Sphenoiditis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sphenoid, or main, sinus. This disease belongs to the group of sinusitis and, fortunately, is the rarest of them. Sphenoiditis is not characterized by pronounced symptoms, and there are no symptoms pathognomonic specifically for this disease. In this regard, the acute form of the disease often proceeds unidentified and becomes chronic, causing anxiety to the patient for many years. However, if this disease is diagnosed in time, its treatment does not present any particular difficulties, and as a result, the patient’s quality of life improves significantly.
Causes of the disease
Acute sphenoiditis is essentially a secondary disease. It develops against the background of previous or current respiratory diseases and tonsillitis. The immediate cause is the infection enters this sinus from the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and other sinuses.
Therefore, the causative agents of the disease are all those microorganisms that caused the primary disease:
- respiratory viruses - influenza, parainfluenza, RS virus, adenovirus;
- bacteria - staphylococci, streptococci;
- fungi - candida.
There are also predisposing factors, the presence of which increases the risk of developing sphenoiditis:
- sinus opening stenosis;
- developmental anomalies of the sphenoid sinus;
- decreased general and local immunity;
- pathological processes in the nasal passages and nasal septum;
- hyperplastic processes of the sinus - cysts, polyps, tumors;
- presence of a foreign body in the sinus cavity;
- mechanical sinus injuries.
Treatment of sphenoiditis
The leading symptoms of sphenoiditis are intense pain in the occipital region, combined with nasal discharge, increased body temperature and other manifestations of intoxication syndrome.
The main principles of treatment of acute inflammation of the sphenoid sinus are:
- elimination of the pathogen that caused the disease;
- elimination of swelling of the sinus mucosa and its anastomosis;
- improving the outflow of secretions from the sinuses.
In case of severe symptoms of intoxication, the presence of purulent discharge flowing down the back wall of the pharynx, the patient is prescribed antibiotic therapy, both systemic and local. The drug must be selected either taking into account the sensitivity of bacteria to it, or one that affects the maximum number of potential pathogens of sphenoiditis (these include aminopenicillins - Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Flemoxin; cephalosporins of II-III generations - Zinnat, Cefodox, Cefix, etc.).
In addition to taking tablet forms of the antibiotic, it is also necessary to treat the affected mucous membrane with antibacterial drugs. This is done by probing the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses using a special sinus catheter. This procedure involves repeated rinsing of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses with an antibiotic solution until the mucus is replaced by a clear, clear liquid. This method is not traumatic and painless even for pediatric patients; in addition, it does not cause complications. Patients notice an improvement in their well-being after the first probing procedure.
In order to reduce swelling of the mucous membrane, a gauze strip pre-moistened with adrenaline is inserted into the upper nasal passage 1-2 times a day for 15-20 minutes. Also for this purpose, conventional vasoconstrictor drops based on xylometazoline or oxymetazoline (Galazolin, Nasonex, etc.) are used.
It is worth noting that immunomodulatory therapy plays a certain role in the treatment of sphenoiditis - immunocorrectors (Echinacea compositum, Betaleukin) can increase the body's resistance to infection and speed up recovery.
At the stage of convalescence (recovery), persons suffering from acute sphenoiditis may be prescribed physiotherapeutic treatment. More often than others, endonasal electrophoresis with solutions of antibiotics or antiseptics and intra-sinus irradiation with a helium-neon laser are used.
If conservative treatment methods are ineffective, surgery is indicated for the patient. Currently, the method of choice is endoscopic surgery, which allows a specialist to freely approach the sinus anastomosis, expand it and smoothly sanitize the cavity. This operation is not traumatic for the patient, lasts no more than half an hour, the patient recovers from it within several days.
In case of chronic sphenoiditis, conservative treatment will not lead to the desired effect, therefore, in the vast majority of cases, this disease is treated surgically. The essence of the operation is to provide access to the sphenoid sinus, eliminate problems existing in it and in the area of the anastomosis, and subsequent sanitation of the mucous membrane. The nature of the access is different: transseptal sphenoidectomy (through the nasal septum), transorbital or transaxillary-maxillary ethmoidosphenoidectomy (through the orbit or maxillary sinus), direct endonasal ethmoidsphenoidectomy (through the nasal cavity).
After the operation, the nasal cavity and nasopharynx are rinsed with isotonic saline using special devices for several days. In addition, to prevent infectious complications after surgery, the patient takes antibiotics.
In the case of a specific etiology of sphenoiditis, it is treated according to protocols for the treatment of the underlying disease (syphilis, tuberculosis).
Pathogenesis of the disease
- The infectious agent has a detrimental effect on mucosal cells.
- An inflammatory catarrhal process is formed.
