- Causes of urinary incontinence
- Mechanism of development of urinary incontinence
- Classification of urinary incontinence
- Diagnosis of urinary incontinence
- Treatment of urinary incontinence
Incontinence, or urinary incontinence, is an involuntary leakage of urine uncontrollable by volition. This is a symptom of a pathological process of various origins; such a condition is not an independent disease.
Incontinence is one of the most frequently diagnosed urological pathologies in the world, leading to a deterioration in the quality of life of people of different ages. According to average statistical data from researchers in the field of urology, from 15 to 40% of the Russian population suffers from one form or another of incontinence, and in 20% of women the condition is permanent. Among children, the figures are higher, ranging from 12 to 70%.
Incontinence is more often observed in older people and preschool children. In the age group under 40 years, incontinence is predominantly diagnosed in women. With age, the frequency of this pathological condition increases in both sexes: in women due to weakening of the sphincters, prolapse of the uterus and other problems; in men due to age-related changes and prostate diseases.
Spontaneous urine leakage affects all aspects of life, leading to psycho-emotional disorders, social, professional, family, and everyday maladjustment.
Causes of the disease
The reasons why urinary incontinence (scientifically called enuresis) may occur can be very diverse, for example:
- After childbirth/during pregnancy. This is due to sprain/damage to the ligaments or muscles of the pelvic floor.
- Menopause period. During this period of time, there is a cessation of stimulation of the female organs by hormones: blood circulation slows down, tissue tone decreases, which leads to problems associated with urinary incontinence.
- At a fairly young age, sometimes girls experience the phenomenon of hyperactivity of the bladder, or more precisely, of its muscles. The bladder, although it is not very full, sends false signals to the brain, which forces the woman to visit the restroom very often. Most likely, the causes of this problem are psychological in nature and are aggravated by stress, frequent alcohol consumption, etc.
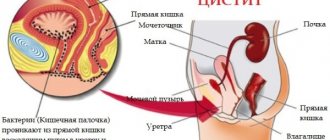
- Inflammatory reactions in the genitourinary system can often cause uncontrolled urine output.
Urinary incontinence in women when walking
The second, or moderate, degree of enuresis in women is involuntary urination when walking or other physical activity (lifting weights, running, sudden changes in body position). The causes of this disease may be: difficult childbirth, hormonal disorders in the body associated with menopause, excess weight, previous operations on the genitourinary system, heavy physical work. The most effective treatment for enuresis is complex. It includes physical exercises that strengthen the muscles of the lower pelvis - for example, Kegel exercises, the use of traditional methods and traditional medicines.
At night
The causes of night incontinence in adult women are:
- frequent stress;
- diabetes;
- relaxation of the bladder muscles;
- genitourinary system infections;
- small bladder capacity;
- decreased elasticity of the bladder walls.
Treatment methods for enuresis include therapy with and without traditional medicine. The first option is aimed at strengthening the muscles of the genitourinary system. These include Kegel exercises. Effective medications for nocturnal enuresis are antispasmodics - for example, Spazmex, Driptan.
Prevention
Prevention of incontinence should be started at a young age.
- Maximum exclusion of hypothermia and inflammation of the genitourinary organs.
- Proper hygiene of the intimate area.
- Prevention of prolapse of the uterus and bladder after childbirth - wearing a bandage and special exercises.
- Combating constipation, obesity and bad habits (smoking, alcohol).
- Timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the urinary system.
- Age-appropriate physical activity.
- Hormonal support during menopause.
- Regular preventive examination at least once a year.
Tags:
women's health urinary system
Treatment methods at home
It is quite possible to cure this problem on your own, but if the process began a long time ago and has taken a chronic form, then consulting a doctor is simply necessary. A qualified specialist will select the optimal treatment: prescribe pills and drugs that will act on the problem.
On a note! It is recommended to supplement the treatment with folk remedies; this will not be superfluous; on the contrary, the effect will be better. In some cases, with unadvanced conditions, it is home procedures that can help get rid of the problem forever.
Which doctor treats urinary incontinence in women?
