Medical Consultant Tests The normal level of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase is greatly increased - what does this mean?
Antibodies are protein-carbohydrate compounds produced by the immune system to recognize and eliminate pathogens. These substances are able to react to the slightest changes and, in some pathologies, begin to consider substances and body cells as foreign.
Testing for the level of antibodies to microsomal thyroid peroxidase helps diagnose pathologies of the thyroid gland or other organs in the early stages of development.
- Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are highly elevated - what does this mean?
- Level of antibodies to TPO (thyroid peroxidase), table
- Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are elevated during pregnancy
- Treatment for elevated antibodies to TPO, drugs
Norm of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (table)
The norm of AT to TPO is almost the same for women and men at a young age.
In women over 50 years of age, menopausal processes sometimes lead to an increase in antibodies to thyroid peroxidase, and this is a normal process of aging.
| Age | Norm, IU/ml (IU/ml) |
| 10-40 years | < 35 |
| After 50 years | < 50 |
A blood test for AT-TPO is prescribed along with other studies of the hormonal system:
- the amount of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH);
- T3 hormone (total and free);
- T4 hormone (total and free).
Norm
In absolutely healthy people under 50 years of age, the level of AT-TPO should not exceed 5.6 mmu/ml. Upon reaching 50 years of age, the concentration of this antibody in the blood may increase.
Indicatively, it is quite stable; it is the same for both males and females. Statistics show that an increase in the concentration of this indicator is diagnosed in 7% of cases.
The level of AT-TPO is of greatest diagnostic importance during gestation. An increased concentration of antibodies in the blood may indicate a threat of miscarriage or the birth of a child with serious abnormalities.
The norm of AT-TPO in pregnant women is from 0 to 2.6 mmu/ml. They always carry out this research without fail.
Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are highly elevated - what does this mean?
Today, medicine does not know the exact causes of immune system failures, but there are assumptions about the factors that lead to an increase in antibodies to TPO in the blood.
There are a number of most likely causes of increased antibodies to thyroid peroxidase:
- genetic predisposition to immune system failures, which manifests itself not only in the destruction of the thyroid gland, but also in other immune disorders (diabetes mellitus, lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis);
- an increase in the size of the thyroid gland due to genetic failures;
- tumors;
- excessive active release of T4 and T3;
- lack of thyroid hormones;
- iodine deficiency or excess;
- neck injuries;
- chronic renal failure;
- long-term radiation therapy;
- inflammatory processes in the large intestine.
In some cases, deviation of the level of AT-TPO from the norm occurs in healthy people (especially women) and antibodies above 300-500 IU/ml do not cause any negative consequences in the body.
Elevated levels of antibodies do not pose a threat to human health, but serve as an important signal for identifying more serious diseases.
High antibodies to TPO, along with a genetic predisposition, can cause hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, autoimmune thyroiditis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis or tumors.
Depending on the level of AT-TPO, one can judge about presumptive diseases:
- A moderate increase (20-30 units of measurement) of AT-TPO indicates possible systemic immune disorders, including insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, systemic autoimmune vasculitis, rheumatoid arthritis.
- If antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are highly elevated (more than 1000 IU/ml), this indicates already manifested diseases (diffuse toxic goiter, thyroiditis, etc.).
The essence of the analysis
Using a test such as antibodies to thyroid peroxidase, doctors establish an indicator of the aggression of the immune system towards the body itself. The main function of thyroid peroxidase is to form the active form of iodine and influence the process of modification of thyroglobulin.
The aggressive effect of some antibodies on the enzyme leads to its blocking. Therefore, the answer to the question: “Anti-TPO is increased, what does this mean?” - there will be a fairly simple conclusion: a violation of one of the functions of the thyroid gland occurs and the formation of the active form of iodine, which is very important for the full functioning of the body, is significantly reduced.
Moreover, this analysis indicates the fact of an autoimmune process specifically in the thyroid gland and in most cases confirms the development of hypothyroidism.
How to treat
Treatment of antibodies to TPO is unjustified, since in each specific case the exact cause and effect of autoimmune processes on the thyroid gland is unclear.
An increase in AT-TPO does not always cause thyroid dysfunction. In some cases, antibodies to TPO increase as the disease progresses.
Pathological processes in the thyroid gland (tumors, nodes) lead to the fact that thyroid peroxidase enters the blood, as a result of which the body produces a large amount of antibodies to the enzyme. In this case, antibodies to TPO are a consequence, not the root cause of disease.
In the case of an increase in AT-TPO, it is necessary to additionally examine the indicators of TSH, T3, T4, on the basis of which the thyroid condition is diagnosed.
For hypofunction
With high levels of antibodies to TPO, it is possible to develop diseases accompanied by hypothyroidism (insufficiency of T4 and T3), namely Hashimoto's thyroiditis, atrophy of the thyroid gland, for the treatment of which the artificial hormone T4 is used:
- Thyroxine;
- L-thyroxine;
- Euthorox.
