There are a large number of antibiotics in different release forms on the pharmacological market. The drug Cefotaxime injections is widely used to treat children and adults and belongs to the group of third-generation cephalosporins. It is capable of influencing different types of pathogenic bacteria and microbes, for this reason it is often prescribed to patients for diseases caused by harmful microflora and viruses.
Contraindications
Cefotaxime (OKPD code 2 21.20.10.191) is prohibited in case of bleeding, individual intolerance to the active substance, severe allergic reactions to cephalosporins and penicillins.
Pregnant women in the first trimester should also not be given injections with this drug. If the patient has a history of enterocolitis, then Cefotaxime injections are prohibited. Breastfeeding and the II-III trimesters of pregnancy are relative contraindications. The use of an antibiotic in these cases is possible if the benefit to the mother outweighs the risk to the child
If therapy with Cefotaxime is carried out while breastfeeding, it is important to monitor the baby’s reaction. If he develops diarrhea or other side effects, stop treatment
Intramuscular injections can be given to children from 2.5 years old, intravenous from the first days of life.
For pathologies of the kidneys and liver, the use of Cefotaxime is possible. However, they first undergo additional examination and receive a conclusion stating that there are no contraindications to the use of cephalosporins. During treatment with Cefotaxime, the consumption of alcoholic beverages is prohibited.
Contraindications to the use of the drug
We will tell you how to dilute the Cefotaxime injection below. It should be noted that this product does not have a very long list of contraindications. According to the instructions, this medication is not prescribed for:
- bleeding;
- pregnancy;
- individual hypersensitivity to the active ingredient;
- enterocolitis (including history).
Is it possible to administer Cefotaxime solution to a child? Injections for children (reviews of the effectiveness of the mentioned medicine will be presented at the end of the article) are allowed only when the patient reaches the age of 2.5 years (for intramuscular administration).
With extreme caution, the medication is prescribed to newborn babies, during breastfeeding (since the drug is excreted in small quantities in breast milk), as well as in the presence of chronic renal failure and UC (including a history).
In case of pathology of the renal and hepatic systems, the patient is required to undergo additional medical examination in order to obtain a conclusion about the absence of contraindications to antibiotic therapy.
pharmachologic effect
What group of antibiotics does Cefotaxime belong to? The drug Cefotaxime belongs to the group of antimicrobial drugs from the third generation cephalosporins. It is highly sensitive to bacteria and has a wide spectrum of antibacterial activity.
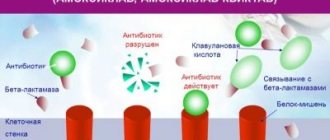
The mechanism of action of Cefotaxime is bactericidal, that is, the active substance destroys the wall of the bacterium, killing the microorganism as a whole.
The drug is sensitive to the following bacteria:
- Escherichia coli is a type of enterobacteria that causes diseases of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Citrobacter spp. – a gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium that causes food toxic infections and dysbacteriosis;
- Klebsiella spp. – causative agent of klebsiellosis;
- Haemophlus influenzae - hemophilus influenzae. This bacterium is the causative agent of respiratory diseases such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and tracheitis.
The drug is less sensitive to representatives of gram-positive rods. These include staphylococci and streptococci.
Pharmacokinetics
The drug is administered parenterally, so it quickly enters the systemic circulation. Maximum concentrations of the drug compound are detected half an hour after a single administration. The bactericidal effect of Cefotaxime lasts for 12 hours.
The active substance penetrates well into many biological fluids and tissues. Cefotaxime is easily detected in synovial, peritoneal, and pleural fluids. The drug compound penetrates the blood-brain barrier.
How long does it take for the drug to be eliminated from the body? The drug is excreted unchanged, without being metabolized. It is excreted mainly in feces and bile. The half-life of Cefotaxime is 48 hours.
Composition and effect of the medicine
Each bottle of the drug contains the active ingredient cefotaxime. The release form of the drug is a white or light cream powder, packaged in hermetically sealed containers. The manufacturer produces bottles containing 1000, 2000 and 500 mg of the substance.
This drug works only when administered intramuscularly or intravenously. To do this, the powder is diluted with Lidocaine, Novocaine and water for injection.
Which group of medications does it belong to?
This drug belongs to antibacterial agents against pathogens of infectious diseases. It is part of the third generation group of cephalosporin antibiotics.
In addition to Cefotaxime, antibiotics in this group include:
- Tizim;
- Fortum;
- Cefix;
- Suprax;
- Pantsef;
- Cefotodx;
- Spectracef;
- Tsedex.
These analogues are also used to combat infectious diseases, but they contain other active substances. Medicines in this series are characterized by a combination of a wide range of applications with good tolerability and minimal impact on the intestinal microflora.
A synonym for Cefotaxime is the drug Claforan, which not only belongs to the same group of antibiotics, but also contains the active substance cefotaxime.
To purchase the drug at a pharmacy, you need a doctor's prescription.
Comparison of Cefotaxime with Ceftriaxone
The main component of Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone is the substance of the same name. Both of these drugs belong to the category of third-generation semisynthetic cephalosporins. This analogue of Cefotaxime is also used only parenterally.
Both drugs are very effective in the fight against microorganisms that have developed resistance to penicillins. They are also often used when patients have hypersensitivity to antibiotics of the penicillin group. The advantages of Cefotaxime are as follows:
- "Cefotaxime" does not affect the absorption of vitamin K. And, in addition, it does not in any way affect the outflow of bile and does not provoke the appearance of pseudocholelithiasis, unlike the same "Ceftriaxone".
- Cefotaxime can be used from birth.
- Cefotaxime has a smaller list of side effects. And, in addition, there are contraindications against the background of a wide range of effects.
The disadvantages of Cefotaxime are as follows:
- Compared to Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime is more unstable in an acidic environment.
- "Cefotaxime" can provoke the development of candidiasis. This is one of the most significant shortcomings, judging by the reviews of patients.
- "Cefotaxime" is ineffective against Haemophilus influenzae, and, in addition, is useless in the fight against pneumococcus, unlike "Ceftriaxone".
Properties and indications of the drug for respiratory diseases
The medicine is prescribed if there are bacteria in the body that are sensitive to the antibiotic.
When is the drug prescribed:
- sinusitis of bacterial origin – sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis;
- tonsillitis;
- nasopharyngitis;
- lower respiratory tract infections - inflammation of the bronchi, lungs, abscesses, pleurisy.
Cefotaxime is often prescribed for sinusitis. Its activity is evident from the first days of treatment. Patients experience relief from the main symptoms – nasal and maxillary sinus congestion, intense pain in the facial area. Ventilation of the sinuses is restored, which prevents the development of congestive processes and reduces the risk of complications.
By suppressing the proliferation of pathogenic microflora, the production of purulent exudate is reduced and nasal breathing is restored. The general indicators of the patient’s condition are gradually improving:
- night sleep;
- appetite;
- physical activity.
Cefotaxime for bronchitis reduces the production of sputum, which often contains pus and promotes its evacuation from the respiratory system . By restoring bronchial patency, the gas exchange function of the lungs is restored, shortness of breath and hypoxia (oxygen starvation) disappear. 2-3 days after the start of antibiotic treatment, the severity of cough attacks decreases. Mucus is coughed up easier, and attacks of suffocation disappear.
Children are prescribed Cefotaxime for sore throat. The drug not only fights infection, eliminates signs of the disease, but also prevents the development of serious complications:
- myocarditis – inflammation of the muscle layer of the heart;
- rheumatism - inflammation of the connective tissue membranes of the heart;
- pyelonephritis – infection of the renal pelvis;
- glomerulonephritis – destruction of the kidney structure with subsequent impairment of glomerular filtration;
- septic arthritis is a systemic infectious inflammation of the joints.
Indications for use
After penetration into the body, the antibiotic has a bactericidal effect, as a result of which the infection is eliminated. The drug Cefotaxime causes the death of streptococci, staphylococci, enterococci, enterobacteria, Klebsiella, gonococci, Proteus and many other microorganisms.
Cefotaxime can be used for the following diseases:
- Infections developing in the respiratory system, including bronchitis, pneumonia;
- Abcesses of various types;
- Inflammatory process in the genitourinary system;
- Kidney dysfunction;
- Diseases affecting the ear or throat, as well as the nasal cavity. Acute otitis media is effectively relieved with Cefotaxime;
- Endocarditis;
- Damage to bone tissue, skin or abdominal area;
- Gynecological infections;
- Bacterial meningitis;
- Lyme disease.
In addition, the drug is prescribed to patients for prophylactic purposes to prevent postoperative complications.
Indications and contraindications
The drug has a wide spectrum of action. Indications for use include:
- diseases of the respiratory system - bronchitis, infection, pneumonia, pleurisy, abscess;
- inflammation of soft tissues - cellulite, hidradenitis and others;
- inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity and pelvic area;
- infections due to burns and wounds;
- inflammatory diseases of the nervous system;
- cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis.
In addition, the drug can be prescribed to patients after surgery in case of complications of an infectious and inflammatory nature. It may help with some diseases of the genitourinary system, kidneys, and so on.
The product has its contraindications. For this reason, before using it, the patient should carefully study the instructions. Among the contraindications:
- presence of intolerance;
- severe allergic reaction to cephalosporin or penicillin;
- renal and hepatic disorders;
- acute renal failure.
Under strict control, administration of the drug is allowed for chronic diseases of internal organs and during breastfeeding.
Directions for use and doses
The method of using this antibiotic is to carry out intramuscular or intravenous injections.
It is not recommended to drink the drug, as it is quickly destroyed by digestive enzymes. Cefotaxime injections are prescribed by the attending physician, since doses must be determined individually, in accordance with the diagnosis, age and condition of the patient.
How to breed
In order to properly prepare an injection solution, you need to know how and for whom the medicine will be used. When administered intravenously, Cefotaxime must be diluted with special water for injection. Some manufacturers of this drug place it in packaging with an antibiotic and ampoules with a solvent in the form of sterile water. When administering the medicine via a dropper, the antibiotic can be dissolved with sodium chloride or glucose.
If it is necessary to administer the drug in a stream, it must be diluted at the rate of 4 ml of solvent per 1 g of antibiotic. The suspension for the dropper is prepared at the rate of 40-100 ml per 1 or 2 g of powder. This wide range of parameters is due to the fact that the injection solution is often diluted depending on the patient's condition.
For intramuscular administration, water is used only if the patient is allergic to solvents that have an analgesic effect. This is due to the pain of the injection.
It is necessary to dilute Cefotaxime Novocaine at the rate of 4 ml of solvent per 1 g of medicine. If it is necessary to give an injection with Lidocaine, then the same proportions of solution formation are maintained as with Novocaine.
The antibiotic is dissolved directly in the bottle.
After introducing the solvent, shake the bottle and wait a few minutes until the solution becomes clear. This means it is ready to use.
How many times a day to apply
The antibiotic Cefotaxime is prescribed according to the individual needs and indications of the patient. However, they inject it in any situation at least 2 times a day. There is also a minimum interval - injections must be given no more than every 6 hours. In severe cases, an interval of 4 hours is allowed.
What do you think are the most important factors when choosing a medical facility? Poll Options are limited because JavaScript is disabled in your browser.
If analogues of Cefotaxime in tablets are used, then you can drink it at regular intervals at least 4 times a day.
How many days to inject
This antibiotic needs to be injected often, but not for long. If its use does not bring the desired treatment result within several days, it is necessary to discontinue it due to ineffectiveness for this disease.