In case of urinary incontinence in women, it is necessary to contact a therapist, who will give an appointment to a specialist, or directly to a urologist. This disease is within his competence.
Workout
Intense pelvic muscle exercises will be very effective. By the way, this method will not take much of your effort, and you will spend no time at all! A few examples:
- Oddly enough, but it strengthens the muscles of urinary control very well. That is, try to control the delay in visiting the restroom, do not go straight to the toilet, be patient. This way you will tense your muscles, thereby training them.
- Another effective exercise: tighten your vaginal muscles, stay in this state for 10 seconds. The actions must be repeated 6 times - you need to make sure that there is no pain or severe fatigue. It is recommended to repeat the exercises 6-10 times during the day. The voltage holding time should be gradually increased to limits that are reasonable for you.
- You can train your muscles in this way: take a comfortable position, sitting on a chair, your feet should rest on the floor, your knees slightly apart in different directions. With your elbows on your hips, lean your torso forward. This position will clearly fix the stomach + buttocks. Then, by tensing the muscles, retract the anus for 10 seconds. Relax for 5 seconds. It is advisable to repeat the steps 6-7 times.
Kegel exercises
Kegel exercises are an effective treatment for mild urinary incontinence. Positive dynamics are observed in 2/3 of cases where incontinence was associated with stress. This improvement is possible because Kegel exercises strengthen the bladder sphincter and pelvic floor muscles. However, a positive effect is possible only with regular exercise without breaks. It is important to gradually increase the duration and complexity of the exercises.
The main complex includes:
- squeeze the muscles of the genitourinary system;
- alternately quickly contract and relax muscles;
- tighten the muscles that are used when a person strains to have a bowel movement.
You need to start the exercises with 7-10 repetitions 4-5 times a day. Then you need to gradually increase the number of repetitions. If difficulties arise, you should consult a doctor.
Yoga
Some patients claim that yoga helps in the fight against urinary incontinence. The exercises are aimed at strengthening the muscles of the genitourinary system, which significantly improves the condition of patients. In addition, yoga helps to relax and cope with stress, which is also important, because frequent stress is a common cause of enuresis.
Doctors in our clinics
Berdichevskaya Anna Alexandrovna
urologist, urogynecologist, urogynecologist, doctor of the second category
Clinic on Arbat Clinic on Leninsky
Bitsoev Timur Borisovich
urologist
Clinic on Arbat Clinic on Leninsky
KMN
Derish Fedor Fedorovich
Urologist, urologist, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category
Clinic on Arbat
KMN
Lomshakov Andrey Alexandrovich
head Department of Urology, urologist, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category
Clinic on Arbat Clinic on Leninsky
Makhrovsky Viktor Pavlovich
urologist
Clinic on Babushkinskaya
Reviews
DOCTORS
Folk remedies
| Ingredients | Preparation + application |
| Marshmallow (root) – 100 g Nettle (leaves) – 100 g Yarrow (herb) – 80 g | Mix the ingredients. Brew overnight (preferably in a thermos) a mixture of herbs (100 g/500 ml boiling water). We filter the solution only in the morning. We take it in doses throughout the day (small portions). We do not stop treatment until the problem disappears completely |
| Wheatgrass (root) – 100 g Violet (herb) – 100 g Yarrow (root) – 80 g | Combine the ingredients, mixing thoroughly. Take 3 tbsp. l. mixture of these herbs, place in a thermos, pour 1 liter of boiling water. Let it sit overnight and separate the liquid from the sediment. Take a glass about 5-6 times a day |
| Recipe for pregnant women: Gryzhnik – 50 g Agrimony – 100 g St. John's wort herb – 70 g | It is advisable to grind the components and then turn them into a homogeneous mass. Next 2 tbsp. l. Pour boiling water (500 ml) into the mixture. Cover the container with a lid and leave for 1.5–2 hours. Afterwards, filter the solution. We take 100 g orally 5 times a day |
| Chicory (root) – 100 g Centaury (herb) – 80 g Yarrow (herb) – 100 g | Mix the ingredients thoroughly and chop. Place 4 tbsp. l. herbs into a container, pour boiling water (1 liter). We insist for at least 1 hour. Strain and drink 5–7 times |
| Agrimony seeds – 50 g Red wine (good quality) – 500 g | Grind the component (you can use a blender or a mortar). Pour the resulting powder with wine and keep it for 1 week in a warm place (but not in the sun). After straining the solution, drink 1 tbsp. l. at least 4 times a day. Unpleasant sensations should noticeably decrease after 14 days of daily use. If there are changes, the dose can be halved - use 1/2 tbsp. l. 4 times |
As you may have noticed, all the recipes are extremely easy to prepare and use, so home treatment for urinary incontinence will not only be effective, but will also take a minimum amount of effort, time and material resources. However, any problem must be approached comprehensively, so you should rethink your lifestyle. Perhaps you are doing something wrong or perhaps not right?