The active ingredient is levothyroxine sodium. The drug in tablet form should be taken daily. The dose of the artificial hormone T4 is selected individually based on TSH tests.
Even if antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are highly elevated, there is no need to repeat tests within 1-2 years. Chronic inflammatory processes associated with thyroid peroxidase increase or stop very slowly.
With hyperfunction
In the event of diseases with hyperthyroidism syndrome (diffuse goiter, nodular goiter, autoimmune thyroiditis), it not only interferes with the absorption of potassium iodide, but also blocks chemical thyreostatic therapy.
Thyreostatics are medications in the form of tablets that inhibit the release of thyroid hormones. There are two groups of thyreostatics:
- Thiamazole (Mercazolil). The action of drugs with thiamazole is aimed at disrupting the absorption of iodine, as a result of which the thyroid gland will begin to produce less thyroid hormones. Preparations containing thiamazole: Methimazole, Tyrozol, Metizol.
- Propylthiouracil. The active substance propylthiouracil processes the conversion of T4 to T3 in the liver. A drug containing propylthiouracil: Propycil.
Drug treatment for hyperthyroidism is long-term and takes from three months to six months.
Treatment of increased AT-TPO with immunosuppressants, in particular prednisolone, is not justified and ineffective.
Causes and symptoms of increased antibodies
Causes:
- Diabetes;
- Chronic renal failure;
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Diseases of viral etiology;
- Massage and physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Leaky gut syndrome;
Symptoms:
- Voice change;
- Edema;
- Irritability;
- Dry skin;
- Hair loss;
- Infertility;
- Mood swings;
- Memory impairment;
- Hypotension;
- Tachycardia.
Disturbances are observed in the following body systems:
- Digestive system;
- Reproductive system;
- Nervous system;
- The cardiovascular system;
- Musculoskeletal system.
All systems are interconnected, so a failure in the endocrine and immune systems disrupts the functioning of other systems.
If TPO AT is elevated during pregnancy, the woman should definitely be examined. The endocrinologist will perform the following actions:
- taking anamnesis;
- referral for TSH and associated T4 tests;
- prescribe an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland;
- in accordance with the results obtained, he will prescribe measures for therapeutic correction.
Before visiting an endocrinologist, a woman should stop taking iodine supplements for a month.
Normally, a woman’s AT TPO content is less than 5.6 U/ml. But sometimes it is elevated. However, the woman does not reveal any pathology that could provoke this phenomenon. Then such a condition is regarded as an individual feature of the female body and should not cause cause for concern.
As for drug therapy, everything here is strictly individual. There is simply no general treatment regimen. Each drug is selected individually for each specific woman. If there is insufficient production of hormones, then drugs are prescribed as part of replacement therapy.
DETAILS: Urethritis in women - symptoms, treatment, causes and prevention
To reduce the activity of autoimmune processes, glucocorticoids are prescribed. We are talking about prednisolone and its analogues. Antihistamine drugs are introduced into the treatment complex. To reduce the manifestation of inflammation in the thyroid gland, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Symptomatic treatment is carried out aimed at relieving the symptoms that arise.
Indeed, there are quite a lot of folk remedies for such conditions, but it is necessary to clearly understand that they are never able to reduce the number of antibodies. You shouldn't even count on it.
The remedies of traditional healers can only alleviate the condition, reducing the manifestation of certain symptoms. They, of course, can serve as a good addition to the main treatment, but in no case replace it.
Traditional medicine will be effective only in combination with treatment prescribed by an endocrinologist.
The growth of goiter causes the occurrence of pain in the area of the projection of the thyroid gland. A compress of dry wormwood will help relieve pain:
- Melt 200 g of pork lard.
- pour wormwood on it
- which also needs to be taken 200 g.
A warm compress is used on the neck area. It is done at night for two weeks.
The patient can be helped with an infusion of seaweed. Kelp is mixed with plantain, honey, pine buds and lemon. The composition must be kept in a water bath for 30 minutes. A tablespoon of infusion is taken before meals.
If a problem arises with the AT TPO hormone, you cannot do without medical help. There is no need to self-medicate and use only folk remedies. The sooner appropriate treatment is prescribed, the greater the chances of a successful outcome.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, various hormonal and immune disruptions in a woman’s body are possible. An antibody test is mandatory in the first trimester of pregnancy. For thyroid diseases, the procedure is performed every trimester.
The results of an analysis for the level of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase indicate possible disturbances in the amount of thyroid hormones in a woman or child.
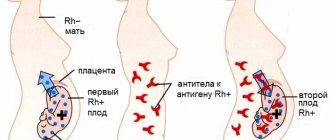
1. For the fetus, a high level of antibodies to TPO in the mother can be dangerous, since antibodies have the ability to cross the placenta and enter the child’s body, destroying thyroid cells.