The course must last at least 7 days. For some diseases, this antibiotic can be injected for 10 days.
Features of use for children
Instructions for use for children prescribe, first of all, to observe the dosage specifications. Cefotaxime is prescribed to children taking into account many factors. The dosage is calculated as follows:
- newborns - 50 mg per 1 kg of weight;
- children over 1 month - the dosage remains the same, but the frequency of use increases;
- for a child who has reached the age of 2.5 years (with a weight of at least 30 kg) it is necessary to calculate the dose based on 50-180 mg per 1 kg;
- For adolescents over 12 years of age, the drug is administered as an adult.
Thus, the use of Cefotaxime for children requires taking into account the age, weight, diagnosis and condition of the patient.
How much and how to give
This antibacterial composition can be injected intramuscularly and administered intravenously; in order for the drug to be ready for use, it must be converted from a powder to a liquid form.
For this purpose you need:
- to prepare an intravenous injection, dilute the powder with sterile water (4 ml of water is needed for 1 g of product);
- to set up a dropper, add sodium chloride and glucose to the powder (40-100 ml of the substance is required for 1-2 grams of the composition);
- to administer the drug intramuscularly, use Novocaine or Lidocaine to dilute the powder (take 4 ml of anesthetic for 1 gram of antibiotic).
Can Cefotaxime be used for children? The instructions for the drug allow, if such a need arises, the administration of the drug even to newborn children, only under strict medical supervision. The choice of a specific dosage regimen depends on the condition of the child and the severity of the developing infectious and inflammatory process.
Features of children's dosages:
- newborns receive 50 mg per day for each kilogram of the baby’s weight (this volume is divided into two or four administrations). Severe infection requires increasing the dose to 200 mg per kilogram;
- children from one to 12 years of age (provided that their weight does not exceed 50 kg) can receive about 150 mg per kilogram of weight. This dose is also divided into 2 or 4 administrations per day;
- Children over 12 years old, weighing more than 50 kg, receive 2-3 injections of Cefotaxime, 1-2 grams per day.
The drug should be administered every 8 hours (according to the doctor’s recommendation, after 12 hours). The course of therapy may vary, it can last from a week to ten days.
The instructions should be strictly adhered to; injections for intravenous administration are not allowed to be diluted with Lidocaine or Novocaine. For this purpose, only saline solution, 5% glucose solution, and water for injection are used.
Analogues of the drug are:
- Tarfetoxime, which is in the form of a powder from which an injection solution is prepared;
- Cefotaxime Lex VM, also available as a powder;
- Talcef, in the form of powder for injections.
Only a doctor who has knowledge that allows him to predict the effect of the new medication on the patient’s body has the right to change the prescribed drug to an analogue.
Cefotaxime injections drug use
The dosage of the medication is selected by the doctor in accordance with the age and nature of the infection. Antibiotic treatment lasts at least 5 days, more often Cefotaxime is prescribed for 7 days. If necessary and on the recommendation of a doctor, the therapeutic course can be extended.
- During surgery (including during caesarean section), the drug is administered in a prophylactic dose of 1 gram. If necessary, the manipulation is repeated after 6 hours.
- For uncomplicated infections of the ENT organs and respiratory tract, as well as the urinary system, administration of the drug at a dose of 1 gram every 12 hours is indicated.
- For gonorrhea, 1 gram is administered once.
- Moderate infections require the use of 1-2 grams of the drug twice a day.
- Severe infections, meningitis and complicated diseases require the use of 2 grams of medication every 4 hours.
For adult patients, the maximum daily dose of antibiotic is 12 grams. For children under 2.5 years of age, the drug is administered only intravenously. The dosage of the medication is calculated according to the child’s body weight.
Next, we’ll talk about how to prepare Cefotaxime powder for injection.
Reviews
Reviews about the drug Cefotaxime are mostly positive.
Doctors
Elena Pavlovna, family doctor, Moscow
In my practice, I prescribe Cefotaxime to patients only after testing the sensitivity of pathogenic microflora to this antibiotic. The advantage of this drug is that it can be administered into the body both intravenously and intramuscularly.
The therapeutic effect occurs quickly. For some diseases, such as gonorrhea, 1 injection is enough.
Evgeniy Petrovich, otorhinolaryngologist, Tula
For purulent tonsillitis, otitis media and other diseases, I prescribe treatment with Cefotaxime. Due to the fact that injection of the drug into the gluteal muscle is painful, I recommend mixing the antibiotic powder with Lidocaine or Novocaine. Claridol or other anti-allergy drugs should be taken together with the antibiotic.
Directions for use: special instructions
How to inject Cefotaxime correctly? Many patients ask this question, especially if the injections are not given by a medical professional with the appropriate education, but by a family member.
In order to relieve some of the painful sensations that invariably accompany the administration of the medicine, the injection solution is diluted with Lidocaine (a composition with an analgesic effect).
To prepare a solution for injections, you need:
- wash your hands with soap;
- wipe all ampoules that will be used with cotton wool moistened with boric alcohol;
- file the ampoules with a special device;
- open all containers and place them on the table;
- take the following liquids into the syringe: 1 g of Cefotaxime, 2 ml of Lidocaine (12% solution), 2 ml of injection water;
- thoroughly mix the contents of the syringe and release excess air, which appears in the form of bubbles;
- We give the patient an injection.
How many days do you inject Cefotaxime? Only the doctor who made the appropriate prescription can answer this question. The duration of drug therapy depends on the patient’s health status, the severity of the infection he develops, and other factors.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=DQZEFjPzGOE
Special conditions for antibiotic use:
- some patients may suffer from pseudomembranous colitis that develops in the first days of therapy (the disease manifests itself as severe intestinal upset). To relieve unpleasant symptoms, therapy with Cefotaxime should be discontinued, and the patient is prescribed other therapy using Metronidazole;
- Patients who have previously suffered from severe reactions to treatment with penicillin antibacterial agents should closely monitor changes in their condition. They are likely to develop high sensitivity to cephalosporins;
- drug therapy lasting more than ten days requires mandatory monitoring of blood counts;
- the period of treatment with Cefotaxime injections can change the values of glucose tests and Coombs tests, which should be taken into account;
- You should not take alcoholic beverages during treatment, as this can cause a deterioration in the person’s condition;
- Cefotaxime solution, which was diluted using Lidocaine, cannot be administered intravenously (this form is only suitable for intramuscular administration);
- For injections, you can only use a freshly prepared solution; the finished mixture cannot be stored.
Side effects
Among the undesirable reactions, the following reactions are most often recorded:
- From the central nervous system: headaches, dizziness, loss of coordination, convulsions, blood pressure surges
- From the genitourinary system: kidney dysfunction, stagnation of urine, the appearance of thrush
- From the digestive tract: attacks of nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, stool upset, bloating, liver dysfunction, various types of colitis, etc.
- From the circulatory system: development of anemia, leukopenia, thrombosis
- From the heart and blood vessels: after injection into a vein, with rapid administration, arrhythmia may develop, which can be life-threatening.
In addition, Cefotaxime can cause an allergic reaction, which is fraught with skin rashes, itching, and bronchospasm. After administration, the antibiotic can also provoke anaphylactic shock and angioedema. Local manifestations often include pain at the site of intravenous or intramuscular injection. In laboratory tests, after injections of this antibiotic, you can notice changes in the blood.
Instructions for use
If the drug is prescribed for intramuscular or intravenous administration, then before using it it is necessary to dilute Cefotaxime with novocaine or lidocaine and be sure to test for sensitivity to the antibiotic.
When a drug is prescribed for intravenous or intravenous administration, the first question patients ask is what and how to dilute Cefotaxime. According to the attached instructions for use, Cefotaxime for preparing injections for injections can be diluted with either lidocaine and water for injection, or with novocaine. If injections are administered intramuscularly, then in this case Cefotaxime is best diluted with lidocaine rather than novocaine.
The drug is approved for intravenous use from birth, but intramuscular administration can be carried out exclusively from 2.5 years.
If the patient is diagnosed with uncomplicated infections or urinary tract infections, then the drug is prescribed for administration at a dose of 1 g every twelve hours. In severe cases of the disease, the dose of the drug is increased to 2 g, which are administered every 4-8 hours. The duration of such treatment is prescribed by the doctor in each individual case individually.
The drug in tablet form is prescribed in the same dosage as injections
As for the use of the tablet form of the drug, there is no significant difference with injections. The drug in tablet form is prescribed in the same dosage as injections. A more precise dosage is selected by the doctor depending on the diagnosis. As for the duration of treatment with this drug, if the medicine is prescribed to children, then the duration of treatment is about one week. In adults, the drug is taken for about ten days. If the course of treatment for any indication exceeds a ten-day period, then the quality of blood particles must be monitored. This study is carried out in the laboratory conditions of a medical institution.
If the patient is diagnosed with liver dysfunction, the dose of the drug is immediately reduced.
More detailed information and a complete description of Cefotaxime tablets and injections can be found in the RLS reference book.
When prescribing Cefotaxime, one should take into account the fact that during its use there may be positive results of a urine test for glucose, as well as a false-positive Coombs test.
During treatment with an antibacterial drug such as Cefotaxime, it is worth remembering that it is completely incompatible with alcohol, and drinking alcohol during treatment is strictly prohibited. This is explained, first of all, by the fact that such a combination can provoke nausea, headaches, pain in the stomach, as well as dizziness, shortness of breath, decreased blood pressure and facial flushing.
"Cefotaxime" is absolutely incompatible with alcohol
Among other things, the drug should not be combined with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as antiplatelet agents, which, when combined, can cause bleeding. As for the compatibility of the cefotaxime solution, it can be used together with other antibacterial drugs in the same dropper or syringe.
It is also recommended to closely monitor your health while taking the drug. This is especially true in situations where an antibacterial drug is prescribed to children and pregnant women, since its use negatively affects the immune system.
Drug dosage
Now you know how to dilute Cefotaxime injections. But what is their dosage? It depends on the indications and severity of the disease.
For urinary tract infections, as well as for uncomplicated infections, the drug is administered intravenously or intramuscularly, 1 g every 9-12 hours.
For moderate infections - 1-2 g every 12 hours.
For uncomplicated acute gonorrhea, the medication is prescribed intramuscularly in a dosage of 1 g (single dose).
For severe infection (for example, meningitis), the drug is used intravenously, 2 g every 6-9 hours. The maximum dose per day is 12 g. The duration of therapy is determined individually.
To prevent the development of infectious diseases, before surgery, the patient is given a single dose of 1 g of Cefotaxime during induction of anesthesia. If required, the injection is repeated after 6-12 hours.
During a caesarean section, during the process of applying clamps to the umbilical vein, the drug is administered intravenously in an amount of 1 g. Then, after 6-12 hours, an additional injection is given in the same dose.
Kinetic features of the drug
How is Cefotaxime absorbed? The abstract (injections are the only form of the drug mentioned) indicates that after intramuscular administration, the highest concentration of the drug in the blood is observed after 35 minutes. Approximately 27-40% of the active substance binds to plasma proteins.
The bactericidal effect of the drug lasts for 12 hours. The drug is found in the gallbladder, myocardium, bone and soft tissues.
It should also be noted that the active component of this drug is able to penetrate the placenta, and can also be detected in pleural, peritoneal, synovial, cerebrospinal and pericardial fluids.