- The combination of infection and predisposing factors aggravates the condition.
- The mucous membrane becomes swollen and blocks the sinus opening. Under these conditions, rapid proliferation of microorganisms occurs - the direct cause of sinusitis.
- Gradually, pus fills the entire cavity of the sphenoid sinus.
What rhinosinusitis is and how it occurs in children and adults is not a mystery, and we talked about it.
A deviated nasal septum can cause acute sinusitis, so be careful.
Treatment of frontal sinusitis in adults and children is carried out using tablets, nasal drops, and in critical cases, surgery.
Causes of sphenoiditis
The above brief description of the structure of the sphenoid bones and sinuses gives an idea of how serious any damage to them can be. Inflammation of the mucous membrane covering the walls of the sphenoid sinus is called “sphenoiditis”. What is this from the perspective of otolaryngology? We will try to explain in language accessible to a wide audience. Any inflammation is the body’s reaction to the influence of unfavorable factors. In the case of sphenoiditis, they can become harmful microorganisms (staphylococcus, streptococcus, viruses or fungi) that have penetrated from the nasal cavity into the sphenoid sinuses through the ethmoid labyrinth and apertures. In addition, the infection can “arrive” from the nasopharyngeal tonsils. In rare cases, the disease develops without infection, due to swelling of the nasopharyngeal mucosa or the presence of pathological formations in the sinuses.
Symptoms
Signs of sphenoiditis are divided into two groups:
- specific symptoms;
- nonspecific symptoms.
Nonspecific symptoms are those that are observed during inflammatory processes in any sinuses:
- rise in body temperature to subfebrile levels;
- headache;
- nasal congestion;
- malaise.
Headache is one of the symptoms.
Specific symptoms are characteristic of this disease:
- headache has its own localization - in the back of the head, deep in the head;
- constant feeling of unpleasant odor;
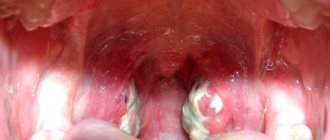
- When examining the oropharynx, a strip of pus is found on its back wall.
Acute sphenoiditis
- severe intoxication;
- pain syndrome - headache, pain in the eyeballs;
- fresh pus on the back of the throat.
Chronic sphenoiditis
The chronic process is characterized by:
- atrophy of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx, the formation of hard-to-remove crusts on it;
- if the inflammation affects the nearby chiasm - the optic chiasm - complaints of such deterioration of vision appear: impaired eye movement, drooping eyelids, lacrimation;
- When the cranial nerves are affected, characteristic symptoms appear - pain in the face, paralysis of half the face, drooping eyelids, and hearing impairment.
The sphenoid sinus is described in the medical literature as a "silent" or "forgotten sinus". This is due to its location - it is located in the thickness of the sphenoid bone, which is located deep in the skull.
Special symptoms
- loss of appetite as a manifestation of intoxication;
- changes in sleep - insomnia at night, drowsiness during the day;
- skin paresthesia - goosebumps, numbness.
These signs are characteristic of a chronic course.
Sphenoiditis - definition of the disease
Doctors call sphenoiditis an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sphenoid sinus. In fact, this disease is a type of sinusitis, which combines different inflammatory processes in the paranasal sinuses.
A person has several sinuses. The sphenoid, which is the main one, is located deep in the nasal cavity and borders on such important components of the human body as the pituitary gland, carotid arteries, base of the skull, and optic nerves. Of course, such a “neighborhood” can threaten serious complications. Fortunately, sphenoiditis is rare; more often the maxillary sinuses and ethmoid labyrinth are affected (sinusitis, ethmoiditis). However, with a low prevalence, most sphenoiditis becomes chronic, is difficult to treat with medications and requires surgical intervention. A person has two sphenoid sinuses, separated by a septum, so the disease can be unilateral or bilateral.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis is based on:
- characteristic complaints of the patient;
- visual examination data for diagnosis are of little significance, since the sphenoid sinus is not accessible either by rhinoscopy or pharyngoscopy;
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging reveals sphenoiditis more informative than other methods;
- if CT and MRI are unavailable, X-ray diagnostics are performed;
- There is such a method as a diagnostic puncture with examination of the contents of the sinus.
CT scan is a study of the sinus using X-rays. CT allows you to identify sinus abnormalities and the degree of mucosal damage. A CT scan determines the level of pus in the sinus.
An even more informative diagnostic method is MRI - it reveals layer-by-layer lesions that may not be noticed on CT.
Diagnostics
Clinically suspected sphenoiditis, the symptoms of which forced a person to seek medical help, is an indication for a detailed examination of the patient. If you want to establish an accurate diagnosis and determine the cause of this condition, then contact Nearmedic. There are 3 compelling arguments for this:
- Equipped with the latest instrumental equipment for diagnosis and treatment.