Diagnostic examination
If incontinence is suspected, a comprehensive examination is carried out. It is based on laboratory and instrumental methods. The examination is carried out not only to identify the fact of the disease itself, but also to determine the cause that provoked it. This information is required in order to prescribe adequate therapy and achieve complete recovery.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include transvaginal ultrasound and cystoscopy. The first type of diagnosis makes it possible to obtain information about the condition of the genitourinary organs. With its help it is determined:
- location of the bottom and walls of the bladder;
- physiological parameters of the urethra;
- anatomy and angle of the urethra.
The research method eliminates the need for x-rays.
With the help of cystoscopy, it is possible to study the structure of the genitourinary system or carry out surgical treatment if this method is used. During cystoscopy, a long tube is used, at the end of which there is a camera and a light bulb. It is inserted through the urethra directly into the bladder.
Additionally, laboratory tests are carried out. The list includes the following tests:
- biochemical analysis of urine and blood serum;
- smear of the internal mucous surface of the vagina;
- detection of bacterial flora in urine.
Additionally, an examination is carried out on a gynecological chair. The action is performed in order to check the condition of the genitourinary system and identify possible problems. The doctor will also perform palpation.
To get rid of pathology, a woman must keep a special diary. Every day it is necessary to record in it the amount of water drunk and the volume of urine excreted. Additionally, it is worth describing any unpleasant sensations - burning, sharp or aching pain. This approach makes it possible to determine how effectively the prescribed therapy helps.
Drug treatment
Depending on the cause of enuresis in women, various drugs and tablets are prescribed. They affect the cause of the pathology and, thus, solve the problem itself. The following groups of drugs can be distinguished, prescribed depending on the cause of urinary incontinence:
- Hormonal drugs - drugs in the form of female hormones progestin or estrogen - are prescribed if incontinence occurs due to a lack of female hormones. This happens during menopause.
- Sympathomimetics – Ephedrine – promotes contraction of the muscles involved in urination. The result is that enuresis stops.
- Anticholinergics - Oxybutin, Driptan, Tolterodine - are prescribed when incontinence is caused by bladder hyperresponsiveness.
- Antidepressants - Duloxitine, Imipramine - are prescribed if the cause of incontinence is stress.
- Desmopressin - reduces the amount of urine produced and is prescribed for temporary incontinence.
For stress-related urinary incontinence in women, several treatment options are available. Only a doctor can choose the best one after conducting research and receiving test results. The drug Gutron, the action of which is aimed at increasing the tone of the organs of the urinary system, can be effective. Ubretide is also prescribed, which increases muscle tone. Most often, antidepressants are prescribed to reduce the number of manifestations of involuntary urination or relax the bladder muscles. Among them are Imipramine and Duloxetine.
Tablets – Driptan
Driptan is an effective antispasmodic agent in the treatment of enuresis in women. Its principle of action is to reduce the tone of the bladder muscles, which increases its capacity. Accordingly, the frequency of the urge to urinate is reduced. Taking Driptan for a long time does not cause addiction. The drug is prescribed 5 mg 2-3 times a day. The daily dose for adults should not exceed 15 mg. Before using the drug, it is important to consult a doctor.