An increase in antibodies to thyroid peroxidase during pregnancy can cause hypothyroidism in the child, which, in turn, impairs the growth and development of the infant. In order to find out possible hypothyroidism in a newborn, tests for TSH and thyroid hormones are required within 3 days after birth.
2. If antibodies to thyroid peroxidase increase against the background of normal amounts of TSH, T4 and T3, then this indicates a high probability of postpartum thyroiditis.
Postpartum thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease that manifests itself with hormonal disorders 3-6 months after childbirth. At the first stage, the disease takes the form of hyperthyroidism, and after 5-8 weeks hypothyroidism occurs.
Consequences of an increased AT-TPO indicator
Many patients who have thyroid diseases, if they consult a specialist in a timely manner, live a full life, because follow the doctor's recommendations and take medications. Treatment should be prescribed after all tests have been completed.
- Eutyroxine. In small doses, the drug helps synthesize proteins and enhances the absorption of calcium.
- Levothyroxine. The drug is contraindicated in case of adrenal insufficiency, heart attack, hyperthyroidism.
- Glucocorticoids. Used if the patient is diagnosed with autoimmune thyroiditis.
- L-thyroxine. Recommended for pregnant women.
Treatment is prescribed by a doctor based on laboratory data on the concentration of AT-TPO, TSH, T3 and T4.
The following drugs are prescribed:
- Drugs that block the thyroid gland: Levothyroxine.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Voltaren, Endomicin.
- Glucocorticoids: Dexamesatone, Prednisolone.
- B-blockers to reduce symptoms.
- Antibiotics by injection.
- Replacement therapy: thyroxine.
- Surgery.
An increased level of AT-TPO for a long time does not go away without a trace for the body. A violation of the immune system of this kind can lead to the following consequences:
- Postpartum thyroiditis. It begins to develop 8-12 weeks after delivery and, according to statistics, occurs in 10% of women giving birth. It was noted that women with antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are 2 times more likely to develop thyroiditis.
- Due to hypofunction of the thyroid gland, the possibility of manifestation (worsening of clinical manifestations) of hypothyroidism increases.
- Due to an increased AT TPO index, spontaneous abortion, pathological changes during the formation and development of the fetus, as well as other obstetric-type problems may occur.
When hypothyroidism begins to progress, a pregnant woman may begin to experience the following symptoms:
- Deterioration of the condition and regenerative capabilities of the skin.
- Decreased level of working capacity.
- Significant reduction in physical activity, slower response to stimuli.
- Deterioration of analytical abilities, memory and thinking.
- Metabolic disorders and some swelling of the face.
- Decreased mental activity.
With hypothyroidism, if timely measures are not taken, hypothyroid coma can develop, which leads to death in 80% of cases.
Due to the fact that an increase in the level of antibodies to TPO does not go away without a trace, and is also not capable of disappearing on its own, without medical assistance, such a condition requires treatment, identification of primary sources and their elimination.
DETAILS: Platelets are elevated in an adult, what is this about?
At the initial stage, the growth of ATTPO has practically no symptomatic manifestations that would clearly indicate the presence of some kind of disorder in the body.
However, as a result, negative changes occur and dysfunction of all organs and their systems is manifested, down to the cellular level.
A disorder of the immune system has both external and internal manifestations. As for changes in appearance, they are as follows:
- the skin becomes dry;
- the tone and sound of the voice changes;
- hearing decreases;
- active hair loss occurs;
- swelling occurs - both in the limbs and in the facial area.
As for changes inside the body, the following systems suffer from an increase in AT-TPO:
- cardiovascular;
- nervous system;
- digestive system;
- reproductive system;
- musculoskeletal system.
Methods for normalizing AT-TPO levels are based on hormonal therapy.
The prescribed drugs and their dosage are selected individually, depending on the body parameters and the capabilities of the patient’s endocrine system.
However, treatment tactics that could completely return this indicator to normal have not yet been developed, so treatment is carried out symptomatically.
When the reasons for the increase are unknown, the only thing the doctor can do is to alleviate the patient’s condition and support his body with the help of hormone replacement therapy.
When the cause of the increase in antibodies is known, then treatment is carried out aimed at eliminating the original source.
With successful treatment and elimination of the provoking pathology, the AT-TPO indicator will still not return to normal, therefore there is no special need to take this test.
Was the article useful and interesting to you?
Oh yes! No
The child has
If a child’s thyroid gland is functioning normally, but an increase in AT-TPO is detected, then this, just like in adults, indicates possible thyroid dysfunction in the future.