- Highly qualified doctors who regularly improve the level of their medical knowledge and practical skills in order to introduce the most innovative methods of helping patients suffering from sphenoiditis.
- A sensitive and attentive attitude towards the person who has applied, which instills in him faith in the possibility of a complete cure and restoration of a full life.
If doctors at Nearmedic centers suspect sphenoiditis, diagnostics must include:
- Anterior and posterior rhinoscopy (respectively, examination of the anterior and posterior sections of the nasal cavity);
- Endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx. To do this, use special devices equipped with a video camera at the end. The magnified image is displayed on the screen, so the doctor can examine in detail the structure of these anatomical formations.
X-ray of the skull is another diagnostic method that allows you to clarify whether there is sphenoiditis or not. Its diagnostic value is especially high in the exudative form of inflammation, when the level of fluid in the sinus is detected.
Often, especially in chronic cases, doctors resort to computed tomography. With its help, it is possible to evaluate the structure of the nose and its paranasal sinuses layer by layer. The main advantage of this method is the ability to determine the size of the anastomosis, which affects the frequency of disease relapses and affects treatment tactics.
Sphenoiditis, the treatment of which involves the use of antimicrobial drugs, necessarily requires a microbiological examination. It will help identify the pathogen, as well as determine its sensitivity to antibiotics (antifungals, etc.).
Treatment methods
Treatment of any sinusitis is a complex and complex process. In the case of sphenoiditis, especially chronic, it becomes even more difficult, because this sinus is difficult to access for therapeutic manipulations.
The main goal of the treatment process is to eliminate the cause - infection. Since the vast majority of sphenoiditis is caused by bacterial flora, antibacterial drugs with a broad spectrum of action are used to treat symptoms:
- penicillins – “Amoxiclav”, “Flemoxin”;
- cephalosporins – “Ceftriaxone”, “Cefepime”;
- macrolides - Azithromycin.
For mild forms of the disease, such drugs are taken orally in tablet form. In severe cases, treatment needs to be more serious - intramuscular injections are prescribed.
All other drugs have a symptomatic and pathogenetic effect:
- treatment of sphenoiditis with hormonal agents - a pronounced anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect (Nasonex, Avamys, Desrinit);
- vasoconstrictors - decongestant effect, free up nasal breathing (Xilen, Tizin, Otrivin);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - elimination of the inflammatory process, lowering body temperature, pain relief (Nurofen, Panadol, Ketoprofen);
- antihistamines - eliminating swelling and nasal congestion (Zyrtec, Claritin, Zodak);
- means for stimulating the immune system (“Immunal”, “Likopid”, “Broncho-munal”);
- homeopathic remedies (“Sinupret”, “Sinuforte”).
Physiotherapy methods have a positive effect on sphenoiditis:
- nasal electrophoresis with drugs;
- ultraviolet irradiation of the sinuses through the nasal passages;
- magnet to the sinus area.
If conservative therapy does not produce the desired effect and the patient’s condition worsens, surgical treatment is used.
Treatment
Acute and chronic sphenoiditis must be treated after consulting with an ENT doctor. If the symptoms of the disease are moderate and there are no signs of complications, conservative therapy is prescribed. If symptoms of complications are detected or conservative therapy is ineffective, then surgery is performed.
Drug treatment
Main directions of drug therapy:
- Relieving nasal congestion.
- Elimination of swelling of the nasal mucosa.
- Improving the discharge of inflammatory exudate from the sphenoid sinuses using sprays for the common cold.
- Use of antibiotics and corticosteroids (if necessary).
The use of vasoconstrictor drop sprays is recommended. However, remember that they cannot be used for more than 3 days. The reason is that traditional spray components stop working effectively after 2-3 days, as addiction occurs, and they gradually begin to have a negative effect.
Nasal sprays
For sphenoiditis, you can use the following remedies for a runny nose:
Average price 300 rub.
- Spray "Rinofluimucil" (Italy). Rhinofluimucil-active components of the spray reduce the secretion of pus, mucus and nasal congestion, improve the discharge of pus, and reduce swelling of the nasal mucosa. Rinofluimucil also combines well with the drugs Sinuforte and Sinupret, which accelerate the cleansing of pus and mucus from the sinuses.
- Spray "Nasonex" (Belgium). Nasonex contains a low dose of glucocorticoids, which makes it possible to relieve swelling of the mucous membrane and nasal congestion. This spray is different in that it can be used in courses of 2-3 months, which is especially important for long-term treatment. Nasonex also combines well with any other drugs.