Candles
Ovestin vaginal suppositories are prescribed if urinary incontinence occurs due to a lack of female hormones. The suppository is administered before bedtime every day for 14–21 days. Then the dose is reduced to two suppositories per week.
Incontinence in older women
Urinary incontinence in older women is often associated with a lack of the female hormone estrogen. In this case, hormonal drugs are prescribed to help restore tissue, normal blood circulation, and restore the desired tone to the pelvic floor muscles. In other words, they remove or smooth out the effects of hormonal changes caused by menopause. Most often, with this diagnosis, Ubretide, Cymbalta, Gutron are prescribed.
There is also urgency incontinence, when the bladder muscles involuntarily contract. In this case, Detrusitol, Driptan, Spazmex, Vesicare help.
Important! Before using any medications, it is necessary to undergo tests, identify the cause and consult a doctor.
Surgical methods for treating urinary incontinence
If the conservative treatment method does not give a positive result, the doctor will recommend surgery to eliminate the problem with urination. It should not be used by people with cancer, diabetes, or during exacerbation of inflammatory processes. There are several types of surgical options for urinary incontinence:
- Loop or sling operations. During surgery, a mesh is inserted under the urethra in the form of a loop.
- Injections into the urethral mucosa of bulk-forming drugs. As a result, the missing tissue is replaced and the urethra is fixed in the correct position.
- Laparoscopic colposuspension according to Burch.
- Colporrhaphy (suturing of the vagina).
Recommendations
- You should limit as much as possible the consumption of foods that irritate the bladder. The most harmful products: coffee, alcohol, tomatoes, citrus fruits, spicy seasonings, milk, chocolate products.
- Smoking worsens the overall health of the body, tobacco tar is an irritant to the walls of the bladder, they destroy the mucous membrane that performs a protective function. This also affects problems with the bladder - enuresis appears.
- Do you suffer from chronic constipation? The condition of the intestines will also have to be improved - the collected feces presses on the walls of the bladder, reducing its tone. Normalize intestinal function, for example, with the help of foods (prunes, beets, apples, dried apricots). They should be consumed daily, or one at a time – not all at once!
- Difficulty passing urine often occurs due to bacterial infections entering the genitourinary system. Take care of the quality of personal hygiene of the genitals at home, try to wear underwear that is made of natural material.
- A common cause of the problem can be overweight (obesity), which weakens the pelvic floor muscles. Obesity should be combated immediately. How? There are many ways: do not overeat, eat low-calorie foods, exercise, etc.
For your information! A common mistake when dealing with the problem of uncontrolled urine output is to drink very little fluid (to avoid running to the toilet less). This approach is completely wrong, since dehydration will occur in the body, and the urine in this case will be too concentrated. This can lead to irritation of the mucous membranes, which will lead to another problem - vaginitis, urethritis. Drink as much water as you want!
Lingerie
When choosing underwear for urinary incontinence, it is important to consider several factors: the patient’s preferences, the causes and degree of urinary incontinence, the person’s physical capabilities, and the availability of outside help. Today, many models of both disposable and reusable panties are produced, differing in size, shape, and absorption capacity. They are quite comfortable and protect against leaks. Disposable panties, or adult diapers, are used for severe cases of illness, bedwetting, and for bedridden patients.
Gaskets
For mild to moderate urinary incontinence, women use regular panty liners or sanitary pads for menstrual periods. However, there are special urological pads for disposable and reusable use. Disposable ones are convenient and practical, but are quite expensive. Reusable ones are a little cheaper, but they need to be washed and dried. They are used with special underpants, to which they are attached. The sizes of urological pads vary depending on the volume of fluid they absorb.
Yes, the problem of urinary incontinence is unpleasant and difficult, but with some effort and perseverance, it can be overcome. A set of folk methods and remedies, muscle training and drug treatment will definitely do their job. Be healthy!
