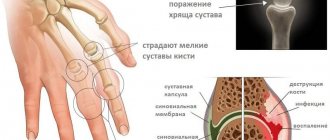
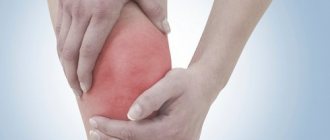
Absolutely no one is safe from an accidental fall, blow or any other injury. A knee bruise is one of the most common injuries, which, in turn, can be treated at home. The knee joint is one of the largest in the human body. It acts as a kind of hinge that allows you to bend and straighten your leg. The joint includes the tibia, femur and patella.
It is very important to know what to do after a fall and how to provide first aid in order to relieve pain in the knee joint and eliminate other unpleasant symptoms. If measures, as such, were not taken, this is fraught with disastrous consequences in the future. That is why you should not ignore even the slightest bruises, since they can serve as the beginning of the development of serious knee diseases.
Symptoms
A knee injury most often occurs due to a fall or blow. In this case, the upper skin is not damaged, only the internal tissues are affected.
The risk group includes active children, dancers, athletes, people whose professional activities involve lifting heavy objects, squats and bending, as well as lovers of high heels.
Pedestrians often suffer bruises during icy conditions.
You can recognize a knee injury by the following symptoms:
- sharp pain immediately after the injury, which may subside while stationary and intensify again when moving;
- slight swelling, skin hyperemia, slight joint deformity;
- cyanosis or redness;
- impaired mobility - it is difficult to bend or straighten the leg at the knee joint.
These symptoms may be supplemented by others if the knee injury is accompanied by a dislocation, ruptured ligament or fracture. If the hematoma is very extensive, the leg does not move or, conversely, is abnormally mobile in the joint, you should immediately call an ambulance.
If treatment is not started as quickly as possible, a knee injury can result in a serious illness for life and even lead to disability. What should you do first if you or someone nearby suffers a similar injury?
Due to inexperience, signs of a knee bruise can be confused with a dislocation. Indeed, in both the first and second cases there is pain in the knee and swelling.
But, with a bruise, the leg is able to move, which cannot be said about a dislocation. Having thus determined the bruise, it is necessary to begin its treatment, because the necessary assistance can be provided at home.
Painful sensations will be accompanied by all sorts of attempts to move, loads on the leg, even if in a calm state no discomfort is felt, then when you press on the damaged area, sharp pain will not be avoided.
Swelling and bruising
There is no need to worry if, a few minutes after injury to the knee joint, in addition to swelling, a hematoma begins to appear, because its appearance is the result of damage to the vessels from which blood flows. A large amount of leaked blood permeates the tissues and bloody swelling appears, which is a hematoma. The hematoma can be small and cover only the area of damage, or it can develop over the entire knee and acquire a burgundy or dark blue color.
In addition to the hematoma, the bruise is accompanied by a compaction, which is accumulated fluid, and a slight touch to the area of the formed lump can provoke severe pain.
Movement with a knee injury becomes limited, because the leg is in a half-bent state, and in order to straighten it, maximum effort will be required.
In addition, movement is accompanied by pain, which makes it difficult.
A knee bruise, which needs to be treated as quickly as possible, leads to its increase in volume. This happens because blood from the damaged vessel enters the joint cavity.
A bruise must be distinguished from a dislocation, fracture and ligament rupture. In severe cases, it is necessary to see a doctor, take an x-ray and undergo surgical treatment.
A severe injury to the knee may require surgical interventions: puncture, injections into the joint, and the use of potent medications. When a joint is injured, the following signs appear.
You can distinguish a bruise from more serious injuries by the following signs:
- the fracture is characterized by limitation of voluntary movements, severe pain, and very severe swelling. When the kneecap is fractured, its unnatural shape may be visible;
- dislocation - disruption of the contours of the knee, low mobility of the joint. Often with bruises, the kneecap becomes displaced. the leg may be twisted at an uncharacteristic angle;
- with a partial rupture of the ligaments, the picture is no different from a severe bruise. A medical examination and diagnosis will be required. The treatment is almost the same, only the rehabilitation period will be longer.
To exclude a fracture, dislocation, or ligament rupture, it is necessary to take an X-ray of the joint. Before contacting a doctor, the victim must be given first aid.
Consequences
During an impact, the load on muscles and joints increases significantly. Under the influence of such a negative factor, various complications can develop, especially if a person has not paid due attention to his injury. During a bruise in the knee area, the following deviations develop:
- Muscle spasm. In a relaxed state, they are subject to damage upon impact. The response to this is a spasm, which can cause pain for several days after the injury.
- Deformation of cartilage tissue. She takes part of the impact, which reduces physical activity.
- Microcracks in bones. They bear the brunt of the impact, since there is not much soft tissue in the knee area.
- Partial ligament rupture. This can result in a severe knee injury. Due to the rupture, a person is unable to raise or lower his leg.
- Vessel rupture. This leads to hemorrhage into the joint cavity. With a strong impact, its volume can reach 100 mm.
Minor knee injuries without damage to bone and joint tissues do not cause serious complications. Too strong blows without timely medical assistance can provoke a number of complications:
- bursitis, including purulent;
- inflammation and degeneration of meniscal tissue;
- rupture and sprain of ligaments or tendons;
- chronic luxation of the kneecap;
- limited joint mobility due to accumulated fluid;
- inflammation in the prepatellar bursa, which can cause bursitis.
Diagnostics
The first thing the doctor does is determine whether the injury has occurred only to the knee joint, or to other tissues as well. In addition, the specialist needs to eliminate the possibility of a crack in the bone or inflammation of the synovial bursa.
For this purpose, radiography is performed, which makes it possible to establish the correct diagnosis with high accuracy.
Is it possible to refuse this procedure and trust what a visual examination gives? No, the doctor must definitely refer the patient for an x-ray, since without it, the accuracy of the diagnosis is significantly reduced.
Important! It is better to do magnetic resonance imaging instead of an x-ray, since this diagnostic technique is much more informative.
Unfortunately, most domestic hospitals do not have this equipment due to its high cost. You can undergo the procedure in large regional centers. In the outback you have to be content with only radiography. What is the fundamental difference between it and MRI?
- MRI produces a three-dimensional video image. After the procedure, the doctor can print out pictures of the most significant moments.
- Magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to identify complications at the earliest stages. When a knee joint is bruised, we are talking about the appearance of cracks in the bone tissue and inflammation of the synovial bursa. The method visualizes not only bone tissue defects, but also muscles, ligaments, and joint capsules.
- Safety of the method. It must be remembered that it is recommended to take x-rays no more than once every six months, while the number of MRIs is not limited in any way.
We also recommend that you pay attention to the article: “Treatment of knee arthrosis at home.”
A bruised knee must be examined by a doctor to rule out the possibility of other pathologies.