Drugs that accelerate the cleansing of sinuses from pus and mucus
They usually contain herbal components that stimulate the function of the ciliated epithelium on the surface of the mucous membrane, which leads to faster cleansing of the sinuses from the mucus and pus that accumulate in them. For inflammation of the sphenoid sinuses, the following medications are recommended:
- Dragees or drops "Sinupret" (Germany). Sinupreactive components of plant origin have an anti-inflammatory effect and facilitate the evacuation of pus and mucus from the sinuses.
- Sinuforte nasal drops (Spain). Sinufortepreparation is produced on the basis of an extract of one of the medicinal plants. Helps clear sinuses.
Antibiotics for sphenoiditis
Depending on the degree of inflammation and the presence or absence of complications, antibiotics may be prescribed intramuscularly or intravenously. The most optimal antibiotic option for sphenoiditis is Amoxicillin in combination with clavulanic acid. There are drugs containing this combination, these are:
Price from 250 rub.
- Amoxiclav;
- Augmentin.
If antibiotics of the penicillin group are intolerant or if they are insufficiently effective, antibiotics of the macrolide group (Azithromycin, Clarithromycin) or the fluoroquinolone group, for example, Ciprofloxacin, can be prescribed.
Surgical treatment of sphenoiditis in adults (surgeries)
If conservative therapy is unsuccessful or symptoms of severe purulent complications are detected at the time of the patient’s treatment, then urgent surgery is performed using an endoscope and microsurgical instruments (with access through the nasal passages).
Don't expect complications. It is better to contact an ENT doctor in a timely manner so that surgical intervention is not required.
Physiotherapy
Any disease of the upper respiratory tract can lead to swelling of the nasopharynx and cause sphenoiditis.
Physiotherapeutic methods for treating sphenoiditis can be used exclusively as an auxiliary therapy and only as prescribed by a doctor.
In the acute phase, inhalations with Hydrocortisone and Ephedrine are prescribed, which will relieve swelling of the mucous membranes and promote the natural evacuation of the contents of the paranasal sinuses. During the recovery period and during remission the following can be used:
- UHF therapy;
- Irradiation with a Sollux lamp;
- Ozokerite compresses.
Remember that none of the methods of physiotherapy can influence the deep processes occurring in the sphenoid sinuses. Only an integrated approach using medication and physiotherapeutic treatment is effective.
Alternative methods of treating the disease
Recently, a new BSP technology has appeared in the arsenal of doctors - balloon sinuplasty, which is a set of endoscopic catheter instruments designed to expand closed anastomoses of the paranasal sinuses. These devices can be used both along with drug treatment and as part of traditional surgical methods for treating sphenoiditis.
Balloon sinuplasty
How to treat at home
Despite many traditional medicine recipes intended to treat inflammatory processes in the nasal sinuses, sphenoiditis cannot be treated using “grandmother’s” recipes. If you want to use any of them at home, be careful and first consult with an ENT doctor.
The main risk is the hyperallergenic nature of herbal remedies: allergic swelling of the outlet of the paranasal sinus can significantly intensify and complicate the course of the disease.
Even if you are not prone to allergies, remember that intoxication caused by inflammation in the sphenoid sinus can itself provoke an allergic reaction.
Complications
If the disease is not treated, it contributes to the development of severe complications:
- chronicity of the process;
- transition of inflammation to other sinuses with the formation of pansinusitis, which will take a very long time to treat;
- transition of inflammation to the orbit with the development of abscesses and phlegmon - they can only be treated surgically;
- pathology of the cranial nerves and corresponding symptoms;
- irreversible visual impairment;
- transition of inflammation to the brain with the development of complications - meningitis and encephalitis.
Predisposing factors
Signs of sphenoiditis may appear against the background of complications of influenza, scarlet fever, or even a simple runny nose. It was mentioned above that pathogenic microbes can cause inflammation of the mucous membrane. But their penetration into the sphenoid sinus does not always lead to sphenoiditis. For a disease to occur, certain factors must be present. These include:
- reduced immunity;
— pathologies in the structure of the sphenoid sinus (curvature of the sphenoid bone, deformation of the septum);
— anomalies (congenital or acquired, for example, after injury) in the structure of the nose;
- growths in the sphenoid sinuses (tumors, cysts).
Lifestyle Features
Treatment of sphenoiditis during an acute process requires the patient to follow special rules:
- It is important to maintain proper nutrition and drinking regime;
- procedures aimed at regularly cleansing the nasopharynx of mucus and pus;
- measures to increase the body's resistance.
Nutrition
A clear eating regimen is developed - at the same hours, in small portions, five times a day.
Foods that contribute to allergies are excluded from the diet. The allergic process in the body causes swelling in the mucous membranes, including the mucous membrane of the sphenoid sinus.