Symptoms and signs of urinary incontinence
Women are more likely than men to face the problem of urinary incontinence. This is explained by the structural features of their genitourinary system. In women, incontinence is expressed by the following symptoms: leakage of urine, sudden uncontrollable urge to go to the toilet, a feeling of an incompletely emptied bladder, a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the vagina.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, a urologist is needed; she prescribes a comprehensive examination:
In addition to this, a general urine test is performed to detect infections (hematuria and glycosuria).
It is important to emphasize that older people often suffer from asymptomatic bacteriuria, which does not cause incontinence and does not require treatment, except in patients whose leakage has recently appeared or is accompanied by high fever or burning when urinating.
Pelvic check
Women need a pelvic examination. The following reasons:
- Atrophic vaginitis causes or worsens the course of urinary incontinence.
- During the test, it is necessary to assess the ability to contract the muscles of the pelvic floor and, according to this, plan treatment.
- Many older women do not take constant gynecological monitoring seriously. A pelvic smear test (Pap smear) can rule out the presence of cervical tumors.
- As part of the check, provocative tests are performed to exclude urine leakage during exertion, including coughing and the Valsalva maneuver. If there is vaginal prolapse, it is necessary to achieve vaginal prolapse during testing with a finger or with a pessary (a device that is inserted into the vagina to support the uterus, bladder and rectum) to rule out occult urinary incontinence due to stress.
Assessment of residual urine in the bladder
Assessing residual urine in the bladder after sufficient voiding provides information about voiding efficiency and the risk of hydronephrosis, renal injury, and infection.
Although testing can be done using a catheter, ultrasound is the preferred method.
It should be remembered that problems such as bloating or intestinal obstruction can make ultrasound examination difficult.
Imaging check
There is no specific imaging test as part of the evaluation of a patient with urinary incontinence. The choice of a specific diagnostic procedure depends on the clinical condition and treatment options.
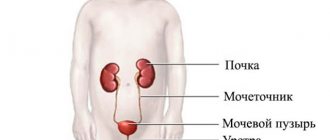
Ultrasound examinations of the kidneys and urinary tract provide information about the volume of the bladder, the amount of residual urine after emptying the bladder, stones or tumors of the urinary system.
Therapy for depression
Treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women begins with the prescription of sedatives. These include antidepressants and nootropics. The first ones normalize sleep, creating conditions so that a person can recognize the desire to urinate in a dream. The second group improves metabolic processes in the tissues of the nervous system and has a slight calming effect.
The main objectives of urinary incontinence tablets for women suffering from stress enuresis are to relieve anxiety and gently calm the nervous system. Due to this, the patient gains greater control over urinary retention during exercise.
Antidepressants
For stress urinary incontinence in women, antidepressants are the most successful treatment.
- Imipramine and drugs containing it (Tofranil, Melipramine) have a calming effect, help cope with involuntary urination during sleep, and relax the walls of the excretory system. Take 1 – 3 tablets per day shortly before bedtime. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. Prescribed to patients at least 6 years of age.
- Duloxetine acts centrally, relaxing the muscles of the urinary reservoir and reducing the likelihood of spontaneous leakage of urine. The standard dosage is from 2 to 4 capsules 1 time per day. Prescribed to patients over 18 years of age.
Antidepressants have a number of side effects, including dry mouth, dizziness, and visual disturbances. They cannot be used for glaucoma, hypertension, liver disease, pregnancy (the substance penetrates the placental barrier to the fetus).
Important! Medicines in this group affect vascular tone and can cause an attack of a sharp increase in blood pressure. The patient taking them should regularly check blood pressure readings in both arms.
Antidepressant medications should not be stopped at once. This provokes interruptions in the functioning of the heart, dizziness and nausea. The withdrawal or replacement of the medication should be done gradually.
Nootropics
They act more gently than antidepressants and have fewer contraindications.
- Phenibut reduces vascular tone, reduces anxiety, and improves sleep quality. The drug reduces excessive emotionality, which provokes neurotic reactions and stress incontinence. The dose and duration of administration depend on the patient’s age and the severity of the disorder.
- Pantogam stimulates metabolic processes in the cells and tissues of the nervous system, has a slight tonic effect without causing excitement. Prescribed 1 - 2 tablets 2 times a day after meals. The course of treatment is 2 – 3 months.
