tumor tumors.
This analysis is one of the mandatory kidney tests that can detect abnormalities in the tubes and tubules of the organ.
Hyperuricemia is not yet regarded as a sufficient basis for making a diagnosis of gout. In this case, characteristic clinical symptoms and X-ray data should be additionally taken into account. Urate deposits and joint deformation are clearly visible on photographs. If the norm is exceeded, but the patient does not complain of pain or deterioration in health, it is customary to speak of “asymptomatic hyperuricemia.”
A quantitative blood test for uric acid is technically simple; it can be carried out in almost any clinic. The test requires special reagents and a photoelectrocolorimeter.
For express analysis, compact devices have been developed that look like glucometers.
Blood uric acid standards in men over 60 years of age
Urea levels are routinely measured as part of a biochemical blood test, which is always required when a patient is referred for hospitalization. Also, for example, the results of a urea test are used as an indicator of the state of the body’s water balance.
When is it appointed?
There may be several reasons that influence pathological changes in uric acid levels and are a good reason to get tested:
- the doctor suspected symptoms of developing gout;
- in case of pathological processes in the kidneys;
- when it is necessary to establish the cause of the process of stone formation in the kidneys;
- with sudden weight loss in the patient.
Doctors also prescribe tests during pregnancy (first and third trimester). More often, the blood of the expectant mother is checked if she complains of toxicosis or doctors suspect a threat of miscarriage.
When taking a test for the level of uric acid in the blood, it is recommended to follow the following tips:
- Do not eat food 8 hours before the procedure. You are only allowed to drink water.
- You should wait until the end of the course of taking medications, as some drugs may affect the objectivity of the indicators. It is imperative to notify your doctor if you have recently taken medications.
- It is recommended to refrain from performing ultrasound and x-ray examinations before taking the test.
- Physical activity should be avoided, and sunbathing should not be done before the procedure.
- Two days before the procedure, it is important to adhere to a diet and exclude foods containing purines (liver, beans).
- It is forbidden to drink alcohol, juices, teas and coffee, as the result may be inaccurate.
Doctors recommend not smoking at least an hour before visiting a medical facility.
How is it carried out?
They do biochemistry in the laboratory, taking blood from a vein. The result is usually known the next business day.
An alternative diagnostic option is to conduct a uric acid test at home. In order to take the test correctly, you will need to purchase a portable blood analyzer and test strips. They work on the same principle of a biochemical analyzer as in a stationary laboratory. To conduct the test, only one drop of blood is needed. The result appears in 6 seconds.
Blood analyzer
Test strips
Normal uric acid levels change with age and also differ between men and women. The acid content increases as a person ages (after 60 years), while in women the levels are lower than in men.
Uric acid is normal for adults and children - table by age.
| Category | Normal value, mmol l. |
| In children under 12 years of age | 0.12-0.13 |
| Women under 60 years old | 0.2-0.3 |
| Women over 60 years old | 0.21-0.43 |
| Women over 90 years old | 0.13-0.46 |
| Men under 60 years old | 0.25-0.40 |
| Men over 60 years old | 0.25-0.48 |
| Men over 90 years old | 0.21-0.49 |
A video about deciphering the results of a biochemical blood test was published by the Health TV channel.
In the early stages, hyperuricemia and hypouricemia do not manifest themselves in any way.
Common symptoms of hyperuricemia:
- high or low blood pressure;
- lower back pain;
- abdominal pain;
- muscle pain;
- joint pain;
- constipation;
- excess weight;
- itching and burning when urinating;
- tartar.
Also, signs of the disease can be disguised as other diseases or be part of them.
To normalize a blood test, you need to:
- stick to a diet;
- comply with medication treatment.
In addition, you can resort to folk remedies, but it is recommended to do this with caution.
If uric acid in the blood is increased or not significantly decreased, the test results and your well-being will be improved by diet. To comply with this, it is recommended to eat small portions 3-5 times a day.
With this diet, the following are excluded from the diet:
- alcohol;
- strong coffee and tea;
- energy;
- marinades;
- soda.
To prevent hyperurecemia, it is recommended:
- Tibetan procedures;
- cardio training;
- sanatorium treatment.
Tibetan procedures include:
- acupuncture;
- phytotherapy;
- stone therapy;
- manual therapy.
During sanatorium treatment, you should choose procedures that improve:
- metabolism;
- circulation;
- removing excess salts from the body.
The following are recommended to prevent low blood uric acid levels:
- eat enough seafood, meat and dairy products;
- maintain good physical shape - optimal physical activity is exercise for at least 30 minutes a day, 5 times a week;
- Do not abuse medications without a doctor’s prescription.
Loading …
Since the level of uric acid in the blood is constantly changing, a short-term increase in its concentration does not affect a person’s health in any way, and the “excess” is quickly excreted in urine and feces. This increase in uric acid levels in the blood can be caused by:
- excess protein foods;
- physical activity;
- prolonged fasting;
- alcohol abuse.
We suggest you read: What are the dangers of hypertension during pregnancy?