Visually, a bruise of the knee joint is determined by the following signs:
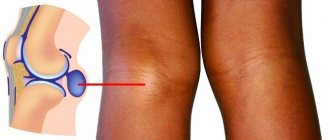
- The appearance of swelling. If you compare two knees, a healthy one and a bruised one, the second one will be larger in diameter.
- Change in skin color. Roughly speaking, a bruise becomes visible. In some situations, it appears only after 3-4 days.
- Pain on palpation.
- It is painful for the patient to bend/extend the knee. It is difficult to carry out this action completely.
An ordinary bruise of the knee joint can have quite serious consequences. These are hemarthrosis, meniscus injury, bone deformation. Therefore, if you experience knee pain, you should definitely make an appointment with a surgeon or orthopedist.
Important! The pain in the knee after a bruise should decrease within a day. Otherwise, there is a high probability of concomitant pathology.
Initially, pain from a knee injury is characterized as acute and quite severe. After 24 hours, its intensity decreases, the sensations acquire a pulling and tingling character.
If the bruise causes minimal tissue damage, the symptoms will disappear fairly quickly. Sometimes patients notice that a week has passed, but the condition of the bruised area is almost unchanged or deterioration is observed.
Don’t hesitate, make an appointment with a traumatologist or orthopedist in the following cases:
- pain increases;
- the hematoma at the site of the injury does not decrease;
- severe swelling does not subside after injury. The critical period is a day; if the tissues are swollen, rush to the doctor;
- The knee is difficult to bend and straighten, and there is a sharp pain when moving.
At the appointment, the doctor will examine the injured area, clarify the circumstances of the injury in order to understand the force of the blow and the extent of possible damage. When diagnosing, it is important to recognize such a dangerous type of injury as damage to the meniscus of the knee joint.
Severe soft tissue contusion and cartilage pad damage have similar symptoms. .
Note! If the blow was tangential, the risk of damage to the meniscus increases; in a direct collision with a hard surface, the anterior area of the knee often suffers, but the cartilage pad remains unharmed.
An accurate diagnosis is impossible without the use of modern diagnostic measures:
- computed tomography;
- arthroscopy;
- Ultrasound of the problem area.
Research will not only show the picture inside the joint, tell you about the condition of the ligaments, but will also confirm (or refute) the suspicion of injury to the ligamentous apparatus.
Causes and types of injuries
In most cases, a knee joint injury occurs during a fall, tripping, or, for example, walking on a slippery surface or running. A knee injury can be caused by an accident. One way or another, the main cause of injury is mechanical impact.
The injury can be complete or partial, with or without a bone fracture and dislocation.
What changes occur with a knee injury? A bruise is damage to the soft tissue of a certain area. When a knee joint is bruised, both the skin and subcutaneous tissue, as well as muscles, cartilage, ligaments and even blood vessels can be injured.
When the skin and tissue are damaged, the appearance of a wound surface is noted:
- muscle fibers - intense pain and spasm appear;
- ligaments – joint mobility is impaired;
- cartilage – damage to the bone and joint is noted;
- vessels - disruption of the knee joint occurs.
All this provokes the appearance of pain, discomfort, difficulty moving a limb, movement. If help is not provided on time, inflammation may develop. The inflammatory process quite often involves bones and cartilage, and as a result, the development of arthritis.
Treatment of a knee bruise
Our great-grandmothers knew very well how to treat a bruised knee at home, with the help of herbs and other natural products. Here are proven, effective and, most importantly, affordable recipes.
When pain from a bruise in the knee joint has just appeared, that is, immediately after receiving an injury, the injured area should be covered with ice or treated with a cooling gel.
Further treatment is carried out after confirming the diagnosis, that is, taking an x-ray and describing the image by a radiologist. Often the therapist does not have sufficient qualifications to identify the occurrence of complications in the initial stages.
Correctly applied cold compress
Treatment with folk remedies
When it comes to a bruised knee joint, treatment with traditional methods implies the following:
- Cold wrap. This procedure is performed in the first minutes after injury. Sharp cooling of tissues can significantly reduce swelling.
- Apply badyagi powder, diluted to a pasty state, to the bruised joint. It can be purchased at a pharmacy.
- Reduces inflammation by applying fresh leaves of coltsfoot, burdock, and cabbage to the bruised area.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy involves the use of a variety of ointments and gels, which include drugs such as Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Ketoprofen and other NSAIDs.
These drugs cannot be used uncontrolledly, as this will lead to side effects and complications. The next point is that ointments of this type are used for a long period of time only as prescribed by a doctor.
The gel is used for local pain relief from joint injuries and injuries.
Important! If, after using available remedies, joint pain does not go away within three days, you should seek help from a specialist.
Seeing a traumatologist is just the first step. If pain increases, it is necessary to have the examination performed by a surgeon or orthopedist.
It must be remembered that a bruise of the knee joint itself is not terrible, but it can cause very serious complications, the treatment of which will require a significant amount of time and money.
Minor injuries to the knee joint, such as a bruise, can be treated at home. For these purposes, use the above methods, as well as a light massage, which is intended to develop damaged tissues and speedy recovery of the knee joint.
Timely, correct help and proper treatment will show good results, even if they occurred on an outpatient basis. In this way, the tissues of the knee joint will be restored, stiffness will go away and no trace will remain of the injury suffered.
Otherwise, the trauma may continue to haunt you throughout your life.
Knee injury from a fall - what to do?
For many years, people have been using traditional methods to treat a bruised knee joint, which show quite good results. The traditional method of treating this damage consists of one very simple recipe. It will require vegetable oil, boiled water and vinegar.
To prepare the solution, you need to take all the ingredients in equal quantities. To make one serving of ointment, use about a tablespoon of each ingredient. Then mix everything thoroughly and apply the mixture to a cotton cloth.
It must be applied to the place that you hurt. It is imperative to cover such a compress with cellophane, and wrap it with a warm cloth, preferably woolen, on top.
You need to keep the compress on your leg for 5 hours, then take a break for 10 hours and repeat the procedure again.
You can also heal a bruised knee at home using regular cabbage. To do this, you need to take a few cabbage leaves and heat them a little.
Using a rolling pin, crush them until they release juice. Next, apply the sheet to the knee joint, and cover the top with a bandage or any other bandage.
This folk method will help remove swelling and the next day the knee will not be so swollen.
Some victims use compresses for home treatment with the addition of raw potatoes, grated, as well as a mixture of rye and white flour with a small amount of water. These methods are also considered effective in removing swelling from the knee.
You can prepare your own medicinal ointment from dry wormwood and Vaseline. The ingredients must be thoroughly mixed and placed in a barely heated oven for several hours. You need to rub the medicine into the damaged knee joint three times a day.
The tactics of the events are as follows:
- Immobilization.
- Absorbable agents.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
The joint must be cooled for the first 24 hours after injury. Then warming ointments, compresses, and physiotherapy are used.