- Glycine helps get rid of insomnia and provides restful “watchdog” sleep (during which a person is able to wake up to go to the toilet). The tablets are dissolved in the mouth (under the tongue), 1 tablet three times a day.
Nootropic medications can enhance the effect of sleeping pills, painkillers, and anticonvulsants and reduce their side effects. Drug treatment is initially carried out with half the selected dose, gradually increasing it to the whole dose by the middle of the course, then the dosage is reduced back until the end of therapy.
Important! Most medications for urinary incontinence in women have contraindications and serious side effects. Under no circumstances should you take them on your own, without a doctor’s prescription. Before starting treatment, it is necessary to check the compatibility of the drugs with other tablets taken continuously.
Using incontinence pills during pregnancy
During pregnancy, women often experience urinary incontinence.
This circumstance is due to an increase in total body weight, the transformation of hormones, an increase and, accordingly, the pressure of the uterus on the bladder. In addition, a pregnant woman experiences an increased physiological load on all pelvic organs.
During this period, it is important for a woman to keep in mind her unusual condition and, if enuresis manifests itself, be sure to consult a specialist. Only a doctor should prescribe an acceptable treatment.
Classification
There are several types of urinary incontinence in women, namely:
- Imperative. Female urinary incontinence can be the result of improper functioning of the central and peripheral nervous systems, as well as disruption of the innervation of the bladder itself. In this case, the woman is bothered by an extremely strong urge to urinate, and sometimes it is impossible to hold in urine through an effort of will. In addition, the patient may suffer from frequent urination during the day (more than 8 times) and at night (more than 1 time). This type of disorder is called imperative and is observed in overactive bladder syndrome.
- Stress urinary incontinence in women is associated with sudden increases in intra-abdominal pressure resulting from lifting heavy objects, coughing or laughter. Most often, doctors have to deal with stress urinary incontinence in women. Experts also associate muscle weakening and pelvic organ prolapse with the amount of collagen content observed in menopausal women. According to medical statistics, 40% of women have experienced stress incontinence at least once in their lives.
- Mixed form - in some cases, women may have a combination of imperative and stress incontinence. This phenomenon is most often observed after childbirth, when traumatic damage to the muscles and tissues of the pelvic organs leads to involuntary urination. This form of urinary incontinence is characterized by a combination of an irresistible desire to urinate with uncontrollable leakage of fluid during exercise. This urinary disorder in women requires a two-pronged approach to treatment.
- Enuresis is a form characterized by involuntary release of urine at any time of the day. When bedwetting is noted in women, we are talking about nocturnal enuresis.
- Urgent urinary incontinence is also characterized by involuntary release of urine, which, however, is preceded by a sudden and irresistible urge to urinate. When such an urge is felt, a woman is unable to stop urinating, she does not even have time to reach the toilet.
- Permanent incontinence is associated with pathology of the urinary tract, abnormal structure of the ureter, sphincter failure, etc.
- Dripping - immediately after urination, a slight dripping of urine occurs, which remains and accumulates in the urethra.
The most common are stress and urgency urinary incontinence; all other forms are rare.
Diagnostics
Not all women who experience symptoms of incontinence consult a doctor. Many people believe that what is happening to them is a consequence of old age and incontinence cannot be cured. But this is the wrong approach. Timely treatment can help 80% of patients.
If symptoms of incontinence appear, you should consult a urologist. Consultations with a gynecologist, psychotherapist, neurologist, and endocrinologist may also be required.
Since urinary incontinence is not an independent disease, but a consequence of some other pathologies, the doctor’s task is to identify the cause of the condition.
The following diagnostic methods are used:
- patient interview,
- gynecological examination,
- Ultrasound of the bladder and pelvic organs,
- general urinalysis and urine analysis according to Nechiporenko,
- tests with urine absorbent pads,
- stress tests,
- cystometry,
- electromyography,
- cystoscopy.