A persistent and pathological increase in uric acid in the blood - hyperuricemia is usually associated with diseases of the internal organs or a genetic predisposition.
There are 2 types of hyperuricemia:
- primary or idiopathic - a hereditary disease associated with disorders of purine metabolism. This type of disease is most often diagnosed in children of the first year of life and is quite rare;
- secondary - excess uric acid and salt deposition are associated with disturbances in the process of its metabolism in the liver or pathology of the excretory organs. This type of disease occurs in 99% of all older patients.
Primary idiopathic hyperuricemia can be caused by:
- Kelly-Siegmiller syndrome;
- Lesch-Negan syndrome;
- congenital fermentopathy.
Secondary hyperuricemia occurs in the following diseases:
- infections of internal organs - an increase in the concentration of uric acid occurs in acute and chronic inflammation of the upper and lower respiratory tract and internal organs;
- inflammatory diseases of the liver and gallbladder - hepatitis, cirrhosis, cholecystitis cause disruption of the formation of uric acid;
- inflammatory kidney diseases - when the filtration and concentration function of the kidneys is impaired, uric acid is not completely eliminated from the body and its level in the blood increases greatly;
- hypo- and avitaminosis - a lack of vitamin B 12 and some others leads to impaired metabolism of purine bases and an increase in uric acid levels;
- diseases of the endocrine system - metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, obesity and other similar pathologies can also cause hyperuricemia;
- allergic diseases - bronchial asthma or urticaria also lead to an increase in the concentration of uric acid;
- dermatological diseases - eczema, psoriasis or dermatitis also affect the level of the substance in the blood;
- toxicosis – severe toxicosis of pregnant women can cause the development of acidosis and an increase in the amount of uric acid in the body;
- oncological diseases;
- changes in alkaline balance - with acidosis, the level of uric acid in the blood increases greatly;
- long-term use of medications - anti-tuberculosis drugs, diuretics, NSAIDs and some other drugs can cause disorders of the metabolism of purine bases;
- alcohol poisoning.
With a slight increase in uric acid levels, a person’s well-being does not suffer; only regularly recurring or constant hyperuricemia is dangerous to health. Its clinical manifestations depend on age.
In children, an increase in uric acid levels causes constant skin problems - these can be diaper dermatitis, diathesis, allergic rashes and even psoriasis. A characteristic feature of such rashes is their resistance to conventional treatment methods and their tendency to ooze. Sometimes such children are treated for years for allergies or skin diseases, without knowing the cause of their occurrence.
Secondary hyperuricemia is most often found in men over 45-50 years of age. They develop pain in the joints due to the deposition of sodium salt crystals in them, and the small joints of the foot are more often affected, and less often the knee and elbow joints. With further development of the disease, the pain intensifies, the joints themselves swell, the skin over them becomes hot and red, and the slightest movement causes severe pain to the patient.
In addition to the joints, the digestive and urinary organs are also affected; the patient experiences pain in the lower back, lower abdomen, or when urinating.
A chronic increase in the level of uric acid in the blood leads to the fact that sodium salts are deposited in all organs and systems, damaging them. Blood vessels become less elastic, which can cause the patient to increase blood pressure, develop angina or myocardial infarction. And if the nervous system is damaged, headaches, attacks of aggression, insomnia or vision problems may occur.
The level of uric acid in the blood can only be diagnosed by conducting a biochemical test of the patient's blood. This allows not only to establish a diagnosis, but also to determine how much the indicators are exceeded.
If the level of uric acid in the blood increases, it is recommended to follow a diet and take medications and, of course, treat the disease that caused hyperuricemia.
Principles of nutrition for increased uric acid:
- Regular meals, in small portions - 3-4 times a day, if the level of uric acid increases, fasting is prohibited and diets are not recommended, with the exception of therapeutic ones;
- Refusal of alcohol, strong coffee, tea, carbonated and energy drinks;
- Reducing the diet of foods rich in purine bases - rich broths, fatty meats, fried, smoked, salted meat and offal, as well as sausages, sausages and any other smoked and salted meat products; legumes, rhubarb, spinach, sorrel, radishes; sweets; butter dough, confectionery;
- Compliance with the drinking regime - the volume of liquid consumed per day should be 2-2.5 liters per day, most of which should be clean water;
- Reduce the amount of salt in the diet - to do this, you need to give up any pickles, marinades, sauces, seasonings and other products containing a large amount of sodium salts;
- It is recommended to eat more vegetables, fruits, berries, dairy products, lean meat and freshly squeezed juices.
- for children under fourteen it ranges from 120 to 320 µmol/l;
- From the age of fourteen, gender differences are observed in the analyses. Uric acid in the blood: the norm in women is from 150 to 350. The normal level of uric acid in men is from 210 to 420.
- gout,
- oncological diseases of the blood,
- Lesch-Nyhan syndrome,
- cystinosis,
- hepatitis of viral etiology,
- polycythemia vera,
- sickle cell anemia,
- severe pneumonia,
- after epileptic seizures,
- hepatocerebral dystrophy.