Have you visited a doctor, taken tests, had a CT scan and ultrasound? Surely the doctor prescribed gels, ointments and creams to resolve bruises, relieve pain and swelling. The list of drugs for external use is given in the section “First aid for bruises”.
Lubricate the sore spot 5-6 times a day, act gently, do not put pressure on the knee. .
How to treat a knee bruise? If there is no meniscus tear, further treatment is carried out at home. The patient is required to take medications prescribed by the doctor and adhere to the rules of behavior after a knee injury. A prerequisite for successful treatment is rest of the problem area.
Most specialists dealing with problems of the musculoskeletal system welcome the use of homemade compositions for the active healing of soft tissues and the prevention of inflammation of joints and cartilage.
The main thing: choose recipes from natural ingredients for a delicate effect on swollen tissue. .
Many folk recipes have a couple more “pluses” in their piggy bank: herbs, vegetable mixtures, oil compositions, natural ointments are less likely to cause allergic reactions and have fewer restrictions. Follow the recipe and application rules exactly, and you will soon forget about bruises and knee pain.
Knee injuries - symptoms
In order to help a person in a timely manner, it is important to know how to identify a knee injury. Among the main symptoms:
- In case of a bruise
, there is a sharp pain, sometimes unbearable, a change in the color of the skin of the affected area, swelling that occurs after the hemorrhage. - In case of ligament damage
- pain, cracking when injured, soft tissue hematoma, joint swelling, problems with joint mobility, inability to lean on the injured leg. - Damage to the meniscus
- sharp pain, especially during physical activity, difficulty in going up or down stairs, a “clicking” symptom, slight atrophy, excess fluid in the joint, fever, enlargement of the joint.
Folk remedies
There are many products used for bruises and produced in the form of gels, ointments and creams. All of them help relieve inflammation and swelling and relieve pain.
The most effective drugs are “Nise”, “Ketonal”, “Dolobene”, “Troxevasin” and others like that. They are applied in an even layer to the damaged area several times a day.
A cabbage leaf compress will relieve swelling
- Using cabbage leaves can relieve inflammation in the knee and relieve pain. To do this, a cabbage leaf is attached to the affected area of the body and secured with a bandage or bandage. Due to the fact that this method of home treatment for bruises is absolutely harmless, the sheet can be left for a long time.
- It is good to treat the knee with white lily infused with alcohol. Such a compress will relieve inflammation and promote the speedy restoration of damaged tissues. You will need to moisten the bandage with this infusion, apply it to the knee, secure it with a bandage and place it in a warm place to achieve the desired effect.
- A common method that has been used for decades is a compress based on water, vinegar and vegetable oil. The listed components are mixed in equal proportions. Dip a bandage into the resulting mixture, apply it to the damaged area of the knee, wrap the leg with film and secure it with a bandage. Within five hours, the compress has an effect on the sore leg, relieves inflammation, pain and swelling.
There are several simple folk recipes that can be used as an addition to treatment:
- An alcohol-drying compress will cool the knee and reduce pain and swelling. Gauze or bandage is moistened with vodka or diluted alcohol and applied to the bruise until the compress dries;
- dressing with vinegar: mix 9% vinegar, water and vegetable oil one tablespoon at a time. The mixture is applied to the fabric, applied to the joint, covered with plastic wrap and bandaged;
- iodine mesh: “paint” the knee with an alcohol solution of iodine, place the strips at a distance of about 1 cm. Use one day after the injury. Iodine has a mild irritant and anti-inflammatory effect.
What to do first?
After an injury, it is not always possible to go to the hospital for help. Therefore, the first task is to ensure complete rest for the joint. Experts recommend:
- Apply ice to the affected area. If it is not nearby, any other cold object will do. This action will prevent swelling and eliminate pain.
- If the pain does not change in intensity towards lessening, take painkillers.
- After a blow, a tight bandage helps a lot. A regular or elastic bandage is suitable for this. If they are not at hand, then use any other material. Try to fix your leg in such a way that the muscles are not damaged during this action.
When all steps are completed, place the patient on a bed or couch. A pillow is placed under the kneecap.
If severe pain is combined with an extensive hematoma of the knee joint, it is necessary to transport the patient to the hospital as soon as possible. This is due to the fact that the tumor occurs due to hemarthrosis. This is a disease where bleeding occurs in the kneecap.
In some situations, a hematoma on the knee leads to an increase in body temperature. The situation requires immediate medical attention, because otherwise the blood begins to saturate the cartilage, and the clots lead to severe inflammation.
Ointments for joints
An effective method of treating a knee bruise is the local use of medications in the form of ointments and compresses. Conventionally, all pharmaceutical ointments can be divided into several groups:
- improving microcirculation in tissues: “Troxevasin”, “Traumel”. These drugs can be used immediately after injury and throughout the recovery period;
- anti-inflammatory: “Indomethacin”, “Diclofenac”, “Diklak”, “Ketonal”;
- warming: “Fastum gel”, “Camphor ointment”, “Analgos”, “Apizartron”, “Viprosal”, “Finalgon”. It is not recommended to use them during periods of acute edema;
- complex ointments containing several components. For example, "Indovazin". It contains indomethacin and troxevasin.
Determining the degree of knee injury
A victim with symptoms of a knee bruise must be taken to the traumatology department to exclude serious deformations of the components of this part of the leg.
- For moving, a comfortable position of the lower limbs is ensured to prevent additional knee injury during transportation. It is advisable to apply a tight bandage to fix the joint.
- Apply cold to the injury site. At home, you can use frozen food or a cloth soaked in cold water. Outside, you can use a bottle of cold water from any store refrigerator.
- Rinse open abrasions with clean water, and if hydrogen peroxide is present, treat the wounds with the liquid to prevent infection.
- Severe pain can be relieved with any painkiller, but it is better to first be examined by a traumatologist.
First aid
Until an accurate diagnosis is established (if doctors are expected to arrive) or the victim has not made it home (if treatment for a knee bruise at home is preferred), here’s what you can do:
- relieve pain - ibuprofen, analgin, diclofenac, indomethacin in tablets or injections will help;
- provide the patient with complete rest by laying him down or sitting him down so that his leg is slightly higher than his body;
- apply a tight bandage;
- Apply ice or a cold compress to relieve swelling.
Advice: Cold compresses and ice are applied to a knee injury only on the first day. Then you need to make hot lotions.
If you bruise your knee, what should you do first?
- Cold. Place an ice pack on the joint area, or if there is no ice, a wet cold towel. The fabric must be changed as it heats up. If possible, use special ampoules or freezing spray used in sports. Cold reduces swelling, reduces pain, and constricts blood vessels.
- Immobilization. Lay the victim down and apply a tight pressure bandage to the knee. In addition to immobilization, the bandage will prevent the development of severe swelling.
- If a knee injury occurs, first aid is aimed at reducing blood flow to the joint and reducing swelling. To do this, you need to slightly lift your leg up and place a pillow under your knee.