Useful products are those that help increase the body's resistance. Such products must contain:
- vitamins;
- proteins, fats and carbohydrates;
- minerals;
- probiotics - bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
Acute sphenoiditis requires limiting fluid intake so as not to increase swelling of the mucous membrane and symptoms of respiratory failure.
Cleansing the nasopharynx
It is necessary to speed up recovery and is directed against the addition of secondary microbial flora. Carried out with washing solutions:
- "Aquamaris";
- "Aqualor";
- "Physiomer";
- "Marimemer";
- "Linakvoy."
What is the sphenoid sinus
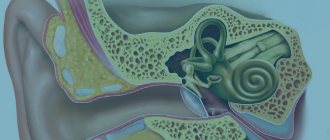
The sphenoid sinus has a second name - the main one. It is located deep in the nasal cavity on both sides of the nasal septum and is a cavity filled with air. In the immediate vicinity of this sinus there are several important anatomical formations, including the base of the skull, part of the brain - the pituitary gland, the left and right carotid arteries, and the optic nerves. The inflammatory process often passes from the mucous membrane of the sphenoid sinus to these formations, causing corresponding symptoms.
Prevention
Prevention of sphenoiditis in adults, as well as other types of sinusitis, includes the following recommendations:
- Do not leave untreated infectious diseases to chance - acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, influenza, measles and others;
- Correct anatomical defects of the sinuses if present - deviated nasal septum, atresia and other pathologies;
- Strengthen your immune system;
- Try to eat food enriched with vitamins and microelements;
- Avoid hypothermia;
- Try to move more, lead an active lifestyle.
Sphenoiditis is a disease that is of infectious origin. It must be treated without fail and immediately after the first signs are detected.
Causes of inflammation
Inflammation can be caused by deformation of the intranasal structure, namely:
- hypertrophic rhinitis;
- structural anomalies;
- deviated nasal septum.
The most common factor that provokes the inflammatory process is viruses. As a result, the mucous membranes produce excessive amounts of mucus. It is dangerous if a bacterial infection is associated with a viral disease.
In addition, inflammation of the amniotic sinuses can be caused by a fungus. It can be caused by the constant use of antibiotics, which have a detrimental effect on the immune system, disrupt the microflora and lead to the occurrence of infectious mycosis.
DETAILS: Effective painkillers for toothache during pregnancy
Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses may not always be caused by microbes. Quite often, cold air and certain chemicals can be the causes. The cause of the development of the inflammatory process may be an allergic reaction. It leads to vasomotor rhinitis and severe swelling of the mucous membrane.
The main cause of such diseases is the entry of microorganisms into the nasal cavity. The symptom appears when there is a sudden change in ambient temperature.
The sinuses become inflamed due to the following factors:
• dental diseases; • curvature of the nasal septum; • nosebleeds;
• allergies; • nasal injuries; • colds;
• inhalation of tobacco smoke; • expansion of blood vessels; • hypothermia;
• performing surgery in the nose area; • deterioration of immunity.
This symptom appears when exposed to excessively dry air. Inflammation may also result from rhinoplasty or other medical procedure. The symptom manifests itself when antibiotics are taken incorrectly. There is a genetic predisposition to inflammation of the nasal passages. Pathology is often diagnosed in patients with diabetes.
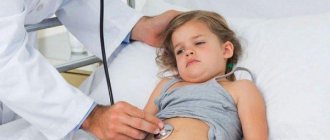
Symptoms in children
Some doctors believe that in children under 6 years of age, the sphenoidal sinuses are not fully formed, so they cannot become inflamed. Naturally, children are not treated. In fact, this opinion is wrong.
Despite the fact that in young children the sphenoid sinuses may still change, inflammation is quite possible. The symptoms of sphenoiditis in children are the same as in adults, except that not every child can accurately describe what is happening to him. Parents should be concerned when their baby:
- persistent runny nose with pus;
- no desire to play or eat;
- elevated temperature;
- labored breathing.
Sphenoiditis in children mainly occurs against the background of inflamed adenoids and redness of the tonsils.
Chronic sphenoiditis
The development of a chronic form refers to the consequences of adequate therapy, self-medication or late consultation with a doctor. The transition to another form of sphenoiditis occurs very quickly, which is due to regular inflammatory processes, due to which the pathological secretion partially comes from the sphenoid sinus.
The chronic version of sphenoiditis can occur as a result of malignant or benign tumors, or cause viral and bacteriological diseases. Inflammation affects the posterior cells of the ethmoid labyrinth.
Symptoms of chronic sphenoiditis:
- The appearance of unpleasant odors;
- Discomfort and pain in the occipital region;
- Discharge of mucous secretion.