About 90% of the drug is excreted in the urine.
When administered intramuscularly, the half-life of the drug is 60-90 minutes, and when administered intravenously – 1 hour. Partially the active ingredient is excreted along with bile. There is no accumulation of the drug.
Pharmacological properties
Do you know what the drug Cefotaxime is? The instructions for use (injections for children are not an easy test, but what to do if such a need is ripe?) states that the drug is prescribed to young patients with extreme caution, because it is a semi-synthetic antibiotic. Its active substance is classified as a third generation cephalosporin.
The medication is used parenterally. It is active against gram-positive flora, as well as gram-negative microorganisms that are highly resistant to aminoglycosides, sulfonamides and penicillin.
The principle of the antimicrobial action of this drug is based on its ability to suppress transpeptidase activity. This happens by blocking peptidoglycan.
Cefotaxime instructions for use
Instructions for use of the drug describe dosages for different ages of patients and methods of diluting the drug. The amount can be increased/decreased at the insistence of the attending physician. Such adjustments are possible after diagnosis and assessment of the patient’s condition.
Directions for use and doses
Cefotaxime lyophilisate is used for parenteral administration. The drug compound can be administered either intravenously or intramuscularly. It is better to give the injection in the gluteal muscle.
Before administration, the drug is diluted.
The medicine Cefotaxime is prescribed to adults and children of various ages.
The maximum daily dose of Cefotaxime for adults and children over 12 years of age is 4 grams per day. Minimum – 500 mg. In severe conditions, this dosage can be increased to 12 grams.
Pediatric doses are calculated based on the patient's weight. For children under 12 years of age, the amount of antimicrobial drug is from 50 to 100 mg per kilogram of body weight.
The interval between injections should be at least 6 hours.
The drug is very rarely prescribed before the age of 2 years. However, in cases of such prescriptions, the amount of the drug is reduced to 25 mg per kilogram of body weight.
How to dilute Cefotaxime
The drug is diluted in the same way as other lyophilisates for injection. The solvent is drawn into the syringe. Then the seal is removed from the bottle. The rubber stopper is pierced with a syringe needle. Shake the bottle and wait until the powder is completely dissolved. The prepared solution is drawn into a syringe and used for injection.
How to dissolve Cefotaxime for intramuscular administration? Immediately before administering the drug, it is diluted with purified water, glucose solution or 0.9 percent saline solution.
For intramuscular injection, the volume of solvent is 2 ml. For perfusion administration, 2 grams of the drug are diluted in 100 ml of isotonic solution.
In addition to solvents (when administered into a muscle), lidocaine can be used to dilute the drug Cefotaxime. Use 2% lidocaine to reduce pain. To dilute Cefotaxime in this way, take 2 ml of the anesthetic lidocaine and 2 ml of water for injection. The solutions are mixed in one syringe, and the lyophilisate is diluted with the finished mixture.
The drug can be diluted with any of the solvents described above. For people with particular sensitivity to lidocaine and proven cardiovascular insufficiency, the use of the anesthetic is not recommended.
It is not recommended to dilute Cefotaxime with novocaine.
How many days to inject Cefotaxime
The course of treatment with Cefotaxime is usually 5-7 days. For complicated infections and peritonitis, the drug can be administered for 14 days.
How many times a day can you inject the drug? Cefotaxime is administered twice daily. In cases of complicated infections, it is possible to administer the medication every 6 hours.
Can the diluted solution be stored? Powder for injection must be diluted immediately before administration. The drug is not stored in its finished form, as it loses its sterility.
How long can you take Cefotaxime? Oral use of the drug is not described in the instructions for use and is inappropriate, since the drug is destroyed by digestive enzymes.
Side effects and overdose
When the drug is administered, the development of undesirable reactions is quite often observed. The most common of them include the following.
- Allergic reactions that manifest themselves as skin rash, redness, itching, hardening upon palpation at the injection site. The most serious manifestations of allergies include anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema.
- Dyspeptic disorders of the gastrointestinal tract - diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, flatulence.
- Pseudomembranous colitis. This symptom occurred in only 2% of all known cases.
- Changes in liver enzymatic activity.
- Hematopoietic disorders - agranulocytosis, neutropenia, eosinophilia, anemia (including hemolytic).
- Increase in body temperature to subfebrile.
- Increased levels of nitrogen urea in urine.
Adverse events occurred in 30% of all reported cases.
How can an overdose occur?
An overdose of Cefotaxime can occur when a person neglects medical recommendations and instructions, which leads to exceeding the dose entering the body required for his treatment.
An overdose of the drug is fraught with increased side effects, which are rare, but occur during treatment with this antibiotic.
Adverse reactions during the use of Cefotaxime:
- Gastrointestinal organs: the development of glossitis, candidal stomatitis, the appearance of excessive dryness in the mouth, ulcers on the oral mucosa, the occurrence of heartburn, dyspepsia, disturbances of appetite, liver function, the development of pancreatitis, colitis;
- organs of the respiratory system: the appearance of shortness of breath, bronchospasms, swelling of the respiratory tract mucosa;
- heart and blood vessels: development of heart rhythm disturbances, tachycardia, decrease in blood pressure, cardiac arrest;
- allergic reactions: the appearance of urticaria, skin rashes, dermatitis accompanied by itching, epidermal necrolysis, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock;
- circulatory system: the occurrence of leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, agranulocytopenia, decreased platelet count, increased prothrombin time;
- organs of the urinary system: disruption of the normal functioning of the kidneys, development of interstitial nephritis, thrush of the genital organs in women;
- local reactions: pain at the injection site, puncture of a vein, development of internal hematomas, the appearance of an infiltrate with severe pain, redness and swelling of the injection site.
During the injection, especially when Cefotaxime is placed inside the veins, the patient may feel a lack of oxygen, increased heart rate, shortness of breath, and chills. If such a reaction occurs, you need to warn the nurse and stop administering the antibacterial agent.
Analogues and cost
There are no drugs with similar effects in the form of tablets. However, there are drugs in powder form. Among the analogues it is worth highlighting:
- Cefoxin;
- Claforan;
- Liforan;
- Intrataxim;
- Clafotaxime;
- Razibelakta;
- Duatax;
- Cefotaxime vial;
- Taksim;
- Cephajet;
- Cephabol;
- Tarfetoxime;
- Talceph.
On average, 5 ampoules containing 1 g of the drug will cost 75 rubles, and 50 pieces - 750. The price of Cefotaxime is low, one ampoule is around 28 rubles. The cost varies from region to region.
Cefotaxime can only be purchased at a pharmacy. In this case, you must provide a doctor's prescription form. Cefotaxime recipe in Latin looks like this:
- drug name Rp. Sol. Cefotaximi;
- dose in grams, for example 1.0 g;
- in column D. td N the amount of the drug is written, for example No. 12 in flac;
- in the S. field the method of administration is written, for example, 1.0 2 times i.v.
Analogues of the antibiotic Cefotaxime
There are quite a lot of different analogues of this medicine in pharmacies. Analogues include: Intrataxim, Clafobrine, Kefotex, Claforan, Liforan, Oritax, Oritaxim. Also in the list of analogues you can find such drugs as Cephabol, Cephantral, Cefosin. Among the analogues there are various forms of Cefotaxime - Lek, DS, sodium, Sandoz, Elfa.
special instructions
Cefotaxime quite often in the first days of use can cause pseudomembranous colitis, which is manifested by prolonged diarrhea. In cases of such manifestations, the drug is discontinued and replaced with antimicrobial agents from other chemical groups.
Cefotaxime injections are performed intramuscularly so that the drug solution is delivered slowly to avoid the occurrence of infiltrates in the soft tissues.
You cannot combine the administration of Cefatoxime with the use of antibiotics from the penicillin group, as this can cause cross-allergy, including anaphylactic shock.
The use of the drug requires constant monitoring of the peripheral blood picture.
The drug may give a false-positive Coombs test reaction and a false-positive test for the presence of sugar in the urine.
Side effects most often develop in childhood and in older people over 65 years of age.
Alcohol compatibility
The drug is incompatible with ethyl alcohol, and, consequently, with alcohol-containing products. Combining Cefotaxime with alcohol can lead to a curare-like effect, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- a sharp decrease or increase in pressure;
- tachycardia;
- dyspnea;
- nausea;
- headaches, dizziness;
- stomach pain, cramps.
Use with other drugs
The drug should not be used in combination with antiplatelet agents, as the risk of bleeding increases.
Cefotaxime enhances the toxic effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
When administered simultaneously with drugs from the aminoglycoside group, the risk of damage to the kidneys and genitourinary system increases.
The drug should not be administered in the same syringe or dropper with other medications. Exceptions are solvents (sodium chloride solution, glucose, lidocaine, water for injection). Cefotaxime and lidocaine - these chemical compounds are completely compatible, but this does not apply to other local anesthetics.
The drug Cefotaxime is prescribed to children only if there are serious indications. If there are alternative options, they try not to use it in childhood.
Drug interactions
To speed up the patient's recovery, antibiotics are prescribed simultaneously with medications from other groups. It is important to know about drug interactions:
- Antacids and H2 receptor blockers reduce the absorption of Cefodox and delay the desired therapeutic effect.
- When used concomitantly with nephrotoxic drugs, it is important to monitor renal function every week.
- In combination with Probenecid, the concentration of cefpodoxime in the blood plasma increases, and there is a risk of intoxication of the body.
Contraindications and side effects
Despite all the advantages and positive description of Cefotaxime that the manufacturers give this drug, taking it without a doctor’s prescription is strictly prohibited. This is because this drug has certain contraindications that can lead to side effects.
Taking Cefotaxime is prohibited in the following situations:
people who have individual intolerance to B-lactam drugs; with bleeding; if a person has nonspecific ulcerative colitis; heart failure;
during pregnancy in the first trimester; when breastfeeding; intramuscular administration of the drug is prohibited for children under 2.5 years of age; the drug is prescribed with caution to persons diagnosed with chronic renal failure; When administered intramuscularly, the drug is prohibited for use by persons allergic to lidocaine.
Since Cefotaxime is a broad-spectrum agent, the drug is low-toxic. But even despite this, the following side effects may occur when using Cefotaxime:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- obstructive jaundice;
- hives;
- itching and irritation;
- change in blood formula;
- eosinophilia;
- swelling at the injection site;
- hyperemia of the skin;
- the appearance of a vascular network.
Side effects
Taking an antibiotic can cause side effects in both children and adults. Among them:
- allergic reactions - skin itching, rash, eosinophilia, in rare cases angioedema appears;
- urinary organs - nephritis;
- digestive organs - vomiting and nausea, diarrhea, hepatitis colitis and so on;
- hematopoietic organs - leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia and neutropenia;
- hypoprothrombinemia;
- local reactions - phlebitis and pain at the injection site.
But these are not all the reactions that occur as a result of taking an antibiotic. For example, the drug has a chemotherapeutic effect, which in rare cases provokes candidiasis.
Analogues in injections
There are many brands on the Russian pharmaceutical market that produce an antibiotic based on the substance “cefotaxime anhydrous” in injections. The price range for analogues is also wide; sometimes the cost per 1 gram of the drug can differ tens of times. So, let's look at the most common of them:
- The drug "Klaforan". This antibiotic is made in France. It is produced in bottles, each of which contains 1 gram of anhydrous cefotaxime, as in Cefotaxime. This analogue is suitable for children from the first days of life. The cost of the bottle is 170 rubles. You can also choose analogues of Cefotaxime in tablets for children.