During the interview, the doctor should collect the following information:
- when the patient began having episodes of involuntary urination;
- in what situations is urine released involuntarily, are there any provoking factors;
- how often urine is released at night and during the day;
- what preceded the onset of the disease;
- whether the disease was previously treated;
- how often did the patient give birth, and how did the birth proceed?
- what chronic diseases does the patient have?
- whether the woman underwent surgery on the pelvic organs.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor is primarily interested in such questions as the degree of prolapse of the bladder and vaginal walls, and the presence of inflammatory diseases.
During a stress test, the patient is asked to cough. This way the doctor can determine whether urine is produced during physical stress.
Urine tests can detect the presence of protein or blood, which usually indicates inflammation in the bladder.
Test with gaskets
For the test, pads are used that intensively absorb urine. The test is used to evaluate fluid leaking involuntarily from the urethra. It is carried out over several hours or days. Before starting and ending testing, the doctor weighs the pad. If it contains urine, the difference in weight can determine the amount of leakage.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
Ultrasound of the bladder, kidneys and urinary tract helps to identify inflammation of these organs or the presence of stones in them, and allows you to determine the volume of the bladder and urine remaining in it after emptying.
Cystometry measures the pressure of a full bladder. Electromyography is aimed at studying the electrical activity of the muscles of the bladder and perineum. Cystoscopy is an endoscopic examination method in which the doctor visually examines the surface of the urethra and bladder.
Urine diary
Also, the doctor often suggests that the patient keep a urinary diary. It is recommended to record the time of each urination and the estimated amount of urine, the moments when urine is released involuntarily, and the amount of liquid drunk per day. A urine diary is kept for several weeks.
Kegel exercises
Kegel exercises can help treat any type of urinary incontinence in women. These exercises help strengthen the muscles of the abdominal cavity and pelvis. When performing exercises, patients should tense their pelvic muscles three times a day for three seconds. The effectiveness of using pessaries and special intravaginal rubber devices largely depends on the type of incontinence and the individual characteristics of the anatomical structure of the body.
Squeeze the muscles of the perineum and hold the compression for 3 seconds, then relax them for the same time. Gradually increase the duration of compression-relaxation to 20 seconds. At the same time, relax gradually. Also use rapid contractions and activation of the muscles used for bowel movements and childbirth.
Involuntary leakage of urine in children
You should seek medical help for urine leakage in a child only if the child has reached 3.5 years of age. At this and older ages, the problem can be caused by:
- Anomalies of intrauterine development of the urinary system.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs that have not been fully treated.
- Physical injury.
- Mental disorders.
In these cases, therapy should be based on the principles of eliminating the pathology that served as the basis for the appearance of such a symptom. When making a diagnosis, it is also worth considering that hyperactive children are more likely to suffer from urine leakage than calm ones.
Types and differences
Manifestations of urinary incontinence vary: from periodic leakage of a few drops to complete emptying during the day or at night. In medical practice, the following types are diagnosed:
- Stress incontinence - a small or significant amount of urine leaks as a result of an increase in intra-abdominal pressure when coughing/sneezing, lifting something heavy (more than 3-5 kg), in advanced cases, even when changing body position. The woman does not feel a preliminary urge to urinate; emptying occurs suddenly.
- Urge incontinence - synonymous with this diagnosis are overactive bladder or urge incontinence. After a sudden feeling of a strong urge, emptying occurs immediately. Often a woman cannot even run to the toilet; more than 8 urges occur per day.
- Mixed is the most common option for women over 50 years old. Sneezing or any strain provokes a strong urge and rapid spontaneous urination.
- Constant dribbling - small amounts of urine are released throughout the day and night. This condition is associated with the formation of a urethral canal diverticulum, a vesical-vaginal fistula. However, most often, dripping is caused by incomplete closure of the urethral sphincter due to its weakness or the formation of scars due to chronic inflammation.
- Enuresis is a severe form of incontinence when the bladder empties completely without even the slightest urge. Enuresis often develops in women in extreme old age, suffering from progressive brain disease (Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease) or bedridden due to a serious illness (oncology, extensive cerebral hemorrhage). In this case, involuntary excretion of feces often occurs.