As the chronic form of sphenoiditis progresses, patients experience symptoms of general intoxication. The patient may be accompanied by constant drowsiness, a feeling of malaise, and poor appetite.
Features of treatment
Treatment of inflammation of the nasal passages begins after accurately determining the cause of inflammation of the nasal passages. Treatment should include medications to reduce swelling and facilitate mucus clearance. Nasal congestion is relieved with the help of vasoconstrictor medications. When taking them, it should be taken into account that the maximum duration of therapy is 7 days, otherwise addiction is possible. Among this group of medications, Protargol, Isofra, and Polydex have proven themselves well.
To alleviate the patient's condition, it is recommended to rinse the nasal cavity with saline and antiseptic solutions. The procedure is carried out alternately for each nostril. Swelling is relieved with the help of anti-inflammatory medications. In clinical settings, the sinuses are washed using the “cuckoo” method. It involves repeating the words “ku-ku”, which prevents liquid from entering the nasopharynx.
The nasal passages are also washed with a Yamik catheter, but it only helps with minor inflammation. Contraindications to the use of this method are
epilepsy
, deviated nasal septum, frequent nosebleeds.
treatment of sinus inflammation Since sinus inflammation is often accompanied by infection, the patient is prescribed antibiotics. The improvement is noticeable after 4 days, but the full course of treatment is 10-14 days. In the chronic form of the disease, therapy can last 6 weeks. After antibiotic therapy, a course of probiotics is recommended. The dosage of medications is prescribed by the doctor.
To relieve inflammation, the patient is prescribed antihistamines. If pus stagnates in the nasal sinuses, the patient is given a puncture. This improves the patency of the nasal passages. After the procedure, antibiotics must be administered. The patient’s recovery is accelerated if drug treatment is supplemented with physical therapy. The following methods have proven themselves well: UHF, electrophoresis, inhalation, ultraviolet treatment.
If there is no effect from drug therapy, the patient is recommended to undergo surgery.
Indications for surgical intervention are:
• curvature of the nasal septum; • blocked sinuses; • chronic course of the disease; • relapses of sinusitis more than 3 times a year; • detection of a cyst in the nasal passages.
The safest treatment for sinuses is laser therapy. The laser relieves swelling and pain, and also makes breathing easier.
When the first symptoms of sinus inflammation appear, treatment should be started immediately to prevent the rapid spread of the pathological process and the occurrence of complications. Systemic therapy includes taking medications such as:
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antihistamines;
- mucolytics.
In addition, nasal drops, rinsing with saline solutions and physical treatment are required. In particularly severe cases, surgery may be required.
Pathogenesis
Both acute and chronic sphenoiditis have quite specific mechanisms of formation and development. Microbes that have penetrated the sphenoid sinus begin to destroy its epithelial cells, which provokes an inflammatory process. If it does not stop immediately, the mucous membrane swells, thereby closing the outlet from the sinus. This prevents the outflow of exudate, which is released by the inflamed mucosa. On the one hand, mucus begins to accumulate in the sphenoid sinuses, which leads to headaches and vision problems, and on the other hand, in the closed volume of the sinuses without an influx of fresh air, an anaerobic infection begins to develop, and, as a result, purulent discharge appears, which also nowhere to go.
Sometimes blockage of the openings of the sphenoid sinus occurs primarily, when the mucous membrane is not yet inflamed. They can be blocked by growths in the nose or large swelling of the nasopharynx. Without air flow, the mucous membrane of the sphenoid sinuses begins to actively take oxygen from its cavities, releasing waste carbon dioxide there. As it accumulates, it destroys mucosal cells, causing inflammation.
The structure of the main sinus, its functions
The main sinus is a cavity in the bone tissue filled with air. Its size and shape are very individual. It can be unpaired, in the form of one cavity, or divided partially or completely into two asymmetrical parts by a thin bone septum. Depending on the size, the sinus can reach the “sella turcica” (the structural part of the sphenoid bone that serves as the location of the pituitary gland).
With significant sizes, the sphenoid sinus is located directly under the saddle. In these cases, it is separated from the pituitary gland by a thin plate of bone. Such individual structural features of the sphenoidal sinus make it possible, if necessary, to perform minimally invasive surgical operations on the structures of the skull through it.
Location of the sphenoid sinus
The sinus communicates with the nasal cavity through narrow ducts that open in the upper nasal passages. The inside of the sinus is lined with a thin layer of mucous membrane, the epithelium of which constantly produces mucus in small quantities. In normal conditions, it is sufficient to ensure the sterility of the sinus and neutralize microorganisms that have entered through the tubules. Through them, drainage of the sinuses occurs with the removal of waste secretions.