- The medicine "Cefosin" is an analogue of Russian production. Vials are available in 1 gram quantities with the same active ingredient as Cefotaxime. Like Klaforan, this drug is suitable for use in newborns and even premature babies. The cost of the bottle is 20 rubles.
- The drug "Cefantral" is an analogue of "Cefotaxime" (Indian production). It has dosages of 250 and 500 milligrams of cefotaxime anhydrous. The price for one unit of goods is 16 rubles.
Analogues of Cefotaxime in injections should be selected by a doctor.
Another analogue antibiotic is a drug called “Vilprafen” produced in Belarus. It is produced in bottles, each of which contains the same active substance as Cefotaxime. This analogue has a low price, which is only 17 rubles.
Dilution of the drug
Doctors categorically prohibit self-medication, especially when it comes to serious medications, including Cefotaxime. It is prohibited to prescribe the drug yourself if there are suspicions of certain types of diseases. Moreover, you cannot use the drug intravenously if you do not know how to do it correctly.
Despite medical prohibitions, there is often a need to not only prescribe medications yourself, but also use them. If you decide to use Cefotaxime on your own, you should know how to do it correctly. Initially, you should remember that children under 2.5 years old can only administer the medicine into a vein. Starting from 2 years of age, antibiotics can be used for both intravenous and intramuscular administration. If you plan to use the medicine intramuscularly, then the daily dosage should be divided into two times. Injections into a vein can be given in full once.
To use the drug for intravenous administration, it must be initially prepared. How to dilute the medicine, and also what excipients can be used? Before using Cefotaxime, it should be diluted with solvents such as glucose or distilled water. For intramuscular administration, you can give preference to such types of solvents as novocaine, lidocaine, saline, as well as special sterile water for injection.
To dilute the medicine, you will need to use a regular disposable syringe with a needle. First, you need to draw 4 ml of solvent into the syringe, after which you should inject it into the ampoule with the powder.
Once the syringe is empty, there is no need to remove it. Now you should thoroughly mix the powder for 1 minute to obtain a homogeneous liquid. Now you should turn the bottle upside down and take the required amount of medicine. After the syringe is removed from the bottle, the air should be squeezed out from it. Before injecting the medicine, you need to use medical alcohol and a cotton swab to treat the injection site.
Release form and composition
This antibacterial agent contains only one active ingredient - cefotaxime, which has the form of sodium salt powder. Each bottle of powder contains 500-1000 mg of the active ingredient; this medicine does not contain other components (doses for children and adults may vary).
Sterile water is used to prepare the injection solution.
Cefotaxime is produced by different companies in Russia, China, India, and Belarus. Some medicines, in addition to the word Cefotaxime, contain a word that is an indicator of its affiliation with the trademark (for example, Cefotaxime - Vial, Cefotaxime - Promed). These medications are no different from one another; they contain an identical dosage form and act on the same range of pathogens.
Cefotaxime has the form of a yellowish-white powder that does not have a characteristic aroma. This substance is packaged in small dark glass bottles, sealed with rubber stoppers. The medicine package can contain 5 or 10 such bottles. A number of manufacturers make it easier for consumers and immediately place the solvent in a 5 ml ampoule into the packaging.
Composition, description, form and packaging of the medicine
What ingredients does Cefotaxime contain? The injections (for children, the dosage of this drug is determined individually) include an active substance such as cefotaxime (sodium salt).
The drug itself is a white or yellowish powder, which is used to prepare a solution intended for intravenous or intramuscular injection.
The medicine can be purchased in glass bottles, packaged in cardboard packaging.
Instructions for use and dosage of the drug
Before diluting the drug, it is recommended to study the dosage of the active substance. To prepare the medicinal solution, distilled water is used (replaced with lidocaine with the doctor's permission). Proportions: 1 mg of drug per 4 ml of liquid. The solution is injected intramuscularly, deep into the tissue of the gluteal muscle.
For intravenous administration of the drug, a less concentrated solution is prepared. For 10 ml of liquid there is only 1 mg of powder.
Adults and adolescents (from 12 years old) are recommended to administer the drug twice. In case of complications, injections are administered more often - up to 4 times a day, but this should only be done with the permission of the doctor.
Features of use during pregnancy and lactation
During gestation or when feeding a child with breast milk, the use of the drug is permitted, but only after a medical examination
Treatment should be carried out with caution and if undesirable manifestations occur, immediately stop administering the medication.
Specifics of use in childhood
Children should use Cefotaxime only after medical consultation. Dosages:
- premature babies - no more than 50 mg/kg;
- newborns - from 50 to 70 mg/kg;
- from one to 12 years - from 60 to 100 mg/kg.
The doctor is able to prescribe a different dosage, taking into account the general health of the child, the characteristics of the body, and possible complications.
If kidney or liver function is impaired
Problems with the functionality of the kidneys and liver are a reason to use the medicine with caution. It is better not to self-medicate and first consult a doctor
Instructions for children
If necessary, Cefotaxime injections are prescribed intravenously to newborns, as well as premature infants under one week of age, in the amount of 50 mg per kg of body weight every 12 hours. At the age of 1-4 weeks, the drug is administered in the same dose, but every 9 hours.
For children over 2.5 years old with a body weight of less than 50 kg, the medication is prescribed intramuscularly or intravenously in the amount of 50-180 mg per kg of weight (in 4 or 6 injections).
For severe infectious diseases, including meningitis, the daily dosage of the drug is increased to 100-200 mg per kg. In this case, injections are carried out intramuscularly or intravenously 4-6 times a day. The maximum dose of the drug per day is 12 g.
Operating principle
Cefotaxime, the annotation to which is attached, is an antibacterial drug classified by the manufacturer as a third-generation cephalosporin group. This medicine easily copes with various bacteria that antibiotics from the group of penicillins, aminoglycosides and sulfonamides cannot get rid of.
Cefotaxime, during its effect on the human body, blocks the cell walls of pathogenic microorganisms. It is especially effective against gram-negative bacteria (for example, E. coli).
Intramuscular injection of the drug allows you to achieve the maximum concentration of the active substance in plasma after 30 minutes. Intravenous infusion shortens this process to five minutes. After binding to plasma proteins, the antibacterial effect begins to build up, which reaches its maximum after 12 hours.
Cefotaxime has another important feature: the active substance of the drug accumulates where inflammatory processes occur (bone tissue, muscle fibers, fatty tissue located under the skin, skin, gall bladder). In addition, the antibiotic easily penetrates into biological fluids (spinal, synovial, pleural)
https://youtube.com/watch?v=NONDezaZgac
The drug does not have a toxic effect on liver cells; almost 90% of the entire composition is excreted outside the body along with urine. Intramuscularly administered medication is half eliminated after an hour and a half; intravenous administration shortens this process to one hour.
Interaction with other drugs
When using an antibiotic with other medications, the risk of bleeding may increase. The use of antibiotics with antiplatelet agents and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is prohibited. If aminoglycosides are taken at the same time, kidney damage cannot be ruled out.
It is prohibited to use an antibiotic with other similar drugs, which can cause not only side symptoms, but also various kinds of complications. The drug has many analogues, among which are: Claforan, Intrataxime, Kefotex and Oritax. The main advantage of the antibiotic is the provision of bactericidal properties by inhibiting the synthesis of the cell wall of pathogenic bacteria.
Analogs
In some cases, it becomes necessary to replace the drug with something else. Moreover, the cost of products with a similar effect may differ. Cefotaxime analogues in injections are available in large quantities, including:
- Claforan is a drug produced in France and is approved even for children from the first days of life. It is in the form of bottles with a capacity of 1 g. The cost is quite high - about 170 rubles for one bottle;
- Cefosin is a Russian analogue with the same dosage. Can be used by newborn children, even approved for premature babies. Cost from 20 rubles;
- Cefantral - the drug is produced in India and has different dosages - from 250 to 1000 mg. The cost is 16 rubles per bottle and above.
If for one reason or another cephalosporin antibiotics cannot be used in the form of injections, they can be replaced with tablets or suspensions. This makes them easier to take at home and eliminates pain when administered intravenously or intramuscularly. Cefotaxime itself is not available in oral form, but there are analogues on the market:
- Pancef - the active component of the drug is cefixime. This is a third generation cephalosporin. In the pharmacy it is presented in the form of tablets and suspensions. Antibacterial activity does not differ from Cefotaxime; it can be prescribed to children aged six months and older. A pack of tablets costs an average of 700 rubles, and a bottle of suspension costs up to 500 rubles, respectively.
- Suprax is an Indian-made product based on the substance cefixime. It comes in the form of tablets and granules for preparing a solution. Can be prescribed to children aged 6 months and older. Depending on the shape, the cost of packaging ranges from 700-900 rubles.
- Ixim Lupine - has a similar active substance. Available in the form of a powder for preparing a suspension; one package contains 25 g of such powder. The finished product has a pleasant strawberry flavor. Its cost at the pharmacy is up to 500 rubles.
- Zinnat is a second generation cephalosporin. The active ingredient is cefuroxime axetil. It comes in the form of tablets and suspensions and is produced in the UK. Its activity against microorganisms is almost the same as that of Cefotaxime. The cost of tablets is about 250 rubles, suspensions are 300 rubles.
- Axosef - the drug is in the form of 500 mg tablets made on the basis of cefuroxime, and is used only for the treatment of adult patients. The cost of one package is about 550 rubles.
Only the attending physician can select one or another analogue. The choice depends on the patient’s age, the causative agent of the disease, the presence of concomitant diagnoses and other factors. The form of release of the product is also important. If we are talking about severe infections, then it is best to administer it by injection. In addition, you must follow the rules for administering and diluting the drug. Not everyone can do this at home.
Analogs in the form of tablets or suspensions are more preferable for taking at home. There is no need to have special skills, and there is no danger of local reactions.
When treating children, you must follow medical recommendations. If you decide to give your child the product in the form of a suspension, then you need to find out in advance what dyes or flavors are present in it that can cause allergies.
How to dilute cefotaxime
For intravenous use, depending on the prescribed dose, dissolve either 0.5 g or 1 g of the drug in two or, respectively, four milliliters of specially sterilized water for injection, add the required amount of solvent until 10 ml of the substance is formed and begin to slowly inject into one of the most large veins
The optimal administration time is three to five minutes. The dosage for children depends on the child's body weight. When dissolving Cefotaxime for a child, you should strictly adhere to the instructions of the attending physician who prescribed the medication.
Cefotaxime can be administered to adults through an IV.
When administered via a dropper for adults, 2 g of the drug is dissolved in 100 ml of a five percent glucose solution or an isotonic sodium chloride solution.
As with intramuscular administration, dosage calculations for intravenous administration in children should be made by a qualified physician. The approximate administration time is from 50 minutes to 1 hour. As a rule, the course of treatment lasts about ten days.
Cefotaxime should be diluted very carefully for children under two and a half years of age. If you follow the doctor's recommendations, the medication is tolerated quite easily
However, when administered intramuscularly, as noted above, taking the drug may be accompanied by pain.
To relieve pain from injections for children, dilution with Novocaine is recommended.
Cefotaxime or Ceftriaxone - which is better?
If you compare Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone, it is very difficult to choose the best one, since they are similar in:
- potency (both are highly effective);
- antibacterial spectrum (broad action);
- group - belongs to the 3rd generation of cephalosporin antibiotics;
- administered only intramuscularly or intravenously.