- For severe pain, take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that have an analgesic effect: Analgin, Ketanov, Oksigan and others.
All of these measures help relieve knee bruises. Treatment can be started before visiting a doctor by applying Troxevasin ointment to the joint. It has a mild analgesic effect and reduces tissue swelling.
To help a victim with such an injury, you need to do the following:
It is not always possible to seek medical help as soon as possible. Every person should know what to do in case of a fall, blow, severe pain, or swelling of the knee.
Description of injury
A bruise (ICD-10 code S80) is a closed injury to the soft tissue above the knee joint. It's easy to earn. Every person probably knows what it’s like to hit your knee on asphalt or another surface.
Under other circumstances, a bruise can be caused by:
- slipping on ice;
- if you fall off your bike;
- in a car accident;
- when you arrive, if you don’t notice a curb or a large stone;
- during training when performing exercises;
- during a fight.
The greatest number of victims is observed in the winter and summer seasons. In the first case, all categories of citizens are injured, as ice appears on the roads. In the second, mainly children and young people, which is explained by school holidays and increased activity of adults.
A slight bruise of the knee due to a fall often occurs in isolation. In serious incidents, soft tissue injury may be combined with a violation of the integrity of the bones, so it is not recommended to refuse diagnostics.
The bruise can occur simultaneously with:
- dislocation;
- subluxation;
- fracture;
- sprained tendons (ligaments);
- abrasions and cuts;
- hematomas;
- meniscal damage.
Older people have a significantly higher risk of fractures. This is due to a decrease in bone density.
If you suspect a bruise, you need to call an ambulance or go to the traumatology center yourself.
Symptoms of a knee injury
The main signs of a bruise include:
- severe or moderate pain in the knee area with pressure and at rest;
- difficulty flexing and extending the joint, tension;
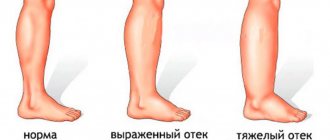
- swelling, which is localized in the cartilage area and spreads to the lower leg or thigh;
- redness;
- bruises and hematomas;
- numbness and tingling.
What such damage looks like can be seen in the photo on the Internet.
With the development of complications such as synovitis (swelling of the synovial membrane of the joint), additional symptoms appear:
- smoothness of the contours of the knee joint due to severe swelling;
- feeling of fullness in the leg area;
- chronic nagging pain;
- increase in general or local body temperature;
- chills, weakness, fever (with purulent forms);
- rapid fatigue of the sore leg.
Hemorrhage into the knee joint (hemarthrosis) is accompanied by:
- main signs of injury;
- swelling of the joint from the front, inside and side;
- bluishness and tightness of the skin at the site of the lesion;
- an increase in local temperature.
Other knee injuries cause similar symptoms, so self-diagnosis is often uninformative.
First aid for falls
The algorithm of action for bruises and other types of injuries is very similar and does not depend on who was injured, an adult or a child:
- Immediately after a fall or other incident, cold is applied to the affected limb. If you don’t have anything like this on hand, you can use a pharmacy cream with a cooling effect.
- Afterwards, it is recommended to immobilize the affected limb using a tight bandage or fixing splint. An elastic bandage, a sheet of plywood, an iron rod or other available means are suitable for this.
- If the skin is damaged, it is recommended to treat the wound with an antiseptic. If there are shards of glass or other objects sticking out of it, it is not recommended to remove them before arrival.
- If bleeding is present, a tourniquet or tight bandage is applied above the knee, and the time is recorded. If you overexpose it more than expected, there is a risk of developing necrosis (gangrene) and amputation of the leg.
- When all pre-medical measures have been completed, it is recommended to call an ambulance or transport the victim to a traumatology center yourself. In case of multiple injuries, it is better to wait for doctors to arrive, because the patient may develop internal bleeding, requiring emergency hospitalization.
Mild and moderate bruises can be treated at home. In advanced cases, they may give you sick leave and even admit you to a hospital.
Why is a bruise dangerous?
Common bruises only affect the soft tissue surrounding the knee. Unlike fractures and dislocations, movement in this part of the leg is preserved, but is extremely painful. When the leg begins to swell greatly, stiffness appears, making it impossible to bend and straighten the knee.
If the bruise is old and the discomfort does not go away for a long time, there is a high probability of developing complications from the joint.
These include:
- hemarthrosis;
- synovitis;
- gonarthrosis.
Often these pathologies occur against the background of severe swelling of the surrounding tissues and lack of treatment. If you fall unsuccessfully, the impact may fall on the periosteum area. In this case, the leg may become very painful. Sometimes this leads to shock.
When a bacterial infection enters the joint cavity, purulent inflammation of the synovial membrane develops, which is accompanied by severe symptoms and can lead to amputation of the limb. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the knee through damaged skin or hematogenously.
Prolonged inflammation in the patella area and lack of adequate therapy contributes to:
- destruction of cartilage tissue;
- development of chronic pain;
- limited mobility;
- crunching when moving.
To avoid possible complications, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor, who will assess the nature of the injury and prescribe effective treatment.
Diagnosis of a knee injury
When you first visit the traumatology department, the doctor evaluates the appearance of the knee. Previously, the diagnosis was made on the basis of special tests to assess joint mobility. Now there are instrumental methods. To make sure there are no fractures, cracks or other types of injuries, X-rays and ultrasound are done. Often this is enough to prescribe treatment.
If complications are suspected, you should do the following:
- MRI or CT;
- arthroscopy;
- examination of synovial fluid.
For minor bruises, you can do without instrumental diagnostics, but it won’t hurt to see a doctor. Soft tissue injuries usually resolve within 10 days. If during this time the condition of the leg has not improved, you need to go to the hospital.
Treatment of bruise
What to do if you bruise your knee depends on the cause and the final diagnosis. Often, inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding the knee joint does not need to be treated with serious medications. The patient is advised to limit the mobility of the sore leg, smear it with special ointments and try not to hit it again.
Help relieve swelling and other unpleasant symptoms:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs);
- corticosteroids;
- analgesics;
- medications with combined effects.
There are expensive and cheap products, so everyone can choose the right option.
In case of severe pain, they resort to injection or oral forms of analgesics and NSAIDs. In severe cases, blockades are indicated - steroid injections into the affected area.
When the knee stops swelling, but the discomfort remains, warming ointments may be prescribed that improve blood flow and tissue nutrition. Bruises are eliminated with absorbable agents.
Ointments can be prescribed separately or in combination (usually two or three types).
Most often used:
- Diclofenac;
- Voltaren;
- Ketorol;
- Troxevasin;
- Troxerutin;
- Finalgon;
- Nise;
- Lidocaine;
- Heparin ointment.
Before starting use, you should read the instructions for the medicinal ointment. NSAIDs are used throughout the course. Warming agents are prescribed only after swelling has resolved.