To prevent diseases in a child with elevated levels of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase, it is necessary to adhere to the following recommendations:
- refuse unnecessary vaccinations (for example, against influenza), since after this the antibodies to thyroid peroxidase increase even more;
- if an acute respiratory viral infection occurs, carry out full treatment of the child in order to exclude the occurrence of complications;
- do not travel to exotic countries, since climate change can trigger the development of autoimmune thyroiditis (different spectrum of sunlight, food, water, air);
- organize a normal diet with plenty of vegetables and fruits;
- minimize stressful situations.
How is biological material collected?
For this procedure, special instructions have been developed, in accordance with the requirements of which all manipulations are carried out:
- Laboratory conditions.
- Qualified health worker;
- Sterile disposable instruments;
- Biological material (venous blood) placed in a test tube is immediately sent for research.
Blood collection using special disposable instruments
Results are usually available the very next day. The price of the procedure differs in different laboratories.
Cases that do not require examination
There are cases in which an AT TPO thyroid test is not necessary.
These include:
- If the patient is in a hospital, then other, more effective examinations can be performed, the results of which will determine the patient's condition.
- When treating hyperthyroidism during the first 3 months, the hormone is determined by other methods that are more effective.
- When starting hormonal therapy, it should be borne in mind that the result may be significantly distorted and there is no point in conducting research.
The test may be prescribed by a doctor based on the development of other diseases and the results of other blood tests.
Therapeutic measures
With such a disease, it is quite important to prescribe timely and correct treatment.
Let us pay attention to the following features of treatment measures:
- Treatment consists solely of medication.
- Hormone replacement therapy can solve the problem. In this case, the dose and course must be prescribed exclusively by a doctor.
- Quite often, several drugs are prescribed, which are alternately tested for effectiveness.
- If there are significant problems with the functioning of the cardiovascular system, then beta-blockers are prescribed.
- Quite often, drug treatment is complex, including taking vitamins and adaptogens.
Quite often, the appearance of the hormone in the blood and the release of antibodies that attack healthy cells are asymptomatic. However, after some time, body weight may change, hair may begin to fall out, and other health problems may arise. The drugs can be prescribed for lifelong use, with the dose being adjusted.
Conditions for blood sampling
In order for the results of the study to be as reliable as possible, increased physical activity should be excluded before the analysis, not eating too fatty foods and under no circumstances drinking alcoholic beverages.
To exclude incorrect interpretation of the data obtained if a woman takes hormonal contraceptives, it is necessary to inform the endocrinologist about this in advance. This is due to the fact that taking oral contraceptives increases the level of AT TPO, but in this case this is considered normal.
Since the examination requires blood serum, the material for the study is blood from a vein.
Venous blood is taken for examination
We also recommend studying this topic:
What does a blood test for a tumor marker show: explanation of research methods
What treatment methods are used in case of deviation from the norm?
If the TPO AT is high, drug treatment is prescribed. The doctor prescribes hormone replacements, determining the dose and duration of the course strictly individually for each patient, depending on the case.
- Autoimmune thyroiditis. With this disease, there is a possibility of further development of hypothyroidism. There is no highly specialized drug for the treatment of this disease, so often the doctor, depending on the result, can prescribe several drugs until he selects the most effective one.
- If symptoms of problems with the cardiovascular system are identified, then therapy with beta-blockers is prescribed.
- If the patient enters a thyrotoxic phase, pharmaceuticals are not prescribed, since there is no hyperfunction of the thyroid gland.
- Replacement therapy is carried out using thyroid drugs, which include levothyroxine (L-thyroxine). It is prescribed, including to pregnant women. The dosage is selected based on the obtained analyzes of the level of thyroid hormones. Periodically, the woman takes tests again so that the doctor can track changes in the clinical picture.
- In subacute thyroiditis, other autoimmune diseases may occur in parallel. In these cases, the patient will receive glucocorticoids, which are part of Prednisolone. The patient is also prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs if an increase in autoantibody titers is observed. If the fact of compression of the mediastinal organs by the thyroid gland is detected, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Treatment is carried out comprehensively with the prescription of vitamins and adaptogenic drugs. Subsequently, the doctor prescribes a maintenance dose of drugs that the person takes throughout his life.
Prevention
As with other systemic diseases, in this case it is easier to observe prevention than to carry out treatment.
If you have a predisposition to the disease in question, then you need to follow the following recommendations:
- You should give up bad habits.
- Particular attention is paid to proper nutrition.
- In some cases, you need to change your area of residence.
- The work and rest regime is observed. Poor sleep quite often causes hormonal imbalance.
Also, do not forget that worries and stress cause hormonal imbalance, and this leads to the appearance of the disease.
In conclusion, we note that the problem under consideration is quite common, since people have a genetic predisposition to it.
With timely diagnosis and treatment, it is possible to reduce the likelihood of the disease becoming chronic, when it is necessary to take medications throughout life to relieve clinical symptoms.