The main differences are the duration of action (Ceftriaxone is administered 1 time, Cefotaxime - 2-4 times), as well as the excretion of the first antibiotic in the urine and bile, and its ability to provoke the precipitation of salts in the kidneys and gall bladder.
For pneumonia
For adult patients, Ceftriaxone is better than Cefotaxime for pneumonia in the following cases:
- bleeding;
- concomitant ulcerative colitis;
- severe heart failure;
- blockade of impulses in the heart (atrioventricular).
Cefotaxime is indicated for newborns rather than Ceftriaxone for pneumonia and the presence of:
- increased bilirubin in the blood;
- jaundice;
- the need to administer calcium salts;
- up to 41 weeks of age, including intrauterine development.
In terms of their potency against pneumonia pathogens, they are completely identical, but there are cases when sensitivity tests reveal that one of the drugs will be more effective.
We recommend reading about how to use Ceftriaxone for pneumonia. From the article you will learn about how antibiotics work for pneumonia, treatment regimens in adults, and duration of therapy. And here is more information about how to use Ceftriaxone for sinusitis.
For sinusitis
Ceftriaxone and Cefotaxime for sinusitis are most often used when the course of the disease is complicated and there is a threat of infection spreading to the choroid. They both penetrate the blood-brain barrier, but for Ceftriaxone this ability is higher. After just 2 hours, its level in the cerebrospinal fluid is many times higher than the required concentration to destroy the main pathogens.
Therefore, for the treatment of severe forms of sinusitis, it is better to choose Ceftriaxone.
For bronchitis
During the inflammatory process in the bronchi, the same features are taken into account as in the treatment of pneumonia; it is important to pay special attention when using antibiotics for pregnant and lactating women:
- Cefotaxime is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding; it penetrates well through the placenta and into breast milk and can adversely affect the fetus or newborn;
- Ceftriaxone can be used in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy if there is a high risk to the mother’s health; it is not completely safe, but there are animal studies that have proven that there are no harmful effects on pregnancy and the fetus;
- In nursing women, Ceftriaxone is used with caution, since the antibiotic is found in milk in low concentrations, but can cause allergic reactions in the child - rash, diarrhea, oral thrush; if high doses are needed, it is better to switch to formula.
Antibiotics during pregnancy
The effect of alcohol on the body
As mentioned above, alcohol can:
- Strengthen the effect of medications.
- Reduce the effect of medications.
- Change the result of drug treatment to the complete opposite.
Sometimes the attending physician cannot even say exactly what consequences await the patient when simultaneous use of medications and alcoholic beverages. In this case, it is necessary to take into account a large number of different factors, which include the characteristics of the human body, the dose of the medication and the specifics of its use.
That is why there are no instructions for medicinal formulations that would indicate that you can take medications and alcoholic beverages at the same time.
As a result of numerous studies, it was found that the combined use of drugs and strong drinks causes the following reaction in the body:
- respiratory arrest;
- increased heart rate;
- nausea leading to vomiting;
- suffocation;
- impaired coordination and balance;
- chills;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- death.
Due to the fact that the combined use of medicine and alcohol leads to the above negative consequences, you should not use them at the same time.
Cefotaxime - how the medicine acts on the body
Cefotaxime is a powerful modern antibiotic, the action of which is determined by a strong bactericidal effect. Numerous patient reviews confirm the effectiveness of this drug, which is used when bacteria and microorganisms are resistant to other types of antibiotics.
As Cefotaxime is administered, this drug reaches its full concentration in the bloodstream within an hour. At the same time, it quickly enters almost all tissues and internal organs. The medicine is eliminated by the kidneys.
It is also worth knowing that Cefotaxime is able to cross the placental barrier, so the composition can easily pass into breast milk.
This antibiotic is used today as an injection and is prescribed for bacterial diseases:
- damage to joints, bones and tissues;
- pathological inflammation of the urinary tract and organs - prostatitis, pyelonephritis;
- infectious diseases of the central nervous system - meningitis;
- abdominal diseases;
- respiratory infections – sinusitis, bronchitis.
Cefotaxime is used for peritonitis, salmonellosis, and wounds caused by infections. Also, indications for its use are gynecological curettage and surgical interventions, and its effectiveness is confirmed by numerous reviews from people. However, the medicinal composition should be taken only after it is recommended by a specialist.
Is it possible to replace Ceftriaxone with Cefotaxime?
Ceftriaxone can be replaced with Cefotaxime, since these drugs have the same resistance to microbes. They are also similar in antibacterial strength. They have similar indications for use.
Such a replacement is strictly prohibited in case of an allergic reaction, since intolerance often extends to all cephalosporin antibiotics. The question of prescribing and replacing medications is decided only by a doctor, who also monitors blood tests and the presence of adverse reactions.
We recommend reading about how to use Ceftriaxone for sore throat. From the article you will learn about the advantages and disadvantages of Ceftriaxone for angina, treatment regimens in adults and children, and side effects. And here is more information about whether Ceftriaxone can be taken during pregnancy.
Ceftriaxone and Cefotaxime are similar in their main medicinal properties. The advantage of the first drug is a single administration, and Cefotaxime can be used more often in newborns.
What is Cefotaxime?
Cefotaxime belongs to the third generation semisynthetic drugs, to the group of cephalosporin antibiotics. This is a broad-spectrum agent, i.e. it is effective against most pathogenic bacteria (even those that are resistant to the penicillin group and sulfonamides). The drug works at the cellular level. It inhibits the production of certain hormones on which the vital activity of bacteria depends.
Note: how to eat properly during pregnancy.
It is recommended to read how to cure cystitis during pregnancy without harming the baby.
The medicine is intended to fight infections:
- respiratory tract (bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia);
- urinary system;
- nasopharynx;
- bones and soft tissues;
- gynecological (chlamydia, gonorrhea);
- abdominal cavity,
- and also for the prevention of infection after surgery.
The main disadvantage of Cefotaxime, like any other antibiotic, is that it kills all bacteria indiscriminately. Including the “good” ones that make up the intestinal microflora. And immunity largely depends on the state of the microflora. Thus, by killing pathogens, antibiotics also attack the body’s defense system. And in expectant mothers, the immune system is already not working at full strength.
Important! The medicine is intended for the treatment of severe infections. Cefotaxime is prescribed to pregnant women only in extreme cases, when the consequences of the disease for the mother are more dangerous than the possible harm to the unborn child.
Cefotaxime and pregnancy
At the beginning of pregnancy, doctors try not to prescribe any antibiotics. In the first trimester, the foundations of the future organism are laid. This is a rather delicate biochemical process, so any external influence on the mother’s body during this period can lead to dire consequences.
In the second and third trimesters, when the placental barrier has already been formed, the use of antibiotics may be justified if all other measures have failed. The list of medications that can cope with severe infections with minimal harm to pregnancy includes drugs of the penicillin and cephalosporin groups.
Doctors believe that after the 23rd week of pregnancy, Cefotaxime is practically safe for expectant mothers. By this time, the fetus has already formed the hearing aid - the most sensitive organ to antibiotics. But this is not a reason to use an antibiotic without a doctor’s prescription. In order not to harm the pregnant woman and the fetus, you need to make sure that the disease is caused by drug-sensitive pathogens and study the medical history of the expectant mother.
Cefotaxime can also be used during a planned caesarean section at 40 weeks, when it is necessary to separate the bodies of the woman and the child.
Manifested action
Semi-synthetic antibiotic. The active component belongs to the third generation cephalosporins, used parenterally. The drug is active against gram-negative and gram-positive flora that are resistant to the action of sulfonamides, aminoglycosides and Penicillin.
- pain during intramuscular injection;
- phlebitis during intravenous infusion.
Nephrotoxicity increases with treatment with loop diuretics and aminoglycosides. NSAIDs and antiplatelet drugs increase the risk of bleeding. It is unacceptable to mix Cefotaxime with other medications in one syringe (with the exception of Novocaine, Lidocaine). Probenecid increases the concentration of the active substance and slows down its excretion.
The drug has the strongest bactericidal effect among cephalosporins. The antibiotic disrupts the formation of cell walls, which leads to the death of microorganisms. Cefotaxime is active against gram-positive and gram-negative microbes, including strains that are resistant to penicillins, aminoglycosides and other cephalosporins.
Cefotaxime may interact with other drugs. Therefore, it is necessary to inform your doctor about all medications used to correct therapy and prevent the development of health-threatening conditions.
It is not recommended to take antibiotics together with:
- aminoglycosides;
- loop diuretics;
- polymyxin;
- colistin;
- tetracyclines;
- chloramphenicol;
- erythromycin;
- nifedipine;
- probenecid.
In what area is it used?
The wide spectrum of action of Cefpodoxime allows it to be used for diseases of various organs. Most often these are urology, surgery, dermatology, otolaryngology, gynecology and pediatrics. Indications for use:
- skin diseases;
- pathologies of the ENT system;
- diseases of the lower and upper respiratory tract;
- urinary system infections.
In the latter case, the disease should be uncomplicated. Prescribed as a treatment for acute gonorrhea.
Compatibility of alcohol and pills: what you need to know about taking them and the consequences
Popular wisdom says: “You can’t protect yourself from prison and money.” We can also add here that it is also not always possible to protect yourself from illness.
Sometimes you have to swallow antibiotics while on vacation at the seaside, where there is so much entertainment that involves the inevitable drinking.
However, it is worth remembering that not all antibiotics can be combined with alcoholic entertainment. What should you do if your doctor recommends treatment with ceftriaxone?
Ceftriaxone is a third generation cephalosporin. This antibiotic is active against many pathological microorganisms: staphylococci, Klebsiella, Escherichia coli, Shigella and many others.
The antibiotic is available in a single form - glass bottles with powder from which a solution for injection into the muscle is made.
Ceftriaxone can be used to treat many infectious diseases:
- meningitis;
- ENT organs;
- abdominal organs, including peritonitis;
- genitals;
- respiratory tract;
- salmonellosis;
- infected wounds, burns.
There is one clearly stated rule in medicine, which is often forgotten in real life.
It states: the combination of alcohol and drugs is mutually exclusive, highly undesirable and even harmful.
Why is there such a strict taboo on the simultaneous use of alcohol and pills? Because alcohol can affect the behavior of drugs in the human body in the most unpredictable ways:
- enhance its effect (potentiate);
- weaken (inhibit);
- or pervert it to the contrary.
Often, even a doctor cannot predict with absolute accuracy what consequences await a patient after drinking alcohol and taking medications at the same time. Too many factors should be taken into account: doses, specificity of pills and alcohol, individual characteristics of the body, etc.
Therefore, you will not find any recommendations in any instructions to drink medications with alcohol. After all, there is not a single beneficial combination of alcohol and medications. And the number of relatively safe ones is small. Everything else is a potential risk and negative. The interaction of alcohol and drugs can cause a wide variety of consequences:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- drop in blood pressure;
- chills;
- lack of coordination;
- suffocation;
- increased heart rate;
- respiratory arrest;
- death.
Therefore, it is extremely important to consciously refuse to simultaneously take alcohol and medications, since they are inherently incompatible. Let's take a closer look at the compatibility of different groups of drugs with alcohol.
Nise tablets are a pharmacological agent that has antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. In addition, it also performs an antiplatelet function - it prevents the formation of blood clots. Nise is a non-narcotic analgesic.