If you apply Finalgon to your feet in the first two days after an injury, the product will not relieve pain; on the contrary, it will provoke the opposite effect and the inflammation will intensify.
In the acute period, anti-inflammatory, cooling or painkillers can be used.
To avoid troubles associated with the incorrect selection of gel or ointment, it is recommended to first consult with a doctor who will tell you how to treat bruised knees. In childhood, some products are contraindicated, so before starting use you need to study the instructions.
Physiotherapy
For severe or complicated bruises, the patient is recommended to undergo additional physical treatment. Simple procedures help tissues regenerate faster, shorten the rehabilitation period and eliminate unpleasant sensations - pain, stiffness, a feeling of fullness in the knee.
Folk remedies
Some folk remedies are effective:
You can use regular onions. Just grate it so that it produces juice, put the resulting pulp on your knee, wrap it in a cloth or gauze folded several times and leave for an hour. You can repeat this procedure several times a day.
Use apple cider vinegar. Heat 500 ml of vinegar in a water bath.
Add two or three tablespoons of sea salt and 10 drops of iodine. Soak a cloth or gauze in the resulting liquid and apply it to the injured knee.
Wrap the limb in a towel to provide an additional warming effect. After an hour, remove the compress.
First of all, having determined that the knee injury is nothing more than a bruise, the patient must be relieved of unnecessary stress. In no case is it recommended to continue moving and thereby put additional stress on the injured leg, which can aggravate the situation.
Therefore, the patient should be placed in a horizontal position or seated.
- Reliable fixation of the knee joint using an elastic bandage, which must be applied as tightly as possible. If you don’t have an elastic bandage at hand, you can use a regular one. Naturally, the effect will be slightly different, but the fixation will be there. For 2-3 days, if possible, various types of stress on the injured leg should be avoided.
- An ice compress is good because it will relieve pain and stop the formation of swelling or hematoma. Ice is placed in a bag, which is wrapped in a towel and applied to the injured knee for no more than 10 minutes, otherwise tissue frostbite is guaranteed.
- Treatment of a bruise accompanied by a hematoma is best done with bodyaga, the purchase of which at the pharmacy is available to everyone today. After the bodyaga has been diluted with water, it should be applied to the affected area.
Knee injury from a fall: symptoms, consequences and what to do
A knee injury is one of the most common types of injuries that can occur in both adults and children.
A bruise is damage to the soft tissues that surround the knee and can be accompanied by a number of complications such as dislocation or fracture. As a rule, a bruise occurs due to a fall (or blow).
Depending on the severity of the injury, in the absence of help, there can be all sorts of consequences, both mild and severe (crack, meniscus tear, etc.).
Why is this dangerous?
The knee joint itself is a fairly complex structure, consisting of several hundred nerve endings. Violation of this structure is a bruise, which can lead to a number of disastrous outcomes.
The dangerous consequences that can occur as a result of a knee injury from a fall include the following:
- Accumulation of fluid in the knee joint.
- Meniscus tear (or inflammation or tear).
- Knee sprain.
- Dislocation.
- Fracture.
And, unfortunately, this is not a complete list of possible consequences of a knee injury, but even the above should be treated as quickly as possible by a qualified specialist, because the consequences can be dire.
Causes
- Active lifestyle. The causes of injury from a fall include an active lifestyle (sports, vigorous activities, etc.), work/living in extreme conditions. For example, bruise is a common occurrence among athletes. An example would be a person involved in athletics (a runner, for example); it is not surprising that during training or competitions he may accidentally fall. An active lifestyle, as is clear from the definition, entails a lot of movements that, by chance, can lead to a fall.
- Accident. In addition to an active lifestyle, literally everyone can get a bruise in an unfortunate situation, examples include: falling due to inattention (hitting a curb, for example), poor position of the center of gravity at the time of the fall, and the like. In other words, there is no point in listing the reasons for an accidental injury, because there are a huge number of such situations.
Symptoms
A bruise can manifest itself in different ways; the main symptoms of a bruise are described below:
- Pain - appears immediately after a fall and manifests itself either on its own, or when touching the damaged area, or when moving.
- Increase in joint volume . Most often, this symptom indicates an accumulation of fluid in the knee joint.
- Joint swelling . Regarding this symptom, it is impossible to say exactly what is wrong without diagnosis; it may be the result of a wound or abrasion, or it may be a manifestation of joint hemorrhage or other inflammatory diseases.
- Difficulty in moving the injured knee . After a bruise, it becomes more difficult for the victim to bend and straighten his leg, and problems appear when moving.
- Hematoma (Hemorrhage caused by rupture of blood vessels, most often manifests itself immediately after injury), etc.
If such symptoms are detected, the best solution would be to seek help from a specialist for immediate treatment.
Diagnostics
Most often, when a knee is bruised, there is no particular need to resort to special diagnostic measures, since diagnosing the disease is not a big problem for a doctor, since all clinical manifestations are visible to the naked eye.
Studies such as ultrasound , x-ray of the knee joint and similar ones are used if the specialist suspects any more serious injuries, an example of which is a banal dislocation of the patella. But even with a minor injury, you should definitely see a specialist, since even a slight bruise can have serious consequences.
Speaking about severe injury, we can say that a complete diagnosis of the patient . The diagnosis itself is carried out by a traumatologist in a hospital. The traumatologist interviews the victim and assesses his condition, after which the appropriate procedures are performed. Depending on the nature of the injury, the traumatologist decides whether it is necessary to perform procedures such as MRI, ultrasound.
In case of severe injury, a full range of diagnostic procedures is carried out. They are carried out to determine the nature of the injury and clarify its severity, as there may be serious complications. After a complete diagnosis, the doctor establishes a diagnosis, prescribes treatment and recommendations to the patient.
Treatment and what to do
First aid
- To begin with, the victim needs to provide rest to the leg on which the knee is injured, in other words, if possible, avoid any movements with it. It is advisable to place the leg higher than the level of the body (put something under it), which will help improve blood flow and, in turn, help reduce swelling.
- Apply something cold to the injured area, be it a cold water bottle, ice, or something else. This will dull the pain.
- Rinse the damaged area, if it is very dirty, and treat it with hydrogen peroxide, and then apply a bandage with an antiseptic.
- Apply a bandage, tightening it tightly. A bandage, like the cold object mentioned above, will dull the pain and also reduce the load on the leg. It is advisable to use an elastic bandage as a bandage, but in the absence of one, you can use clothing (or part of it).
Treatment at home
- Treatment in any case should be carried out under the supervision of a traumatologist, because first you need to determine the nature of the injury and its severity.
- At the beginning, as with first aid, apply a cold compress for about 3-4 days, this will help relieve swelling.
- To remove hematomas, they usually use ointments like Heparin ointment; it thins the blood and stops inflammation.
- When moving, it is again worth applying an elastic bandage.