Like all paranasal sinuses, the main sinus performs important functions. It participates in the structure of the human skull, forms the human voice, and cold air entering the nose from the outside is warmed by mixing with warm air portions from all sinuses. Etiological factors of diseases of the main sinus
Diseases of the main sinus are represented by one nosology: inflammation. It is the most rarely diagnosed of all sinusitis and is very often combined with other types, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis or ethmoiditis. Inflammation of the sphenoid sinus is caused by the penetration of harmful microflora into the cavity through narrow channels.
As a rule, this occurs when a person is infected with an acute respiratory infection, when the primary inflammatory focus is localized in the nasal mucosa. This microflora has tropism (the property of attaching to epithelial cells) and to the mucous membrane of the main sinus.
Various individual structural features of the facial skull or nasal cavity also contribute to the development of sphenoiditis (inflammation of the main sinus). This is a severe curvature of the nasal septum in the upper part, polyps or a cyst blocking the drainage channels. Many skull injuries with a violation of the integrity of the sphenoid sinus contribute to the penetration of a huge number of microorganisms into it, which also leads to the development of the inflammatory process.
Types of disease
Classification of sphenoiditis by etiology distinguishes bacterial, viral and fungal forms. By severity - mild, moderate and severe forms of sphenoiditis.
By localization:
- Left-handed
- Right-handed
- Bilateral
By form:
- Exudative: catarrhal and purulent;
- Productive: polypous, cystic, and parietal hyperplastic.
By etiology:
- Traumatic
- Viral
- Bacterial
- Fungal
- Mixed
Prevention of sphenoiditis
Those who keep the nasal mucosa sufficiently moist will prevent most problems. Inhalation of a decoction of medicinal herbs will be effective; refusal to stay in a room filled with cigarette smoke; limiting the consumption of alcohol and caffeine, known for their drying effect.
Early detection eliminates the possibility of more serious complications, which include neurological damage and, rarely, death. Given the possibility of rapid progression of the disease, you need to pay attention to any changes in your health, and if your condition worsens, immediately go to the hospital.
to the content?
Disease prevention
With proper treatment, the prognosis is favorable: patients almost always make a full recovery. But people who have had sphenoiditis should take into account that they may well get sick again. To prevent recurrence of the disease, you need to monitor your health.
This means that you should not treat flu, sinusitis and other infectious diseases on your own. If you have any problems with nasal breathing, you should consult a doctor (even if there are no other unpleasant symptoms).
It is advisable to avoid any dusty or gas-filled rooms. If you are prone to allergies, you need to consult with an allergist, determine what exactly the reaction is to, and eliminate contact with allergy-causing substances.
Proper hardening of the body reduces the risk of catching seasonal colds. Thanks to this, the possibility of contracting viral and bacterial infections, which can develop into sphenoiditis, is significantly reduced.
Acute sphenoiditis: what is it, why does it occur, how does it develop?
Based on the nature of the disease, two forms of sphenoiditis are diagnosed - acute and chronic. If inflammation in the sphenoid sinuses occurs due to infection entering them or acts as a complication of inflammatory processes occurring in the nasopharynx (rhinitis, influenza, ethmoiditis), a diagnosis of “acute sphenoiditis” is made. His symptoms are as follows:
- headaches (usually in the back of the head, less often in the temples, in the frontal part of the head or in the parietal);
- copious nasal discharge;
- rise in temperature;
- weakness and weakness;
- decrease in olfactory sensations;
- decreased vision.
A complication of the acute form of sphenoiditis can be a brain tumor.
Surgery
There are patients in whom sphenoiditis occurs due to injuries in the nasal regions or the appearance of growths in the sphenoid sinuses. In such cases, surgery is the only possible treatment method.
Depending on the doctor’s decision, either local anesthesia or general anesthesia is used. The patient's ethmoidal labyrinth bone is opened (sphenoidotomy), then an endoscope is inserted into the sphenoid sinus (endoscopic sphenotomy).
This device allows you to examine in detail where the cyst has grown, where a polyp has formed, what changes are observed in the mucosa, and also to carry out surgical manipulations. After their completion, the patient is injected with the necessary medications into the sphenoid sinus and further treatment is prescribed.
Symptoms of sphenoiditis in adults
Sphenoiditis practically does not have any “original” symptoms, so the diagnosis of this disease is quite difficult. Most often, patients may be bothered by the following symptoms:
- headache;
- asthenovegetative manifestations;
- pathological discharge;
- impairment of vision and smell.
- damage to the cranial nerves.
The following circumstances may aggravate them:
- exposure to the sun;
- too warm air (heat and dryness) in the room;
- intense movements (bending, jumping).