When taking alcohol and medication simultaneously, the absorption of the latter from the gastrointestinal tract is accelerated. However, at the same time, alcohol greatly increases the damaging effect on the liver and gastric mucosa.
The interaction of the active substances of the drug with ethanol causes negative consequences: extremely toxic substances are released that can accumulate in the kidneys. For narcotic analgesics, alcohol will enhance the inhibitory effect on the respiratory center and nervous system.
Source: alkogolizm.top
How to choose antibiotics for chronic, acute or bacterial prostatitis?
Treatment of inflammation in the prostate gland is carried out using groups of medications. If there is a bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed for prostatitis. They eliminate the influence of harmful microorganisms and inflammation, speed up the healing process. For therapy to be effective, it is important to determine with your doctor which antibiotic for prostatitis in men is more effective. This can be done based on the test results.
How to choose a drug?
The use of antibiotics for prostatitis is indicated when a bacterial form of the disease is detected. The infection can be eliminated by determining the type of pathogenic microflora and its sensitivity to antibacterial agents.
Drugs for treatment
Treatment of prostatitis with antibiotics is carried out with a preliminary analysis of prostate secretions. Until this moment, any medications other than anti-inflammatory, painkillers and decongestants are prohibited. Otherwise, negative side effects may appear and the therapy will not give a positive result.
The patient needs to know that there is no universal answer to the question of how to treat inflammation in the prostate gland. Therefore, examination must be carried out necessarily. Antibacterial therapy can then be administered at home.
An antibiotic is prescribed by a urologist after examination
Antibiotics in tablets
Antibiotics for prostatitis in men in the form of tablets can contain various active ingredients. The list of drugs used for bacterial prostatitis includes many names.
Josamycin
Treatment of prostatitis with antibiotics can be carried out using macrolides. These include Josamycin, which has a bacteriostatic effect. It concentrates in the inflammatory focus and eliminates the influence of harmful microorganisms.
Antibiotic Astellas Vilprafen (Josamycin)
The product has virtually no side effects. Some patients report loss of interest in food, nausea and heartburn.
Roxithromycin
Roxithromycin is a semisynthetic antibiotic of the macrolide group. At a reduced dosage it has a bacteriostatic effect. If the treatment regimen for prostatitis is prescribed using increased doses, then the drug eliminates pathogenic microflora.
Roxithromycin, 10 tablets.
The drug is contraindicated in patients suffering from liver failure and allergies to the active substance.
Doxycycline
At home, prostatitis can be treated with Doxycycline. It fights mycoplasma and chlamydia. A tetracycline antibiotic inhibits the synthesis of bacterial proteins.
Doxycycline (Doxycyclinum) is a broad-spectrum tetracycline antibiotic.
Absorption of the active component occurs instantly in the gastrointestinal tract. If you take the tablet with food, the process slows down slightly.
Cefotaxime
The drug Cefotaxime
For prostatitis and incipient adenoma, you can take Cefotaxime, which can eliminate the influence of:
- anaerobes;
- gram-negative microorganisms;
- gram-positive bacteria.
Before taking the drug, the patient needs to make sure that there is no allergic reaction to cephalosporins and penicillins. The drug may cause angioedema.
Ciprofloxacin 250 mg
Ciprofloxacin
For chronic prostatitis, the antibiotic Ciprofloxacin is prescribed. It is commercially available in tablet form.
Ciprofloxacin (Ciprofloxacinum) is prescribed for chronic prostatitis
Ciprofloxacin should be taken before meals. It is worth remembering that the drug is not prescribed for:
- colitis;
- allergic reaction to the active substance;
- treatment of chronic diseases of other organs with medications.
Ceftriaxone
The third generation cephalosporin is Ceftriaxone. It eliminates anaerobic and gram-negative bacteria and successfully fights gram-positive microflora. The drug helps suppress the synthesis of cell membranes.
Ceftriaxone vial
It is recommended that men who suffer from an allergic reaction to:
- cephalosporins;
- carbalenemes;
- penicillins.
Caution is exercised during the treatment of chronic prostatitis with antibiotics for liver and kidney pathologies, enteritis and colitis.
Ceftriaxone injections
During treatment, you should avoid drinking alcohol. Otherwise, various disorders may appear in the body.
Azithromycin
Effective antibiotics for the treatment of prostatitis are products based on azithromycin. They are used in the treatment of infectious diseases of various body systems.
Azithromycin is a semisynthetic broad-spectrum antibiotic.
The drug can be used in both acute and chronic stages of the disease. It is prescribed after tests reveal a large number of leukocytes and harmful microorganisms.
Amoxicillin
A good semi-synthetic antibiotic used in the treatment of inflammation in the prostate gland is Amoxicillin. It has an enhanced bactericidal effect, so the symptoms are eliminated within a few days after using the drug.
Amoxicillin tablets
Lomefloxacin
An antimicrobial drug with a bactericidal effect is Lomefloxacin of the fluoroquinolone group. It is a vital and essential medicine.
Lomefloxacin for prostatitis
The drug has various contraindications for use. It should be taken with caution when:
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- epilepsy;
- dysfunction of the central nervous system;
- hypokalemia.
In the presence of liver cirrhosis, no adjustment of treatment is required. This rule applies to patients who do not have kidney problems.
Levofloxacin
Levofloxacin has a wide spectrum of action. It is used in the treatment of prostatitis caused by various pathogenic microorganisms.
Levofloxacin is an antibacterial drug of the fluoroquinolone group.
The drug may impair kidney function. Therefore, people suffering from kidney pathologies should take pills only under the supervision of a doctor.
Ofloxacin
The antibiotic Ofloxacin easily penetrates the prostate tissue. Due to this, it quickly affects the source of inflammation and harmful microorganisms.
Despite its high effectiveness, Ofloxacin can cause adverse reactions. Among them are:
- dizziness;
- lethargy;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- drowsiness;
- nausea and vomiting.
Ofloxacin Darnitsa
Overdose is treated symptomatically.
There are some contraindications to taking the drug. These include deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenases, epilepsy, reduced seizure threshold, high sensitivity to the active substance Ofloxacin. Patients who have atherosclerosis of blood vessels in the brain, circulatory disorders, kidney pathologies, or organic damage to the central nervous system should be careful.
Antibiotic suppositories
In addition to general remedies, patients can be prescribed suppositories for prostatitis with antibiotics. They are effective due to their local effect on the source of inflammation.
Antibiotic suppositories are an effective local remedy.
Proctosedyl
Proctosedyl suppositories are prescribed for the treatment of acute and chronic stages of the disease. They consist of six active ingredients, including an antibacterial component. Due to this drug:
- eliminates itching of the genitals;
- eliminates the inflammatory process;
- reduces pain;
- fights pathogenic microflora;
- accelerates tissue restoration.
Use of suppositories
Suppositories with Erythromycin
To treat prostatitis, suppositories with the antibiotic Erythromycin are used. They quickly eliminate the influence of pathogenic microflora. The drug does not cause side effects.
Sometimes Erythromycin suppositories can cause side effects
The drug rarely causes side effects. Nausea, dizziness and impaired hearing may sometimes occur. All symptoms quickly disappear after discontinuation of suppositories.
Levomycetin suppositories
For the treatment of acute and chronic prostatitis, Levomycetin suppositories are prescribed. In case of pronounced symptoms, suppositories are used three times a day.
Treatment of prostatitis with rectal suppositories
Due to the effects of chloramphenicol, the cellular proteins of bacteria are destroyed. Therefore, the product is able to fight any microorganisms, except for Mycobacterium tuberculosis, coccal, and methicillin-resistant infections.
Sintomycin
Many doctors prescribe suppositories with Syntomycin when treating inflammation in the prostate gland. The antibiotic acts on cell membranes, making it impossible for pathogenic microflora to divide and reproduce. In this case, not only the inflammatory process is eliminated, but also the likelihood of further development of infection is eliminated.
The drug is prescribed for diseases caused by the activity of:
- shigella;
- Escherichia;
- salmonella;
- staphylococcus;
- streptococcus;
- protea;
- Treponema.
Antibiotics should be selected exclusively by a doctor. Self-medication can lead to various complications.
| Chronic cystitis in men: causes, symptoms, treatment |
What antibiotics are taken for cystitis?
Cystitis is an acute or chronic infectious disease of the bladder, most often caused by bacteria, as well as viruses or fungi.
Provoking factors in the development of the inflammatory process are:
- hypothermia;
- chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- failure to maintain personal hygiene;
- structural features of the genitourinary system;
- rare emptying of the bladder;
- wearing tight underwear.
Symptoms
The manifestations of cystitis primarily include pain. By nature, this can be a pulling, aching pain in the lower abdomen, as well as cutting pain when urinating.
Frequent urination, more than 10 times a day while maintaining the usual drinking regime, is also a manifestation of the disease.
An increase in body temperature and the appearance of blood in the urine are signs of the spread of infection and worsening of the disease.
Diagnostics
If cystitis is suspected, a standard laboratory and instrumental examination is carried out, including blood tests, urine tests, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, X-ray diagnostics, and cystoscopy.
Therapy
Antibiotics for bladder inflammation are etiotropic therapy, that is, their use is aimed at the bacteria that cause the disease.
Treatment of cystitis with antibiotics is prescribed by the attending physician after a complete examination.
What drugs to treat?
The most commonly used antibiotics for cystitis include the following drugs:
Penicillin
This is a group of broad-spectrum antibiotics and therefore affects all types of bacteria.
The advantages of these drugs are low toxicity, good bioavailability and rapidity of the achieved effect.
The disadvantages include:
- frequent allergic reactions;
- resistance;
- short period of elimination from the body - so you will have to take them often, about 4-5 times a day.
Most penicillins are produced only in injectable form.
Fortunately, the pharmaceutical industry does not stand still and now you can buy tablet protected drugs such as Augmentin and Amoxiclav at the pharmacy. These drugs can be taken 1-2 times a day, and can also be taken by pregnant and lactating women.
Cephalosporins
The advantages of these drugs are:
- wide spectrum of action;
- high bactericidal activity;
- relatively high, compared to penicillin, resistance to bacterial enzymes that destroy antibiotics - beta-lactamases.
Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone are most often used in the treatment of cystitis. These drugs are available in powder form for injection and are prescribed at a dose of at least 60 mg per kilogram of body weight for 5-7 days.
Cefuroxime is an antibiotic for cystitis, a group of cephalosporins, which is available in tablets. Often it can be taken in case of chronic form and when other drugs are ineffective.
| Which doctor treats cystitis in women: gynecologist, urologist and therapist |
| The effectiveness of the antibiotic Azithromycin for cystitis and prostatitis |
| Sex with cystitis: contraindications and recommendations, treatment |
| Interstitial cystitis: causes, symptoms and treatment |
Due to the rather powerful effect on the body, they are used only in advanced cases, or when other means have failed. They are taken only as prescribed and under the supervision of a doctor, often in a hospital setting.
Macrolides
Low-toxic and safe drugs of this group are prescribed for cystitis in women with penicillin intolerance, and for cystitis caused by chlamydia.
Representatives of macrolides are Rossithromycin and Azithromycin (Sumamed) - available in forms for oral administration (tablets, suspension). They are contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy; they should also not be taken if you have allergies or during breastfeeding.
Fluoroquinolones
Ciprofloxacin and Nolicin are broad-spectrum antibiotics for the treatment of cystitis.