- The wound must be washed daily.
- In accordance with the doctor's recommendation, use various painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Deprive the victim of any movements as much as possible, strictly bed rest.
- Since a bruise may result in an accumulation of blood or fluid in the knee joint, after providing first aid, you should not immediately begin home treatment, but rather go straight to the emergency room.
- If the above actions do not help, the pain does not go away, then you should either call an ambulance or go to a specialist for further treatment.
If the nature of the injury is severe enough and can have disastrous consequences, the doctor will immediately have to begin treatment of the patient.
What happens when there is a bruise? What are the consequences of such an injury?
In general, a bruise is damage to the soft tissues of one or another part of the body. Yes, soft tissues regenerate much faster than hard ones (in particular, bone), but treatment is still necessary. It's worth explaining why.
So, first, let's list the tissues that will be involved in the process of a knee injury:
- Skin, subcutaneous tissue. Damage often affects the skin, although in some cases its integrity may be preserved. If the integrity is broken, then a wound surface will certainly form.
- Muscles. Yes, they suffer too. Muscle tissue will respond to damage with strong tension, that is, spasm. And spasm is pain.
- Ligaments can also be damaged when injured. And if articular ligaments are involved in the process, then the integrity of the joint may be compromised, which will certainly affect mobility.
- Cartilage tissue can also be damaged, but cartilage plays the role of a kind of shock absorber and softens all movements. Without them, the ends of the bones would rub against each other and gradually collapse.
- Vessels can also be damaged. If a large vessel ruptures, the blood passing through it can accumulate, for example, in the cavity of the joint (and this will significantly disrupt its functioning).
Now it’s worth directly touching on the consequences of an injury such as a knee bruise. Why is it worth treating?
The functioning of the tissues will be disrupted, which will greatly complicate leg movements and movement. The most dangerous thing is cartilage damage. But ligaments and muscles also provide mobility, so their work is no less important.
And another reason why injuries need to be treated. Violation of integrity can provoke inflammation.
And if treatment is not carried out in this case, the inflammation will begin to spread. In this case, not only cartilage tissue, but also bone tissue may be involved in the process.
As a result, an unpleasant disease such as arthritis can develop. Irreversible dystrophic changes will also begin, which will lead to tissue destruction.
Important advice from the editors!
Everyone uses cosmetics, but studies have shown terrible results. A terrible figure for the year - 97.5% of popular shampoos contain substances that poison our body. Check the composition of your shampoo for the presence of sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium laureth sulfate, coco sulfate, PEG. These chemicals destroy the structure of the curls, the hair becomes brittle, loses elasticity and strength.
The worst thing is that this nasty thing accumulates in the organs through the pores and blood and can cause cancer. We strongly recommend that you avoid using products that contain these substances. Experts from our editorial team tested shampoos, where products from Mulsan Cosmetic took first place.
The only manufacturer of completely natural cosmetics. All products are manufactured under the strict control of certification systems. We recommend visiting the official online store (mulsan.ru). If you doubt the naturalness of your cosmetics, check the expiration date; it should not exceed 11 months.
Symptoms and diagnosis of knee injury
Manifestations of injury can be very diverse. In most cases, the pathology is characterized by:
- Intense pain, especially when moving.
- Hemarthrosis of the knee joint is an accumulation of blood in the joint. This symptom can be expressed to varying degrees, but the severity of other symptoms will depend on it.
- Swelling of the damaged area.
- Blue skin in the area of the bruise.
- Impaired joint mobility.
Swelling of the knee joint may indicate hemarthrosis, i.e. accumulation of blood in the joint cavity.
The area of the damaged area, the location of the injury, the force of impact on the tissue - all this will affect the severity of the symptoms.
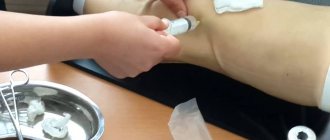
A bruise is diagnosed based on examination and palpation of the affected area. Next, a therapeutic and diagnostic puncture is performed, due to which the presence or absence of blood in the cavity is determined. In case of a knee injury, the following is prescribed:
- radiography;
- ultrasound examination;
- endoscopy.
Medical intervention
A knee injury may require surgery and other medical procedures:
- Puncture – puncture of the bursa and suction of accumulated fluid.
- Prescribing injections into the joint of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: analgin, voltaren, indomethacin.
- UHF – therapy, electrophoresis.
If you have injured your knee, apply a cold compress with ice for 20-30 minutes, then bandage the joint tightly. To rule out serious damage, it is better to consult a doctor. The specialist will conduct the necessary diagnostics and prescribe appropriate treatment. In any case, stay in bed and use warming and anti-inflammatory ointments. Remember that the knee is a very complex and vulnerable joint, so poorly treated injuries can subsequently be complicated by various diseases.
Provoking factors
Why do some people develop joint problems very early, while others lead an active lifestyle until old age?
There are several categories of people predisposed to bone or connective tissue diseases:
- Professional athletes. Joints and sprains are a big problem for such people. Their joints endure not only heavy loads, but also excessive activity, which leads to premature wear. The athlete's muscle often cramps and twitches. According to statistics, the left leg is less often affected;
- Workers with heavy physical labor. Heavy stress destroys joints and accelerates the pathological process. If a problem appears and the cause is not eliminated, this can lead to disability;
- People after operations or infectious diseases. Pulling pain in the area of the popliteal fossa may appear as a result of innervation of nerve endings from other foci of inflammation.
Treatment
After first aid is provided, the person is taken home or to the hospital. At home, a person should try to keep the injured limb in an elevated position more often. If the pain does not go away, repeat pain relief by taking a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (indomethacin, ketorol, oxygan).
Treatment of a bruised kneecap is usually carried out using conservative techniques. Only in the presence of complications do they resort to surgical intervention. If a person is being treated at home and his swelling does not subside within 24 hours and the hematoma is growing, he should definitely see a doctor. Most likely, complications occur after a bruise.
At this time, the clinical manifestations of hemarthrosis (hemorrhage) are already clearly expressed, which allows the specialist to easily identify this complication. The pain is very severe, the knee is swollen, the victim cannot lean on the limb. When large vessels rupture, the joint capsule is greatly stretched due to the blood entering there. If you palpate the knee, fluid movement is felt.
The general condition of a person also changes. His temperature rises and he becomes restless due to discomfort. At this time, it is important to provide assistance, otherwise blood will begin to flow into the cartilage tissue, causing inflammation.
Treatment is carried out using a puncture. The blood is pumped out from the joint, then the knee is fixed with a bandage, which must be worn for 3 weeks. At this time, the patient is prescribed chondroprotectors (collagen-ultra, fermatron), anti-inflammatory drugs in tablets and ointments. Heparin ointment and Lyoton gel help well. They restore blood vessels and strengthen their walls.
After a week, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. These are UHF, massage, electrophoresis, dynamic current therapy, a little later physical therapy is indicated.