Most often, sphenoiditis is accompanied by ethmoiditis, and a combination of symptoms is observed.
However, a combination of all these symptoms is very rare. Often the patient has one or two symptoms for a long time. For example, a person experiences a constant headache in the back of his head for a long time, sometimes for months.
Conventional drugs for headaches do not bring relief, the patient turns to therapists, neurologists, psychotherapists, he is prescribed treatment for cervical osteochondrosis, astheno-neurotic syndrome and other diseases that are likely to be found after consultation with these specialists.
Acute sphenoiditis
An acute form of sphenoiditis, which occurs as a complication after respiratory diseases, acute respiratory viral infections, and influenza. The patient in this case complains of the following symptoms:
- temperature increase,
- general weakness,
- headache,
- nasal discharge.
Acute sphenoiditis is treated with conservative methods. If, after the spread of the inflammatory process from the paranasal sinuses, adequate therapy has not been carried out, the acute phase of the disease becomes chronic.
Symptoms of the chronic form
The reason for visiting a doctor for chronic sphenoiditis is often a progressive deterioration of vision, for which ophthalmologists cannot explain. Signs of nasal diseases are weakly expressed, discharge is insignificant or absent.
The chronic phase of the disease is dangerous due to the spontaneous development of complications as a result of exacerbation of infection and the formation of purulent exudate. Damage to parts of the brain during massive infection is manifested by characteristic neurological symptoms. Repeated exacerbations of the chronic form of the disease also lead to various life-threatening complications, usually against the background of destructive and degenerative bone lesions.
Diagnosis of sphenoiditis
Sphenoiditis, especially chronic, is very difficult to diagnose. 78% of sphenoiditis is initially misdiagnosed. This is explained, firstly, by the fact that the disease is quite rare and doctors simply forget about the existence of such a diagnosis. Secondly, it is practically impossible to detect using routine diagnostic methods. Conventional radiography of the paranasal sinuses in a direct projection can easily reveal other sinusitis (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis). The sphenoid sinus is poorly visible in this projection.
Indirect signs of sphenoiditis when examined by an ENT doctor are swelling of the mucous membrane in the area of the mouth of the sphenoid sinus and a path of pus flowing down the wall of the nasopharynx. Unilateral pharyngitis (left-sided or right-sided inflammation of the pharyngeal wall) is also alarming.
The main method for diagnosing sphenoiditis today is CT of the paranasal sinuses or MRI.
Computed tomography allows you to determine the condition of all sinuses with 100% accuracy. MRI provides less information, but this method often reveals sphenoiditis during an MRI scan of the brain prescribed to a patient for persistent headaches or other neurological symptoms.
Drug treatment
How to cure sinus inflammation? Only a doctor can determine this after examination. At the initial stage of the disease, the nose is washed with saline solutions. Saline solution or sea salt sprays work well for this. Products such as Aquamaris or Humer have proven themselves well.
DETAILS: Aloe for gum disease
They dilute the secretions of the nasal sinuses, eliminate swelling, and reduce inflammation. These drugs contribute to the narrowing of blood vessels in the mucous membrane. Along with the liquid, mucus, viruses and foreign particles are removed. However, it is impossible to use only saline solutions as monotherapy.
Treatment with vasoconstrictors will help quickly eliminate the symptoms of sinus inflammation. These drugs have certain pros and cons. This medicine helps eliminate swelling for 12 hours, which promotes healing and reduces discomfort. However, it is worth remembering that with prolonged use these drops are addictive.
When treating purulent inflammation of the sinuses, it may be necessary to use mucolytics to help remove thick mucus. In addition, these agents help improve epithelial function. The drug "Sinupret" has good properties. It has a natural composition, so it rarely provokes side effects. Mucolytics have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. They have a beneficial effect on the course of the disease.
To eliminate swelling and more quickly remove mucus, hormonal agents are prescribed. This is an effective medicine for inflammation of the sinuses, which does not have a harmful effect on the body. That is why hormonal drugs can be used even to treat children. Such drugs as “Nasonex”, “Avamys”, “Flixonase” have proven themselves well.
In the event of a bacterial infection, antibiotics are required for inflammation of the sinuses. Mostly penicillin drugs are prescribed, in particular such as Amoxicillin. They act very quickly on bacteria. In some cases, this drug is not enough. Bacteria are very adaptable and produce drug-resistant strains. This makes therapy much more difficult.
For sinusitis, as well as allergies to penicillin, macrolides, in particular such as Erythromycin or Azithromycin, can be prescribed. These agents effectively act on bacteria and rarely cause resistance in pathogens.
It is worth remembering that the medicine for sinus inflammation should only be selected by the attending doctor, taking into account the existing indications and contraindications.