The advantage of these drugs is that they are taken infrequently - once every 12-24 hours, the course of therapy is 3-7 days. Prescribed for acute cystitis caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and in cases where other drugs are not effective.
Urological antibiotics for cystitis
This group includes drugs such as:
- Furadonin;
- Monural;
- Nevigramon;
- Levomycetin.
These drugs are highly effective, well tolerated and have a small list of side effects (stool disorders, heartburn).
Only a doctor should decide which antibiotics are best to take for cystitis.
If signs of cystitis appear, antibiotics are prescribed only after examination and identification of the cause of the disease - this is associated with the risk of developing bacterial resistance, the disease becoming chronic, and the development of side effects.
Side effects of antibiotics
Antibiotics for cystitis in women can cause the development of thrush, intestinal and vaginal dysbiosis, and menstrual irregularities.
In men, antibacterial drugs against cystitis reduce the quality of sperm and cause dysbacteriosis.
In addition to treatment with antibiotics, other drugs are prescribed for cystitis, which together will speed up the healing process.
Such means include:
- Herbal preparations (Canephron, Cyston, Fitolysin);
- Herbal infusions, including lingonberries, fennel, chamomile, marshmallow and others;
- Antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Papaverine);
- Compliance with the drinking regime - if you have cystitis, you need to drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid.
Cystitis after antibiotics
After taking antibiotics, cystitis can develop for a number of reasons:
- decreased general and local immunity;
- activation of pathogenic microflora, including fungi;
- the drug for treatment is not selected correctly;
- The doses and timing of treatment of the disease are not observed.
Prevention
Prevention of cystitis and side effects from its treatment is to follow the following recommendations:
- Regular examination and treatment of identified diseases of the genitourinary system;
- Good hygiene;
- Avoid hypothermia;
- Take antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor;
- Drink at least one and a half liters of fluid per day;
- Empty your bladder regularly;
- Drink herbal medicines twice a year as a disease prevention;
- Drink caffeinated drinks as rarely as possible;
- Eat a nutritious diet, including dairy products;
- Eliminate alcohol, carbonated drinks, and fast food from your diet;
- Perform physical exercises that strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
Conclusion
To summarize, it should be noted that cystitis is a fairly serious disease that requires an integrated approach to therapy. Antibiotic treatment for cystitis is prescribed only by a doctor after an examination. When transitioning to a chronic form, it is necessary to identify the infectious agent and conduct a sensitivity test to antibiotics.
Alcoholic drinks and Cefotaxime
It is not recommended to accompany treatment with any antibiotic with alcohol. The compatibility of Cefotaxime and alcohol is no exception to the rule. The antibacterial drug should not be taken with:
- antiplatelet agents;
- NSAIDs;
- aminoglycosides;
- other antibiotics;
- alcohol, drugs, etc.
What are the risks of drinking alcohol during Cefotaxime therapy?
- enhancing the effect of the drug;
- decreased effectiveness of drug treatment;
- occurrence or catalysis of undesirable phenomena.
Antibiotic use is associated with increased stress on the liver and kidneys. Alcoholic drinks have the same properties. These 2 organs suffer to a greater extent with the simultaneous use of Cefotaxime and alcohol.
The harm caused to the body depends on the dose of alcohol taken, degree and body weight. Low weight women are more at risk of side effects from drinking alcohol.
Use of Cefepime in combination with other medications
It is prohibited to use Cefepime analogues and the original drug simultaneously to avoid exceeding the maximum dose of the active substance.
In addition, parallel use of any other antibiotics with the drug is undesirable. If this is still necessary, each antibiotic is administered separately; mixing them in one syringe is strictly prohibited.
It is prohibited to mix Cefepime with heparin and other antimicrobial drugs in one syringe.
You cannot combine the drug with Metronidazole solution. If the use of Metronidazole is necessary, the infusion system is first flushed of Cefepime. This usually happens during surgery to protect against possible infections.
Peculiarities
In the first days of treatment, diarrhea may occur, in which case the drug should be discontinued. If patients have atypical allergic reactions to a group of penicillin antibiotics, they may also develop an allergy to cephalosporins.
If long-term use of an antibiotic is necessary, it is necessary to donate blood for control after 10 days. In some cases, during treatment with Cefotaxime, a false positive reaction to the Coombs test and glucose is observed.
While taking Cefotaxime, alcoholic beverages should be strictly prohibited, since in combination with alcohol the drug can provoke tachycardia, nausea, headache, decreased blood pressure, shortness of breath, and stomach cramps.
Despite the minimal impact of the drug on the gastrointestinal tract, during treatment it is recommended to eat fermented milk products containing live bacteria.
Features of application
Cefotaxime can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. It is the doctor who will determine the cause and severity of the disease and select the appropriate doses of the drug, as well as the duration of treatment.
Since the drug is used only in the form of injections and infusions, treatment most often takes place in a hospital. In this case, it will not be superfluous to know the basic rules for using this tool:
- Before starting treatment, you should be sure to read the instructions, which contain all the necessary information about the antibiotic. If anything becomes unclear and raises questions, you should consult your doctor.
- It is prohibited to change the dose and mode of administration at your own discretion.
- It is necessary to conduct a skin test for sensitivity to the drug before its first use.
- Before injecting Cefotaxime into the gluteal muscles, it is diluted with water for injection, a solution of novocaine or lidocaine.
- If the drug is injected into a vein, the solvent can only be water for injection or sodium chloride solution.
- Before administering dropwise into a vein, the antibiotic is dissolved in a solution of glucose or sodium chloride.
- The drug is used 2 times a day, with an interval of 12 hours between injections.
- The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and can range from 3 to 10 days.
- If any unwanted effects occur, you should consult a doctor. It is possible that the antibiotic will be discontinued and another drug will be prescribed.
- If severe diarrhea occurs during or after treatment, you should seek medical help. This may be a sign of pseudomembranous colitis, which cannot be treated with antidiarrheals.
- When taking oral contraceptives, you should take additional measures to prevent unwanted pregnancy, since Cefotaxime reduces the effectiveness of these drugs.
About the drug
Cefotaxime is an antibacterial agent belonging to the group of cephalosporins. It exerts its antimicrobial effect by inhibiting the synthesis of biological substances that make up the cell walls of bacteria.
The drug is produced in glass bottles containing 0.25, 0.5 and 1 gram of white fine-crystalline powder without a specific odor, which is the sodium salt of cefotaxime.
Most often, this antibacterial agent, diluted with novocaine or water for injection, is administered parenterally (intravenously or intramuscularly), but in the practice of otolaryngologists it is often used for instillation into the nose of children and adults.
Cefotaxime analogues
- Claforan;
- Cefantral;
- Cephosin.
The product can be produced under the trade names:
- Claforan;
- Clafotaxime;
- Cefotaxime produced by Biokhimik Saransk;
- Razibelakta;
- Cephabol;
- Cefotaxime, Lecco;
- Liforan;
- Intrataxim;
- Duatax;
- Cefotaxime, Biosynthesis;
- Taksim;
- Cephajet.
Drugs marketed under the trade names Cephabol and Claforan have a similar composition to Cefotaxime.
Cefotaxime inhalation
Cefotaxime is one of the modern drugs belonging to the group of 3rd generation antibiotics. What is its effectiveness and what are the indications for use, we will consider in more detail in our article.
Features of Cefotaxime and indications for use
The drug is especially effective in combating various types of bacteria. In addition, it has a bactericidal effect on those types of bacteria that are highly resistant to penicillin and sulfonamides. The elimination of microbes is facilitated by the active activity of the enzyme transpeptidase.
Cefotaxime is a member of the Cephalosporin group of antibiotics. It is produced in powder form. The antibiotic Cefotaxime is used both in the form of an injection solution and in the form of a solution for inhalation.
It has a bactericidal effect based on the failure of the synthesis of mucopeptide in the microbial cell wall. The product is especially effective in the fight against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms, which are highly resistant to many antibiotics.
Cefotaxime quickly binds to blood amino acids by 40%. It is instantly transported to all tissues and cells of the human body. It has a high therapeutic effect for meningitis, as it reaches high concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid.
In addition, it has the ability to penetrate the placenta and is also excreted in breast milk. 40-60% of one serving of the drug is removed from the body 24 hours after administration through the urinary system, 20% - in the form of metabolic products.
This antibiotic fights bacterial infections that are especially severe.
Many of our readers actively use
. It contains 16 medicinal plants that are extremely effective in the treatment of chronic COUGH, bronchitis and cough caused by smoking.
As a rule, doctors prescribe this drug to eliminate peritonitis, chlamydia, heart disease, pneumonia, gonorrhea, tick-borne borreliosis, and to prevent the development of blood poisoning.
Thus, Cefotaxime fights infections of the following organs, tissues and body systems:
- ears;
- urinary tract;
- central nervous system (in particular meningitis);
- pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi;
- reproductive system;
- skin and soft tissues.
This drug effectively eliminates salmonellosis and abdominal infections, as well as those diseases that arise due to immunodeficiency.
It can be used as a prophylactic drug after surgery.
Method of use for various ailments and duration of therapy
The drug is prescribed to adults and children over 12 years of age, their body weight must be more than 50 kg. Despite the fact that the suspension is perceived by children much better than the injection, the result from Cefotaxime is higher, it cannot be compared with many modern suspensions.
If there is an uncomplicated infectious disease or urinary tract infection, it is recommended to inject Cefotaxime intramuscularly 1 g every 8 or 12 hours.
Feedback from our reader - Natalia Anisimova
I recently read an article that talks about the Intoxic product for removing PARASITES from the human body. With the help of this drug you can FOREVER get rid of colds, respiratory problems, chronic fatigue, migraines, stress, constant irritability, gastrointestinal pathologies and many other problems.
I’m not used to trusting any information, but I decided to check and ordered a package. I noticed changes within a week: worms literally began to fly out of me. I felt a surge of strength, I stopped coughing, my constant headaches went away, and after 2 weeks they disappeared completely.
If a person has a mild form of gonorrhea, then injections are given intramuscularly 1 g once a day.
When infected with moderate infections, the drug is administered intramuscularly or intravenously every 12 hours, 1-2 g.
DETAILS: Andrey Gubin - biography, information, personal life. Andrey Gubin: biography, personal life, family, wife, children - photo Live broadcast with Gubin comments
For severe forms of infectious diseases, for example, meningitis: 2 g intravenously every 4-8 hours, but not more than 12 g per day. The duration of the course is prescribed individually by the attending physician.
As a preventive measure, it is used before surgery: once during the administration of anesthesia.
Ceftriaxone injections are used for bronchitis in adults intramuscularly, intravenously and in the form of droppers.
How to prepare the solution for injection is described below:
- For intravenous injections: 1 g of powder should be diluted in 4 ml of sterile water. The drug must be administered slowly, over about 3-5 minutes.
- For intravenous infusion: 1-2 g of powder should be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% glucose solution. The infusion should last approximately an hour.
- Intramuscular injection involves diluting 1 g in 4 ml of special water from a pharmacy or in a 1% solution of Lidocaine.
Pneumonia in a hospital setting is treated with antibiotics; doctors resort to the use of Cefotaxime when previously used drugs are ineffective. That is, if the human body is resistant to penicillin, then doctors prescribe third-generation cephalosporins.
Is it possible during pregnancy?