Electrophoresis of the knee joint
Rehabilitation after injury
This is a mandatory step in the treatment of any injury to the knee joint. Depending on the type of injury, it can last from 14 days to a year. Restoring the functions of all parts of the joint is possible only with an integrated approach.
- Physiotherapeutic methods help to quickly relieve swelling, inflammation and pain. This could be paraffin or mud therapy, electrophoresis or a magnet. They improve blood circulation and metabolic processes in tissues, stimulate muscles and prevent the development of complications.
- Massage is very useful at any stage of recovery from injury. It improves blood supply to the joint and helps keep muscles toned.
- But the most important thing during rehabilitation is physical activity. At first it may be as simple as raising and lowering your leg, straining your muscles, or moving other joints. Then you can add more complex exercises. But until the knee functions are completely restored, it is necessary to avoid squats.
Knee injuries are very dangerous because they can lead to disruption of its function and the inability to move normally. Therefore, it is necessary to provide timely assistance and visit a doctor even with a minor injury.
The main causes of closed knee injuries in adults and children – who is at risk?
There may be several reasons for the pathological condition in question:
- Impact with the kneecap. This is especially relevant for those who are involved in contact sports: hockey, football, biathlon, wrestling, etc. Although in everyday life a person is also capable of injuring his knee.
- Falls in which the landing is carried out on straight legs. This could be an unsuccessful parachute jump, a fall from a horse, or a work injury.
- Adverse weather conditions.
- Car accident.
- Increased load on the knee joint. The reason for this may be obesity, weightlifting, etc.
- Wearing uncomfortable shoes. This primarily applies to female representatives who prefer high-heeled shoes.
- Incorrect position of the foot while walking , which is a consequence of flat feet.
- Movements that involve strong twisting of the joint . A similar phenomenon is typical for those who do yoga and gymnastics.
The risk of knee injury increases significantly in the following situations:
- After crossing the 60-year mark.
- Diseases that lead to degenerative changes in the joints: osteoarthritis, lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis.
- Cystic formations in the popliteal region.
- Infection of the skin, bone tissue, joints around the knee.
- Pathological changes in the structure of the hip joint.
Classification of ointments for bruises
Knee injuries are accompanied by characteristic symptoms. The victim experiences pain, swelling, and hematoma. For treatment, the best local agents are used. Ointments help restore joint function and eliminate bruise symptoms. Depending on the composition, there are three groups of medicines:
- Synthetic. They are characterized by speed, high efficiency, and active penetration into the affected area.
- Plant-based - have a minimum of contraindications.
- Homeopathic - safe to use, long-term treatment is required.
Ointments that are used for bruises have a variety of effects. The following remedies can be used to treat a damaged knee:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Elimination of pain, swelling, inflammation
Effect on skin receptors
Warming – improves blood circulation
Cooling - soothe, relieve swelling, pain due to menthol, camphor in the composition
Accelerates metabolism in cells
Normalize blood circulation, resolve hemorrhages
Steroid based ointments
Counteracts severe inflammation
Promotes regeneration of cartilage tissue, restores knee function
Source vrachmedik.ru
A knee injury is one of the most common injuries not only among children, but also among adults. Not everyone understands the seriousness of such an injury, believing that “it will pass.” But this condition is fraught with complications. That is why, if a knee joint bruise occurs, treatment cannot be ignored.
Methods for diagnosing hemorrhages
If discomfort or lumps appear under the knees, the patient can contact:
- To the therapist. He will suggest why your knees may hurt when stretching or walking, and then refer you to a specialist;
- If your child is bothered by leg pain, you need to go to the pediatrician;
- Orthopedist – specialist in diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- Surgeon;
- Neuropathologist.
After asking about the nature of the pain and how long ago it appeared, the doctor may send the patient for an x-ray or ultrasound to see the presence of pathology or destructive processes.
Effective folk recipes
If a person has at least 1-2 days left to get rid of a bruise on his face, many home remedies can be used:
- A thoroughly pounded onion, combined with 20 g of table salt and wrapped in cloth, placed on the bruised area, causes the bruise to resolve in a matter of hours. It is recommended to repeat this compress 2-3 times a day. It is recommended to prepare a new compress each time.
- The most effective remedy has long been cabbage or plantain leaves - thoroughly washed and beaten with a culinary hammer, they effectively eliminate the consequences of a local injury - a bruise.
- Combine equal amounts of grated beets and buckwheat honey. Apply a generous layer over the damaged area of the dermis. After a minute, rinse everything thoroughly with heated liquid. Repeat procedures 3-4 times a day.
- Apply a thick mixture of starch diluted with distilled water to the hematoma site for several hours. An effective remedy will help remove the problem in just 1-2 days.
- Another highly effective compress that provides quick relief is made from iodine (4-5 drops), apple cider vinegar (30 ml) and salt (20 g). Mix all components thoroughly and apply a compress to the desired area of the dermis. An effective remedy even for brown-purple bruises.
We invite you to read: How cytomegalovirus is transmitted from person to person: how can you become infected with CMV, is the carrier infectious to others, the main routes of infection and inheritance
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation measures are necessary after a long stay of the leg in a cast, as well as after operations.
These include:
- therapeutic exercises;
- massage treatments;
- physiotherapy;
- gentle regime of physical activity;
- sometimes - medications (chondroprotectors that protect cartilage: Dona, Structum, Elbona; as well as NSAIDs that prevent inflammation: Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Piroxicam).
After severe injuries, an athlete may be advised to take a long break or retire from professional sports.
Click on photo to enlarge
Examples of exercise therapy exercises for rehabilitation of the knee joint. Click on photo to enlarge
Ointment for joint bruises
The most commonly injured joints are the elbow and knee joints. Joint bruises often occur in athletes and representatives of dangerous professions (rescuers, firefighters). When a joint is bruised, the integrity of the bone and cartilage tissues is preserved. If the blow was not severe and the internal hemorrhage was small, the pain goes away after 12 hours. If the blow was stronger, the periarticular tissues were injured with the formation of noticeable hemorrhage, then swelling occurs, and the pain persists for several days.
The bruise greatly limits the mobility of the joint, making it painful to flex, extend, rotate and other movements. In order to quickly get rid of the consequences of a bruise, it is necessary to apply cold immediately after the injury. And after 6-8 hours - apply an ointment with a decongestant, absorbable and warming effect .
Nervous and vascular problems
Sometimes the leg behind the knee hurts due to diseases not related to the musculoskeletal system. So, nervous pathologies can also cause unpleasant symptoms. These include the inflammatory process in the tibial nerve. The nerve is located in the area of the fossa under the knee; if it becomes inflamed, a sharp pain syndrome is observed along the back of the leg. It intensifies with extension and flexion of the joint, walking, and radiates to the foot and calf. In severe cases, the pain is similar to electrical discharges, swelling and redness of the skin is observed.