We invite you to read: Atarax - instructions for use, doses, analogues, indications
The main reasons why a uric acid test is taken
Uric acid and urate: what is it and what is the difference?
Uric acid is a crystal made up of nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen that forms in the liver during the breakdown of purines.
Uric acid is removed from the human body by the kidneys.
Purines are found in foods such as liver, legumes, anchovies and beer. Uric acid is present in small amounts in the blood, sweat, urine, and brain and liver tissues.
Urates are potassium and sodium salts of uric acid that form sediment in the urine. Urates are synthesized from uric acid. Uric acid in the urine is measured using a urinalysis test, and in the blood using a blood chemistry test.
The normal content of uric acid does not cause any harm to the human body, but on the contrary performs a number of vital functions such as:
- increases the effect of catecholamines on the cells of the body, activating the work of the brain and other parts of the nervous system;
- protects the body from the negative effects of free radicals;
- controls the qualitative composition of body cells.
At the same time, elevated uric acid in the blood is a serious signal of certain diseases and requires a series of studies to determine the causes and eliminate them. After all, excess uric acid is a poison that poisons the body from the inside.
Why is the level below normal?
A low level of this substance in the body is influenced by the following circumstances:
- Medications that affect the reduction of uric acid in the blood - allopurinol, ACTH, cortisol.
- Conditions that impair the functioning of the liver, for example a disease such as Wilson-Konovalov syndrome.
- Fanconi syndrome. This is a condition where the kidneys are unable to retain uric acid in the body.
- Gigantism and acromegaly. This is a condition when uric acid begins to spend its costs on its own cells, as a result of which they produce active growth.
- Celiac disease.
- Xyntinuria. This condition is characterized by the absence of an enzyme due to which uric acid is produced; if it is not there, then this substance is not there.
- Hodgkin's disease, bronchogenic carcinoma, myeloma. With these diseases, a decrease in uric acid levels is possible, but for what reasons this happens, doctors still cannot figure out.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the renal tubules.
- Passion for vegetarianism.
Reference! The level of uric acid may decrease due to the use of birth control pills in women.
The antibiotic Azathioprine, the antilipemic drugs Fenofibrate and Clofibrate, and the antipsychotic Chlorprothixene have the same feature.
Drug therapy
To eliminate hyperuricemia, specialists prescribe several types of drugs.
Scroll:
- Drugs responsible for removing excess uric acid from the body. For example, probenecid, which, subject to a properly selected dose and an adequate dosage regimen, can quickly remove the substance and bring its content to the normal level of 6 mg/dl. It is important to remember: taking aspirin has a slowing effect on probenecid and inhibits its effects. In addition to this drug, sodium bicarbonate is actively used.
- Drugs that are responsible for reducing the level of acid produced by the body: are prescribed to patients with a history of urolithiasis, gout, and problems with kidney function.
- Drugs that transfer uric acid from body tissues into the blood plasma and also promote its rapid excretion through the kidneys (for example, Zinchofen).
Treatment for low uric acid levels in the body has 2 categories:
- Therapy of the underlying disease, which caused a decrease in the concentration of the substance in the blood (liver cirrhosis, burns and other pathologies):
- the appointment of hepatic protectors, which restore liver cells and protect them from harmful environmental influences;
- the use of glucocorticosteroids aimed at reducing inflammation;
- use of vitamin-mineral complexes;
- Antibiotics and antiviral drugs are used to treat infections.
- The patient must consume foods that are rich in proteins and purine compounds, and are also active sources of uric acid metabolic processes.
Hyper-or hypouricemia (increased or decreased levels of uric acid in the blood) is a dangerous condition that can provoke a host of diseases, ranging from gout to kidney failure.
This process provokes the occurrence of pain, inflammation and serious diseases.
If the reasonable number of such crystals in the joint tissue is exceeded, a disruption of their functions occurs: the joints stop fully working to flex and extend the limbs, each movement begins to cause severe pain to the person and makes him completely disabled. Thus, a dangerous disease develops - gout.
Healthy and large joint
As a rule, the first sign of the presence of this disease is pain in the area of the big toe, followed by inflammation in the joint tissue.
In addition to gout, uric acid can cause serious kidney disease. Crystals accumulate in the kidney tissues, gradually merging into stones, which cause severe pain and can damage the kidney tissue, thereby disrupting their function. Stones of this type can cause maximum harm to the organ due to the complexity of their composition and structure.
Deviations from the norm in uric acid levels can cause the following consequences:
- the occurrence of diseases of the endocrine system;
- disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- decreased intellectual activity of the brain;
- development of arthritis, osteochondrosis of different parts of the spine and coxarthrosis.
The level of uric acid, which is necessarily contained in a person’s blood, is an indicator to which one should strive. Timely monitoring of the content of this substance and bringing it to optimal levels is the key to health and the absence of pain and inflammation in various organs and systems of the human body.
All medications are used strictly as prescribed by a doctor and under his supervision, with regular measurements of acid levels in the blood and urine (see medications for gout).