This antibiotic is extremely contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women. Cefotaxime should not be used during pregnancy, especially in the 1st trimester. If serious diseases occur that cannot be treated without this antibiotic, Cefotaxime is allowed, but only in the 2nd and 3rd trimester. It all depends on how severe the disease is.
If the expected effect of Cefotaxime for the expectant mother exceeds the expected risk to the fetus, then the use of the drug becomes possible. After using 1 g of powder after 2-3 hours, the maximum concentration of the active substance in breast milk is about 0.3 μg/ml.
A child may develop oropharyngeal candidiasis. Experiments conducted on animals did not reveal teratogenic and embryotoxic effects from taking Cefotaxime.
Many expectant mothers are concerned about the question: “Can antibiotics be used during pregnancy?” Through experimental studies, American and European scientists have proven that penicillin is safe for the fetus.
Third generation antibiotics are toxic, but if there is a threat to the mother’s life, for example, with sepsis or severe pneumonia, then drugs of this type are allowed. Therefore, we can conclude that Cefotaxime has a negative effect on the fetus during pregnancy.
Duration of treatment with the drug and its compatibility with Novocaine
How many days to inject Cefotaxime depends directly on the disease itself and its severity. You need to inject the antibiotic for at least 5 days. If treatment is interrupted, the course of the disease may only worsen, which will require an even stronger remedy.
The course of treatment for children is usually 7 days, for adults – 10 days. The number of days of using Cefotaxime depends on the type and nature of the disease.
If the course of treatment has exceeded the 10-day period, then it is necessary to monitor the number of formed blood particles in the laboratory conditions of a medical institution.
To prepare a solution for intramuscular injections you will need powder and water. Pharmacy water for injection can be replaced with 1% Lidocaine or 0.5% Novocaine, which will reduce pain. The use of Novocaine is allowed because it does not react with Cefotaxime itself.
These solvents can be purchased at the pharmacy; they are sold in packages, each containing 10 ampoules. Water for injection and Lidocaine contain 2 ml of solution in an ampoule, Novocaine - 5 ml. It is important to know how to dilute Cefotaxime, or more precisely, in what proportions. Diluting the antibiotic will take a couple of minutes: you need to add 4 ml of solvent to 1 g of powder.
It is worth noting that Novocain is contraindicated in children under 12 years of age.
Contraindications, side effects and special instructions
Contraindications include:
- hypersensitivity;
- pregnancy;
- children under 12 years of age;
- breastfeeding period;
- ulcerative colitis;
- chronic renal failure.
Cefotaxime may cause a false-positive Coombs test and result in positive urine glucose test results.
Therapy with this antibiotic involves completely stopping the use of alcohol-containing products; this can cause facial flushing, nausea, headaches, stomach pain, dizziness, shortness of breath and a decrease in blood pressure.
If the doctor prescribed Cefotaxime during lactation, the woman must stop breastfeeding.
Taking Cefotaxime can cause bleeding if combined with antiplatelet agents and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Combining the use of this antibiotic with aminoglycosides, polymyxin B and loop diuretics has an extremely negative effect on kidney function.
Since the drug belongs to the group of new generation antibiotics and copes with infection by inhibiting cell synthesis, doctors often prescribe it as a “panacea”, which is not always rational.
It is especially important to monitor the health of young children and try to avoid taking such serious drugs, this can affect the immune system. It is better to consult with another specialist once again than to harm your health.
Are you sure you are not infected with parasites?
According to the latest WHO data, more than 1 billion people are infected with parasites. The worst thing is that parasites are extremely difficult to detect. We can say with confidence that absolutely everyone has parasites. Common symptoms such as:
- nervousness, sleep and appetite disturbances...
- frequent colds, problems with the bronchi and lungs...
- headaches…
- bad breath, plaque on teeth and tongue...
- change in body weight...
- diarrhea, constipation and stomach pain...
- exacerbation of chronic diseases...
All these are possible signs of the presence of PARASITES in your body. PARASITES are very DANGEROUS, they can penetrate the human brain, lungs, bronchi and multiply there, which can lead to dangerous diseases. Diseases caused by parasites take a chronic form.
Compound
Cefpodoxime is used as an active component in the semisynthetic antibiotic. The substance has a bactericidal effect on pathogenic microflora. Thanks to this, it is possible to disrupt the formation of cell walls of bacteria dangerous to the human body.
Many gram-negative (Proteus mirabilis, Haemophilus influenzae, Escherechia coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Proteus) and gram-positive microbes (streptococci, corynebacterium diphtheria, pneumococci, staphylococci) exhibit sensitivity to cefpodoxime. Anaerobes are insensitive to the active substance. In case of infection with strains of clostridia, enterococci, mycoplasmas, chlamydia and legionella, it is not advisable to use this substance for treatment.
The bioavailability of cefpodoxime is about 52%. Absorption of the active substance occurs in the small intestine. Cefpodoxime accumulates in the tissues of the lungs, liver, kidneys, and muscles. It is eliminated from the body to a greater extent through the kidneys.
Auxiliary components are substances such as iron oxide, silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, opadry OY-L white, sodium lauryl sulfate, corn starch, simethicone emulsion, sucrose.
Ceftriaxone and Cefotaxime: how to compare based on basic characteristics
Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone have many of the same characteristics: indications, release forms. They have differences in use, contraindications and side effects.
Indications
Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone are prescribed for the same infections:
- ENT organs: otitis media, tonsillitis, sinusitis;
- respiratory system: pneumonia, bronchitis, pleurisy, abscess;
- kidney and urinary system: pyelonephritis, urethritis, cystitis;
- genital organs: endometritis, adnexitis, gonorrhea, prostatitis;
- skin, soft tissues: carbuncle, phlegmon, erysipelas;
- blood: sepsis, bacteremia;
- intra-abdominal: peritonitis, biliary tract, digestive organs;
- infections of bones and joints: osteomyelitis, purulent arthritis;
- meninges: meningitis;
- in a wound (during injury or surgery).
Antibiotics can also be prescribed for prophylaxis after abdominal surgery.
Release forms
Ceftriaxone and Cefotaxime are available in 1 g bottles. They are suitable for intramuscular and intravenous administration. It is important to consider that for injections you will need water and Lidocaine 2% solution in ampoules.
Rules for making injections and doses
General rules for preparing an antibiotic solution and performing injections:
- Before treatment, a tolerance test is required;
- The solution should be prepared immediately before the injection;
- Novocain is not suitable for breeding;
- intravenous drugs are administered only with water for injection - 10 ml of water is required for 1 g; Lidocaine cannot be used;
- for a dropper, take 2 g and 40 ml of saline solution or 5% glucose;
- for intramuscular use, 1 g of the drug requires 2 ml of water for injection and 2 ml of a 2% lidocaine solution, since the injections are painful;
- after the temperature has normalized, drugs are usually administered for another 2-3 days; a short course leads to the emergence of microbial resistance, and a long course is dangerous for complications.
Dosing features are indicated in the table.
| Patient group | Ceftriaxone | Cefotaxime |
| Adults and teenagers from 12 years old | 1-2 g 1 time per day | 1 g 2 times a day |
| Severe infections after 12 years | 2 g 2 times a day | 1 g 3-4 times a day, for meningitis 2 g every 6 hours |
| Children under 2 weeks | 20-50 mg/kg 1 time per day | 50 mg/kg, divided into 2 doses, IV only |
| Children 2 weeks-12 years | 20-80 mg/kg 1 time per day | 50-100 mg/kg, divided into 3 times (up to 2 years only into a vein) |
| Meningitis in children under 12 years of age | 100 mg/kg body 1-2 times | 100-200 mg/kg per day, this dose is divided into 4-6 times |
| Prevention of infection during abdominal surgery | 1-2 g an hour before surgery and then according to the usual regimen | One hour before surgery 1 g |
| Liver and kidney failure | No dose adjustment needed | If renal function is impaired, use half the dose |
Contraindications
Contraindications for the administration of Ceftriaxone and Cefotaxime are different. The first drug cannot be used for:
- intolerance to cephalosporins, penicillin antibiotics;
- the age of a premature baby up to 41 weeks, taking into account the gestation time;
- increased bilirubin in the baby’s blood;
- the need to administer calcium supplements to newborns and young children.
Cefotaxime is prohibited for:
- intolerance to beta-lactam antibiotics (for example, Tienam), cephalosporins;
- bleeding (regardless of the source and intensity);
- previous intestinal inflammation, especially ulcerative colitis;
- atrioventricular block;
- circulatory disorders due to weakness of the heart muscle.
Watch this video about the indications and contraindications for the use of Ceftriaxone, instructions for use:
Side effects
In most cases, Ceftriaxone and Cefotaxime are well tolerated by patients, but side effects are still possible; the most common reactions are listed in the table.
| Body system | Ceftriaxone | Cefotaxime |
| Blood | Decreased platelets, leukocytes, red blood cells, increased eosinophils, increased creatinine and liver tests | |
| Immunity | Decreased allergic reactions | Allergic and anaphylactic reactions, shock |
| Digestion | Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, inflammation in the oral cavity, pancreatitis, precipitation of salts in the gallbladder | Bloating and abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, dysbacteriosis, constipation, jaundice |
| Leather | Rash, inflammation, itching, urticaria, swelling, red spots, detachment of the epidermis | Redness, rash, itching, urticaria, epidermal detachment |
| Kidneys | Decreased urine output, increased red blood cells, glucose, sand and stones | Inflammation (nephritis), swelling, increased blood pressure |
| Nervous system | Headache, dizziness | Weakness, dizziness, convulsions |
Cefotaxime and alcohol - compatibility
Antimicrobial drugs such as Cefotaxime and others like it, if taken together with alcoholic beverages, can cause serious damage to the liver, which is called hepatoxicity.
In simultaneous combination with alcoholic products, this antibiotic can cause the following reactions in the body:
- severe pain in the temples;
- nausea turning into vomiting;
- facial hyperemia;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- the appearance of shortness of breath;
- cramps in the stomach and abdomen.
That is why those who ask whether it is possible to drink Cefotaxime and alcohol at the same time should know that it is undesirable to do this. First, the patient notices a clouding of his mind, then his body begins to become intoxicated. In severe cases, the use of alcohol and Cefotaxime can lead to coma.
Also, reviews from patients who took Cefotaxime indicate that this drug significantly reduces a person’s ability to drive, so you should not drive during treatment.
It is worth knowing that various negative reviews of the drug are most often based on its side effects. If the drug did not help in the presence of unaccounted contraindications, but only worsened the health condition, this also causes a negative reaction from the patient.
If the drug causes disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, which is expressed in a deterioration in appetite, as well as diarrhea and nausea, then treatment with Cefotaxime is not canceled.
If allergies develop (rash, swelling), the side condition is treated. It is also worth knowing that long-term use of this drug can cause blood diseases and candidiasis.
Source: alcoholism.com
Dosage
How to correctly determine the dosage of the drug "Cefodox"? The instructions contain general recommendations that are suitable for most patients. The tablets can be used by adolescents over 12 years of age and adults. For mild to moderate inflammation, 200 mg of cefpodoxime should be taken per day. The dose is divided into two doses. In severe cases, for example, with pneumonia or soft tissue damage, the dosage is increased to 400 mg.
The instructions recommend giving the Cefodox 100 suspension to children with meals. The dosage of the active substance is calculated individually and depends on the weight of the baby. Per 1 kg of body weight take 10 mg of cefpodoxime. That is, if a child weighs 10 kg, he can be given no more than 100 mg of the active substance per day.