Why does it hurt under the knee if all the described pathologies are excluded? Sometimes the reason is vascular problems:
- Arterial aneurysm. A rare pathology with pulling and pulsating sensations. Due to the separation of the walls, the vessel begins to bulge and lead to compression of the nerve roots. Swelling is noticeable only with a large aneurysm.
- Varicose veins Even the initial stages of damage to the popliteal veins can cause discomfort, especially in the evenings when the legs are tired.
- Thrombosis of the vein under the knee. If a person has varicose veins, there is a risk of thrombosis - the appearance of a blood clot in a superficial or deep vein. At the same time, there is swelling under the knee, severe pain in the calf, lower leg, and sometimes blueness and redness of the leg.
- Sometimes vascular pain appears in adolescents during rapid growth. Usually, if the child is healthy, such sensations disappear as they grow older.
Diagnosis of the problem
In order to make a diagnosis, surgeons refer patients with this problem to undergo an MRI, which allows them to effectively identify existing damage to the muscular and ligamentous apparatus, as well as negative changes in the knee joint. If certain reasons do not allow such an examination, then the joint is examined with ultrasound.
As an additional diagnostic point, an x-ray of the knee joint in several projections may be prescribed in order to exclude all existing causes of the disease . Such a “photo” of the damaged area will allow the doctor to examine the joint in all projections, while understanding what caused the development of the disease.
If it is known for sure that there is blood in the joint, then an injection is made at the site of the bruise and the accumulated clots are pumped out from there, so that on an x-ray you can see whether the joint is damaged.
puncture for analysis
If fat cells are found in the joint fluid, the doctor can confidently say that the patient has a fracture . Well, if hemarthrosis is in question, then this injection, also known as puncture, allows it to be identified by the presence of blood clots in the punctuation.
An injection (puncture) into the site of injury is often used to pump out collected blood or fluid, thus reducing swelling, pain and making the limb more mobile. The extracted punctuate is used in analysis to detect various infections.
If an injection (puncture) reveals fragments in the punctuation, then surgeons send such a patient for arthroscopy to obtain the exact cause of the disease. It is also used to remove small bone fragments found in the joint fluid.
Nagging pain in the knee - causes
The most “popular” cause of regular nagging or aching pain is arthrosis. 80% of people over 65 years old have its signs, but they are not always expressed in the same way. With arthrosis, all the cartilage of the knee is gradually deformed, resulting in obsessive pain syndrome.
Initially, when the synovial membrane begins to deteriorate, there are no symptoms. Then the cartilage becomes thinner, the joint space narrows. A characteristic crunching, clicking, nagging pain appears in the morning, when the leg is not yet fully developed. The sensations can be localized in any area of the joint, often radiating to the calves. Usually, at first one knee suffers more, then the symptoms level out. In the final stages, the pain becomes severe and the person stops walking.
If the leg is pulled under the knee at the back, there is swelling there, the cause may be a Baker's cyst. It usually occurs after an injury and is more common in athletes. When the synovial membrane becomes inflamed, the latter loses its strength, and a lot of inflammatory exudate begins to be produced inside it. Fluid accumulates under the knee and a cyst appears in the popliteal fossa. It may be painless, but periodically becomes inflamed and causes pain. Large cysts lead to chronic discomfort - they compress blood vessels and nerves.
Patella bruise: treatment at home
The use of alternative medicine as an additional element of therapy speeds up recovery. The best drugs against bruises are homemade ointments based on interior fat and juice of plantain leaves, decoctions and alcohol tinctures of cinquefoil.
Ointment
To prepare plantain ointment, you will need several large leaves of the plant. They are washed, crushed, the juice is squeezed out and mixed with interior fat to create a creamy consistency. It is used to lubricate the sore knee three times a day. The ointment is stored in a cool place.
Tincture
You can buy cinquefoil tincture at a pharmacy or prepare it yourself. To do this, 6-7 tablespoons of dry raw materials are poured with 0.5 liters of vodka or alcohol. Place in a dark, cool place for a couple of days. Compresses are made from the resulting tincture on the sore joint.
Why do bruises appear for no reason?
A common cause of a bruise on the knee is a lack of vitamins in the body. They strengthen the walls of blood vessels and help normalize blood circulation. Particular attention should be paid to the following groups of vitamins:
- Vitamin K is involved in blood coagulation and promotes clotting. This vitamin is found in green vegetables. If a person consumes a small amount of vegetables, then minor hemorrhages on the legs may be a consequence of hypovitaminosis. The opposite effect also develops with an excess of vitamin K. It is possible that similar symptoms will develop. This is due to increased blood clotting. In this case, hemorrhages are also possible.
- Vitamin PP or nicotinic acid helps normalize the functioning of blood vessels. Therefore, nicotinic acid is often prescribed for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
- Vitamin C performs a huge number of functions in our body. It is found in citrus fruits and sweet bell peppers. One of the functions is the normal elasticity of blood vessels, so a lack of vitamin leads to fragility of blood vessels.
Types of injuries
Classification of injuries and their causes:
| Name of knee injury | Possible causes, risk factors |
| Injury | Direct contact with a hard surface - impact, fall from the height of your own body |
| Medial ligament injury | Tucking the shin outward |
| Damage to the lateral ligament | Tucking the shin to the inside |
| Cruciate ligament injury | Flexion and extension of the knee under load with a large amplitude during sports activity (sprinting, bench press) Complex movement, for example, turning the hip when the lower leg is motionless, striking directly to the knee Commonly found in runners, hockey players, wrestlers, figure skaters |
| Injury to the patellar ligament | Bend the knee sharply if the thigh muscles are tense Kick, jumping The last stage of tendonitis of the patellar tendon (the disease occurs with constant increased loads on the joint) Chronic diseases that weaken the ligament (rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus) |
| Quadriceps tendon rupture | Sudden flexion of the shin if the thigh muscles are tight Hitting the foot on a hard surface |
| Meniscus injuries (tears, tears, flattening) | Strong physical activity Landing when jumping from height to feet Severe stage of knee arthrosis |
| Patella fracture | Falling with a blow to the front of the knee (sometimes even from one’s own height) |
| Fractures of the condyles of the femur or tibia (condyles are thickenings of the bone on which muscles are attached) | Falls from height Accidents or other traumatic situations |
Anatomical structure of the knee. Click on photo to enlarge
What tests are needed to determine the diagnosis?
No treatment will be prescribed without testing, examination and diagnosis. Therefore, as soon as you walk into the doctor's office, you will be given:
- The question was asked about what happened and when, what treatment was undertaken by you personally, what worries you.
- An examination was carried out, during which the doctor will palpate to determine whether there is internal bleeding, a lump, swelling and redness.
- An ultrasound of the joint was prescribed.
- An x-ray examination was prescribed.
- After receiving all these results, the doctor prescribes treatment.